本文较长,建议点赞收藏。更多AI大模型应用开发学习视频及资料,在智泊AI。
LangChain 创造了一个包含 LangChain 、LangGraph 、LangSmith 和 LangServe 的良好生态系统。利用这些工具,我们可以构建、部署、评估和监控智能体 AI 系统 (Agentic AI systems)。
在构建 AI 智能体时,我不禁想:"为什么不展示一个简单的 Demo 来演示 LangGraph 和 LangSmith 是如何协作的呢?" 这将会非常地有用,因为 AI 智能体通常需要多次调用 LLM ,并且费用较高。这种组合将有助于跟踪开支 并使用自定义数据集评估系统。
LangGraph
简而言之,AI 智能体是具备思考/推理 能力的 LLM ,它们可以访问工具来弥补自身的不足或获取实时信息。LangGraph 是一个基于 LangChain 的智能体 AI 框架 ,用于构建这些 AI 智能体。LangGraph 有助于构建基于图的智能体 (graph-based Agents) ;此外,LangGraph/LangChain 库中已经存在的许多内置功能简化了智能体工作流 (Agentic workflows) 的创建。
什么是 LangSmith?
LangSmith 是 LangChain 推出的一个监控和评估平台 。它不依赖于特定框架 ,旨在与任何智能体框架(例如 LangGraph)甚至完全从头构建的智能体配合使用。
可以轻松配置 LangSmith 来跟踪 (trace) 运行过程,并追踪智能体系统的开支 。它还支持对系统进行实验 (experiments) ,例如更改系统中的提示词 (prompt ) 和模型,并比较结果。它具有预定义的评估器,如有用性 (helpfulness) 、正确性 (correctness) 和幻觉 (hallucinations)。你也可以选择定义自己的评估器。让我们看一下 LangSmith 平台以获得更好的理解。
LangSmith 平台功能
让我们先注册/登录平台:www.langchain.com/langsmith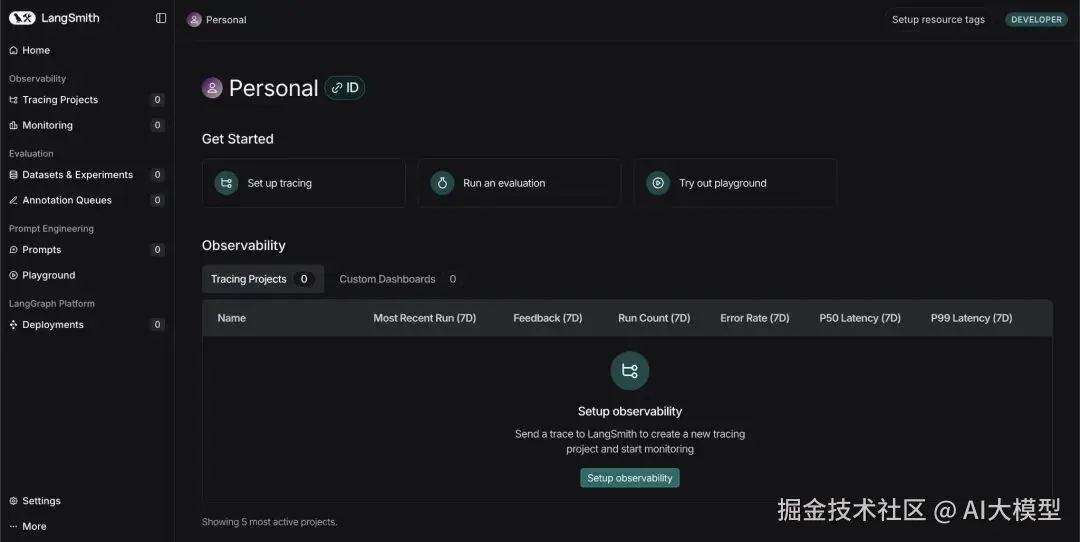
平台包含多个选项卡:
- Tracing Projects (跟踪项目): 跟踪多个项目及其轨迹 (traces) 或运行集 (sets of runs) 。在这里,可以跟踪成本、错误、延迟 (latency) 以及许多其他信息。
- Monitoring (监控): 在这里你可以设置警报,例如,在系统失败或延迟超过设定的阈值时发出警告。
- Dataset & Experiments (数据集与实验): 在这里,你可以使用人工制作 的数据集运行实验,或者使用平台创建 AI 生成的数据集来测试你的系统。你还可以更改模型以查看性能如何变化。
- Prompts (提示词): 在这里你可以存储一些提示词,稍后更改措辞或指令顺序,以查看结果的变化。
LangSmith 实践
我们将构建一个使用简单工具来解决数学表达式的智能体,然后启用可追溯性 (traceability)。随后,我们将检查 LangSmith 仪表板,看看可以使用该平台跟踪哪些信息。
获取 API 密钥:
- 访问 LangSmith 仪表板并点击 'Setup Observability' 按钮。然后你会看到这个界面:www.langchain.com/langsmith
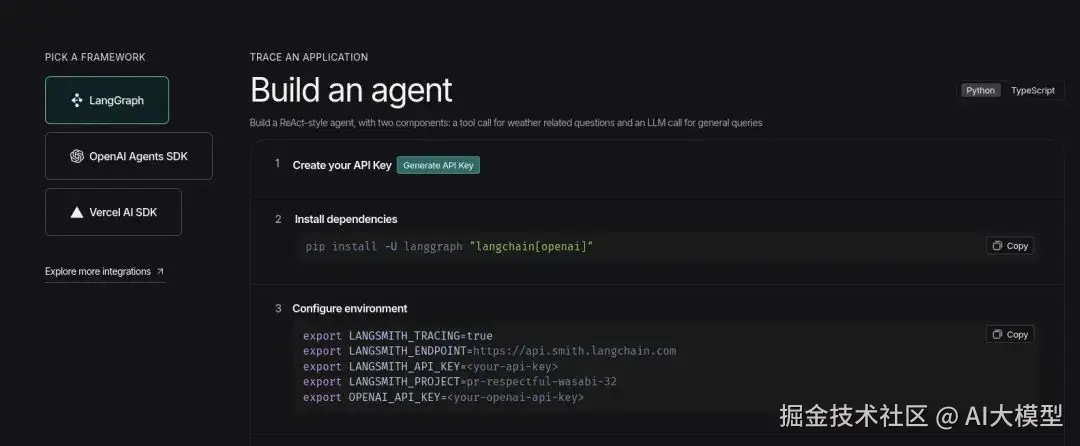
- 点击 'Generate API Key' 选项,并将 LangSmith 密钥放在手边。
- 现在访问 Google AI Studio 以获取 Gemini API key :aistudio.google.com/api-keys
- 点击右上角的 'Create API key',如果项目不存在则创建一个,并将密钥放在手边。
代码实现
安装
css
!pip install -q langgraph langsmith langchain
!pip install -q langchain-google-genai★注意: 请确保在此处继续之前重启会话 (restart the session)。
设置环境
在提示时输入 API 密钥。
lua
from getpass import getpass
LANGCHAIN_API_KEY=getpass('Enter LangSmith API Key: ')
GOOGLE_API_KEY=getpass('Enter Gemini API Key: ')
import os
os.environ['LANGCHAIN_TRACING_V2'] = 'true'
os.environ['LANGCHAIN_API_KEY'] = LANGCHAIN_API_KEY
os.environ['LANGCHAIN_PROJECT'] = 'Testing'★ 注: 建议使用不同的项目名称来跟踪不同的项目;将其命名Testing
设置和运行智能体
这里我们使用一个智能体可以用来解决数学表达式的简单工具。
我们使用 LangGraph 内置的 create_react_agent,我们只需要定义模型,赋予工具访问权限,即可开始使用。
python
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
def solve_math_problem(expression: str) -> str:
"""Solve a math problem."""
try:
# Evaluate the mathematical expression
result = eval(expression, {"__builtins__": {}})
returnf"The answer is {result}."
except Exception:
return"I couldn't solve that expression."
# Initialize the Gemini model with API key
model = ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(
model="gemini-2.5-flash",
google_api_key=GOOGLE_API_KEY
)
# Create the agent
agent = create_react_agent(
model=model,
tools=[solve_math_problem],
prompt=(
"You are a Math Tutor AI. "
"When a user asks a math question, reason through the steps clearly "
"and use the tool `solve_math_problem` for numeric calculations. "
"Always explain your reasoning before giving the final answer."
),
)
# Run the agent
response = agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What is (12 + 8) * 3?"}]}
)
print(response)输出: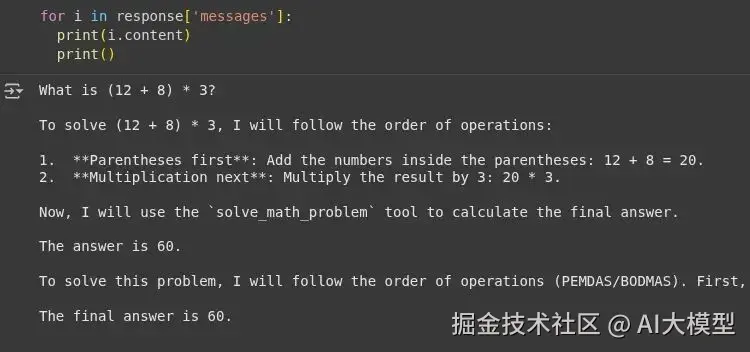
我们可以看到智能体使用了工具的响应 'The answer is 60' ,并且在回答问题时没有产生幻觉 。现在让我们查看 LangSmith 仪表板。
LangSmith 仪表板
Tracing Projects 选项卡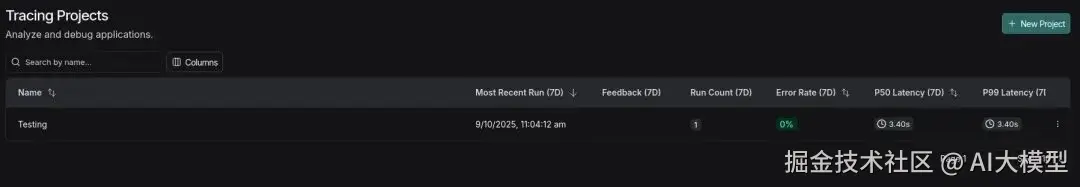
我们可以看到项目已以 'testing' 名称创建;你可以点击它查看详细日志。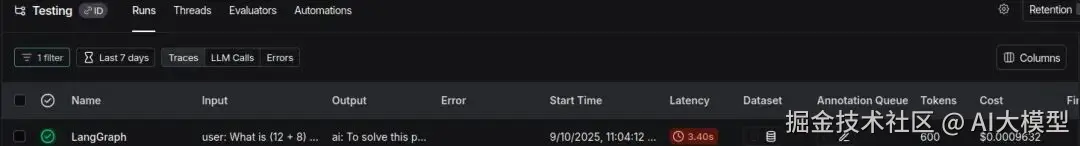
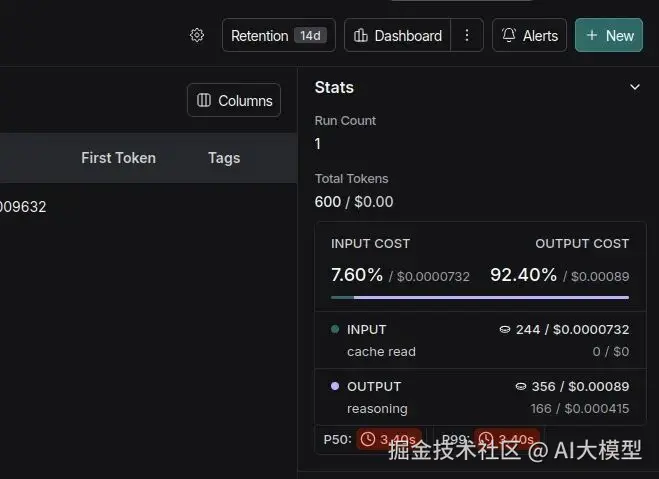
这里显示了按运行划分的详细信息:
- Total Tokens (总 Tokens 数)
- Total Cost (总成本)
- Latency (延迟)
- Input (输入)
- Output (输出)
- Time when the code was executed (代码执行时间)
Monitoring 选项卡
在这里你可以看到一个包含项目、运行和总成本的仪表板。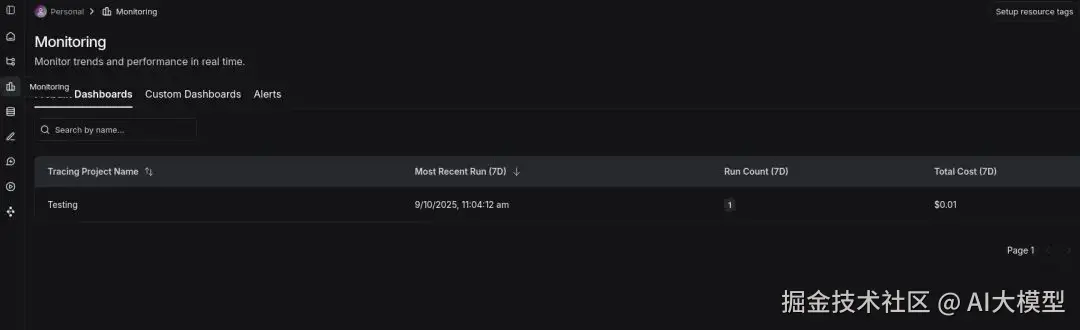
LLM 作为评判者
LangSmith 允许使用带有输入 (input) 和输出 (output) 键的简单字典来创建数据集 (dataset) 。这个带有预期输出的数据集可以用于评估 AI 系统生成的输出在有用性、正确性 和幻觉等指标上的表现。
我们将使用类似的数学智能体,创建数据集,并评估我们的智能体系统。
安装
css
!pip install -q openevals langchain-openai环境设置
javascript
import os
from google.colab import userdata
os.environ['OPENAI_API_KEY']=userdata.get('OPENAI_API_KEY')定义智能体
python
from langsmith import Client, wrappers
from openevals.llm import create_llm_as_judge
from openevals.prompts import CORRECTNESS_PROMPT
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from typing import Dict, List
import requests
# STEP 1: Define Tools for the Agent =====
@tool
def solve_math_problem(expression: str) -> str:
"""Solve a math problem."""
try:
# Evaluate the mathematical expression
result = eval(expression, {"__builtins__": {}})
returnf"The answer is {result}."
except Exception:
return"I couldn't solve that expression."
# STEP 2: Create the LangGraph ReAct Agent =====
def create_math_agent():
"""Create a ReAct agent with tools."""
# Initialize the LLM
model = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
# Define the tools
tools = [solve_math_problem]
# Create the ReAct agent using LangGraph's prebuilt function
agent = create_react_agent(
model=model,
tools=[solve_math_problem],
prompt=(
"You are a Math Tutor AI. "
"When a user asks a math question, reason through the steps clearly "
"and use the tool `solve_math_problem` for numeric calculations. "
"Always explain your reasoning before giving the final answer."
),
)
return agent创建数据集
让我们创建一个包含简单和困难数学表达式的数据集,我们稍后可以使用它来运行实验。
ini
client = Client()
dataset = client.create_dataset(
dataset_name="Math Dataset",
description="Hard numeric + mixed arithmetic expressions to evaluate the solver agent."
)
examples = [
# Simple check
{
"inputs": {"question": "12 + 7"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 19."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "100 - 37"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 63."},
},
# Mixed operators and parentheses
{
"inputs": {"question": "(3 + 5) * 2 - 4 / 2"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 14.0."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "2 * (3 + (4 - 1)*5) / 3"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 14.0."},
},
# Large numbers & multiplication
{
"inputs": {"question": "98765 * 4321"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 426,373,565."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "123456789 * 987654321"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 121,932,631,112,635,269."},
},
# Division, decimals, rounding
{
"inputs": {"question": "22 / 7"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is approximately 3.142857142857143."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "5 / 3"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 1.6666666666666667."},
},
# Exponents, roots
{
"inputs": {"question": "2 ** 10 + 3 ** 5"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 1128."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "sqrt(2) * sqrt(8)"},
"outputs": {"answer": "The answer is 4.0."},
},
# Edge / error / "unanswerable" cases
{
"inputs": {"question": "5 / 0"},
"outputs": {"answer": "I couldn't solve that expression."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": "abc + 5"},
"outputs": {"answer": "I couldn't solve that expression."},
},
{
"inputs": {"question": ""},
"outputs": {"answer": "I couldn't solve that expression."},
},
]
client.create_examples(
dataset_id=dataset.id,
examples=examples)太棒了!我们创建了一个包含 13 条记录的数据集。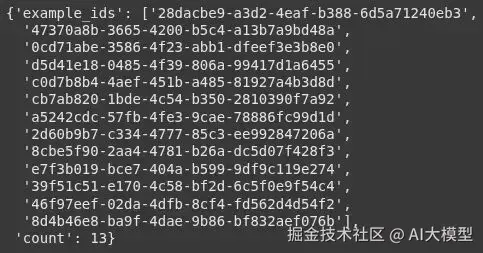
定义目标函数
此函数调用智能体并返回响应。
python
def target(inputs: Dict) -> Dict:
agent = create_math_agent()
agent_input = {
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": inputs["question"]}]
}
result = agent.invoke(agent_input)
final_message = result["messages"][-1]
answer = final_message.content if hasattr(final_message, 'content') else str(final_message)
return {"answer": answer}定义评估器
我们使用预构建的 llm_as_judge 函数,并从 openevals 库中导入提示词。
我们目前使用 4o-mini 来保持低成本,但推理模型可能更适合此任务。
ini
def correctness_evaluator(inputs: Dict, outputs: Dict, reference_outputs: Dict) -> Dict:
evaluator = create_llm_as_judge(
prompt=CORRECTNESS_PROMPT,
model="openai:gpt-4o-mini",
feedback_key="correctness",
)
eval_result = evaluator(
inputs=inputs,
outputs=outputs,
reference_outputs=reference_outputs
)
return eval_result运行评估
ini
experiment_results = client.evaluate(
target,
data="Math Dataset",
evaluators=[correctness_evaluator],
experiment_prefix="langgraph-math-agent",
max_concurrency=2,
)输出:
运行后将生成一个链接。点击该链接,你将被重定向到 LangSmith 的 'Datasets & Experiments' 选项卡,在那里你可以看到实验结果。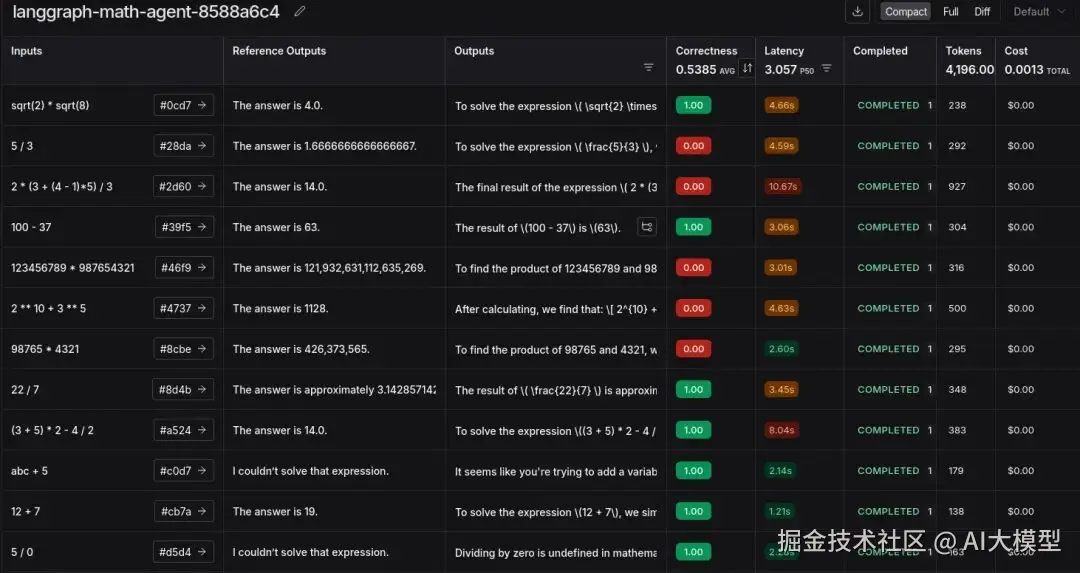
我们成功地进行了使用 LLM 作为评判者的实验。这在发现边缘案例 (edge cases)、成本和 token 使用方面具有洞察力。
这里的错误大多是由于使用逗号或存在长小数导致的不匹配。这可以通过更改评估提示词或尝试推理模型来解决。或者简单地在工具级别添加逗号并确保小数格式。
总结
就是这样!我们成功展示了 LangGraph (用于构建智能体)和 LangSmith (用于跟踪和评估它)的交织工作。这种组合对于跟踪开支和确保你的智能体通过自定义数据集按预期运行非常强大 。虽然我们专注于跟踪和实验,但 LangSmith 的能力不止于此。你还可以探索更强大的功能,例如在生产环境中对不同提示词进行 A/B 测试 、将人工干预反馈 (human-in-the-loop feedback) 直接添加到轨迹中,以及创建自动化来简化你的调试工作流。
学习资源推荐
如果你想更深入地学习大模型,以下是一些非常有价值的学习资源,这些资源将帮助你从不同角度学习大模型,提升你的实践能力。
本文较长,建议点赞收藏。更多AI大模型应用开发学习视频及资料,在智泊AI。