在 Spring 框架中,Bean 的生命周期是理解容器管理机制的核心。本文将通过图示和代码示例,详细解析 Spring Bean 从创建到销毁的完整流程,并解答常见疑问:是否可以在初始化前跳过属性赋值?
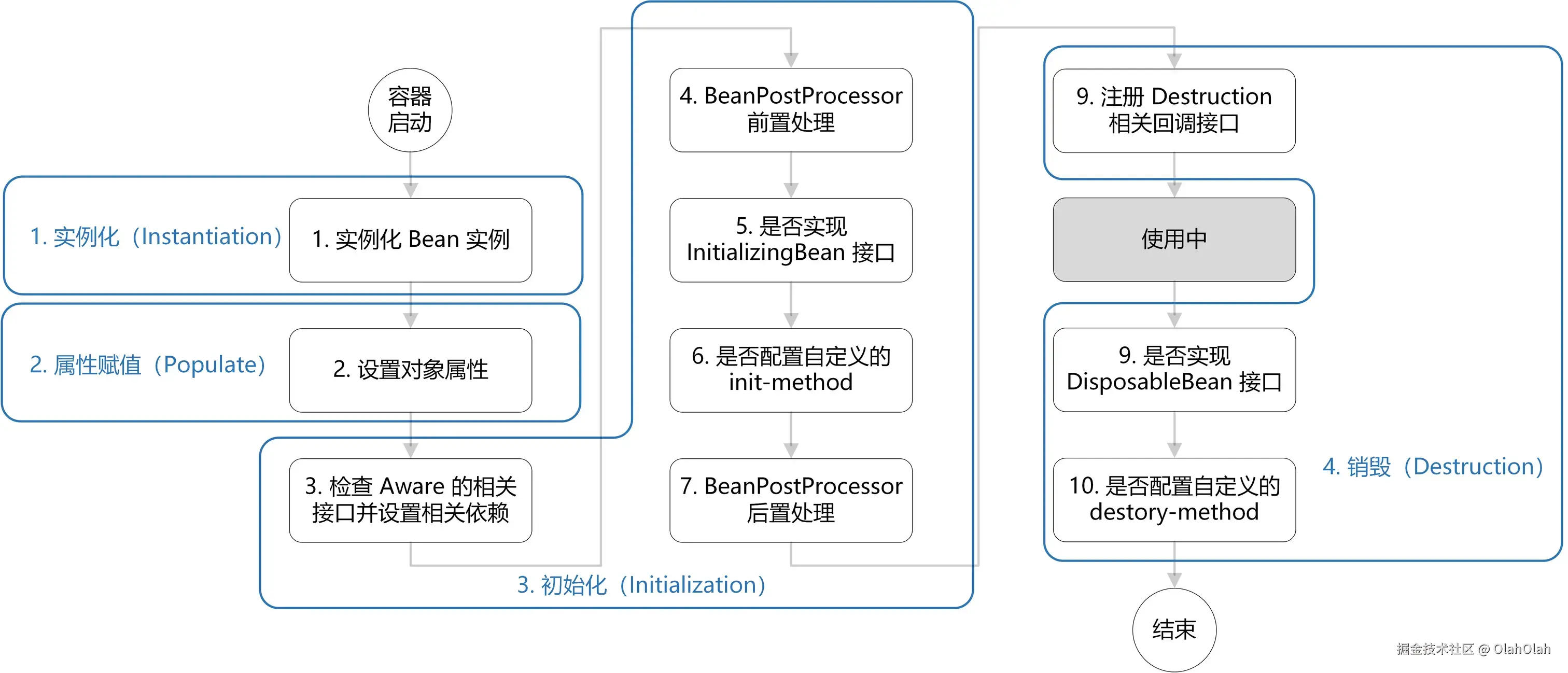
Bean 生命周期概览
Spring Bean 的生命周期大致分为以下几个阶段:
- 实例化:通过构造方法创建 Bean 对象。
- 属性赋值:为 Bean 的依赖和属性注入值。
- BeanNameAware:设置 Bean 名称。
- BeanFactoryAware:设置 BeanFactory。
- ApplicationContextAware:设置 ApplicationContext。
- 初始化前处理 :
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization。 - @PostConstruct 注解方法:初始化逻辑执行。
- InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet:属性设置完成后的回调。
- 自定义 init 方法 :通过
@Bean(initMethod)指定。 - 初始化后处理 :
BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization。 - Bean 使用阶段:Bean 已准备就绪,可用于业务逻辑。
- @PreDestroy 注解方法:销毁前回调。
- DisposableBean.destroy:销毁方法执行。
- 自定义 destroy 方法 :通过
@Bean(destroyMethod)指定。
代码示例
1. 主配置类
less
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example.lifecycle")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean(initMethod = "customInit", destroyMethod = "customDestroy")
public ExampleBean exampleBean() {
return new ExampleBean();
}
}2. Bean 生命周期类
csharp
public class ExampleBean implements
BeanNameAware,
BeanFactoryAware,
ApplicationContextAware,
InitializingBean,
DisposableBean {
private String name;
public ExampleBean() {
System.out.println("1. Bean 实例化 - 构造函数执行");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("2. 属性赋值 - 设置属性值: " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("3. BeanNameAware - Bean 名称: " + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("4. BeanFactoryAware - 设置 BeanFactory");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("5. ApplicationContextAware - 设置 ApplicationContext");
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct() {
System.out.println("7. @PostConstruct - 初始化方法");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("8. InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet - 属性设置完成后");
}
public void customInit() {
System.out.println("9. 自定义 init 方法 - @Bean(initMethod)");
}
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println("11. Bean 使用中 - 业务方法执行");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("12. @PreDestroy - 销毁前方法");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("13. DisposableBean.destroy - 销毁方法");
}
public void customDestroy() {
System.out.println("14. 自定义 destroy 方法 - @Bean(destroyMethod)");
}
}3. BeanPostProcessor 实现
typescript
@Component
public class CustomBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof ExampleBean) {
System.out.println("6. BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization - 初始化前处理");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof ExampleBean) {
System.out.println("10. BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization - 初始化后处理");
}
return bean;
}
}4. 测试类
arduino
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class LifecycleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== Spring Bean 生命周期演示 ===");
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
ExampleBean exampleBean = context.getBean(ExampleBean.class);
exampleBean.doSomething();
System.out.println("=== 关闭 Spring 容器 ===");
context.close();
}
}输出结果
markdown
=== Spring Bean 生命周期演示 ===
1. Bean 实例化 - 构造函数执行
2. 属性赋值 - 设置属性值: null
3. BeanNameAware - Bean 名称: exampleBean
4. BeanFactoryAware - 设置 BeanFactory
5. ApplicationContextAware - 设置 ApplicationContext
6. BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization - 初始化前处理
7. @PostConstruct - 初始化方法
8. InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet - 属性设置完成后
9. 自定义 init 方法 - @Bean(initMethod)
10. BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization - 初始化后处理
11. Bean 使用中 - 业务方法执行
=== 关闭 Spring 容器 ===
12. @PreDestroy - 销毁前方法
13. DisposableBean.destroy - 销毁方法
14. 自定义 destroy 方法 - @Bean(destroyMethod)初始化前是否可以跳过属性赋值?
答案是否定的。Spring 的设计理念是:
属性赋值必须在初始化阶段之前完成
原因如下:
- 初始化逻辑通常依赖 Bean 已经注入的属性。
- 如果初始化方法提前执行,未注入属性可能导致
NullPointerException或状态不完整。 - Bean 的生命周期有严格顺序,确保每个阶段都能安全执行。
因此,即便在 @PostConstruct、InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet 或自定义初始化方法中访问 Bean 属性,也可以放心使用,不会出现未赋值的情况。