这个条款揭示了C++面向对象设计的核心理念:定义新class就是定义新type。优秀的class设计应该让用户定义类型与内置类型无缝协作,这要求我们在设计时考虑类型系统的完整性、一致性和直观性。
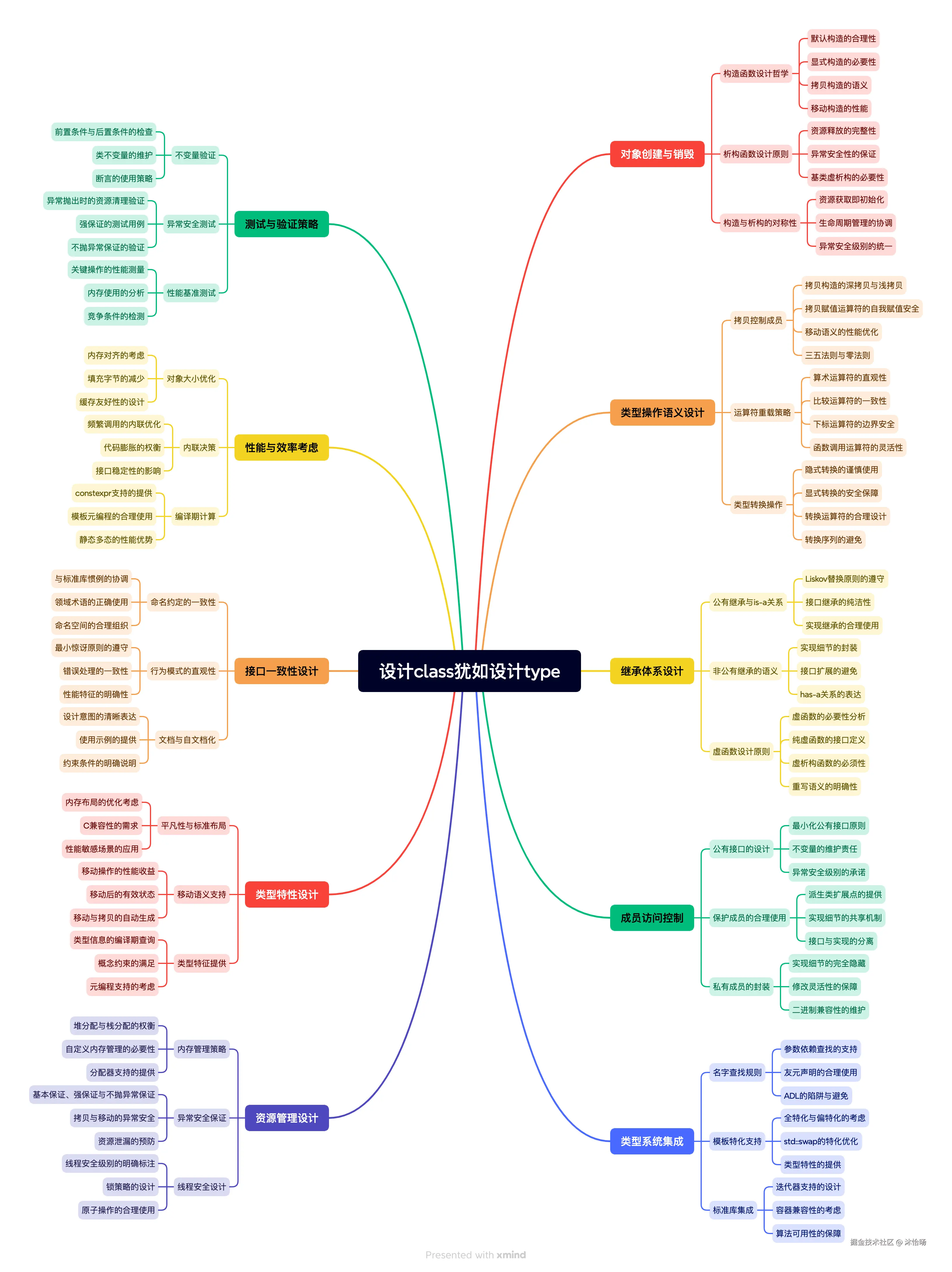
思维导图:class设计的完整体系
关键洞见与行动指南
必须遵守的核心原则:
- 类型完整性:用户定义类型应该提供完整的行为语义,与内置类型无缝协作
- 资源安全:遵循RAII原则,确保资源的正确获取和释放
- 接口一致性:提供直观、一致的接口,符合用户的心理预期
- 异常安全:明确标注并保证不同级别的异常安全性
现代C++开发建议:
- 三五法则应用:根据需要定义拷贝控制成员,或使用=default/=delete
- 移动语义支持:为资源管理类提供移动操作以获得性能优势
- noexcept正确使用:对不抛异常的操作正确标记noexcept
- constexpr支持:为可在编译期计算的操作提供constexpr
设计原则总结:
- 最小完整原则:提供最小但完整的接口集合
- 语义明确原则:每个操作都有明确、一致的语义
- 资源自治原则:类型负责管理自己的资源
- 扩展开放原则:设计允许合理的扩展而不破坏现有代码
需要警惕的陷阱:
- 隐式转换陷阱:单参数构造函数和转换运算符的误用
- 切片问题:值语义下的对象切片
- 异常安全漏洞:资源泄漏和不一致状态
- 线程安全混淆:错误的线程安全假设
最终建议: 将每个class设计视为语言扩展的机会。培养"语言设计者思维"------在设计每个class时都思考:"这个类型应该怎样融入C++类型系统?它的行为应该像内置类型吗?用户会怎样使用它?" 这种思维方式是构建优秀C++代码库的关键。
记住:在C++中,设计class就是设计type。优秀的用户定义类型应该让使用者忘记它是用户定义的。 条款19教会我们的不仅是一组技术规则,更是面向对象设计哲学在C++中的具体体现。
深入解析:class设计的核心挑战
1. 问题根源:类型语义的完整性
典型的不完整类型设计:
cpp
// 糟糕的字符串类型设计 - 语义不完整
class BadString {
public:
BadString(const char* str) {
if (str) {
data_ = new char[strlen(str) + 1];
strcpy(data_, str);
}
}
~BadString() {
delete[] data_;
}
// 缺少拷贝构造函数!
// 缺少拷贝赋值运算符!
// 缺少移动操作!
const char* c_str() const { return data_; }
private:
char* data_ = nullptr;
};
void demonstrate_incomplete_type() {
BadString s1("hello");
// 灾难!默认拷贝是浅拷贝
// BadString s2 = s1; // 双重删除!
// 同样的问题!
// BadString s3("world");
// s3 = s1; // 内存泄漏 + 双重删除!
// 无法高效返回!
// auto createString() -> BadString {
// BadString local("local");
// return local; // 昂贵的拷贝!
// }
}资源管理的不完整设计:
cpp
// 资源管理不完整的文件类
class BadFile {
public:
BadFile(const std::string& filename)
: handle_(fopen(filename.c_str(), "r")) {
if (!handle_) {
throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件");
}
}
~BadFile() {
if (handle_) {
fclose(handle_);
}
}
// 读取文件内容
std::string read(size_t size) {
std::string result(size, '\0');
fread(&result[0], 1, size, handle_);
return result;
}
private:
FILE* handle_;
// 禁止拷贝,但没有提供移动语义!
BadFile(const BadFile&) = delete;
BadFile& operator=(const BadFile&) = delete;
};
void demonstrate_bad_resource_management() {
BadFile file1("data.txt");
auto content = file1.read(100);
// 无法在容器中使用!
// std::vector<BadFile> files;
// files.push_back(BadFile("test.txt")); // 编译错误!
// 无法高效返回!
// auto openConfig() -> BadFile {
// BadFile local("config.txt");
// return local; // 编译错误!没有移动构造函数
// }
}解决方案:完整的类型设计
1. 三五法则的正确应用
完整的字符串类型设计:
cpp
// 优秀的字符串类型 - 遵循三五法则
class GoodString {
public:
// 默认构造函数
GoodString() = default;
// 构造函数
explicit GoodString(const char* str) {
if (str) {
size_ = std::strlen(str);
data_ = new char[size_ + 1];
std::strcpy(data_, str);
}
}
GoodString(const std::string& str)
: GoodString(str.c_str()) {}
// 1. 析构函数
~GoodString() {
delete[] data_;
}
// 2. 拷贝构造函数
GoodString(const GoodString& other)
: size_(other.size_) {
if (other.data_) {
data_ = new char[size_ + 1];
std::strcpy(data_, other.data_);
}
}
// 3. 拷贝赋值运算符
GoodString& operator=(const GoodString& other) {
if (this != &other) { // 自我赋值检查
GoodString temp(other); // 拷贝构造
swap(temp); // 交换 - 强异常安全保证
}
return *this;
}
// 4. 移动构造函数
GoodString(GoodString&& other) noexcept
: data_(other.data_), size_(other.size_) {
other.data_ = nullptr;
other.size_ = 0;
}
// 5. 移动赋值运算符
GoodString& operator=(GoodString&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
delete[] data_; // 释放当前资源
data_ = other.data_;
size_ = other.size_;
other.data_ = nullptr;
other.size_ = 0;
}
return *this;
}
// 交换操作
void swap(GoodString& other) noexcept {
std::swap(data_, other.data_);
std::swap(size_, other.size_);
}
// 访问接口
const char* c_str() const noexcept {
return data_ ? data_ : "";
}
size_t size() const noexcept { return size_; }
bool empty() const noexcept { return size_ == 0; }
// 运算符重载
friend bool operator==(const GoodString& lhs, const GoodString& rhs) {
if (lhs.size_ != rhs.size_) return false;
return std::strcmp(lhs.c_str(), rhs.c_str()) == 0;
}
friend bool operator!=(const GoodString& lhs, const GoodString& rhs) {
return !(lhs == rhs);
}
// 流输出支持
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const GoodString& str) {
return os << str.c_str();
}
private:
char* data_ = nullptr;
size_t size_ = 0;
};
void demonstrate_good_string() {
// 各种构造都正常工作
GoodString s1;
GoodString s2("hello");
GoodString s3 = s2; // 拷贝构造
GoodString s4 = std::move(s2); // 移动构造
// 赋值操作
s1 = s3; // 拷贝赋值
s3 = GoodString("world"); // 移动赋值
// 在容器中工作良好
std::vector<GoodString> strings;
strings.emplace_back("item1");
strings.push_back(GoodString("item2"));
// 可以高效返回
auto createString = []() -> GoodString {
GoodString local("created");
return local; // 移动构造或NRVO
};
auto s5 = createString(); // 高效!
std::cout << "s1: " << s1 << ", s3: " << s3 << ", s5: " << s5 << std::endl;
}2. 零法则的现代应用
使用标准库组件,遵循零法则:
cpp
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
// 遵循零法则的类 - 让编译器生成特殊成员函数
class ZeroRuleClass {
public:
// 不需要显式定义析构函数、拷贝/移动操作
// 编译器生成的版本完全正确
ZeroRuleClass(std::string name, std::vector<int> data)
: name_(std::move(name))
, data_(std::move(data))
, cache_(std::make_shared<Cache>())
{}
// 业务接口
void process() {
cachedValue_ = std::accumulate(data_.begin(), data_.end(), 0);
cache_->update(cachedValue_);
}
int getCachedValue() const { return cachedValue_; }
const std::string& getName() const { return name_; }
private:
struct Cache {
void update(int value) {
// 缓存更新逻辑
lastValue = value;
}
int lastValue = 0;
};
std::string name_;
std::vector<int> data_;
std::shared_ptr<Cache> cache_; // 共享所有权,浅拷贝正确
int cachedValue_ = 0;
};
void demonstrate_zero_rule() {
ZeroRuleClass obj1("test", {1, 2, 3, 4, 5});
obj1.process();
// 编译器生成的拷贝操作完全正确
ZeroRuleClass obj2 = obj1;
// 编译器生成的移动操作高效
ZeroRuleClass obj3 = std::move(obj1);
// 在容器中工作良好
std::vector<ZeroRuleClass> objects;
objects.push_back(ZeroRuleClass("item", {1, 2, 3}));
objects.emplace_back("emplace", std::vector<int>{4, 5, 6});
std::cout << "obj2: " << obj2.getName()
<< ", value: " << obj2.getCachedValue() << std::endl;
std::cout << "obj3: " << obj3.getName()
<< ", value: " << obj3.getCachedValue() << std::endl;
}继承体系设计
1. 公有继承与is-a关系
正确的继承层次设计:
cpp
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
// 形状基类 - 接口定义
class Shape {
public:
virtual ~Shape() = default; // 基类必须有虚析构函数!
// 纯虚函数 - 接口契约
virtual double area() const = 0;
virtual double perimeter() const = 0;
virtual std::string name() const = 0;
// 非虚函数 - 不变行为
void printInfo() const {
std::cout << name() << ": area=" << area()
<< ", perimeter=" << perimeter() << std::endl;
}
// 虚函数 - 可重写的默认行为
virtual void scale(double factor) = 0;
protected:
// 保护成员 - 派生类实现辅助函数
void validateFactor(double factor) const {
if (factor <= 0.0) {
throw std::invalid_argument("缩放因子必须为正数");
}
}
};
// 矩形 - 具体实现
class Rectangle : public Shape {
public:
Rectangle(double width, double height)
: width_(width), height_(height) {
if (width <= 0 || height <= 0) {
throw std::invalid_argument("宽度和高度必须为正数");
}
}
// 实现纯虚函数
double area() const override {
return width_ * height_;
}
double perimeter() const override {
return 2 * (width_ + height_);
}
std::string name() const override {
return "Rectangle";
}
void scale(double factor) override {
validateFactor(factor);
width_ *= factor;
height_ *= factor;
}
// 矩形特有操作
double getWidth() const { return width_; }
double getHeight() const { return height_; }
private:
double width_;
double height_;
};
// 圆形 - 具体实现
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
explicit Circle(double radius) : radius_(radius) {
if (radius <= 0) {
throw std::invalid_argument("半径必须为正数");
}
}
// 实现纯虚函数
double area() const override {
return 3.141592653589793 * radius_ * radius_;
}
double perimeter() const override {
return 2 * 3.141592653589793 * radius_;
}
std::string name() const override {
return "Circle";
}
void scale(double factor) override {
validateFactor(factor);
radius_ *= factor;
}
// 圆形特有操作
double getRadius() const { return radius_; }
private:
double radius_;
};
void demonstrate_good_inheritance() {
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Shape>> shapes;
shapes.push_back(std::make_unique<Rectangle>(10.0, 5.0));
shapes.push_back(std::make_unique<Circle>(3.0));
// 多态行为 - 符合Liskov替换原则
for (const auto& shape : shapes) {
shape->printInfo(); // 正确调用各个派生类的实现
// 可以安全地缩放
shape->scale(2.0);
shape->printInfo();
}
// 类型安全的向下转型
if (auto rect = dynamic_cast<Rectangle*>(shapes[0].get())) {
std::cout << "矩形宽度: " << rect->getWidth() << std::endl;
}
}2. 非公有继承的正确使用
使用组合而非私有继承:
cpp
// 使用组合而不是私有继承的例子
class Timer {
public:
void start() { /* 启动计时器 */ }
void stop() { /* 停止计时器 */ }
double elapsed() const { /* 返回经过时间 */ return 0.0; }
};
// 糟糕的设计 - 私有继承误用
class BadTask : private Timer {
public:
void execute() {
start();
// 执行任务...
stop();
std::cout << "耗时: " << elapsed() << "秒" << std::endl;
}
// 问题:Timer的接口暴露给了BadTask的用户吗?
};
// 优秀的设计 - 使用组合
class GoodTask {
public:
void execute() {
timer_.start();
// 执行任务...
timer_.stop();
std::cout << "耗时: " << timer_.elapsed() << "秒" << std::endl;
}
// 明确的接口,没有意外的Timer方法暴露
private:
Timer timer_; // 组合,不是继承
};
// 私有继承的正当使用场景
class Base {
protected:
void protectedMethod() { /* 受保护的方法 */ }
int protectedData;
};
// 正当的私有继承:需要重写虚函数或访问受保护成员
class Derived : private Base {
public:
void useBaseFunctionality() {
protectedMethod(); // 可以访问基类受保护成员
protectedData = 42;
}
// 不暴露Base的接口给Derived的用户
};
void demonstrate_composition_over_inheritance() {
GoodTask task;
task.execute();
// 清晰的接口,没有意外的Timer方法
// task.start(); // 编译错误!这正是我们想要的
BadTask badTask;
badTask.execute();
// badTask.start(); // 编译错误,但设计意图不如组合清晰
}类型转换设计
1. 显式转换的安全设计
安全的类型转换接口:
cpp
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <stdexcept>
// 安全的数值类型
class SafeNumber {
public:
// 显式构造函数 - 避免隐式转换
explicit SafeNumber(int value) : value_(value) {}
// 从字符串构造 - 显式,带验证
static std::optional<SafeNumber> fromString(const std::string& str) {
try {
std::size_t pos;
int value = std::stoi(str, &pos);
// 验证整个字符串都被解析
if (pos != str.length()) {
return std::nullopt;
}
return SafeNumber(value);
} catch (const std::exception&) {
return std::nullopt;
}
}
// 转换到其他类型 - 显式命名函数
int toInt() const noexcept { return value_; }
std::string toString() const { return std::to_string(value_); }
explicit operator int() const { return value_; } // 显式转换运算符
// 算术运算符
SafeNumber operator+(const SafeNumber& other) const {
return SafeNumber(value_ + other.value_);
}
SafeNumber operator-(const SafeNumber& other) const {
return SafeNumber(value_ - other.value_);
}
// 比较运算符
bool operator==(const SafeNumber& other) const = default;
private:
int value_;
};
// 使用显式转换的日期类
class Date {
public:
Date(int year, int month, int day)
: year_(year), month_(month), day_(day) {
validate();
}
// 显式转换函数 - 清晰的语义
std::string toIsoString() const {
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << year_ << "-"
<< (month_ < 10 ? "0" : "") << month_ << "-"
<< (day_ < 10 ? "0" : "") << day_;
return oss.str();
}
// 明确的转换,而不是隐式转换
explicit operator std::string() const {
return toIsoString();
}
// 不允许到int的隐式转换 - 语义不明确!
// operator int() const = delete; // 或者不提供
private:
void validate() const {
if (month_ < 1 || month_ > 12) {
throw std::invalid_argument("月份必须在1-12之间");
}
if (day_ < 1 || day_ > 31) {
throw std::invalid_argument("日期必须在1-31之间");
}
// 更复杂的验证...
}
int year_, month_, day_;
};
void demonstrate_safe_conversions() {
// 安全的数值创建
auto num1 = SafeNumber(42);
auto num2 = SafeNumber::fromString("100");
if (num2) {
auto result = num1 + *num2;
std::cout << "结果: " << result.toInt() << std::endl;
}
// 失败的转换安全处理
auto invalid = SafeNumber::fromString("abc");
if (!invalid) {
std::cout << "无效的数字字符串" << std::endl;
}
// 明确的日期转换
Date today(2023, 10, 15);
std::string isoDate = today.toIsoString(); // 明确调用
std::string explicitStr = static_cast<std::string>(today); // 显式转换
// 以下代码不会编译 - 这正是我们想要的!
// std::string implicitStr = today; // 编译错误!没有隐式转换
// int invalidInt = today; // 编译错误!
std::cout << "ISO日期: " << isoDate << std::endl;
std::cout << "显式字符串: " << explicitStr << std::endl;
}异常安全设计
1. 强异常安全保证
提供强异常安全保证的类:
cpp
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stdexcept>
// 强异常安全的容器包装器
template<typename T>
class SafeVector {
public:
SafeVector() = default;
// 拷贝构造函数 - 强异常安全
SafeVector(const SafeVector& other)
: data_(other.data_) // vector的拷贝构造函数提供强保证
{}
// 拷贝赋值运算符 - 强异常安全(拷贝并交换惯用法)
SafeVector& operator=(SafeVector other) noexcept {
swap(other);
return *this;
}
// 移动操作 - noexcept
SafeVector(SafeVector&& other) noexcept = default;
SafeVector& operator=(SafeVector&& other) noexcept = default;
// 交换 - noexcept
void swap(SafeVector& other) noexcept {
data_.swap(other.data_);
}
// 强异常安全的插入操作
void push_back(const T& value) {
// 创建副本,如果拷贝构造抛出异常,不影响当前对象
SafeVector temp = *this;
// 修改副本 - 如果这个操作失败,temp会被销毁,但*this不变
temp.data_.push_back(value);
// 交换 - noexcept,不会抛出
swap(temp);
// temp离开作用域,清理旧数据
}
// 强异常安全的插入操作 - 移动版本
void push_back(T&& value) {
SafeVector temp = *this;
temp.data_.push_back(std::move(value));
swap(temp);
}
// 强异常安全的批量插入
template<typename InputIt>
void insert(InputIt first, InputIt last) {
SafeVector temp = *this;
temp.data_.insert(temp.data_.end(), first, last);
swap(temp);
}
// 强异常安全的删除操作
void erase(size_t index) {
if (index >= data_.size()) {
throw std::out_of_range("索引越界");
}
SafeVector temp = *this;
temp.data_.erase(temp.data_.begin() + index);
swap(temp);
}
// 访问接口
const T& at(size_t index) const {
if (index >= data_.size()) {
throw std::out_of_range("索引越界");
}
return data_[index];
}
T& at(size_t index) {
if (index >= data_.size()) {
throw std::out_of_range("索引越界");
}
return data_[index];
}
size_t size() const noexcept { return data_.size(); }
bool empty() const noexcept { return data_.empty(); }
// 迭代器支持
auto begin() noexcept { return data_.begin(); }
auto end() noexcept { return data_.end(); }
auto begin() const noexcept { return data_.begin(); }
auto end() const noexcept { return data_.end(); }
private:
std::vector<T> data_;
};
// 异常安全的数据库事务包装器
class DatabaseTransaction {
public:
explicit DatabaseTransaction(const std::string& dbName)
: committed_(false) {
// 模拟数据库连接
std::cout << "开始事务: " << dbName << std::endl;
}
// 禁止拷贝
DatabaseTransaction(const DatabaseTransaction&) = delete;
DatabaseTransaction& operator=(const DatabaseTransaction&) = delete;
// 移动语义
DatabaseTransaction(DatabaseTransaction&& other) noexcept
: committed_(other.committed_) {
other.committed_ = false; // 移动后源对象不再拥有事务
}
DatabaseTransaction& operator=(DatabaseTransaction&& other) noexcept {
if (this != &other) {
rollbackIfNeeded(); // 回滚当前事务
committed_ = other.committed_;
other.committed_ = false;
}
return *this;
}
// 析构函数 - 自动回滚未提交的事务
~DatabaseTransaction() noexcept {
try {
rollbackIfNeeded();
} catch (...) {
// 析构函数不应该抛出异常
std::cerr << "回滚事务时发生异常" << std::endl;
}
}
// 业务操作 - 提供基本异常安全保证
void execute(const std::string& query) {
validateActive();
// 模拟可能失败的操作
if (query.empty()) {
throw std::invalid_argument("查询不能为空");
}
std::cout << "执行: " << query << std::endl;
// 实际数据库操作...
}
// 提交 - 如果不成功则抛出异常
void commit() {
validateActive();
// 模拟可能失败的提交
std::cout << "提交事务..." << std::endl;
committed_ = true; // 标记为已提交
}
private:
void validateActive() const {
if (committed_) {
throw std::logic_error("事务已提交,不能继续操作");
}
}
void rollbackIfNeeded() {
if (!committed_) {
std::cout << "回滚事务" << std::endl;
// 实际回滚逻辑...
}
}
bool committed_;
};
void demonstrate_exception_safety() {
// 强异常安全的容器使用
SafeVector<int> numbers;
try {
numbers.push_back(1);
numbers.push_back(2);
numbers.push_back(3);
// 即使这里抛出异常,numbers仍保持有效状态
numbers.erase(1);
std::cout << "容器内容: ";
for (const auto& num : numbers) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "操作失败: " << e.what() << std::endl;
// numbers仍然处于一致状态!
}
// 异常安全的数据库事务
try {
DatabaseTransaction tx("test.db");
tx.execute("INSERT INTO users VALUES (1, 'Alice')");
tx.execute("UPDATE stats SET count = count + 1");
// 如果提交失败,析构函数会自动回滚
tx.commit();
std::cout << "事务提交成功" << std::endl;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "事务失败: " << e.what() << std::endl;
// 不需要手动回滚 - RAII处理了!
}
}现代C++特性集成
1. constexpr与编译期计算
编译期友好的类型设计:
cpp
#include <array>
#include <type_traits>
// 编译期有理数类型
class Rational {
public:
// constexpr构造函数
constexpr Rational(int numerator = 0, int denominator = 1)
: num_(numerator), den_(denominator) {
if (denominator == 0) {
throw "分母不能为零"; // 在编译期会导致错误
}
normalize();
}
// constexpr访问器
constexpr int numerator() const noexcept { return num_; }
constexpr int denominator() const noexcept { return den_; }
// constexpr算术运算
constexpr Rational operator+(const Rational& other) const {
return Rational(
num_ * other.den_ + other.num_ * den_,
den_ * other.den_
);
}
constexpr Rational operator-(const Rational& other) const {
return Rational(
num_ * other.den_ - other.num_ * den_,
den_ * other.den_
);
}
constexpr Rational operator*(const Rational& other) const {
return Rational(num_ * other.num_, den_ * other.den_);
}
constexpr Rational operator/(const Rational& other) const {
return Rational(num_ * other.den_, den_ * other.num_);
}
// constexpr比较运算符
constexpr bool operator==(const Rational& other) const {
return num_ * other.den_ == other.num_ * den_;
}
constexpr bool operator!=(const Rational& other) const {
return !(*this == other);
}
// 转换到double - constexpr
constexpr double toDouble() const {
return static_cast<double>(num_) / den_;
}
// 编译期计算的最大公约数
static constexpr int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
private:
constexpr void normalize() {
if (den_ < 0) {
num_ = -num_;
den_ = -den_;
}
int g = gcd(num_ < 0 ? -num_ : num_, den_);
num_ /= g;
den_ /= g;
}
int num_;
int den_;
};
// 编译期计算的数学函数
template<typename T>
constexpr T compileTimePower(T base, int exp) {
static_assert(std::is_arithmetic_v<T>, "必须是算术类型");
if (exp < 0) {
return T(1) / compileTimePower(base, -exp);
}
T result = 1;
while (exp > 0) {
if (exp % 2 == 1) {
result *= base;
}
base *= base;
exp /= 2;
}
return result;
}
void demonstrate_constexpr_design() {
// 编译期计算
constexpr Rational r1(1, 2);
constexpr Rational r2(1, 3);
constexpr Rational sum = r1 + r2; // 5/6
constexpr double result = sum.toDouble();
std::cout << "1/2 + 1/3 = " << result << std::endl;
// 编译期幂计算
constexpr int square = compileTimePower(5, 2); // 25
constexpr double cube = compileTimePower(2.0, 3); // 8.0
std::cout << "5^2 = " << square << ", 2.0^3 = " << cube << std::endl;
// 在编译期数组中使用
constexpr std::array<Rational, 3> fractions = {
Rational(1, 2),
Rational(2, 3),
Rational(3, 4)
};
static_assert(fractions[0].numerator() == 1);
static_assert(fractions[0].denominator() == 2);
std::cout << "编译期分数数组: ";
for (const auto& frac : fractions) {
std::cout << frac.numerator() << "/" << frac.denominator() << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 运行时使用同样的接口
Rational a(3, 5), b(2, 7);
auto c = a * b;
std::cout << "3/5 * 2/7 = " << c.numerator()
<< "/" << c.denominator() << std::endl;
}实战案例:真实世界类设计
案例1:线程安全的观察者模式
cpp
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <mutex>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
// 线程安全的观察者模式
template<typename... Args>
class Observable {
public:
using Observer = std::function<void(Args...)>;
using ObserverId = size_t;
Observable() = default;
// 禁止拷贝(移动允许)
Observable(const Observable&) = delete;
Observable& operator=(const Observable&) = delete;
// 注册观察者,返回可用于取消注册的ID
ObserverId registerObserver(Observer observer) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
ObserverId id = nextId_++;
observers_.emplace_back(id, std::move(observer));
return id;
}
// 取消注册观察者
void unregisterObserver(ObserverId id) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
observers_.erase(
std::remove_if(observers_.begin(), observers_.end(),
[id](const auto& item) { return item.first == id; }),
observers_.end()
);
}
// 通知所有观察者
void notify(Args... args) const {
// 拷贝观察者列表以避免死锁
auto observersCopy = getObserversCopy();
for (const auto& [id, observer] : observersCopy) {
try {
observer(args...);
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
// 观察者异常不应该影响其他观察者
std::cerr << "观察者 " << id << " 异常: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
}
}
// 观察者数量
size_t observerCount() const {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
return observers_.size();
}
private:
std::vector<std::pair<ObserverId, Observer>> getObserversCopy() const {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
return observers_;
}
mutable std::mutex mutex_;
std::vector<std::pair<ObserverId, Observer>> observers_;
ObserverId nextId_ = 1;
};
// 使用观察者的温度传感器
class TemperatureSensor {
public:
using TemperatureObserver = Observable<double>;
TemperatureSensor() = default;
// 注册温度观察者
TemperatureObserver::ObserverId
registerTemperatureObserver(TemperatureObserver::Observer observer) {
return temperatureObservable_.registerObserver(std::move(observer));
}
void unregisterTemperatureObserver(TemperatureObserver::ObserverId id) {
temperatureObservable_.unregisterObserver(id);
}
// 更新温度并通知观察者
void updateTemperature(double temperature) {
currentTemperature_ = temperature;
temperatureObservable_.notify(temperature);
}
double getCurrentTemperature() const { return currentTemperature_; }
private:
TemperatureObserver temperatureObservable_;
double currentTemperature_ = 0.0;
};
void demonstrate_observer_pattern() {
TemperatureSensor sensor;
// 注册多个观察者
auto id1 = sensor.registerTemperatureObserver([](double temp) {
std::cout << "观察者1: 温度更新为 " << temp << "°C" << std::endl;
});
auto id2 = sensor.registerTemperatureObserver([](double temp) {
if (temp > 30.0) {
std::cout << "观察者2: 警告!温度过高: " << temp << "°C" << std::endl;
}
});
// 模拟温度更新
sensor.updateTemperature(25.5);
sensor.updateTemperature(32.1);
std::cout << "当前观察者数量: " << sensor.observerCount() << std::endl;
// 取消注册一个观察者
sensor.unregisterTemperatureObserver(id1);
sensor.updateTemperature(28.0);
std::cout << "取消注册后观察者数量: " << sensor.observerCount() << std::endl;
}案例2:策略模式与类型擦除
cpp
#include <memory>
#include <type_traits>
// 类型擦除的绘制策略
class DrawStrategy {
public:
template<typename T>
DrawStrategy(T&& strategy)
: pImpl_(std::make_unique<Model<T>>(std::forward<T>(strategy)))
{}
// 默认操作
DrawStrategy() = default;
DrawStrategy(DrawStrategy&&) = default;
DrawStrategy& operator=(DrawStrategy&&) = default;
// 禁止拷贝
DrawStrategy(const DrawStrategy&) = delete;
DrawStrategy& operator=(const DrawStrategy&) = delete;
// 绘制操作
void draw(int x, int y, int width, int height) const {
pImpl_->draw(x, y, width, height);
}
private:
struct Concept {
virtual ~Concept() = default;
virtual void draw(int x, int y, int width, int height) const = 0;
};
template<typename T>
struct Model : Concept {
Model(T&& strategy) : strategy_(std::forward<T>(strategy)) {}
void draw(int x, int y, int width, int height) const override {
strategy_.draw(x, y, width, height);
}
T strategy_;
};
std::unique_ptr<Concept> pImpl_;
};
// 具体的绘制策略
class SolidDrawStrategy {
public:
void draw(int x, int y, int width, int height) const {
std::cout << "实心绘制: 位置(" << x << "," << y
<< "), 大小(" << width << "x" << height << ")" << std::endl;
}
};
class BorderDrawStrategy {
public:
void draw(int x, int y, int width, int height) const {
std::cout << "边框绘制: 位置(" << x << "," << y
<< "), 大小(" << width << "x" << height << ")" << std::endl;
}
};
// 使用策略模式的图形类
class Shape {
public:
Shape(int x, int y, int width, int height, DrawStrategy drawer)
: x_(x), y_(y), width_(width), height_(height)
, drawer_(std::move(drawer))
{}
virtual ~Shape() = default;
// 绘制操作
virtual void draw() const {
drawer_.draw(x_, y_, width_, height_);
}
// 移动和位置操作
void move(int dx, int dy) {
x_ += dx;
y_ += dy;
}
void setPosition(int x, int y) {
x_ = x;
y_ = y;
}
// 访问器
int getX() const { return x_; }
int getY() const { return y_; }
int getWidth() const { return width_; }
int getHeight() const { return height_; }
private:
int x_, y_, width_, height_;
DrawStrategy drawer_;
};
// 具体的图形类型
class Rectangle : public Shape {
public:
Rectangle(int x, int y, int width, int height, DrawStrategy drawer)
: Shape(x, y, width, height, std::move(drawer))
{}
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "矩形 - ";
Shape::draw();
}
};
class Circle : public Shape {
public:
Circle(int x, int y, int radius, DrawStrategy drawer)
: Shape(x, y, radius * 2, radius * 2, std::move(drawer))
, radius_(radius)
{}
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "圆形(半径=" << radius_ << ") - ";
Shape::draw();
}
private:
int radius_;
};
void demonstrate_strategy_pattern() {
// 创建不同的绘制策略
SolidDrawStrategy solidDrawer;
BorderDrawStrategy borderDrawer;
// 创建使用不同策略的图形
Rectangle rect1(10, 10, 100, 50, DrawStrategy(solidDrawer));
Rectangle rect2(50, 50, 80, 60, DrawStrategy(borderDrawer));
Circle circle(100, 100, 25, DrawStrategy(solidDrawer));
// 绘制所有图形
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Shape>> shapes;
shapes.push_back(std::make_unique<Rectangle>(rect1));
shapes.push_back(std::make_unique<Rectangle>(rect2));
shapes.push_back(std::make_unique<Circle>(circle));
for (const auto& shape : shapes) {
shape->draw();
}
// 运行时切换策略
std::cout << "\n切换绘制策略后:" << std::endl;
Rectangle dynamicRect(0, 0, 200, 100, DrawStrategy(solidDrawer));
dynamicRect.draw();
// 动态更换策略
dynamicRect = Rectangle(0, 0, 200, 100, DrawStrategy(borderDrawer));
dynamicRect.draw();
}