【Agent】 ACE(Agentic Context Engineering)源码阅读笔记 ---(2)--- 训练
0x00 概要
本篇我们介绍训练。训练过程(也称为适应过程)实现在adaptation.py中。训练过程如下:
- Generator 使用当前的策略手册生成答案。
- TaskEnvrionment 评估答案并提供反馈(与标准答案进行比较)。
- Reflector 分析结果并对策略进行标记。
- Curator 决定如何更新策略手册。
- Playbook 根据新策略进行更新。
通过训练,ACE让模型像导演一样给自己写剧本,把提示词进化为会生长的剧本。
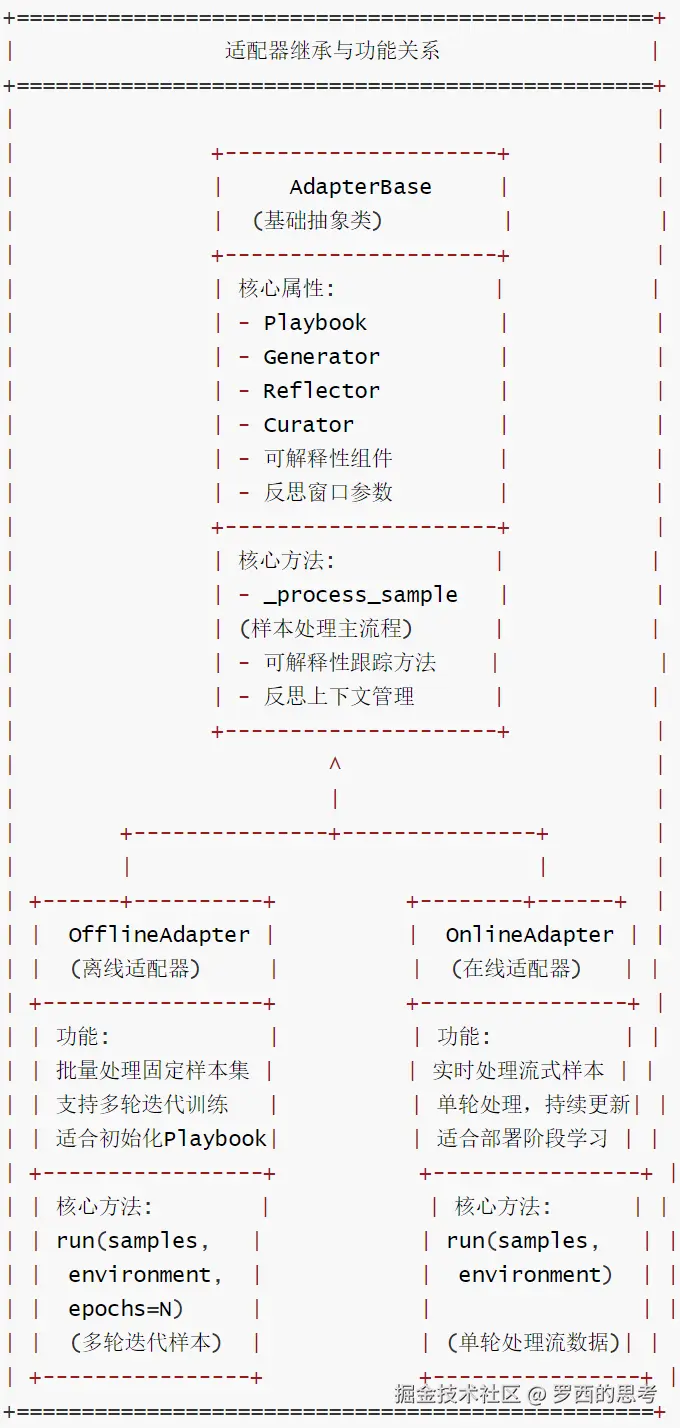
0x01 AdapterBase
AdapterBase是基类,AdapterBase封装了通用逻辑,包括样本处理流程、可解释性数据跟踪、反思上下文管理等;核心方法是:
- _apply_bullet_tags:依据反思更新策略标签。
- _process_sample:通过完整的ACE周期处理单个样本。
- _update_recent_reflections:维护最近的反思记录,后续提供给上下文。
OfflineAdapter 和 OnlineAdapter是派生类。
- OfflineAdapter:即离线训练,run() 函数对固定数据集进行多次迭代以实现充分学习,可以生成初始的Playbook,适用于需要持续改进的生产部署
- OnlineAdapter:即在线训练或者生产模式,run() 函数从流中顺序处理样本,每个样本仅处理一次,立即适配,可以根据新任务实时更新 Playbook。
1.1 定义
AdapterStepResult 和 AdapterBase 定义如下。
python
@dataclass
class AdapterStepResult:
"""记录单次适配步骤的完整结果,包含各组件输出与中间状态"""
# 当前处理的样本数据
sample: Sample
# 生成器的输出结果
generator_output: GeneratorOutput
# 环境评估结果
environment_result: EnvironmentResult
# 反思器的输出结果
reflection: ReflectorOutput
# 管理者的输出结果
curator_output: CuratorOutput
# 行动手册的快照(字符串形式)
playbook_snapshot: str
# 可解释性元数据
epoch: int = 0 # 当前轮次编号
step: int = 0 # 当前步骤编号
# 条目元数据字典(键为条目ID,值为该条目属性的字典)
bullet_metadata: Dict[str, Dict] = field(default_factory=dict)
class AdapterBase:
"""离线与在线ACE适配的共享编排逻辑基类"""
def __init__(
self,
*,
playbook: Optional[Playbook] = None,
generator: Generator,
reflector: Reflector,
curator: Curator,
max_refinement_rounds: int = 1,
reflection_window: int = 3,
enable_explainability: bool = True,
) -> None:
# 行动手册(若未提供则初始化新实例)
self.playbook = playbook or Playbook()
# 生成器组件(负责生成答案生成)
self.generator = generator
# 反思器组件(用于结果分析与策略评估)
self.reflector = reflector
# 管理者组件(用于更新行动手册)
self.curator = curator
# 最大优化轮次(反思器的迭代次数)
self.max_refinement_rounds = max_refinement_rounds
# 反思窗口大小(保留最近反思的数量)
self.reflection_window = reflection_window
# 存储最近的反思结果(用于上下文传递)
self._recent_reflections: List[str] = []
# 可解释性相关组件
self.enable_explainability = enable_explainability
if enable_explainability:
self.evolution_tracker = EvolutionTracker() # 跟踪行动手册演化
self.attribution_analyzer = AttributionAnalyzer() # 分析策略归因
self.interaction_tracer = InteractionTracer() # 追踪组件交互
else:
self.evolution_tracker = None
self.attribution_analyzer = None
self.interaction_tracer = None1.2 核心流程
AdapterBase的核心流程如下:

ace-2
1.3 主要功能
AdapterBase 的主要函数如下。
python
# ------------------------------------------------------------------ #
def _reflection_context(self) -> str:
"""生成反思上下文字符串(拼接最近的反思结果)"""
return "\n---\n".join(self._recent_reflections)
def _update_recent_reflections(self, reflection: ReflectorOutput) -> None:
"""更新最近反思列表,确保不超过窗口大小"""
# 将反思结果序列化为JSON字符串
serialized = json.dumps(reflection.raw, ensure_ascii=False)
self._recent_reflections.append(serialized)
# 若超出窗口大小,保留最近的N条
if len(self._recent_reflections) > self.reflection_window:
self._recent_reflections = self._recent_reflections[
-self.reflection_window :
]
def _apply_bullet_tags(self, reflection: ReflectorOutput) -> None:
"""应用反思器输出的条目标记(更新helpful/harmful等计数)"""
for tag in reflection.bullet_tags:
try:
# 为指定条目添加标记
self.playbook.tag_bullet(tag.id, tag.tag)
except ValueError:
# 忽略不支持的标记类型
continue
def _question_context(
self, sample: Sample, environment_result: EnvironmentResult
) -> str:
"""生成问题上下文字符串(整合样本与环境反馈信息)"""
parts = [
f"question: {sample.question}", # 问题文本
f"context: {sample.context}", # 问题上下文
f"metadata: {json.dumps(sample.metadata)}", # 样本元数据
f"feedback: {environment_result.feedback}", # 环境反馈
f"ground_truth: {environment_result.ground_truth}", # 真实答案
]
return "\n".join(parts)
def _progress_string(
self, epoch: int, total_epochs: int, step: int, total_steps: int
) -> str:
"""生成进度字符串(用于跟踪训练进度)"""
return f"epoch {epoch}/{total_epochs} · sample {step}/{total_steps}"
def _process_sample(
self,
sample: Sample,
environment: TaskEnvironment,
*,
epoch: int,
total_epochs: int,
step_index: int,
total_steps: int,
) -> AdapterStepResult:
"""处理单个样本的完整流程,返回步骤结果"""
# 生成器基于当前行动手册和反思上下文生成答案
generator_output = self.generator.generate(
question=sample.question,
context=sample.context,
playbook=self.playbook,
reflection=self._reflection_context(),
)
# 环境评估生成器的输出结果
env_result = environment.evaluate(sample, generator_output)
# 反思器分析生成结果、真实答案和反馈,生成反思报告
reflection = self.reflector.reflect(
question=sample.question,
generator_output=generator_output,
playbook=self.playbook,
ground_truth=env_result.ground_truth,
feedback=env_result.feedback,
max_refinement_rounds=self.max_refinement_rounds,
)
# 应用反思器生成的条目标记
self._apply_bullet_tags(reflection)
# 更新最近反思列表
self._update_recent_reflections(reflection)
# 管理者基于反思结果生成行动手册更新操作
curator_output = self.curator.curate(
reflection=reflection,
playbook=self.playbook,
question_context=self._question_context(sample, env_result),
progress=self._progress_string(
epoch, total_epochs, step_index, total_steps
),
)
# 若启用可解释性,跟踪相关数据
if self.enable_explainability:
self._track_explainability_data(
sample, generator_output, env_result, reflection, curator_output,
epoch, step_index
)
# 应用管理者生成的更新操作到行动手册
self.playbook.apply_delta(curator_output.delta)
# 收集条目元数据用于可解释性分析
bullet_metadata = {}
if self.enable_explainability:
for bullet in self.playbook.bullets():
bullet_metadata[bullet.id] = {
'section': bullet.section,
'content': bullet.content,
'helpful': bullet.helpful,
'harmful': bullet.harmful,
'neutral': bullet.neutral
}
# 返回该步骤的完整结果
return AdapterStepResult(
sample=sample,
generator_output=generator_output,
environment_result=env_result,
reflection=reflection,
curator_output=curator_output,
playbook_snapshot=self.playbook.as_prompt(),
epoch=epoch,
step=step_index,
bullet_metadata=bullet_metadata,
)1.4 OfflineAdapter
OfflineAdapter(离线适配器)会针对固定训练集执行多轮迭代式学习,通过反复处理相同样本,让行动手册(Playbook)逐步优化,最终构建出鲁棒的初始策略集合,为后续部署奠定基础。
OfflineAdapter 的特色是:以 "多轮训练 + 固定样本" 为核心模式,适合在部署前对模型进行充分的离线训练,确保行动手册覆盖核心场景的策略需求,其工作流程是:
- 按生成器→环境→反思器→管理者的流程处理每个样本
- 每个样本处理后更新行动手册
- 按指定轮次重复上述过程
- 返回详细结果用于分析
OfflineAdapter 的代码如下。
ini
class OfflineAdapter(AdapterBase):
"""
Orchestrates offline ACE adaptation over multiple training epochs.
用于多轮训练周期的离线ACE适配编排。
The OfflineAdapter processes a fixed training set multiple times,
allowing the playbook to evolve and improve through repeated exposure
to the same examples. This is useful for building a robust initial
playbook before deployment.
该适配器会对固定训练集进行多次处理,通过反复接触相同示例使行动手册逐步演进优化。这有助于在部署前构建一个鲁棒的初始行动手册。
Args:
playbook: Initial playbook (creates empty one if None)
初始行动手册(若为None则创建空手册)
generator: Generator instance for producing answers
用于生成答案的生成器实例
reflector: Reflector instance for analyzing outcomes
用于分析结果的反思器实例
curator: Curator instance for updating playbook
用于更新行动手册的管理者实例
max_refinement_rounds: Max reflection refinement attempts (default: 1)
反思优化的最大尝试轮次(默认:1)
reflection_window: Number of recent reflections to maintain (default: 3)
保留的近期反思数量(默认:3)
Example:
>>> from ace import OfflineAdapter, Generator, Reflector, Curator
>>> from ace.llm_providers import LiteLLMClient
>>>
>>> # Initialize components with same LLM
>>> client = LiteLLMClient(model="gpt-4")
>>> generator = Generator(client)
>>> reflector = Reflector(client)
>>> curator = Curator(client)
>>>
>>> # Create adapter
>>> adapter = OfflineAdapter(
... generator=generator,
... reflector=reflector,
... curator=curator
... )
>>>
>>> # Prepare training samples
>>> samples = [
... Sample(question="What is 2+2?", ground_truth="4"),
... Sample(question="What is 5*3?", ground_truth="15")
... ]
>>>
>>> # Run adaptation for 3 epochs
>>> results = adapter.run(samples, environment, epochs=3)
>>>
>>> # Access evolved playbook
>>> print(adapter.playbook.as_prompt())
"""
def run(
self,
samples: Sequence[Sample],
environment: TaskEnvironment,
epochs: int = 1,
) -> List[AdapterStepResult]:
"""
Run offline adaptation over training samples.
对训练样本执行离线适配。
Args:
samples: Training samples to process
待处理的训练样本
environment: Environment for evaluating generator outputs
用于评估生成器输出的环境
epochs: Number of times to iterate over samples (default: 1)
样本迭代轮次(默认:1)
Returns:
List of AdapterStepResult for each processed sample
每个处理样本对应的AdapterStepResult列表
Note:
The playbook is updated in-place during adaptation.
适配过程中行动手册会就地更新。
Access the evolved playbook via adapter.playbook after running.
运行后可通过adapter.playbook访问演进后的行动手册。
"""
results: List[AdapterStepResult] = []
total_steps = len(samples)
for epoch_idx in range(1, epochs + 1):
for step_idx, sample in enumerate(samples, start=1):
result = self._process_sample(
sample,
environment,
epoch=epoch_idx,
total_epochs=epochs,
step_index=step_idx,
total_steps=total_steps,
)
results.append(result)
return results1.5 OnlineAdapter
OnlineAdapter(在线适配器)会在生产环境中对实时到来的样本进行逐次处理,每个样本处理后立即更新行动手册,实现系统的持续学习与实时优化,及时适配新场景、纠正错误。
OnlineAdapter以 "流式处理 + 单次迭代" 为核心模式,支持无限样本流的持续处理,是生产部署中实现动态改进的关键组件。
ini
class OnlineAdapter(AdapterBase):
"""
Orchestrates online ACE adaptation for continuous learning.
用于持续学习的在线ACE适配编排。
The OnlineAdapter processes samples sequentially as they arrive,
updating the playbook after each one. This enables continuous
improvement during deployment, adapting to new patterns and
correcting mistakes in real-time.
该适配器会按样本到达顺序依次处理,每个样本处理后更新行动手册。这使得部署期间可持续改进,实时适应新模式并纠正错误。
Args:
playbook: Initial playbook (creates empty one if None)
初始行动手册(若为None则创建空手册)
generator: Generator instance for producing answers
用于生成答案的生成器实例
reflector: Reflector instance for analyzing outcomes
用于分析结果的反思器实例
curator: Curator instance for updating playbook
用于更新行动手册的管理者实例
max_refinement_rounds: Max reflection refinement attempts (default: 1)
反思优化的最大尝试轮次(默认:1)
reflection_window: Number of recent reflections to maintain (default: 3)
保留的近期反思数量(默认:3)
Example:
>>> from ace import OnlineAdapter, Generator, Reflector, Curator
>>> from ace.llm_providers import LiteLLMClient
>>>
>>> # Initialize with pre-trained playbook
>>> playbook = Playbook.load_from_file("pretrained_playbook.json")
>>>
>>> client = LiteLLMClient(model="gpt-4")
>>> adapter = OnlineAdapter(
... playbook=playbook,
... generator=Generator(client),
... reflector=Reflector(client),
... curator=Curator(client)
... )
>>>
>>> # Process streaming samples
>>> def sample_stream():
... while True:
... yield get_next_sample() # Your sample source
>>>
>>> # Run online adaptation
>>> results = adapter.run(sample_stream(), environment)
>>>
>>> # Playbook evolves with each sample
>>> print(f"Bullets: {len(adapter.playbook.bullets)}")
"""
def run(
self,
samples: Iterable[Sample],
environment: TaskEnvironment,
) -> List[AdapterStepResult]:
"""
Run online adaptation over a stream of samples.
对样本流执行在线适配。
Args:
samples: Iterable of samples (can be infinite stream)
样本可迭代对象(可为无限流)
environment: Environment for evaluating generator outputs
用于评估生成器输出的环境
Returns:
List of AdapterStepResult for each processed sample
每个处理样本对应的AdapterStepResult列表
Note:
- Processes samples sequentially, updating after each one
按顺序处理样本,每个样本后更新
- The playbook evolves continuously during processing
处理过程中行动手册持续演进
- Can handle infinite streams for continuous deployment
可处理无限流以支持持续部署
"""
results: List[AdapterStepResult] = []
step_idx = 0
for step_idx, sample in enumerate(samples, start=1):
result = self._process_sample(
sample,
environment,
epoch=1,
total_epochs=1,
step_index=step_idx,
total_steps=step_idx,
)
results.append(result)
return results1.6 小结
三类适配器逻辑关系如下:
ace-2-1
0x02 关键组件
2.1 TaskEnvironment
TaskEnvironment负责评估生成器输出,并且其evaluate 方法返回一个包含ground_truth的EnvironmentResult。在实际使用中,Environment可能会提供其他形式的反馈,而非依赖ground_truth,比如在代码执行任务中,Environment会运行生成的代码并检查是否运行正确。在问答任务中,可能通过用户反馈或者其他方式来评估答案质量。
2.1.1 EnvironmentResult
EnvironmentResult 会封装任务环境对生成器输出的评估结果,包括文本反馈、真实答案(可选)和量化指标,是连接环境与 ACE 框架其他组件(如反思器)的关键数据载体。特色:通过结构化数据整合定性反馈与定量指标,为后续的策略优化提供明确依据。
python
@dataclass
class EnvironmentResult:
"""Feedback returned by the task environment after executing the generator output.
任务环境在执行生成器输出后返回的反馈结果。
"""
feedback: str # 对生成器输出的反馈信息(如正确性评价、错误原因等)
ground_truth: Optional[str] # 真实答案(可选,用于对比生成结果)
metrics: Dict[str, float] = field(default_factory=dict) # 评估指标字典(如准确率、得分等)2.1.2 TaskEnvironment
TaskEnvironment作为抽象接口定义了评估生成器输出的规范,要求子类实现具体任务的评估逻辑,是 ACE 框架实现任务适应性的核心扩展点。特色如下:
- 抽象性:通过抽象方法强制规范评估流程,确保不同任务的评估结果格式统一。
- 灵活性:允许针对特定任务(如数学计算、文本生成等)定制评估逻辑,使 ACE 框架能适配多样化场景。
- 指导性:生成的反馈信息直接影响反思器对策略有效性的判断,是框架实现学习与改进的基础。
TaskEnvironment 的代码如下:
python
class TaskEnvironment(ABC):
"""
Abstract interface for evaluating generator outputs.
用于评估生成器输出的抽象接口。
Implement this class to define how your specific task evaluates
the Generator's answers. The environment provides feedback that
helps ACE learn what works and what doesn't.
实现此类以定义特定任务如何评估生成器的答案。环境提供的反馈能帮助ACE了解哪些策略有效、哪些无效。
Example Implementation:
>>> class MathEnvironment(TaskEnvironment):
... def evaluate(self, sample, generator_output):
... # 解析答案
... predicted = extract_number(generator_output.final_answer)
... correct = str(predicted) == sample.ground_truth
...
... # 提供反馈
... if correct:
... feedback = "Correct!"
... else:
... feedback = f"Incorrect. Expected {sample.ground_truth}"
...
... return EnvironmentResult(
... feedback=feedback,
... ground_truth=sample.ground_truth,
... metrics={'accuracy': 1.0 if correct else 0.0}
... )
"""
@abstractmethod
def evaluate(
self, sample: Sample, generator_output: GeneratorOutput
) -> EnvironmentResult:
"""
Evaluate the generator's output for a given sample.
针对给定样本评估生成器的输出结果。
Args:
sample: The input sample with question and context
包含问题和上下文的输入样本
generator_output: The Generator's produced answer
生成器生成的答案
Returns:
EnvironmentResult with feedback and optional ground truth
包含反馈和可选真实答案的EnvironmentResult对象
The feedback should be informative enough for the Reflector
to understand what went right or wrong.
反馈信息应足够详细,以便反思器理解生成结果的优缺点及错误原因。
"""不同环境实现不同,比如下面的MathEnvironment。
ini
class MathEnvironment(TaskEnvironment):
def evaluate(self, sample, output):
try:
# Evaluate mathematical correctness
result = eval(output.final_answer)
correct = (result == eval(sample.ground_truth))
return EnvironmentResult(
feedback="Correct!" if correct else "Incorrect",
ground_truth=sample.ground_truth, # 从样本中获取
metrics={"accuracy": 1.0 if correct else 0.0}
)
except:
return EnvironmentResult(
feedback="Invalid mathematical expression",
ground_truth=sample.ground_truth,
metrics={"accuracy": 0.0}
)2.2 样本数据结构
Sample 类定义了样本数据结构。
python
@dataclass
class Sample:
"""Single task instance presented to ACE."""
question: str # 要解决的任务
context: str = "" # 额外的上下文或者要求
ground_truth: Optional[str] = None # 用于评估的正确答案
metadata: Dict[str, object] = field(default_factory=dict) # 元数据2.3 真实值
ground_truth在ACE系统中起到了"裁判"的作用。它不仅用于评估当前模型的表现,还为系统的自我反思和策略优化提供了必要的依据。没有ground_truth,系统就无法获得有效的学习信号,也无法实现持续改进。
2.3.1 作用
ground_truth主要体现在以下几个方面:
- 性能评估。ground_truth是衡量模型输出正确与否的黄金标准。通过将模型预测结果与ground_truth进行比较,可以计算出各种评估指标,如准确率、F1分数、精确率和召回率等。
- 反馈生成。在评估环境中(例如GenericBenchmarkEnvironment、FinerEnvironment等),ground_truth被用来生成具体的反馈信息。这些反馈信息对于后续的反思(Reflector)和策略优化(Curator)至关重要。
- 策略评估。Reflector组件会使用ground_truth来判断Generator的输出是否正确,并据此分析哪些playbook中的策略是有效的(helpful)、有害的(harmful)还是中性的(neutral)。这有助于系统识别哪些策略需要保留、改进或删除。
- 学习信号。Curator组件依赖ground_truth提供的信息来决定如何更新playbook。有了明确的正确答案作为参照,系统才能进行有针对性的学习和改进。
- 质量控制。ground_truth确保了系统能够客观地区分正确和错误输出,从而实现持续的自我优化。
2.3.2 和组件的关系
ACE流程:用户问题 → Generator生成答案 → nvironment提供反馈 → Reflector进行分析 → Curaotr 更新策略。这个流程中,不同角色对ground_truth的依赖关系如下:
- Generator:不依赖ground_truth,只依赖当前的playbook和问题本身。
- Reflector:在训练阶段依赖ground_truth来分析Generator的输出是否正确,在实际使用中,则依赖Envrionment提供的反馈。
- Curator:在训练阶段,依赖Reflector的分析结果来更新playbook,间接依赖Reflector。
2.3.3 获取方式
ground_truth用于训练和评估阶段,帮助系统学习哪些策略有效,哪些无效。ground_truth的获取方式主要包括:
-
预标注数据集:在训练阶段,ground_truth通常时预先标注好的正确答案,直接存储在训练样本中。
-
环境提供:在评估阶段,任务环境通常会提供ground_truth,可能来源于:
- 样本本身包含的真实答案。
- 环境内部的计算结果
- 外部验证服务
- 动态计算(比如数学任务)
示例如下。
训练阶段,会从训练样本中获取:
ini
samples = [
Sample(question="What is 2+2?", ground_truth="4"),
Sample(question="What is 5*3?", ground_truth="15")
]评测时,TaskEnvironment负责评估生成器输出,并且其evaluate 方法返回一个包含ground_truth的EnvironmentResult。
ini
output = self.generator.generate(
question="What is 2+2?",
context="Calculate",
playbook=self.playbook
)2.4 上下文窗口
在ACE中,reflection_window控制着在生成答案时候能思考的历史反思(reflection)的数量。具体而言:
- 定义了历史反思缓冲区大小。
- 允许生成器基于近期学习经验来改善当前的回答。
- 帮助模型从最近的错误和成功中快速学习并调整策略。
比如,当设置reflection_window为3时,系统会在新生成答案时考虑最近三次的反思内容。这些反思会作为额外上下文传递给生成器,帮助其避免重复错误。随着处理更多样本,这个窗口内的反思内容会不断更新。
对于大多数应用,3~5的窗口大小比较合理,平衡了上下文长度和学习效果,避免过长的历史记录导致提示词过大。
具体代码如下。
python
class AdapterBase:
self.reflection_window = reflection_window
self._recent_reflections: List[str] = []
def _update_recent_reflections(self, reflection: ReflectorOutput) -> None:
# 把最新反思添加到缓冲区
serialized = json.dumps(reflection.raw, ensure_ascii=False)
self._recent_reflections.append(serialized)
# 如果超出大小,则移除最近的反思
if len(self._recent_reflections) > self.reflection_window:
self._recent_reflections = self._recent_reflections[
-self.reflection_window :
] 本文使用 markdown.com.cn 排版