stack和queue的使用
- stack是容器适配器
- stack的构造
- 其他的使用
- queue
- 通过题来理解使用
-
-
- 1.[最小栈](https://leetcode.cn/problems/min-stack/)
- 2[栈的压入,弹出序列](https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/d77d11405cc7470d82554cb392585106?tpId=13&&tqId=11174&rp=1&ru=/activity/oj&qru=/ta/coding-interviews/question-ranking)
- 3.[逆波兰表达式求值](https://leetcode.cn/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/description/)
- 4.队列题[树的层序遍历](https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/description/)
-
- stack的实现(适配器)
- 队列的底层实现
stack是容器适配器

contaniner就是容器的意思,deque是双端队列的意思,包括vector list的功能
stack的构造

匿名对象的默认构造
cpp
std::stack<std::vector<int>> d5;//无参构造没有括号,不然会被认为函数
std::vector<int> d3(4);
d5.push(d3);
cpp
std::stack<int> d1;其他的使用
跟我们前面实现的一样,简单的使用一下
cpp
std::stack<int> d1;
d1.push(1);
d1.push(2);
d1.push(3);
d1.push(4);
while (!d1.empty()) {
auto e = d1.top();
std::cout << e << std::endl;
d1.pop();
}queue
- 队列的构造跟stack一样。
- 在使用方面就是多一个返回头和尾的数据
cpp
std::queue<int> d2;
d2.push(2);
d2.push(3);
d2.push(3);
d2.push(4);
std::cout << d2.front() << std::endl;
std::cout << d2.back() << std::endl;通过题来理解使用
1.最小栈
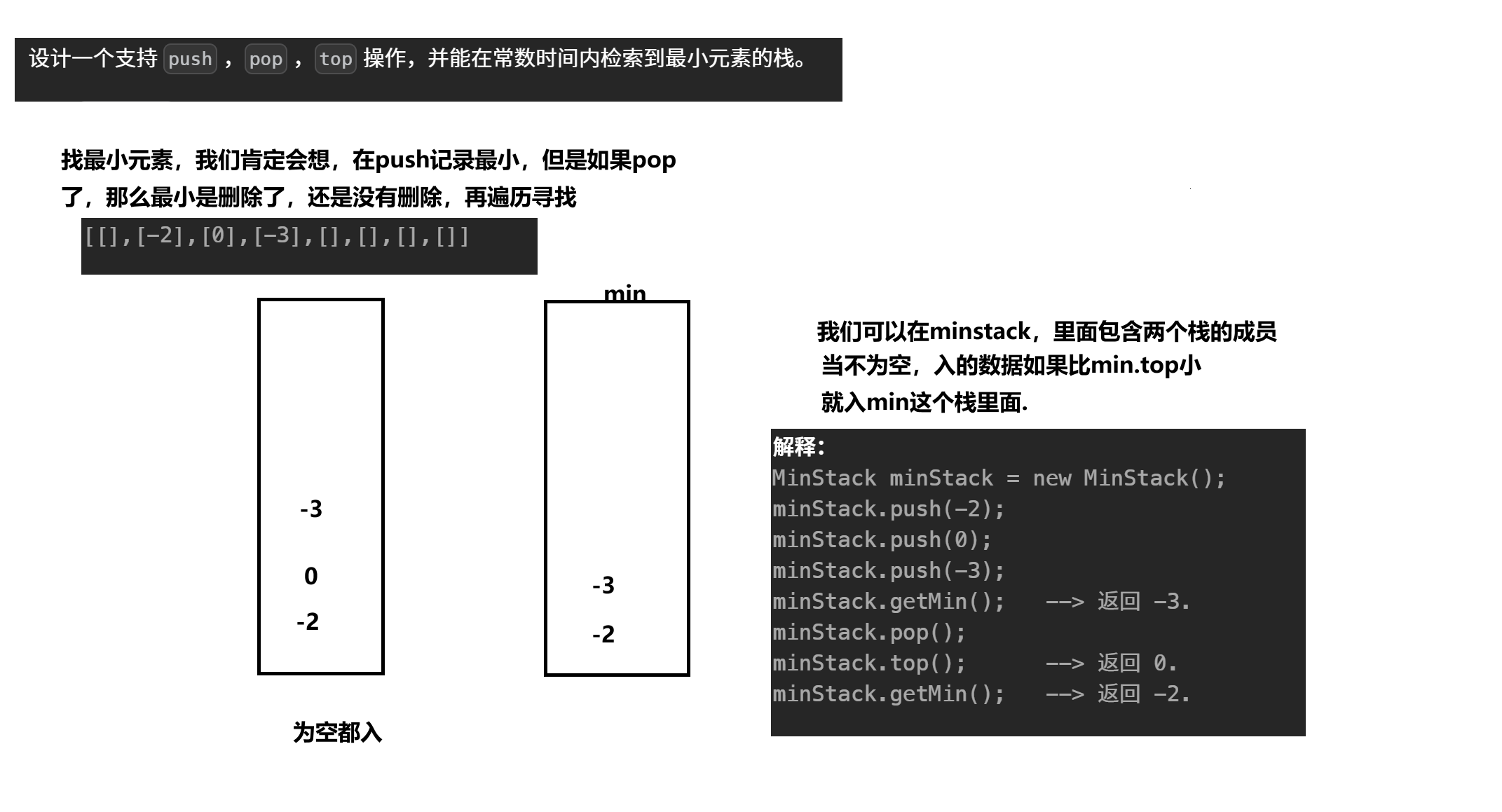
cpp
class MinStack {
public:
MinStack() {
}
void push(int val) {
if(minsta.empty()||val<=minsta.top()){
minsta.push(val);
}
sta.push(val);
}
void pop() {//两个栈都要pop
if(sta.top()==minsta.top()){
minsta.pop();
}
sta.pop();
}
int top() {//sta这个栈表示记录栈,所以返回它的pop
return sta.top();
}
int getMin() {
return minsta.top();
}
stack<int> sta;
stack<int> minsta;
};

2栈的压入,弹出序列
解题思路:首先题目就给两个栈,一个是入栈和出栈的数组,判断出栈是否是入栈的数组的正确出栈顺序
首先都i,j==0,都从头开始遍历,设置出一个栈,先把push[i]入栈,再判断stack.top是否跟popV[j]相等,如果相等,就pop,j++.如果不等就i++,继续入栈,直到相等,出栈,如果i大于push.size就要结束,再判断栈是否为空,为空就是true
cpp
class Solution {
public:
/**
* 代码中的类名、方法名、参数名已经指定,请勿修改,直接返回方法规定的值即可
*
*
* @param pushV int整型vector
* @param popV int整型vector
* @return bool布尔型
*/
bool IsPopOrder(vector<int>& pushV, vector<int>& popV) {
// write code here
size_t i=0;
size_t j=0;
stack<int> d1;
while(i<pushV.size()){
d1.push(pushV[i]);
while(!(d1.empty())&&j<popV.size()&&popV[j]==d1.top()){
d1.pop();
j++;
}
i++;
}
if(j==popV.size()){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
};3.逆波兰表达式求值

给了一个数组里面包含的是逆波兰表达式,我们怎么能求值呢。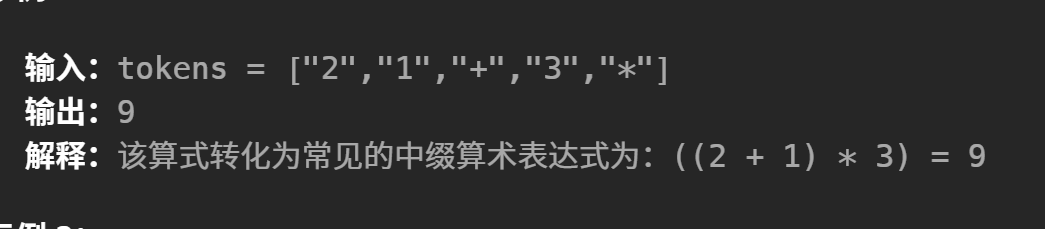
思路:因为这个逆波兰有个特点,符号前面肯定有两个数,所以我们利用栈,如果不是符号就入栈,先入2,1,遇到加号,出栈2,1两个相加的结果入栈,依次入栈,当遍历完就结束,最后栈顶的数就是结果。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
// int i = 0;
// stack<int> d1;
// while (i < tokens.size()) {
// string str=tokens[i];
// if (str == "*" ||str =="/"|| str == "+" ||
// str == "-") {
// int left=d1.top();
// d1.pop();
// int right=d1.top();
// d1.pop();
// int ret=0;
// switch (str[0]) {//switch里面必须是整型,什么int,char
// case '*': ret=right*left;
// d1.push(ret);
// break;
// case '/': ret=right/left;
// d1.push(ret);
// break;
// case '+': ret=right+left;
// d1.push(ret);
// break;
// case '-': ret=right-left;
// d1.push(ret);
// break;
// }
// }
// else
// d1.push(stoi(str));//自动把string转换为int类型
// i++;
// }
// return d1.top();
stack<int> d1;
for (auto& str : tokens) {
if (str == "*" || str == "/" || str == "+" || str == "-") {
int left = d1.top();
d1.pop();
int right = d1.top();
d1.pop();
switch (str[0]) {//这里字符串的第一个字符就是char整形
case '*':
d1.push(right * left);
break;
case '/':
d1.push(right /left);
break;
case '+':
d1.push(right + left);
break;
case '-':
d1.push(right - left);
break;
}
}
else
d1.push(stoi(str));
}
return d1.top();
}
};注释了的是没有优化的。
4.队列题树的层序遍历
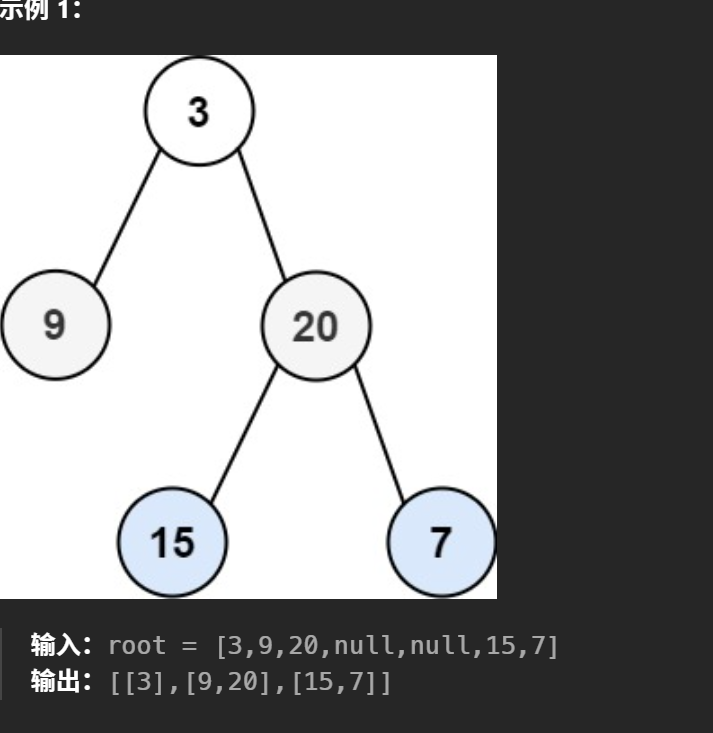
这个层序遍历的难点就是他这个返回的是一个二维数组,每一层都是一个数组。
思路:对于这个我肯定先入头节点,再判断左节点和右孩子是否为空,如果不为空,出3,入9,20.因为我们每次都要判断左右孩子是否为空,所以队列肯定要存指针。
cpp
vector<vector<int>> d1;
if(!root){
return d1;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);先声明一个二维数组,为入头节点,因为我们这个是层序遍历,所以出完一层的节点之后,下一层的节点肯定要全部入队列。
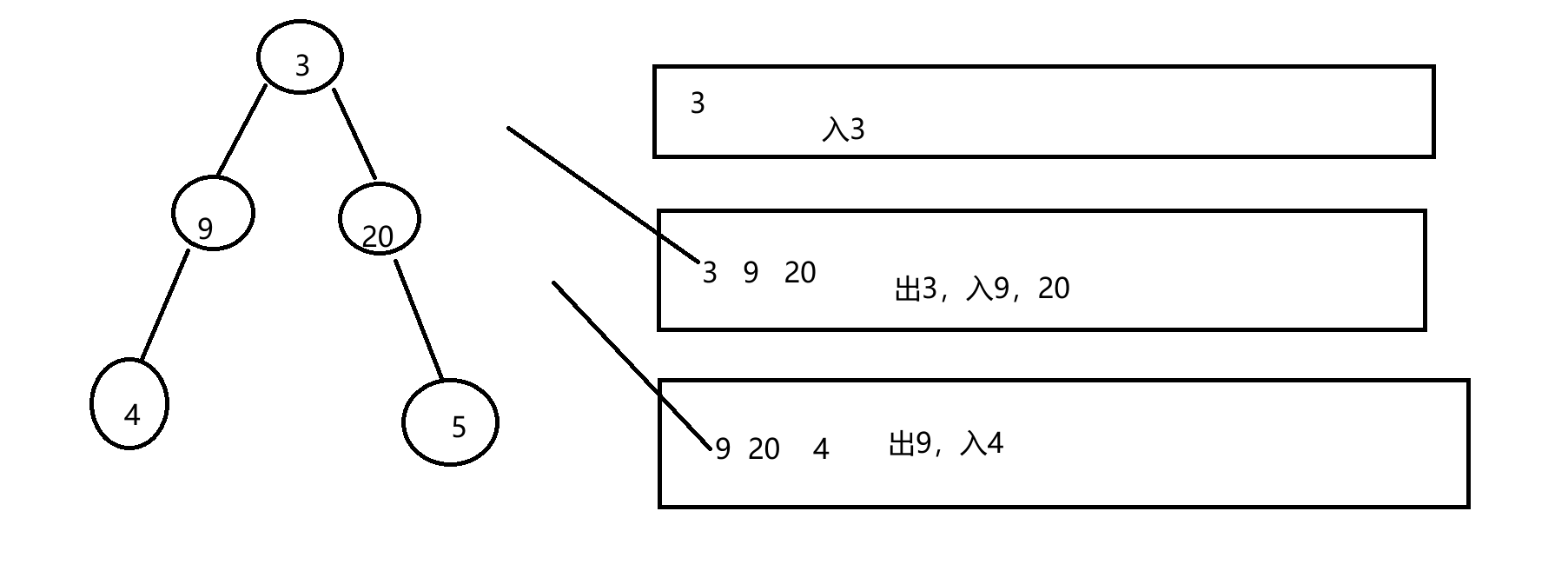
- 注意第一层一个节点,为了更快解决,我们需要队列的size(),意思是每层的节点,第一层1,就遍历一次,判断左右,入9,20.第二层2个节点,两次循环,分别判断左右,再入4,5.
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> d1;
if(!root){
return d1;
}
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
vector<int> flag;
for (int i = q.size(); i > 0; i--) {
auto node = q.front();
flag.push_back(node->val);
if (node->left) {
q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right) {
q.push(node->right);
}
q.pop();
}
d1.push_back(flag);
}
return d1;
}
};还有就是再vector<vector>d1并没有开辟内存,还,没有为任何元素开辟内存,千万不能d1[0].push_back(数据),这个d1[0]导致越界,崩溃。我们可以先把数据push_back进一个数组,push_back有开辟空间扩容操作,然后再把数组push_back给二维数组。
stack的实现(适配器)
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
#include<vector>
template <class T, class Container = std::deque<T> >//==给了双端队列作为缺省值。
class stack {
public:
stack() {
}
void push(const T& val) {
_con.push_back(val);//以数组的尾部作为头这样效率更高
}
void pop() {
_con.pop_back();
}
size_t size() {
return _con.size();
}
T& top() {
return _con.back();
}
bool empty() {
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;//容器适配器,声明一个容器的对象
};
cpp
stack<int, std::vector<int>> d1;//形参传参可以只传int,因为给了缺省值,可以传队列和vector<int>
d1.push(3);
d1.push(1);
d1.push(2);
d1.push(3);
d1.push(3);
while (!d1.empty()) {
std::cout << d1.top()<<" ";
d1.pop();
}
test();栈只要满足一端入,这一端出,就行,所以vector,list都可以作为它的适配器
队列的底层实现
对于队列就需要满足一端入,一端出,这样vector不满足了,只能使用list.
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<deque>
#include<list>
template <class T, class Container = std::deque<T> >
class queue {
public:
queue() {
}
void push(const T& val) {
_con.push_back(val);
}
void pop() {
_con.pop_front();
}
void size() {
_con.size();
}
T& front() {
return _con.front();
}
T& back() {
return _con.back();
}
bool empty() {
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;//容器变量
};
cpp
void test() {
queue<int, std::list<int>> d1;
d1.push(1);
d1.push(2);
d1.push(3);
d1.push(4);
while (!d1.empty()) {
std::cout << d1.front() << d1.back()<<" ";
d1.pop();
}
}栈和队列的实现很简单,以前vector给的内存池,我们不用写,这个适配器我们可以写。