前言
在提升Android能力的多种方式中,阅读Android源码是一种相当重要的方式,并且只有在熟悉了源码之后,我们才能处理一些需求。
在Android源码中,我认为首先需要阅读的就是Android系统启动流程。实际上已经有很多的文章、书籍和视频都讲过这个了,但我还是想写写Android系统启动流程的文章:一方面是对过往知识做一个总结,加深自己的理解;另一方面是分享出来,如果可以帮助到一些人也是很好的。
注意:本文出现的源码基于Android - 15.0.0_r1。另外本文关注主要逻辑,省略部分代码。
一、 Android系统启动大致流程
本文是介绍init进程,那么我们先看下Android系统启动流程: 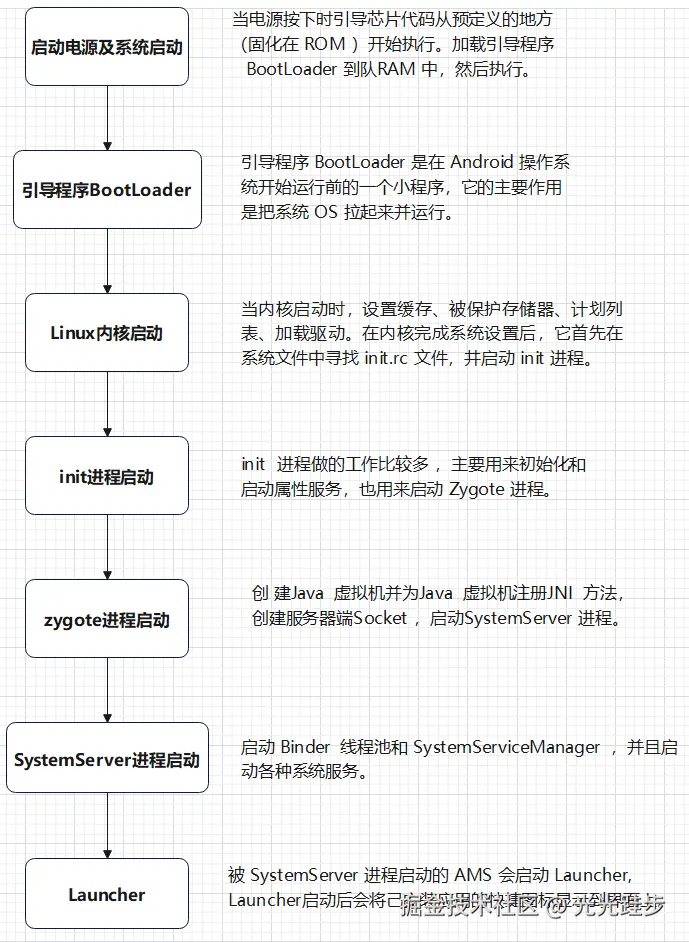 启动电源及系统启动 -> Bootloader -> Linux内核启动 -> init -> Zygote -> SystemServer -> Launcher
启动电源及系统启动 -> Bootloader -> Linux内核启动 -> init -> Zygote -> SystemServer -> Launcher
二、Init进程
init 进程是用户空间启动的第1个进程,它会依次执行 FirstStageMain -> SetupSelinux -> SecondStageMain 三个阶段。 我们知道,C++中的main方法,是函数的入口,Android中也不例外,它的入口函数是:/system/core/init/main.cpp
C++
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
...
if (argc > 1) {
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "selinux_setup")) {
return SetupSelinux(argv);
}
if (!strcmp(argv[1], "second_stage")) {
return SecondStageMain(argc, argv);
}
}
return FirstStageMain(argc, argv);
}在main函数刚进来时,会进到FirstStageMain中去。看看FirstStageMain做了什么。
2.1 FirstStageMain
FirstStageMain的代码的位置:/system/core/init/first_stage_init.cpp
源码较长,只看比较重要的部分
C++
int FirstStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
...
CHECKCALL(mount("tmpfs", "/dev", "tmpfs", MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755"));
...
CHECKCALL(mount("devpts", "/dev/pts", "devpts", 0, NULL));
#define MAKE_STR(x) __STRING(x)
CHECKCALL(mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, "hidepid=2,gid=" MAKE_STR(AID_READPROC)));
#undef MAKE_STR
...
CHECKCALL(mount("sysfs", "/sys", "sysfs", 0, NULL));
CHECKCALL(mount("selinuxfs", "/sys/fs/selinux", "selinuxfs", 0, NULL));
...
InitKernelLogging(argv);
...
const char* path = "/system/bin/init";
const char* args[] = {path, "selinux_setup", nullptr};
...
execv(path, const_cast<char**>(args));
...
return 1;
}FirstStageMain函数主要做了挂载文件系统,创建目录,初始化Kernel log。介绍下5个重要的文件系统:
- tmpfs:用于存放设备节点和动态生成的设备文件,支持运行时设备管理。
- devpts):提供伪终端(PTY)接口,让用户空间终端/shell 能与内核终端子系统交互。
- procfs:暴露进程和内核状态、配置信息给用户空间,可用于系统监控与参数调整。
- sysfs:用于暴露内核设备模型、驱动和子系统的信息与控制接口,支撑硬件管理。
- selinuxfs:提供 SELinux 安全策略与状态的接口,用于系统的强制访问控制机制。
InitKernelLogging(argv)代码如下:
/system/core/init/first_stage_init.cpp
C++
void InitKernelLogging(char** argv) {
SetFatalRebootTarget();
android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger, InitAborter);
}这里着重看看android::base::InitLogging(argv, &android::base::KernelLogger, InitAborter), 先看KernelLogger做了什么
/system/libbase/logging.cpp
C++
void KernelLogger(android::base::LogId, android::base::LogSeverity severity, const char* tag,
const char*, unsigned int, const char* full_message) {
SplitByLines(full_message, KernelLogLine, severity, tag);
}继续跟KernelLogLine
/system/libbase/logging.cpp
C++
#if defined(__linux__)
static void KernelLogLine(const char* msg, int length, android::base::LogSeverity severity,
...
static int klog_fd = OpenKmsg();
if (klog_fd == -1) return;
...
}实际上,KernelLogLine就是调用了OpenKmsg
/system/libbase/logging.cpp
C++
#if defined(__linux__)
static int OpenKmsg() {
#if defined(__ANDROID__)
// 尝试从环境变量获取预打开的文件描述符
const auto val = getenv("ANDROID_FILE__dev_kmsg");
if (val != nullptr) {
int fd;
// 解析环境变量值为文件描述符
if (android::base::ParseInt(val, &fd, 0)) {
// 验证文件描述符有效性
auto flags = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
if ((flags != -1) && ((flags & O_ACCMODE) == O_WRONLY))
return fd; // 返回可用的 fd
}
}
// init进程启动时,此时没有任何预先存在的文件描述符可继承,因此会打开/dev/kmsg
return TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(open("/dev/kmsg", O_WRONLY | O_CLOEXEC));
}再看看InitLogging代码
/system/libbase/logging.cpp
C++
void InitLogging(char* argv[], LogFunction&& logger, AbortFunction&& aborter) {
SetLogger(std::forward<LogFunction>(logger));
SetAborter(std::forward<AbortFunction>(aborter));
if (gInitialized) { // gInitialized是一个静态变量,防止重复调用
return;
}
gInitialized = true;
if (argv != nullptr) {
// 设置默认日志标签
SetDefaultTag(basename(argv[0]));
}
// 获取环境变量配置
const char* tags = getenv("ANDROID_LOG_TAGS");
if (tags == nullptr) {
return;
}
// 根据环境变量,设置日志级别
std::vector<std::string> specs = Split(tags, " ");
for (size_t i = 0; i < specs.size(); ++i) {
std::string spec(specs[i]);
if (spec.size() == 3 && StartsWith(spec, "*:")) {
switch (spec[2]) {
case 'v':
SetMinimumLogSeverity(VERBOSE);
continue;
case 'd':
SetMinimumLogSeverity(DEBUG);
continue;
case 'i':
SetMinimumLogSeverity(INFO);
continue;
case 'w':
SetMinimumLogSeverity(WARNING);
continue;
case 'e':
SetMinimumLogSeverity(ERROR);
continue;
case 'f':
SetMinimumLogSeverity(FATAL_WITHOUT_ABORT);
continue;
// liblog will even suppress FATAL if you say 's' for silent, but fatal should
// never be suppressed.
case 's':
SetMinimumLogSeverity(FATAL_WITHOUT_ABORT);
continue;
}
}
LOG(FATAL) << "unsupported '" << spec << "' in ANDROID_LOG_TAGS (" << tags
<< ")";
}
}小结一下FirstStageMain
- 创建目录和挂载文件系统
- 初始化Kernel日志 (打开/dev/kmsg,并根据环境变量ANDROID_LOG_TAGS,设置日志级别)
完成这些后,会通过execv回到Main.cpp,此时会执行SetupSelinux 阶段
2.2 SetupSelinux
它负责加载并启用 SELinux 安全策略
/system/core/init/selinux.cpp
C++
int SetupSelinux(char** argv) {
// 设置 stdio 到 /dev/null
SetStdioToDevNull(argv);
// 初始化 kernel 日志
InitKernelLogging(argv);
if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {
InstallRebootSignalHandlers();
}
boot_clock::time_point start_time = boot_clock::now();
SelinuxSetupKernelLogging();
// 加载SELinux策略
if (IsMicrodroid()) {
LoadSelinuxPolicyMicrodroid();
} else {
LoadSelinuxPolicyAndroid();
}
// 切换到 Selinux enforcement 模式
SelinuxSetEnforcement();
...
const char* path = "/system/bin/init";
const char* args[] = {path, "second_stage", nullptr};
// 重新启动 init 本身,进入SecondStageMain
execv(path, const_cast<char**>(args));
...
}这一阶段提供了整个用户空间服务启动的安全基础:在 SELinux 策略生效之后,后续解析 .rc、启动服务、fork 应用进程,才能在预期的安全域下执行。
2.3 SecondStageMain
之后便进入了我们着重关注的第二阶段初始化。
/system/core/init/init.cpp
C++
int SecondStageMain(int argc, char** argv) {
...
InitKernelLogging(argv);
...
// 初始化属性服务
PropertyInit();
// 创建Epoll对象
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
PLOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
epoll.SetFirstCallback(ReapAnyOutstandingChildren);
// 注册epoll
InstallSignalFdHandler(&epoll);
InstallInitNotifier(&epoll);
// 开启属性服务
StartPropertyService(&property_fd);
// 加载init.rc文件
LoadBootScripts(am, sm);
...
}2.3.1 初始化属性服务
我们看看PropertyInit具体是怎么初始化属性服务的,先看下PropertyInit代码 /system/core/init/property_service.cpp
C++
void PropertyInit() {
...
mkdir("/dev/__properties__", S_IRWXU | S_IXGRP | S_IXOTH);
CreateSerializedPropertyInfo();
// 初始化属性内存区域
if (__system_property_area_init()) {
LOG(FATAL) << "Failed to initialize property area";
}
...
}__system_property_area_init是定义在system_property_api.cpp中的一个方法
/bionic/libc/bionic/system_property_api.cpp
C++
int __system_property_area_init() {
bool fsetxattr_fail = false;
return system_properties.AreaInit(PROP_DIRNAME, &fsetxattr_fail) && !fsetxattr_fail ? 0 : -1;
}只是调用了system_properties.AreaInit,继续跟这个方法,看看做了什么 /bionic/libc/system_properties/system_properties.cpp
C++
bool SystemProperties::AreaInit(const char* filename, bool* fsetxattr_failed) {
return AreaInit(filename, fsetxattr_failed, false);
}
bool SystemProperties::AreaInit(const char* filename, bool* fsetxattr_failed,
bool load_default_path) {
...
if (!serial_contexts->Initialize(true, properties_filename_.c_str(), fsetxattr_failed,
load_default_path)) {
return false;
}
...
return true;
}继续跟serial_contexts->Initialize
/bionic/libc/system_properties/contexts_serialized.cpp
C++
bool ContextsSerialized::Initialize(bool writable, const char* dirname, bool* fsetxattr_failed,
bool load_default_path) {
dirname_ = dirname;
tree_filename_ = PropertiesFilename(dirname, "property_info");
serial_filename_ = PropertiesFilename(dirname, "properties_serial");
if (!InitializeProperties(load_default_path)) {
return false;
}
if (writable) {
...
if (open_failed || !MapSerialPropertyArea(true, fsetxattr_failed)) {
FreeAndUnmap();
return false;
}
} else {
if (!MapSerialPropertyArea(false, nullptr)) {
FreeAndUnmap();
return false;
}
}
return true;
}后续执行MapSerialPropertyArea方法
/bionic/libc/system_properties/contexts_serialized.cpp
C++
bool ContextsSerialized::MapSerialPropertyArea(bool access_rw, bool* fsetxattr_failed) {
if (access_rw) {
serial_prop_area_ = prop_area::map_prop_area_rw(
serial_filename_.c_str(), "u:object_r:properties_serial:s0", fsetxattr_failed);
} else {
serial_prop_area_ = prop_area::map_prop_area(serial_filename_.c_str());
}
return serial_prop_area_;
}若是可写,执行map_prop_area_rw
不可写,执行map_prop_area
先看看执行map_prop_area_rw代码
/bionic/libc/system_properties/prop_area.cpp
C++
prop_area* prop_area::map_prop_area_rw(const char* filename, const char* context,
bool* fsetxattr_failed) {
...
void* const memory_area = mmap(nullptr, pa_size_, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
...
}这个方法就是调用了mmap做内存映射,再看看map_prop_area代码 /bionic/libc/system_properties/prop_area.cpp
C++
prop_area* prop_area::map_prop_area(const char* filename) {
int fd = open(filename, O_CLOEXEC | O_NOFOLLOW | O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1) return nullptr;
prop_area* map_result = map_fd_ro(fd);
close(fd);
return map_result;
}
prop_area* prop_area::map_fd_ro(const int fd) {
...
void* const map_result = mmap(nullptr, pa_size_, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
...
}同样最终也是调用了mmap方法。
因此PropertyInit() 初始化属性服务,其实就是通过 mmap 系统调用 来完成属性内存区域的初始化与映射的, 建立了 /dev/properties 共享内存区,供所有进程读写系统属性,如 getprop/setprop 命令操作的数据来源。
2.3.2 开启属性服务
/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
C++
void StartPropertyService(int* epoll_socket) {
// 初始化属性版本
InitPropertySet("ro.property_service.version", "2");
// 创建 socketpair,用来让 init 与其属性服务线程之间做通信
int sockets[2];
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET | SOCK_CLOEXEC, 0, sockets) != 0) {
PLOG(FATAL) << "Failed to socketpair() between property_service and init";
}
*epoll_socket = from_init_socket = sockets[0];
init_socket = sockets[1];
// 开启消息接收通道
StartSendingMessages();
// 启动系统属性服务线程和普通属性服务线程
StartThread(PROP_SERVICE_FOR_SYSTEM_NAME, 0660, AID_SYSTEM, property_service_for_system_thread,
true);
StartThread(PROP_SERVICE_NAME, 0666, 0, property_service_thread, false);
...
}我们先看看StartSendingMessages方法
/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
C++
void StartSendingMessages() {
auto lock = std::lock_guard{accept_messages_lock};
accept_messages = true;
}StartSendingMessages方法很简单,accept_messages是静态变量,这里使用了互斥锁来保证它的写操作,并设置为true,后续属性变更时,会判断accept_messages为true才会执行。
再看看StartThread方法
/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
C++
void StartThread(const char* name, int mode, int gid, std::thread& t, bool listen_init) {
int fd = -1;
// 创建一个 socket
if (auto result = CreateSocket(name, SOCK_STREAM | SOCK_CLOEXEC | SOCK_NONBLOCK,
/*passcred=*/false, /*should_listen=*/false, mode, /*uid=*/0,
/*gid=*/gid, /*socketcon=*/{});
result.ok()) {
fd = *result;
} else {
LOG(FATAL) << "start_property_service socket creation failed: " << result.error();
}
// 对 fd 进行监听
listen(fd, 8);
// 创建一个新线程
auto new_thread = std::thread(PropertyServiceThread, fd, listen_init);
t.swap(new_thread);
}StartPropertyService会创建启动系统属性服务线程和普通属性服务线程,系统属性使用0660,普通属性使用0666。 这里说下Linux中各个数字代表什么权限:4 、2 和 1表示读、写、执行权限 0abc, a表示拥有者,b表示所属组,c表示其他用户。因此系统属性使用0660,表示拥有者,所属组有读写权限;普通属性使用0666表示所有用户均有读写权限。
这里使用2个线程,因为系统属性可能有敏感属性,所以使用了更严格的权限。后续创建了一个新的线程,看看PropertyServiceThread里面做了什么
/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
C++
static void PropertyServiceThread(int fd, bool listen_init) {
Epoll epoll;
if (auto result = epoll.Open(); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
// 监听fd,当有更新时, 调用handle_property_set_fd来进行处理。
if (auto result = epoll.RegisterHandler(fd, std::bind(handle_property_set_fd, fd));
!result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
// 监听init_socket(init_socket在StartPropertyService已经初始化了), 当更新时, 调用HandleInitSocket来进行处理。
if (listen_init) {
if (auto result = epoll.RegisterHandler(init_socket, HandleInitSocket); !result.ok()) {
LOG(FATAL) << result.error();
}
}
while (true) {
// 进入事件等待循环
auto epoll_result = epoll.Wait(std::nullopt);
if (!epoll_result.ok()) {
LOG(ERROR) << epoll_result.error();
}
}
}在PropertyServiceThread中监听了fd和init_socket,继续看看handle_property_set_fd里的代码
/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
C++
static void handle_property_set_fd(int fd) {
...
uint32_t cmd = 0;
// // 从 socket 中获取cmd
if (!socket.RecvUint32(&cmd, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: error while reading command from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_CMD);
return;
}
switch (cmd) {
// 设置属性
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP: {
char prop_name[PROP_NAME_MAX];
char prop_value[PROP_VALUE_MAX];
// 从 socket 中获取name, value
if (!socket.RecvChars(prop_name, PROP_NAME_MAX, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvChars(prop_value, PROP_VALUE_MAX, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP): error while reading name/value from the socket";
return;
}
...
// 在HandlePropertySetNoSocket中处理
auto result = HandlePropertySetNoSocket(prop_name, prop_value, source_context, cr, &error);
...
break;
}
// 设置属性
case PROP_MSG_SETPROP2: {
std::string name;
std::string value;
// 从 socket 中获取name, value
if (!socket.RecvString(&name, &timeout_ms) ||
!socket.RecvString(&value, &timeout_ms)) {
PLOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop(PROP_MSG_SETPROP2): error while reading name/value from the socket";
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_READ_DATA);
return;
}
// 在HandlePropertySet中处理
auto result = HandlePropertySet(name, value, source_context, cr, &socket, &error);
...
break;
}
default:
LOG(ERROR) << "sys_prop: invalid command " << cmd;
socket.SendUint32(PROP_ERROR_INVALID_CMD);
break;
}
}handle_property_set_fd 根据 socket 中获取到的cmd, 调用HandlePropertySetNoSocket 或HandlePropertySet去设置属性。而 HandlePropertySetNoSocket 也会调用到 HandlePropertySet,因此我们直接看HandlePropertySet代码
/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
C++
std::optional<uint32_t> HandlePropertySet(const std::string& name, const std::string& value,
const std::string& source_context, const ucred& cr,
SocketConnection* socket, std::string* error) {
if (auto ret = CheckPermissions(name, value, source_context, cr, error); ret != PROP_SUCCESS) {
return {ret};
}
// 控制属性
if (StartsWith(name, "ctl.")) {
return {SendControlMessage(name.c_str() + 4, value, cr.pid, socket, error)};
}
// 设备重新启动属性
if (name == "sys.powerctl") {
std::string cmdline_path = StringPrintf("proc/%d/cmdline", cr.pid);
std::string process_cmdline;
std::string process_log_string;
if (ReadFileToString(cmdline_path, &process_cmdline)) {
process_log_string = StringPrintf(" (%s)", process_cmdline.c_str());
}
LOG(INFO) << "Received sys.powerctl='" << value << "' from pid: " << cr.pid
<< process_log_string;
if (value == "reboot,userspace" && !is_userspace_reboot_supported().value_or(false)) {
*error = "Userspace reboot is not supported by this device";
return {PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE};
}
}
if (name == kRestoreconProperty && cr.pid != 1 && !value.empty()) {
static AsyncRestorecon async_restorecon;
async_restorecon.TriggerRestorecon(value);
return {PROP_SUCCESS};
}
// 普通属性
return PropertySet(name, value, socket, error);
}HandlePropertySet中,设置普通属性会调用PropertySet,继续看看PropertySet代码
/system/core/init/property_service.cpp
C++
static std::optional<uint32_t> PropertySet(const std::string& name, const std::string& value,
SocketConnection* socket, std::string* error) {
size_t valuelen = value.size();
if (!IsLegalPropertyName(name)) {
*error = "Illegal property name";
return {PROP_ERROR_INVALID_NAME};
}
if (auto result = IsLegalPropertyValue(name, value); !result.ok()) {
*error = result.error().message();
return {PROP_ERROR_INVALID_VALUE};
}
if (name == "sys.powerctl") {
// No action here - NotifyPropertyChange will trigger the appropriate action, and since this
// can come to the second thread, we mustn't call out to the __system_property_* functions
// which support multiple readers but only one mutator.
} else {
// __system_property_find
prop_info* pi = (prop_info*)__system_property_find(name.c_str());
if (pi != nullptr) {
// ro.* properties are actually "write-once".
if (StartsWith(name, "ro.")) {
*error = "Read-only property was already set";
return {PROP_ERROR_READ_ONLY_PROPERTY};
}
__system_property_update(pi, value.c_str(), valuelen);
} else {
int rc = __system_property_add(name.c_str(), name.size(), value.c_str(), valuelen);
if (rc < 0) {
*error = "__system_property_add failed";
return {PROP_ERROR_SET_FAILED};
}
}
// Don't write properties to disk until after we have read all default
// properties to prevent them from being overwritten by default values.
bool need_persist = StartsWith(name, "persist.") || StartsWith(name, "next_boot.");
if (socket && persistent_properties_loaded && need_persist) {
if (persist_write_thread) {
persist_write_thread->Write(name, value, std::move(*socket));
return {};
}
WritePersistentProperty(name, value);
}
}
NotifyPropertyChange(name, value);
return {PROP_SUCCESS};
}/system/core/init/property_service.cpp\]([xrefandroid.com/android-](https://link.juejin.cn?target=https%3A%2F%2Fxrefandroid.com%2Fandroid- "https://xrefandroid.com/android-") PropertySet方法中,先调用__system_property_find方法,如果已经当前属性存在,则更新它,不存在,则添加。先看看__system_property_find方法。
[/bionic/libc/system_properties/system_properties.cpp](https://link.juejin.cn?target=https%3A%2F%2Fxrefandroid.com%2Fandroid-15.0.0_r1%2Fxref%2Fbionic%2Flibc%2Fsystem_properties%2Fsystem_properties.cpp%23162 "https://xrefandroid.com/android-15.0.0_r1/xref/bionic/libc/system_properties/system_properties.cpp#162")
```C++
const prop_info* SystemProperties::Find(const char* name) {
if (!initialized_) {
return nullptr;
}
prop_area* pa = contexts_->GetPropAreaForName(name);
if (!pa) {
async_safe_format_log(ANDROID_LOG_WARN, "libc", "Access denied finding property \"%s\"", name);
return nullptr;
}
return pa->find(name);
}
```
SystemProperties方法先调用了contexts_-\>GetPropAreaForName, 然后再调用了pa-\>find。contexts_是在初始化属性流程中赋值的(auto serial_contexts = new (contexts_data_) ContextsSerialized();)。通过调用ContextsSerialized返回了prop_area对象,这里就不跟进去看怎么返回prop_area对象了,我们直接看prop_area里面的find方法
[/bionic/libc/system_properties/prop_area.cpp](https://link.juejin.cn?target=https%3A%2F%2Fxrefandroid.com%2Fandroid-15.0.0_r1%2Fxref%2Fbionic%2Flibc%2Fsystem_properties%2Fprop_area.cpp%23229 "https://xrefandroid.com/android-15.0.0_r1/xref/bionic/libc/system_properties/prop_area.cpp#229")
```C++
const prop_info* prop_area::find(const char* name) {
return find_property(root_node(), name, strlen(name), nullptr, 0, false);
}
```
find方法直接调用了find_property方法,那么看看find_property的实现
[/bionic/libc/system_properties/prop_area.cpp](https://link.juejin.cn?target=https%3A%2F%2Fxrefandroid.com%2Fandroid-15.0.0_r1%2Fxref%2Fbionic%2Flibc%2Fsystem_properties%2Fprop_area.cpp%23278 "https://xrefandroid.com/android-15.0.0_r1/xref/bionic/libc/system_properties/prop_area.cpp#278")
```C++
const prop_info* prop_area::find_property(prop_trie_node* const trie, const char* name,
uint32_t namelen, const char* value, uint32_t valuelen,
bool alloc_if_needed) {
if (!trie) return nullptr;
const char* remaining_name = name;
prop_trie_node* current = trie;
while (true) {
const char* sep = strchr(remaining_name, '.');
const bool want_subtree = (sep != nullptr);
const uint32_t substr_size = (want_subtree) ? sep - remaining_name : strlen(remaining_name);
if (!substr_size) {
return nullptr;
}
prop_trie_node* root = nullptr;
uint_least32_t children_offset = atomic_load_explicit(¤t->children, memory_order_relaxed);
if (children_offset != 0) {
root = to_prop_trie_node(¤t->children);
} else if (alloc_if_needed) {
uint_least32_t new_offset;
root = new_prop_trie_node(remaining_name, substr_size, &new_offset);
if (root) {
atomic_store_explicit(¤t->children, new_offset, memory_order_release);
}
}
if (!root) {
return nullptr;
}
current = find_prop_trie_node(root, remaining_name, substr_size, alloc_if_needed);
if (!current) {
return nullptr;
}
if (!want_subtree) break;
remaining_name = sep + 1;
}
uint_least32_t prop_offset = atomic_load_explicit(¤t->prop, memory_order_relaxed);
if (prop_offset != 0) {
return to_prop_info(¤t->prop);
} else if (alloc_if_needed) {
uint_least32_t new_offset;
prop_info* new_info = new_prop_info(name, namelen, value, valuelen, &new_offset);
if (new_info) {
atomic_store_explicit(¤t->prop, new_offset, memory_order_release);
}
return new_info;
} else {
return nullptr;
}
}
```
在find_property方法里面,我们就可以看到属性是通过树来存储的。__system_property_find是从树里找节点,而__system_property_add最终也会调用到find_property方法,它是往这个树里添加节点。
#### 2.3.3 加载init.rc文件
加载init.rc文件是在LoadBootScripts方法中,看看它做了什么
[/system/core/init/init.cpp](https://link.juejin.cn?target=http%3A%2F%2Fxrefandroid.com%2Fandroid-15.0.0_r1%2Fxref%2Fsystem%2Fcore%2Finit%2Finit.cpp%23337 "http://xrefandroid.com/android-15.0.0_r1/xref/system/core/init/init.cpp#337")
```C++
static void LoadBootScripts(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
// 创建解析器
Parser parser = CreateParser(action_manager, service_list);
std::string bootscript = GetProperty("ro.boot.init_rc", "");
if (bootscript.empty()) {
parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init/hw/init.rc");
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/system/etc/init");
}
// late_import is available only in Q and earlier release. As we don't
// have system_ext in those versions, skip late_import for system_ext.
parser.ParseConfig("/system_ext/etc/init");
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/vendor/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/vendor/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/odm/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/odm/etc/init");
}
if (!parser.ParseConfig("/product/etc/init")) {
late_import_paths.emplace_back("/product/etc/init");
}
} else {
parser.ParseConfig(bootscript);
}
}
```
首先看看 CreateParser 中的代码
[/system/core/init/init.cpp](https://link.juejin.cn?target=https%3A%2F%2Fxrefandroid.com%2Fandroid-15.0.0_r1%2Fxref%2Fsystem%2Fcore%2Finit%2Finit.cpp%23270 "https://xrefandroid.com/android-15.0.0_r1/xref/system/core/init/init.cpp#270")
```C++
Parser CreateParser(ActionManager& action_manager, ServiceList& service_list) {
Parser parser;
parser.AddSectionParser("service", std::make_unique