热部署
A,什么是热部署
在不重启项目的时候,改变代码,实现实时的更新
B,引入依赖
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> |
C,验证
(引入依赖后,启动项目,改动代码,看是否能够正确显示)
java
package com.qcby.firstspringboot.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
@RequestMapping
public class HelloController {
// 将方法的返回值直接以指定的格式
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello,worlddddd";
}
}-------------------------------------------------------
核心(最常用的是):yaml将对应字段的值映射到实体类或者配置类中
随之引入两个注解,我将重点介绍这两个注解
@ConfigurationPreperties(prefix = "person")自动配置application.yaml中的person的值@PropertySource(value = "classpath:qy.properties")放在固定的配置文件里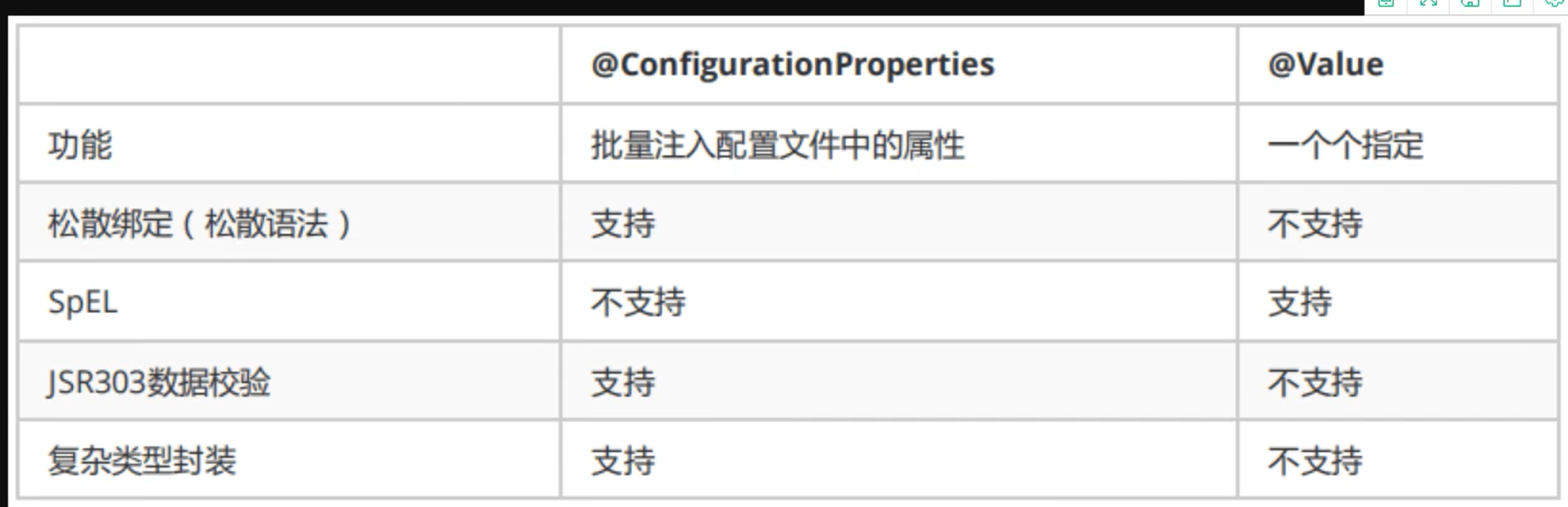
一,springBoot的配置文件的作用,application.yaml
- 配置应用基础参数:定义应用端口(server.port)、上下文路径(server.servlet.context-path)、编码格式等基础信息。
- 配置外部依赖 / 服务:设置数据库连接(spring.datasource)、缓存(spring.redis)、消息队列、第三方 API 密钥等依赖项参数。
- 多环境配置切换:配合 spring.profiles.active 实现开发(dev)、测试(test)、生产(prod)等环境的配置隔离,无需修改核心配置。
- 自定义属性配置:定义业务相关的自定义属性(如之前的 person.name、person.age),可通过 @Value 或 @ConfigurationProperties 绑定到 Java 实体类。
- Spring 框架配置:调整 Spring 核心组件行为,如日志级别(logging.level)、Bean 扫描规则、自动配置开关(spring.autoconfigure.exclude)等。
二,application.yaml 优点
- 采用缩进式层级结构,无需重复写前缀,比 properties 文件更易读、易维护。
- 支持列表、Map 等复杂数据结构,适合配置多组关联参数(如多数据源、多 Redis 节点)。
- 支持占位符和 SpEl 表达式,可动态引用其他配置项(如
${spring.datasource.url})。
三,基础:yaml的语法
a.普通的语法
(与perperties相比,更加的简洁,但对空格要求严格)
#这个是properties
#properties只能存键值对
#普通的key-value
spring.application.name=FirstSpringBoot
server.port=8082
#这个是yaml
#修改spring boot的自动配置
#普通的key-value
name: qinjiangb.对象的语法
下一行空两格;key:(一个空格)value,对象用大括号
student:
name: qin
age: 3
#行内写法
student1: {name: qinl,age: 3}c.数组的语法
#数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- monkey
#数组的行内写法
pets1: [cat,dog]d.值的写法
字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
其中字符串,较为特殊:默认不需要加单引号和双引号
使用双引号,特殊字符不进行转义,保持原来的意思
单引号,会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
双引号:
dog:
name: "xiaoxiao \n lll"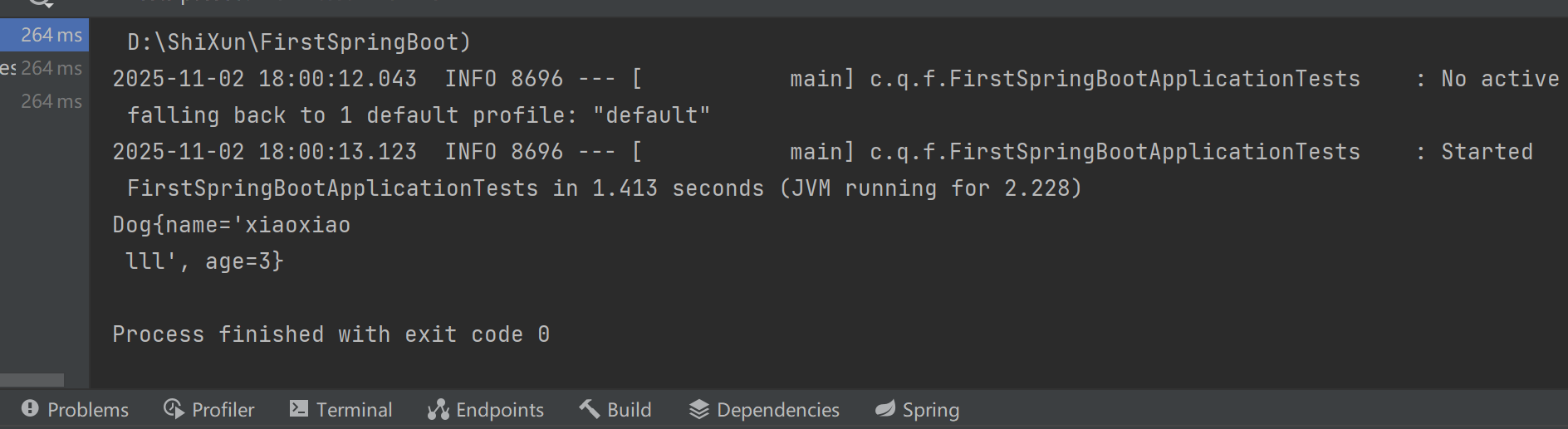
单引号
dog:
name: 'xiaoxiao \n lll'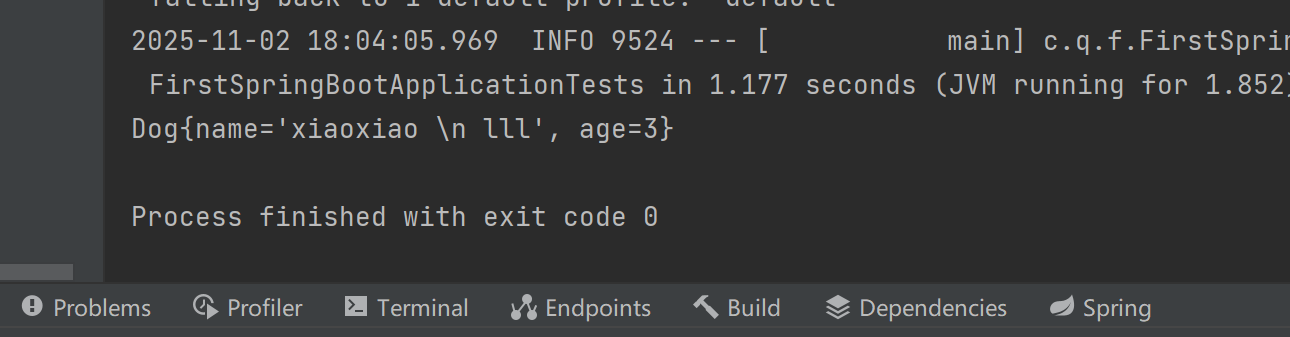
四,两个注解(映射)
映射,给配置里的 "key" 和类里的 "属性" 搭个桥,让值能准确传过去
@ConfigurationPreperties(prefix = "person")自动配置application.yaml中的person的值@PropertySource(value = "classpath:qy.properties")放在固定的配置文件里
a.@ConfigurationPreperties(prefix = "")
prefix后的值,需与applicaton.yaml一致
java
package com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dog")
public class Dog {
//放到字段或者set方法上
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// @Value("旺财")
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
@Value("3")
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Dog() {
}
public Dog(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
java
package com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
//实体类和配置类绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
//制定配置文件,加在制定的配置文件
//@PropertySource(value = "classpath:qy.properties")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
public Person(String name, Integer age, Boolean happy, Date birth, Map<String, Object> maps, List<Object> lists, Dog dog) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.happy = happy;
this.birth = birth;
this.maps = maps;
this.lists = lists;
this.dog = dog;
}
public Person() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Boolean getHappy() {
return happy;
}
public void setHappy(Boolean happy) {
this.happy = happy;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", happy=" + happy +
", birth=" + birth +
", maps=" + maps +
", lists=" + lists +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
}application.yaml
java
person:
name: ll${random.int}
age: ${random.int}
happy: true
birth: 2020/1/2
maps: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- cc
- ${person.hello:hello}_dd
dog: {name: wang,age: 2}测试类
java
package com.qcby.firstspringboot;
import com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo.Dog;
import com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class FirstSpringBootApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
private Person person;
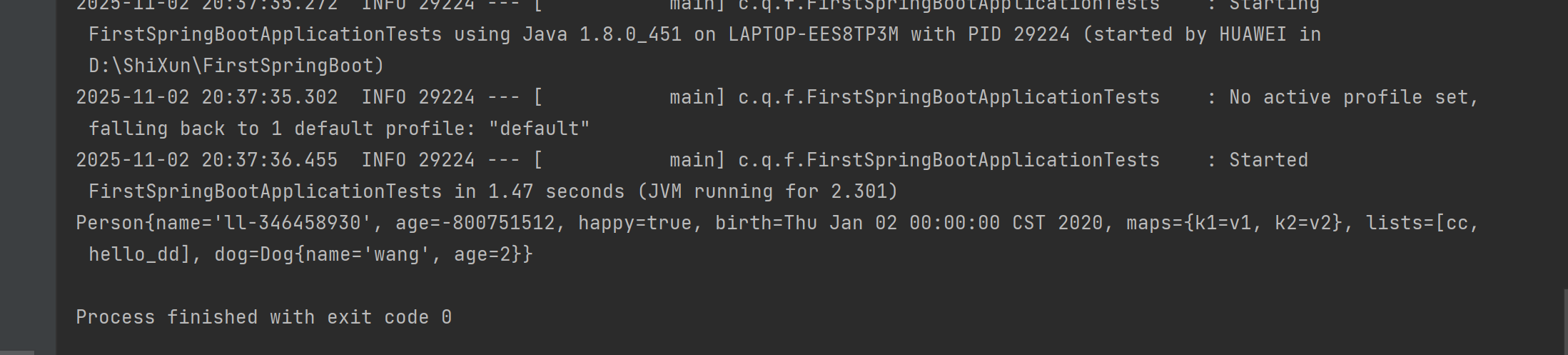
@Test
void contextLoads() {
// System.out.println(dog);
System.out.println(person);
}
}测试结果
b.自定义的配置类@PropertySource(value = "")
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:qy.properties")
这个必须要在相对应的属性前加上@Value,与配置类的key一致;否则无法映射
java
package com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dog")
public class Dog {
//放到字段或者set方法上
private String name;
private Integer age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
// @Value("旺财")
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
@Value("3")
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Dog() {
}
public Dog(String name, Integer age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
java
package com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
//实体类和配置类绑定
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
//制定配置文件,加在制定的配置文件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:qy.properties")
public class Person {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
public Person(String name, Integer age, Boolean happy, Date birth, Map<String, Object> maps, List<Object> lists, Dog dog) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.happy = happy;
this.birth = birth;
this.maps = maps;
this.lists = lists;
this.dog = dog;
}
public Person() {
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Boolean getHappy() {
return happy;
}
public void setHappy(Boolean happy) {
this.happy = happy;
}
public Date getBirth() {
return birth;
}
public void setBirth(Date birth) {
this.birth = birth;
}
public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
public Dog getDog() {
return dog;
}
public void setDog(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", happy=" + happy +
", birth=" + birth +
", maps=" + maps +
", lists=" + lists +
", dog=" + dog +
'}';
}
}qy.properpties
java
name =张三测试类
java
package com.qcby.firstspringboot;
import com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo.Dog;
import com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class FirstSpringBootApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
// System.out.println(dog);
System.out.println(person);
}
}测试结果
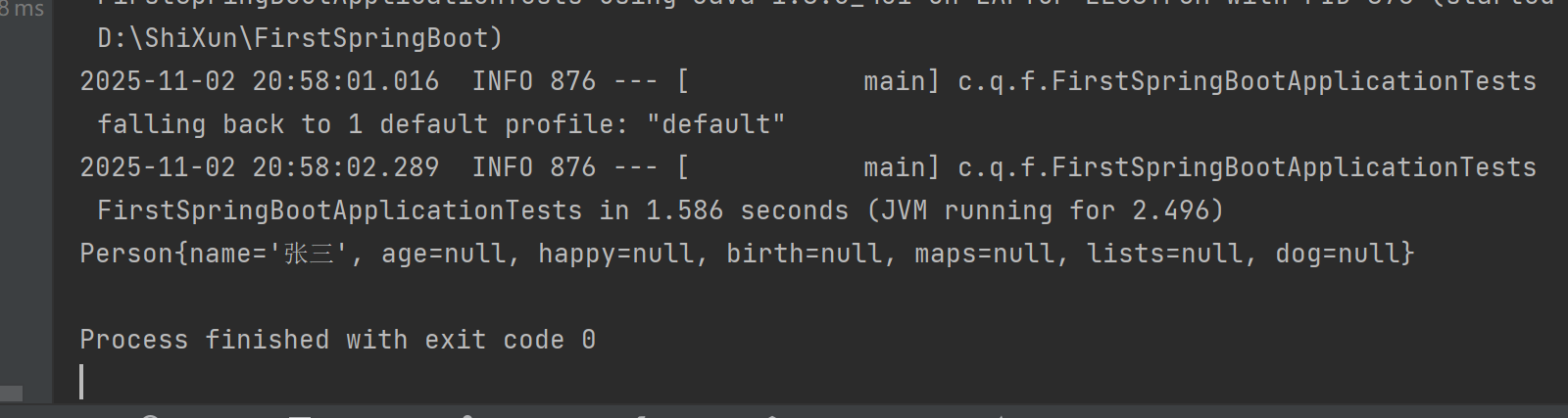
c.优先级的问题
自定义的配置文件和application.yaml优先级的问题
还是b中的代码,在application.yaml中添加(将其他代码注释掉,只保留以下代码)
java
name: 李四测试结果
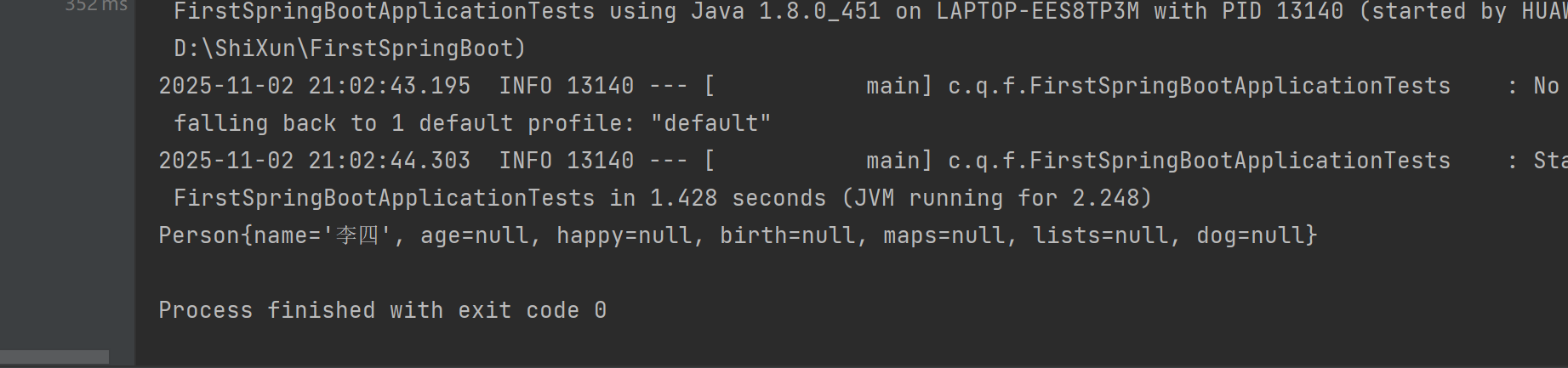
原因:相同 key 的配置时,在bean初始化的阶段,@PropertySource(value = "classpath:qy.properties")引用qy.properties先加载;application.yaml作为springboot的配置文件后加载;但是application.yaml会覆盖原来加载qy.properties的name,所以会出现李四
五,占位符
1、随机数
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| {random.value}、{random.int}、{random.long} {random.int(10)}、${random.int[1024,65536]} |
2、占位符获取之前配置的值,如果没有可以是用:指定默认值
|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| person.last‐name=张三{random.uuid} person.age={random.int} person.birth=2017/12/15 person.boss=false person.maps.k1=v1 person.maps.k2=14 person.lists=a,b,c person.dog.name=${person.hello:hello}_dog person.dog.age=15 |
${person.hello:hello}
如果person中有hello,那么使用 person.hello中的值;如果没有hello,那么使用hello
六,导入配置文件处理器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring‐boot‐configuration‐processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
在编写配置文件application.yaml,application.properties的时候,会自动提示,如下图所示
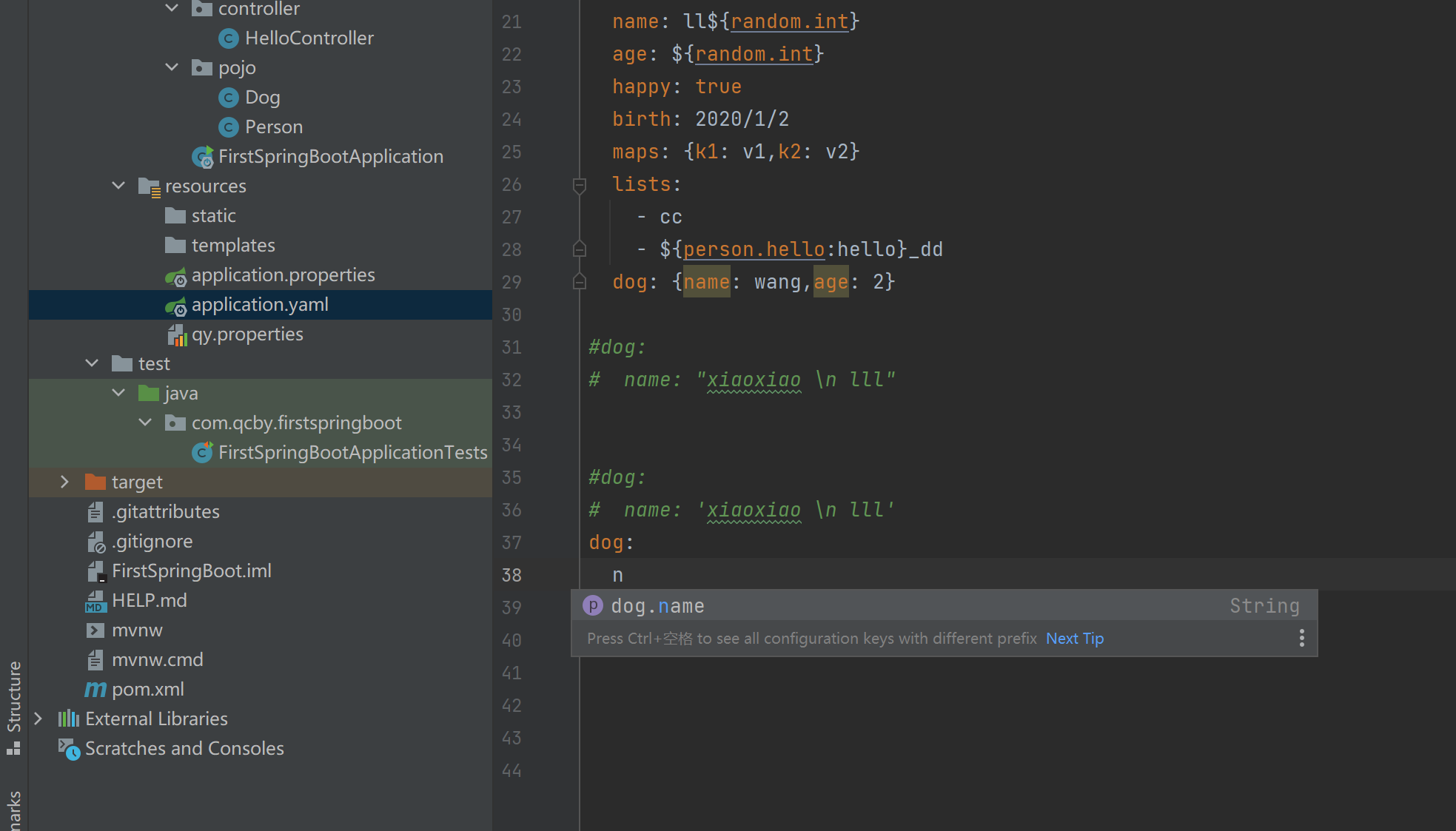
七,@ConfigurationProperties和@Value的区别

松散绑定:类里面lastName和application.yml的last-name

Test类
java
package com.qcby.firstspringboot;
import com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo.Dog;
import com.qcby.firstspringboot.pojo.Person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class FirstSpringBootApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Dog dog;
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(dog);
// System.out.println(person);
}
}测试的结果
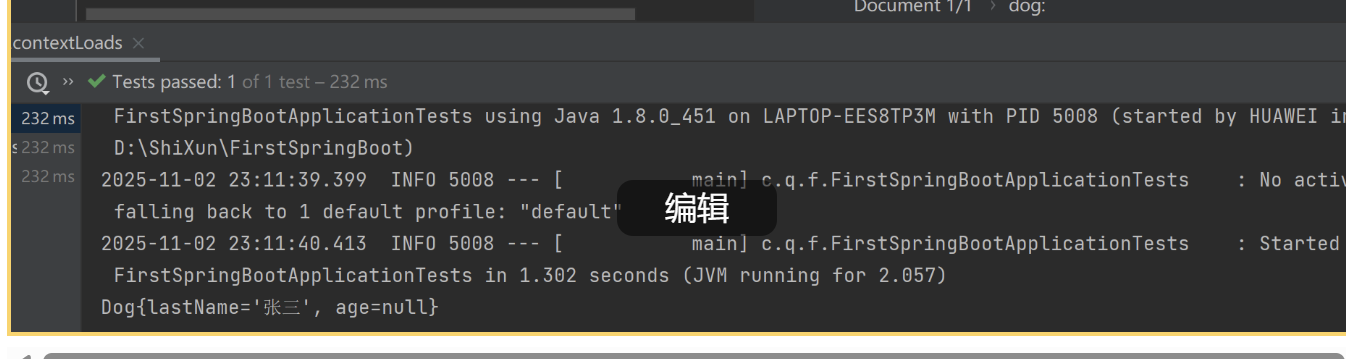
说明,可以映射