
🎁个人主页:User_芊芊君子
🎉欢迎大家点赞👍评论📝收藏⭐文章
🔍系列专栏:Java.数据结构


【前言】
数据结构中,栈(后进先出)和队列(先进先出)特性迥异。本系列聚焦LeetCode经典题:队列实现栈与栈实现队列,剖析如何突破结构限制,实现特性互模拟,助你深入理解两者本质。
文章目录:
一、队列实现栈
1.思路分析
两个队列实现栈,使用LinkedList来模拟队列,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口,支持队列的标准
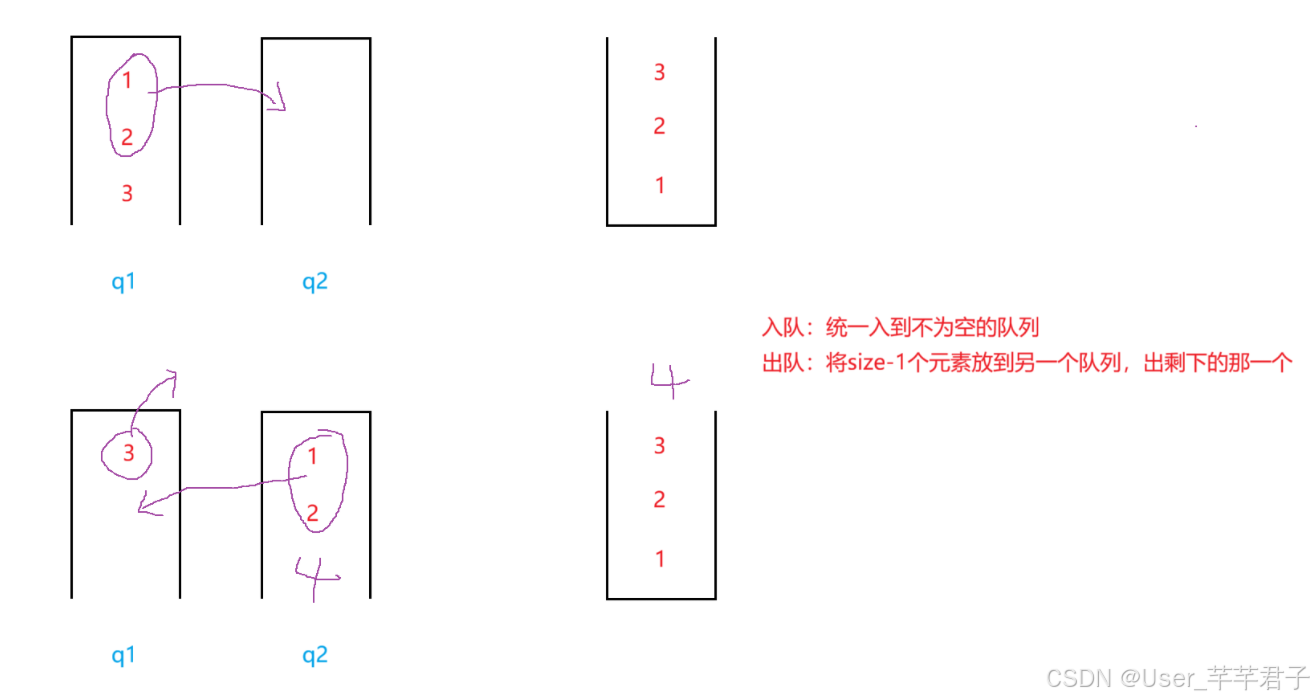
- 入队:统一入到不为空的队列中;
- 出队:将size-1个元素放到另一个队列,出剩下的那一个
2.代码详解
创建q1,q2两个队列,并实例化,因为LinkedList实现了Queue接口
java
public Queue<Integer> q1;
public Queue<Integer> q2;
public MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}当两个队列都为空时,则栈空
java
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty()&& q2.isEmpty();
}2.1 push(int x)
判断q1,q2是否为空,直接添加元素到不为空的那个队列,如果都为空,就添加到q1
java
public void push(int x) {
if(!q1.isEmpty()) {
q1.offer(x);
}else if(!q2.isEmpty()) {
q2.offer(x);
}else{
q1.offer(x);
}
}2.2 pop()
如果队列都为空,就返回-1。然后分开判断,q1不为空时,将它的size-1个元素转移到q2,然后出剩下的那个元素,q2不为空时,将它的size-1个元素转移到q1,然后出剩下的那个元素
java
public int pop() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!q1.isEmpty()){
int size = q1.size();
while (size - 1 != 0) {
int val = q1.poll();
q2.offer(val);
size--;
}
return q1.poll();
} else{
int size = q2.size();
while (size - 1 != 0) {
int val = q2.poll();
q1.offer(val);
size--;
}
return q2.poll();
}
}2.3 top()
跟pop()一样,需要改变的就是转移元素的个数为·size·,这样转移完成时,载体val中保留的就是最后要获取的那个元素,直接返回就行
java
public int top() {
int val = 1;
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!q1.isEmpty()){
int size = q1.size();
while (size != 0) {
val = q1.poll();
q2.offer(val);
size--;
}
return val;
} else{
int size = q2.size();
while (size != 0) {
val = q2.poll();
q1.offer(val);
size--;
}
return val;
}
}二、栈实现队列
1.思路分析
用两个双端队列Deque当作栈,LinkedList实现了Deque接口(也可以用LinkedList当作栈)
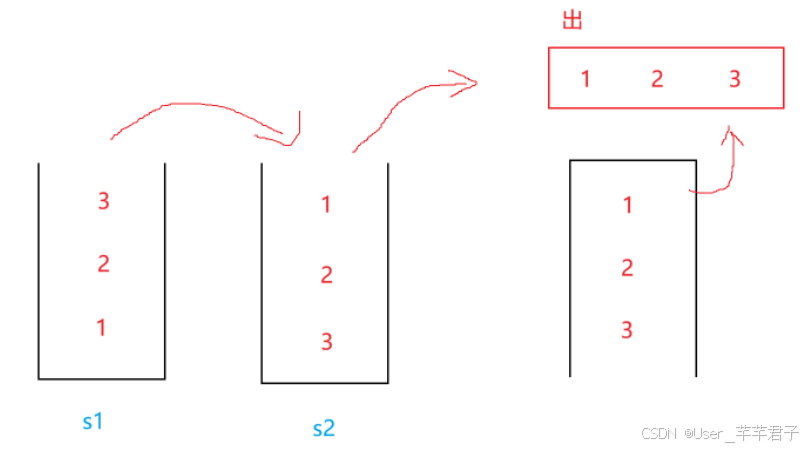
- 入栈:所有元素先放到第一个栈中;
- 出栈:
1.如果第二个栈为空,就将s1栈中元素放到s2中,这样就会倒过来;
2.如果不为空,直接出s2栈顶元素- 两个队列都为空,则模拟的栈是空的
2.代码分析
先创建两个栈,然后实例化。LinkedList实现了Deque接口(也可以用LinkedList当作栈)
java
public Deque<Integer> s1;
public Deque<Integer> s2;
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new LinkedList<>();
s2 = new LinkedList<>();
}当两个栈都为空时,则队列空
java
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty()&& s2.isEmpty();
}2.1 push(int x)
直接放到s1中
java
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}2.2 pop()
先判断栈是否为空,然后当s2为空时,就可以将s1中所有元素,转移过来,然后出s2栈顶元素
java
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}2.3 peek()
与pop() 一样,转移过来后,获取s2栈顶元素
java
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}四、完整代码
1.队列实现栈
java
public class MyStack {
public Queue<Integer> q1;
public Queue<Integer> q2;
public MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
if(!q1.isEmpty()) {
q1.offer(x);
}else if(!q2.isEmpty()) {
q2.offer(x);
}else{
q1.offer(x);
}
}
public int pop() {
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!q1.isEmpty()){
int size = q1.size();
while (size - 1 != 0) {
int val = q1.poll();
q2.offer(val);
size--;
}
return q1.poll();
} else{
int size = q2.size();
while (size - 1 != 0) {
int val = q2.poll();
q1.offer(val);
size--;
}
return q2.poll();
}
}
public int top() {
int val = 1;
if (empty()) {
return -1;
}
if (!q1.isEmpty()){
int size = q1.size();
while (size != 0) {
val = q1.poll();
q2.offer(val);
size--;
}
return val;
} else{
int size = q2.size();
while (size != 0) {
val = q2.poll();
q1.offer(val);
size--;
}
return val;
}
}
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty()&& q2.isEmpty();
}
}2.栈实现队列
java
public class MyQueue {
public Deque<Integer> s1;
public Deque<Integer> s2;
public MyQueue() {
s1 = new LinkedList<>();
s2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
s1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(empty()) {
return -1;
}
if(s2.isEmpty()) {
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.push(s1.pop());
}
}
return s2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return s1.isEmpty()&& s2.isEmpty();
}
}三、总结
- "队列实现栈"与"栈实现队列"均通过双结构协作+元素转移实现特性突破:前者借两个队列的转移让"先进先出"模拟"后进先出";后者靠两个栈的分工让"后进先出"模拟"先进先出"。
- 核心收获是理解结构特性的灵活转化------看似对立的栈和队列,可通过逻辑设计实现功能互通。掌握这种思维,能为解决复杂算法问题拓宽思路,助力你在数据结构领域的学习与实践。
