我们知道在 DSL 中我们可以轻松地使用 RRF 及线性来针对多路搜索进行混合搜索。我们可以使用如下的命令来进行 RRF 混合搜索:
bash
`
1. GET /imdb_movies/_search?pretty
2. {
3. "retriever": {
4. "rrf": {
5. "retrievers": [
6. {
7. "standard": {
8. "query": {
9. "term": {
10. "overview": "clueless slackers"
11. }
12. }
13. }
14. },
15. {
16. "knn": {
17. "field": "overview_dense",
18. "query_vector_builder": {
19. "text_embedding": {
20. "model_id": ".multilingual-e5-small_linux-x86_64",
21. "model_text": "clueless slackers"
22. }
23. },
24. "k": 5,
25. "num_candidates": 5
26. }
27. },
28. {
29. "standard": {
30. "query": {
31. "text_expansion": {
32. "overview_sparse": {
33. "model_id": ".elser_model_2_linux-x86_64",
34. "model_text": "clueless slackers"
35. }
36. }
37. }
38. }
39. }
40. ],
41. "rank_window_size": 5,
42. "rank_constant": 1
43. }
44. },
45. "size": 3,
46. "fields": [
47. "names",
48. "overview"
49. ],
50. "_source": false
51. }
`AI写代码收起代码块请详细阅读之前的文章 "Elasticsearch:介绍 retrievers - 搜索一切事物"。在上面,我们使用了 RRF。有关 RRF 的介绍,请阅读文章 "Elasticsearch:倒数排序融合 - Reciprocal rank fusion (RRF)"。
我们也可以使用线性组合来平衡混合搜索。请详细阅读文章 "平衡尺度:利用权重使倒数排序融合 (RRF) 更加智能"。
markdown
`
1. {
2. "retriever": {
3. "rrf": {
4. "retrievers": [
5. {
6. "retriever": {
7. "standard": {
8. "query": {
9. "match": {
10. "cuisine_type": "Italian"
11. }
12. }
13. }
14. },
15. "weight": 0.4
16. },
17. {
18. "retriever": {
19. "standard": {
20. "query": {
21. "match": {
22. "menu_items": "cacio e pepe"
23. }
24. }
25. }
26. },
27. "weight": 0.6
28. }
29. ]
30. }
31. }
32. }
`AI写代码随着 ES|QL 的推出,越来越多的查询会使用 ES|QL 来做查询,那么我们该如何实现混合搜索呢?
Elastic 在 9.1 中开始推出 FORK 及 FUSE 命令来帮助我们来实现这种混合搜索。
准备数据
我们首先创建如下的数据集:
bash
`
1. PUT /people
2. {
3. "mappings": {
4. "properties": {
5. "id": {
6. "type": "integer"
7. },
8. "name": {
9. "type": "text"
10. },
11. "description": {
12. "type": "text",
13. "copy_to": "des_semantic"
14. },
15. "des_semantic": {
16. "type": "semantic_text",
17. "inference_id": ".multilingual-e5-small-elasticsearch"
18. },
19. "sex": {
20. "type": "keyword"
21. },
22. "age": {
23. "type": "integer"
24. },
25. "address": {
26. "type": "text"
27. },
28. "location": {
29. "type": "geo_point"
30. }
31. }
32. }
33. }
`AI写代码
bash
`
1. POST /_bulk
2. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "1" } }
3. { "id": 1, "name" : "John Doe", "description" : "A software developer", "sex" : "Male", "age" : 30, "address" : "123 Elm Street, Springfield", "location": {"lat": 37.7749, "lon": -122.4194} }
4. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "2" } }
5. { "id": 2, "name" : "Jane Smith", "description" : "A project manager", "sex" : "Female", "age" : 28, "address" : "456 Maple Avenue, Anytown", "location": {"lat": 40.7128, "lon": -74.0060} }
6. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "3" } }
7. { "id": 3, "name" : "Alice Johnson", "description" : "A graphic designer", "sex" : "Female", "age" : 26, "address" : "789 Oak Lane, Metropolis", "location": {"lat": 34.0522, "lon": -118.2437} }
8. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "4" } }
9. { "id": 4, "name" : "Bob Brown", "description" : "A marketing specialist", "sex" : "Male", "age" : 32, "address" : "321 Pine Street, Gotham", "location": {"lat": 41.8781, "lon": -87.6298} }
10. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "5" } }
11. { "id": 5, "name" : "Charlie Davis", "description" : "An IT analyst", "sex" : "Male", "age" : 29, "address" : "654 Cedar Blvd, Star City", "location": {"lat": 29.7604, "lon": -95.3698} }
12. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "6" } }
13. { "id": 6, "name" : "Diana Prince", "description" : "A diplomat", "sex" : "Female", "age" : 35, "address" : "987 Birch Road, Themyscira", "location": {"lat": 39.9526, "lon": -75.1652} }
14. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "7" } }
15. { "id": 7, "name" : "Evan Wright", "description" : "A journalist", "sex" : "Male", "age" : 27, "address" : "213 Willow Lane, Central City", "location": {"lat": 33.4484, "lon": -112.0740} }
16. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "8" } }
17. { "id": 8, "name" : "Fiona Gallagher", "description" : "A nurse", "sex" : "Female", "age" : 31, "address" : "546 Spruce Street, South Side", "location": {"lat": 32.7157, "lon": -117.1611} }
18. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "9" } }
19. { "id": 9, "name" : "George King", "description" : "A teacher", "sex" : "Male", "age" : 34, "address" : "879 Elm St, Smallville", "location": {"lat": 39.7392, "lon": -104.9903} }
20. { "index" : { "_index" : "people", "_id" : "10" } }
21. { "id": 10, "name" : "Helen Parr", "description" : "A full-time superhero", "sex" : "Female", "age": 37, "address" : "123 Metro Avenue, Metroville", "location": {"lat": 47.6062, "lon": -122.3321} }
`AI写代码如上所示,我们的 people 索引含有一个 description 字段。它是 text 类型的。而另外一个字段 des_semantic 其实是一个密集向量。它的类型是 semantic_text。其向量值由 E3 多语言模型产生。
我们可以针对 des_semantic 字段做如下的向量查询:
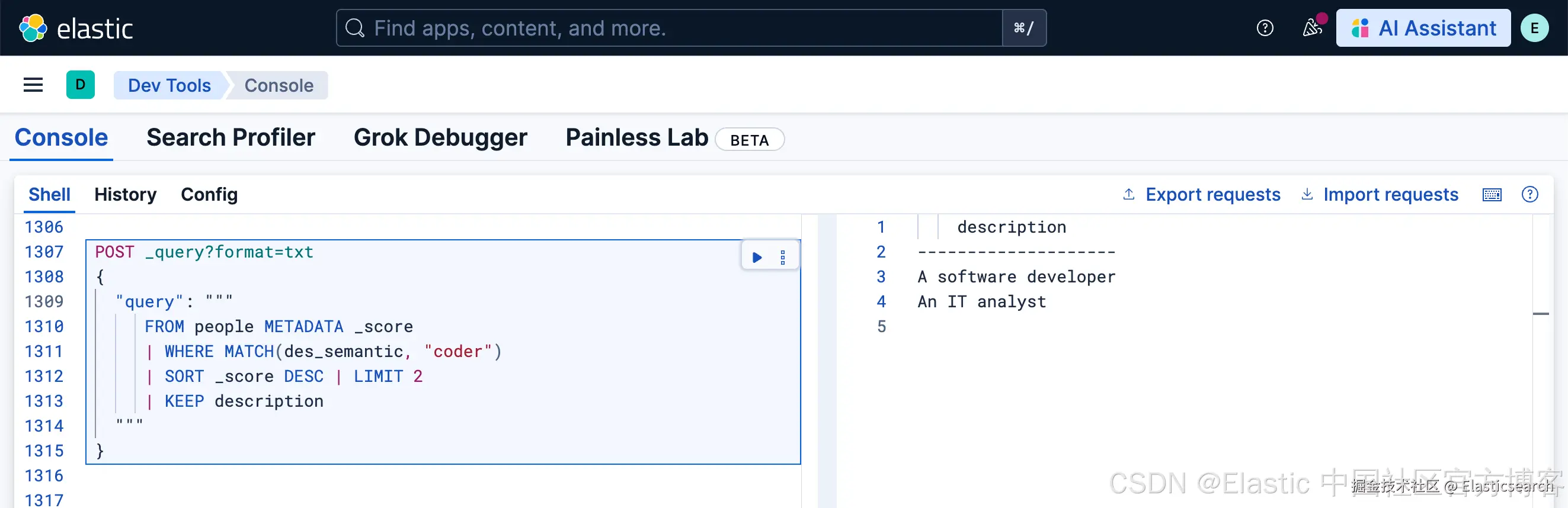
python
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _score
5. | WHERE MATCH(des_semantic, "coder")
6. | SORT _score DESC | LIMIT 2
7. | KEEP description
8. """
9. }
`AI写代码我们做如上的查询:
FORK
FORK 处理命令会创建多个执行分支,对相同的输入数据进行操作,并将结果合并为一个输出表。
scss
`FORK ( <processing_commands> ) ( <processing_commands> ) ... ( <processing_commands> )`AI写代码说明
FORK 处理命令会创建多个执行分支,对相同的输入数据进行操作,并将结果合并为一个输出表。会添加一个区分列(_fork)来标识每一行来自哪个分支。
结合 FUSE 命令,FORK 可以实现混合搜索,用来合并并给多个查询的结果打分。想要了解更多关于使用 ES|QL 做搜索的内容,请参考 ES|QL for search。
例子:
python
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _score
5. | FORK (WHERE MATCH(des_semantic, "coder"))
6. (WHERE MATCH(description, "journalist"))
7. | SORT _score DESC
8. | KEEP description
9. | LIMIT 2
10. """
11. }
`AI写代码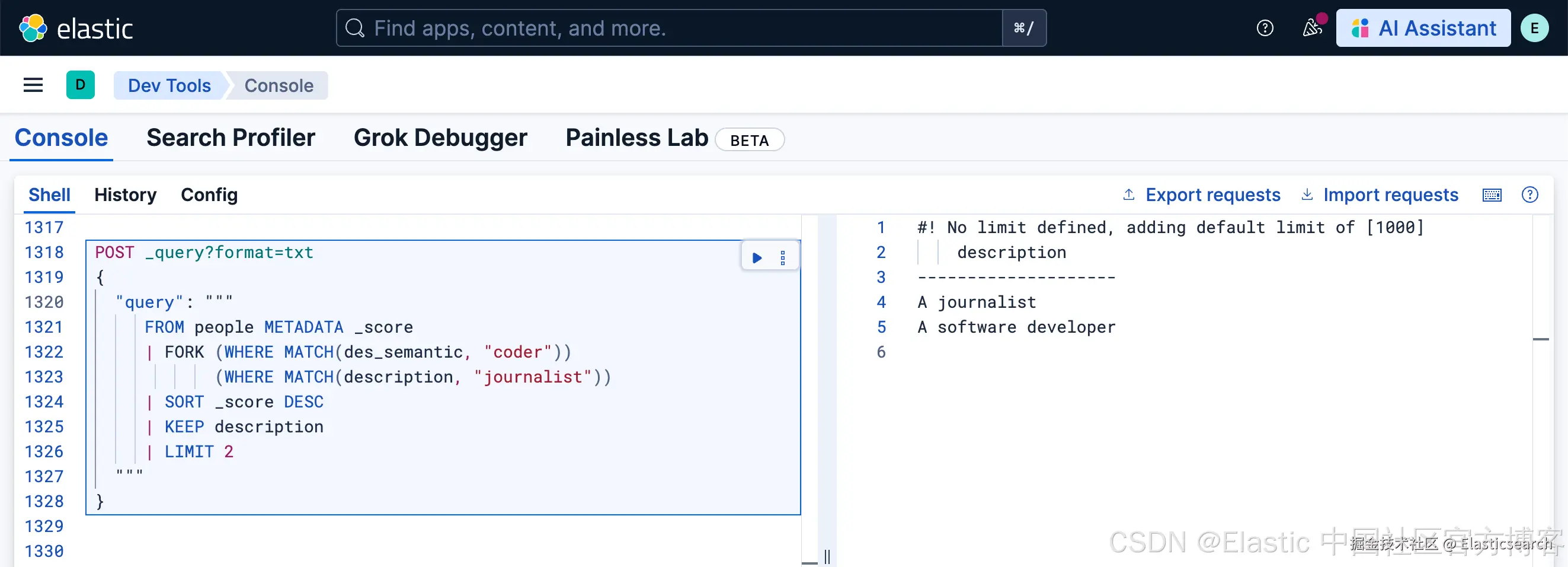
很显然,我们得到了搜索既是 jounalist 也是是 coder 的搜索结果。虽然这种结果是很好,返回了多路查询的结果,但是毕竟 WHERE MATCH(description, "journalist") 使用的是 BM25 的搜索方法,而 HERE MATCH(des_semantic, "coder") 使用的是向量搜索的方法。两种打分的方式是不一样的。相似性的分数在 0-1 之间。
我们再次修改我们的查询方法:
python
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _score
5. | FORK (WHERE MATCH(des_semantic, "coder"))
6. (WHERE MATCH(description, "journalist"))
7. | KEEP description, _score
8. | LIMIT 2
9. """
10. }
`AI写代码在上面,我们保留了 _score 的值:
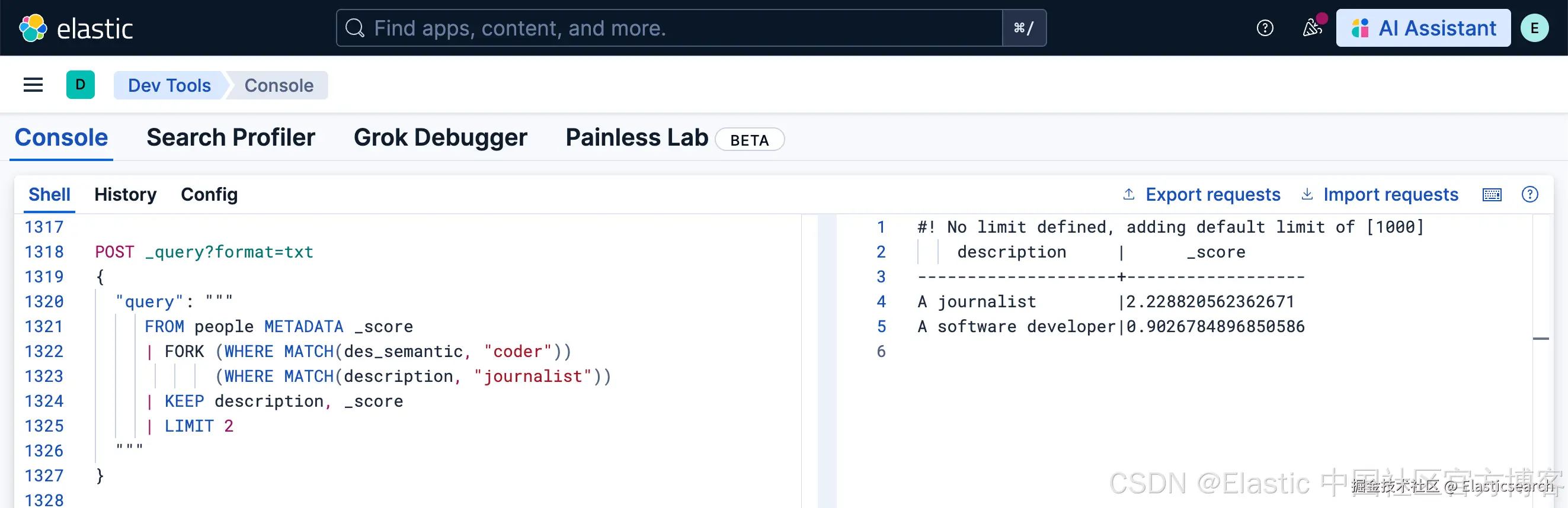
FUSE 命令
从上面的结果中,我们可以看出来,FORK 命令虽然可以帮我进行多路召回,但是他们各自的打分体现是不同的。我们需要使用一种方法把多路查询的结果来进行统一打分,并最终给出结果。 FUSE 就是为这种混合搜索而生。FUSE 处理命令会合并多个结果集的行,并分配新的相关性分数。
FUSE 与 FORK 命令结合,可以实现混合搜索,用来合并并给多个查询的结果打分。
FUSE 的工作方式包括:
-
合并具有匹配
<key_columns>值的行 -
使用指定的
<fuse_method>算法,根据<group_column>和<score_column>的值分配新的相关性分数
提示 :FUSE 用于搜索用例:它会合并已排序的结果集并计算相关性。想了解更多 ES|QL 中搜索的工作方式。
示例:
使用 RRF
python
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _id, _index, _score
5. | FORK (WHERE des_semantic: "coder" | SORT _score DESC)
6. (WHERE description: "journalist" | SORT _score DESC)
7. | FUSE
8. | KEEP description, _score
9. | LIMIT 2
10. """
11. }
`AI写代码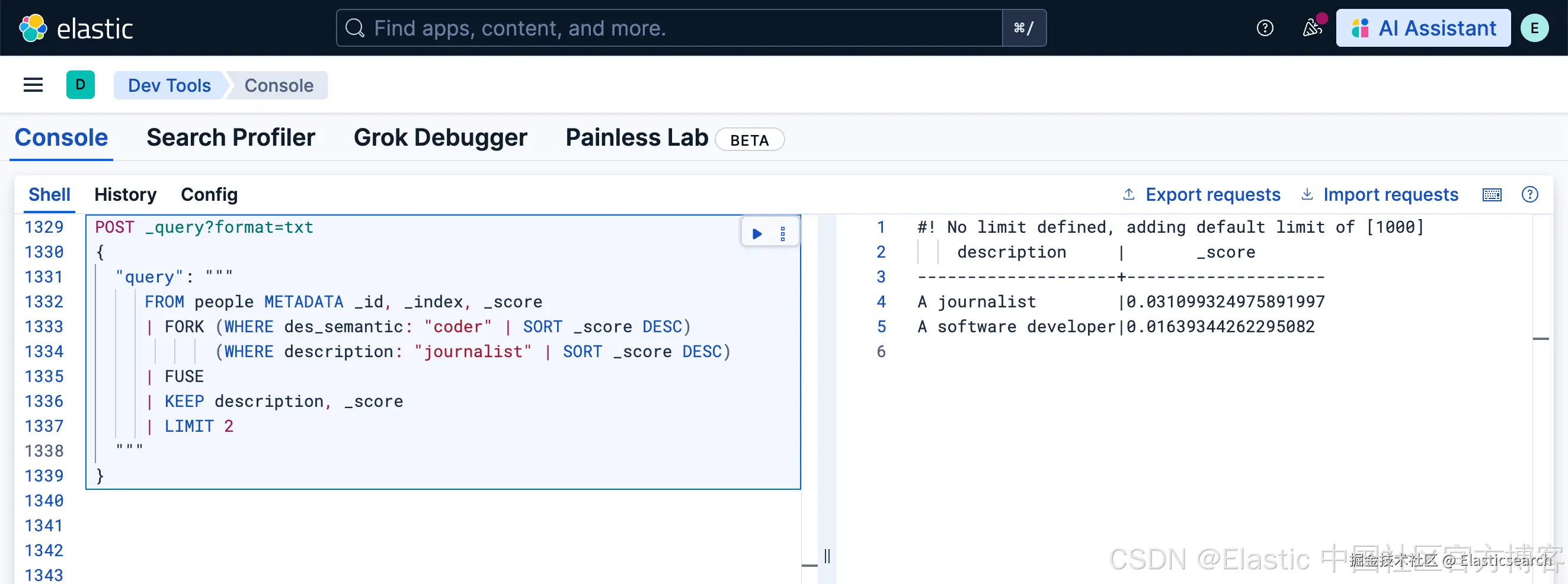
注意:针对上面的搜索,我们必须在 METADATA 里指名 _id, _index 及 _score。否则会有错误!
上面的搜索是针对两种不同的职业来进行搜索的。比较少见。我们直接针对 coder 来进行搜索:
python
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _id, _index, _score
5. | FORK (WHERE des_semantic: "coder" | SORT _score DESC)
6. (WHERE description: "coder" | SORT _score DESC)
7. | FUSE
8. | KEEP description, _score
9. | LIMIT 2
10. """
11. }
`AI写代码
为了更加清楚地说明问题,我们添加一个 search_type 来展示:
python
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _id, _index, _score
5. | FORK (WHERE des_semantic: "coder" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "semantic" )
6. (WHERE description: "coder" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "bm25")
7. | FUSE
8. | KEEP description, _score, search_type
9. | LIMIT 2
10. """
11. }
`AI写代码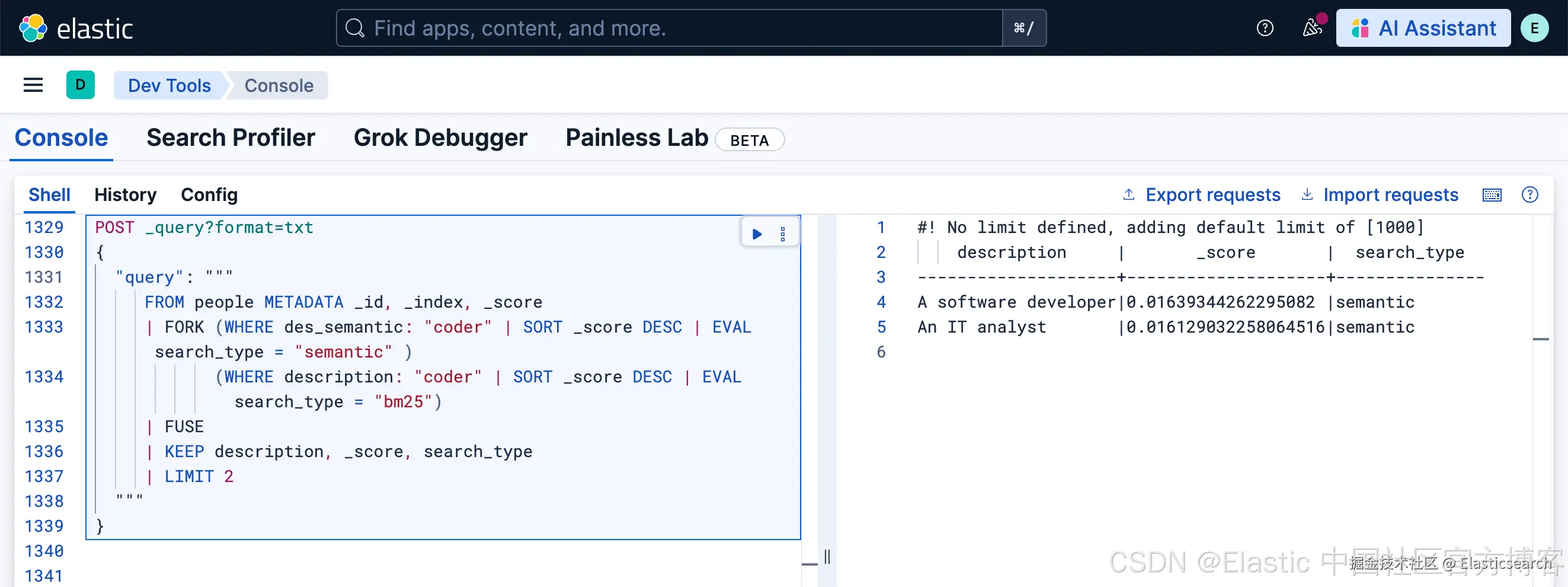
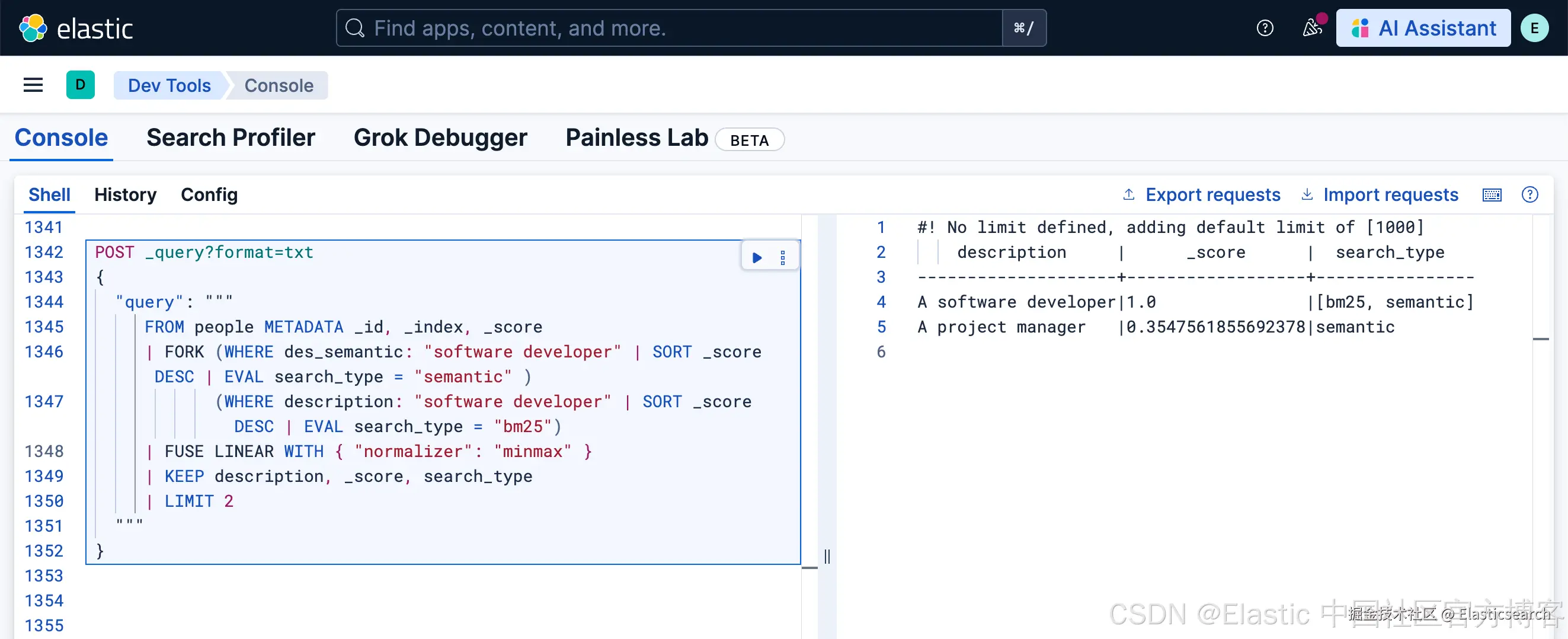
我们可以直接查询 software developer:
python
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _id, _index, _score
5. | FORK (WHERE des_semantic: "software developer" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "semantic" )
6. (WHERE description: "software developer" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "bm25")
7. | FUSE
8. | KEEP description, _score, search_type
9. | LIMIT 2
10. """
11. }
`AI写代码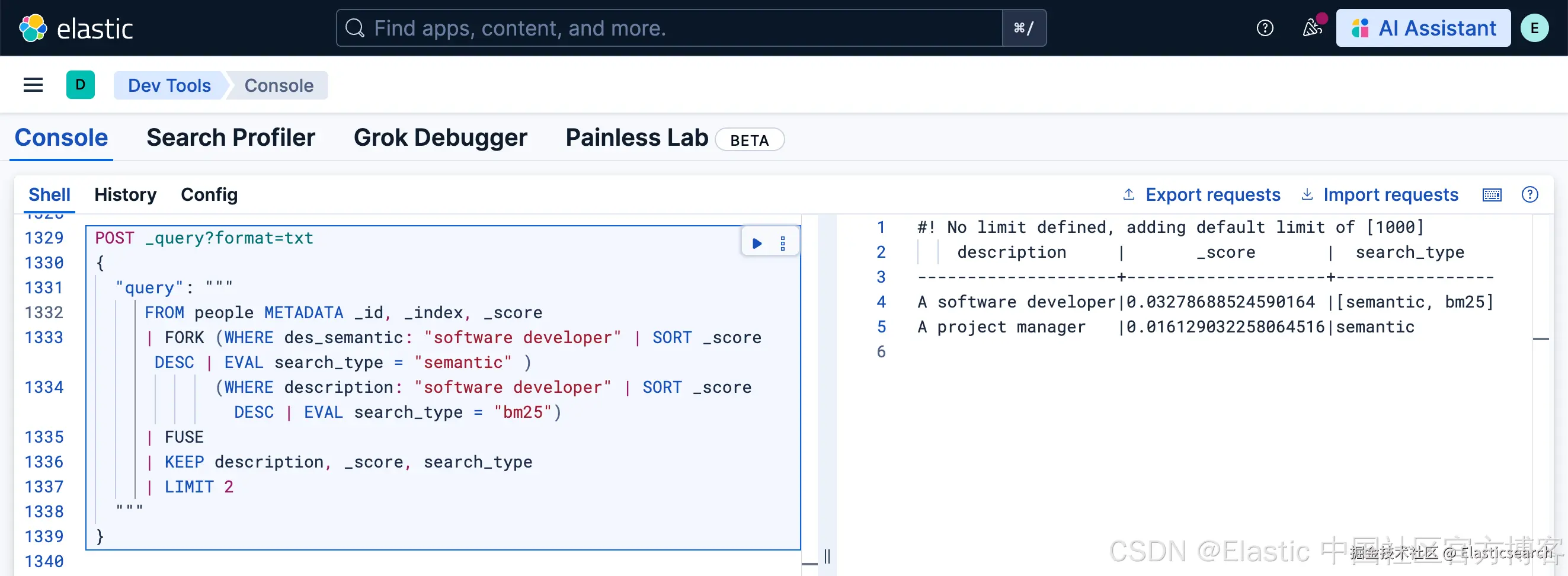
使用线性组合
FUSE 也可以使用 线性 分数组合:
python
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _id, _index, _score
5. | FORK (WHERE des_semantic: "software developer" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "semantic" )
6. (WHERE description: "software developer" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "bm25")
7. | FUSE LINEAR
8. | KEEP description, _score, search_type
9. | LIMIT 2
10. """
11. }
`AI写代码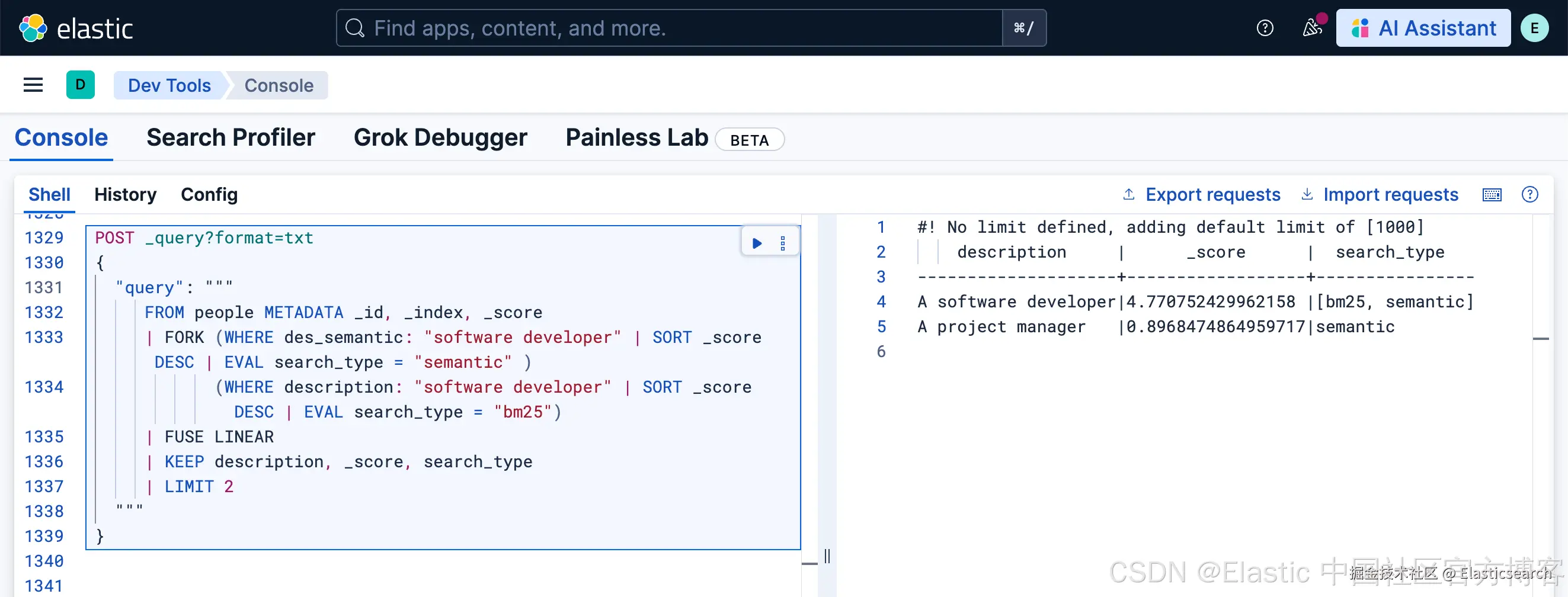
我们也可以使用定制的 weights。FUSE 允许你基于 _fork 列的值为分数指定不同的权重,让你可以控制每个查询分支在最终结果中的相对重要性。
bash
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _id, _index, _score
5. | FORK (WHERE des_semantic: "software developer" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "semantic" )
6. (WHERE description: "software developer" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "bm25")
7. | FUSE LINEAR WITH { "weights": { "fork1": 0.7, "fork2": 0.3 }, "normalizer": "minmax" }
8. | KEEP description, _score, search_type
9. | LIMIT 2
10. """
11. }
`AI写代码
归一化 分数
当使用 线性 组合将语义查询和词法查询的结果合并时,我们建议先对每个结果集的分数进行归一化。
下面的示例使用 minmax 分数归一化。这意味着在合并行之前,分数会归一化为 0 到 1 之间的值:
bash
`
1. POST _query?format=txt
2. {
3. "query": """
4. FROM people METADATA _id, _index, _score
5. | FORK (WHERE des_semantic: "software developer" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "semantic" )
6. (WHERE description: "software developer" | SORT _score DESC | EVAL search_type = "bm25")
7. | FUSE LINEAR WITH { "normalizer": "minmax" }
8. | KEEP description, _score, search_type
9. | LIMIT 2
10. """
11. }
`AI写代码