应用层自定义协议与序列化
一.应用层
我们程序员写的一个个解决我们实际问题, 满足我们日常需求的网络程序, 都是在应用层.
1. 再谈 "协议"
协议是一种 "约定". socket api的接口, 在读写数据时, 都是按 "字符串" 的方式来发送接收的. 如果我们要传输一些 "结构化的数据" 怎么办呢?
其实,协议就是双方约定好的结构化的数据
我们未来定制的协议:
1.结构化的字段,提供好序列和反序列化方案
2.解决因为字节流问题导致读取报文不完整的问题(只处理读取)
2. 网络版计算器
例如, 我们需要实现一个服务器版的加法器. 我们需要客户端把要计算的两个加数发过去, 然后由服务器进行计算, 最后再把结果返回给客户端.
约定方案一:
- 客户端发送一个形如"1+2"的字符串;
- 这个字符串中有两个操作数, 都是整形;
- 两个数字之间会有一个字符是运算符, 运算符只能是 + ;
- 数字和运算符之间没有空格;
- ...
约定方案二:
- 定义结构体来表示我们需要交互的信息;
- 发送数据时将这个结构体按照一个规则转换成字符串, 接收到数据的时候再按照相同的规则把字符串转化回结构体;
- 这个过程叫做 "序列化" 和 "反序列化"
3. 序列化 和 反序列化
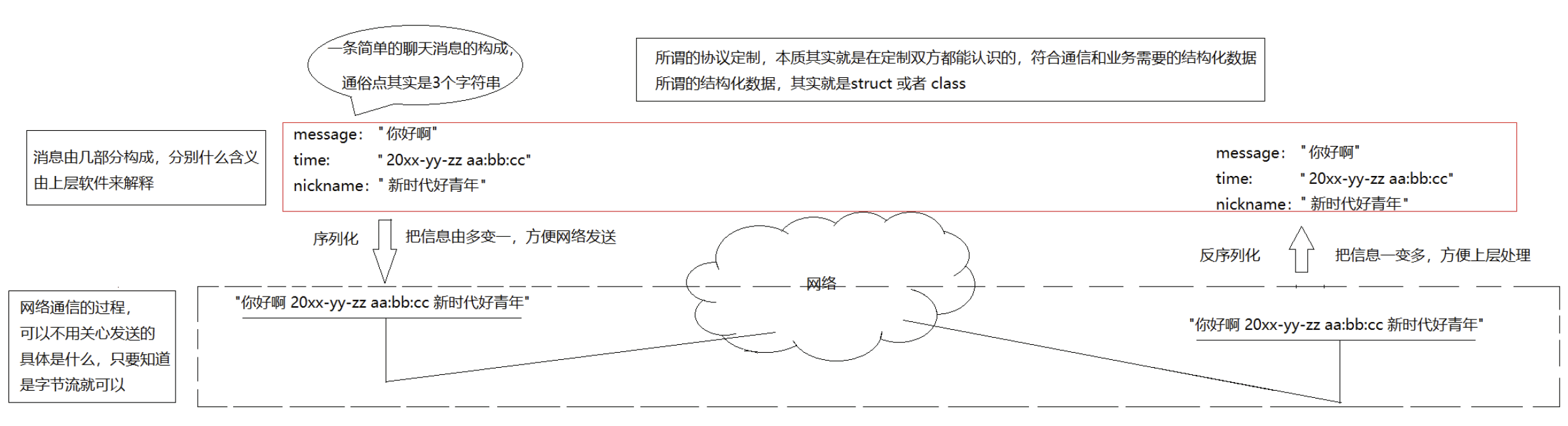
无论我们采用方案一, 还是方案二, 还是其他的方案, 只要保证, 一端发送时构造的数据, 在另一端能够正确的进行解析, 就是ok的. 这种约定, 就是 应用层协议
但是,为了让我们深刻理解协议,我们打算自定义实现一下协议的过程。
- 我们采用方案2,我们也要体现协议定制的细节
- 我们要引入序列化和反序列化,只不过我们采用现成的方案 -- jsoncpp库
- 我们要对socket进行字节流的读取处理
从今天开始:如果我们要进行网络协议式的通信,在应用层,强烈建议使用序列化和反序列化方案;
至于直接传递结构体的方案,除场景特殊,否则,不建议。
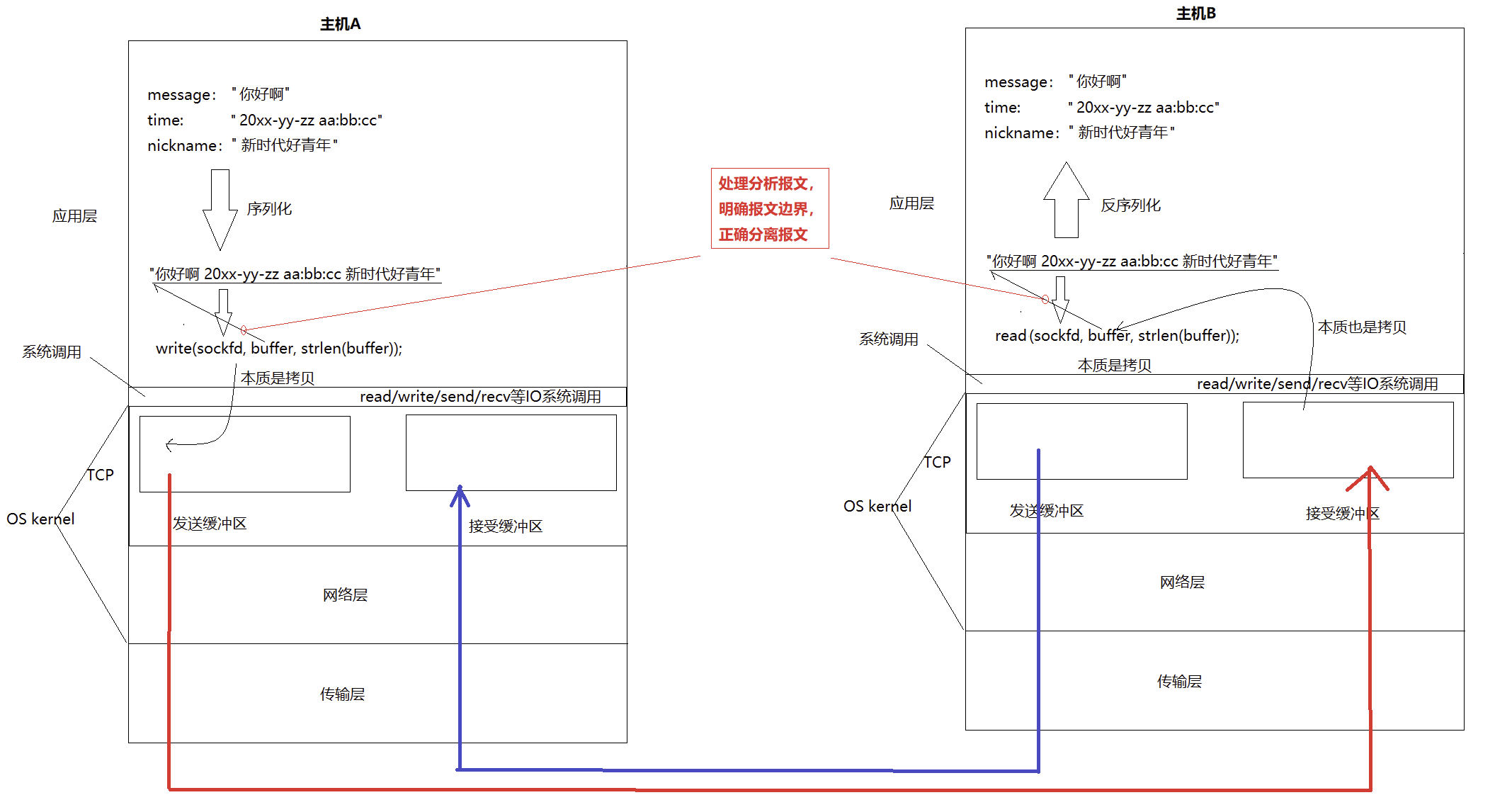
二.重新理解read、write、recv、send和tcp为什么支持全双工
TCP面向字节流:发送次数和接受次数不一定一样。
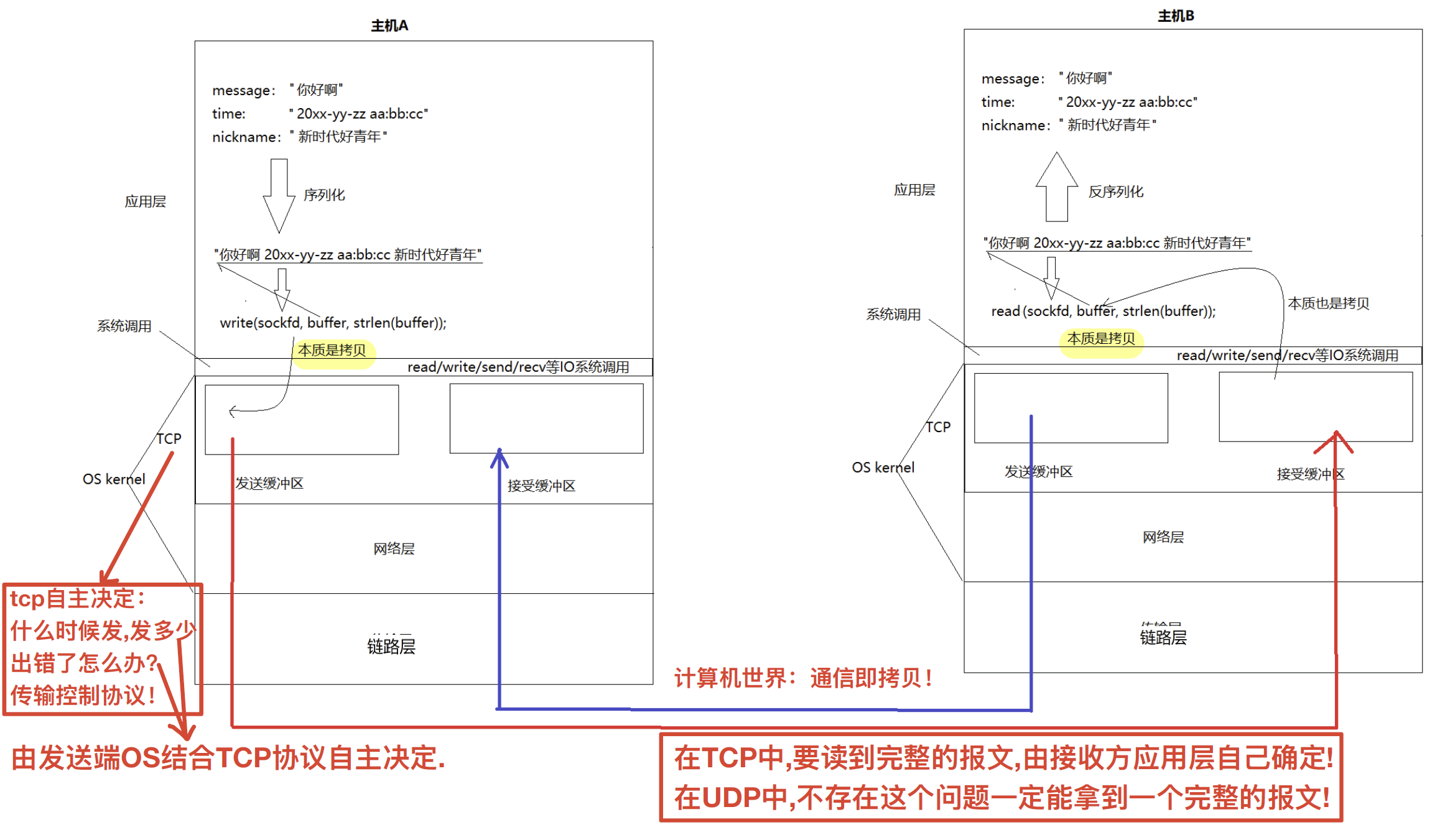
所以:
- 在任何一台主机上,TCP连接既有发送缓冲区,又有接受缓冲区,所以,在内核中,可以在发消息的同时,也可以收消息,即全双工
- 这就是为什么一个tcp sockfd读写都是它的原因
- 实际数据什么时候发,发多少,出错了怎么办,由TCP控制,所以TCP叫做传输控制协议
- 当我们tcp中读取数据的时候,读取到的报文不完整,或者多读了,导致下一个报文不完整了,这个问题叫做"粘报"问题!
总结:
- recv(read)和send(write)的本质是数据拷贝;
- 机间通信的本质是把发送方的发送缓冲区内部的数据,拷贝到对端的接受缓冲区;
- 为什么TCP通信的时候,是全双工的?因为有两对发送和接受缓冲区!
三.开始实现
1. 接口补充
daemon(系统调用)
作用:把一个普通进程转化为守护进程(daemon process),即在后台长期运行、不依赖终端的系统服务进程。调用该函数后,程序会自动脱离控制终端、会话组,并可选择是否切换工作目录和关闭标准输入输出。
函数原型:
cpp
#include <unistd.h>
int daemon(int nochdir, int noclose);-
参数:
- nochdir:
- 取值 0 → 切换当前工作目录到根目录
/; - 取值非 0 → 保留当前目录不变;
- 一般建议传 0,防止占用挂载点导致卸载失败。
- 取值 0 → 切换当前工作目录到根目录
- noclose:
- 取值 0 → 重定向标准输入、输出、错误到
/dev/null; - 取值非 0 → 保留原来的标准输入输出;
- 一般传 0,让守护进程不在终端输出内容。
- 取值 0 → 重定向标准输入、输出、错误到
- nochdir:
-
返回值:
- 成功:0
- 失败:-1,并设置 errno
2. 网络计算器(NetCal)
实现一个基于TCP的网络计算器,支持加减乘除模运算,使用JSON协议进行通信;
实现了上线软件全流程的开发,可以支持安装软件。
(1). Common.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <cstring>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
enum ExitCode
{
OK = 0,
USAGE_ERR,
SOCKET_ERR,
BIND_ERR,
LISTEN_ERR,
CONNECT_ERR,
FORK_ERROR,
OPEN_ERROR
};
class NoCopy
{
public:
NoCopy() {}
~NoCopy() {}
NoCopy(const NoCopy &) = delete;
const NoCopy &operator=(const NoCopy &) = delete;
};
#define CONV(addr) ((struct sockaddr*)&addr)(2). Inet_Addr.hpp
网络地址转换模块(与远程控制和字典服务器项目(TcpEchoServer)中的Inet_Addr.hpp完全相同)
(3). Log.hpp
日志模块(与远程控制和字典服务器项目(TcpEchoServer)中的Log.hpp完全相同)
(4). Mutex.hpp
互斥锁封装模块(与远程控制和字典服务器项目(TcpEchoServer)中的Mutex.hpp完全相同)
(5). Socket.hpp(模板方法模式)
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <cstdlib>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Common.hpp"
#include "Inet_Addr.hpp"
namespace SocketModule
{
using namespace LogModule;
const static int gbacklog = 16;
// 模板方法模式(固定套路代码常用)
// 基类socket,大部分方法,都是纯虚方法
class Socket
{
public:
virtual ~Socket() {}
virtual void SocketOrDie() = 0;
virtual void BindOrDie(uint16_t port) = 0;
virtual void ListenOrDie(int blacklog) = 0;
virtual std::shared_ptr<Socket> Accept(InetAddr* client) = 0;
virtual void Close() = 0;
virtual int Recv(std::string *out) = 0;
virtual int Send(const std::string& message) = 0;
virtual int Connect(const std::string &server_ip, uint16_t server_port) = 0;
public:
void BuildTcpSocketMethod(uint16_t port, int blacklog = gbacklog)
{
SocketOrDie();
BindOrDie(port);
ListenOrDie(blacklog);
}
void BuildTcpClientSocketMethod()
{
SocketOrDie();
}
};
const static int defaultfd = -1;
class TcpSocket : public Socket
{
public:
TcpSocket():_sockfd(defaultfd)
{}
TcpSocket(int fd):_sockfd(fd)
{}
~TcpSocket() {}
void SocketOrDie() override
{
_sockfd = ::socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0); // ::表示默认使用更外部(全局)的socket函数
if(_sockfd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "socket error";
exit(SOCKET_ERR);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "socket success";
}
void BindOrDie(uint16_t port) override
{
InetAddr localaddr(port);
int n = ::bind(_sockfd, localaddr.NetAddrPtr(), localaddr.NetAddrLen());
if(n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "bind error";
exit(BIND_ERR);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "bind success";
}
void ListenOrDie(int blacklog) override
{
int n = ::listen(_sockfd, blacklog);
if(n < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "listen error";
exit(LISTEN_ERR);
}
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "listen success";
}
std::shared_ptr<Socket> Accept(InetAddr* client) override
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
int fd = ::accept(_sockfd, CONV(peer), &len);
if(fd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "accept warning ...";
return nullptr; //TODO
}
client->SetAddr(peer);
return std::make_shared<TcpSocket>(fd);
}
int Recv(std::string *out) override //返回值等同read的返回值
{
// 流式读取,并不关心读到的是什么
char buffer[1024];
ssize_t n = ::recv(_sockfd,&buffer,sizeof(buffer)-1, 0);
if(n > 0)
{
buffer[n] = 0;
*out += buffer;
}
return n;
}
int Send(const std::string& message) override
{
return ::send(_sockfd, message.c_str(), message.size(), 0);
}
void Close() override
{
if(_sockfd > 0)
::close(_sockfd);
}
int Connect(const std::string &server_ip, uint16_t server_port) override
{
InetAddr server(server_ip, server_port);
return ::connect(_sockfd, server.NetAddrPtr(), server.NetAddrLen());
}
private:
int _sockfd; // _sockfd,listensockfd,sockfd
};
}(6). Protocol.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
#include <functional>
// 实现一个自定义的网络版本的计算器
using namespace SocketModule;
// 约定好各个字段的含义,本质就是约定好协议!
// 如何做好序列化和反序列化
// 1.我们自己写(知道怎么做就可以) ---> 往往不具备很好的扩展性
// 2.使用现成的方案(采取这个) ---> json ->jsoncpp
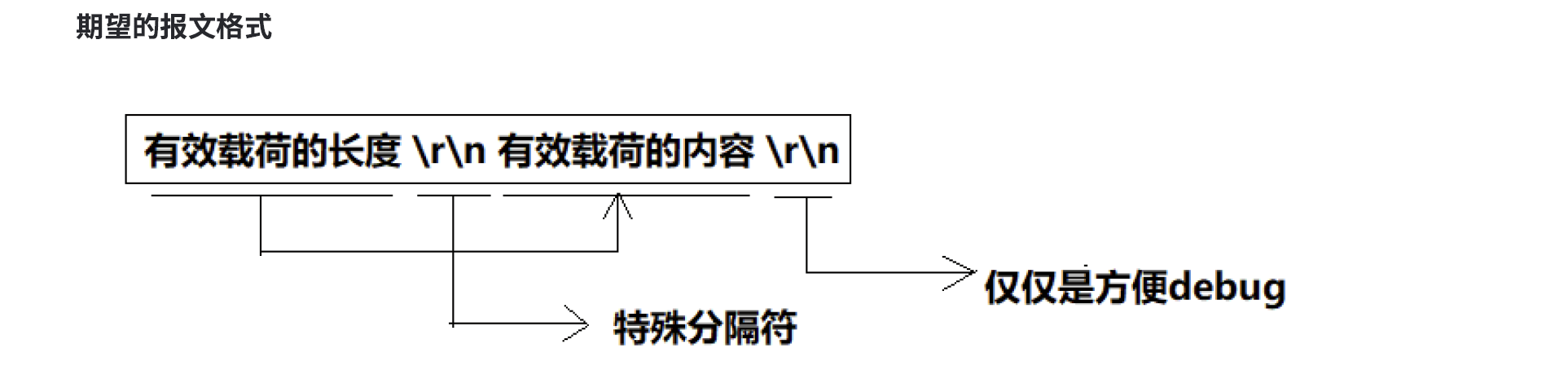
// client -> server
// content_len jsonstring
// 50\r\n{"x": 10, "y" : 20, "oper" : '+'}\r\n
// 打印出来:
// 50
// {"x": 10, "y" : 20, "oper" : '+'}
class Request
{
public:
Request(){}
Request(int x,int y,char oper):_x(x),_y(y),_oper(oper)
{}
std::string Serialize()
{
Json::Value root;
root["x"] = _x;
root["y"] = _y;
root["oper"] = _oper;
Json::FastWriter writer;
std::string s = writer.write(root);
return s;
}
bool Deserialize(std::string& in)
{
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader reader;
bool ok = reader.parse(in,root);
if(ok)
{
_x = root["x"].asInt();
_y = root["y"].asInt();
_oper = static_cast<char>(root["oper"].asInt());;
}
return ok;
}
~Request(){}
int X() { return _x; }
int Y() { return _y; }
char Oper() { return _oper; }
private:
int _x;
int _y;
char _oper; //+-*/% (_x oper _y)
};
// server -> client
class Response
{
public:
Response(){}
Response(int result, int code):_result(result),_code(code)
{}
std::string Serialize()
{
Json::Value root;
root["result"] = _result;
root["code"] = _code;
Json::FastWriter writer;
std::string s = writer.write(root);
return s;
}
bool Deserialize(std::string& in)
{
Json::Value root;
Json::Reader reader;
bool ok = reader.parse(in,root);
if(ok)
{
_result = root["result"].asInt();
_code = root["code"].asInt();
}
return ok;
}
~Response(){}
void SetResult(int res)
{
_result = res;
}
void SetCode(int code)
{
_code = code;
}
int Code() { return _code; }
int Result() { return _result; }
private:
int _result; //运算结果,无法区分清楚应答是jisuan结果,还是异常值
int _code; // 0:success; 1,2,3,4->不同运算异常情况
};
// 协议(基于Tcp的)需要解决两个问题:
// 1.request和response必须得有序列化和反序列化
// 2.必须保证,读取的时候读到完整的请求(TCP才需要,UDP不用考虑)
const std::string sep = "\r\n";
template<typename Fn>
class Protocol
{
public:
Protocol() {}
Protocol(Fn func)
:_func(func)
{
}
std::string Encode(const std::string& jsonstr)
{
std::string len = std::to_string(jsonstr.size());
std::string package = len + sep + jsonstr + sep; //应用层封装报头
return package;
}
// Decode工作:
// 1.判断报文完整性
// 2.如果包含至少一个完整请求,提取他,并从缓冲区里移除它,方便处理下一个
bool Decode(std::string& buffer, std::string *package)
{
ssize_t pos = buffer.find(sep);
if(pos == std::string::npos) return false; //让调用方继续从内核中读取数据
std::string package_len_str = buffer.substr(0, pos);
int package_len_int = std::stoi(package_len_str);
// 到这buffer一定有长度,但不一定有完整报文
int target_len = package_len_str.size() + package_len_int + 2 * sep.size();
if(buffer.size() < target_len)
return false;
// 到这buffer一定有至少有完整报文
*package = buffer.substr(pos+sep.size(), package_len_int);
buffer.erase(0, target_len);
return true;
}
void GetRequest(std::shared_ptr<Socket> &sock, InetAddr &client)
{
// 读取
std::string buffer_queue;
while (true)
{
int n = sock->Recv(&buffer_queue);
if(n > 0)
{
std::string json_package;
// 1.解析报文,提取完整json请求,如果不完整,就让服务器继续读取
while(Decode(buffer_queue, &json_package)) //while解决:buffer_queue一次性读到多个报文的情况
{
// 100%保证,一定拿到了一个完整的报文
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << client.StringAddr() << " 请求: " << json_package; // {"x": 10, "y" : 20, "oper" : '+'}
// 2.请求json串,反序列化
Request req;
bool ok = req.Deserialize(json_package);
if(!ok)
continue; //报文有问题,直接丢弃
// 3.一定得到了一个内部属性被设置了的req了.
// 通过req,得到resp;就是要完成计算功能,计算功能不属于协议,是一种业务
Response resp = _func(req);
// 4.序列化
std::string json_str = resp.Serialize();
// 5.添加自定义长度(报头)
std::string send_str = Encode(json_str); //send_str是携带长度的应答报文:"len\r\n{result:XXX,code:XX}\r\n"
// 6.发送
sock->Send(send_str);
}
}
else if(n == 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::INFO) << "client" << client.StringAddr() << "Quit!";
break;
}
else
{
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "client" << client.StringAddr() << ",recv error";
break;
}
}
}
void GetResponse(std::shared_ptr<Socket> &sock)
{
// 读取
static std::string buffer_queue;
while (true)
{
int n = sock->Recv(&buffer_queue);
if(n > 0)
{
std::string json_package;
// 1.解析报文,提取完整json请求,如果不完整,就让服务器继续读取
while(Decode(buffer_queue, &json_package))
{
// 100%保证,一定拿到了一个完整的报文
// {"result" : 计算结果, "code" : 0/1/2/3}
// 2.请求json串,反序列化
Response resp;
bool ok = resp.Deserialize(json_package);
if(!ok)
{
std::cout << "网络错误" << std::endl;
continue; //报文有问题,直接丢弃
}
// 3.一定得到了一个内部属性被设置了的req了.
bool ans = _func(resp);
if(!ans) continue; //code不为0,_func已经打印了错误信息
else
{
std::cout << "计算结果是:" << resp.Result() << std::endl;
}
}
return;
}
else if(n == 0)
{
std::cout << "server quit " << std::endl;
return;
}
else
{
std::cout << "recv error" << std::endl;
return;
}
}
}
std::string BuildRequestString(int x,int y,char oper)
{
// 1.构建一个完整的请求
Request req(x, y, oper);
// 2.序列化
std::string json_req = req.Serialize();
// 3.添加自定义长度(报头)
return Encode(json_req);
}
~Protocol()
{
}
private:
Fn _func;
// 多进程可以下面这两个变量可以定义成成员变量,会写时拷贝各进程不影响(多线程不能这样定义)
// Request _req;
// Response _resp;
};
(7). NetCal.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include "Protocol.hpp"
#include <iostream>
class Cal
{
public:
Response Execute(Request&req)
{
Response resp(0,0);
switch (req.Oper())
{
case '+':
resp.SetResult(req.X() + req.Y());
break;
case '-':
resp.SetResult(req.X() - req.Y());
break;
case '*':
resp.SetResult(req.X() * req.Y());
break;
case '/':
if(req.Y() == 0)
{
resp.SetCode(1); //1除零错误
}
else
{
resp.SetResult(req.X() / req.Y());
}
break;
case '%':
if(req.Y() == 0)
{
resp.SetCode(2); //2模零错误
}
else
{
resp.SetResult(req.X() % req.Y());
}
break;
default:
resp.SetCode(3); //非法操作
break;
}
return resp;
}
private:
};(8). TcpServer.hpp
cpp
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <functional>
using namespace SocketModule;
using namespace LogModule;
using ioservice_t = std::function<void(std::shared_ptr<Socket> &sock, InetAddr &client)>;
// TcpServer主要解决:1.连接的问题; 2.IO通信的问题
// 细节:TcpServer不需要关系自己未来传递的信息是什么
// 网络版本的计算机,长服务
class TcpServer
{
public:
TcpServer(uint16_t port,ioservice_t service)
:_port(port)
,_listensockptr(std::make_unique<TcpSocket>())
,_isrunning(false)
,_service(service)
{
_listensockptr->BuildTcpSocketMethod(_port);
}
void Start()
{
_isrunning = true;
while(_isrunning)
{
InetAddr client;
auto sock = _listensockptr->Accept(&client); // 获得1.和client通信的sockfd 2.client网络地址
if(sock == nullptr)
{
continue;
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "accept success ..." << client.StringAddr();
// 获得了:1.与客户端通信socket;2.客户端地址和端口号
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "fork error ...";
exit(FORK_ERROR);
}
else if(id == 0)
{
//子进程 ->关闭listen socket
_listensockptr->Close();
if(fork() > 0)
exit(0);
//孙子进程在执行任务,已经是孤儿进程了
_service(sock,client);
sock->Close();
exit(OK);
}
else
{
//父进程 ->关闭clinet socket(即:auto sock)
sock->Close();
pid_t rid = ::waitpid(-1, nullptr, 0);
(void)rid;
}
}
_isrunning = false;
}
~TcpServer() {}
private:
uint16_t _port;
std::unique_ptr<Socket> _listensockptr;
bool _isrunning;
ioservice_t _service;
};(9). Daemon.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdio>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Common.hpp"
using namespace LogModule;
const std::string dev = "/dev/null";
// 将服务进行守护进程化的服务
void Daemon(int nochdir, int noclose)
{
// 1.忽略IO,子进程退出等相关信号
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN);
// 2.父进程直接结束
if(fork() > 0)
exit(0);
// 3.设置新会话,只能是子进程(孤儿进程,被领养,父进程就是1)
setsid(); //称为一个独立的会话
if(nochdir == 0)
{
chdir("/"); //更改进程的工作路径???为什么??
}
// 4.由于不同版本内核,依旧可能和显示器,键盘,stdin,stdout,stderr关联
// 守护进程,不从键盘输入,也不需要向显示器打印
// 方法1:关闭0,1,2 -- 不推荐
// 方法2:打开/dev/null, 重定向标准输入,标准输出,标准错误到/dev/null
if(noclose == 0)
{
int fd = ::open(dev.c_str(), O_RDWR);
if(fd < 0)
{
LOG(LogLevel::FATAL) << "open "<<dev<<" error";
exit(OPEN_ERROR);
}
else
{
dup2(fd, 0);
dup2(fd, 1);
dup2(fd, 2);
close(fd);
}
}
}(10). main.cc
cpp
#include "NetCal.hpp"
#include "Protocol.hpp"
#include "TcpServer.hpp"
#include "Daemon.hpp"
#include <memory>
#include <unistd.h>
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << proc << " port" << std::endl;
}
// ./tcpserver 8080
int main(int argc, char*argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(USAGE_ERR);
}
std::cout << "服务器已经启动,已经是一个守护进程了" << std::endl;
// 守护进程化
// Daemon(0,0); //自己实现的库函数
daemon(0, 0);
Enable_File_Log_Strategy();
// 1.顶层--应用层
std::unique_ptr<Cal> cal = std::make_unique<Cal>();
// 2.协议层--表示层
using func_t_s = std::function<Response(Request&req)>; //定义GetRequest调用的函数类型
std::unique_ptr<Protocol<func_t_s>> protocol = std::make_unique<Protocol<func_t_s>>([&cal](Request&req)->Response{
return cal->Execute(req);
});
// 3.服务器层--会话层
std::unique_ptr<TcpServer> tsvr = std::make_unique<TcpServer>(std::stoi(argv[1]),
[&protocol](std::shared_ptr<Socket> &sock, InetAddr &client){
protocol->GetRequest(sock,client);
});
tsvr->Start();
return 0;
}(11). TcpClient.cc
cpp
#include "Socket.hpp"
#include "Common.hpp"
#include "Protocol.hpp"
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/socket.h>
#include<netinet/in.h>
#include<arpa/inet.h>
#include<memory>
using namespace SocketModule;
void Usage(std::string proc)
{
std::cerr << "Usage: " << proc << " server_ip server_port" << std::endl;
}
void GetDataFromStdin(int* x,int* y,char* oper)
{
std::cout << "Please Enter x:";
std::cin >> *x;
std::cout << "Please Enter y:";
std::cin >> *y;
std::cout << "Please Enter oper:";
std::cin >> *oper;
}
// ./tcpclient server_ip server_port
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
if (argc != 3)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(USAGE_ERR);
}
std::string server_ip = argv[1];
uint16_t server_port = std::stoi(argv[2]);
std::shared_ptr<Socket> client = std::make_shared<TcpSocket>();
client->BuildTcpClientSocketMethod();
if(client->Connect(server_ip, server_port) != 0)
{
// 失败
std::cerr << "connect error" << std::endl;
exit(CONNECT_ERR);
}
// 连接服务器成功
using func_t_c = std::function<bool(Response& resp)>; //定义GetResponse调用的函数类型
std::unique_ptr<Protocol<func_t_c>> protocol = std::make_unique<Protocol<func_t_c>>([](Response& resp){
int code = resp.Code();
if(code == 0) return true;
else if(code == 1)
{
std::cout << "除零错误" << std::endl;
return false;
}
else if(code == 2)
{
std::cout << "模零错误" << std::endl;
return false;
}
else if(code == 3)
{
std::cout << "非法操作" << std::endl;
return false;
}
return false;
});
while (true)
{
// 1.从标准输入中获取数据
int x, y;
char oper;
GetDataFromStdin(&x, &y, &oper);
// 2.构建一个请求
std::string req_str = protocol->BuildRequestString(x, y, oper);
// 3.发送请求
client->Send(req_str);
// 4.获取应答(判断,输出)
protocol->GetResponse(client);
}
client->Close();
return 0;
}(12). Makefile
makefile
.PHONY:all
all:ServerNetCald client_netcal #守护进程喜欢以d结尾
client_netcal:TcpClient.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -ljsoncpp
ServerNetCald:main.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++17 -ljsoncpp
.PHONY:output
output:
@mkdir output
@mkdir -p output/bin
@mkdir -p output/conf
@mkdir -p output/log
@cp ServerNetCald output/bin
@cp client_netcal output/bin
@cp test.conf output/conf
@cp install.sh output/
@cp uninstall.sh output/
@tar -czf output.tgz output
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf ServerNetCald client_netcal output output.tgzmake之后直接将安装压缩包发给别人,解压之后进入output目录,直接sudo ./install.sh软件就安装好了,软件日志记录在/var/log/my.log;卸载同理sudo ./uninstall.sh即可。
(13). install.sh
bash
#!/usr/bin/bash
cp -f ./bin/ServerNetCald /usr/bin
cp -f ./bin/client_netcal /usr/bin(14). uninstall.sh
bash
#!/usr/bin/bash
rm -rf /usr/bin/ServerNetCald
rm -rf /usr/bin/client_netcal(15). test.conf
//空(16). 项目结构
shell
NetCal/
├── client_netcal
├── Common.hpp
├── Daemon.hpp
├── Inet_Addr.hpp
├── install.sh
├── Log.hpp
├── main.cc
├── Makefile
├── Mutex.hpp
├── NetCal.hpp
├── output
│ ├── bin
│ │ ├── client_netcal
│ │ └── ServerNetCald
│ ├── conf
│ │ └── test.conf
│ ├── install.sh
│ ├── log
│ └── uninstall.sh
├── output.tgz
├── Protocol.hpp
├── ServerNetCald
├── Socket.hpp
├── TcpClient.cc
├── TcpServer.hpp
├── test.conf
└── uninstall.sh(17). 结果
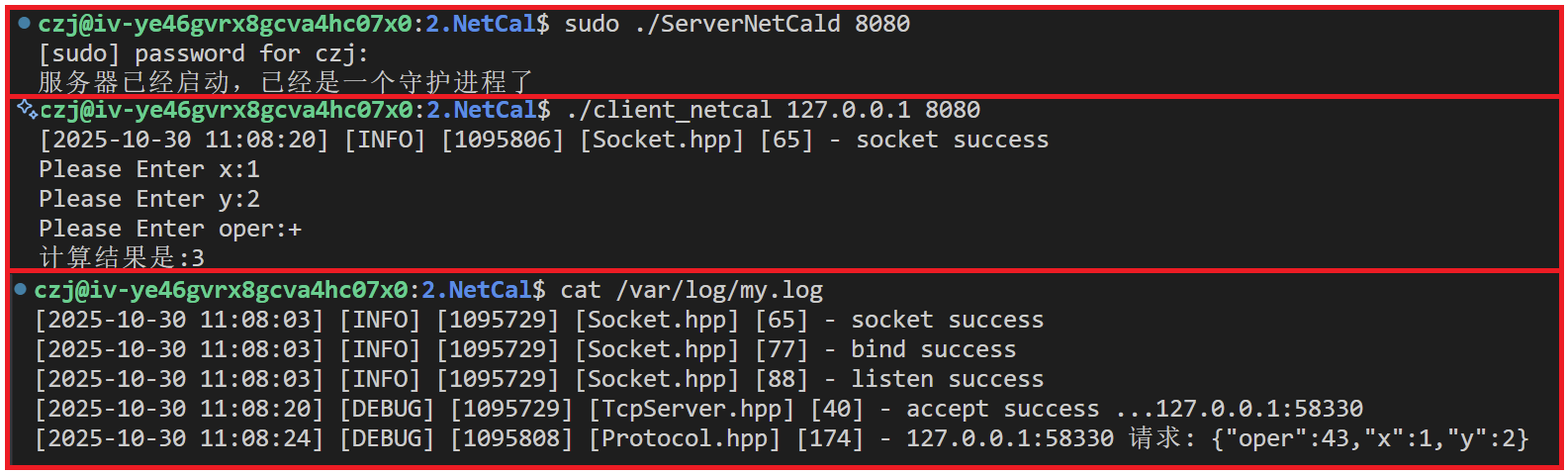
所以,完整的处理过程应该是:
四.附录--Jsoncpp
同样的序列化和反序列化的库还有xml,protobuf
Jsoncpp 是一个用于处理 JSON 数据的 C++ 库。它提供了将 JSON 数据序列化为字符串以及从字符串反序列化为 C++ 数据结构的功能。Jsoncpp 是开源的,广泛用于各种需要处理 JSON 数据的 C++ 项目中。
特性
- 简单易用:Jsoncpp 提供了直观的 API,使得处理 JSON 数据变得简单。
- 高性能:Jsoncpp 的性能经过优化,能够高效地处理大量 JSON 数据。
- 全面支持:支持 JSON 标准中的所有数据类型,包括对象、数组、字符串、数字、布尔值和 null。
- 错误处理:在解析 JSON 数据时,Jsoncpp 提供了详细的错误信息和位置,方便开发者调试。
当使用Jsoncpp库进行JSON的序列化和反序列化时,确实存在不同的做法和工具类可供选择。以下是对Jsoncpp中序列化和反序列化操作的详细介绍:
1. 安装
ubuntu:sudo apt-get install libjsoncpp-dev
Centos: sudo yum install jsoncpp-devel2. 序列化
Json串转成字符串打印,在新版本都会变成转移符,需要设置才可以正常显示字符(设置方法见序列化的第二种使用方法)。
序列化指的是将数据结构或对象转换为一种格式,以便在网络上传输或存储到文件中。Jsoncpp提供了多种方式进行序列化:
(1).使用 Json::Value 的toStyledString 方法:
- 优点:将
Json::Value对象(万能对象)直接转换为格式化的JSON字符串。 - 示例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
int main()
{
Json::Value root;
root["name"] = "joe";
root["sex"] = "男";
std::string s = root.toStyledString();
std::cout << s << std::endl;
return 0;
}
$ ./test.exe
{
"name" : "joe",
"sex" : "男"
}(2).使用 Json::StreamWriter (推荐用这种方法序列化) :
- 优点:提供了更多的定制选项,如缩进、换行符等。
- 示例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <memory>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
int main()
{
Json::Value root;
root["name"] = "joe";
root["sex"] = "男";
Json::StreamWriterBuilder wbuilder; // StreamWriter的工厂
writerBuilder["emitUTF8"]=true;//关键设置:允许直接输出UTF-8
std::unique_ptr<Json::StreamWriter> writer(wbuilder.newStreamWriter());
std::stringstream ss;
writer->write(root, &ss);
std::cout << ss.str() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
$ ./test.exe
{
"name" : "joe",
"sex" : "男"
}(3).使用 Json::FastWriter :
- 优点:比 StyledWriter 更快,因为它不添加额外的空格和换行符。
- 示例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <memory>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
int main()
{
//去掉换行,网络传输的数据量变小了
Json::Value root;
root["name"] = "joe";
root["sex"] = "男";
Json::FastWriter writer;
std::string s = writer.write(root);
std::cout << s << std::endl;
return 0;
}
$ ./test.exe
{"name":"joe","sex":"男"}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <memory>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
int main()
{
//用\n给我们进行按行设置了,可读性比较好
Json::Value root;
root["name"] = "joe";
root["sex"] = "男";
// Json::FastWriter writer;
Json::StyledWriter writer;
std::string s = writer.write(root);
std::cout << s << std::endl;
return 0;
}
$ ./test.exe
{
"name" : "joe",
"sex" : "男"
}3. 反序列化
注:json没有asCharO函数,char类型直接用aslnt0,多然后强转成char就可以
反序列化指的是将序列化后的数据重新转换为原来的数据结构或对象。Jsoncpp提供了以下方法进行反序列化:
(1).使用 Json::Reader :
- 优点:提供详细的错误信息和位置,方便调试。
- 示例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <jsoncpp/json/json.h>
int main() {
// JSON 字符串
std::string json_string = "{\"name\":\"张三\", \"age\":30, \"city\":\"北京\"}";
// 解析 JSON 字符串
Json::Reader reader;
Json::Value root;
// 从字符串中读取 JSON 数据
bool parsingSuccessful = reader.parse(json_string, root);
if (!parsingSuccessful) {
// 解析失败,输出错误信息
std::cout << "Failed to parse JSON: " << reader.getFormattedErrorMessages() << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 访问 JSON 数据
std::string name = root["name"].asString();
int age = root["age"].asInt();
std::string city = root["city"].asString();
// 输出结果
std::cout << "Name: " << name << std::endl;
std::cout << "Age: " << age << std::endl;
std::cout << "City: " << city << std::endl;
return 0;
}
$ ./test.exe
Name: 张三
Age: 30
City: 北京(2).使用 Json::CharReader 的派生类(不推荐了,上面的足够了):
- 在某些情况下,你可能需要更精细地控制解析过程,可以直接使用 Json::CharReader 的派生类。
- 但通常情况下,使用 Json::parseFromStream 或Json::Reader 的parse 方法就足够了。
4. 总结
-
toStyledString 、StreamWriter 和FastWriter 提供了不同的序列化选项,你可以根据具体需求选择使用。
-
Json::Reader 和parseFromStream 函数是Jsoncpp中主要的反序列化工具,它们提供了强大的错误处理机制。
-
在进行序列化和反序列化时,请确保处理所有可能的错误情况,并验证输入和输出的有效性。
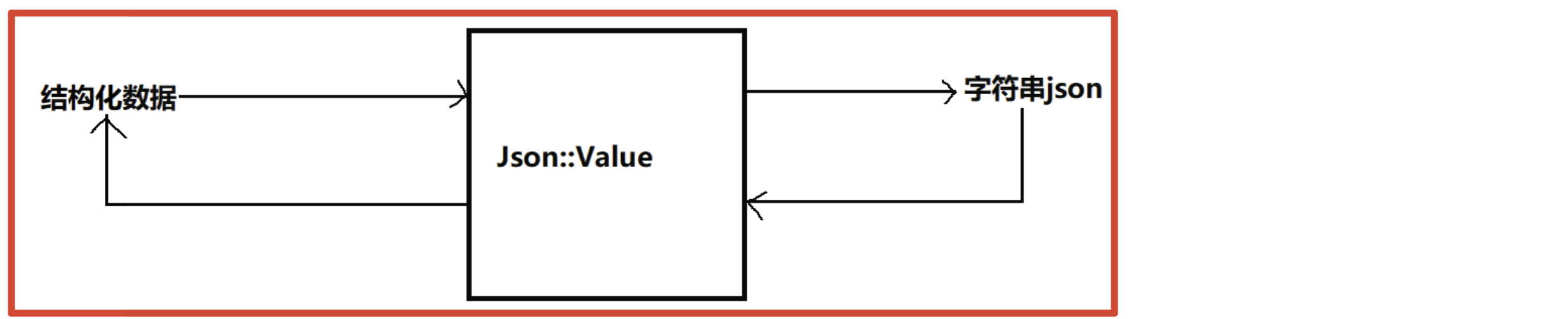
5. Json::Value
Json::Value 是 Jsoncpp 库中的一个重要类,用于表示和操作 JSON 数据结构。以下是一些常用的 Json::Value 操作列表:
(1).构造函数
Json::Value():默认构造函数,创建一个空的 Json::Value 对象。Json::Value(ValueType type, bool allocated = false):根据给定的ValueType (如 nullValue , intValue , stringValue 等)创建一个Json::Value 对象。
(2).访问元素
Json::Value& operator[](const char* key):通过键(字符串)访问对象中的元素。如果键不存在,则创建一个新的元素。Json::Value& operator[](const std::string& key):同上,但使用std::string 类型的键。Json::Value& operator[](ArrayIndex index):通过索引访问数组中的元素。如果索引超出范围,则创建一个新的元素。Json::Value& at(const char* key):通过键访问对象中的元素,如果键不存在则抛出异常。Json::Value& at(const std::string& key):同上,但使用 std::string 类型的键。
(3).类型检查
bool isNull():检查值是否为 null。bool isBool():检查值是否为布尔类型。bool isInt():检查值是否为整数类型。bool isInt64():检查值是否为 64 位整数类型。bool isUInt():检查值是否为无符号整数类型。bool isUInt64():检查值是否为 64 位无符号整数类型。bool isIntegral():检查值是否为整数或可转换为整数的浮点数。bool isDouble():检查值是否为双精度浮点数。bool isNumeric():检查值是否为数字(整数或浮点数)。bool isString():检查值是否为字符串。bool isArray():检查值是否为数组。bool isObject():检查值是否为对象(即键值对的集合)。
(4).赋值和类型转换
Json::Value& operator=(bool value):将布尔值赋给 Json::Value 对象。Json::Value& operator=(int value):将整数赋给 Json::Value 对象。Json::Value& operator=(unsigned int value):将无符号整数赋给Json::Value 对象。Json::Value& operator=(Int64 value):将 64 位整数赋给 Json::Value 对象。Json::Value& operator=(UInt64 value):将 64 位无符号整数赋给 Json::Value对象。Json::Value& operator=(double value):将双精度浮点数赋给 Json::Value 对象。Json::Value& operator=(const char* value):将 C 字符串赋给 Json::Value对象。Json::Value& operator=(const std::string& value):将 std::string 赋给 Json::Value 对象。bool asBool():将值转换为布尔类型(如果可能)。int asInt():将值转换为整数类型(如果可能)。Int64 asInt64():将值转换为 64 位整数类型(如果可能)。unsigned int asUInt():将值转换为无符号整数类型(如果可能)。UInt64 asUInt64():将值转换为 64 位无符号整数类型(如果可能)。double asDouble():将值转换为双精度浮点数类型(如果可能)。std::string asString():将值转换为字符串类型(如果可能)。
(5).数组和对象操作
-
size_t size():返回数组或对象中的元素数量。 -
bool empty():检查数组或对象是否为空。 -
void resize(ArrayIndex newSize):调整数组的大小。 -
void clear():删除数组或对象中的所有元素。 -
void append(const Json::Value& value):在数组末尾添加一个新元素。 -
Json::Value& operator[](const char* key, const Json::Value& defaultValue = Json::nullValue):在对象中插入或访问一个元素,如果键不存在则使用默认值。 -
Json::Value& operator[](const std::string& key, const Json::Value& defaultValue = Json::nullValue):同上,但使用 std::string 类型的这两个operator[]和访问元素里不同的是如果 key 不存在:不会创建 key,返回 defaultValue。