线性表
线性表是n个具有相同特性元素的有限序列 。线性表是一种在实际中广泛使用的数据结构,常见的线性表有顺序表,链表,栈,队列...
线性表在逻辑上是线性结构 ,但是在物理结构上不一定是连续的 ,线性表在物理结构上储存时,通常是以数组和链式结构的形式存储
顺序表
顺序表时一段物理连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据上的增删查改
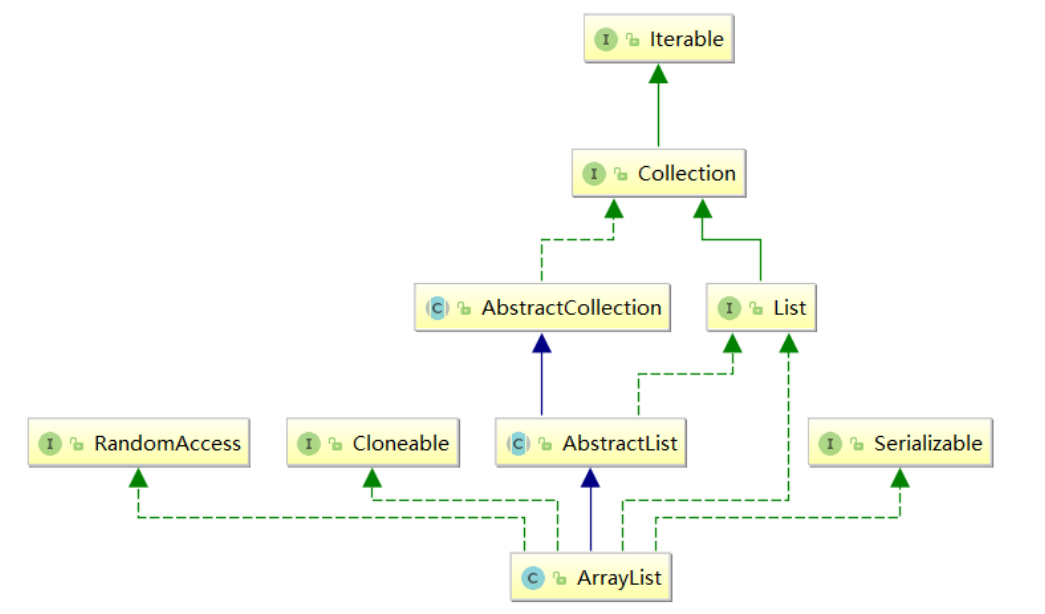
ArrayList简介
注意:
1.ArrayList是以泛型方式实现的 ,使用时必须要先实例化
2.ArrayList实现了RandomAccess接口 ,表明ArrayList支持随机访问
3.ArrayList实现了Cloneable接口 ,表明ArrayList是可以clone的
4.ArrayList实现了Serializable接口 ,表明ArrayList支持序列化
5.和Vector不同,ArrayList不是线程安全的,在单线程 下可以使用,在多线程中可以选择Vector或者CopyOnWriteArrayList
6.ArrayList是一段连续的空间 ,并且可以动态扩容 ,是一个动态类型的顺序表
ArrayList使用
ArrayList的构造
构造方法:

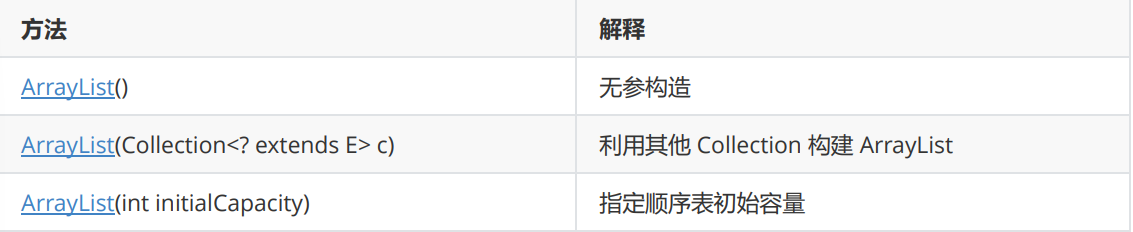
ArrayList()
无参构造

并没有分配内存
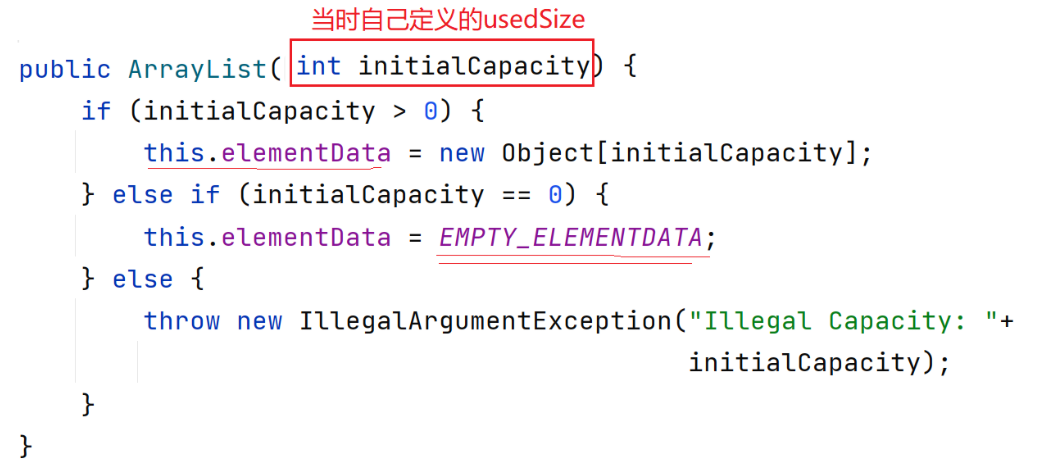
ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
指定了初始内存
java
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(10);如果参数大于0则让数组指向开辟的这块空间(Object)类型 ,如果参数为0则指向定义的没有分配空间的数组
ArrayList(Collection<? extends E>c)

其中参数表示实现了Collection接口并且是E或者E的子类
java
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>(10);
ArrayList<Integer> list2=new ArrayList<>(list);E代表ArrayList尖括号的内容 ,此时list是整型 并且实现了Collection接口 并且list2继承了list的数据。
两个方法的比较
java
//ArrayList实现了List接口
//方法一
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
//方法二
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>()方法一: 通过list这个引用可以调用当前类所有可以被调用的方法
方法二: 只要实现这个接口 的都可以被调用,可以向上转型或者多态 ,但是只能调用这个接口实现的方法
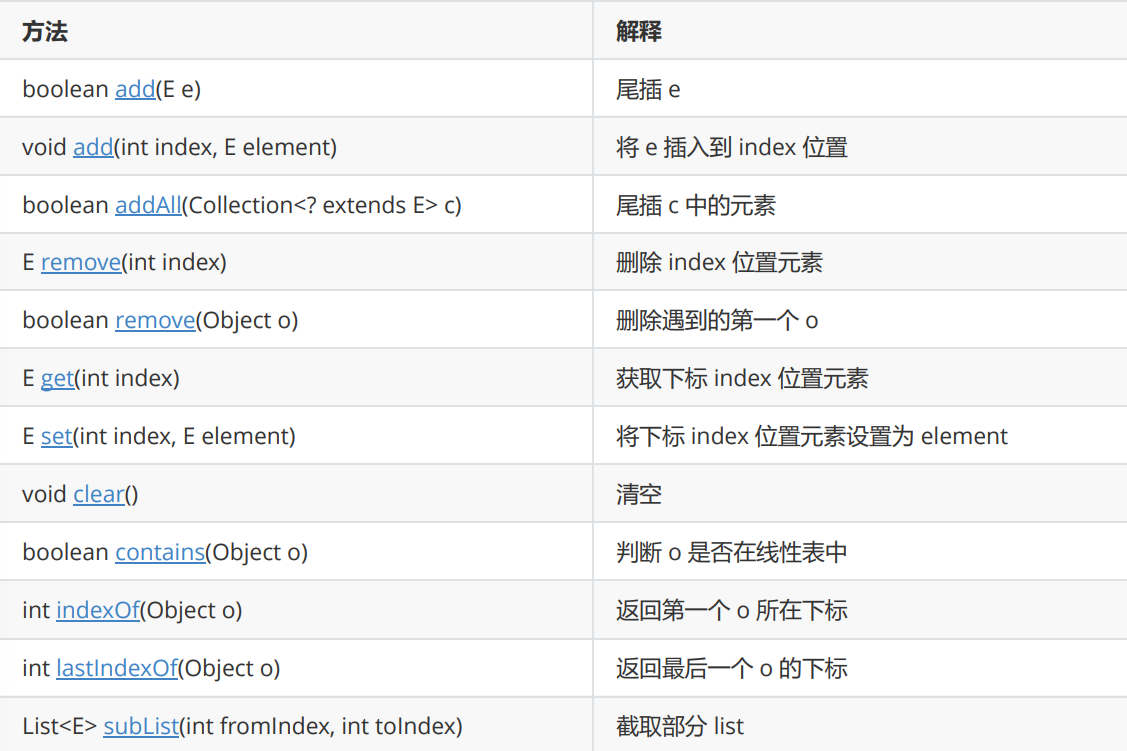
ArrayList常见操作
ADD操作
扩容1.5
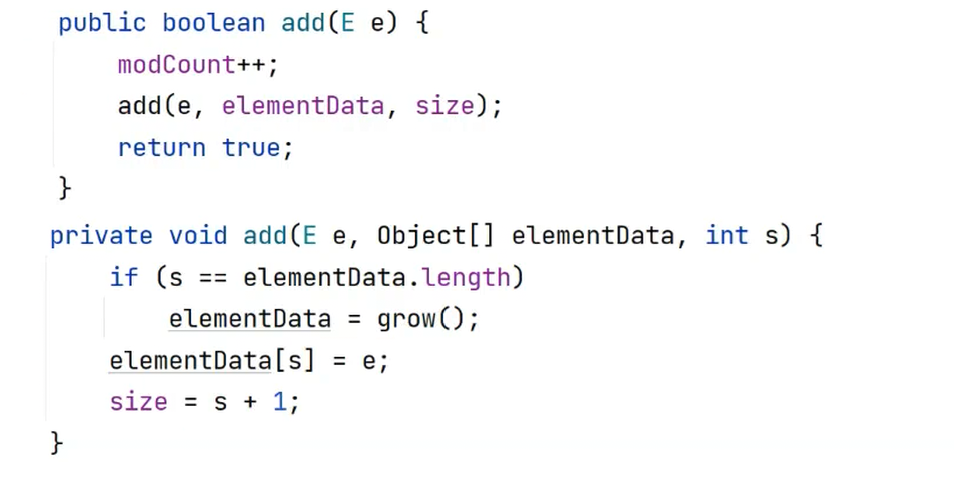
首先调用add方法 ,将要添加的数据,数组以及目前元素个数传过去
在add方法中进行判断,如果目前的元素个数和数组大小相等 ,则调用扩容方法 ,如果不相等则插入数据
grow方法:
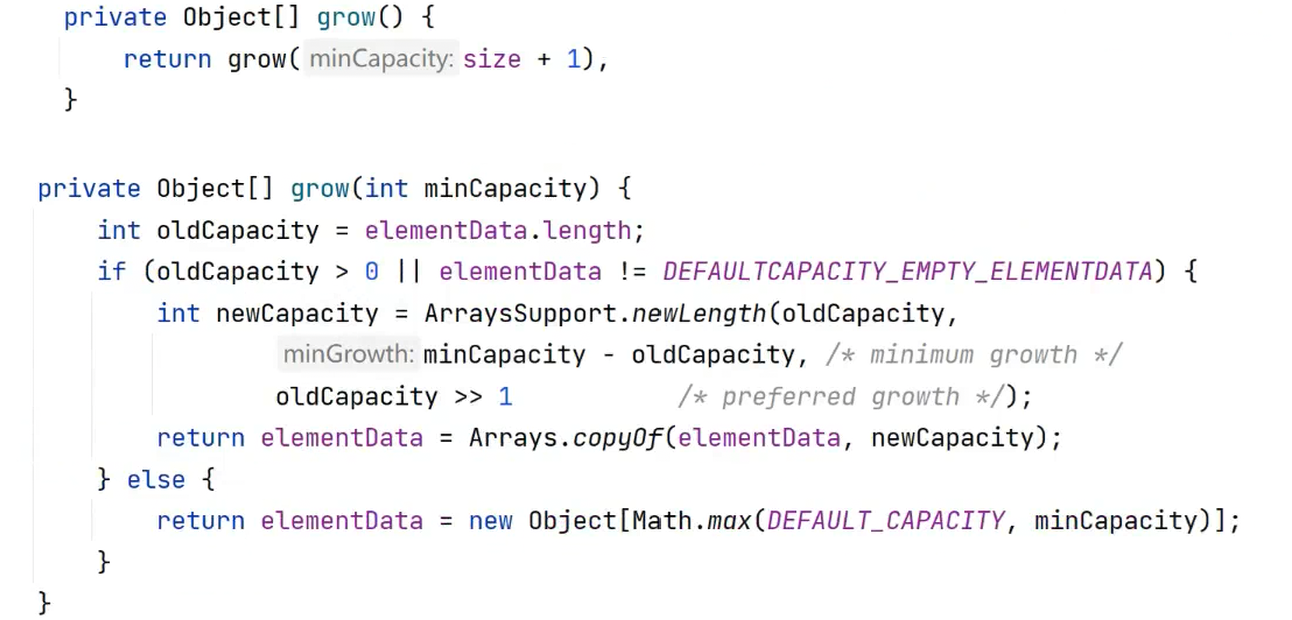
假设目前的数组大小是10 ,元素个数也是10
1.将10+1 传给grow方法,oldCapacity=10
2.如果原来的数组长度不为0,将10,11-10,10/2 传入newLength方法
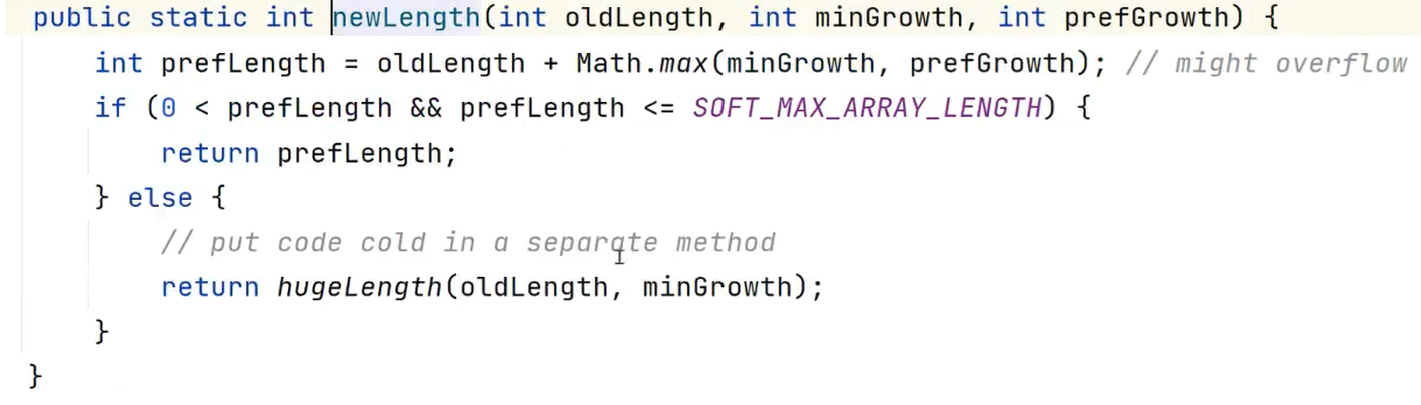
prefLength=10+(1,5)之间的最大值,也就是说prefLength=15
如果prefLength大于0并且小于int最大值-8 ,然后返回prefLength 。否则进入hugeLength方法 ,他的逻辑是:将oldLength+minGrowth赋给一个int类型的值a ,如果oldLength+minGrowth大于整形的最大值,那么a小于0 ,直接报异常。如果a小于整形的最大值-8 那么直接返回整型的最大值-8 ,否则直接返回a
3.接收到返回值后调用copyOf方法 ,新数组返回
4.如果原数组长度为0,那么返回一个长度为10的新数组
remove(Object o)
这里在需要传递一个包装类型对象
java
list.remove(new Integer(10));subList
截取之后返回的是地址 ,也就说新对象指向的也是原数组的空间
java
List<Integer> list2=list.subList(2,3);ArrayList的遍历
1.通过for循环
java
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}2.foreach循环
java
for (Integer integer : list) {
System.out.print(integer + " ");
}3.使用迭代器输出
java
Iterator<Integer> it = list.listIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");//往后走一步,然后打印
}
//从指定位置出发
ListIterator<Integer> it=list.listIterator(list.size());
while(it.hasPrevious()){
System.out.print(it.previous()+" ");
}//从后往前简单的洗牌算法
java
public class Card {
public String id;
public String flower;
public Card(String id, String flower) {
this.id = id;
this.flower = flower;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "{" +
flower+
id +
"} ";
}
}
public class CardList {
List<Card> card=new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Card>> cardList=new ArrayList<>();
public static final String[] flower = {"♠", "♥", "♣", "♦"};
public static final String[] En={"J","Q","K","A"};
public void buyCard(){
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
for(int j=2;j<11;j++){
Card card=new Card(j+"",flower[i]);
this.card.add(card);
}
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
Card card=new Card(En[k],flower[i]);
this.card.add(card);
}
}
}
public void Swap( List<Card> card){
cardList.add(card);
Random random=new Random();
for(int i=0;i<52;i++){
int tmp=random.nextInt(52);
int tmp1 =random.nextInt(52);
var tmpcard=card.get(tmp);
card.set(tmp,card.get(tmp1));
card.set(tmp1,tmpcard);
}
}
public void getCard(List<Card> card){
List<List<Card>> people =new ArrayList<>();
people.add(new ArrayList<>());
people.add(new ArrayList<>());
people.add(new ArrayList<>());
for(int i=0;i<5;i++){
people.get(0).add(card.remove(0));
people.get(1).add(card.remove(0));
people.get(2).add(card.remove(0));
}
System.out.println("p1"+people.get(0));
System.out.println("p2"+people.get(1));
System.out.println("p3"+people.get(2));
}
}