C语言需要掌握的基础知识点之线性表
线性表是最基本、最常用的一种数据结构,它是由n个数据元素组成的有限序列。在C语言中,线性表可以通过数组或链表来实现。
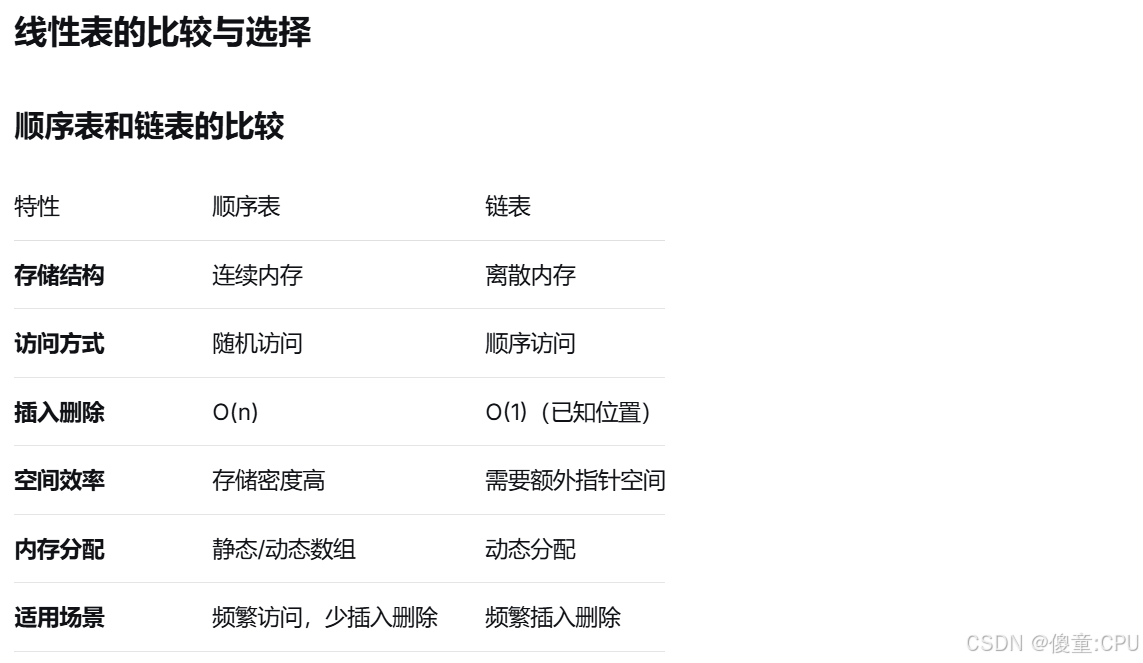
线性表的基本概念
线性表是具有相同数据类型的n(n≥0)个数据元素的有限序列。通常表示为:
L = (a₁, a₂, ..., aᵢ, ..., aₙ)
线性表的特点
有限性:元素个数是有限的
有序性:元素有先后顺序
同类型:所有元素属于同一数据类型
抽象性:只关心逻辑关系,不关心具体存储方式
线性表的顺序存储(数组实现)
基本顺序表实现
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
#define INIT_SIZE 10
// 顺序表结构定义
typedef struct {
int *data; // 存储数组
int length; // 当前长度
int capacity; // 总容量
} SeqList;
// 初始化顺序表
bool initSeqList(SeqList *list) {
list->data = (int*)malloc(INIT_SIZE * sizeof(int));
if (list->data == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败\n");
return false;
}
list->length = 0;
list->capacity = INIT_SIZE;
return true;
}
// 扩展顺序表容量
bool expandSeqList(SeqList *list) {
int new_capacity = list->capacity * 2;
if (new_capacity > MAX_SIZE) {
new_capacity = MAX_SIZE;
}
int *new_data = (int*)realloc(list->data, new_capacity * sizeof(int));
if (new_data == NULL) {
printf("内存扩展失败\n");
return false;
}
list->data = new_data;
list->capacity = new_capacity;
printf("顺序表容量扩展到: %d\n", new_capacity);
return true;
}
// 在指定位置插入元素
bool insertSeqList(SeqList *list, int index, int element) {
// 检查位置合法性
if (index < 0 || index > list->length) {
printf("插入位置不合法\n");
return false;
}
// 检查是否需要扩容
if (list->length >= list->capacity) {
if (!expandSeqList(list)) {
return false;
}
}
// 移动元素
for (int i = list->length; i > index; i--) {
list->data[i] = list->data[i - 1];
}
// 插入新元素
list->data[index] = element;
list->length++;
return true;
}
// 删除指定位置的元素
bool deleteSeqList(SeqList *list, int index, int *element) {
// 检查位置合法性
if (index < 0 || index >= list->length) {
printf("删除位置不合法\n");
return false;
}
// 保存被删除的元素
*element = list->data[index];
// 移动元素
for (int i = index; i < list->length - 1; i++) {
list->data[i] = list->data[i + 1];
}
list->length--;
return true;
}
// 按值查找元素位置
int locateSeqList(SeqList *list, int element) {
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; i++) {
if (list->data[i] == element) {
return i;
}
}
return -1; // 未找到
}
// 按位置获取元素
bool getSeqList(SeqList *list, int index, int *element) {
if (index < 0 || index >= list->length) {
printf("位置不合法\n");
return false;
}
*element = list->data[index];
return true;
}
// 修改指定位置的元素
bool setSeqList(SeqList *list, int index, int element) {
if (index < 0 || index >= list->length) {
printf("位置不合法\n");
return false;
}
list->data[index] = element;
return true;
}
// 获取顺序表长度
int lengthSeqList(SeqList *list) {
return list->length;
}
// 判断顺序表是否为空
bool isEmptySeqList(SeqList *list) {
return list->length == 0;
}
// 判断顺序表是否已满
bool isFullSeqList(SeqList *list) {
return list->length >= list->capacity;
}
// 打印顺序表
void printSeqList(SeqList *list) {
if (isEmptySeqList(list)) {
printf("顺序表为空\n");
return;
}
printf("顺序表内容: ");
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; i++) {
printf("%d ", list->data[i]);
}
printf("\n");
printf("长度: %d, 容量: %d\n", list->length, list->capacity);
}
// 清空顺序表
void clearSeqList(SeqList *list) {
list->length = 0;
}
// 销毁顺序表
void destroySeqList(SeqList *list) {
free(list->data);
list->data = NULL;
list->length = 0;
list->capacity = 0;
}
// 顺序表操作演示
void seqListDemo() {
SeqList list;
printf("=== 顺序表操作演示 ===\n");
// 初始化
if (!initSeqList(&list)) {
return;
}
// 插入元素
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
insertSeqList(&list, i, (i + 1) * 10);
}
printSeqList(&list);
// 在指定位置插入
insertSeqList(&list, 5, 999);
printf("在位置5插入999后:\n");
printSeqList(&list);
// 删除元素
int deleted_element;
deleteSeqList(&list, 3, &deleted_element);
printf("删除位置3的元素: %d\n", deleted_element);
printSeqList(&list);
// 查找元素
int search_element = 999;
int position = locateSeqList(&list, search_element);
if (position != -1) {
printf("元素 %d 在位置 %d\n", search_element, position);
} else {
printf("元素 %d 未找到\n", search_element);
}
// 获取和修改元素
int element;
getSeqList(&list, 2, &element);
printf("位置2的元素: %d\n", element);
setSeqList(&list, 2, 888);
printf("修改位置2为888后:\n");
printSeqList(&list);
// 清空和销毁
clearSeqList(&list);
printf("清空后: ");
printSeqList(&list);
destroySeqList(&list);
}
int main() {
seqListDemo();
return 0;
}线性表的链式存储(链表实现)
单链表实现
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// 单链表节点定义
typedef struct ListNode {
int data;
struct ListNode *next;
} ListNode;
// 单链表结构定义
typedef struct {
ListNode *head;
int length;
} LinkedList;
// 初始化单链表
bool initLinkedList(LinkedList *list) {
list->head = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (list->head == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败\n");
return false;
}
list->head->next = NULL;
list->length = 0;
return true;
}
// 在指定位置插入元素
bool insertLinkedList(LinkedList *list, int index, int element) {
if (index < 0 || index > list->length) {
printf("插入位置不合法\n");
return false;
}
ListNode *new_node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));
if (new_node == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败\n");
return false;
}
new_node->data = element;
ListNode *current = list->head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current->next;
}
new_node->next = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
list->length++;
return true;
}
// 删除指定位置的元素
bool deleteLinkedList(LinkedList *list, int index, int *element) {
if (index < 0 || index >= list->length) {
printf("删除位置不合法\n");
return false;
}
ListNode *current = list->head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current->next;
}
ListNode *temp = current->next;
*element = temp->data;
current->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
list->length--;
return true;
}
// 按值查找元素位置
int locateLinkedList(LinkedList *list, int element) {
ListNode *current = list->head->next;
int position = 0;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->data == element) {
return position;
}
current = current->next;
position++;
}
return -1; // 未找到
}
// 按位置获取元素
bool getLinkedList(LinkedList *list, int index, int *element) {
if (index < 0 || index >= list->length) {
printf("位置不合法\n");
return false;
}
ListNode *current = list->head->next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current->next;
}
*element = current->data;
return true;
}
// 修改指定位置的元素
bool setLinkedList(LinkedList *list, int index, int element) {
if (index < 0 || index >= list->length) {
printf("位置不合法\n");
return false;
}
ListNode *current = list->head->next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current->next;
}
current->data = element;
return true;
}
// 获取链表长度
int lengthLinkedList(LinkedList *list) {
return list->length;
}
// 判断链表是否为空
bool isEmptyLinkedList(LinkedList *list) {
return list->length == 0;
}
// 打印链表
void printLinkedList(LinkedList *list) {
if (isEmptyLinkedList(list)) {
printf("链表为空\n");
return;
}
printf("链表内容: ");
ListNode *current = list->head->next;
while (current != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", current->data);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
printf("长度: %d\n", list->length);
}
// 清空链表
void clearLinkedList(LinkedList *list) {
ListNode *current = list->head->next;
while (current != NULL) {
ListNode *temp = current;
current = current->next;
free(temp);
}
list->head->next = NULL;
list->length = 0;
}
// 销毁链表
void destroyLinkedList(LinkedList *list) {
clearLinkedList(list);
free(list->head);
list->head = NULL;
list->length = 0;
}
// 链表操作演示
void linkedListDemo() {
LinkedList list;
printf("=== 单链表操作演示 ===\n");
// 初始化
if (!initLinkedList(&list)) {
return;
}
// 插入元素
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
insertLinkedList(&list, i, (i + 1) * 10);
}
printLinkedList(&list);
// 在指定位置插入
insertLinkedList(&list, 5, 999);
printf("在位置5插入999后:\n");
printLinkedList(&list);
// 删除元素
int deleted_element;
deleteLinkedList(&list, 3, &deleted_element);
printf("删除位置3的元素: %d\n", deleted_element);
printLinkedList(&list);
// 查找元素
int search_element = 999;
int position = locateLinkedList(&list, search_element);
if (position != -1) {
printf("元素 %d 在位置 %d\n", search_element, position);
} else {
printf("元素 %d 未找到\n", search_element);
}
// 获取和修改元素
int element;
getLinkedList(&list, 2, &element);
printf("位置2的元素: %d\n", element);
setLinkedList(&list, 2, 888);
printf("修改位置2为888后:\n");
printLinkedList(&list);
// 清空和销毁
clearLinkedList(&list);
printf("清空后: ");
printLinkedList(&list);
destroyLinkedList(&list);
}
int main() {
seqListDemo();
printf("\n");
linkedListDemo();
return 0;
}线性表的应用实例
学生成绩管理系统
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_NAME_LEN 50
// 学生结构定义
typedef struct {
int id;
char name[MAX_NAME_LEN];
float score;
} Student;
// 学生顺序表
typedef struct {
Student *students;
int length;
int capacity;
} StudentList;
// 初始化学生列表
bool initStudentList(StudentList *list, int capacity) {
list->students = (Student*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(Student));
if (list->students == NULL) {
return false;
}
list->length = 0;
list->capacity = capacity;
return true;
}
// 添加学生
bool addStudent(StudentList *list, int id, const char *name, float score) {
if (list->length >= list->capacity) {
printf("学生列表已满\n");
return false;
}
list->students[list->length].id = id;
strcpy(list->students[list->length].name, name);
list->students[list->length].score = score;
list->length++;
return true;
}
// 按学号查找学生
int findStudentById(StudentList *list, int id) {
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; i++) {
if (list->students[i].id == id) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 按姓名查找学生
int findStudentByName(StudentList *list, const char *name) {
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; i++) {
if (strcmp(list->students[i].name, name) == 0) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 删除学生
bool deleteStudent(StudentList *list, int id) {
int index = findStudentById(list, id);
if (index == -1) {
printf("未找到学号为 %d 的学生\n", id);
return false;
}
for (int i = index; i < list->length - 1; i++) {
list->students[i] = list->students[i + 1];
}
list->length--;
return true;
}
// 计算平均分
float calculateAverage(StudentList *list) {
if (list->length == 0) {
return 0.0f;
}
float sum = 0.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; i++) {
sum += list->students[i].score;
}
return sum / list->length;
}
// 按成绩排序(从高到低)
void sortByScore(StudentList *list) {
for (int i = 0; i < list->length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < list->length - i - 1; j++) {
if (list->students[j].score < list->students[j + 1].score) {
Student temp = list->students[j];
list->students[j] = list->students[j + 1];
list->students[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
// 打印学生列表
void printStudentList(StudentList *list) {
if (list->length == 0) {
printf("学生列表为空\n");
return;
}
printf("学号\t姓名\t\t成绩\n");
printf("----\t----\t\t----\n");
for (int i = 0; i < list->length; i++) {
printf("%d\t%s\t\t%.1f\n",
list->students[i].id,
list->students[i].name,
list->students[i].score);
}
}
// 学生管理系统演示
void studentManagementDemo() {
StudentList list;
printf("=== 学生成绩管理系统 ===\n");
if (!initStudentList(&list, 20)) {
printf("初始化失败\n");
return;
}
// 添加学生
addStudent(&list, 1001, "张三", 85.5);
addStudent(&list, 1002, "李四", 92.0);
addStudent(&list, 1003, "王五", 78.5);
addStudent(&list, 1004, "赵六", 88.0);
addStudent(&list, 1005, "钱七", 95.5);
printf("所有学生:\n");
printStudentList(&list);
// 查找学生
int search_id = 1003;
int index = findStudentById(&list, search_id);
if (index != -1) {
printf("\n找到学号 %d: %s, 成绩: %.1f\n",
list.students[index].id,
list.students[index].name,
list.students[index].score);
}
// 计算平均分
printf("\n平均成绩: %.2f\n", calculateAverage(&list));
// 按成绩排序
sortByScore(&list);
printf("\n按成绩排序后:\n");
printStudentList(&list);
// 删除学生
deleteStudent(&list, 1002);
printf("\n删除学号1002后:\n");
printStudentList(&list);
// 释放内存
free(list.students);
}
int main() {
studentManagementDemo();
return 0;
}多项式运算
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
// 多项式项结构
typedef struct PolyTerm {
float coef; // 系数
int exp; // 指数
struct PolyTerm *next;
} PolyTerm;
// 多项式结构
typedef struct {
PolyTerm *head;
int length;
} Polynomial;
// 初始化多项式
bool initPolynomial(Polynomial *poly) {
poly->head = (PolyTerm*)malloc(sizeof(PolyTerm));
if (poly->head == NULL) {
return false;
}
poly->head->next = NULL;
poly->length = 0;
return true;
}
// 添加多项式项(按指数降序)
bool addPolyTerm(Polynomial *poly, float coef, int exp) {
PolyTerm *new_term = (PolyTerm*)malloc(sizeof(PolyTerm));
if (new_term == NULL) {
return false;
}
new_term->coef = coef;
new_term->exp = exp;
PolyTerm *current = poly->head;
while (current->next != NULL && current->next->exp > exp) {
current = current->next;
}
// 合并同类项
if (current->next != NULL && current->next->exp == exp) {
current->next->coef += coef;
free(new_term);
// 如果系数为0,删除该项
if (current->next->coef == 0) {
PolyTerm *temp = current->next;
current->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
poly->length--;
}
return true;
}
new_term->next = current->next;
current->next = new_term;
poly->length++;
return true;
}
// 多项式相加
Polynomial* addPolynomials(Polynomial *poly1, Polynomial *poly2) {
Polynomial *result = (Polynomial*)malloc(sizeof(Polynomial));
if (!initPolynomial(result)) {
return NULL;
}
PolyTerm *p1 = poly1->head->next;
PolyTerm *p2 = poly2->head->next;
while (p1 != NULL && p2 != NULL) {
if (p1->exp == p2->exp) {
float sum_coef = p1->coef + p2->coef;
if (fabs(sum_coef) > 1e-6) { // 避免浮点数精度问题
addPolyTerm(result, sum_coef, p1->exp);
}
p1 = p1->next;
p2 = p2->next;
} else if (p1->exp > p2->exp) {
addPolyTerm(result, p1->coef, p1->exp);
p1 = p1->next;
} else {
addPolyTerm(result, p2->coef, p2->exp);
p2 = p2->next;
}
}
// 处理剩余项
while (p1 != NULL) {
addPolyTerm(result, p1->coef, p1->exp);
p1 = p1->next;
}
while (p2 != NULL) {
addPolyTerm(result, p2->coef, p2->exp);
p2 = p2->next;
}
return result;
}
// 多项式求值
float evaluatePolynomial(Polynomial *poly, float x) {
float result = 0.0f;
PolyTerm *current = poly->head->next;
while (current != NULL) {
result += current->coef * powf(x, current->exp);
current = current->next;
}
return result;
}
// 打印多项式
void printPolynomial(Polynomial *poly) {
if (poly->length == 0) {
printf("0\n");
return;
}
PolyTerm *current = poly->head->next;
int first = 1;
while (current != NULL) {
if (current->coef > 0 && !first) {
printf(" + ");
} else if (current->coef < 0) {
printf(" - ");
}
float abs_coef = fabs(current->coef);
if (current->exp == 0) {
printf("%.1f", abs_coef);
} else if (current->exp == 1) {
if (fabs(abs_coef - 1.0f) < 1e-6) {
printf("x");
} else {
printf("%.1fx", abs_coef);
}
} else {
if (fabs(abs_coef - 1.0f) < 1e-6) {
printf("x^%d", current->exp);
} else {
printf("%.1fx^%d", abs_coef, current->exp);
}
}
current = current->next;
first = 0;
}
printf("\n");
}
// 多项式运算演示
void polynomialDemo() {
Polynomial poly1, poly2;
printf("=== 多项式运算演示 ===\n");
// 初始化多项式
initPolynomial(&poly1);
initPolynomial(&poly2);
// 构建多项式1: 3x^3 + 2x^2 + 5
addPolyTerm(&poly1, 3.0f, 3);
addPolyTerm(&poly1, 2.0f, 2);
addPolyTerm(&poly1, 5.0f, 0);
// 构建多项式2: 4x^3 + 3x^2 + 2x + 1
addPolyTerm(&poly2, 4.0f, 3);
addPolyTerm(&poly2, 3.0f, 2);
addPolyTerm(&poly2, 2.0f, 1);
addPolyTerm(&poly2, 1.0f, 0);
printf("多项式1: ");
printPolynomial(&poly1);
printf("多项式2: ");
printPolynomial(&poly2);
// 多项式相加
Polynomial *sum = addPolynomials(&poly1, &poly2);
printf("相加结果: ");
printPolynomial(sum);
// 多项式求值
float x = 2.0f;
float value1 = evaluatePolynomial(&poly1, x);
float value2 = evaluatePolynomial(&poly2, x);
float value_sum = evaluatePolynomial(sum, x);
printf("当 x = %.1f 时:\n", x);
printf("多项式1的值: %.1f\n", value1);
printf("多项式2的值: %.1f\n", value2);
printf("相加多项式的值: %.1f\n", value_sum);
// 释放内存
// 实际使用时需要实现destroyPolynomial函数
}