前言
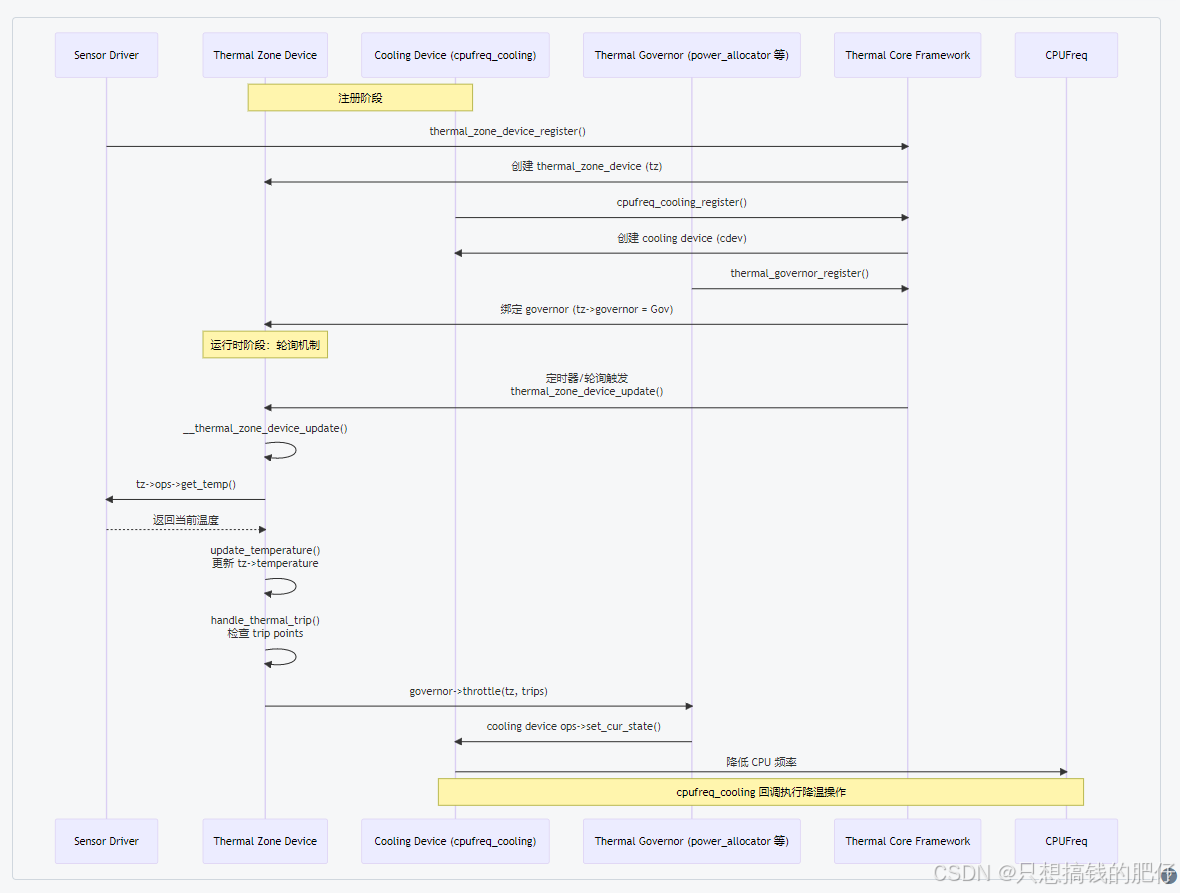
前文分析过thermal zone、cooling devic以及thermal governor,这几个部分都是独立实现的,彼此之间需要一个串接者,将各部逻辑串联到一起。所以,thermal core来了。
thermal core 是 Linux 内核热管理的核心模块,属于 thermal subsystem 的中心调度层。连接 温度传感器 (thermal zone) 和 散热装置 (cooling device) 的"大脑",并通过 governor 制定调节策略。具体作用如下:
- 抽象出 thermal zone(热源/温度监控点)。
- 抽象出 cooling device(散热设备/降温手段)。
- 提供 governor 策略(调度策略,例如 step_wise, power_allocator)。
- 提供 用户空间接口(sysfs,UEvent,netlink)。
- 负责 协调 温度检测与散热执行,让系统不会过热或功耗过高。
thermal core 的组成:
- Thermal Zone (热区/热源):温度传感器或逻辑区域(CPU/GPU/Battery)。
- Cooling Device (散热设备):可以降低热量的硬件/软件机制。
- Governor (调度器/策略):决定如何在 cooling device 上施加控制。
- Core 管理逻辑:注册/注销前面几个对象,定期采样温度或响应中断,调用 governor 来决定 cooling device 的状态等。
- 用户空间接口:生成sysfs 节点:/sys/class/thermal/。kobject_uevent_env() 向用户空间发送 thermal 事件。
源码说明:
- (1)thermal_core:三大模块注册、管理等函数实现
- (2)thermal_of:以thermal_of开头的函数,一般作用是初始化 thermal zone 和 cooling device的基本配置
- (3)thermal_netlink:用户空间的接口
- (4)thermal_sysfs:/sys/class/thermal/ 节点创建、维护函数
- (5)thermal_helpers:thermal zone 和 cooling device 对状态、温度等值读/写的方法
- (6)thermal_trip:thermal zone trip相关的函数实现
1 thermal core的初始化
1.1 thermal_init
thermal_init() 是 thermal 子系统的启动入口(以 postcore_initcall 在内核启动流程中被调用),依次完成:netlink 初始化 → 注册 governor → 分配并注册 class → 注册电源管理通知;在任一步骤失败时按逆序清理已分配的资源并返回错误码。
函数定义 __init:只在内核启动阶段使用,函数和常量可在启动完成后被丢弃(节约内存)。
c
static int __init thermal_init(void)
{
int result; // 用于保存被调用函数的返回值,为初始化各阶段的判断依据。
// 通常用于创建一个 netlink 通道 / socket,让内核 thermal subsystem 能与用户空间(daemon、test tools)通信
result = thermal_netlink_init();
if (result)
goto error;
// 注册内核中可用的 thermal governor,后面详细看。
result = thermal_register_governors();
if (result)
goto unregister_netlink; // 错误处理,清理上一步创建成功的结果,回滚。
// 为 struct class 分配内存并置零(kzalloc)。GFP_KERNEL 表示可睡眠分配(在初始化时通常允许)。
thermal_class = kzalloc(sizeof(*thermal_class), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!thermal_class) {
result = -ENOMEM;
goto unregister_governors; // 错误处理,清理上一步创建成功的结果,回滚。
}
thermal_class->name = "thermal"; // 把 class 的 name 指向字面量 "thermal"
thermal_class->dev_release = thermal_release; // 设置 dev_release 回调为 thermal_release
// class_register() 将 class 注册到 sysfs(/sys/class/thermal)
// 户空间可见并可创建基于该 class 的设备节点(如 thermal_zone*、cooling_device*
result = class_register(thermal_class);
if (result) {
kfree(thermal_class); // 释放之前分配的 thermal_class 内存
thermal_class = NULL;
goto unregister_governors; // 错误处理,清理上一步创建成功的结果,回滚。
}
// 向电源管理子系统注册一个 notifier(thermal_pm_nb)
// 用于在系统 suspend/resume(或其他 PM 事件)时得到回调,thermal core 可借此做特殊处理
result = register_pm_notifier(&thermal_pm_nb);
if (result)
// 如果注册 PM notifier 失败:不是致命错误。可以继续。
pr_warn("Thermal: Can not register suspend notifier, return %d\n",
result);
return 0;
unregister_governors:
thermal_unregister_governors(); // 卸载之前注册的 governors
unregister_netlink:
thermal_netlink_exit(); // 关闭并释放 netlink 资源
error:
// 销毁(destroy)两个 mutex(thermal_list_lock 与 thermal_governor_lock)
mutex_destroy(&thermal_list_lock);
mutex_destroy(&thermal_governor_lock);
return result; //返回错误码
}
// postcore_initcall 在内核启动流程中被调用,向内核添加thermal core
postcore_initcall(thermal_init); 【关键步骤】
步骤一 :
调用 thermal_netlink_init():通常用于创建一个 netlink 通道 / socket,让内核 thermal subsystem 能与用户空间(daemon、test tools)通信。这一步让 thermal 文件系统有意义了,/sys/class/thermal 可以被用户空间访问。
步骤二 :
thermal_register_governors 向内核注册thermal governor管理策略,策略决定温控的执行效率。
步骤三 :
register_pm_notifier():向电源管理子系统注册一个 notifier(thermal_pm_nb),用于在系统 suspend/resume(或其他 PM 事件)时得到回调,thermal core 可借此做特殊处理(例如在 suspend 时调整策略)。温升/功耗基本是不分家的,因此在控温的情况,是否需要严格控制功耗,需要电源管理系统支持。
1.2 thermal_netlink
genl_family 声明 + thermal_netlink_init/exit 在内核启动时构造并注册了一个 Generic Netlink family(用于 thermal ←→ userspace 的控制与事件通道)。
thermal_netlink_init() 调用 genl_register_family() 注册该 family,thermal_netlink_exit() 注销。此 family 的名字/版本/属性/多播组/命令/属性解析规则都在 thermal_gnl_family 里声明。
1.2.1 thermal_gnl_family
c
static struct genl_family thermal_gnl_family __ro_after_init = {
.hdrsize = 0,
.name = THERMAL_GENL_FAMILY_NAME,
.version = THERMAL_GENL_VERSION,
.maxattr = THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_MAX,
.policy = thermal_genl_policy,
.small_ops = thermal_genl_ops,
.n_small_ops = ARRAY_SIZE(thermal_genl_ops),
.resv_start_op = THERMAL_GENL_CMD_CDEV_GET + 1,
.mcgrps = thermal_genl_mcgrps,
.n_mcgrps = ARRAY_SIZE(thermal_genl_mcgrps),
};- __ro_after_init
该属性把数据放到 .data...ro_after_init 段,内核在初始化结束后会把这段内存变为只读。适合"只在 init 写一次、之后只读"的静态数据(比如这个 family 描述)。 - .hdrsize = 0
指定 generic-netlink 的"私有 header"大小;0 表示不添加额外的家族特定 header(handlers 直接使用 standard genl header + attrs)。 - .name = THERMAL_GENL_FAMILY_NAME / .version = THERMAL_GENL_VERSION
family 的名字与版本,由 UAPI 宏定义(userspace 通过相同名字/版本来打开该 family)。不同内核树/版本里宏名或字符串可能略有差别(比如 "thermal"、"thermal_event" 等),要以目标内核的 include/uapi/linux/thermal.h 为准。 - .maxattr = THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_MAX / .policy = thermal_genl_policy
① maxattr:声明属性的最大编号(用于 attribute 索引与边界检查)。
② policy:是一个 struct nla_policy[],用来对收到 netlink 消息的 attribute 做类型与长度校验(例如 NLA_U32, NLA_NESTED 等),避免 userspace 传入非法 TLV。thermal 的 policy 会定义像 TZ、TZ_ID、TZ_TEMP、CDEV 等属性的类型/嵌套结构。 - .small_ops / .n_small_ops
这里使用了 generic-netlink 的 small_ops 接口(相对于传统 .ops/.n_ops)。small_ops 是后来加入的一个轻量化注册方式,适合那些处理逻辑简单、消息体小的命令,可以减少内核在处理时的开销。thermal 使用 thermal_genl_ops 把若干命令映射到处理函数。 - .resv_start_op = THERMAL_GENL_CMD_CDEV_GET + 1
这是个兼容性/策略项:generic-netlink core 对于小于 resv_start_op 的操作允许不使用 policy(即老命令/保留命令不会由 core 自动解析/验证 attributes),而从 resv_start_op 开始的命令如果没有 policy 将被拒绝。这个机制帮助保持向后兼容并区分"老命令"和"新命令"的 attribute 验证策略。简而言之:作者把 THRMAL_GENL_CMD_CDEV_GET 及之前的命令视作"保留/兼容"区。 - .mcgrps / .n_mcgrps
定义该 family 的 multicast groups(热事件通常通过 multicast 发送给订阅的 userspace)。thermal 常见的组名有 event / sampling 等,userspace 可以订阅这些组以接收 trip、critical、device-fault、采样等事件通知。
1.2.2 thermal_genl_xxx
(1)struct nla_policy thermal_genl_policy[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_MAX + 1]
nla_policy 数组,列出每个 attribute 的类型(例如 THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_ID → NLA_U32,THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ → NLA_NESTED),用于由 netlink core/handler 做 attribute 验证并安全抽取数据.
c
static const struct nla_policy thermal_genl_policy[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_MAX + 1] = {
/* Thermal zone */
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ] = { .type = NLA_NESTED },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_ID] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_TEMP] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_TRIP] = { .type = NLA_NESTED },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_TRIP_ID] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_TRIP_TEMP] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_TRIP_TYPE] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_TRIP_HYST] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_MODE] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_CDEV_WEIGHT] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_NAME] = { .type = NLA_STRING,
.len = THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH },
/* Governor(s) */
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_GOV] = { .type = NLA_NESTED },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_TZ_GOV_NAME] = { .type = NLA_STRING,
.len = THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH },
/* Cooling devices */
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CDEV] = { .type = NLA_NESTED },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CDEV_ID] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CDEV_CUR_STATE] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CDEV_MAX_STATE] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CDEV_NAME] = { .type = NLA_STRING,
.len = THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH },
/* CPU capabilities */
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CPU_CAPABILITY] = { .type = NLA_NESTED },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CPU_CAPABILITY_ID] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CPU_CAPABILITY_PERFORMANCE] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
[THERMAL_GENL_ATTR_CPU_CAPABILITY_EFFICIENCY] = { .type = NLA_U32 },
};(2)struct genl_small_ops thermal_genl_ops[]
命令到处理函数的映射表(例如 THERMAL_GENL_CMD_CDEV_GET → thermal_genl_cmd_cdev_get()),在 small_ops 模式下这些处理函数会被 generic-netlink core 调用来响应请求。
c
static const struct genl_small_ops thermal_genl_ops[] = {
{
.cmd = THERMAL_GENL_CMD_TZ_GET_ID,
.validate = GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_STRICT | GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_DUMP,
.dumpit = thermal_genl_cmd_dumpit,
},
{
.cmd = THERMAL_GENL_CMD_TZ_GET_TRIP,
.validate = GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_STRICT | GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_DUMP,
.doit = thermal_genl_cmd_doit,
},
{
.cmd = THERMAL_GENL_CMD_TZ_GET_TEMP,
.validate = GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_STRICT | GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_DUMP,
.doit = thermal_genl_cmd_doit,
},
{
.cmd = THERMAL_GENL_CMD_TZ_GET_GOV,
.validate = GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_STRICT | GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_DUMP,
.doit = thermal_genl_cmd_doit,
},
{
.cmd = THERMAL_GENL_CMD_CDEV_GET,
.validate = GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_STRICT | GENL_DONT_VALIDATE_DUMP,
.dumpit = thermal_genl_cmd_dumpit,
},
};(3)struct genl_multicast_group thermal_genl_mcgrps[]
列出可用的 multicast 组(事件/采样分类),用于 genl_multicast_group 注册和 genlmsg_multicast() 发送事件。
c
static const struct genl_multicast_group thermal_genl_mcgrps[] = {
{ .name = THERMAL_GENL_SAMPLING_GROUP_NAME, },
{ .name = THERMAL_GENL_EVENT_GROUP_NAME, },
};1.2.3 init() & exit()
c
int __init thermal_netlink_init(void)
{
return genl_register_family(&thermal_gnl_family);
}
void __init thermal_netlink_exit(void)
{
genl_unregister_family(&thermal_gnl_family);
}- genl_register_family
把 thermal_gnl_family 注册到 generic-netlink core ------ 分配 family id、注册 ops 和 multicast group 等。返回 0 表示成功,否则返回负 errno。thermal 的初始化流程(thermal_init)会把该返回值用于失败回退处理。 - genl_unregister_family
注销该 family,清理 core 的数据结构,多播组也随之失效。用于模块卸载或 init 失败后的回滚。
1.3 thermal_pm_notify
notifier_block:Linux 内核的通知链机制(notifier chain),允许多个子系统监听某些事件。这里 thermal core 定义了一个 电源管理(PM)通知回调块,当系统进入 suspend/hibernate 或恢复时,会调用 thermal_pm_notify()。
参数:
- nb:对应的 notifier_block(这里就是 thermal_pm_nb)。
- mode:通知类型,表示当前 PM 事件,例如 PM_SUSPEND_PREPARE、PM_POST_SUSPEND 等。
- _unused:没用到的额外参数。
c
static struct notifier_block thermal_pm_nb = {
.notifier_call = thermal_pm_notify,
};
static int thermal_pm_notify(struct notifier_block *nb,
unsigned long mode, void *_unused)
{
struct thermal_zone_device *tz;
switch (mode) {
// 系统进入休眠/挂起前
case PM_HIBERNATION_PREPARE:
case PM_RESTORE_PREPARE:
case PM_SUSPEND_PREPARE:
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
// 遍历 thermal core 管理的所有 thermal zone
list_for_each_entry(tz, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
// 进入具体的 thermal zone,需要加 tz->lock 保护 zone 内部状态
mutex_lock(&tz->lock);
// 设置挂起状态。标记 thermal zone 已挂起,意味着
// (1) 不会再触发温度更新。
// (2) 不会调用 cooling device 进行调节。
// (3) 防止 thermal 干扰系统挂起流程。
tz->suspended = true;
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
}
// 遍历结束,解开全局 thermal list 锁
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
break;
// 系统恢复后,系统从休眠/挂起恢复。
case PM_POST_HIBERNATION:
case PM_POST_RESTORE:
case PM_POST_SUSPEND:
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
// 逐个恢复 thermal zone。
list_for_each_entry(tz, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
mutex_lock(&tz->lock);
// 解除挂起状态
tz->suspended = false;
// 重新初始化 thermal zone
thermal_zone_device_init(tz);
// 主动触发一次温度更新
__thermal_zone_device_update(tz, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
}
// 解全局锁
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
break;
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}【关键点】
thermal_zone_device_init :重新初始化 zone。可能重新配置 trip 点。重新启用 sensor 回调。为恢复后的正常 thermal 调度做准备。
__thermal_zone_device_update:立即触发 thermal 更新流程,读取最新温度,判断是否越过 trip 点,通知 cooling device 执行相应操作(如 CPU 降频)。参数 THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED 表示这是一次普通更新,不对应特定事件(如高温报警)。
【注】
thermal core 初始化过程中,没有看到 thermal zone 和 cooling device 的注册。这是因为在最新的kernel中,这两部分的注册调用都在对应的硬件初始化时进行了。如thermal sensor初始化时,就调用过 thermal zone 的注册逻辑。
因此,对于thermal core 我们需要关注的是如何实现这些注册逻辑的,如何管理这些温控策略的,如何有效触发温控设备运行或者上报的。
2 thermal设备注册
2.1 thermal zone 注册
thermal zone的注册流程如下:
c
rockchip_thermal_register_sensor // 从[thermal sensor]那章节切入
↓
devm_thermal_of_zone_register // [thermal zone] 可以看
↓
thermal_of_zone_register // [thermal zone] 可以看
↓
thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips2.1.1 thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips
thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips函数是 Linux kernel thermal 子系统里最核心的注册函数之一,负责注册一个 thermal zone(温度传感器管理单元)函数。函数定义如下:
函数参数:
- type:zone 名称字符串
- trips:热触发点数组(trip points,例如温度阈值)
- num_trips:trip 数量
- mask:bitmask,标记哪些 trip 支持写操作
- devdata:驱动私有数据指针
- ops:操作函数集(回调,比如 .get_temp, .set_trips 等)
- tzp:platform 参数(如 governor 名称、是否禁用 hwmon)
- passive_delay / polling_delay:轮询延迟(被动冷却 / 温度检测)
c
/**
* thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips() - register a new thermal zone device
* @type: the thermal zone device type
* @trips: a pointer to an array of thermal trips
* @num_trips: the number of trip points the thermal zone support
* @mask: a bit string indicating the writeablility of trip points
* @devdata: private device data
* @ops: standard thermal zone device callbacks
* @tzp: thermal zone platform parameters
* @passive_delay: number of milliseconds to wait between polls when
* performing passive cooling
* @polling_delay: number of milliseconds to wait between polls when checking
* whether trip points have been crossed (0 for interrupt
* driven systems)
*
* This interface function adds a new thermal zone device (sensor) to
* /sys/class/thermal folder as thermal_zone[0-*]. It tries to bind all the
* thermal cooling devices registered at the same time.
* thermal_zone_device_unregister() must be called when the device is no
* longer needed. The passive cooling depends on the .get_trend() return value.
*
* Return: a pointer to the created struct thermal_zone_device or an
* in case of error, an ERR_PTR. Caller must check return value with
* IS_ERR*() helpers.
*/
struct thermal_zone_device *
thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips(const char *type, struct thermal_trip *trips, int num_trips, int mask,
void *devdata, struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops,
const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp, int passive_delay,
int polling_delay)
{
struct thermal_zone_device *tz; //thermal zone对象指针
int id;
int result;
int count;
struct thermal_governor *governor; // governor对象指针
// 判断type是否非空
if (!type || strlen(type) == 0) {
pr_err("No thermal zone type defined\n");
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
// 判断type字节长度
if (strlen(type) >= THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH) {
pr_err("Thermal zone name (%s) too long, should be under %d chars\n",
type, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH);
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
/*
* Max trip count can't exceed 31 as the "mask >> num_trips" condition.
* For example, shifting by 32 will result in compiler warning:
* warning: right shift count >= width of type [-Wshift-count- overflow]
*
* Also "mask >> num_trips" will always be true with 32 bit shift.
* E.g. mask = 0x80000000 for trip id 31 to be RW. Then
* mask >> 32 = 0x80000000
* This will result in failure for the below condition.
*
* Check will be true when the bit 31 of the mask is set.
* 32 bit shift will cause overflow of 4 byte integer.
*/
// 校验 trip 参数
// 限制 trip 数量(必须在 0 ~ 31 内)。避免位移溢出 (mask >> num_trips)。
if (num_trips > (BITS_PER_TYPE(int) - 1) || num_trips < 0 || mask >> num_trips) {
pr_err("Incorrect number of thermal trips\n");
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
// 回调对象校验
if (!ops) {
pr_err("Thermal zone device ops not defined\n");
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
}
// 校验trips
if (num_trips > 0 && !trips)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
// 校验全局 thermal_class 是否初始化
// thermal 子系统还没初始化时,不能注册 zone
if (!thermal_class)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
// 分配 thermal_zone_device 存储单元
tz = kzalloc(sizeof(*tz), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!tz)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
// 判断传入参数 thermal_zone_params *tzp 有效性
if (tzp) {
// 拷贝参数到定义的thermal zone
tz->tzp = kmemdup(tzp, sizeof(*tzp), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!tz->tzp) {
result = -ENOMEM;
goto free_tz;
}
}
// 初始化链表、ID 管理器、互斥锁和移除完成量
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tz->thermal_instances); // struct list_head thermal_instances
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tz->node); // struct list_head node
ida_init(&tz->ida); // struct ida ida
mutex_init(&tz->lock); // struct mutex lock
init_completion(&tz->removal); // struct completion removal
// 分配一个全局 thermal zone id,例如 thermal_zone0
id = ida_alloc(&thermal_tz_ida, GFP_KERNEL);
if (id < 0) {
result = id;
goto free_tzp;
}
//thermal zone:id 赋值
tz->id = id;
//thermal zone:type保存,即名称
strscpy(tz->type, type, sizeof(tz->type));
// ops->critical 没实现,使用默认实现 thermal_zone_device_critical 函数。
if (!ops->critical)
ops->critical = thermal_zone_device_critical;
tz->ops = ops; // ops 赋值给本地对象
tz->device.class = thermal_class; // class 赋值给本地对象
tz->devdata = devdata; // devdata 赋值给本地对象
tz->trips = trips; // trips 赋值给本地对象
tz->num_trips = num_trips; // num_trips 赋值给本地对象
// 把 delay 转换为 jiffies 存储
thermal_set_delay_jiffies(&tz->passive_delay_jiffies, passive_delay); // 高温轮询间隔
thermal_set_delay_jiffies(&tz->polling_delay_jiffies, polling_delay); // 常规轮询间隔
/* sys I/F */
/* Add nodes that are always present via .groups */
// 创建 sysfs 属性组,即 /sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone%d/下面的节点
result = thermal_zone_create_device_groups(tz, mask);
if (result)
goto remove_id;
/* A new thermal zone needs to be updated anyway. */
atomic_set(&tz->need_update, 1);
// 设置设备名字 thermal_zone%d
result = dev_set_name(&tz->device, "thermal_zone%d", tz->id);
if (result) {
thermal_zone_destroy_device_groups(tz);
goto remove_id;
}
// 初始化 thermal zone device,注册到 device model
// 得到完整节点:sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0 这种
thermal_zone_device_init(tz);
result = device_register(&tz->device);
if (result)
goto release_device;
// 遍历 trips,如果 trip 无效或温度为 0,则禁用
for (count = 0; count < num_trips; count++) {
struct thermal_trip trip;
result = thermal_zone_get_trip(tz, count, &trip);
if (result || !trip.temperature)
set_bit(count, &tz->trips_disabled);
}
/* Update 'this' zone's governor information */
mutex_lock(&thermal_governor_lock);
// 依据 struct thermal_zone_params *tzp 指定的 governor 或系统默认 governor
if (tz->tzp)
governor = __find_governor(tz->tzp->governor_name); // __find_governor 根据名称找到 governor 对象
else
governor = def_governor;
// 设置控制策略,之后 thermal zone 可以直接调用 governor
result = thermal_set_governor(tz, governor);
if (result) {
mutex_unlock(&thermal_governor_lock);
goto unregister;
}
mutex_unlock(&thermal_governor_lock);
// 注册 hwmon 接口
if (!tz->tzp || !tz->tzp->no_hwmon) {
// 默认会在 /sys/class/hwmon/ 下导出温度传感器节点
result = thermal_add_hwmon_sysfs(tz);
if (result)
goto unregister;
}
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
mutex_lock(&tz->lock);
// 将该 thermal zone 挂到全局 thermal_tz_list
list_add_tail(&tz->node, &thermal_tz_list);
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
/* Bind cooling devices for this zone */
// 自动尝试绑定 cooling device。》》》》》》》》》 重要的!!!
bind_tz(tz);
// 初始化延迟工作队列 delayed_work,用于轮询温度。
// tz->poll_queue 的回调函数是 thermal_zone_device_check
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&tz->poll_queue, thermal_zone_device_check);
/* Update the new thermal zone and mark it as already updated. */
// 第一次强制更新温度状态
// 设置 thermal zone need_update=1
if (atomic_cmpxchg(&tz->need_update, 1, 0))
thermal_zone_device_update(tz, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);
// 通知用户空间 thermal zone 已创建
thermal_notify_tz_create(tz->id, tz->type);
return tz;
// 按照分配顺序逆序清理,避免内存泄漏
unregister:
device_del(&tz->device);
release_device:
put_device(&tz->device);
remove_id:
ida_free(&thermal_tz_ida, id);
free_tzp:
kfree(tz->tzp);
free_tz:
kfree(tz);
return ERR_PTR(result);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips);【INIT_DELAYED_WORK】
INIT_DELAYED_WORK 对延迟队列对进行回调绑定,tz->poll_queue 的回调函数是 thermal_zone_device_check。
INIT_WORK(&(_work)->work, _func) 会把 _func 作为回调函数绑定到 work_struct 里。
c
#define __INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func, _tflags) \
do { \
INIT_WORK(&(_work)->work, (_func)); \
__init_timer(&(_work)->timer, \
delayed_work_timer_fn, \
(_tflags) | TIMER_IRQSAFE); \
} while (0)
#define INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func) \
__INIT_DELAYED_WORK(_work, _func, 0)调用流程:
- 检查参数(type、trips、ops 等合法性)
- 分配并初始化 thermal_zone_device
- 注册 sysfs 节点和 device
- 初始化 trips、governor、hwmon
- 加入全局链表
- 绑定 cooling device 并开始轮询工作
- 更新一次温度并通知用户空间
2.1.2 thermal_zone_create_device_groups
thermal_zone_create_device_groups() 是 thermal zone 注册过程里负责 生成 sysfs 属性组(attribute groups) 的函数。它的主要作用就是把标准属性(比如 temp, mode, type 等)和动态生成的 trip 属性(trip_point_*)一起挂到 thermal_zoneX 的 sysfs 目录下。
c
// path: drivers/thermal/thermal_sysfs.c
int thermal_zone_create_device_groups(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
int mask)
{
const struct attribute_group **groups;
int i, size, result;
/* we need one extra for trips and the NULL to terminate the array */
// thermal_zone_attribute_groups 是内核里定义好的 静态属性组数组(一组 sysfs 属性,始终存在
// 一个位置预留给 trips 动态属性组(tz->trips_attribute_group),需要 +1
// 一个位置预留给 NULL 结尾(sysfs 要求 groups 数组以 NULL 结尾,需要 +1
size = ARRAY_SIZE(thermal_zone_attribute_groups) + 2;
/* This also takes care of API requirement to be NULL terminated */
// 分配一个数组,每个元素指向 struct attribute_group
groups = kcalloc(size, sizeof(*groups), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!groups)
return -ENOMEM;
// 将标准属性组(如 temp, mode, policy 等)复制到 groups 前面部分。
// 留下最后两个槽位:一个给 trips,一个 NUL
for (i = 0; i < size - 2; i++)
groups[i] = thermal_zone_attribute_groups[i];
// 创建 trip 属性组
if (tz->num_trips) {
result = create_trip_attrs(tz, mask);
if (result) {
kfree(groups);
return result;
}
// 成功后,将该 trips属性组 挂到 groups[size - 2]
groups[size - 2] = &tz->trips_attribute_group;
}
// 把 groups 挂到 tz->device.groups,这样在 device_register() 时,sysfs 会自动创建这些属性
tz->device.groups = groups;
return 0;
}进一步看下 create_trip_attrs 函数。
c
// path: drivers/thermal/thermal_sysfs.c
/**
* create_trip_attrs() - create attributes for trip points
* @tz: the thermal zone device
* @mask: Writeable trip point bitmap.
* * helper function to instantiate sysfs entries for every trip
* point and its properties of a struct thermal_zone_device.
* * Return: 0 on success, the proper error value otherwise.
*/
static int create_trip_attrs(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int mask)
{
struct attribute **attrs;
int indx;
/* This function works only for zones with at least one trip */
// 检查是否有 trip
if (tz->num_trips <= 0)
return -EINVAL;
// 分配三类属性数组
// step 1: 分配数组 type
tz->trip_type_attrs = kcalloc(tz->num_trips, sizeof(*tz->trip_type_attrs),
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!tz->trip_type_attrs)
return -ENOMEM;
// step 2: 分配数组 temp
tz->trip_temp_attrs = kcalloc(tz->num_trips, sizeof(*tz->trip_temp_attrs),
GFP_KERNEL);
// 失败,需要回滚清理之前的内存分配
if (!tz->trip_temp_attrs) {
kfree(tz->trip_type_attrs);
return -ENOMEM;
}
// step 3: 分配数组 hyst
tz->trip_hyst_attrs = kcalloc(tz->num_trips,
sizeof(*tz->trip_hyst_attrs),
GFP_KERNEL);
// 失败,需要回滚清理之前的内存分配
if (!tz->trip_hyst_attrs) {
kfree(tz->trip_type_attrs);
kfree(tz->trip_temp_attrs);
return -ENOMEM;
}
// 每个 trip 有 3 个属性,因此分配 num_trips * 3 + 1 个 struct attribute 指针
// 末尾留一个 NULL,sysfs 需要 NULL 结尾的属性数组
attrs = kcalloc(tz->num_trips * 3 + 1, sizeof(*attrs), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!attrs) {
kfree(tz->trip_type_attrs);
kfree(tz->trip_temp_attrs);
kfree(tz->trip_hyst_attrs);
return -ENOMEM;
}
for (indx = 0; indx < tz->num_trips; indx++) {
/* create trip type attribute */
// trip_point_%d_type 节点
snprintf(tz->trip_type_attrs[indx].name, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH,
"trip_point_%d_type", indx);
sysfs_attr_init(&tz->trip_type_attrs[indx].attr.attr);
tz->trip_type_attrs[indx].attr.attr.name =
tz->trip_type_attrs[indx].name; // 名字:trip_point_%d_type
tz->trip_type_attrs[indx].attr.attr.mode = S_IRUGO; // 权限:S_IRUGO(只读)
tz->trip_type_attrs[indx].attr.show = trip_point_type_show; // show 回调:trip_point_type_show()
attrs[indx] = &tz->trip_type_attrs[indx].attr.attr; // 挂到 attrs[indx]
/* create trip temp attribute */
// trip_point_%d_temp 节点
snprintf(tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].name, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH,
"trip_point_%d_temp", indx);
sysfs_attr_init(&tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].attr.attr);
tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].attr.attr.name =
tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].name;
tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].attr.attr.mode = S_IRUGO; // 默认只读
tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].attr.show = trip_point_temp_show; // 回调:trip_point_temp_show()(显示温度值
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_THERMAL_WRITABLE_TRIPS) &&
mask & (1 << indx)) {
// 如果 CONFIG_THERMAL_WRITABLE_TRIPS 打开且 mask 对应位为 1 → 变成可写 0644
tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].attr.attr.mode |= S_IWUSR;
tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].attr.store =
trip_point_temp_store; // 回调(可选):trip_point_temp_store()(允许写入修改 trip 温度阈值)
}
attrs[indx + tz->num_trips] = &tz->trip_temp_attrs[indx].attr.attr; // 挂到 attrs[indx + num_trips]
// trip_point_%d_hyst 节点
// 操作基本一样
snprintf(tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].name, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH,
"trip_point_%d_hyst", indx);
sysfs_attr_init(&tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].attr.attr);
tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].attr.attr.name =
tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].name;
tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].attr.attr.mode = S_IRUGO;
tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].attr.show = trip_point_hyst_show;
if (tz->ops->set_trip_hyst) {
tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].attr.attr.mode |= S_IWUSR;
tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].attr.store =
trip_point_hyst_store;
}
attrs[indx + tz->num_trips * 2] =
&tz->trip_hyst_attrs[indx].attr.attr; // 挂到 attrs[indx + num_trips*2]
}
attrs[tz->num_trips * 3] = NULL; // 设置 NULL 结尾。sysfs 属性数组必须以 NULL 结尾
// 将属性数组挂到 tz->trips_attribute_group,供上层 thermal_zone_create_device_groups() 使用
tz->trips_attribute_group.attrs = attrs;
return 0;
}最终效果如下:
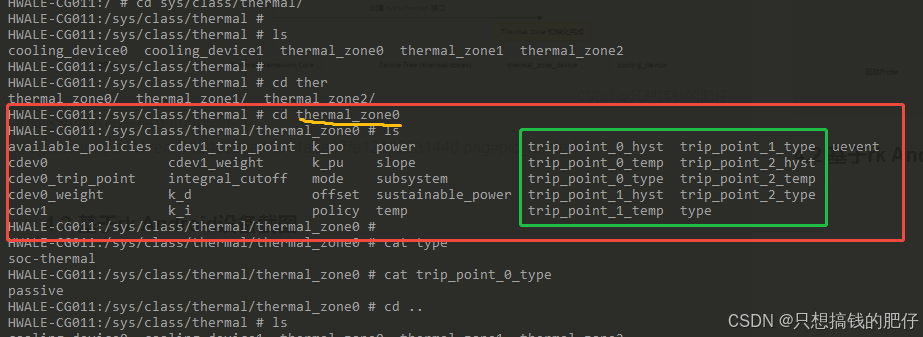
【总结】
create_trip_attrs() 为每个 trip 动态创建 sysfs 属性:
- type:trip 类型(always read-only)
- temp:trip 温度(只读或可写,取决于配置和 mask)
- hyst:滞回值(只读或可写,取决于驱动是否实现 set_trip_hyst)
最终挂到 tz->trips_attribute_group,然后再由 thermal_zone_create_device_groups() 放入 tz->device.groups,在 sysfs 节点里暴露。
2.1.3 thermal_notify_tz_create
thermal_notify_tz_create() 和 thermal_genl_send_event() 两个函数,它们主要负责 thermal 子系统通过 Generic Netlink 向用户空间广播事件。
当 thermal zone(热区)被创建时,调用此函数,通过 netlink 向用户态发送 THERMAL_GENL_EVENT_TZ_CREATE 事件。
c
//path: drivers/thermal/thermal_netlink.c
int thermal_notify_tz_create(int tz_id, const char *name)
{
struct param p = { .tz_id = tz_id, .name = name };
return thermal_genl_send_event(THERMAL_GENL_EVENT_TZ_CREATE, &p);
}
/*
* Generic netlink event encoding
*/
static int thermal_genl_send_event(enum thermal_genl_event event,
struct param *p)
{
struct sk_buff *msg;
int ret = -EMSGSIZE;
void *hdr;
// 申请一个 sk_buff,作为 netlink 消息缓冲区
msg = genlmsg_new(NLMSG_GOODSIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!msg)
return -ENOMEM;
p->msg = msg;
// 添加 Generic Netlink 消息头
// thermal_gnl_family 是 thermal 子系统的 netlink family,注册时定义了 family 名称、id 等
// event 指定消息的命令码
hdr = genlmsg_put(msg, 0, 0, &thermal_gnl_family, 0, event);
if (!hdr)
goto out_free_msg;
// 调用对应事件的编码回调函数,将 thermal zone 的信息写入 netlink 消息
ret = event_cb[event](p);
if (ret)
goto out_cancel_msg;
// 设置 netlink 消息尾部,修正消息长度
genlmsg_end(msg, hdr);
// 将消息广播给所有订阅 thermal generic netlink 组的用户进程
// 用户空间可以通过 genetlink socket 接收 thermal 事件,比如 tz create/destroy, trip trigger 等
genlmsg_multicast(&thermal_gnl_family, msg, 0, 1, GFP_KERNEL);
return 0;
out_cancel_msg:
genlmsg_cancel(msg, hdr);
out_free_msg:
nlmsg_free(msg);
return ret;
}当内核创建一个新的 thermal zone 时,用户空间会收到一个 netlink 事件通知,携带该 zone 的 id 和 name。
2.1.4 归纳梳理
(1)得到了什么?------ thermal zone 对象
整个注册过程,从 thermal_sensor 注册 thermal zone 对象开始,始终都是要返回一个 thermal_zone_device * 指针。因此,后续对 thermal zone 的操作都是基于这个指针对象来进行的。去掉不必要的信息,简化如下:
c
// 用个指针指向这样一个结构体对象,装载众多信息
struct thermal_zone_device {
...
// 通过这个thermal zone函数回调集合,能够轻松通过 ops 指针这个执行想要的行为。
// 这就是指针的遍历。
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;
// thermal zone的一些参数,随用随取
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;
// 绑定一个 governor 对象,通过thermal zone就能找到自己的governor,不乱不错很迅速
struct thermal_governor *governor;
...
};(2)thermal_zone ops 回调绑定
thermal_zone_device_ops 对应这一堆回调函数,在不同的地方,搞一个 "tz->ops->xxx" 就开始调用了。下面就把这梳理以下,都是什么回调:
- ops->bind / ops->unbind
c
static struct thermal_zone_device *thermal_of_zone_register(struct device_node *sensor,
int id, void *data,
const struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops)
{
of_ops->bind = thermal_of_bind;
of_ops->unbind = thermal_of_unbind;
}- ops->get_temp / ops->set_trips
将 rockchip_of_thermal_ops 作为参数传入devm_thermal_of_zone_register。
c
static const struct thermal_zone_device_ops rockchip_of_thermal_ops = {
.get_temp = rockchip_thermal_get_temp,
.set_trips = rockchip_thermal_set_trips,
};- ops->critical
c
struct thermal_zone_device *
thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips(const char *type, struct thermal_trip *trips,
int num_trips, int mask,
void *devdata, struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops,
const struct thermal_zone_params *tzp, int passive_delay,
int polling_delay)
{
if (!ops->critical)
ops->critical = thermal_zone_device_critical;
}2.2 cooling device 注册
以 devfreq cooling 注册来看,如下:
c
devfreq_cooling_register
↓
of_devfreq_cooling_register_power
↓
thermal_of_cooling_device_register2.2.1 thermal_of_cooling_device_register
注册一个 cooling device(冷却设备,例如 CPUFreq、GPUIfreq、风扇等)到 thermal framework,使其可以被 thermal zone 调度使用。
c
/**
* thermal_of_cooling_device_register() - register an OF thermal cooling device
* @np: a pointer to a device tree node.
* @type: the thermal cooling device type.
* @devdata: device private data.
* @ops: standard thermal cooling devices callbacks.
*
* This function will register a cooling device with device tree node reference.
* This interface function adds a new thermal cooling device (fan/processor/...)
* to /sys/class/thermal/ folder as cooling_device[0-*]. It tries to bind itself
* to all the thermal zone devices registered at the same time.
*
* Return: a pointer to the created struct thermal_cooling_device or an
* ERR_PTR. Caller must check return value with IS_ERR*() helpers.
*/
struct thermal_cooling_device *
thermal_of_cooling_device_register(struct device_node *np,
const char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
{
return __thermal_cooling_device_register(np, type, devdata, ops);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(thermal_of_cooling_device_register);thermal_of_cooling_device_register做一次外部封装,EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL 说明这是 GPL-only 内核导出符号,驱动开发者可直接调用。
实际实现注册功能的函数是 __thermal_cooling_device_register 。
参数说明:
- struct device_node *np → cooling device 对应的设备树节点(可能为 NULL)。
- char *type → cooling device 类型字符串(如 "cpufreq", "gpu", "fan")。
- void *devdata → 驱动传入的私有数据指针(比如 CPU 的 policy、GPU 的控制句柄)。
- struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops → cooling device 的操作函数集(必须提供 get_max_state、get_cur_state、set_cur_state)。
c
/**
* __thermal_cooling_device_register() - register a new thermal cooling device
* @np: a pointer to a device tree node.
* @type: the thermal cooling device type.
* @devdata: device private data.
* @ops: standard thermal cooling devices callbacks.
*
* This interface function adds a new thermal cooling device (fan/processor/...)
* to /sys/class/thermal/ folder as cooling_device[0-*]. It tries to bind itself
* to all the thermal zone devices registered at the same time.
* It also gives the opportunity to link the cooling device to a device tree
* node, so that it can be bound to a thermal zone created out of device tree.
*
* Return: a pointer to the created struct thermal_cooling_device or an
* ERR_PTR. Caller must check return value with IS_ERR*() helpers.
*/
static struct thermal_cooling_device *
__thermal_cooling_device_register(struct device_node *np,
const char *type, void *devdata,
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops)
{
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev; // cooling device 对象
struct thermal_zone_device *pos = NULL; // thermal zone,更建议改一下名字,易混淆。
int id, ret;
// 校验 ops,至少要实现 3 个核心方法:
// get_max_state() → 最大冷却级别。get_cur_state() → 当前状态。set_cur_state() → 设置状态。
if (!ops || !ops->get_max_state || !ops->get_cur_state ||
!ops->set_cur_state)
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
if (!thermal_class)
return ERR_PTR(-ENODEV);
// 分配一个 struct thermal_cooling_device 结构体
cdev = kzalloc(sizeof(*cdev), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdev)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
// 使用 IDA 分配唯一 ID(如 0, 1, 2...),给 cooling device 命名时使用
ret = ida_alloc(&thermal_cdev_ida, GFP_KERNEL);
if (ret < 0)
goto out_kfree_cdev;
cdev->id = ret;
id = ret;
// cdev->type → cooling device 类型字符串
cdev->type = kstrdup(type ? type : "", GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cdev->type) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out_ida_remove;
}
mutex_init(&cdev->lock);
// thermal_instances 链表(存储它和各个 thermal zone 的绑定关系
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cdev->thermal_instances);
// 设置 ops、设备树节点、devdata等
cdev->np = np;
cdev->ops = ops;
cdev->updated = false;
cdev->device.class = thermal_class;
cdev->devdata = devdata;
// 调用驱动提供的 get_max_state() 填充最大状态值
ret = cdev->ops->get_max_state(cdev, &cdev->max_state);
if (ret)
goto out_cdev_type;
// 在 /sys/class/thermal/cooling_deviceX/ 下创建属性文件节点
thermal_cooling_device_setup_sysfs(cdev);
// 给 device 命名,比如 "cooling_device0"
ret = dev_set_name(&cdev->device, "cooling_device%d", cdev->id);
if (ret)
goto out_cooling_dev;
// 注册到内核设备模型,挂到 /sys/devices/virtual/thermal/
ret = device_register(&cdev->device);
if (ret) {
/* thermal_release() handles rest of the cleanup */
put_device(&cdev->device);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}
/* Add 'this' new cdev to the global cdev list */
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
// 把新注册的 cooling device 加入全局链表 thermal_cdev_list
list_add(&cdev->node, &thermal_cdev_list);
/* Update binding information for 'this' new cdev */
// bind_cdev(cdev) 会尝试将该 cdev 与已有的 thermal zone 绑定
// 》》》》》》》》》 重要的!!!
bind_cdev(cdev);
// 遍历全局 thermal_tz_list,已注册的 thermal zones。从thermal zone列表中找。
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node)
// 如果某个 thermal zone 需要更新(need_update=1),就调用 thermal_zone_device_update()
// thermal zone 设置这个值,这里可以用。
if (atomic_cmpxchg(&pos->need_update, 1, 0))
// 重新检查温度并可能重新分配冷却策略
thermal_zone_device_update(pos,
THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
return cdev;
out_cooling_dev:
thermal_cooling_device_destroy_sysfs(cdev);
out_cdev_type:
kfree(cdev->type);
out_ida_remove:
ida_free(&thermal_cdev_ida, id);
out_kfree_cdev:
kfree(cdev);
return ERR_PTR(ret);
}【总结流程】
- 校验 ops → 必须支持 get_max_state/get_cur_state/set_cur_state。
- 分配 cooling device 结构体和 ID。
- 设置类型、ops、devdata。
- 查询最大状态值。
- 创建 sysfs 节点。
- 注册到内核设备模型,出现在 /sys/class/thermal/cooling_deviceX。
- 加入全局 thermal_cdev_list,尝试绑定到已有 thermal zone。
- 通知所有 thermal zone 更新策略。
2.2.2 thermal_cooling_device_setup_sysfs
cooling device 注册过程中 给 sysfs 准备属性文件 的关键逻辑。
c
void thermal_cooling_device_setup_sysfs(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
cooling_device_stats_setup(cdev);
cdev->device.groups = cooling_device_attr_groups;
}主要工作:
- 调用 cooling_device_stats_setup(cdev):为该 cooling device 设置统计结构体,并准备统计类的sysfs 属性。
- 设置 cdev->device.groups:将属性组数组挂到 cdev->device,这样 device_register() 时,sysfs 会自动在 /sys/class/thermal/cooling_deviceX/ 下创建这些文件。
核心的函数实现,如下:
c
static void cooling_device_stats_setup(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
// 指向统计信息的 sysfs 属性组
const struct attribute_group *stats_attr_group = NULL;
struct cooling_dev_stats *stats;
/* Total number of states is highest state + 1 */
// cooling device 的状态数(最大状态 + 1)
unsigned long states = cdev->max_state + 1;
int var;
// 计算分配内存的大小
var = sizeof(*stats); // struct cooling_dev_stats 本体大小
var += sizeof(*stats->time_in_state) * states; // 每个状态停留的时间
var += sizeof(*stats->trans_table) * states * states; // 状态迁移表,统计从某个状态切换到另一个状态的次数
stats = kzalloc(var, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!stats)
goto out;
stats->time_in_state = (ktime_t *)(stats + 1); // 指向 stats 结构体后面的数组
stats->trans_table = (unsigned int *)(stats->time_in_state + states); // trans_table 紧接着 time_in_state 数组
cdev->stats = stats; // 把统计结构挂到 cooling device
stats->last_time = ktime_get(); // 记录当前时间,便于后续计算停留时间
spin_lock_init(&stats->lock);
// 指向 cooling_device_stats_attr_group,说明要给 sysfs 增加统计相关的属性组
stats_attr_group = &cooling_device_stats_attr_group;
out:
/* Fill the empty slot left in cooling_device_attr_groups */
// cooling_device_attr_groups 是 cooling device 的 sysfs 属性组数组
// 数组里预留了一个空位(倒数第 2 个位置),专门用来放统计信息属性组
var = ARRAY_SIZE(cooling_device_attr_groups) - 2;
cooling_device_attr_groups[var] = stats_attr_group;
}2.2.3 归纳梳理
thermal_cooling_device 注册完成,得到thermal_cooling_device 类型的指针。最重要的是在thermal_cooling_device 有一个 const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops 成员。后续,通过thermal zone 找到 cooling device 就可以拿到 thermal_cooling_device_ops 。
c
struct thermal_cooling_device *
of_devfreq_cooling_register_power(struct device_node *np, struct devfreq *df,
struct devfreq_cooling_power *dfc_power)
{
...
ops = &dfc->cooling_ops;
ops->get_max_state = devfreq_cooling_get_max_state;
ops->get_cur_state = devfreq_cooling_get_cur_state;
ops->set_cur_state = devfreq_cooling_set_cur_state;
em = em_pd_get(dev);
if (em && !em_is_artificial(em)) {
dfc->em_pd = em;
ops->get_requested_power =
devfreq_cooling_get_requested_power;
ops->state2power = devfreq_cooling_state2power;
ops->power2state = devfreq_cooling_power2state;
dfc->power_ops = dfc_power;
num_opps = em_pd_nr_perf_states(dfc->em_pd);
}
...
}同样,governor也可以更好操作 thermal_cooling_device_ops。后面在 governor 中也能找到 这两者的关系。
2.3 governor 注册
governor 注册过程:
c
thermal_init // thermal core 初始化函数
↓
thermal_register_governors
↓
thermal_register_governor2.3.1 __init thermal_register_governors
__init:这是内核初始化段函数(only used during init):执行完后其内存可被回收。该函数通常在内核启动或模块初始化里被调用。
c
static int __init thermal_register_governors(void)
{
int ret = 0;
struct thermal_governor **governor; // *(*governor) 指针的指针,这样好理解。可以表示一个thermal_governor 数组了。
// for_each_governor_table 迭代注册表中每个 governor 条目
// governor 指向表中当前元素的地址, *governor 是当前(struct thermal_governor *)指针对象
// 二级指针,可以接把迭代变量表示为数组元素的地址。然后*governor就是我们要的thermal_governor型指针了。
for_each_governor_table(governor) {
ret = thermal_register_governor(*governor); // 调用注册函数
if (ret) {
// ret > 0,表示注册失败,能拿到一个 governor 地址
pr_err("Failed to register governor: '%s'",
(*governor)->name); // 打印失败 governor 名字
break;
}
pr_info("Registered thermal governor '%s'",
(*governor)->name); // 打印成功 governor 名字
}
if (ret) {
struct thermal_governor **gov;
// 之前保存了失败 governor 的地址,因为变量命名问题,导致地址变量名与Governor策略对象容易混淆。
// 遍历注册表,有机会对所有的 Governor 遍历一下
for_each_governor_table(gov) {
// 匹配一下失败的地址,是不是当前的遍历位置。通俗的说,背锅到人。
if (gov == governor)
break;
// 不是有问题的 governor,释放后就可以通过了。
thermal_unregister_governor(*gov);
}
}
return ret;
}需要注意,for_each_governor_table 这个宏定义如下:
c
// path: drivers/thermal/thermal_core.h
#define for_each_governor_table(__governor) \
for (__governor = __governor_thermal_table; \
__governor < __governor_thermal_table_end; \
__governor++)2.3.2 thermal_register_governor
单个 governor 的注册函数。负责把 governor 插入全局 governor 列表、设定默认 governor(如果匹配),并为当前系统中未设 governor 但在 tzp 中指定了 governor_name 的 thermal zone 分配该 governor。
c
int thermal_register_governor(struct thermal_governor *governor)
{
int err;
const char *name;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos; // 单个 thermal zone 对象
// 有效性判断
if (!governor)
return -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&thermal_governor_lock);
err = -EBUSY;
// 根据governor的名称检索是否存在
if (!__find_governor(governor->name)) {
bool match_default;
err = 0;
// 将此 governor 加入内核链表 thermal_governor_list
// list_add 是将元素插入到链表头(LIFO);因此注册顺序与链表顺序会倒置,后来居上的倒序表。
list_add(&governor->governor_list, &thermal_governor_list);
// 用 strncmp(区分大小写)比较前 THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH 字符是否与预定义默认名相等
// strncmp 返回 0 表示相等
match_default = !strncmp(governor->name,
DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR,
THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH);
// 符合要求,就设置该governor作为默认的governor
if (!def_governor && match_default)
def_governor = governor;
}
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
// 遍历 thermal zone 列表
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
/*
* only thermal zones with specified tz->tzp->governor_name
* may run with tz->govenor unset
*/
// 如果 zone 已经有 governor(即已经被设置),跳过,不做覆盖
if (pos->governor)
continue;
// thermal_zone_device -> thermal_zone_params -> char governor_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH]
// 获取名字
name = pos->tzp->governor_name;
// thermal_zone 的 governor 与当前 governor 的名字进行比较
if (!strncasecmp(name, governor->name, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH)) {
// 若相等(strncasecmp 返回 0),配对成功,开始搞事。
int ret;
// 调用 thermal_set_governor() 将该 zone 的 governor 设置为当前注册进来的 governor
ret = thermal_set_governor(pos, governor);
if (ret)
dev_err(&pos->device,
"Failed to set governor %s for thermal zone %s: %d\n",
governor->name, pos->type, ret);
}
}
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
mutex_unlock(&thermal_governor_lock);
return err;
}调用 thermal_set_governor() 要求 thermal zone 配置的 governor 名字(字符串)必须和注册进来的 governor 的名字匹配,才会进行绑定。否则不会调用 thermal_set_governor()。
thermal zone 的 governor 必须和注册 governor 的名字匹配,否则不会自动设置 governor。thermal zone 的 governor 名称是在 zone 创建时就指定的(比如从设备树里读取 governor-name 字段)。系统启动时,内核会遍历所有注册 governor,把它们和 thermal zone 的配置名字做匹配,只有名字一致的才会被绑定。
【举例】
c
cpu_thermal: cpu-thermal {
polling-delay-passive = <250>;
polling-delay = <1000>;
thermal-sensors = <&cpu_sensor 0>;
sustainable-power = <2000>;
governor-name = "power_allocator";
};当 power_allocator governor 注册时,thermal_register_governor("power_allocator") 会遍历所有 thermal zone,找到 cpu-thermal 的 governor_name == "power_allocator",就会执行 thermal_set_governor(cpu_thermal, power_allocator)。
如果其他的 zone 如果写了 "step_wise",就只能等 step_wise governor 注册时才会匹配成功。
2.3.3 thermal_set_governor
把某个 thermal zone 绑定到一个新的 thermal governor 上,也就是给这个温控区域选择具体的调节策略。
参数说明:
- tz: struct thermal_zone_device *,代表一个 thermal zone(温控区域,比如 CPU、GPU的温度监控点)。
- new_gov: struct thermal_governor *,新的 governor 策略(如 step_wise、fair_share、user_space、power_allocator 等)。
c
/**
* thermal_set_governor() - Switch to another governor
* @tz: a valid pointer to a struct thermal_zone_device
* @new_gov: pointer to the new governor
*
* Change the governor of thermal zone @tz.
*
* Return: 0 on success, an error if the new governor's bind_to_tz() failed.
*/
static int thermal_set_governor(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
struct thermal_governor *new_gov)
{
int ret = 0; // 返回值,初始化为 0,表示默认成功
// 旧 governor 的解绑
if (tz->governor && tz->governor->unbind_from_tz)
// governor 提供了 unbind_from_tz 回调函数
// 以 power_allocator 为例就是 power_allocator_unbind
tz->governor->unbind_from_tz(tz);
// 新 governor 的绑定
if (new_gov && new_gov->bind_to_tz) {
// 以 power_allocator 为例就是 power_allocator_bind
ret = new_gov->bind_to_tz(tz);
if (ret) {
// 调用 bind_previous_governor(tz, new_gov->name) 尝试回退(重新绑定到之前的 governor,保证系统不丧失控制能力)
bind_previous_governor(tz, new_gov->name);
return ret;
}
}
// 如果绑定成功,就更新 tz->governor 指针,表示 thermal zone 已经切换到新的 governor
tz->governor = new_gov;
return ret;
}继续看下 bind_previous_governor:
c
/**
* bind_previous_governor() - bind the previous governor of the thermal zone
* @tz: a valid pointer to a struct thermal_zone_device
* @failed_gov_name: the name of the governor that failed to register
*
* Register the previous governor of the thermal zone after a new
* governor has failed to be bound.
*/
static void bind_previous_governor(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
const char *failed_gov_name)
{
if (tz->governor && tz->governor->bind_to_tz) {
// 以 power_allocator 为例就是 power_allocator_bind
if (tz->governor->bind_to_tz(tz)) {
dev_err(&tz->device,
"governor %s failed to bind and the previous one (%s) failed to bind again, thermal zone %s has no governor\n",
failed_gov_name, tz->governor->name, tz->type);
tz->governor = NULL; `
}
}
}2.3.4 归纳梳理
注册时序如下图:
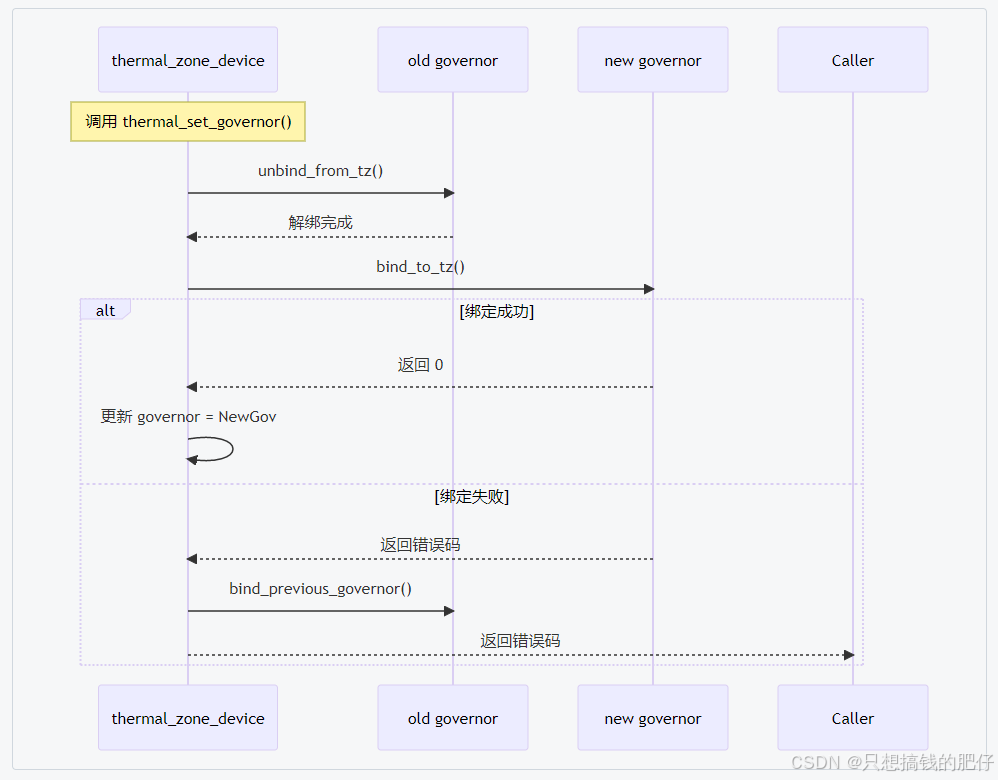
【问】
如果 tz->tzp->governor_name 配置了一个不存在的 governor 名称,会发生什么情况?
① thermal zone 创建时(thermal_zone_device_register())当一个 thermal zone 被注册时,会把 tzp->governor_name 赋值到 tz->tzp->governor_name。此时并不会立刻检查这个名字是否存在对应的 governor。
② governor 注册流程(thermal_register_governor())注册 governor 时,会尝试去匹配还没有绑定 governor 的 thermal zone。如果 tzp->governor_name 写的是一个不存在的名字(比如 "foobar"),那么在 governor 注册过程中 不会有任何 governor 名称匹配成功,因此 tz->governor 仍然是 NULL。
③ 只有明确指定 governor 名称的 zone,才可能出现 governor 为空的情况。thermal 框架的核心是定时轮询传感器温度,然后通过 governor 决定 cooling device 的限制级别。如果 tz->governor == NULL,那这个 zone 就无法做出调节动作,等于"监控但不干预"。
④ 在 thermal_register_governor() 中match_default = !strncmp(governor->name, DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR, THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH) 如果 tzp->governor_name 没写(为空) → 内核会尝试用 def_governor 来填充。有可能在编译时定义的 DEFAULT_THERMAL_GOVERNOR(通常是 "step_wise",需要找代码的)标记为全局的默认 governor。
⑤ 实际运行效果:thermal zone 会继续运行,传感器还能上报温度。但由于没有 governor 绑定,调节 cooling device 的环节失效,相当于"监控但不控温"。内核日志不会报错,只会静悄悄地没有 governor。
2.4 模块关系
对于 thermal zone、cooling device 和 thermal governor 的关系逻辑确定,必须要关注到 thermal_instance,结合这个结构体,我们继续分析:
2.4.1 thermal_instance
从结构体注释看:
thermal_zone_device 负责监测温度(温度传感器)。
thermal_cooling_device 负责降温(CPU/GPU 降频、风扇、限速)。
thermal_instance 负责把二者在一个 trip point 上绑定起来,并且携带这个绑定关系的上下文信息。
c
/*
* This structure is used to describe the behavior of
* a certain cooling device on a certain trip point
* in a certain thermal zone
*/
struct thermal_instance {
int id; // 唯一 ID,在内核中分配,主要用于区分不同 instance
char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH]; // 名称,通常由 zone 类型 + cdev 类型 + trip 点信息拼接而成,用于调试和 sysfs 命名
struct thermal_zone_device *tz; // 指向 thermal zone。说明这个 instance 是属于哪个 thermal zone 的。
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev; // 指向 cooling device。说明这个 instance 控制的具体冷却设备是谁。
const struct thermal_trip *trip; // trip 点描述。即 "在某个温度阈值触发时执行的 cooling 策略"。
bool initialized; // 表示该 instance 是否已经初始化完成
// upper = 最大可用的 cooling state
unsigned long upper; /* Highest cooling state for this trip point */
// lower = 最小可用的 cooling state
unsigned long lower; /* Lowest cooling state for this trip point */
// governor 计算出的 目标 cooling state
unsigned long target; /* expected cooling state */
// sysfs 的 权重属性
char attr_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device_attribute attr;
char weight_attr_name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH];
struct device_attribute weight_attr;
// 把这个 instance 挂到 thermal zone 的 tz->thermal_instances 链表里
struct list_head tz_node; /* node in tz->thermal_instances */
// 把这个 instance 挂到 cooling device 的 cdev->thermal_instances 链表里
struct list_head cdev_node; /* node in cdev->thermal_instances */
// 权重值(相对值),用于 governor 在多 cooling device 下分配 cooling target 时的比例因子
unsigned int weight; /* The weight of the cooling device */
bool upper_no_limit;
};thermal_instance 就是一个 "绑定关系",定义:在某个 trip 上,把某个 cooling device 绑定进来,并带上上下限、权重、target state 等运行时数据。
最终,governor 在每次温度超阈时,会遍历 tz->thermal_instances,算出每个 instance 的 target,再调用对应 cdev 的 .set_cur_state()。
2.4.2 bind list
thermal zone、cooling device 通过 thermal_instances 建立对象list,进一步看下这些list怎么组成,怎样添加数据。
(1)list_head
① struct list_head
内核的双向循环链表通用头,定义很短。
c
// path:include/linux/types.h。
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};这是一个双向且环形(circular)的链表实现:链表头本身也是一个 struct list_head 节点,空表时 head->next == head 且 head->prev == head。把 struct list_head 放到其它结构体里,使那个结构体能被挂到相应的链表上。
为什么要这样设计?
Linux 的链表是 环形双向链表。链表头不是"哑节点",而是真正的节点,只是它不存放业务数据。
② INIT_LIST_HEAD
c
// path: include/linux/list.h
/**
* INIT_LIST_HEAD - Initialize a list_head structure
* @list: list_head structure to be initialized.
*
* Initializes the list_head to point to itself. If it is a list header,
* the result is an empty list.
*/
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
WRITE_ONCE(list->next, list); // 宏 WRITE_ONCE(x, val) 相当于 list->next = list;
WRITE_ONCE(list->prev, list); // 相当于 list->prev = list;
}初始化后的结构,假设 struct list_head head;,执行 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&head) 后:
head->next == head,head->prev == head 表示这是一个空链表。
关键定义:
c
// drivers/thermal/thermal_core.c
thermal_core.c:892: INIT_LIST_HEAD(&cdev->thermal_instances);
thermal_core.c:1299: INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tz->thermal_instances);
thermal_core.c:1300: INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tz->node);③ list_add
插入到 head 之后(链表头部插入)。
c
/*
* Insert a new entry between two known consecutive entries.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
if (!__list_add_valid(new, prev, next))
return;
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
WRITE_ONCE(prev->next, new);
}
/**
* list_add - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it after
*
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
*/
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}④ list_for_each_entry
正向遍历(不在循环中删除当前元素)。
c
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_head within the struct.
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_first_entry(head, typeof(*pos), member); \
!list_entry_is_head(pos, head, member); \
pos = list_next_entry(pos, member))⑤ LIST_HEAD
c
/*
* Circular doubly linked list implementation.
*
* Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when
* manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as
* sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can
* generate better code by using them directly rather than
* using the generic single-entry routines.
*/
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)重要的 thermal list,都是全局定义:
c
// drivers/thermal/thermal_core.c
static LIST_HEAD(thermal_tz_list); // thermal zone 列表
static LIST_HEAD(thermal_cdev_list); // cooling device 列表
static LIST_HEAD(thermal_governor_list); // thermal governor 列表(2)bind_tz
bind_tz() 的作用是:当一个新的 thermal zone 注册时,尝试把它绑定到系统中所有已存在的 cooling device。
c
static void bind_tz(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
int ret;
struct thermal_cooling_device *pos = NULL;
// 判断thermal zone的ops中是否有绑定bind函数
if (!tz->ops->bind)
return;
mutex_lock(&thermal_list_lock);
// 遍历 全局 thermal_cdev_list(系统里注册的所有 thermal_cooling_device)
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_cdev_list, node) {
// 执行 thermal zone 的 bind 操作,把遍历的 cdev(cooling device) 绑定到 tz(thermal zone)
ret = tz->ops->bind(tz, pos); // 绑定关系
if (ret)
print_bind_err_msg(tz, pos, ret);
}
mutex_unlock(&thermal_list_lock);
}tz->ops->bind 详解:
- 获取 thermal_zone_device -> thermal_zone_device_ops
- 执行 thermal_zone_device_ops -> bind = thermal_of_bind, thermal_of_zone_register 中 of_ops->bind = thermal_of_bind
(3)bind_cdev
bind_cdev() 的作用是:当一个新的 cooling device 注册时,尝试把它绑定到系统中所有已存在的 thermal zone。
c
static void bind_cdev(struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev)
{
int ret;
struct thermal_zone_device *pos = NULL;
// 遍历 全局 thermal_tz_list(系统里注册的所有 thermal_zone_device)
list_for_each_entry(pos, &thermal_tz_list, node) {
if (pos->ops->bind) {
// 执行 thermal zone 的 bind 操作,把传入的 cdev(cooling device) 绑定到 tz(thermal zone)
ret = pos->ops->bind(pos, cdev); // 绑定关系
if (ret)
print_bind_err_msg(pos, cdev, ret);
}
}
}调用的绑定函数都是 thermal_zone_device -> thermal_zone_device_ops -> bind。不同的是传入参数不同。这样,可以适配不同的使用场景。
2.4.3 关系梳理
(1)关系说明
简化一下几个模块的结构体定义,如下:
c
struct thermal_instance {
...
struct thermal_zone_device *tz; // 每个 thermal_instance 存一个关联的 thermal_zone_device
struct thermal_cooling_device *cdev; // 每个 thermal_instance 存一个关联的 thermal_cooling_device
const struct thermal_trip *trip;
struct device_attribute weight_attr;
/* node in tz->thermal_instances */
struct list_head tz_node; // 给 thermal_zone_device 存储用的标识
/* node in cdev->thermal_instances */
struct list_head cdev_node; // 给 thermal_cooling_device 存储用的标识
...
};
struct thermal_cooling_device {
...
const struct thermal_cooling_device_ops *ops;
struct list_head thermal_instances; // 一个链表,存着struct thermal_instance的cdev_node,这样就是一串tz_node,标识着不同的thermal_instance对象
struct list_head node;
};
struct thermal_zone_device {
...
struct thermal_zone_device_ops *ops;
struct thermal_zone_params *tzp;
struct thermal_governor *governor; // thermal_zone_device 绑定着的thermal_governor
struct list_head thermal_instances; // 一个链表,存着struct thermal_instance的tz_node,这样就是一串tz_node,标识着不同的thermal_instance对象
struct list_head node;
...
};
struct thermal_governor {
char name[THERMAL_NAME_LENGTH]; // thermal_governor 名称,能标识这个策略的,用于取数据
int (*bind_to_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz);
void (*unbind_from_tz)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz);
int (*throttle)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip);
struct list_head governor_list; // governor 策略实例的集合
};归纳如下:
- ① 这些结构体的list_head成员怎么初始化,前面有描述,不多阐述
- ② thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device 中,list_add_tail(&dev->tz_node, &tz->thermal_instances) 将thermal_instance->tz_node,添加到 thermal_zone_device->thermal_instances 下面,串成链表
- ③ thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device 中,list_add_tail(&dev->cdev_node, &cdev->thermal_instances) 将 thermal_instance->cdev_node,添加到 thermal_cooling_device->thermal_instances 下面,串成链表
- ④ thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device 中,把 thermal_cooling_device、thermal_zone_device 赋值给 thermal_instance 的 *tz、*cdev。至此,达成三者桥接。
- ⑤ thermal_zone_device 中有个 thermal_governor,这样三大模块关联在一起。
(2)通俗易懂解释
① thermal子系统这些结构体都是存放内存中的,每个变量值、变量结构体都是有地址的,互相包含也没关系,都是指针获取地址,不存在重复套娃定义,初始化后的对象地址不会错乱,无论怎么包含还是那个地址对应的对象。
② struct list_head 这些变量,涉及到相互挂在问题,看似难以理解,打个比方就跟小说里元婴修士在长老会挂职一样。在小团队中挂了职位,直接找到对应的负责人后,让具体的人把事情带走。大佬配上几个小弟,小弟需要到处填坑,毕竟大佬不需要干活,小弟需要干多分工作的。
套用到thermal系统就是:
- thermal子系统中,thermal_cooling_device,thermal_zone_device 都在 thermal_instance 挂个名,以后有事都可以找到 thermal_instance。
- thermal_cooling_device,thermal_zone_device 都可以通过 thermal_instance 找到对方,thermal_instance 是一个小弟,每个小弟有自己指定的 2 个分管大佬,不是随便乱改的。
- thermal_cooling_device,thermal_zone_device 都是大佬,底下必须要有一些小弟干活,struct list_head thermal_instances 一串小弟都在这里集合,花名册拿在手。
- 两个大佬 thermal_cooling_device,thermal_zone_device 碰面了,总归有大长老、二长老的分别,那么很简单thermal系统中,thermal_zone_device-大长老,thermal_cooling_device-二长老
- thermal_cooling_device,thermal_zone_device两个大佬,重要工作会------thermal_zone_bind_cooling_device。
- thermal_zone_device 找来自己所有的小弟【list_for_each_entry(pos, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node)】,仔细筛选。发现有些人也是 thermal_cooling_device 的心腹【if (pos->tz == tz && pos->trip == trip && pos->cdev == cdev)】,那还说啥,自己人放一边去。
- 但如果 thermal_zone_device 的小弟,不是 thermal_cooling_device 的小弟,赶紧派过去【list_add_tail(&dev->tz_node, &tz->thermal_instances);list_add_tail(&dev->cdev_node, &cdev->thermal_instances);】以后好办事。
- 最后发个广播【atomic_set(&tz->need_update, 1)】,小弟参与啥啥啥的工作,各方面注意。
3 温控管理逻辑
thermal 子系统通过轮询的方式,触发温度数据获取,来进行温控条件的判断并确认是否开始降温措施。接下来,就看下如何轮询温度、触发温控。
3.1 轮询机制
3.1.1 thermal_zone_device_check
通过 thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips 注册 thermal_zone 节点时,INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&tz->poll_queue, thermal_zone_device_check);
在delay时间结束时,可以回调 thermal_zone_device_check 函数。执行如下:
c
static void thermal_zone_device_check(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct thermal_zone_device *tz = container_of(work, struct
thermal_zone_device,
poll_queue.work);
thermal_zone_device_update(tz, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED); // 执行thermal zone更新
}3.1.2 thermal_zone_device_update
Linux thermal 子系统中核心的温度更新与调度函。
c
void thermal_zone_device_update(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
enum thermal_notify_event event)
{
mutex_lock(&tz->lock);
if (thermal_zone_is_present(tz)) // 确认 tz 对应的热区(thermal zone)是否仍然存在
__thermal_zone_device_update(tz, event);
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(thermal_zone_device_update);
void __thermal_zone_device_update(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
enum thermal_notify_event event)
{
int count;
if (tz->suspended) // 检查是否 suspend。如果系统挂起 (suspend),则不再更新温度。
return;
// thermal zone 必须提供 get_temp() 回调,否则无法获取温度。
if (WARN_ONCE(!tz->ops->get_temp,
"'%s' must not be called without 'get_temp' ops set\n",
__func__))
return;
// 检查 thermal zone 是否启用
if (!thermal_zone_device_is_enabled(tz))
return;
// 更新温度,调用 tz->ops->get_temp() 获取当前温度。
update_temperature(tz);
// 设置 trip point
__thermal_zone_set_trips(tz);
tz->notify_event = event;
// 遍历所有 trip point(临界温度点)
for (count = 0; count < tz->num_trips; count++)
handle_thermal_trip(tz, count); //逐个处理 trip 点
// 启动/调整监控定时器,用于定期更新。保证 thermal zone 持续监控温度变化。
monitor_thermal_zone(tz);
}3.1.3 monitor_thermal_zone
monitor_thermal_zone 启动/调整监控定时器,用于定期更新。进一步调用 thermal_zone_device_set_polling 配合真延迟时间,进行轮询回调。
c
static void monitor_thermal_zone(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
if (tz->mode != THERMAL_DEVICE_ENABLED)
thermal_zone_device_set_polling(tz, 0);
else if (tz->passive)
thermal_zone_device_set_polling(tz, tz->passive_delay_jiffies); // 高温轮询
else if (tz->polling_delay_jiffies)
thermal_zone_device_set_polling(tz, tz->polling_delay_jiffies); // 常规轮询
}
static void thermal_zone_device_set_polling(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
unsigned long delay)
{
// 执行或不执行delay,之后执行操作(看有没有),再做回调tz->poll_queue,即回调thermal_zone_device_check
if (delay)
mod_delayed_work(system_freezable_power_efficient_wq,
&tz->poll_queue, delay);
else
cancel_delayed_work(&tz->poll_queue);
}至此,轮询机制形成闭环。可以通过此方式,反复获取温度。
对于温度来源(update_temperature)和 温控临界点处理(handle_thermal_trip)下一步看。
3.2 温控触发
在轮询机制中,就调用 handle_thermal_trip 来处理所有遍历的 trip point。以此入口,逐步分析:
3.2.1 handle_thermal_trip
handle_thermal_trip 的职责是:
- 判断当前温度是否触发了 trip point
- 通知用户空间或内核其他部分
- 调用合适的 cooling 策略
参数说明:
thermal_zone_device *tz:当前的 thermal zone(热区)。
int trip_id:trip point 索引。
c
static void handle_thermal_trip(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip_id)
{
struct thermal_trip trip; // 临时存放该 trip 的配置
/* Ignore disabled trip points */
// 检查该 trip 是否被禁用
if (test_bit(trip_id, &tz->trips_disabled))
return; // 如果该 trip 被禁用,直接退出。
// 从 thermal zone 获取 trip 配置(温度阈值、hysteresis、类型等)。
__thermal_zone_get_trip(tz, trip_id, &trip);
// 无效温度,退出
if (trip.temperature == THERMAL_TEMP_INVALID)
return;
// 判断上一次温度数据是否有效,需要判断温度变化趋势
if (tz->last_temperature != THERMAL_TEMP_INVALID) {
// 温度上升
if (tz->last_temperature < trip.temperature &&
tz->temperature >= trip.temperature)
thermal_notify_tz_trip_up(tz->id, trip_id,
tz->temperature);
// 温度下降
// hysteresis(滞后)防止温度在边界来回抖动,不断触发上下事件。
if (tz->last_temperature >= trip.temperature &&
tz->temperature < (trip.temperature - trip.hysteresis))
thermal_notify_tz_trip_down(tz->id, trip_id,
tz->temperature);
}
// 关键级 trip (THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL, THERMAL_TRIP_HOT)
if (trip.type == THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL || trip.type == THERMAL_TRIP_HOT)
handle_critical_trips(tz, trip_id, trip.temperature, trip.type);
else
// 非关键级 trip(如 PASSIVE、ACTIVE)
handle_non_critical_trips(tz, trip_id);
}3.2.2 handle_critical_trips
调用 handle_critical_trips() 通常是立即关机、重启、进入紧急保护状态(避免硬件损坏)。
c
static void handle_critical_trips(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
int trip, int trip_temp, enum thermal_trip_type trip_type)
{
/* If we have not crossed the trip_temp, we do not care. */
if (trip_temp <= 0 || tz->temperature < trip_temp)
return;
trace_thermal_zone_trip(tz, trip, trip_type);
// 执行thermal_zone_device_ops的回调函数
if (trip_type == THERMAL_TRIP_HOT && tz->ops->hot)
tz->ops->hot(tz);
else if (trip_type == THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL)
tz->ops->critical(tz);
}其中 hot 回调没有看到绑定关系,但是 critical 的回调函数,直接指向 thermal_zone_device_critical,在thermal_zone_device_register_with_trips中绑定回调的(ops->critical = thermal_zone_device_critical)。继续,
c
void thermal_zone_device_critical(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
/*
* poweroff_delay_ms must be a carefully profiled positive value.
* Its a must for forced_emergency_poweroff_work to be scheduled.
*/
int poweroff_delay_ms = CONFIG_THERMAL_EMERGENCY_POWEROFF_DELAY_MS;
dev_emerg(&tz->device, "%s: critical temperature reached, "
"shutting down\n", tz->type);
// 执行高温关机,有个delay时间
hw_protection_shutdown("Temperature too high", poweroff_delay_ms);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL(thermal_zone_device_critical);3.2.3 handle_non_critical_trips
handle_non_critical_trips 需要 governor 温控策略支持。
c
static void handle_non_critical_trips(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip)
{
tz->governor ? tz->governor->throttle(tz, trip) :
def_governor->throttle(tz, trip);
}如果在注册过程,配置了thermal zone的专属governor,这里就会直接调用,如果没有,使用默认的那个。回调 thermal_governor -> int (*throttle)(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int trip)。
3.2.4 温控执行
以 power_allocator 为例,就回调 power_allocator_throttle 函数,这是在 thermal_gov_power_allocator 添加到平台就绑定好的。接下来就是 power_allocator_throttle 的调用链了,之前有所分析,如下图:
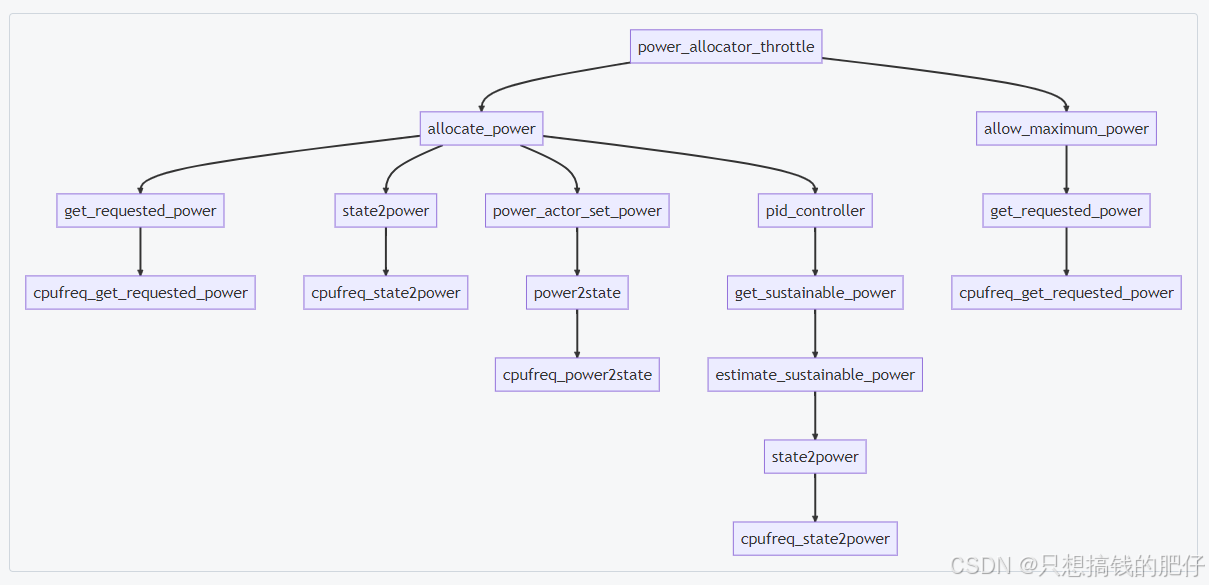
简单看下这条调用逻辑:
c
power_allocator_throttle
↓
allow_maximum_power
↓
↓list_for_each_entry(instance, &tz->thermal_instances, tz_node)
↓
thermal_cooling_device *cdev = instance->cdev
↓
cdev->ops->get_requested_power(cdev, &req_power)
↓
cpufreq_cooling: cpufreq_get_requested_power由此,thermal zone -> cooling device 的温控调用完成一次。
3.3 辅助函数
在上面的过程分析中,部分调用函数,集中在这看一下:
3.3.1 update temperature过程
(1)update_temperature
update_temperature 是 thermal zone 更新当前温度的关键函数。它的任务就是:
- 调用驱动获取温度
- 更新 thermal zone 的温度缓存字段
- 记录 trace 信息
- 通知用户空间(netlink)
c
static void update_temperature(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
int temp, ret;
// 调用 __thermal_zone_get_temp() 从底层获取温度。
ret = __thermal_zone_get_temp(tz, &temp);
if (ret) {
if (ret != -EAGAIN)
dev_warn(&tz->device,
"failed to read out thermal zone (%d)\n",
ret);
return;
}
// 读取成功后,更新刚刚读取到的温度值,保存之前温度值作为last,用于比较温度趋势
tz->last_temperature = tz->temperature;
tz->temperature = temp;
// 记录 tracepoint,用于 ftrace/perf 等内核跟踪
trace_thermal_temperature(tz);
// 通过 generic netlink 向用户空间发送温度采样数据
thermal_genl_sampling_temp(tz->id, temp);
}进一步向下分析:
(2)__thermal_zone_get_temp
c
int __thermal_zone_get_temp(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int *temp)
{
int ret = -EINVAL;
int count;
int crit_temp = INT_MAX;
struct thermal_trip trip;
lockdep_assert_held(&tz->lock);
// 通过 thermal_zone_device+_ops的get_temp函数,读取底层温度
//
ret = tz->ops->get_temp(tz, temp);
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_THERMAL_EMULATION) && tz->emul_temperature) {
for (count = 0; count < tz->num_trips; count++) {
ret = __thermal_zone_get_trip(tz, count, &trip);
if (!ret && trip.type == THERMAL_TRIP_CRITICAL) {
crit_temp = trip.temperature;
break;
}
}
/*
* Only allow emulating a temperature when the real temperature
* is below the critical temperature so that the emulation code
* cannot hide critical conditions.
*/
if (!ret && *temp < crit_temp)
*temp = tz->emul_temperature;
}
if (ret)
dev_dbg(&tz->device, "Failed to get temperature: %d\n", ret);
return ret;
}在thermal zone注册时,就把这个函数传进来了,以就 rockchip_thermal 为例是这个:
c
static const struct thermal_zone_device_ops rockchip_of_thermal_ops = {
.get_temp = rockchip_thermal_get_temp,
.set_trips = rockchip_thermal_set_trips,
};
static int rockchip_thermal_get_temp(struct thermal_zone_device *tz, int *out_temp)
{
struct rockchip_thermal_sensor *sensor = thermal_zone_device_priv(tz);
struct rockchip_thermal_data *thermal = sensor->thermal;
const struct rockchip_tsadc_chip *tsadc = sensor->thermal->chip;
int retval;
retval = tsadc->get_temp(&tsadc->table,
sensor->id, thermal->regs, out_temp);
return retval;
}(3)rk_tsadcv4_get_temp
前文在【thermal sensor】中是以 rk3588_tsadc_data 为例的,此处还以此为例,则 ".get_temp = rk_tsadcv4_get_temp, // 从寄存器读出温度并转换成摄氏度"
c
static int rk_tsadcv4_get_temp(const struct chip_tsadc_table *table,
int chn, void __iomem *regs, int *temp)
{
u32 val;
val = readl_relaxed(regs + TSADCV3_DATA(chn));
// 对照 rk3588_code_table 查表,将寄存器值转换成温度
return rk_tsadcv2_code_to_temp(table, val, temp);
}这样,内核可以拿到温升 sensor 的温度值。
3.3.2 thermal_zone_xxx
thermal_zone 相关的状态函数。
c
// thermal zone 开启
int thermal_zone_device_enable(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
return thermal_zone_device_set_mode(tz, THERMAL_DEVICE_ENABLED);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(thermal_zone_device_enable);
// thermal zone 关闭
int thermal_zone_device_disable(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
return thermal_zone_device_set_mode(tz, THERMAL_DEVICE_DISABLED);
}
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(thermal_zone_device_disable);
// thermal zone 可用判断
int thermal_zone_device_is_enabled(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
lockdep_assert_held(&tz->lock);
return tz->mode == THERMAL_DEVICE_ENABLED;
}
// 对指定的 thermal zone 进行判断
static bool thermal_zone_is_present(struct thermal_zone_device *tz)
{
return !list_empty(&tz->node);
}thermal_zone_device_set_mode(),这是 Linux thermal 框架中用于设置 thermal zone 工作模式的函数。它的主要职责是:
- 启用或禁用 thermal zone
- 调用驱动回调进行模式切换
- 更新当前 thermal zone 的温度状态
- 向用户空间或其他内核模块发出通知
c
static int thermal_zone_device_set_mode(struct thermal_zone_device *tz,
enum thermal_device_mode mode)
{
int ret = 0;
mutex_lock(&tz->lock);
/* do nothing if mode isn't changing */
// 如果新模式和当前 tz->mode 一致,则无需做任何事情
if (mode == tz->mode) {
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
return ret;
}
// 检查 tz 对应的 device 是否已经注册到内核设备模型
if (!device_is_registered(&tz->device)) {
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
return -ENODEV;
}
// 如果驱动提供了 change_mode 回调,就调用它
if (tz->ops->change_mode)
ret = tz->ops->change_mode(tz, mode);
if (!ret)
tz->mode = mode; // 如果 change_mode 执行成功(ret == 0),更新 tz->mode
// 刷新当前 thermal zone 的状态
// 如果启用 → 重新获取温度、处理 trip points。
// 如果禁用 → 也会更新状态,可能停止 cooling device 调用。
__thermal_zone_device_update(tz, THERMAL_EVENT_UNSPECIFIED);
mutex_unlock(&tz->lock);
// 根据新模式,发送通知
if (mode == THERMAL_DEVICE_ENABLED)
thermal_notify_tz_enable(tz->id);
else
thermal_notify_tz_disable(tz->id);
return ret;
}4 总结
4.1 thermal core 的作用
thermal core 是 Linux 内核热管理子系统的核心框架,位于 drivers/thermal/thermal_core.c 等文件中。它的主要职责是:
-
统一框架
提供热管理的基础框架,协调 热源(sensor/zone) 与 散热设备(cooling device)。
将各类硬件温度传感器、风扇、CPU/GPU 降频、设备功耗管理等抽象统一起来。
-
热区管理(Thermal Zone Management)
每个 thermal zone 代表一个热源或逻辑区域(比如 CPU、GPU、battery)。
通过驱动提供的回调函数获取温度、设置 trip point、定义温控策略。
-
冷却设备管理(Cooling Device Management)
定义通用 cooling device 框架,例如 CPUFreq、Devfreq、CPUIdle、风扇控制等。
提供功率限制或性能限制的手段,来降低温度。
-
策略调度(Governor)
内置多种 governor(例如 step_wise、power_allocator、user_space)。
根据当前温度和 trip point,决定如何调整 cooling device。
-
用户空间接口
提供 /sys/class/thermal/ sysfs 节点。
用户空间可以读取温度、trip 信息,并可选择策略或注入用户空间 governor。
支持 UEvent 通知用户空间(如 Android framework thermal service)。
4.2 热管理流程(工作机制)
thermal core 的热管理大体可以分为以下几个步骤:
(1) 注册阶段
- 设备驱动注册 thermal zone(thermal_zone_device_register)。
- 设备驱动注册 cooling device(thermal_cooling_device_register)。
- thermal core 将 zone 与 device 绑定(通过 bind() 回调或 device tree 绑定)。
(2) 监测阶段
- thermal core 定期轮询 thermal zone(或由传感器中断触发)。
- 调用 zone ops → get_temp() 获取当前温度。
- 比较温度和 trip point(如 passive, active, critical)。
(3) 决策阶段
- 如果温度超过阈值 → governor 介入:
step_wise governor: 按步进方式提高 cooling device 的等级。
power_allocator governor: 根据 PID 算法分配 cooling device 功率。
user_space governor: 把信息抛给用户空间,让策略由上层决定。
(4) 执行阶段
- governor 调用 thermal_cooling_device->ops->set_cur_state() 等接口。
比如:降低 CPU 频率(cpufreq)、限制 GPU 带宽(devfreq)、开启风扇。
(5) 用户空间交互
- 通过 sysfs 查看和调节参数:
/sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone*/temp,/sys/class/thermal/cooling_device*/cur_state - 通过 kobject_uevent_env() 通知用户空间 thermal 事件(Android 就是监听这些事件)。
4.3 时序参考