目录
[1.1 模块化系统演进背景](#1.1 模块化系统演进背景)
[1.2 模块化核心概念解析](#1.2 模块化核心概念解析)
[2.1 模块声明语法详解](#2.1 模块声明语法详解)
[2.2 模块依赖解析机制](#2.2 模块依赖解析机制)
[3.1 迁移路径规划](#3.1 迁移路径规划)
[3.2 分阶段迁移实战](#3.2 分阶段迁移实战)
[4.1 Maven模块化配置](#4.1 Maven模块化配置)
[4.2 模块化构建流程](#4.2 模块化构建流程)
[5.1 服务绑定与松耦合架构](#5.1 服务绑定与松耦合架构)
[5.2 动态模块化与容器集成](#5.2 动态模块化与容器集成)
[6.1 迁移问题诊断表](#6.1 迁移问题诊断表)
[6.2 模块化架构设计模式](#6.2 模块化架构设计模式)
摘要
Java 9引入的模块化系统(JPMS,Java Platform Module System)是Java平台近十年来最重要的架构变革。本文深入解析模块化系统的设计理念、核心机制,并通过完整的实战案例展示从传统应用向模块化系统迁移的全过程,帮助开发者构建更安全、更可维护的Java应用架构。
第一章:模块化系统核心概念与架构设计
1.1 模块化系统演进背景
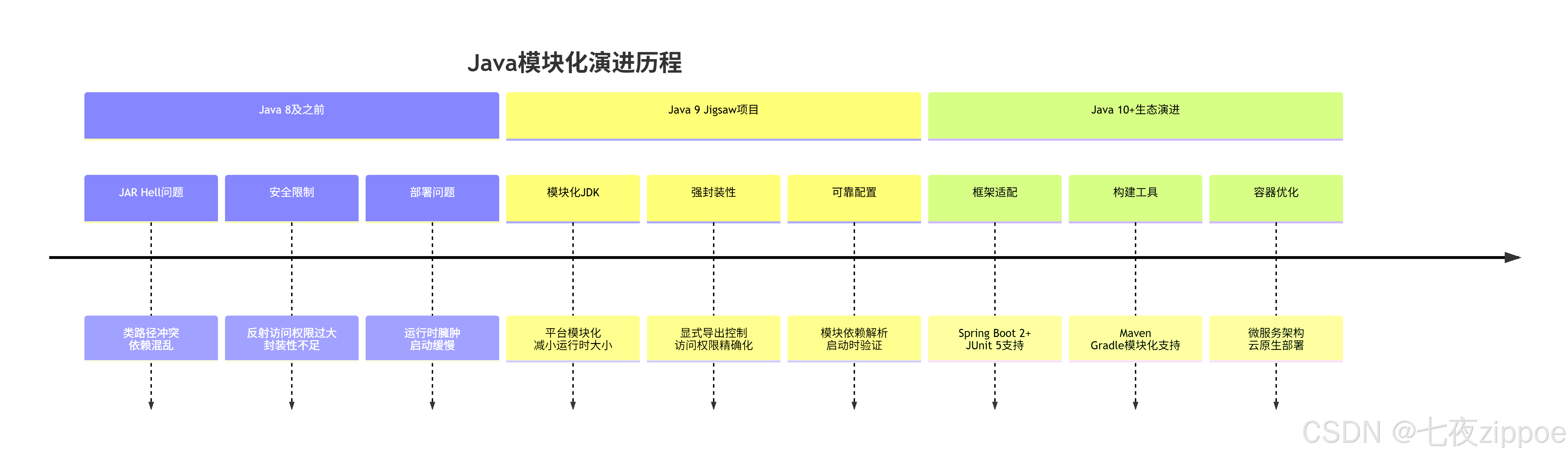
模块化要解决的核心问题:
java
/**
* 传统JAR包方式的问题演示
*/
public class TraditionalJarProblems {
// 1. 类路径冲突问题
public class ClasspathConflict {
// 应用依赖不同版本的库
// lib/commons-lang3-3.1.jar
// lib/commons-lang3-3.9.jar ❌ 冲突!
}
// 2. 反射滥用问题
public class ReflectionAbuse {
public void accessPrivate() throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.internal.InternalClass");
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("secret");
field.setAccessible(true); // 传统方式可以任意访问
Object value = field.get(null);
}
}
// 3. 隐式依赖问题
public class ImplicitDependencies {
// 编译时不知道运行时需要哪些依赖
// 缺少依赖直到运行时才报错
}
}1.2 模块化核心概念解析
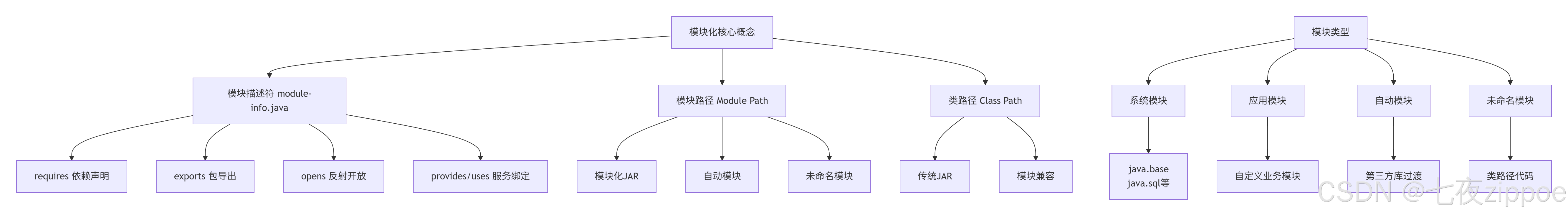
模块描述符(module-info.java)详解:
java
/**
* 完整的模块描述符示例
*/
// module-info.java
module com.example.ebookstore {
// 1. 依赖声明
requires java.base; // 隐式依赖,可省略
requires java.sql;
requires java.net.http;
requires transitive com.example.utils; // 传递依赖
// 2. 包导出控制
exports com.example.ebookstore.api;
exports com.example.ebookstore.model to com.example.webapp;
// 3. 服务使用声明
uses com.example.spi.PaymentService;
uses com.example.spi.NotificationService;
// 4. 服务提供声明
provides com.example.spi.PaymentService
with com.example.payment.CreditCardService;
// 5. 反射开放权限
opens com.example.ebookstore.internal;
opens com.example.ebookstore.entity to org.hibernate;
// 6. 开放反射但不可编译时访问
opens com.example.ebookstore.config;
}第二章:模块描述符与依赖管理
2.1 模块声明语法详解
java
/**
* 模块描述符完整语法规范
*/
public class ModuleDescriptorSyntax {
// 基本模块声明结构
/**
* module <module.name> {
* requires [transitive] <module>;
* exports <package>;
* opens <package>;
* provides <service> with <implementation>;
* uses <service>;
* }
*/
// 1. 依赖声明 requires
module com.example.library {
requires java.logging; // 编译时+运行时依赖
requires static java.sql; // 编译时依赖,运行时可选
requires transitive commons.math; // 传递依赖
}
// 2. 包导出控制 exports
module com.example.api {
exports com.example.api.public; // 导出到所有模块
exports com.example.api.internal
to com.example.impl; // 限定导出到特定模块
}
// 3. 反射开放 opens
module com.example.persistence {
opens com.example.persistence.entity; // 运行时反射开放
opens com.example.persistence.internal
to org.hibernate, spring.core; // 限定反射开放
}
// 4. 服务绑定 provides/uses
module com.example.application {
uses com.example.spi.EncoderService; // 声明服务消费者
provides com.example.spi.EncoderService
with com.example.encoder.Base64Encoder,
com.example.encoder.MD5Encoder; // 提供服务实现
}
}2.2 模块依赖解析机制
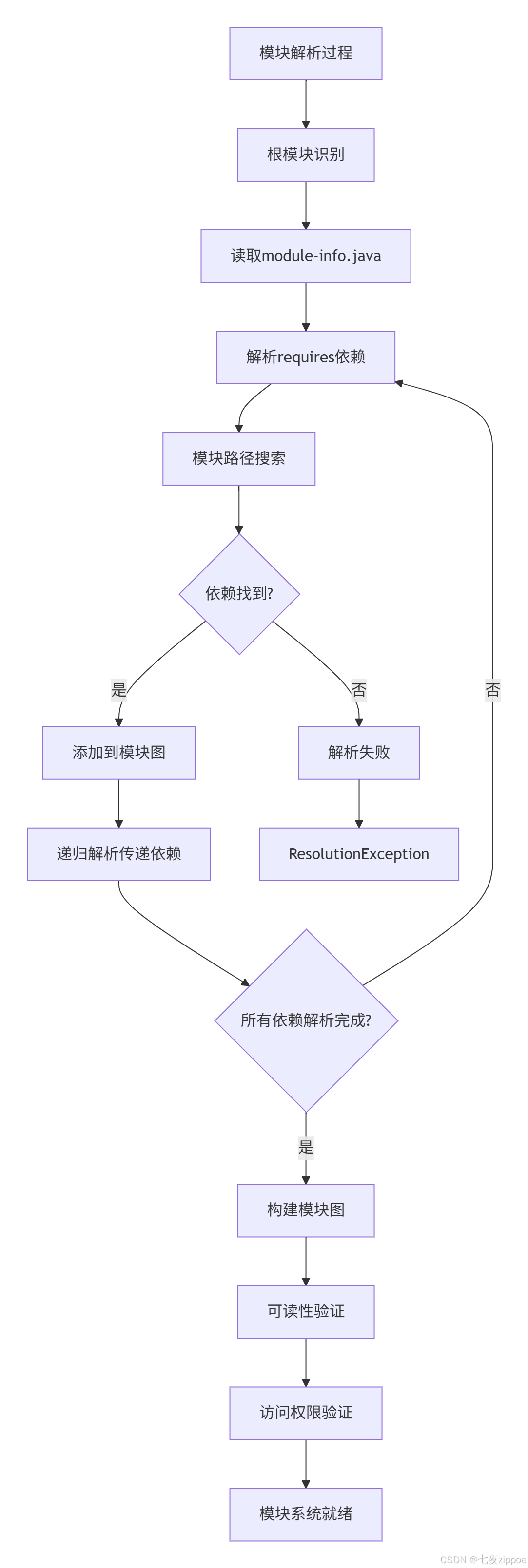
块依赖解析实战:
java
/**
* 模块依赖解析示例
*/
// 模块A:基础工具模块
module com.example.utils {
exports com.example.utils;
requires transitive java.logging;
}
// 模块B:业务逻辑模块
module com.example.service {
requires transitive com.example.utils; // 传递依赖
requires java.sql;
exports com.example.service.api;
uses com.example.spi.Processor;
}
// 模块C:Web应用模块
module com.example.webapp {
requires com.example.service; // 自动获得utils依赖
requires java.net.http;
provides com.example.spi.Processor
with com.example.webapp.HttpProcessor;
}第三章:模块化迁移实战策略
3.1 迁移路径规划
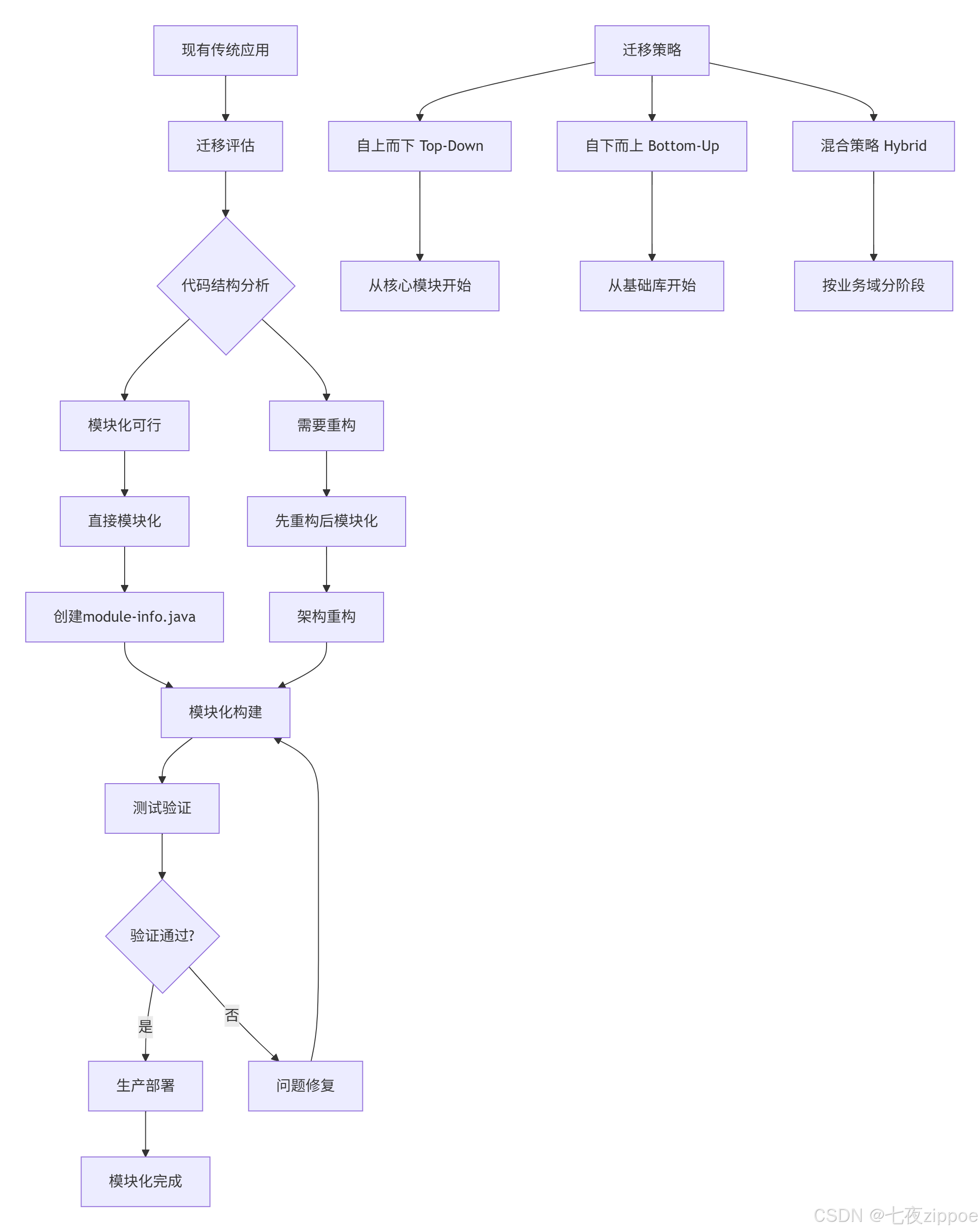
迁移评估检查清单:
java
/**
* 模块化迁移评估工具
*/
public class MigrationAssessment {
// 1. 依赖分析
public void analyzeDependencies(Project project) {
// 使用jdeps分析依赖
// jdeps --multi-release 11 -recursive myapp.jar
Map<String, Set<String>> dependencies =
analyzeDependencyGraph(project);
// 检查循环依赖
checkCyclicDependencies(dependencies);
// 识别隐式依赖
identifyImplicitDependencies(project);
}
// 2. 反射使用检查
public void checkReflectionUsage(Project project) {
// 搜索反射调用模式
Pattern reflectionPatterns = Pattern.compile(
"setAccessible|getDeclared|invoke"
);
List<ReflectionUsage> usages =
findReflectionCalls(project);
// 评估反射迁移难度
assessReflectionMigrationComplexity(usages);
}
// 3. 服务加载检查
public void checkServiceLoading(Project project) {
// 检查META-INF/services使用
checkServiceLoaderUsage(project);
}
}3.2 分阶段迁移实战
java
/**
* 电商系统模块化迁移实战
*/
// 阶段1:基础库模块化
module com.ebookstore.utils {
requires java.base;
requires transitive java.logging;
exports com.ebookstore.utils.json;
exports com.ebookstore.utils.validation;
// 为反射框架保留开放
opens com.ebookstore.utils.internal to spring.core;
}
// 阶段2:领域模型模块化
module com.ebookstore.domain {
requires transitive com.ebookstore.utils;
requires java.persistence;
exports com.ebookstore.domain.model;
exports com.ebookstore.domain.repository;
opens com.ebookstore.domain.entity to org.hibernate;
}
// 阶段3:业务服务模块化
module com.ebookstore.service {
requires transitive com.ebookstore.domain;
requires java.sql;
requires transitive java.transaction;
exports com.ebookstore.service.api;
uses com.ebookstore.spi.PaymentService;
uses com.ebookstore.spi.NotificationService;
}
// 阶段4:Web应用模块化
module com.ebookstore.webapp {
requires com.ebookstore.service;
requires spring.web;
requires spring.boot;
requires spring.boot.autoconfigure;
exports com.ebookstore.webapp;
opens com.ebookstore.webapp to spring.core, spring.beans;
provides org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner
with com.ebookstore.webapp.ApplicationRunner;
}第四章:构建工具与模块化集成
4.1 Maven模块化配置
XML
<!-- 父POM:多模块项目管理 -->
<project>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.ebookstore</groupId>
<artifactId>ebookstore-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<modules>
<module>utils</module>
<module>domain</module>
<module>service</module>
<module>webapp</module>
</modules>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.release>11</maven.compiler.release>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.11.0</version>
<configuration>
<release>11</release>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>--module-version</arg>
<arg>${project.version}</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
<!-- 子模块:工具模块配置 -->
<project>
<parent>
<groupId>com.ebookstore</groupId>
<artifactId>ebookstore-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</parent>
<artifactId>ebookstore-utils</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<compilerArgs>
<arg>--module-name</arg>
<arg>com.ebookstore.utils</arg>
</compilerArgs>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifestFile>src/main/resources/META-INF/MANIFEST.MF</manifestFile>
</archive>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>4.2 模块化构建流程
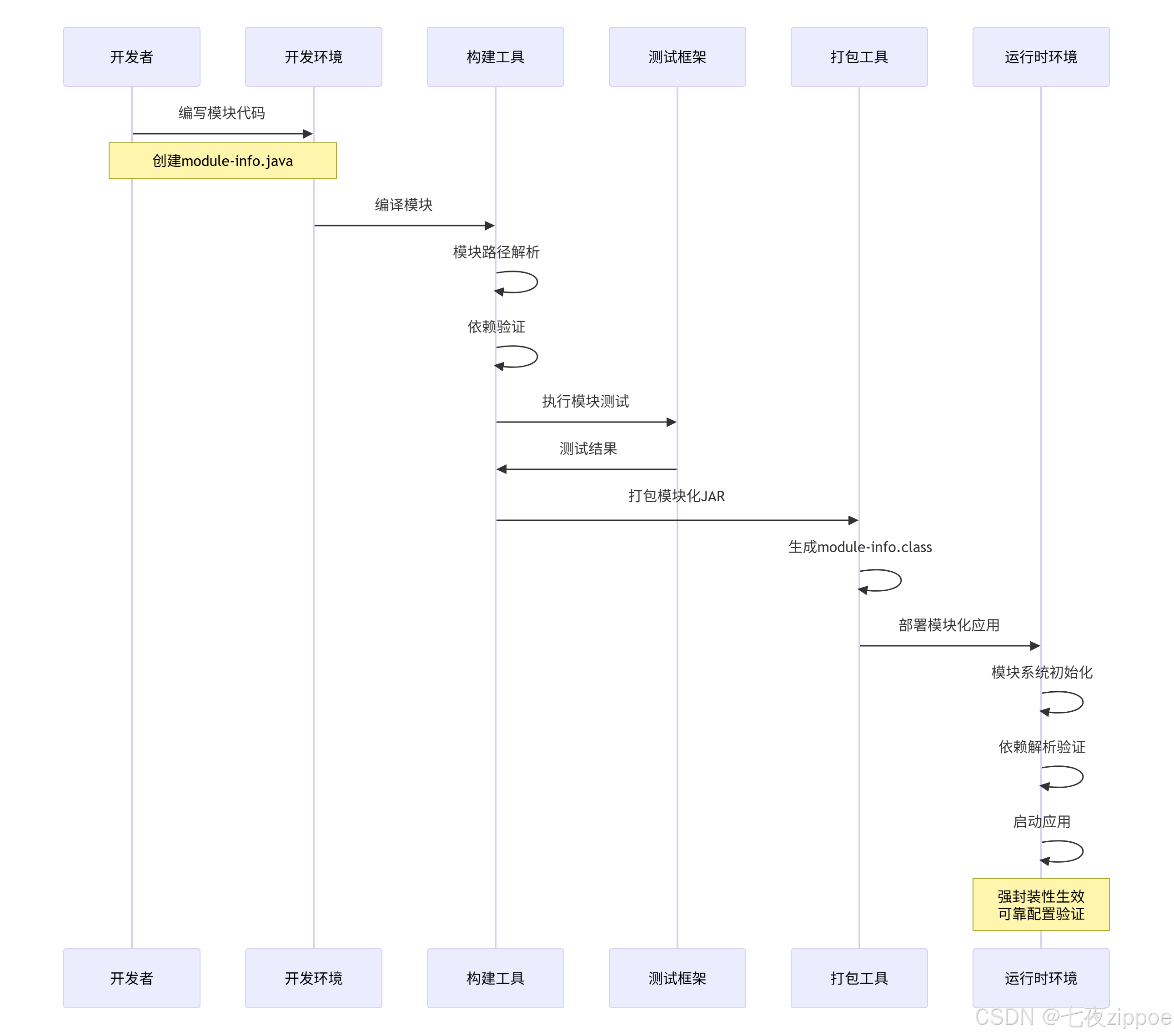
第五章:高级特性与最佳实践
5.1 服务绑定与松耦合架构
java
/**
* 基于服务的模块化架构
*/
// 服务接口模块
module com.ebookstore.spi {
exports com.ebookstore.spi;
}
// 服务提供者模块
module com.ebookstore.payment.creditcard {
requires com.ebookstore.spi;
requires transitive java.sql;
provides com.ebookstore.spi.PaymentService
with com.ebookstore.payment.creditcard.CreditCardService;
}
// 服务消费者模块
module com.ebookstore.order {
requires com.ebookstore.spi;
uses com.ebookstore.spi.PaymentService;
public class OrderProcessor {
public void processOrder(Order order) {
ServiceLoader<PaymentService> loader =
ServiceLoader.load(PaymentService.class);
for (PaymentService service : loader) {
if (service.supports(order.getPaymentMethod())) {
service.processPayment(order);
break;
}
}
}
}
}5.2 动态模块化与容器集成
java
/**
* 动态模块加载与管理
*/
public class DynamicModuleManager {
private final ModuleLayer.Controller layerController;
private final Map<String, ModuleLayer> applicationLayers;
public DynamicModuleManager() {
this.applicationLayers = new HashMap<>();
this.layerController = ModuleLayer.defineModulesWithOneLoader(
Configuration.empty(),
List.of(),
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader()
).controller();
}
// 动态加载业务模块
public void loadBusinessModule(Path modulePath, String moduleName) {
try {
// 解析模块配置
Configuration config = layerController.configuration()
.resolve(ModuleFinder.of(modulePath),
ModuleFinder.of(),
Set.of(moduleName));
// 创建新模块层
ModuleLayer newLayer = layerController.defineModules(config)
.layer();
applicationLayers.put(moduleName, newLayer);
// 初始化模块
Optional<Module> module = newLayer.findModule(moduleName);
module.ifPresent(this::initializeModule);
} catch (ResolutionException e) {
throw new ModuleLoadException("Failed to load module: " + moduleName, e);
}
}
// 动态卸载模块
public void unloadModule(String moduleName) {
ModuleLayer layer = applicationLayers.remove(moduleName);
if (layer != null) {
// 清理模块资源
cleanupModuleResources(layer);
}
}
// 模块间服务调用
public <T> Optional<T> getService(String moduleName, Class<T> serviceType) {
return applicationLayers.get(moduleName)
.findModule(moduleName)
.flatMap(module -> ServiceLoader.load(module, serviceType)
.findFirst());
}
}第六章:常见问题与解决方案
6.1 迁移问题诊断表
java
/**
* 模块化迁移常见问题及解决方案
*/
public class MigrationTroubleshooting {
// 问题诊断表
public enum CommonIssues {
// 编译时问题
MODULE_NOT_FOUND("模块找不到", "检查requires声明和模块路径"),
PACKAGE_NOT_EXPORTED("包未导出", "添加exports声明或opens声明"),
// 运行时问题
CLASS_NOT_FOUND("类找不到", "检查模块依赖和导出设置"),
ILLEGAL_ACCESS("非法访问", "使用opens开放反射访问权限"),
// 构建问题
CIRCULAR_DEPENDENCY("循环依赖", "重构模块结构,引入服务抽象"),
BUILD_FAILURE("构建失败", "检查编译器版本和模块配置")
}
// 解决方案示例
public class ReflectionMigration {
// 迁移前:滥用反射
public void illegalReflectionAccess() throws Exception {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName("com.internal.Config");
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("secretKey");
field.setAccessible(true); // ❌ 模块化后失败
String key = (String) field.get(null);
}
// 迁移后:合法访问方式
public void modularReflectionAccess() {
// 方案1:使用opens声明
// module-info.java: opens com.internal to current.module;
// 方案2:使用标准API
Optional<String> key = Config.getSecretKey();
// 方案3:服务接口方式
ConfigService service = ServiceLoader.load(ConfigService.class)
.findFirst()
.orElseThrow();
String key = service.getSecretKey();
}
}
// 自动模块迁移策略
public class AutomaticModuleMigration {
// 非模块化JAR作为自动模块使用
// 在module-info.java中:
requires legacy.lib; // 自动模块名称来自JAR文件名
// 自动模块特性:
// - 导出所有包
// - 依赖所有模块
// - 开放所有包用于反射
// - 临时迁移方案,最终需要真正模块化
}
}6.2 模块化架构设计模式
java
/**
* 模块化架构最佳实践模式
*/
public class ModularArchitecturePatterns {
// 模式1:层状架构模式
module com.ebookstore.infrastructure {
requires transitive com.ebookstore.domain;
requires java.persistence;
exports com.ebookstore.infrastructure.persistence;
exports com.ebookstore.infrastructure.messaging;
}
module com.ebookstore.application {
requires transitive com.ebookstore.domain;
requires com.ebookstore.infrastructure;
exports com.ebookstore.application.service;
exports com.ebookstore.application.dto;
}
module com.ebookstore.presentation {
requires com.ebookstore.application;
requires spring.web;
exports com.ebookstore.presentation.web;
}
// 模式2:端口适配器架构
module com.ebookstore.core {
exports com.ebookstore.core.port; // 端口接口
}
module com.ebookstore.persistence.adapter {
requires transitive com.ebookstore.core;
requires java.sql;
provides com.ebookstore.core.port.RepositoryPort
with com.ebookstore.persistence.JpaRepository;
}
// 模式3:事件驱动架构
module com.ebookstore.events {
exports com.ebookstore.events.api;
exports com.ebookstore.events.model;
uses com.ebookstore.events.handler.EventHandler;
}
}总结
Java模块化系统(JPMS)为Java应用带来了架构级的改进,通过本文的详细解析和实战案例,我们可以看到:
核心价值
-
强封装性:显式控制API暴露,增强代码安全性
-
可靠配置:编译时依赖验证,避免运行时类找不到问题
-
可扩展性:服务绑定机制支持松耦合架构
-
性能优化:类加载优化,启动时间减少
迁移建议
-
渐进式迁移:从基础库开始,逐步向上层应用扩展
-
工具链支持:充分利用jdeps、Maven/Gradle插件等工具
-
测试验证:每个迁移阶段都要充分测试
-
团队培训:确保团队成员理解模块化概念
未来展望
随着云原生和微服务架构的普及,Java模块化系统将在以下场景发挥更大作用:
-
微服务粒度控制
-
• 容器镜像优化
-
动态功能加载
-
安全权限管控
模块化是Java平台面向未来的重要演进方向,虽然迁移过程需要投入,但带来的架构收益将是长期且显著的。
参考链接
-
Oracle官方JPMS指南
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/9/docs/api/java/lang/module/package-summary.html
-
Java模块化规范(JSR 376)
-
OpenJDK Jigsaw项目
-
Maven模块化指南
-
Gradle模块化插件
https://docs.gradle.org/current/userguide/java_library_plugin.html
-
模块化迁移案例研究
https://blogs.oracle.com/javamagazine/post/java-modularity-migration-case-study