一、SELinux 概念
1.SELinux 核心概念
SELinux 是Linux 内核的安全模块,通过强制访问控制(MAC)增强系统安全性。与传统的自主访问控制(DAC,基于文件权限如 chmod 和归属)相比,SELinux 基于策略强制执行权限,是为数不多能限制超级管理员行为的安全机制。
- DAC:自主访问控制(传统的权限和归属,包括ACL);但文件系统属性,如挂载时的ro\rw,或sudo授权模式,均不属于传统的权限
- MAC:强制访问控制(SELinux)
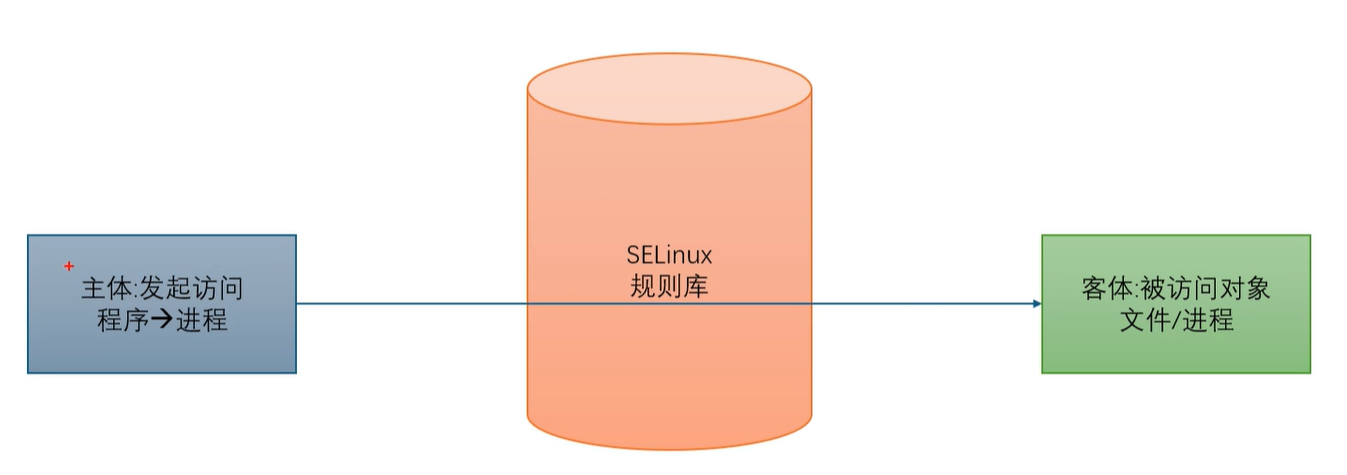
一般情况下能当主体的都是进程,而进程运行的时候一定要有用户身份
由SELinux规则库这个第三方工具决定主体在访问客体时,这个访问是否被允许
2.SELinux 安全机制
注:对比CentOS6/7、Rocky9几个版本;SELinux是对内的防护,用户行为安全机制
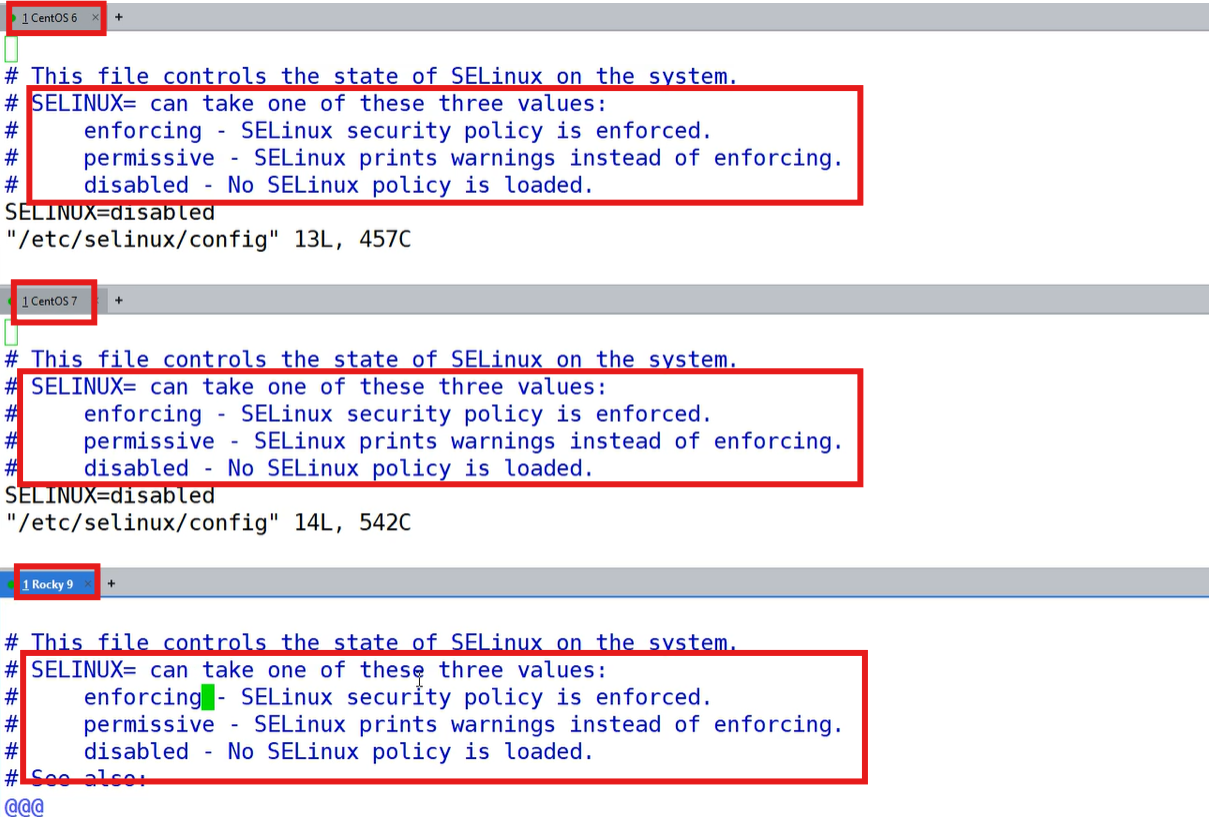
- enforcing:强制开启模式
- permissive:警告模式,一般不永久设置【setenforce 0|1】
- disabled:强制关闭模式
注:修改SELINUX之后,需要重启虚拟机才能生效
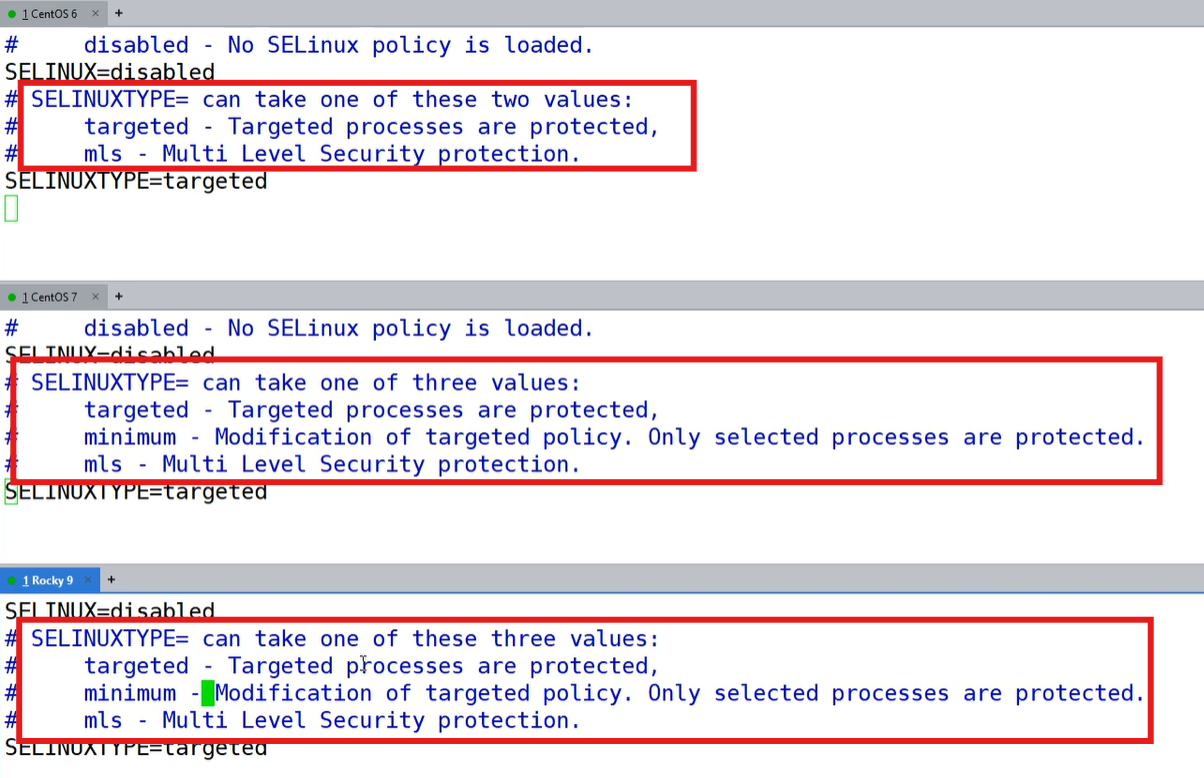
注:SELINUXTYPE指的是SELinux的安全等级
- mls:最高安全等级
targeted: **默认选项,**只针对预定义的特定进程进行保护,对用户程序限制较少minimum: 只对少量选定的进程进行保护,是targeted的一个子集
3.安全上下文
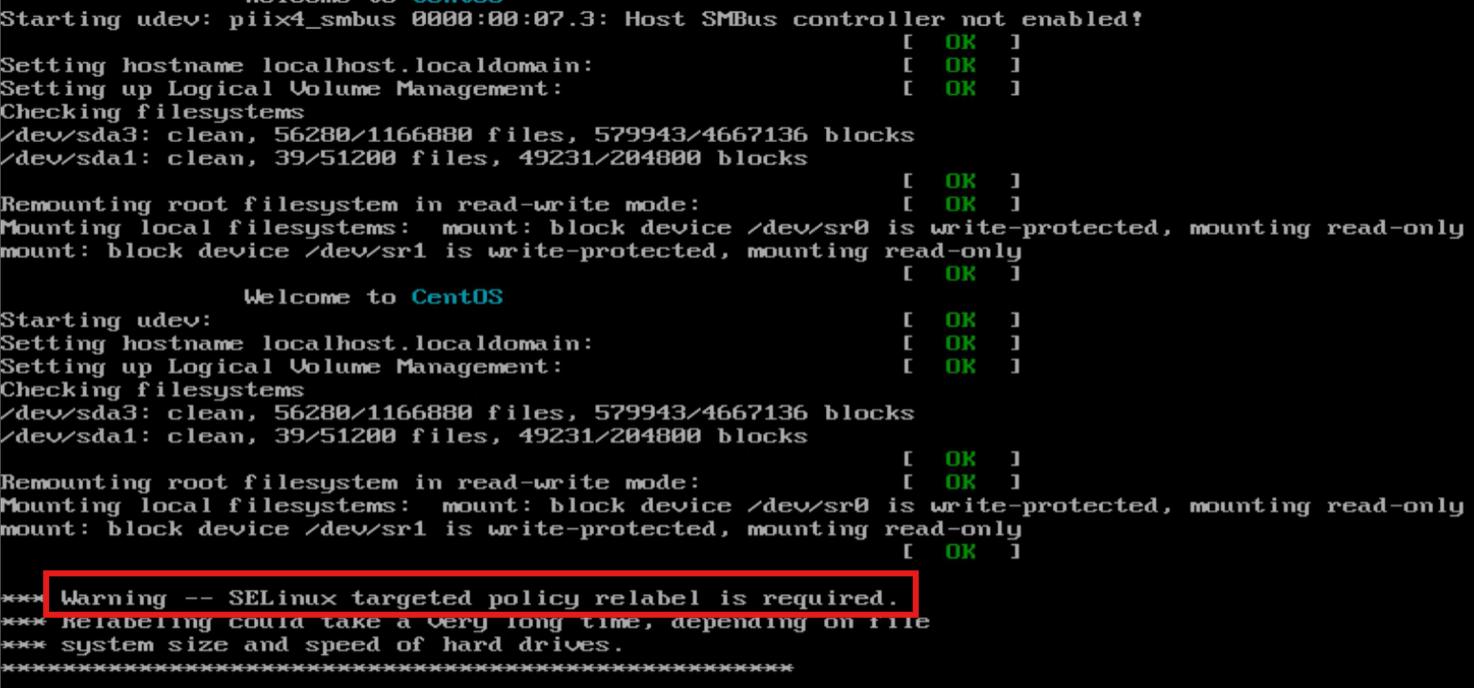
注:为每个资源分配标签(用户:角色:类型),控制访问行为;若在关闭SELinux期间创建了许多新文件,重启SELinux之后会进行扫描,逐个打上标签进行限制,被叫做安全上下文信息
查看文件/目录安全上下文信息
# 查文件
[root@localhost ~]# ls -lZ anaconda-ks.cfg
-rw-------. 1 root root system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 1099 8月 30 09:49 anaconda-ks.cfg
# 查目录
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ldZ /root/
dr-xr-x---. 4 root root system_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 4096 10月 27 16:31 /root/查看进程的安全上下文信息
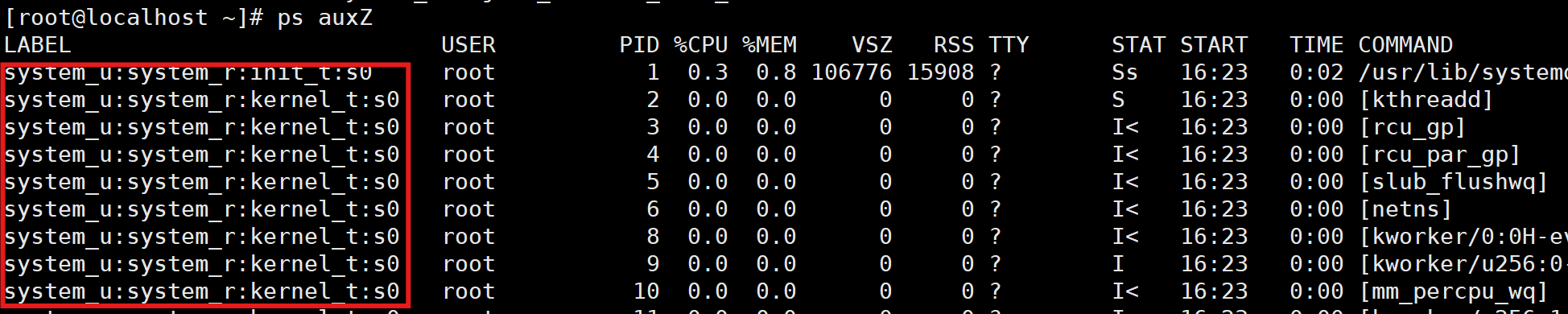
结构:*_u:*_r:*_t:s0
- u:user,用户,如 system_u (系统用户)、 unconfined_u (无限制用户)
- r:role,角色,如 system_r (系统角色)、 object_r (对象角色)
- t:type,类型,定义访问权限
- -Z:显示文件/进程的安全上下文信息
注:若关闭SELinux,则新创建的文件不会有安全上下文信息
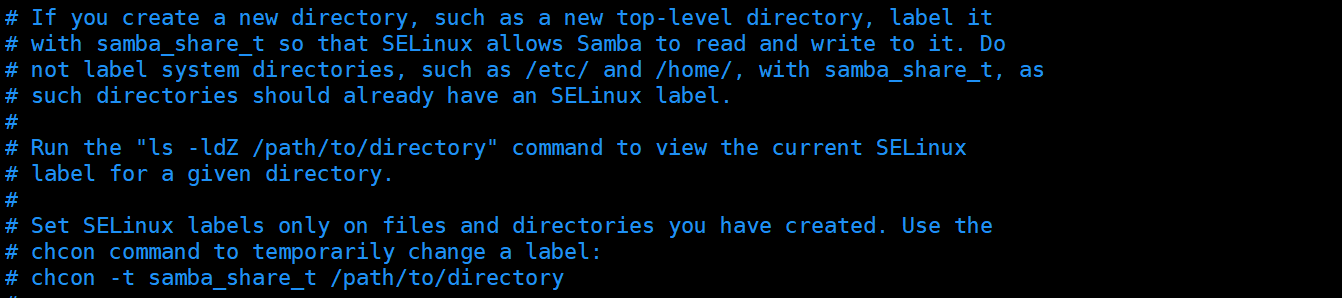
4.补充:samba服务
注:网络文件系统cifs,类似于NFS网络文件系统,都支持文件共享,且samba只支持局域网协议,不支持互联网协议,适配性较差
(1)安装samba
[root@localhost ~]# dnf -y install samba samba-client(2)创建共享目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /data
[root@localhost ~]# cd /etc/samba/
[root@localhost samba]# cp -a smb.conf.example smb.conf
[root@localhost samba]# vi smb.conf
[hf2506]
comment = Public Stuff
path = /data
writable = yes
browseable = yes
[root@localhost samba]# useradd zhangsan
# 创建samba用户
[root@localhost samba]# pdbedit -a zhangsan
new password:
retype new password:
# 单独针对用户设置的acl权限
[root@localhost samba]# setfacl -m u:zhangsan:rwx /data/
# 默认acl权限
[root@localhost samba]# setfacl -m d:u:zhangsan:rwx /data/
[root@localhost samba]# systemctl enable --now smb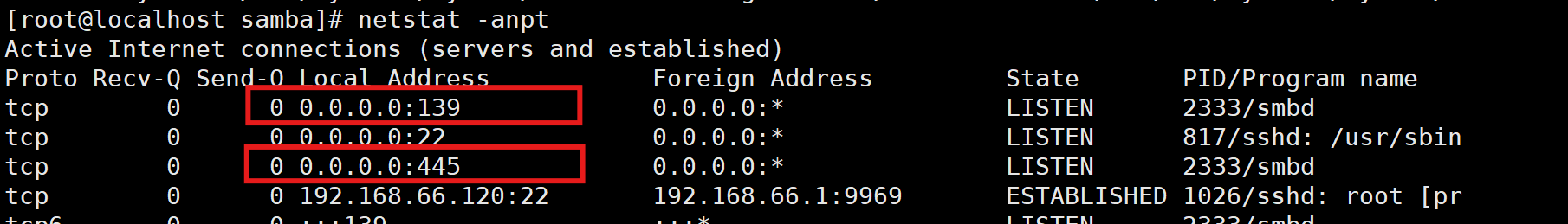
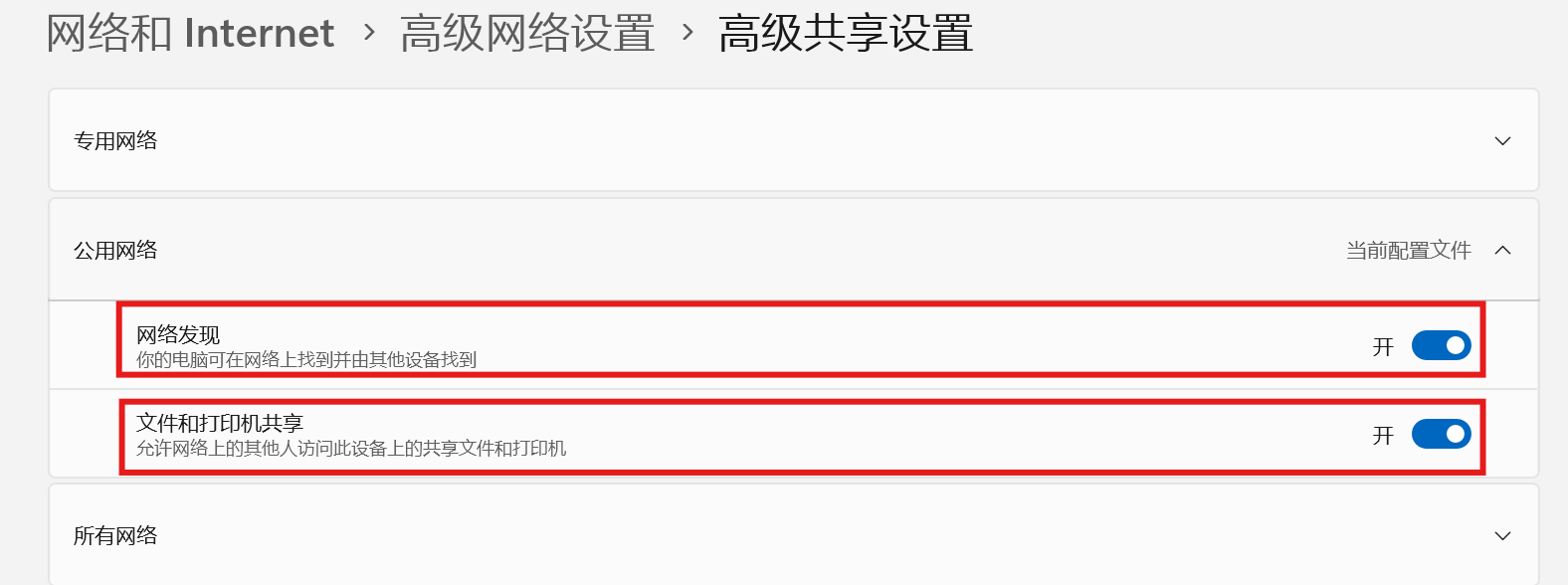
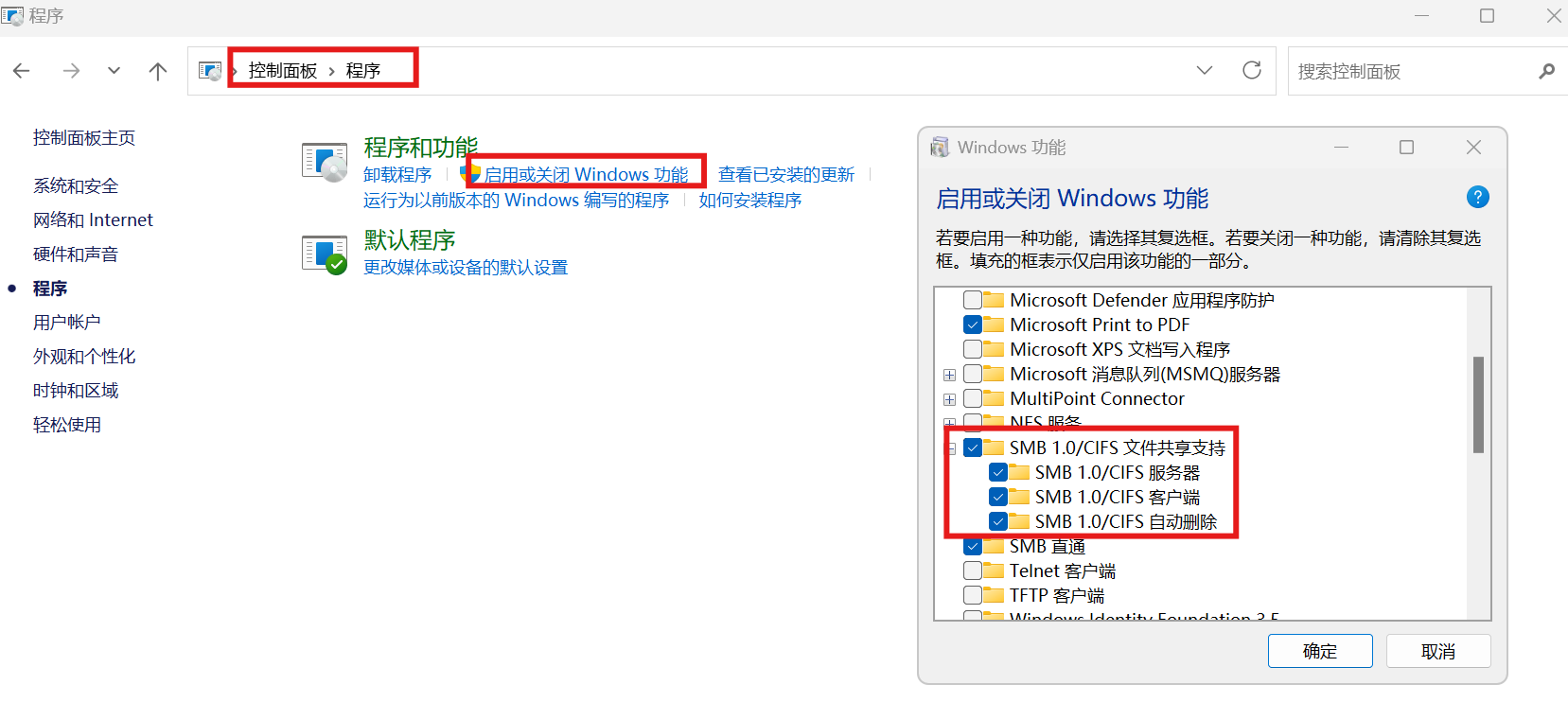
(3)启用网络发现和文件共享
(4)关闭SELinux,查看共享目录
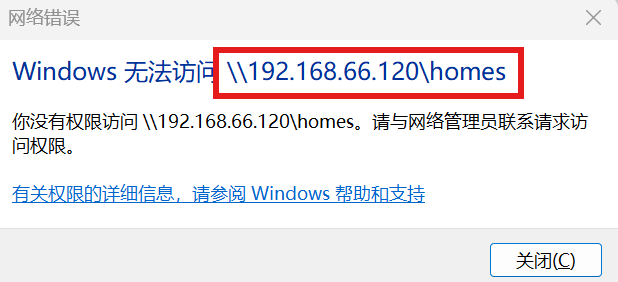
注:若开启SELinux,则windows没有权限访问
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 0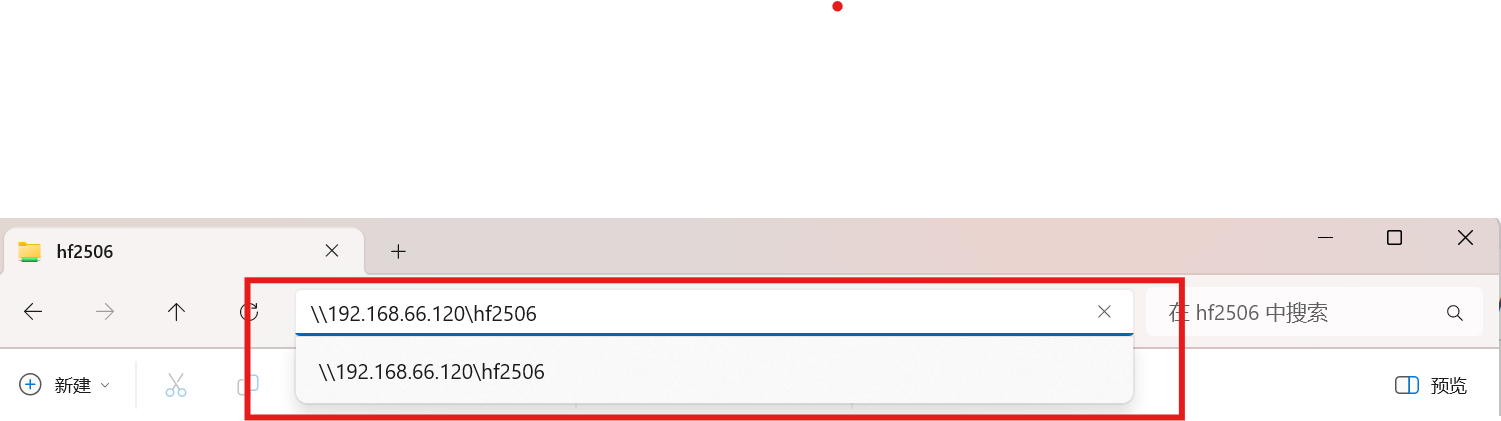
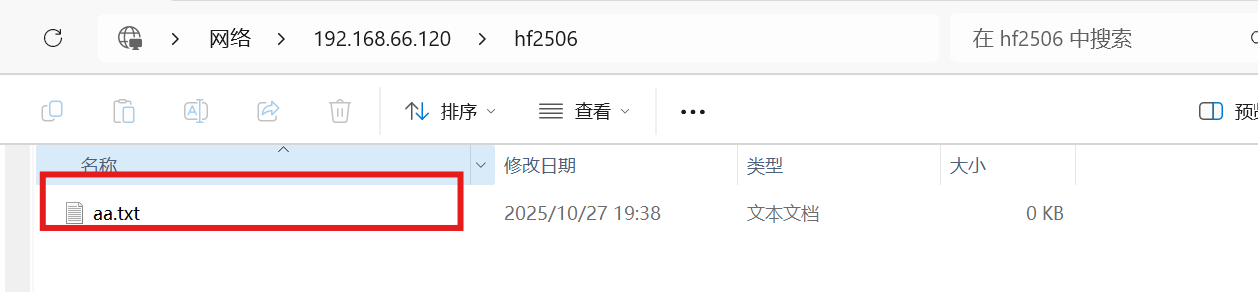
注:连接时,使用创建的samba用户zhangsan,和密码
(5)清空windows中samba的缓存
5.在开启了SELinux后如何正常维护Linux的使用?
- 方案一:修改安全上下文信息
- 方案二:修改布尔值开关
- 方案三:直接修改SELinux规则
二、SELinux 实践操作
1.检查与设置SELinux模式
查看当前模式
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce
Enforcing临时切换模式
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce
usage: setenforce [ Enforcing | Permissive | 1 | 0 ]
# setenforce 0 # 切换到 Permissive
# setenforce 1 # 切换到 Enforcing永久设置模式(编辑 /etc/selinux/config)
sed -i 's/SELINUX=.*$/SELINUX=enforcing/' /etc/selinux/config2.安装apache服务
[root@localhost ~]# dnf -y install httpd
# 修改网页根目录
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /www
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
DocumentRoot "/www"
<Directory "/www">
[root@localhost ~]# echo "aaaa" > /www/index.html
[root@localhost ~]# echo "hello world" > /var/www/html/index.html
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start httpd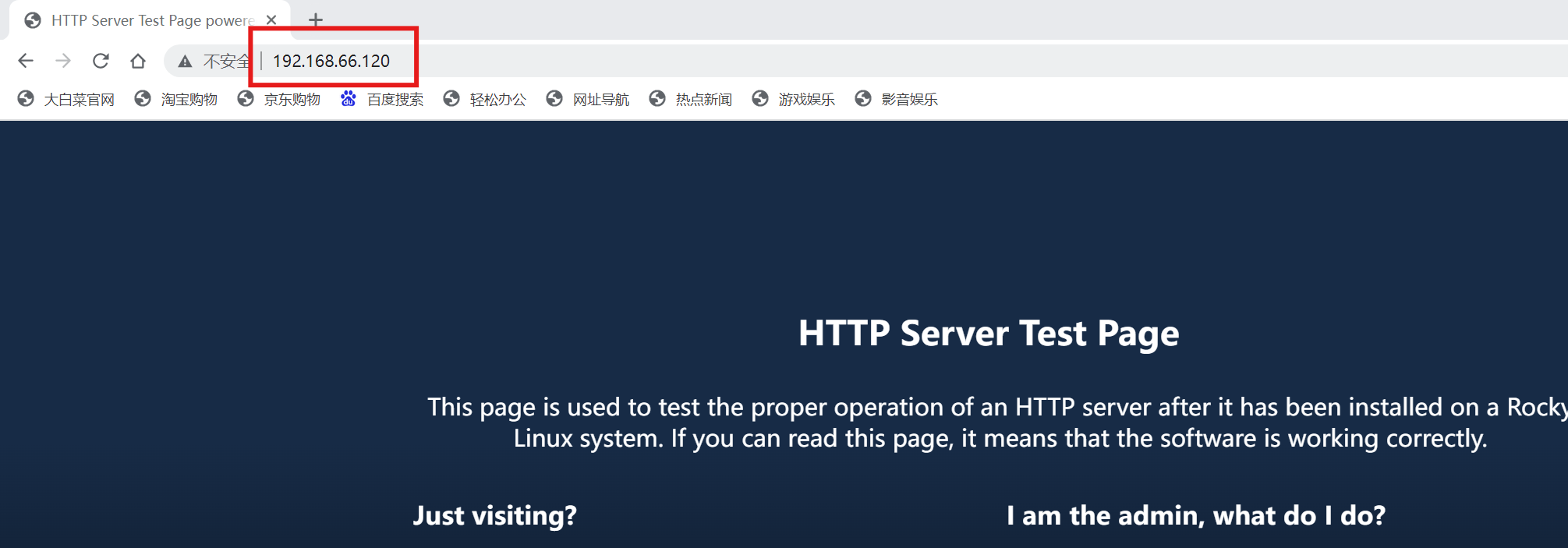
注:可以看到即便修改了网页根目录,配置也没有生效,只有关掉SELinux安全机制才行,这是因为文件的安全上下文起到了作用
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ldZ /var/www/html/index.html
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 12 10月 27 18:24 /var/www/html/index.html
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ldZ /www/
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 24 10月 27 18:15 /www/3.修改文件安全上下文
[root@localhost ~]# chcon -R -t httpd_sys_content_t /www/
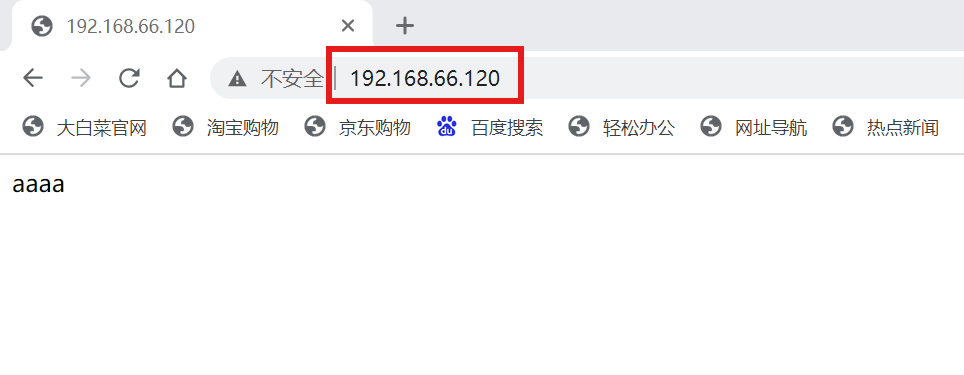
注:此时即便SELinux处于开启状态,也能够正常访问修改后的网页根目录
4.查看samba配置文件
注:这里讲了如何在开启SELinux机制的基础上共享文件目录
5.修改samba安全上下文
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ldZ /data/
drwxrwxr-x+ 2 root root unconfined_u:object_r:default_t:s0 20 10月 27 19:39 /data/
[root@localhost ~]# chcon -R -t samba_share_t /data/
[root@localhost ~]# ls -ldZ /data/
drwxrwxr-x+ 2 root root unconfined_u:object_r:samba_share_t:s0 20 10月 27 19:39 /data/
[root@localhost ~]# setenforce 1
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce
Enforcing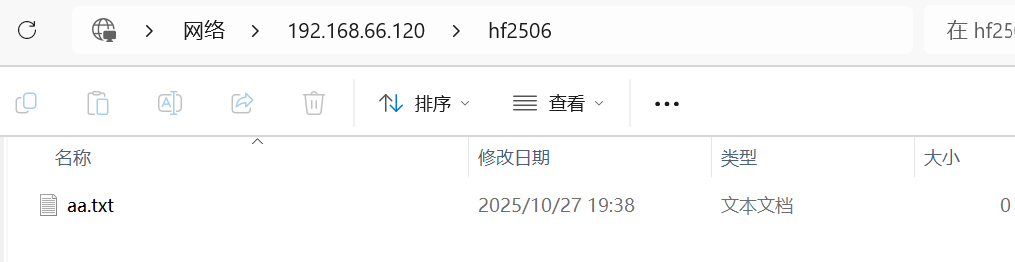
注:此时即便SELinux开启,依旧能够正常共享samba服务的共享目录
6.总结
- apache服务和samba服务均是通过修改安全上下文的方式,在迎合SELinux的规则之后,才可以被访问
三、修改布尔值开关
注:布尔值控制服务的特定功能,适合动态调整策略
1.管理布尔值开关
# 查看布尔值
[root@localhost ~]# getsebool -a | grep samba
samba_create_home_dirs --> off
samba_domain_controller --> off
samba_enable_home_dirs --> off
samba_export_all_ro --> off
samba_export_all_rw --> off
samba_load_libgfapi --> off
samba_portmapper --> off
samba_run_unconfined --> off
samba_share_fusefs --> off
samba_share_nfs --> off
sanlock_use_samba --> off
tmpreaper_use_samba --> off
use_samba_home_dirs --> off
virt_use_samba --> off2.查看samba服务家目录
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce
Enforcing
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/samba/smb.conf
2.开启家目录布尔值
[root@localhost ~]# setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs on
[root@localhost ~]# getsebool -a | grep samba | grep home
samba_create_home_dirs --> off
samba_enable_home_dirs --> on
use_samba_home_dirs --> off
注:此时就可以正常访问,访问链接也可以是\\192.168.66.120\zhangsan
3.对比普通用户和root用户

- 普通用户家目录都是user_home_dir_t
- 超级管理员root则是admin_home_t
四、直接修改SELinux规则
注:借助httpd修改默认端口的例子来查看
1.环境准备
[root@localhost ~]# getenforce
Enforcing
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl start httpd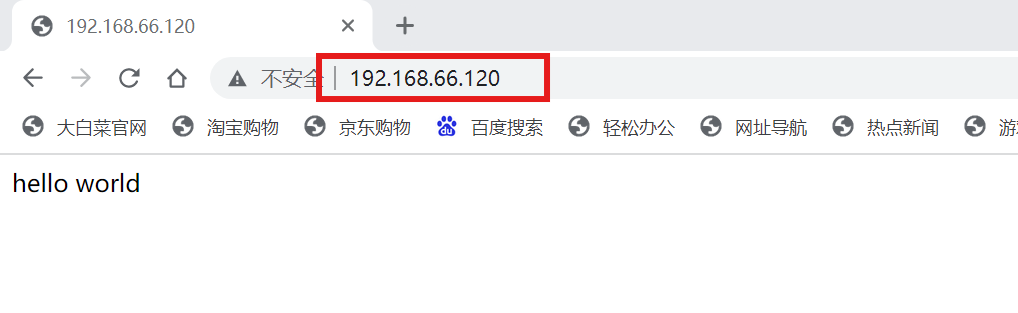
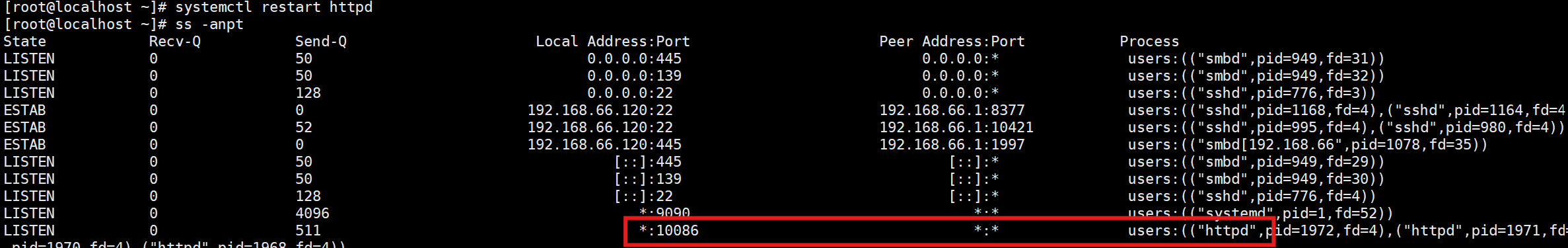
2.修改监听端口为10086
[root@localhost ~]# vi /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
Listen 10086
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl restart httpd
Job for httpd.service failed because the control process exited with error code.
See "systemctl status httpd.service" and "journalctl -xeu httpd.service" for details.-
这里禁止使用10086端口,我们查看可用的端口,发现没有10086端口,手动添加
[root@localhost ~]# semanage port -l | grep http
http_cache_port_t tcp 8080, 8118, 8123, 10001-10010
http_cache_port_t udp 3130
http_port_t tcp 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443, 9000
pegasus_http_port_t tcp 5988
pegasus_https_port_t tcp 5989
[root@localhost ~]# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 10086
[root@localhost ~]# semanage port -l | grep http
http_cache_port_t tcp 8080, 8118, 8123, 10001-10010
http_cache_port_t udp 3130
http_port_t tcp 10086, 80, 81, 443, 488, 8008, 8009, 8443, 9000
pegasus_http_port_t tcp 5988
pegasus_https_port_t tcp 5989
备注:刹那绽放的恋之花火(二姐才是众望所归,遗憾男主是黑皮体育生(o(╥﹏╥)o))
