资料来源
目录
-
[1. 简介](#1. 简介)
-
[2. 导入库](#2. 导入库)
-
[3. 基础探索](#3. 基础探索)
-
[4. 数据预处理](#4. 数据预处理)
-
[5. 机器学习模型](#5. 机器学习模型)
-
[6. 结论](#6. 结论)
-
[7. 作者寄语](#7. 作者寄语)
1 | 简介
1.1 | 问题陈述
该数据集的目标是构建一个预测模型,用于诊断至少21岁且具有皮马印第安血统的女性患者是否患有糖尿病。该模型应根据多项诊断指标预测患者是否患有糖尿病(结果=1)或未患糖尿病(结果=0),这些指标包括葡萄糖水平、血压、皮肤厚度、胰岛素水平、BMI、糖尿病谱系功能和年龄。
1.2 | 数据描述
| 编号 | 列名 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pregnancies | 怀孕次数 |
| 2 | Glucose | 血糖葡萄糖水平 |
| 3 | BloodPressure | 血压测量值 |
| 4 | SkinThickness | 皮肤厚度 |
| 5 | Insulin | 血液胰岛素水平 |
| 6 | BMI | 身体质量指数 |
| 7 | DiabetesPedigreeFunction | 糖尿病遗传概率 |
| 8 | Age | 年龄 |
| 9 | Outcome | 最终结果 (1: 患有糖尿病; 0: 未患糖尿病) |
2 | 导入库
python
#导包
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, cross_val_score
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, VotingClassifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier, GradientBoostingClassifier
import joblib
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')3 | 基础探索
3.1 | 读取数据集
python
df = pd.read_csv('diabetes.csv')3.2 | 基础信息
3.2.1 | 显示数据内容
python
styled_df = df.head(5).style
# 设置整个DataFrame的背景颜色、文字颜色和边框
styled_df.set_properties(**{"background-color": "#254E58", "color": "#e9c46a", "border": "1.5px solid black"})
# 修改表头(th)的颜色和背景颜色
styled_df.set_table_styles([
{"selector": "th", "props": [("color", 'white'), ("background-color", "#333333")]}
])3.2.2 | 行数与列数
python
rows , col = df.shape
print(f"行数 : {rows} \n列数 : {col}")输出:
行数 : 768
列数 : 93.2.3 | 基本信息
python
df.info()输出:
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 768 entries, 0 to 767
Data columns (total 9 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Pregnancies 768 non-null int64
1 Glucose 768 non-null int64
2 BloodPressure 768 non-null int64
3 SkinThickness 768 non-null int64
4 Insulin 768 non-null float64
5 BMI 768 non-null float64
6 DiabetesPedigreeFunction 768 non-null float64
7 Age 768 non-null int64
8 Outcome 768 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(3), int64(6)
memory usage: 54.1 KB3.2.4 | 统计空值/缺失值
python
df.isnull().sum()结果:
Pregnancies 0
Glucose 0
BloodPressure 0
SkinThickness 0
Insulin 0
BMI 0
DiabetesPedigreeFunction 0
Age 0
Outcome 0
dtype: int64未发现缺失值
3.2.5 | 数据描述
python
styled_df = df.describe().style \
.set_table_styles([
{'selector': 'th', 'props': [('background-color', '#254E58'), ('color', 'white'), ('font-weight', 'bold'), ('text-align', 'left'), ('padding', '8px')]},
{'selector': 'td', 'props': [('padding', '8px')]}
]) \
.set_properties(**{'font-size': '14px', 'background-color': '#F5F5F5', 'border-collapse': 'collapse', 'margin': '10px'})
# Display the styled DataFrame
styled_df
python
import missingno as msno
num_columns = len(df.columns)
colors = plt.cm.viridis(np.linspace(0, 1, num_columns))
msno.bar(df, color=colors)
plt.show()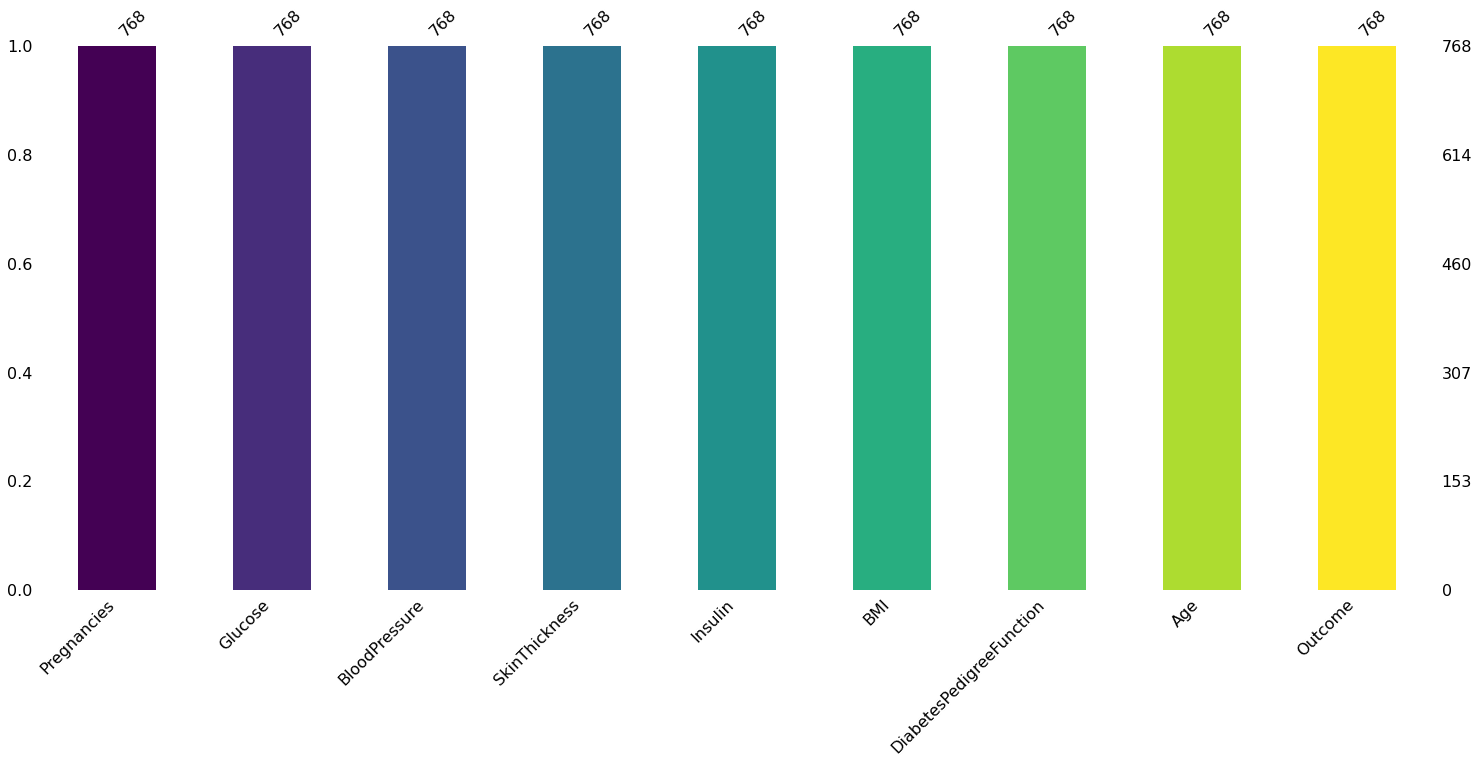
3.3 | 数据可视化
3.3.1 | 属性分布
python
df.hist(figsize = (10,10))
plt.show()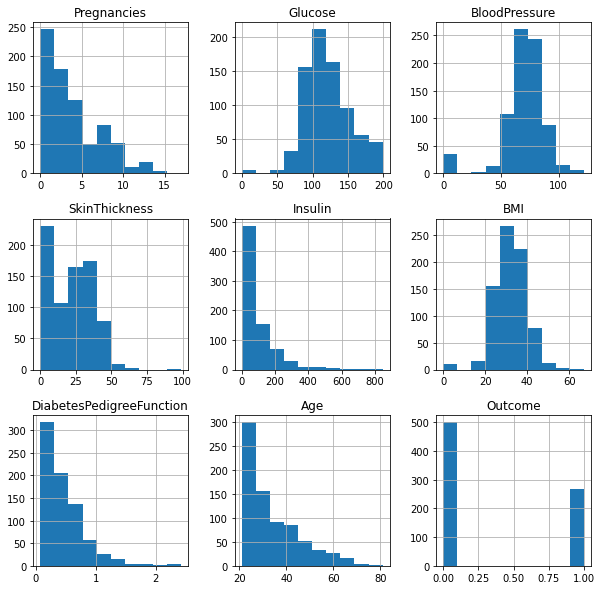
3.3.2 | 箱线图
python
num_rows, num_cols = 3, 3
# Create subplots
fig, axes = plt.subplots(num_rows, num_cols, figsize=(15, 10))
# Flatten the axes for easier iteration
axes = axes.flatten()
# Loop through numeric columns and create boxplots
for i, column in enumerate(df.columns):
sns.boxplot(data=df, x=column, ax=axes[i])
axes[i].set_title(f'Boxplot for {column}')
# Remove any remaining empty subplots
for j in range(len(df.columns), len(axes)):
fig.delaxes(axes[j])
# Adjust layout
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()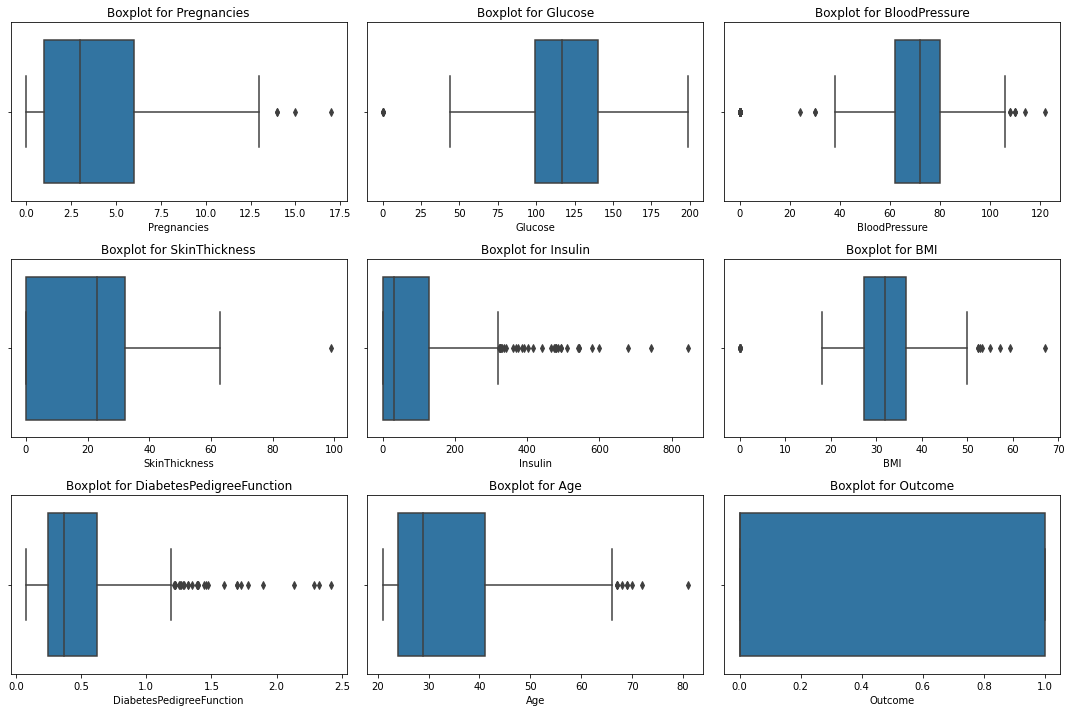
3.3.3 | 属性配对图
python
sns.pairplot(data = df, hue = 'Outcome' )
plt.show()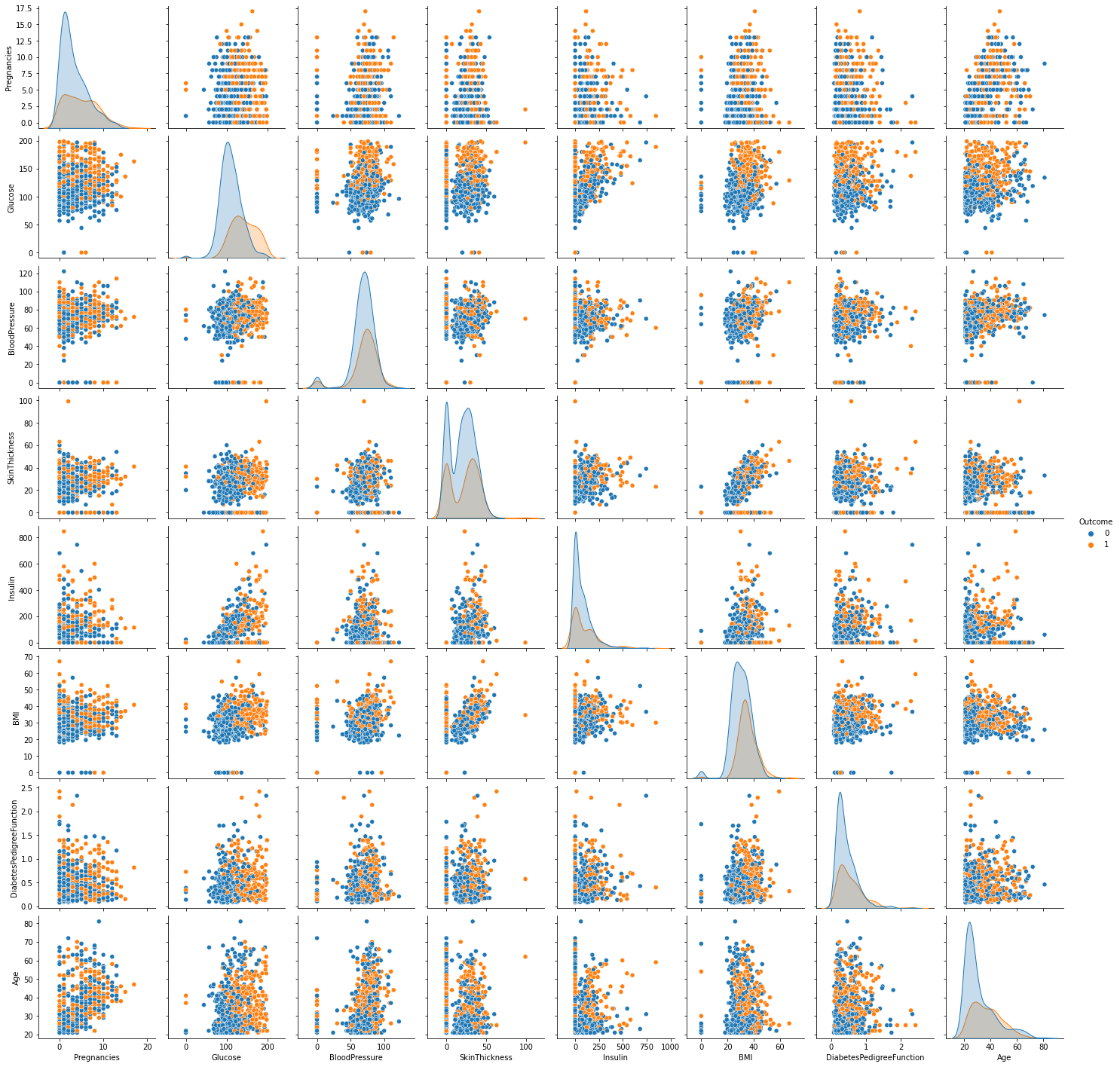
3.3.4 | 年龄与结果
python
sns.set(rc={"axes.facecolor":"#EAE7F9","figure.facecolor":"#EAE7F9"})
p=sns.catplot(x="Outcome",y="Age", data=df, kind='box')
plt.title("Age and Outcome Correlation", size=20, y=1.0);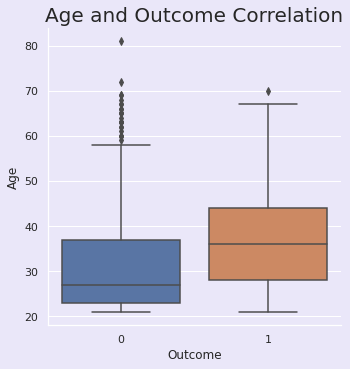
3.3.5 | Glucose and Outcome Correlation
python
sns.set(rc={"axes.facecolor":"#EAE7F9","figure.facecolor":"#EAE7F9"})
p=sns.catplot(x="Outcome",y="Glucose", data=df, kind='box')
plt.title("Glucose and Outcome Correlation", size=20, y=1.0);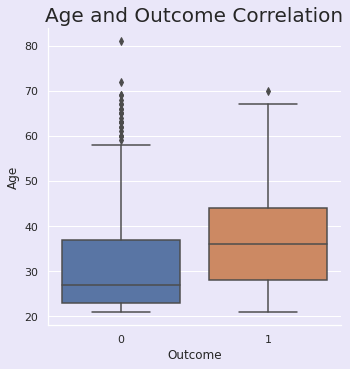
3.3.6 | 属性间相关性
python
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 17))
matrix = np.triu(df.corr())
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), annot=True, linewidth=.8, mask=matrix, cmap="rocket");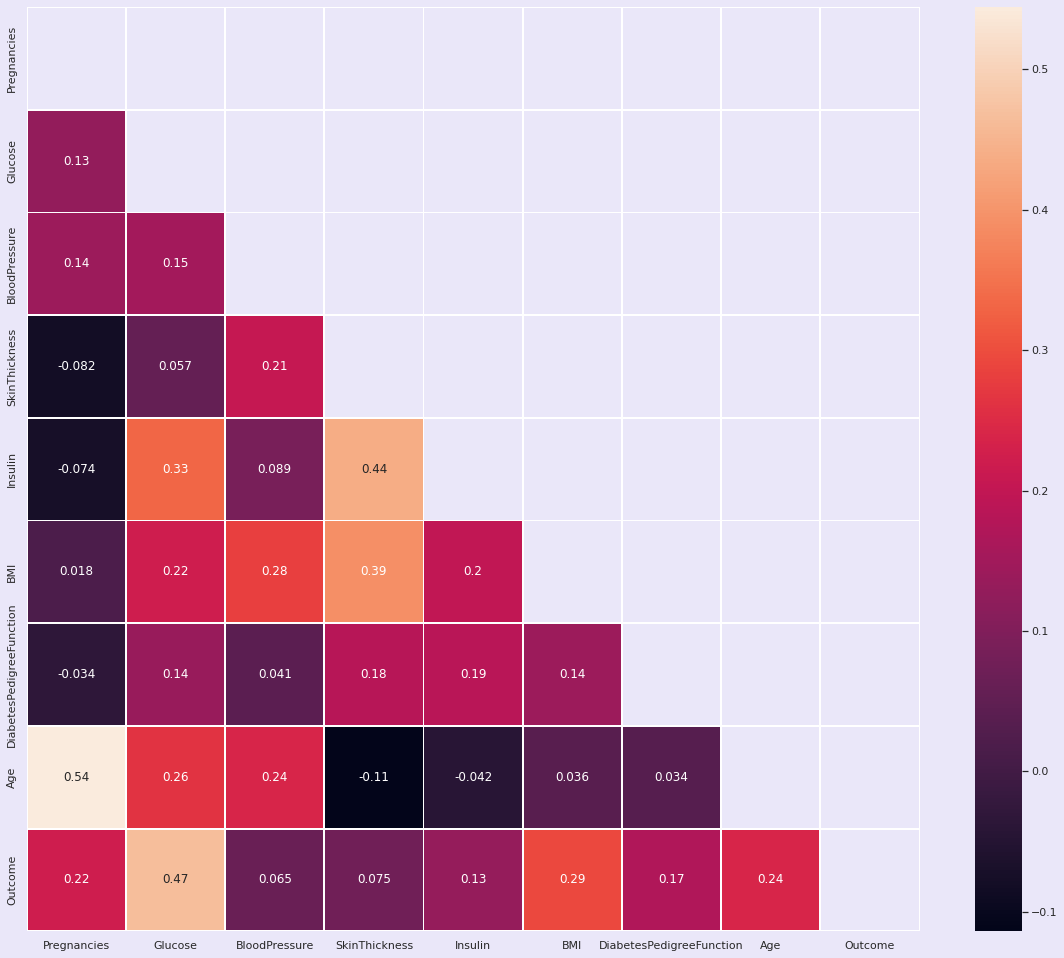
python
plt.figure(figsize=(16,9))
sns.heatmap(df.corr(), annot=True);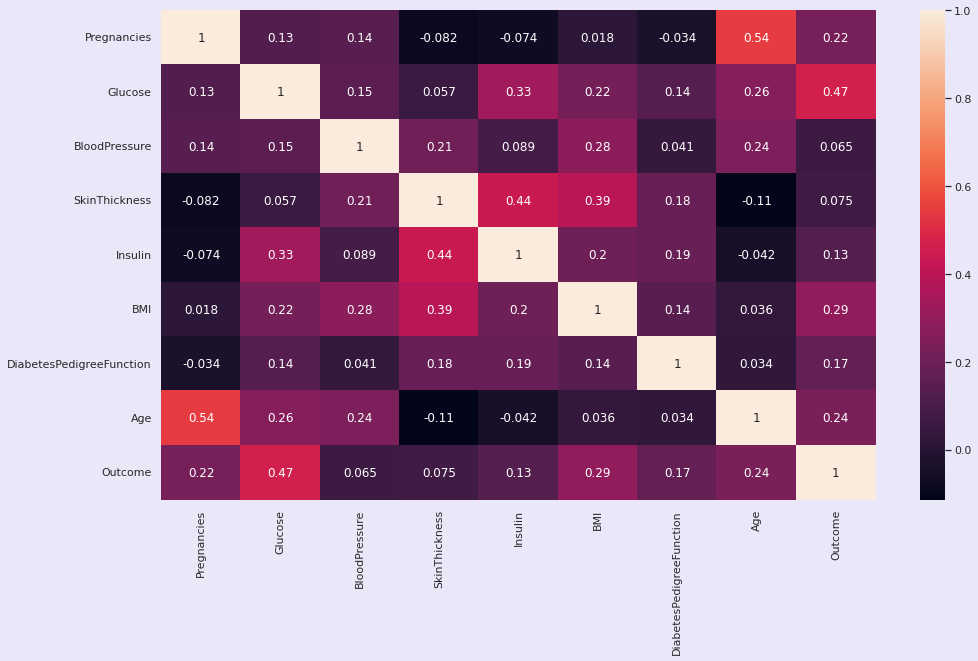
python
hig_corr = df.corr()
hig_corr_features = hig_corr.index[abs(hig_corr["Outcome"]) >= 0.2]
hig_corr_features结果:
Index(['Pregnancies', 'Glucose', 'BMI', 'Age', 'Outcome'], dtype='object')3.3.7 | 标准差
python
#Standard Deviation
df.var()结果:
Pregnancies 11.354056
Glucose 1022.248314
BloodPressure 374.647271
SkinThickness 254.473245
Insulin 13281.180078
BMI 62.159984
DiabetesPedigreeFunction 0.109779
Age 138.303046
Outcome 0.227483
dtype: float644 | 数据预处理
处理异常值
python
numeric_columns = ['Insulin', 'DiabetesPedigreeFunction',]
for column_name in numeric_columns:
Q1 = np.percentile(df[column_name], 25, interpolation='midpoint')
Q3 = np.percentile(df[column_name], 75, interpolation='midpoint')
IQR = Q3 - Q1
low_lim = Q1 - 1.5 * IQR
up_lim = Q3 + 1.5 * IQR
# Find outliers in the specified column
outliers = df[(df[column_name] < low_lim) | (df[column_name] > up_lim)][column_name]
# Replace outliers with the respective lower or upper limit
df[column_name] = np.where(df[column_name] < low_lim, low_lim, df[column_name])
df[column_name] = np.where(df[column_name] > up_lim, up_lim, df[column_name])获取
输入和目标列
python
X = df.drop('Outcome', axis = 1)
y = df['Outcome']划分训练数据
python
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y, test_size = 0.20)5 | 机器学习模型
5.1 | 逻辑回归
python
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
log_reg = LogisticRegression(C=1, penalty='l2', solver='liblinear', max_iter=200)
log_reg.fit(X_train, y_train)结果:
LogisticRegression(C=1, max_iter=200, solver='liblinear')
python
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, accuracy_score
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
def predict_and_plot(model, inputs, targets, name=''):
preds = model.predict(inputs)
accuracy = accuracy_score(targets, preds)
print("Accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(accuracy * 100))
cf = confusion_matrix(targets, preds, normalize='true')
plt.figure()
sns.heatmap(cf, annot=True)
plt.xlabel('Prediction')
plt.ylabel('Target')
plt.title('{} Confusion Matrix'.format(name))
return preds
# Predict and plot on the training data
train_preds = predict_and_plot(log_reg, X_train, y_train, 'Train')
# Predict and plot on the validation data
val_preds = predict_and_plot(log_reg, X_test, y_test, 'Validation')输出:
Accuracy: 78.18%
Accuracy: 75.32%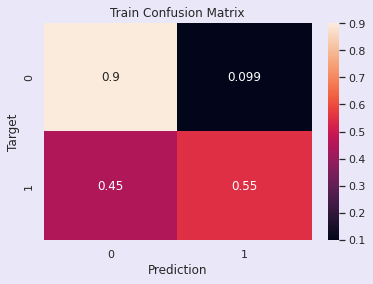
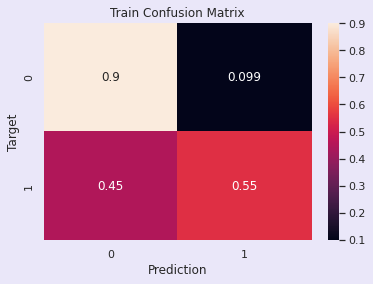
评估:逻辑回归模型
训练准确率 - 77.54%
验证准确率 - 77.68%
5.2 | 随机森林
python
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
model_2 = RandomForestClassifier(n_jobs =-1, random_state = 42)
model_2.fit(X_train,y_train)结果:
RandomForestClassifier(n_jobs=-1, random_state=42)
python
model_2.score(X_train,y_train)结果:
1.0
python
def predict_and_plot(model, inputs,targets, name = ''):
preds = model.predict(inputs)
accuracy = accuracy_score(targets, preds)
print("Accuracy: {:.2f}%".format(accuracy*100))
cf = confusion_matrix(targets, preds, normalize = 'true')
plt.figure()
sns.heatmap(cf, annot = True)
plt.xlabel('Prediction')
plt.ylabel('Target')
plt.title('{} Confusion Matrix'. format(name))
return preds
train_preds = predict_and_plot(model_2, X_train, y_train, 'Train')
# Predict and plot on the validation data
val_preds = predict_and_plot(model_2, X_test, y_test, 'Validation')输出:
Accuracy: 100.00%
Accuracy: 74.03%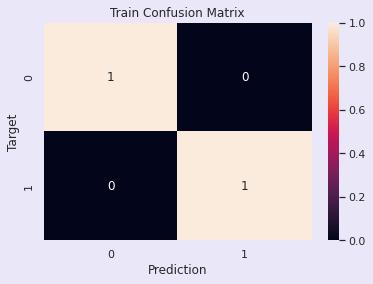
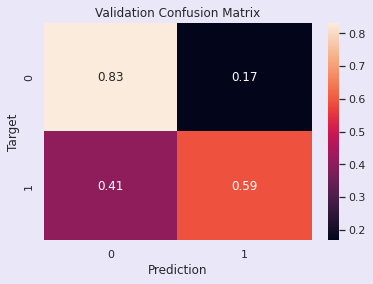
评估:随机森林模型:调优前
训练准确率 - 96.00%
验证准确率 - 78.08%
该模型似乎存在过拟合,因为训练准确率很高而验证准确率相对较低。
随机森林超参数调优
python
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
param_grid = {
'n_estimators': [10, 20, 30], # Adjust the number of trees in the forest
'max_depth': [10, 20, 30], # Adjust the maximum depth of each tree
'min_samples_split': [2, 5, 10, 15, 20], # Adjust the minimum samples required to split a node
'min_samples_leaf': [1, 2, 4, 6, 8] # Adjust the minimum samples required in a leaf node
}
model = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42, n_jobs=-1)
grid_search = GridSearchCV(model, param_grid, cv=5, n_jobs=-1, scoring='accuracy')
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
best_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
best_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Evaluate the model on the training and validation data
train_accuracy = best_model.score(X_train, y_train)
val_accuracy = best_model.score(X_test, y_test)
# Print the results
print("Training Accuracy:", train_accuracy)
print("Validation Accuracy:", val_accuracy)输出:
Training Accuracy: 89.2%
Validation Accuracy: 87.6%评估:超参数调优后的随机森林模型
训练准确率 - 89.2%
验证准确率 - 87.6%
与初始模型相比,过拟合现象有所减少,且准确率得到了提升。
5.4 | 决策树
python
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
decision_tree_model = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
decision_tree_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_accuracy = decision_tree_model.score(X_train, y_train)
val_accuracy = decision_tree_model.score(X_test, y_test)
print("Training Accuracy:", train_accuracy)
print("Validation Accuracy:", val_accuracy)输出:
Training Accuracy: 1.0
Validation Accuracy: 0.9415584415584416评估:决策树模型:调优前
训练准确率 - 100%
验证准确率 - 75.0%
决策树模型对训练数据存在过拟合,在训练数据上达到了完美准确率,但在验证数据上准确率较低。
决策树超参数调优
python
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_grid = {
'max_depth': [None, 5, 10, 15, 20],
'min_samples_split': [2, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25],
'min_samples_leaf': [1, 3, 5, 7],
'criterion': ['gini', 'entropy'] # Add criterion hyperparameter
}
decision_tree_model = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
grid_search = GridSearchCV(decision_tree_model, param_grid, cv=5, n_jobs=-1, scoring='accuracy')
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
best_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
best_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
train_accuracy = best_model.score(X_train, y_train)
val_accuracy = best_model.score(X_test, y_test)
print("Training Accuracy:", train_accuracy)
print("Validation Accuracy:", val_accuracy)评估:决策树模型
训练准确率 - 82.2%
验证准确率 - 85.5%
与初始模型相比,过拟合现象有所减少,且结果得到了改善。
5.6 | K近邻分类器模型
python
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
knn_model = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
knn_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_train_pred = knn_model.predict(X_train)
y_val_pred = knn_model.predict(X_val)
train_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred)
val_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_val, y_val_pred)
print("Training Accuracy:", train_accuracy)
print("Validation Accuracy:", val_accuracy)
confusion = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_val_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 4))
sns.heatmap(confusion, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues', cbar=False)
plt.xlabel('Predicted')
plt.ylabel('Actual')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix (Validation)')
plt.show()输出:
Training Accuracy: 0.8045602605863192
Validation Accuracy: 0.6688311688311688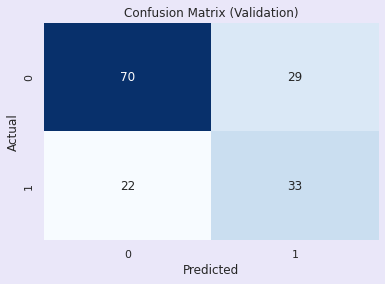
评估:K近邻分类器:调优前
训练准确率 - 80.0%
验证准确率 - 66.00%
KNN超参数调优
python
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
param_grid = {
'n_neighbors': [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] # Adjust the number of neighbors to explore
}
knn_model = KNeighborsClassifier()
grid_search = GridSearchCV(knn_model, param_grid, cv=5, scoring='accuracy')
grid_search.fit(X_train, y_train)
best_model = grid_search.best_estimator_
y_train_pred = best_model.predict(X_train)
y_val_pred = best_model.predict(X_val)
train_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred)
val_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_val, y_val_pred)
print("Training Accuracy with Best Hyperparameters:", train_accuracy)
print("Validation Accuracy with Best Hyperparameters:", val_accuracy)输出:
Training Accuracy with Best Hyperparameters: 0.7947882736156352
Validation Accuracy with Best Hyperparameters: 0.7272727272727273评估:调优后的KNN模型
训练准确率 - 79.4%
验证准确率 - 72.7%
5.8 | 支持向量分类器
python
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
svm_model = SVC(kernel='linear')
svm_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_train_pred = svm_model.predict(X_train)
y_val_pred = svm_model.predict(X_val)
train_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred)
val_accuracy = accuracy_score(y_val, y_val_pred)
print("Training Accuracy:", train_accuracy)
print("Validation Accuracy:", val_accuracy)
train_confusion = confusion_matrix(y_train, y_train_pred)
val_confusion = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_val_pred)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
sns.heatmap(train_confusion, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues', cbar=False)
plt.xlabel('Predicted')
plt.ylabel('Actual')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix (Training)')
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
sns.heatmap(val_confusion, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues', cbar=False)
plt.xlabel('Predicted')
plt.ylabel('Actual')
plt.title('Confusion Matrix (Validation)')
plt.show()输出:
Training Accuracy: 0.7785016286644951
Validation Accuracy: 0.7727272727272727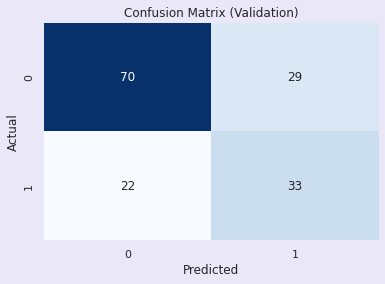
评估:支持向量分类器
训练准确率 - 77.8%
验证准确率 - 77.2%
5.9 | AdaBoost分类器
python
from sklearn.ensemble import AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix
adaboost_model = AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=50, random_state=42)
adaboost_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_train_pred_adaboost = adaboost_model.predict(X_train)
y_val_pred_adaboost = adaboost_model.predict(X_val)
train_accuracy_adaboost = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred_adaboost)
val_accuracy_adaboost = accuracy_score(y_val, y_val_pred_adaboost)
print("AdaBoost Training Accuracy:", train_accuracy_adaboost)
print("AdaBoost Validation Accuracy:", val_accuracy_adaboost)
confusion_adaboost = confusion_matrix(y_val, y_val_pred_adaboost)
# Plot the confusion matrix
plt.figure()
sns.heatmap(confusion_adaboost, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues', cbar=False)
plt.xlabel('Predicted')
plt.ylabel('Actual')
plt.title('AdaBoost Confusion Matrix (Validation)')
plt.show()输出:
AdaBoost Training Accuracy: 0.8224755700325733
AdaBoost Validation Accuracy: 0.7402597402597403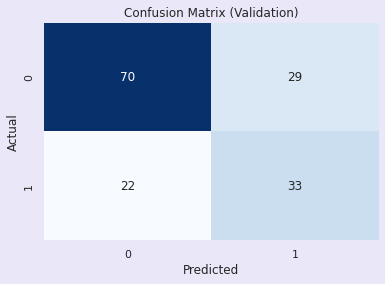
评估:AdaBoost分类器
训练准确率 - 82.4%
验证准确率 - 74.0%
5.7 | Gradient Boosting Classifier
python
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingClassifier
# 创建梯度提升分类器
gbm_model = GradientBoostingClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=3, random_state=42)
# 将GBM模型拟合到训练数据
gbm_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 对训练数据进行预测
y_train_pred_gbm = gbm_model.predict(X_train)
# 对验证数据进行预测
y_val_pred_gbm = gbm_model.predict(X_val)
# 计算训练准确率
train_accuracy_gbm = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred_gbm)
# 计算验证准确率
val_accuracy_gbm = accuracy_score(y_val, y_val_pred_gbm)
# 打印训练和验证准确率
print("GBM训练准确率:", train_accuracy_gbm)
print("GBM验证准确率:", val_accuracy_gbm)输出:
GBM Training Accuracy: 0.9429967426710097
GBM Validation Accuracy: 0.7532467532467533评估:梯度提升分类器
训练准确率 - 94.2%
验证准确率 - 75.3%
5.11 | XGBoost分类器
python
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
# Create an XGBoost classifier
xgboost_model = XGBClassifier(n_estimators=100, max_depth=3, random_state=42)
# Fit the XGBoost model to the training data
xgboost_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Make predictions on the training data
y_train_pred_xgboost = xgboost_model.predict(X_train)
# Make predictions on the validation data
y_val_pred_xgboost = xgboost_model.predict(X_val)
# Calculate the training accuracy
train_accuracy_xgboost = accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred_xgboost)
# Calculate the validation accuracy
val_accuracy_xgboost = accuracy_score(y_val, y_val_pred_xgboost)
# Print the training and validation accuracies
print("XGBoost Training Accuracy:", train_accuracy_xgboost)
print("XGBoost Validation Accuracy:", val_accuracy_xgboost)输出:
[14:40:09] WARNING: ../src/learner.cc:1115: Starting in XGBoost 1.3.0, the default evaluation metric used with the objective 'binary:logistic' was changed from 'error' to 'logloss'. Explicitly set eval_metric if you'd like to restore the old behavior.
XGBoost Training Accuracy: 0.988599348534202
XGBoost Validation Accuracy: 0.7272727272727273评估:XGBoost分类器
训练准确率 - 98.4%
验证准确率 - 72.7%
6 | 总结
结论
评估:超参数调优后的随机森林模型
训练准确率 - 89.2%
验证准确率 - 87.6%
未来可能的工作
- 使用不同的超参数进行调优以改进结果
- 实现更多模型以获得更好的结果
- 使用相同的方法预测响应