引言:为什么 RabbitMQ 是微服务架构的必备神器?
在当今的分布式系统和微服务架构中,消息队列已经成为不可或缺的核心组件。而 RabbitMQ 作为其中的佼佼者,凭借其强大的功能、灵活的路由机制和卓越的性能,被广泛应用于各大互联网公司的生产环境中。
你是否遇到过这些问题:
- 系统峰值流量过高导致服务崩溃?
- 微服务之间耦合度太高,修改一个服务影响一片?
- 数据一致性难以保证,分布式事务处理复杂?
- 异步任务处理效率低下,影响用户体验?
RabbitMQ 正是解决这些问题的利器。本文将带你从理论到实践,全面掌握 SpringBoot 集成 RabbitMQ 的方方面面,让你在实际项目中能够游刃有余地使用这一强大工具。
一、RabbitMQ 核心概念与工作原理
在开始编码之前,我们必须先理解 RabbitMQ 的核心概念和工作原理,这是后续一切操作的基础。
1.1 核心组件
RabbitMQ 基于 AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)协议实现,包含以下核心组件:
- Producer:消息生产者,负责发送消息
- Consumer:消息消费者,负责接收并处理消息
- Exchange:交换机,接收生产者发送的消息,并根据路由规则将消息路由到一个或多个队列
- Queue:消息队列,用于存储消息,直到被消费者消费
- Binding:绑定,用于建立 Exchange 和 Queue 之间的关联,并指定路由规则
- Connection:网络连接,如 TCP 连接
- Channel:信道,建立在 Connection 之上的虚拟连接,是进行消息读写的通道
graph LRA [Producer] -->| 发送消息 | B [Exchange]B -->| 路由消息 | C [Queue1]B -->| 路由消息 | D [Queue2]C -->| 消费消息 | E [Consumer1]D -->| 消费消息 | F [Consumer2]
1.2 交换机类型
RabbitMQ 提供了四种主要的交换机类型,每种类型对应不同的路由策略:
- Direct Exchange:直接交换机,根据消息携带的路由键(Routing Key)与绑定的路由键完全匹配来路由消息
- Topic Exchange:主题交换机,通过通配符匹配路由键,比直接交换机更灵活
- Fanout Exchange:扇形交换机,将消息路由到所有与之绑定的队列,忽略路由键
- Headers Exchange:头交换机,根据消息的头部信息进行路由,不依赖路由键
1.3 消息流转过程
flowchart TDA [生产者创建消息] --> B [设置消息属性包括路由键]B --> C [发送到指定交换机]C --> D [交换机根据类型和绑定规则]D --> E [将消息路由到匹配的队列]E --> F [消费者监听队列获取消息]F --> G [处理消息]
二、环境准备
2.1 安装 RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ 基于 Erlang 语言开发,因此首先需要安装 Erlang 环境。
2.1.1 Windows 系统安装
-
下载并安装 Erlang:https://www.erlang.org/downloads
-
下载并安装 RabbitMQ:https://www.rabbitmq.com/download.html
-
启动 RabbitMQ 服务:
安装管理插件
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
启动服务
net start RabbitMQ
2.1.2 Linux 系统安装(以 CentOS 为例)
# 安装Erlang
yum install -y erlang
# 安装RabbitMQ
wget https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/releases/download/v3.13.0/rabbitmq-server-3.13.0-1.el8.noarch.rpm
rpm -ivh rabbitmq-server-3.13.0-1.el8.noarch.rpm
# 启动服务
systemctl start rabbitmq-server
# 设置开机启动
systemctl enable rabbitmq-server
# 启用管理插件
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management2.2 访问 RabbitMQ 管理界面
安装完成后,通过浏览器访问http://localhost:15672(默认端口),使用默认账号密码guest/guest登录(注意:默认账号只允许本地访问,远程访问需要创建新用户)。
创建新用户命令:
# 创建用户
rabbitmqctl add_user admin 123456
# 设置用户角色为管理员
rabbitmqctl set_user_tags admin administrator
# 设置权限
rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / admin ".*" ".*" ".*"三、SpringBoot 项目搭建与配置
3.1 创建 Maven 项目
首先,我们创建一个 SpringBoot 项目,添加必要的依赖。
3.1.1 pom.xml 配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.ken</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-rabbitmq-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-rabbitmq-demo</name>
<description>SpringBoot集成RabbitMQ实战教程</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<mybatis-plus.version>3.5.5</mybatis-plus.version>
<fastjson2.version>2.0.32</fastjson2.version>
<guava.version>32.1.3-jre</guava.version>
<swagger.version>2.2.0</swagger.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- SpringBoot Web -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- SpringBoot RabbitMQ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- MyBatis-Plus -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${mybatis-plus.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL Connector -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Fastjson2 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.fastjson2</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson2</artifactId>
<version>${fastjson2.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Guava -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>${guava.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Swagger3 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springdoc</groupId>
<artifactId>springdoc-openapi-starter-webmvc-ui</artifactId>
<version>${swagger.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.amqp</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-rabbit-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>3.2 配置文件
创建application.yml配置文件,配置 RabbitMQ 连接信息和其他必要配置。
spring:
application:
name: springboot-rabbitmq-demo
# RabbitMQ配置
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: admin
password: 123456
virtual-host: /
# 生产者确认配置
publisher-confirm-type: correlated
publisher-returns: true
# 消费者配置
listener:
simple:
# 手动确认模式
acknowledge-mode: manual
# 消费者线程数
concurrency: 1
# 最大消费者线程数
max-concurrency: 5
# 每次从队列中获取的消息数量
prefetch: 1
direct:
acknowledge-mode: manual
# 数据库配置
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/rabbitmq_demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: root
# MyBatis-Plus配置
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/**/*.xml
type-aliases-package: com.ken.entity
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 日志配置
logging:
level:
com.ken: debug
org.springframework.amqp: info
# 服务端口
server:
port: 8080
# Swagger配置
springdoc:
api-docs:
path: /api-docs
swagger-ui:
path: /swagger-ui.html
operationsSorter: method
packages-to-scan: com.ken.controller3.3 主启动类
package com.ken;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* SpringBoot集成RabbitMQ示例项目主启动类
*
* @author ken
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.ken.mapper")
public class SpringbootRabbitmqDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootRabbitmqDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}四、RabbitMQ 核心配置类
为了更好地管理 RabbitMQ 的交换机、队列和绑定关系,我们创建一个配置类来集中定义这些组件。
4.1 队列、交换机和绑定配置
package com.ken.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* RabbitMQ核心配置类,定义交换机、队列和绑定关系
*
* @author ken
*/
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfig {
// ========================== 简单队列示例 ==========================
/**
* 简单队列名称
*/
public static final String SIMPLE_QUEUE = "simple_queue";
/**
* 创建简单队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue simpleQueue() {
/*
* 队列参数说明:
* 1. 队列名称
* 2. 是否持久化(true:队列会在RabbitMQ重启后保留)
* 3. 是否排他性(true:仅限当前连接使用,连接关闭后自动删除)
* 4. 是否自动删除(true:当最后一个消费者取消订阅后自动删除)
* 5. 队列属性参数
*/
return QueueBuilder.durable(SIMPLE_QUEUE)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
// ========================== 工作队列示例 ==========================
/**
* 工作队列名称
*/
public static final String WORK_QUEUE = "work_queue";
/**
* 创建工作队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue workQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(WORK_QUEUE)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
// ========================== 发布/订阅模式 ==========================
/**
* 扇形交换机名称
*/
public static final String FANOUT_EXCHANGE = "fanout_exchange";
/**
* 发布订阅队列1
*/
public static final String FANOUT_QUEUE1 = "fanout_queue1";
/**
* 发布订阅队列2
*/
public static final String FANOUT_QUEUE2 = "fanout_queue2";
/**
* 创建扇形交换机
*
* @return 交换机实例
*/
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() {
/*
* 交换机参数说明:
* 1. 交换机名称
* 2. 是否持久化
* 3. 是否自动删除
* 4. 交换机属性参数
*/
return new FanoutExchange(FANOUT_EXCHANGE, true, false);
}
/**
* 创建发布订阅队列1
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(FANOUT_QUEUE1)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 创建发布订阅队列2
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(FANOUT_QUEUE2)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 绑定队列1到扇形交换机
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding1() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
/**
* 绑定队列2到扇形交换机
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding fanoutBinding2() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2()).to(fanoutExchange());
}
// ========================== 路由模式 ==========================
/**
* 直接交换机名称
*/
public static final String DIRECT_EXCHANGE = "direct_exchange";
/**
* 路由队列1(接收error级别日志)
*/
public static final String DIRECT_QUEUE_ERROR = "direct_queue_error";
/**
* 路由队列2(接收info、warn、error级别日志)
*/
public static final String DIRECT_QUEUE_ALL = "direct_queue_all";
/**
* 路由键:error
*/
public static final String ROUTING_KEY_ERROR = "error";
/**
* 路由键:info
*/
public static final String ROUTING_KEY_INFO = "info";
/**
* 路由键:warn
*/
public static final String ROUTING_KEY_WARN = "warn";
/**
* 创建直接交换机
*
* @return 交换机实例
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(DIRECT_EXCHANGE, true, false);
}
/**
* 创建错误日志队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue directQueueError() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(DIRECT_QUEUE_ERROR)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 创建所有级别日志队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue directQueueAll() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(DIRECT_QUEUE_ALL)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 绑定错误日志队列到直接交换机,路由键为error
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding directBindingError() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueueError())
.to(directExchange())
.with(ROUTING_KEY_ERROR);
}
/**
* 绑定所有级别日志队列到直接交换机,路由键为info
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding directBindingInfo() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueueAll())
.to(directExchange())
.with(ROUTING_KEY_INFO);
}
/**
* 绑定所有级别日志队列到直接交换机,路由键为warn
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding directBindingWarn() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueueAll())
.to(directExchange())
.with(ROUTING_KEY_WARN);
}
/**
* 绑定所有级别日志队列到直接交换机,路由键为error
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding directBindingAllError() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueueAll())
.to(directExchange())
.with(ROUTING_KEY_ERROR);
}
// ========================== 主题模式 ==========================
/**
* 主题交换机名称
*/
public static final String TOPIC_EXCHANGE = "topic_exchange";
/**
* 主题队列1(接收订单相关消息)
*/
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_ORDER = "topic_queue_order";
/**
* 主题队列2(接收用户相关消息)
*/
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_USER = "topic_queue_user";
/**
* 主题队列3(接收所有系统消息)
*/
public static final String TOPIC_QUEUE_ALL = "topic_queue_all";
/**
* 订单路由键前缀
*/
public static final String ROUTING_KEY_ORDER = "system.order.#";
/**
* 用户路由键前缀
*/
public static final String ROUTING_KEY_USER = "system.user.#";
/**
* 所有系统路由键
*/
public static final String ROUTING_KEY_ALL = "system.#";
/**
* 创建主题交换机
*
* @return 交换机实例
*/
@Bean
public TopicExchange topicExchange() {
return new TopicExchange(TOPIC_EXCHANGE, true, false);
}
/**
* 创建订单主题队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueOrder() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(TOPIC_QUEUE_ORDER)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 创建用户主题队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueUser() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(TOPIC_QUEUE_USER)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 创建所有系统消息队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue topicQueueAll() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(TOPIC_QUEUE_ALL)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 绑定订单队列到主题交换机
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding topicBindingOrder() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueOrder())
.to(topicExchange())
.with(ROUTING_KEY_ORDER);
}
/**
* 绑定用户队列到主题交换机
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding topicBindingUser() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueUser())
.to(topicExchange())
.with(ROUTING_KEY_USER);
}
/**
* 绑定所有系统消息队列到主题交换机
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding topicBindingAll() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(topicQueueAll())
.to(topicExchange())
.with(ROUTING_KEY_ALL);
}
// ========================== 死信队列 ==========================
/**
* 死信交换机名称
*/
public static final String DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE = "dead_letter_exchange";
/**
* 死信队列名称
*/
public static final String DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE = "dead_letter_queue";
/**
* 死信路由键
*/
public static final String DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY = "dead_letter_routing_key";
/**
* 普通队列(可能产生死信的队列)
*/
public static final String NORMAL_QUEUE = "normal_queue";
/**
* 普通交换机
*/
public static final String NORMAL_EXCHANGE = "normal_exchange";
/**
* 普通队列路由键
*/
public static final String NORMAL_ROUTING_KEY = "normal_routing_key";
/**
* 创建死信交换机
*
* @return 交换机实例
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange deadLetterExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE, true, false);
}
/**
* 创建死信队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue deadLetterQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 绑定死信队列到死信交换机
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding deadLetterBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(deadLetterQueue())
.to(deadLetterExchange())
.with(DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY);
}
/**
* 创建普通交换机
*
* @return 交换机实例
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange normalExchange() {
return new DirectExchange(NORMAL_EXCHANGE, true, false);
}
/**
* 创建普通队列,并设置死信相关参数
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue normalQueue() {
Map<String, Object> arguments = new HashMap<>(3);
// 设置死信交换机
arguments.put("x-dead-letter-exchange", DEAD_LETTER_EXCHANGE);
// 设置死信路由键
arguments.put("x-dead-letter-routing-key", DEAD_LETTER_ROUTING_KEY);
// 设置队列消息过期时间(毫秒),也可以在发送消息时单独设置
arguments.put("x-message-ttl", 10000);
// 设置队列最大长度
arguments.put("x-max-length", 5);
return QueueBuilder.durable(NORMAL_QUEUE)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.withArguments(arguments)
.build();
}
/**
* 绑定普通队列到普通交换机
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding normalBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(normalQueue())
.to(normalExchange())
.with(NORMAL_ROUTING_KEY);
}
// ========================== 延迟队列 ==========================
/**
* 延迟交换机(基于插件的延迟交换机)
*/
public static final String DELAY_EXCHANGE = "delay_exchange";
/**
* 延迟队列
*/
public static final String DELAY_QUEUE = "delay_queue";
/**
* 延迟队列路由键
*/
public static final String DELAY_ROUTING_KEY = "delay_routing_key";
/**
* 创建延迟交换机(注意类型是x-delayed-message)
*
* @return 交换机实例
*/
@Bean
public CustomExchange delayExchange() {
Map<String, Object> arguments = new HashMap<>(1);
// 设置延迟交换机类型为direct
arguments.put("x-delayed-type", "direct");
/*
* 参数说明:
* 1. 交换机名称
* 2. 交换机类型(x-delayed-message是延迟交换机的类型)
* 3. 是否持久化
* 4. 是否自动删除
* 5. 其他属性
*/
return new CustomExchange(DELAY_EXCHANGE, "x-delayed-message", true, false, arguments);
}
/**
* 创建延迟队列
*
* @return 队列实例
*/
@Bean
public Queue delayQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable(DELAY_QUEUE)
.autoDelete(false)
.exclusive(false)
.build();
}
/**
* 绑定延迟队列到延迟交换机
*
* @return 绑定关系
*/
@Bean
public Binding delayBinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(delayQueue())
.to(delayExchange())
.with(DELAY_ROUTING_KEY)
.noargs();
}
}4.2 消息转换器配置
为了更好地处理消息的序列化和反序列化,我们配置一个消息转换器,使用 Fastjson2 来处理 JSON 格式的消息。
package com.ken.config;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSONReader;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSONWriter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.AbstractMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.DefaultClassMapper;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessageProperties;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* 消息转换器配置,用于消息的序列化和反序列化
*
* @author ken
*/
@Configuration
public class MessageConverterConfig {
/**
* 配置Fastjson2消息转换器
*
* @return 消息转换器
*/
@Bean
public MessageConverter fastJsonMessageConverter() {
return new AbstractMessageConverter() {
private final DefaultClassMapper classMapper = new DefaultClassMapper();
@Override
protected Message createMessage(Object object, MessageProperties messageProperties) {
// 设置消息内容类型为JSON
messageProperties.setContentType(MessageProperties.CONTENT_TYPE_JSON);
// 将对象序列化为JSON字符串
byte[] bytes = JSON.toJSONBytes(object, JSONWriter.Feature.WriteClassName);
return new Message(bytes, messageProperties);
}
@Override
public Object fromMessage(Message message) throws IOException {
// 从消息中获取字节数组
byte[] body = message.getBody();
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(body)) {
return null;
}
// 将JSON字节数组反序列化为对象
try (InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(body)) {
return JSON.parseObject(is, Object.class, JSONReader.Feature.SupportAutoType);
}
}
};
}
}4.3 生产者确认和返回机制配置
为了确保消息的可靠传递,我们需要配置生产者的消息确认和返回机制。
package com.ken.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* RabbitMQ消息确认配置
* 包括生产者发送消息到交换机的确认,以及消息无法路由时的返回机制
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Configuration
public class RabbitMQConfirmConfig implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback, RabbitTemplate.ReturnsCallback {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* 初始化方法,设置确认回调和返回回调
*/
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
// 设置消息确认回调
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this);
// 设置消息返回回调
rabbitTemplate.setReturnsCallback(this);
// 设置消息发送失败时的策略:true表示消息在未被路由到队列时会返回给生产者,false表示直接丢弃
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
}
/**
* 消息发送到交换机的确认回调
*
* @param correlationData 关联数据,包含消息ID等信息
* @param ack 消息是否成功到达交换机
* @param cause 失败原因,如果ack为true则为null
*/
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack, String cause) {
String messageId = correlationData != null ? correlationData.getId() : "unknown";
if (ack) {
log.info("消息[{}]已成功发送到交换机", messageId);
} else {
log.error("消息[{}]发送到交换机失败,原因:{}", messageId, cause);
// 这里可以添加消息重发或持久化到数据库等处理逻辑
}
}
/**
* 消息无法路由到队列时的返回回调
*
* @param returnedMessage 返回的消息对象,包含消息内容、交换机、路由键等信息
*/
@Override
public void returnedMessage(ReturnedMessage returnedMessage) {
log.error("消息无法路由到队列,消息内容:{},交换机:{},路由键:{},回复码:{},回复文本:{}",
new String(returnedMessage.getMessage().getBody()),
returnedMessage.getExchange(),
returnedMessage.getRoutingKey(),
returnedMessage.getReplyCode(),
returnedMessage.getReplyText());
// 这里可以添加消息重发或持久化到数据库等处理逻辑
}
}五、通用工具类
为了简化开发,我们创建一些通用的工具类。
5.1 消息实体类
package com.ken.entity;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.IdType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableId;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.TableName;
import lombok.Data;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 消息实体类,用于在系统中传递和存储消息
*
* @author ken
*/
@Data
@TableName("t_message_log")
public class Message implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* 消息ID,主键
*/
@TableId(type = IdType.ASSIGN_UUID)
private String id;
/**
* 消息内容
*/
private String content;
/**
* 交换机名称
*/
private String exchange;
/**
* 路由键
*/
private String routingKey;
/**
* 消息状态:0-待发送,1-已发送,2-已消费,3-发送失败,4-消费失败
*/
private Integer status;
/**
* 重试次数
*/
private Integer retryCount;
/**
* 创建时间
*/
private LocalDateTime createTime;
/**
* 更新时间
*/
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
}5.2 消息日志服务
为了实现消息的可靠传递和追踪,我们创建一个消息日志服务,用于记录消息的发送和消费情况。
package com.ken.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.ken.entity.Message;
/**
* 消息日志服务接口
*
* @author ken
*/
public interface MessageLogService extends IService<Message> {
/**
* 记录消息发送日志
*
* @param message 消息对象
*/
void recordSendLog(Message message);
/**
* 更新消息发送状态
*
* @param messageId 消息ID
* @param status 状态:1-已发送,3-发送失败
*/
void updateSendStatus(String messageId, Integer status);
/**
* 更新消息消费状态
*
* @param messageId 消息ID
* @param status 状态:2-已消费,4-消费失败
*/
void updateConsumeStatus(String messageId, Integer status);
/**
* 增加消息重试次数
*
* @param messageId 消息ID
* @return 最新的重试次数
*/
int incrementRetryCount(String messageId);
}
package com.ken.service.impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.LambdaQueryWrapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.ken.entity.Message;
import com.ken.mapper.MessageMapper;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 消息日志服务实现类
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Service
public class MessageLogServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<MessageMapper, Message> implements MessageLogService {
/**
* 记录消息发送日志
*
* @param message 消息对象
*/
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void recordSendLog(Message message) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(message)) {
log.warn("消息对象为空,不记录发送日志");
return;
}
message.setStatus(0); // 0-待发送
message.setRetryCount(0);
message.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
message.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
boolean saveResult = save(message);
if (saveResult) {
log.info("消息[{}]发送日志记录成功", message.getId());
} else {
log.error("消息[{}]发送日志记录失败", message.getId());
}
}
/**
* 更新消息发送状态
*
* @param messageId 消息ID
* @param status 状态:1-已发送,3-发送失败
*/
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void updateSendStatus(String messageId, Integer status) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(messageId) || ObjectUtils.isEmpty(status)) {
log.warn("消息ID或状态为空,不更新发送状态");
return;
}
Message message = new Message();
message.setId(messageId);
message.setStatus(status);
message.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
int updateCount = baseMapper.updateById(message);
if (updateCount > 0) {
log.info("消息[{}]发送状态更新为{}成功", messageId, status);
} else {
log.error("消息[{}]发送状态更新为{}失败", messageId, status);
}
}
/**
* 更新消息消费状态
*
* @param messageId 消息ID
* @param status 状态:2-已消费,4-消费失败
*/
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public void updateConsumeStatus(String messageId, Integer status) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(messageId) || ObjectUtils.isEmpty(status)) {
log.warn("消息ID或状态为空,不更新消费状态");
return;
}
Message message = new Message();
message.setId(messageId);
message.setStatus(status);
message.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
int updateCount = baseMapper.updateById(message);
if (updateCount > 0) {
log.info("消息[{}]消费状态更新为{}成功", messageId, status);
} else {
log.error("消息[{}]消费状态更新为{}失败", messageId, status);
}
}
/**
* 增加消息重试次数
*
* @param messageId 消息ID
* @return 最新的重试次数
*/
@Override
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public int incrementRetryCount(String messageId) {
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(messageId)) {
log.warn("消息ID为空,不增加重试次数");
return 0;
}
Message message = getById(messageId);
if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(message)) {
log.warn("消息[{}]不存在,不增加重试次数", messageId);
return 0;
}
int newRetryCount = message.getRetryCount() + 1;
message.setRetryCount(newRetryCount);
message.setUpdateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
baseMapper.updateById(message);
log.info("消息[{}]重试次数增加为{}", messageId, newRetryCount);
return newRetryCount;
}
}5.3 MyBatis-Plus Mapper 接口
package com.ken.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.ken.entity.Message;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
/**
* 消息日志Mapper接口
*
* @author ken
*/
@Mapper
public interface MessageMapper extends BaseMapper<Message> {
}5.4 消息发送工具类
package com.ken.util;
import com.alibaba.fastjson2.JSON;
import com.ken.entity.Message;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.CorrelationData;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.ObjectUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.UUID;
/**
* 消息发送工具类,封装RabbitMQ消息发送的通用逻辑
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class RabbitMQMessageSender {
@Resource
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 发送消息到指定交换机
*
* @param exchange 交换机名称
* @param routingKey 路由键
* @param data 消息内容
* @return 消息ID
*/
public String sendMessage(String exchange, String routingKey, Object data) {
// 生成消息ID
String messageId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
try {
// 记录消息发送日志
Message messageLog = new Message();
messageLog.setId(messageId);
messageLog.setContent(JSON.toJSONString(data));
messageLog.setExchange(exchange);
messageLog.setRoutingKey(routingKey);
messageLogService.recordSendLog(messageLog);
// 发送消息
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(messageId);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, data, correlationData);
log.info("消息[{}]发送成功,交换机:{},路由键:{},内容:{}",
messageId, exchange, routingKey, JSON.toJSONString(data));
return messageId;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("消息[{}]发送失败,交换机:{},路由键:{},内容:{},异常:{}",
messageId, exchange, routingKey, JSON.toJSONString(data), e.getMessage(), e);
// 更新消息发送状态为失败
messageLogService.updateSendStatus(messageId, 3);
throw new RuntimeException("消息发送失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 发送延迟消息
*
* @param exchange 交换机名称(需要是延迟交换机)
* @param routingKey 路由键
* @param data 消息内容
* @param delayTime 延迟时间(毫秒)
* @return 消息ID
*/
public String sendDelayMessage(String exchange, String routingKey, Object data, long delayTime) {
if (delayTime <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("延迟时间必须大于0");
}
// 生成消息ID
String messageId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
try {
// 记录消息发送日志
Message messageLog = new Message();
messageLog.setId(messageId);
messageLog.setContent(JSON.toJSONString(data));
messageLog.setExchange(exchange);
messageLog.setRoutingKey(routingKey);
messageLogService.recordSendLog(messageLog);
// 发送延迟消息,设置延迟头部信息
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(messageId);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, data, message -> {
// 设置延迟时间
message.getMessageProperties().setHeader("x-delay", delayTime);
return message;
}, correlationData);
log.info("延迟消息[{}]发送成功,交换机:{},路由键:{},延迟时间:{}ms,内容:{}",
messageId, exchange, routingKey, delayTime, JSON.toJSONString(data));
return messageId;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("延迟消息[{}]发送失败,交换机:{},路由键:{},延迟时间:{}ms,内容:{},异常:{}",
messageId, exchange, routingKey, delayTime, JSON.toJSONString(data), e.getMessage(), e);
// 更新消息发送状态为失败
messageLogService.updateSendStatus(messageId, 3);
throw new RuntimeException("延迟消息发送失败:" + e.getMessage());
}
}
}六、实战示例
接下来,我们通过具体的示例来演示 RabbitMQ 的各种使用场景。
6.1 简单队列示例
简单队列是 RabbitMQ 中最基础的模式,一个生产者发送消息到一个队列,一个消费者从该队列接收消息。
6.1.1 生产者
package com.ken.producer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.util.RabbitMQMessageSender;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 简单队列消息生产者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/simple")
@Tag(name = "简单队列示例", description = "简单队列的消息发送接口")
public class SimpleQueueProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitMQMessageSender messageSender;
/**
* 发送消息到简单队列
*
* @param message 消息内容
* @return 消息ID
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@Operation(summary = "发送消息到简单队列", description = "向简单队列发送一条消息")
public String sendMessage(
@Parameter(description = "消息内容", required = true)
@RequestParam String message) {
return messageSender.sendMessage("", RabbitMQConfig.SIMPLE_QUEUE, message);
}
}6.1.2 消费者
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 简单队列消息消费者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class SimpleQueueConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听简单队列,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.SIMPLE_QUEUE)
public void consumeMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
log.info("简单队列消费者接收到消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, new String(message.getBody()));
try {
// 处理消息逻辑
if (StringUtils.hasText(new String(message.getBody()))) {
log.info("简单队列消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} else {
log.error("简单队列消息内容为空,拒绝消费");
// 拒绝消息,并将消息丢弃(不重新入队)
channel.basicReject(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("简单队列消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队(可以设置重试次数限制)
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
// 增加重试次数
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}6.2 工作队列示例
工作队列(Work Queue)用于将耗时的任务分发给多个消费者处理,实现负载均衡。
6.2.1 生产者
package com.ken.producer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.util.RabbitMQMessageSender;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 工作队列消息生产者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/work")
@Tag(name = "工作队列示例", description = "工作队列的消息发送接口")
public class WorkQueueProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitMQMessageSender messageSender;
/**
* 发送消息到工作队列
*
* @param message 消息内容
* @param count 发送消息数量
* @return 消息发送结果
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@Operation(summary = "发送消息到工作队列", description = "向工作队列发送指定数量的消息")
public String sendMessage(
@Parameter(description = "消息内容", required = true)
@RequestParam String message,
@Parameter(description = "发送消息数量", required = true, example = "10")
@RequestParam Integer count) {
if (count <= 0) {
return "消息数量必须大于0";
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
String msg = message + " - " + (i + 1);
messageSender.sendMessage("", RabbitMQConfig.WORK_QUEUE, msg);
}
return "成功发送" + count + "条消息到工作队列";
}
}6.2.2 消费者
我们创建两个消费者来演示工作队列的负载均衡效果。
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 工作队列消息消费者1
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WorkQueueConsumer1 {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听工作队列,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.WORK_QUEUE)
public void consumeMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【消费者1】接收到工作队列消息,时间:{},消息ID:{},内容:{}",
LocalTime.now(), messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 模拟处理耗时任务(1秒)
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
log.info("【消费者1】工作队列消息处理成功,消息ID:{}", messageId);
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【消费者1】工作队列消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalTime;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* 工作队列消息消费者2
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class WorkQueueConsumer2 {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听工作队列,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.WORK_QUEUE)
public void consumeMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【消费者2】接收到工作队列消息,时间:{},消息ID:{},内容:{}",
LocalTime.now(), messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 模拟处理耗时任务(2秒)
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
log.info("【消费者2】工作队列消息处理成功,消息ID:{}", messageId);
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【消费者2】工作队列消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}6.3 发布 / 订阅模式示例
发布 / 订阅模式(Publish/Subscribe)允许将一条消息发送给多个消费者,每个消费者都能收到相同的消息副本。
6.3.1 生产者
package com.ken.producer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.util.RabbitMQMessageSender;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 发布/订阅模式消息生产者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/fanout")
@Tag(name = "发布/订阅模式示例", description = "发布/订阅模式的消息发送接口")
public class FanoutProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitMQMessageSender messageSender;
/**
* 发送消息到扇形交换机
*
* @param message 消息内容
* @return 消息ID
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@Operation(summary = "发送消息到扇形交换机", description = "向扇形交换机发送消息,所有绑定的队列都会收到消息")
public String sendMessage(
@Parameter(description = "消息内容", required = true)
@RequestParam String message) {
// 扇形交换机忽略路由键,所以这里可以传空字符串
return messageSender.sendMessage(RabbitMQConfig.FANOUT_EXCHANGE, "", message);
}
}6.3.2 消费者
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 发布/订阅模式消息消费者1
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FanoutConsumer1 {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听扇形交换机绑定的队列1,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.FANOUT_QUEUE1)
public void consumeMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【发布订阅消费者1】接收到消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 处理消息逻辑
log.info("【发布订阅消费者1】消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【发布订阅消费者1】消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 发布/订阅模式消息消费者2
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class FanoutConsumer2 {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听扇形交换机绑定的队列2,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.FANOUT_QUEUE2)
public void consumeMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【发布订阅消费者2】接收到消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 处理消息逻辑
log.info("【发布订阅消费者2】消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【发布订阅消费者2】消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}6.4 路由模式示例
路由模式(Routing)允许根据消息的路由键将消息发送到不同的队列,实现消息的定向分发。
6.4.1 生产者
package com.ken.producer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.util.RabbitMQMessageSender;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.enums.ParameterIn;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 路由模式消息生产者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/direct")
@Tag(name = "路由模式示例", description = "路由模式的消息发送接口")
public class DirectProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitMQMessageSender messageSender;
/**
* 发送消息到直接交换机
*
* @param message 消息内容
* @param level 日志级别(info、warn、error)
* @return 消息ID
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@Operation(summary = "发送消息到直接交换机", description = "向直接交换机发送消息,根据日志级别路由到不同队列")
public String sendMessage(
@Parameter(description = "消息内容", required = true)
@RequestParam String message,
@Parameter(description = "日志级别", required = true, example = "info",
in = ParameterIn.QUERY, allowableValues = {"info", "warn", "error"})
@RequestParam String level) {
String routingKey;
switch (level.toLowerCase()) {
case "info":
routingKey = RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY_INFO;
break;
case "warn":
routingKey = RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY_WARN;
break;
case "error":
routingKey = RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY_ERROR;
break;
default:
return "不支持的日志级别,请使用info、warn或error";
}
return messageSender.sendMessage(RabbitMQConfig.DIRECT_EXCHANGE, routingKey, message);
}
}6.4.2 消费者
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 路由模式消息消费者(处理错误日志)
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DirectErrorConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听错误日志队列,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.DIRECT_QUEUE_ERROR)
public void consumeErrorMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.error("【错误日志消费者】接收到错误消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 处理错误消息逻辑,例如发送邮件通知、记录到错误日志系统等
log.info("【错误日志消费者】错误消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【错误日志消费者】错误消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 路由模式消息消费者(处理所有级别日志)
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DirectAllConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听所有级别日志队列,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.DIRECT_QUEUE_ALL)
public void consumeAllMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String routingKey = message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
switch (routingKey) {
case RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY_INFO:
log.info("【全量日志消费者】接收到info消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
break;
case RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY_WARN:
log.warn("【全量日志消费者】接收到warn消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
break;
case RabbitMQConfig.ROUTING_KEY_ERROR:
log.error("【全量日志消费者】接收到error消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
break;
default:
log.info("【全量日志消费者】接收到未知级别消息,消息ID:{},路由键:{},内容:{}",
messageId, routingKey, msgContent);
}
try {
// 处理消息逻辑,例如统一记录到日志系统
log.info("【全量日志消费者】消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【全量日志消费者】消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}6.5 主题模式示例
主题模式(Topic)是路由模式的扩展,允许使用通配符来匹配路由键,提供更灵活的路由规则。
6.5.1 生产者
package com.ken.producer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.util.RabbitMQMessageSender;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 主题模式消息生产者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/topic")
@Tag(name = "主题模式示例", description = "主题模式的消息发送接口")
public class TopicProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitMQMessageSender messageSender;
/**
* 发送消息到主题交换机
*
* @param message 消息内容
* @param type 消息类型(order/create, order/pay, user/login, user/register等)
* @return 消息ID
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@Operation(summary = "发送消息到主题交换机", description = "向主题交换机发送消息,根据消息类型路由到不同队列")
public String sendMessage(
@Parameter(description = "消息内容", required = true)
@RequestParam String message,
@Parameter(description = "消息类型", required = true, example = "order/create")
@RequestParam String type) {
String routingKey = "system." + type;
return messageSender.sendMessage(RabbitMQConfig.TOPIC_EXCHANGE, routingKey, message);
}
}6.5.2 消费者
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 主题模式消息消费者(处理订单相关消息)
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicOrderConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听订单相关消息队列,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.TOPIC_QUEUE_ORDER)
public void consumeOrderMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID和路由键
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String routingKey = message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【订单消息消费者】接收到消息,路由键:{},消息ID:{},内容:{}", routingKey, messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 处理订单相关消息逻辑
log.info("【订单消息消费者】消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【订单消息消费者】消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 主题模式消息消费者(处理用户相关消息)
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicUserConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听用户相关消息队列,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.TOPIC_QUEUE_USER)
public void consumeUserMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID和路由键
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String routingKey = message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【用户消息消费者】接收到消息,路由键:{},消息ID:{},内容:{}", routingKey, messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 处理用户相关消息逻辑
log.info("【用户消息消费者】消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【用户消息消费者】消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 主题模式消息消费者(处理所有系统消息)
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class TopicAllConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听所有系统消息队列,消费消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.TOPIC_QUEUE_ALL)
public void consumeAllMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID和路由键
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String routingKey = message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey();
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【全量系统消息消费者】接收到消息,路由键:{},消息ID:{},内容:{}", routingKey, messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 处理所有系统消息的通用逻辑,例如记录系统操作日志
log.info("【全量系统消息消费者】消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【全量系统消息消费者】消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}6.6 死信队列示例
死信队列(Dead Letter Queue)用于处理无法被正常消费的消息,例如过期消息、被拒绝的消息或队列满时的消息。
6.6.1 生产者
package com.ken.producer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.util.RabbitMQMessageSender;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 死信队列消息生产者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/deadletter")
@Tag(name = "死信队列示例", description = "死信队列的消息发送接口")
public class DeadLetterProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitMQMessageSender messageSender;
/**
* 发送消息到普通队列,该队列配置了死信队列
*
* @param message 消息内容
* @param count 发送消息数量
* @return 消息发送结果
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@Operation(summary = "发送消息到普通队列", description = "向配置了死信的普通队列发送消息,当消息成为死信时会被路由到死信队列")
public String sendMessage(
@Parameter(description = "消息内容", required = true)
@RequestParam String message,
@Parameter(description = "发送消息数量", required = true, example = "10")
@RequestParam Integer count) {
if (count <= 0) {
return "消息数量必须大于0";
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
String msg = message + " - " + (i + 1);
messageSender.sendMessage(
RabbitMQConfig.NORMAL_EXCHANGE,
RabbitMQConfig.NORMAL_ROUTING_KEY,
msg);
}
return "成功发送" + count + "条消息到普通队列";
}
}6.6.2 消费者
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 普通队列消息消费者(故意拒绝部分消息,使其成为死信)
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class NormalQueueConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听普通队列,消费消息,故意拒绝偶数编号的消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.NORMAL_QUEUE)
public void consumeMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【普通队列消费者】接收到消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 提取消息编号
int index = msgContent.lastIndexOf("-");
if (index > 0 && index < msgContent.length() - 1) {
String numStr = msgContent.substring(index + 1).trim();
int num = Integer.parseInt(numStr);
// 处理奇数编号的消息,拒绝偶数编号的消息
if (num % 2 == 1) {
// 处理消息逻辑
log.info("【普通队列消费者】消息处理成功,消息ID:{}", messageId);
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} else {
log.warn("【普通队列消费者】故意拒绝偶数消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
// 拒绝消息,不重新入队,使其成为死信
channel.basicReject(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
}
}
} else {
log.error("【普通队列消费者】消息格式不正确,拒绝消费,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
// 拒绝消息,不重新入队,使其成为死信
channel.basicReject(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【普通队列消费者】消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,不重新入队,使其成为死信
channel.basicReject(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
}
}
}
}
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* 死信队列消息消费者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DeadLetterConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听死信队列,消费死信消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.DEAD_LETTER_QUEUE)
public void consumeDeadLetterMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.error("【死信队列消费者】接收到死信消息,消息ID:{},内容:{}", messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 处理死信消息的逻辑,例如记录到错误日志、人工干预等
log.info("【死信队列消费者】死信消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【死信队列消费者】死信消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 死信消息再次处理失败,可以根据业务需求决定是否再次入队或做其他处理
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
}
}
}
}6.7 延迟队列示例
延迟队列用于处理需要延迟执行的任务,例如订单超时取消、定时提醒等场景。
要使用延迟队列,需要先安装 RabbitMQ 的延迟插件:rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange。
安装方法:
- 下载插件:https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-delayed-message-exchange/releases
- 将插件复制到 RabbitMQ 的插件目录
- 启用插件:rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_delayed_message_exchange
- 重启 RabbitMQ 服务
6.7.1 生产者
package com.ken.producer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.util.RabbitMQMessageSender;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Operation;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.Parameter;
import io.swagger.v3.oas.annotations.tags.Tag;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 延迟队列消息生产者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/delay")
@Tag(name = "延迟队列示例", description = "延迟队列的消息发送接口")
public class DelayProducer {
@Resource
private RabbitMQMessageSender messageSender;
/**
* 发送延迟消息到延迟交换机
*
* @param message 消息内容
* @param delayTime 延迟时间(毫秒)
* @return 消息ID
*/
@GetMapping("/send")
@Operation(summary = "发送延迟消息", description = "向延迟交换机发送消息,指定延迟时间后才会被消费")
public String sendDelayMessage(
@Parameter(description = "消息内容", required = true)
@RequestParam String message,
@Parameter(description = "延迟时间(毫秒)", required = true, example = "5000")
@RequestParam Long delayTime) {
if (delayTime <= 0) {
return "延迟时间必须大于0";
}
String fullMessage = message + "(发送时间:" + LocalDateTime.now() + ")";
return messageSender.sendDelayMessage(
RabbitMQConfig.DELAY_EXCHANGE,
RabbitMQConfig.DELAY_ROUTING_KEY,
fullMessage,
delayTime);
}
}6.7.2 消费者
package com.ken.consumer;
import com.ken.config.RabbitMQConfig;
import com.ken.service.MessageLogService;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* 延迟队列消息消费者
*
* @author ken
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class DelayQueueConsumer {
@Resource
private MessageLogService messageLogService;
/**
* 监听延迟队列,消费延迟消息
*
* @param message 消息对象
* @param channel 信道
* @throws IOException IO异常
*/
@RabbitListener(queues = RabbitMQConfig.DELAY_QUEUE)
public void consumeDelayMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException {
// 获取消息ID
String messageId = message.getMessageProperties().getHeader("spring_returned_message_correlation");
String msgContent = new String(message.getBody());
log.info("【延迟队列消费者】接收到延迟消息,接收时间:{},消息ID:{},内容:{}",
LocalDateTime.now(), messageId, msgContent);
try {
// 处理延迟消息的逻辑,例如订单超时取消、定时提醒等
log.info("【延迟队列消费者】延迟消息处理成功");
// 手动确认消息已消费
channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false);
// 更新消息消费状态
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 2);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("【延迟队列消费者】延迟消息处理异常,消息ID:{},异常:{}", messageId, e.getMessage(), e);
// 拒绝消息,并将消息重新入队
channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, true);
// 更新消息消费状态为失败
if (StringUtils.hasText(messageId)) {
messageLogService.updateConsumeStatus(messageId, 4);
messageLogService.incrementRetryCount(messageId);
}
}
}
}七、数据库脚本
为了存储消息日志,我们需要创建相应的数据库表。
-- 创建数据库
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS rabbitmq_demo CHARACTER SET utf8mb4 COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
-- 使用数据库
USE rabbitmq_demo;
-- 创建消息日志表
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t_message_log (
id VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL COMMENT '消息ID',
content TEXT COMMENT '消息内容',
exchange VARCHAR(255) COMMENT '交换机名称',
routing_key VARCHAR(255) COMMENT '路由键',
status TINYINT DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '消息状态:0-待发送,1-已发送,2-已消费,3-发送失败,4-消费失败',
retry_count INT DEFAULT 0 COMMENT '重试次数',
create_time DATETIME COMMENT '创建时间',
update_time DATETIME COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (id)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COMMENT='消息日志表';八、RabbitMQ 高级特性与最佳实践
8.1 消息确认机制
RabbitMQ 提供了完善的消息确认机制,确保消息的可靠传递:
-
生产者确认机制:确保消息成功发送到交换机
- 配置
publisher-confirm-type: correlated启用确认机制 - 通过
ConfirmCallback回调处理确认结果
- 配置
-
消息返回机制:当消息无法路由到队列时返回给生产者
- 配置
publisher-returns: true和mandatory: true启用返回机制 - 通过
ReturnsCallback回调处理返回的消息
- 配置
-
消费者确认机制:确保消息被成功消费
- 配置
acknowledge-mode: manual启用手动确认 - 消费成功调用
basicAck()确认 - 消费失败调用
basicReject()或basicNack()拒绝
- 配置
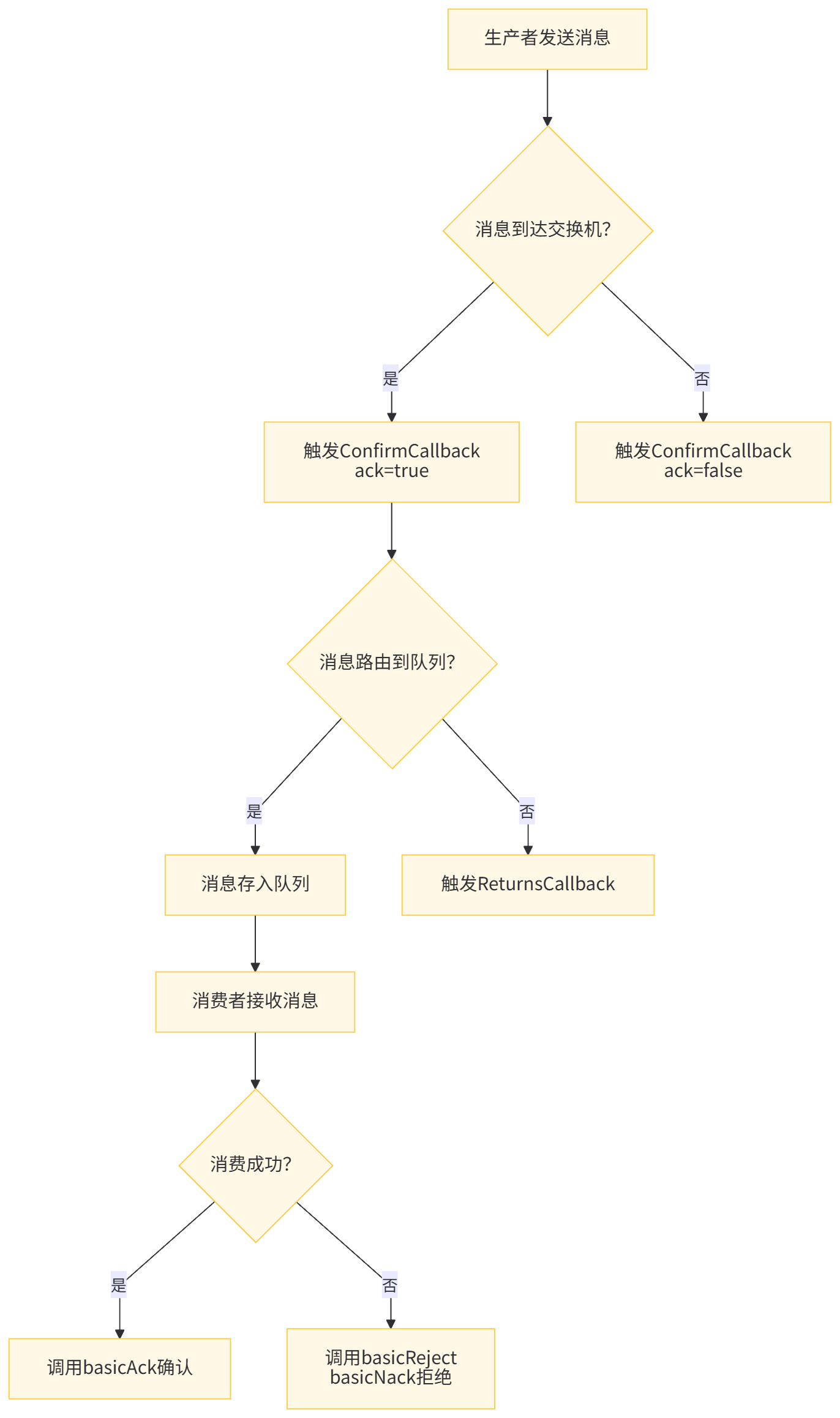
8.2 消息持久化
为了防止 RabbitMQ 服务重启导致消息丢失,需要配置消息持久化:
-
交换机持久化 :创建交换机时设置
durable: true -
队列持久化 :创建队列时设置
durable: true -
消息持久化 :发送消息时设置
deliveryMode: MessageDeliveryMode.PERSISTENT// 发送持久化消息的示例
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routingKey, data, message -> {
message.getMessageProperties().setDeliveryMode(MessageDeliveryMode.PERSISTENT);
return message;
}, correlationData);
8.3 消息幂等性处理
在分布式系统中,消息重复消费是常见问题,需要保证消息处理的幂等性:
-
基于消息 ID 的幂等处理:
- 为每条消息生成唯一 ID
- 消费前检查该 ID 是否已处理
- 已处理则直接返回,未处理则执行处理逻辑并记录 ID
-
基于业务唯一标识的幂等处理:
- 使用业务相关的唯一标识(如订单号)
- 结合业务逻辑确保重复处理不会产生副作用
// 幂等性处理示例
public void processMessage(String messageId, String orderId, String messageContent) {
// 1. 检查消息是否已处理
if (messageLogService.isMessageProcessed(messageId)) {
log.info("消息[{}]已处理,无需重复处理", messageId);
return;
}// 2. 检查业务是否已处理(以订单为例) if (orderService.isOrderProcessed(orderId)) { log.info("订单[{}]已处理,无需重复处理", orderId); // 标记消息为已处理 messageLogService.markAsProcessed(messageId); return; } // 3. 处理业务逻辑 orderService.processOrder(orderId, messageContent); // 4. 标记消息为已处理 messageLogService.markAsProcessed(messageId);}
8.4 消息重试机制
当消息处理失败时,需要有合理的重试机制:
-
本地重试:通过 Spring 的重试机制在消费者本地进行有限次数的重试
-
消息重入队:消费失败时将消息重新入队,等待再次消费
-
定时重试:结合延迟队列实现指数退避策略的定时重试
// 消息重试配置示例
@Bean
public SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory rabbitListenerContainerFactory(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory factory = new SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory();
factory.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
factory.setAcknowledgeMode(AcknowledgeMode.MANUAL);
// 重试配置
factory.setRetryTemplate(retryTemplate());
return factory;
}@Bean
public RetryTemplate retryTemplate() {
RetryTemplate retryTemplate = new RetryTemplate();// 重试策略:最多重试3次 SimpleRetryPolicy retryPolicy = new SimpleRetryPolicy(); retryPolicy.setMaxAttempts(3); retryTemplate.setRetryPolicy(retryPolicy); // 退避策略:指数退避,初始间隔1秒,乘数2,最大间隔10秒 ExponentialBackOffPolicy backOffPolicy = new ExponentialBackOffPolicy(); backOffPolicy.setInitialInterval(1000); backOffPolicy.setMultiplier(2); backOffPolicy.setMaxInterval(10000); retryTemplate.setBackOffPolicy(backOffPolicy); return retryTemplate;}
8.5 性能优化建议
- 合理设置消费者数量:根据服务器性能和业务需求设置适当的消费者数量
- 设置 prefetchCount:控制每次从队列中获取的消息数量,避免消费者过载
- 使用批量操作:对于大量消息,考虑使用批量发送和批量确认
- 避免消息过大:过大的消息会影响性能,可考虑拆分或存储到外部系统
- 合理设置交换机和队列:根据业务场景选择合适的交换机类型
- 监控和调优:通过 RabbitMQ 管理界面监控队列状态,及时发现和解决问题
九、常见问题及解决方案
-
消息丢失问题:
- 解决方案:启用消息持久化、生产者确认机制和消费者确认机制
-
消息重复消费问题:
- 解决方案:实现消息幂等性处理,使用唯一标识判断消息是否已处理
-
消息堆积问题:
- 解决方案:增加消费者数量、优化消费逻辑、设置合理的预取数量、考虑使用死信队列处理无法消费的消息
-
RabbitMQ 性能问题:
- 解决方案:合理配置硬件资源、优化消息大小、使用批量操作、避免同步阻塞操作
-
网络分区问题:
- 解决方案:配置合适的网络分区处理策略、使用集群部署提高可用性
-
消费者阻塞问题:
- 解决方案:设置合理的超时时间、避免在消费逻辑中执行耗时操作、使用异步处理
十、总结
本文详细介绍了 SpringBoot 集成 RabbitMQ 的全过程,从基础概念到实战示例,再到高级特性和最佳实践,涵盖了 RabbitMQ 在实际项目中的各种使用场景。