目录
[1. 计算布尔二叉树的值](#1. 计算布尔二叉树的值)
[1.1 解题思路](#1.1 解题思路)
[1.2 代码实现](#1.2 代码实现)
[2. 求根节点到叶子节点数字之和](#2. 求根节点到叶子节点数字之和)
[2.1 解题思路](#2.1 解题思路)
[2.2 代码实现](#2.2 代码实现)
[3. 二叉树剪枝](#3. 二叉树剪枝)
[3.1 解题思路](#3.1 解题思路)
[3.2 代码实现](#3.2 代码实现)
[4. 验证二叉搜索树](#4. 验证二叉搜索树)
[4.1 解题思路](#4.1 解题思路)
[4.2 代码实现](#4.2 代码实现)
[5. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素](#5. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素)
[5.1 解题思路](#5.1 解题思路)
[5.2 代码实现](#5.2 代码实现)
[6. 二叉树的所有路径](#6. 二叉树的所有路径)
[6.1 解题思路](#6.1 解题思路)
[6.2 代码实现](#6.2 代码实现)
[7. 全排列(回溯)](#7. 全排列(回溯))
[7.1 解题思路](#7.1 解题思路)
[7.2 代码实现](#7.2 代码实现)
[8. 子集(回溯)](#8. 子集(回溯))
[8.1 解题思路](#8.1 解题思路)
[8.2 代码实现](#8.2 代码实现)
[9. 找出所有子集的异或总和再求和](#9. 找出所有子集的异或总和再求和)
[9.1 解题思路](#9.1 解题思路)
[9.2 代码实现](#9.2 代码实现)
[10. 全排列II](#10. 全排列II)
[10.1 解题思路](#10.1 解题思路)
[10.2 代码实现](#10.2 代码实现)
[11 电话号码的字母组合](#11 电话号码的字母组合)
[11.1 解题思路](#11.1 解题思路)
[11.2 代码实现](#11.2 代码实现)
[12. 括号生成](#12. 括号生成)
[12.1 解题思路](#12.1 解题思路)
[12.2 代码实现](#12.2 代码实现)
[13. 组合](#13. 组合)
[13.1 解题思路](#13.1 解题思路)
[13.2 代码实现](#13.2 代码实现)
[14. 目标和](#14. 目标和)
[14.1 解题思路](#14.1 解题思路)
[14.2 代码实现](#14.2 代码实现)
[15. 组合总和](#15. 组合总和)
[15.1 解题思路](#15.1 解题思路)
[15.2 代码实现](#15.2 代码实现)
[16. 字母大小写全排列](#16. 字母大小写全排列)
[16.1 解题思路](#16.1 解题思路)
[16.2 代码实现](#16.2 代码实现)
[17. 优美的排列](#17. 优美的排列)
[17.1 解题思路](#17.1 解题思路)
[17.2 代码实现](#17.2 代码实现)
[18. N皇后](#18. N皇后)
[18.1 解题思路](#18.1 解题思路)
[18.2 代码实现](#18.2 代码实现)
[19. 有效数独](#19. 有效数独)
[19.1 解题思路](#19.1 解题思路)
[19.2 代码实现](#19.2 代码实现)
[20. 解数独](#20. 解数独)
[20.1 解题思路](#20.1 解题思路)
[20.2 代码实现](#20.2 代码实现)
[21. 单词搜索](#21. 单词搜索)
[21.1 解题思路](#21.1 解题思路)
[21.2 代码实现](#21.2 代码实现)
[22. 黄金矿工](#22. 黄金矿工)
[22.1 解题思路](#22.1 解题思路)
[22.2 代码实现](#22.2 代码实现)
[23. 不同路径3](#23. 不同路径3)
[23.1 解题思路](#23.1 解题思路)
[23.2 代码实现](#23.2 代码实现)
1. 计算布尔二叉树的值
1.1 解题思路

这道题给我们一个完整二叉树(每个节点没有子节点或者有两个子节点),并且节点中0代表false,1代表true,2代表or(||),3代表and(&&),并且叶子节点是0或者1,其他节点是2或者3,让我们从叶子节点开始进行运算,返回最后的运算结果。

1.2 代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean evaluateTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return root.val == 1 ? true : false;
}
boolean b1 = evaluateTree(root.left);
boolean b2 = evaluateTree(root.right);
if(root.val == 2) {
return b1 || b2;
}else {
return b1 && b2;
}
}
}2. 求根节点到叶子节点数字之和
2.1 解题思路

这道题给我们一个二叉树,每个二叉树的节点是0~9范围的数字,让我们求每条根节点到叶子节点的组成的数的和。

这时候递归的方法头需要传入节点和该节点的头节点的sum值,此时将当前sum分别传给左子树和右子树经过计算分别返回求得的到叶子节点的数,最后再将左右节点返回的两条线路的数加起来。
2.2 代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
int sum = 0;
return dfs(root,sum);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, int sum) {
sum = sum * 10 + root.val;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return sum;
}
int left = 0;
if(root.left != null) {
left = dfs(root.left,sum);
}
int right = 0;
if(root.right != null) {
right = dfs(root.right,sum);
}
return left + right;
}
}3. 二叉树剪枝
3.1 解题思路
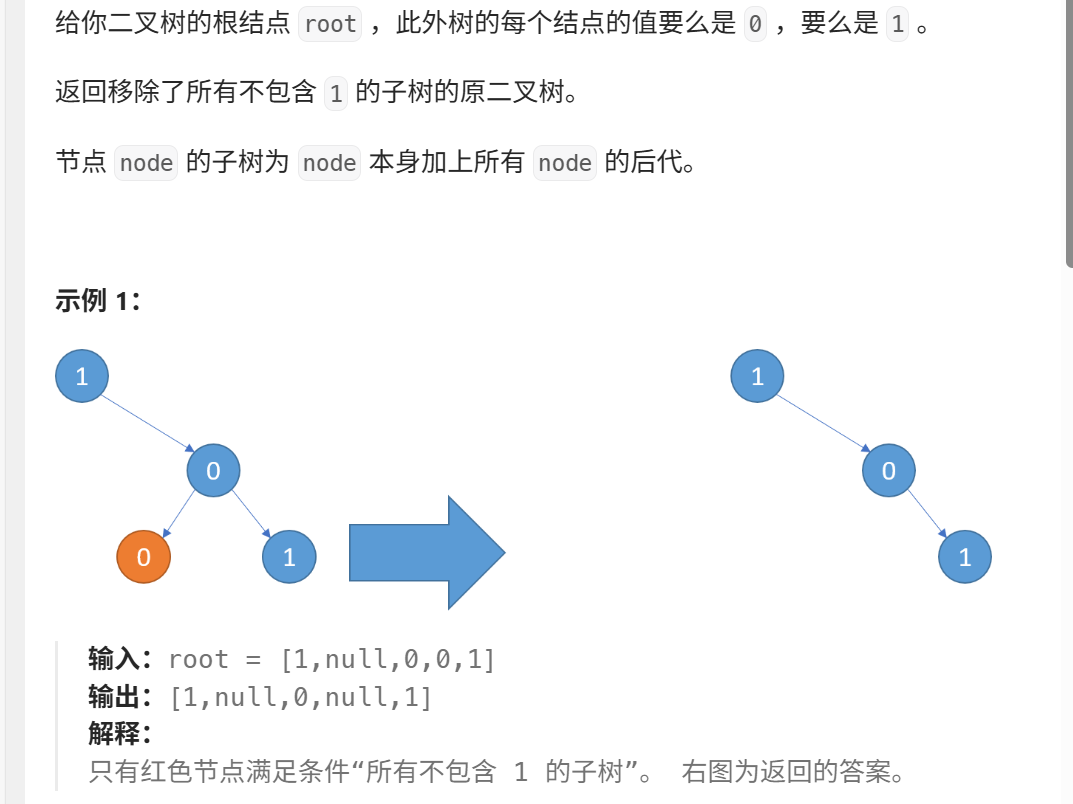
这道题给我们一个二叉树的头节点,让我们将二叉树中的不包含1的子树删掉,返回新的二叉树。

我们可以先将左子树和右子树进行修改,返回修改后的树。
3.2 代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode pruneTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return null;
}
root.left = pruneTree(root.left);
root.right = pruneTree(root.right);
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && root.val == 0) {
root = null;
}
return root;
}
}4. 验证二叉搜索树
4.1 解题思路

这道题给我们一个二叉树判断是不是二叉搜索树。二叉搜索树是左子树的数据都小于当前节点的数据,右子树的数据都大于当前节点的数据。

我们可以利用二叉搜索树中序遍历出的数据是有序的概念来解决这道题。
我们可以设置一个全局变量表示遍历到的节点的上一个节点的数据,每次遍历到一个节点判断这个节点的值是否大于全局变量的值。
此时我们需要判断左子树是不是二叉搜索树,右子树是不是二叉搜索树,以及整个子树是不是二叉搜索树,如果满足这三个条件就能证明整个树是二叉搜索树。
这里如果我们可以利用剪枝的原理,当遇到左子树不是二叉搜索树时候,直接返回false,不用再判断右子树。
4.2 代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
long prev = Long.MIN_VALUE;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return true;
}
boolean left = isValidBST(root.left);
//剪枝
if(left == false) {
return false;
}
boolean tmp = false;
if(root.val > prev) {
tmp = true;
}
if(tmp == false) return false;
prev = root.val;
boolean right = isValidBST(root.right);
return left && tmp && right;
}
}5. 二叉搜索树中第K小的元素
5.1 解题思路

这道题给我们一个二叉搜索树和一个数K,让我们返回二叉搜索树中的第K小的数。

我们可以利用中序遍历,设置两个全局变量,count表示第几个数,ret表示目标数,在遍历过程中,count--,当count==0时候就是目标节点。
5.2 代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
int count = 0;
int ret = 0;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
count = k;
dfs(root);
return ret;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null || count == 0) {
return;
}
dfs(root.left);
count--;
if(count == 0) {
ret = root.val;
}
//剪枝
if(count == 0) {
return;
}
dfs(root.right);
}
}6. 二叉树的所有路径
6.1 解题思路

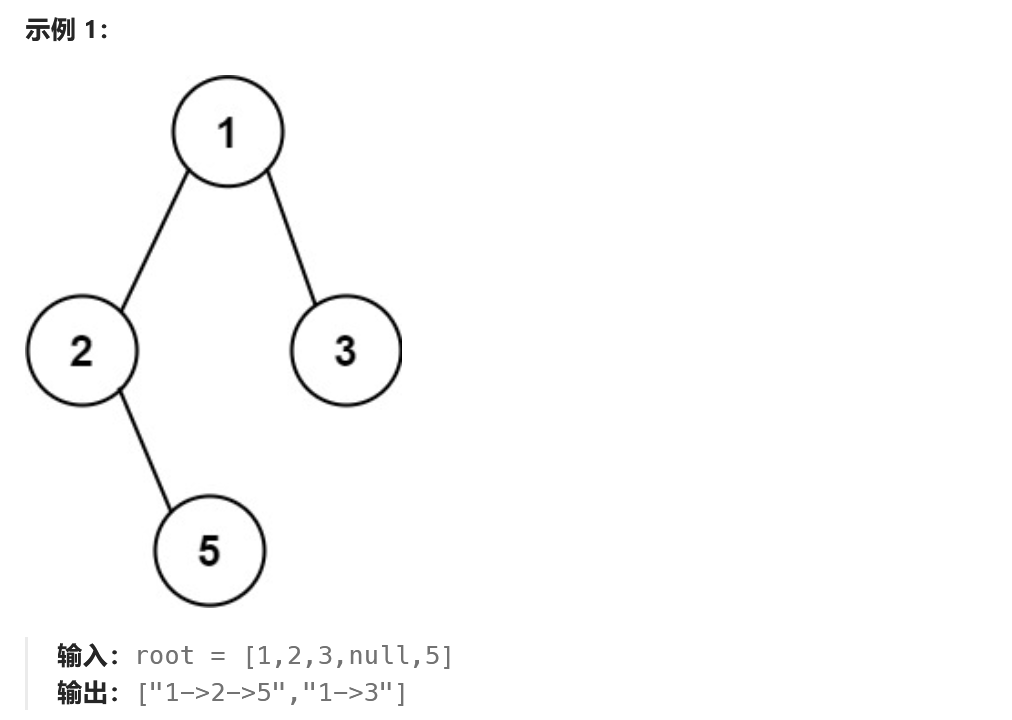
这道题给我们一个二叉树,让我们返回所有的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
我们想到可以使用先序遍历的过程,来遍历二叉树。
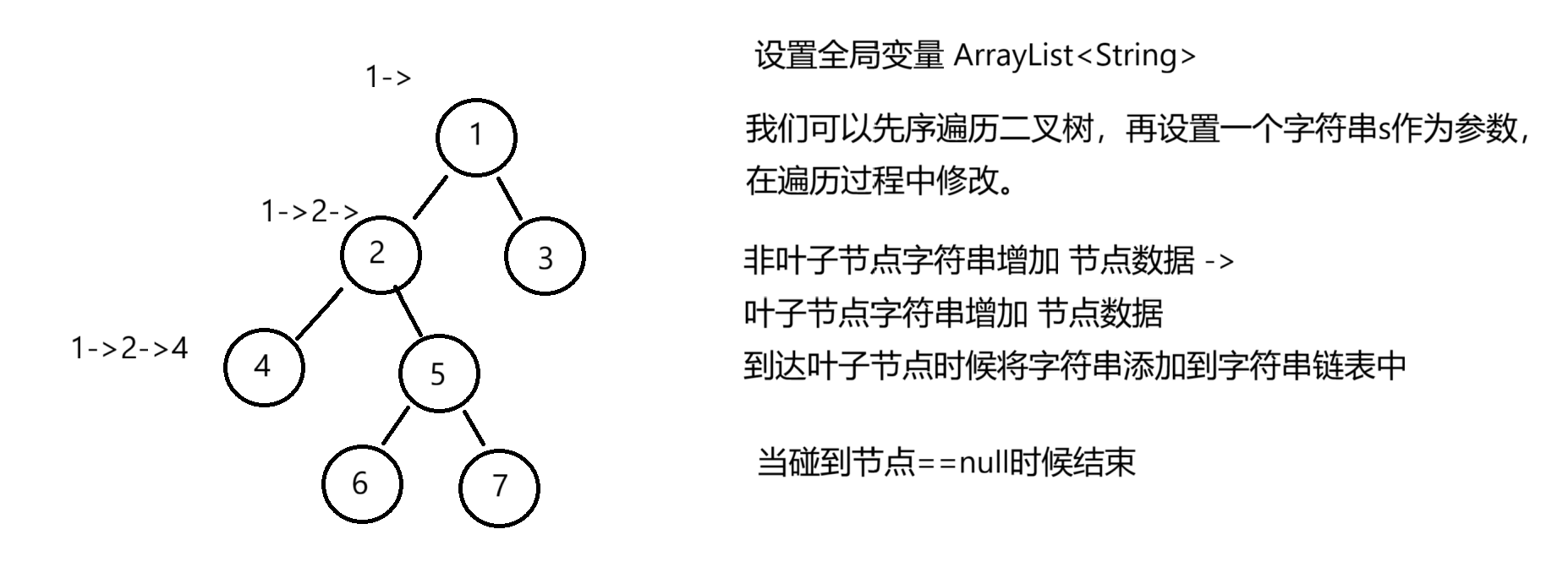
我们可以定义一个全局变量字符串数组来1存储所有结果,然后先序遍历二叉树,参数设置一个字符串用来记录变量的结果。
此时我们应该注意在进行回溯的时候上一层的字符串不应该受到下一层的字符串的影响,这里可以让字符串定义成局部变量,每一层有自己的字符串。
6.2 代码实现
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>();
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder ss = new StringBuilder();
dfs(root,ss);
return arrayList;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root, StringBuilder ss) {
//这层的修改不影响上一层的字符串
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder(ss);
if(root == null) {
return;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null) {
s.append(root.val);
arrayList.add(s.toString());
}else {
s.append(root.val);
s.append("->");
}
dfs(root.left,s);
dfs(root.right,s);
}
}7. 全排列(回溯)
7.1 解题思路

这道题给我们一个数组,让我们枚举数组中所有的全排列,存储在一个数组中,返回。
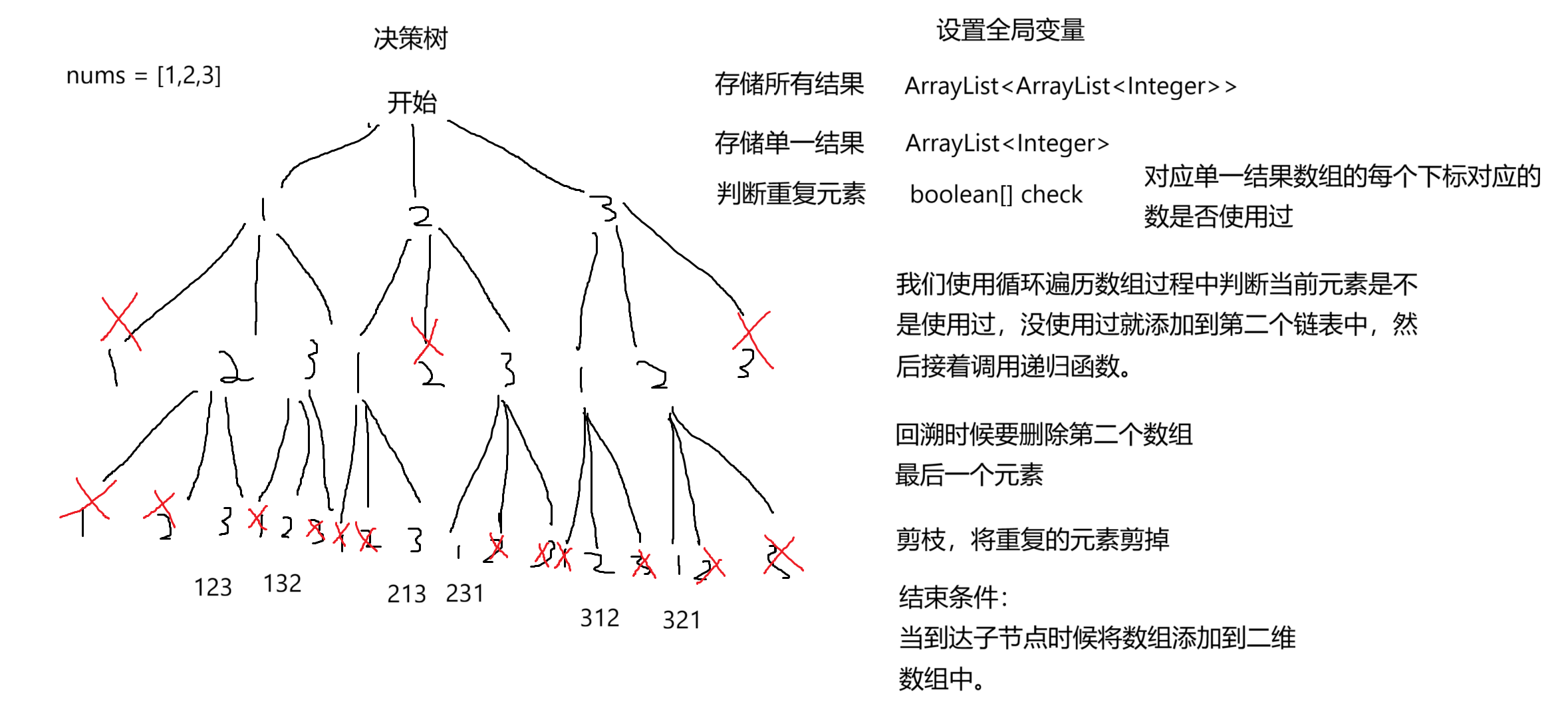
这道题我们利用回溯和剪枝以及递归的算法,将数组中每个元素都遍历,利用全局变量来记录,第一个全局变量记录所有的全排列数,第二个链表记录遍历过程中一个全排列数,设置一个数组来判断此时的全排列树中那些数遍历过,那些数没有遍历过。结束条件就是到达叶子节点时候就将此时的第二个链表存储到第一个链表里面,这时候往上回溯时候,要记得将此时的第二个链表使用过的数删除和更该第三个数组中的使用记录。
7.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<Integer>();
boolean[] check;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
check = new boolean[nums.length];
dfs(nums);
return ret;
}
void dfs(int[] nums) {
//结束条件
if(path.size() == nums.length) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
//判断当前数组元素是否被使用过
if(check[i] == false) {
//将未使用的数添加到数组中,然后设置该数使用过
path.add(nums[i]);
check[i] = true;
dfs(nums);
//进行回溯,删除最后一个数,并设置未使用删除的数
check[i] = false;
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}8. 子集(回溯)
8.1 解题思路

这道题给我们一个数组,让我们将该数组的所有子集都存储到一个数组中,返回该数组。
这道题我们在画决策树的时候,会有两种画法,因此解法也就有两种:
方法一是利用选择数组里面的元素和不选择数组里面的元素来画出决策树的。
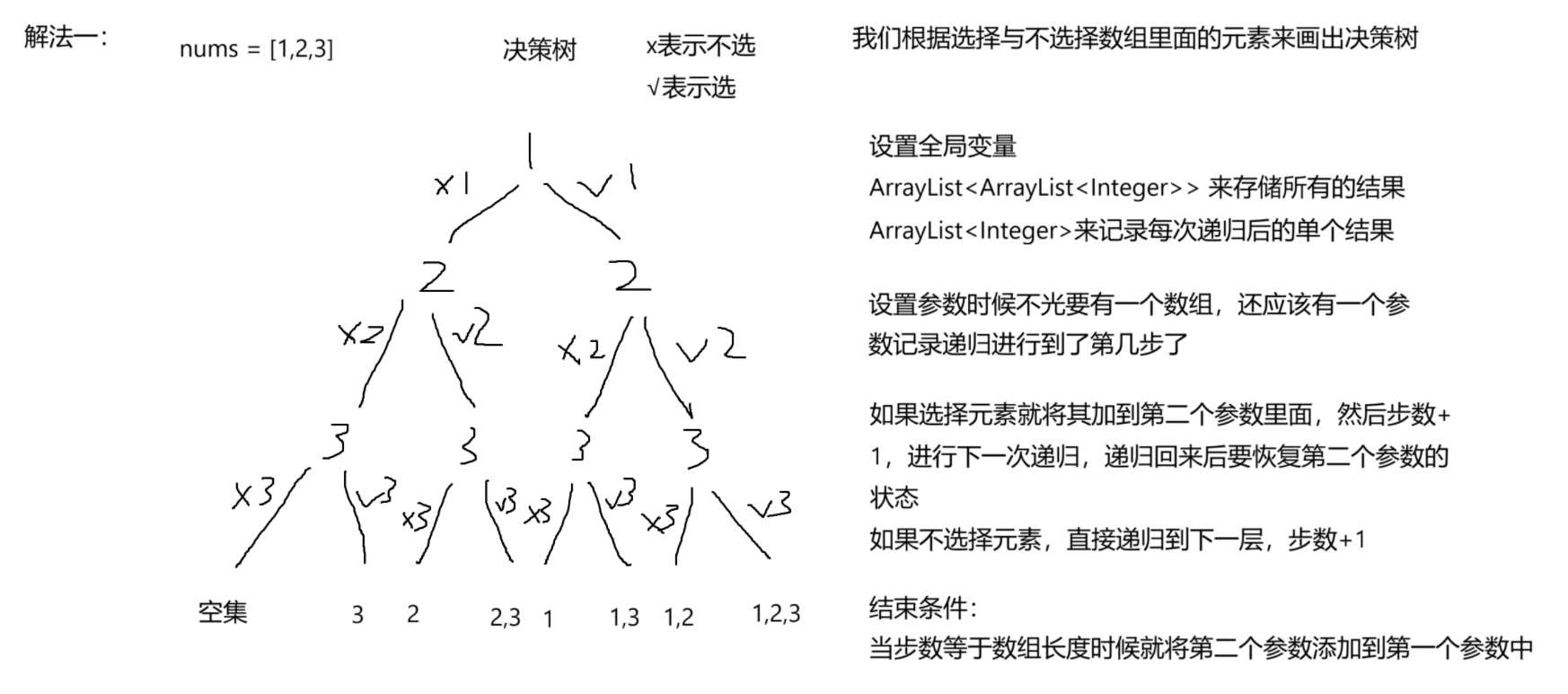
方法二是利用子数组的个数来画决策树的。
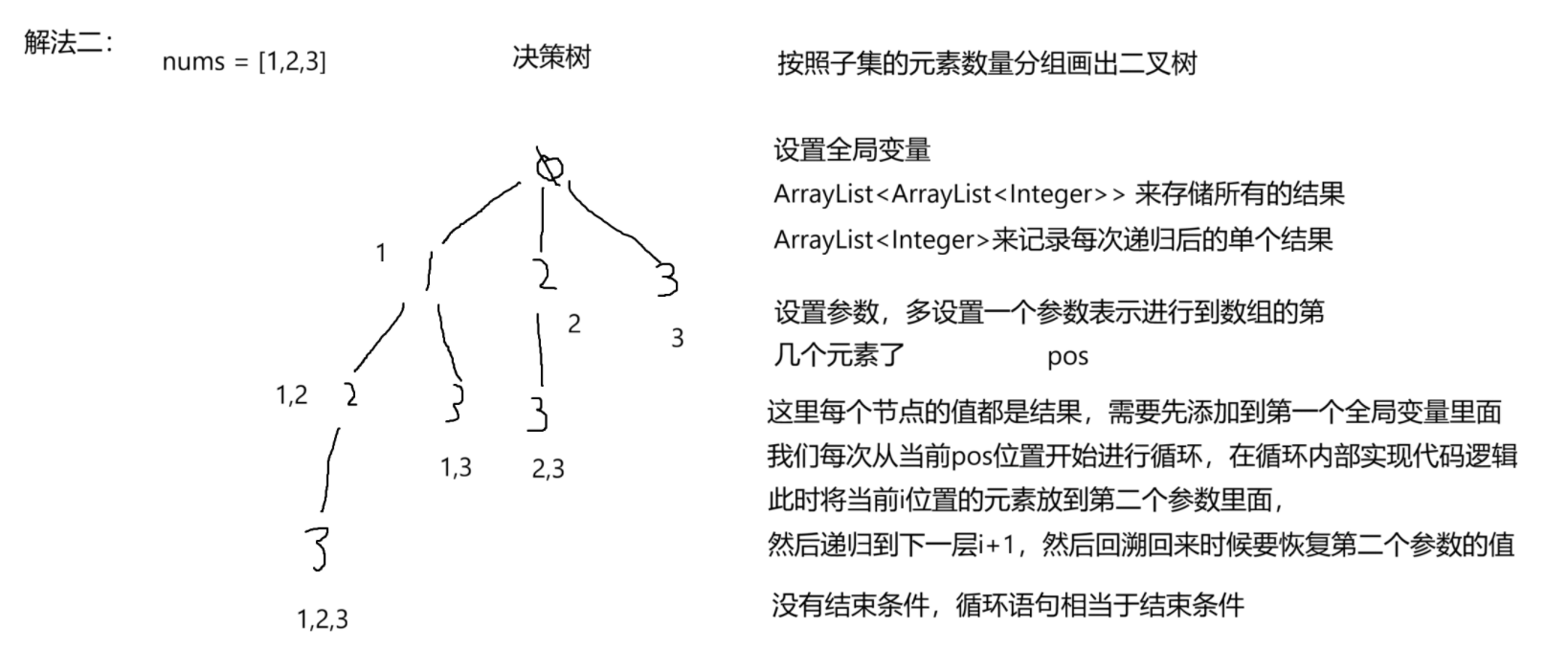
8.2 代码实现
方法一:
java
class Solution {
//记录所有子集的数组
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
//递归过程中记录单个子集
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
//记录遍历到数组第几个元素
int pos = 0;
dfs(nums, pos);
return ret;
}
void dfs(int[] nums, int pos) {
//结束条件
if (pos == nums.length) {
ret.add(new ArrayList(path));
return;
}
//选择当前位置元素
path.add(nums[pos]);
dfs(nums, pos + 1);
//回溯将数组中最后元素移除
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
//不选择当前位置元素
dfs(nums, pos + 1);
}
}方法2:
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> subsets(int[] nums) {
int pos = 0;
dfs(nums, pos);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums, int pos) {
ret.add(new ArrayList(path));
for (int i = pos; i < nums.length; i++) {
path.add(nums[i]);
dfs(nums,i+1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}9. 找出所有子集的异或总和再求和
9.1 解题思路

这道题给我们一个数组,让我们求出这个数组所有的子集,然后将所有子集的异或和的结果加在一起返回最终结果。
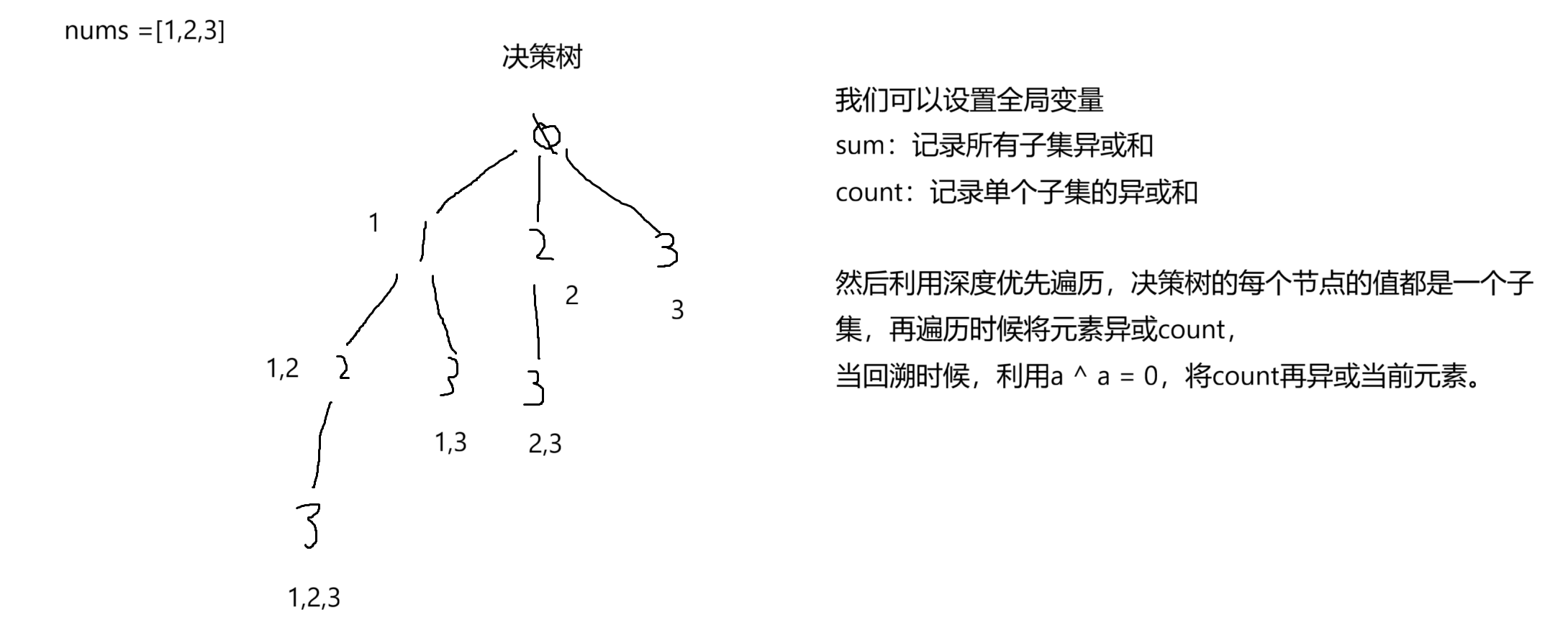
9.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
//统计所有子集异或总和
int sum = 0;
//统计单个自己的异或和
int count = 0;
public int subsetXORSum(int[] nums) {
int pos = 0;
dfs(nums,pos);
return sum;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums, int pos) {
sum += count;
for(int i = pos; i < nums.length; i++) {
count ^= nums[i];
dfs(nums,i + 1);
count ^= nums[i];//回溯现场
}
}
}10. 全排列II
10.1 解题思路

这道题给我们一个数组,里面包含重复元素,让我们找到数组中所有不重复的全排列放到一个数组中返回二位数组。

我们首先要画出决策树,找到剪枝的条件,也就是那些分支不满足条件,此时结束条件是当第二个全局变量的长度等于数组长度时候结束,找到一个全排列。
10.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
//记录元素是否使用过
boolean[] check = null;
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
check = new boolean[nums.length];
//对数组进行排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
dfs(nums);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums) {
//结束条件
if(path.size() == nums.length) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<Integer>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(check[i] == false && (i == 0 || nums[i] != nums[i-1] || check[i-1] == true)) {
//此时接着往下遍历决策树
path.add(nums[i]);
check[i] = true;
dfs(nums);
check[i] = false;
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}11 电话号码的字母组合
11.1 解题思路


这道题给我们一个字符串,让我们找到所有字符串中的数字对应的字符串之间的组合的所有情况,将所有情况存在一个顺序表中,返回这个顺序表。

我们需要先设置一个哈希表来表示题目中数字对应的字符串是那个,然后我们先获取到字符串中对应pos位置对应的字符串,然后遍历这个字符串,将字母添加到第二个全局变量中,然后递推下一个字符串对应的pos位置的字符串,回溯时候要把第二个全局变量删除最后一个字母。
11.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
String[] s = {"","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"};
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
//字符串为空时候,返回空数组
if(digits.length() == 0){
return list;
}
dfs(digits,0);
return list;
}
public void dfs(String digits,int pos) {
//结束条件
if(path.length() == digits.length()) {
list.add(path.toString());
return;
}
String tmp = s[digits.charAt(pos) - '0'];
for(int i = 0; i < tmp.length(); i++) {
path.append(tmp.charAt(i));
dfs(digits,pos+1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
}
}
}12. 括号生成
12.1 解题思路

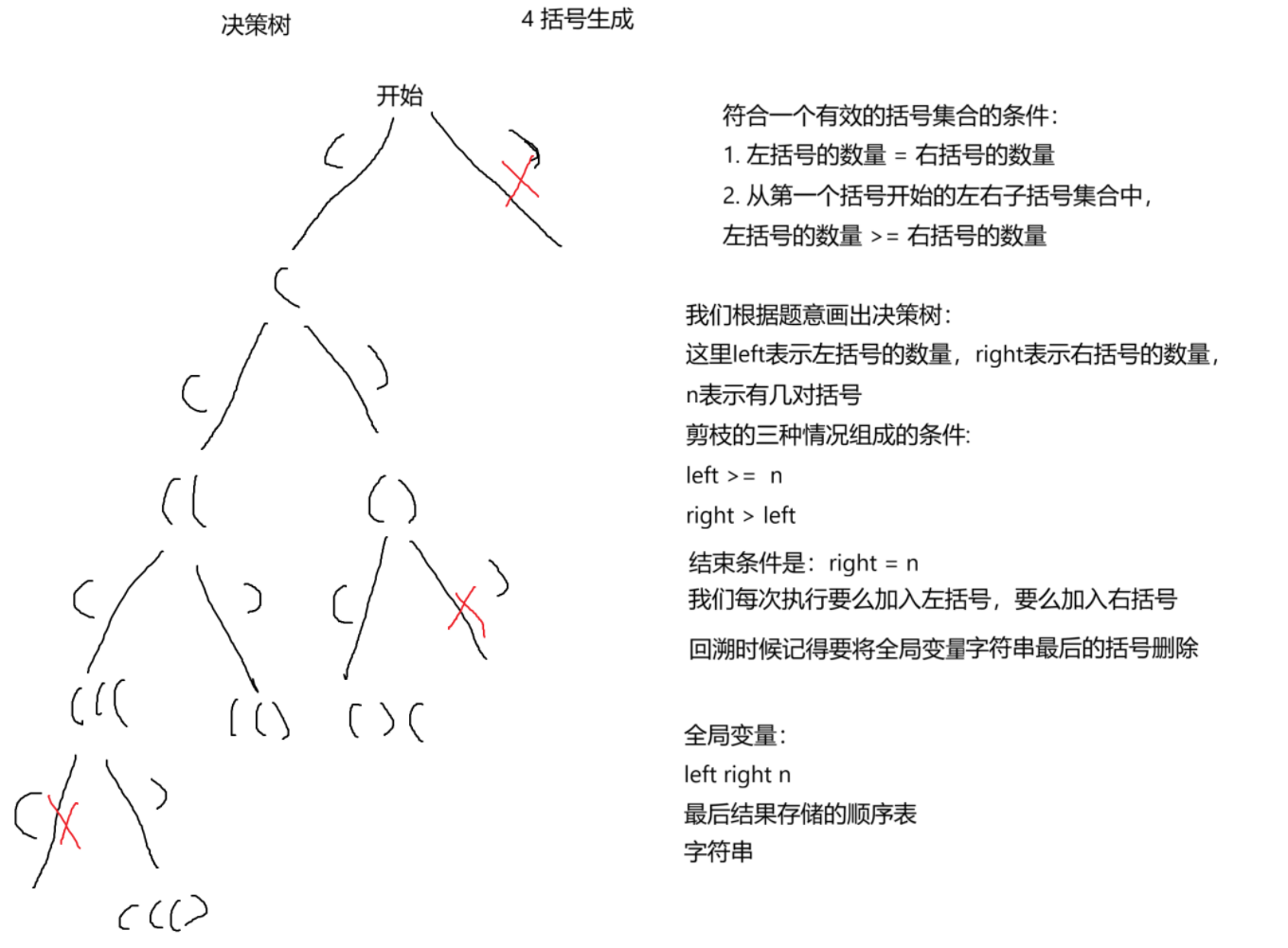
12.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
//左括号的数量
int left = 0;
//右括号的数量
int right = 0;
//括号的对数
int count = 0;
List<String> ret = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder path = null;
public List<String> generateParenthesis(int n) {
count = n;
path = new StringBuilder();
dfs();
return ret;
}
public void dfs() {
//结束条件
if(right == count) {
ret.add(path.toString());
return;
}
//添加左括号
if(left < count) {
path.append("(");
left++;
dfs();
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
left--;
}
//添加右括号
if(right < left) {
path.append(")");
right++;
dfs();
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
right--;
}
}
}13. 组合
13.1 解题思路


13.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combine(int n, int k) {
dfs(n,k,1);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int n, int k, int pos) {
if(path.size() == k) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = pos; i <= n; i++) {
path.add(i);
dfs(n,k,i+1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}14. 目标和
14.1 解题思路

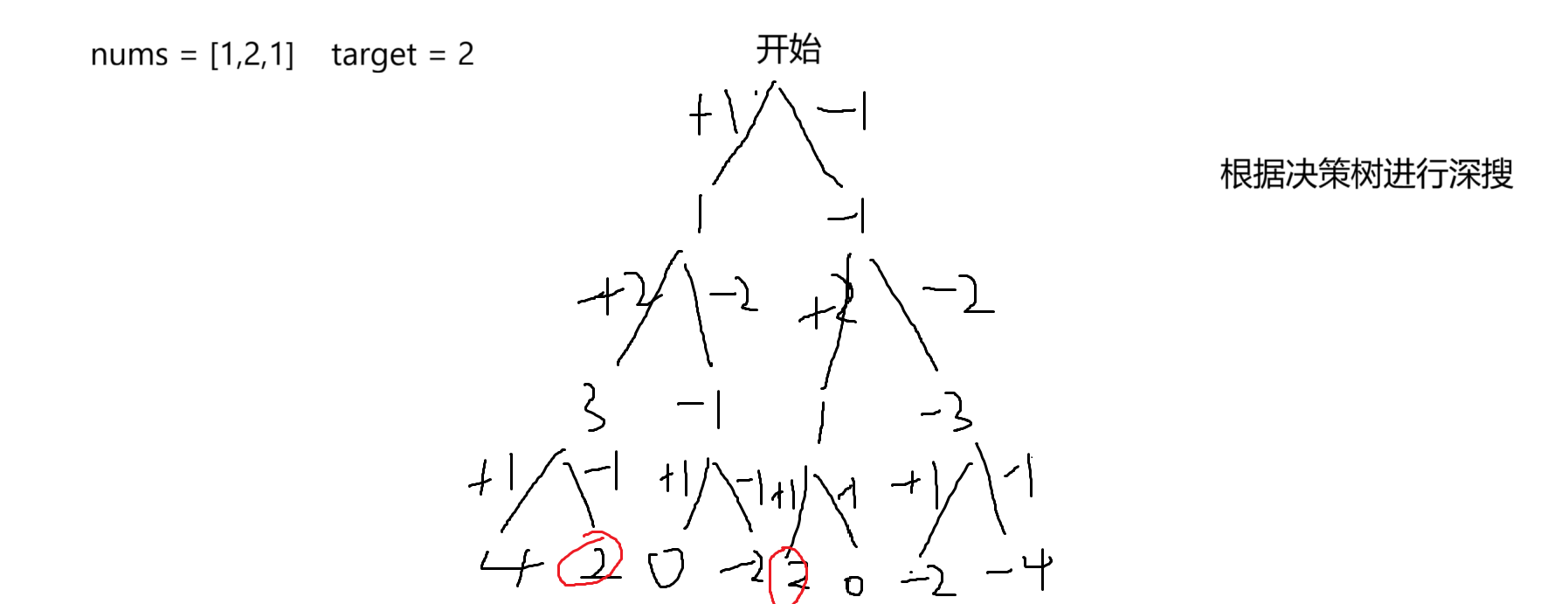
14.2 代码实现
将path设置为全局变量:
java
class Solution {
int count = 0;
int path = 0;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
dfs(nums,target,0);
return count;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums, int target, int pos) {
if(pos == nums.length) {
if(path == target) {
count++;
}
return;
}
path += nums[pos];
dfs(nums,target,pos+1);
path -= nums[pos];
path -= nums[pos];
dfs(nums,target,pos+1);
path += nums[pos];
}
}将path设置为参数:
java
class Solution {
int count = 0;
public int findTargetSumWays(int[] nums, int target) {
dfs(nums,target,0,0);
return count;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums, int target, int pos, int path) {
if(pos == nums.length) {
if(path == target) {
count++;
}
return;
}
dfs(nums,target,pos+1,path + nums[pos]);
dfs(nums,target,pos+1,path - nums[pos]);
}
}15. 组合总和
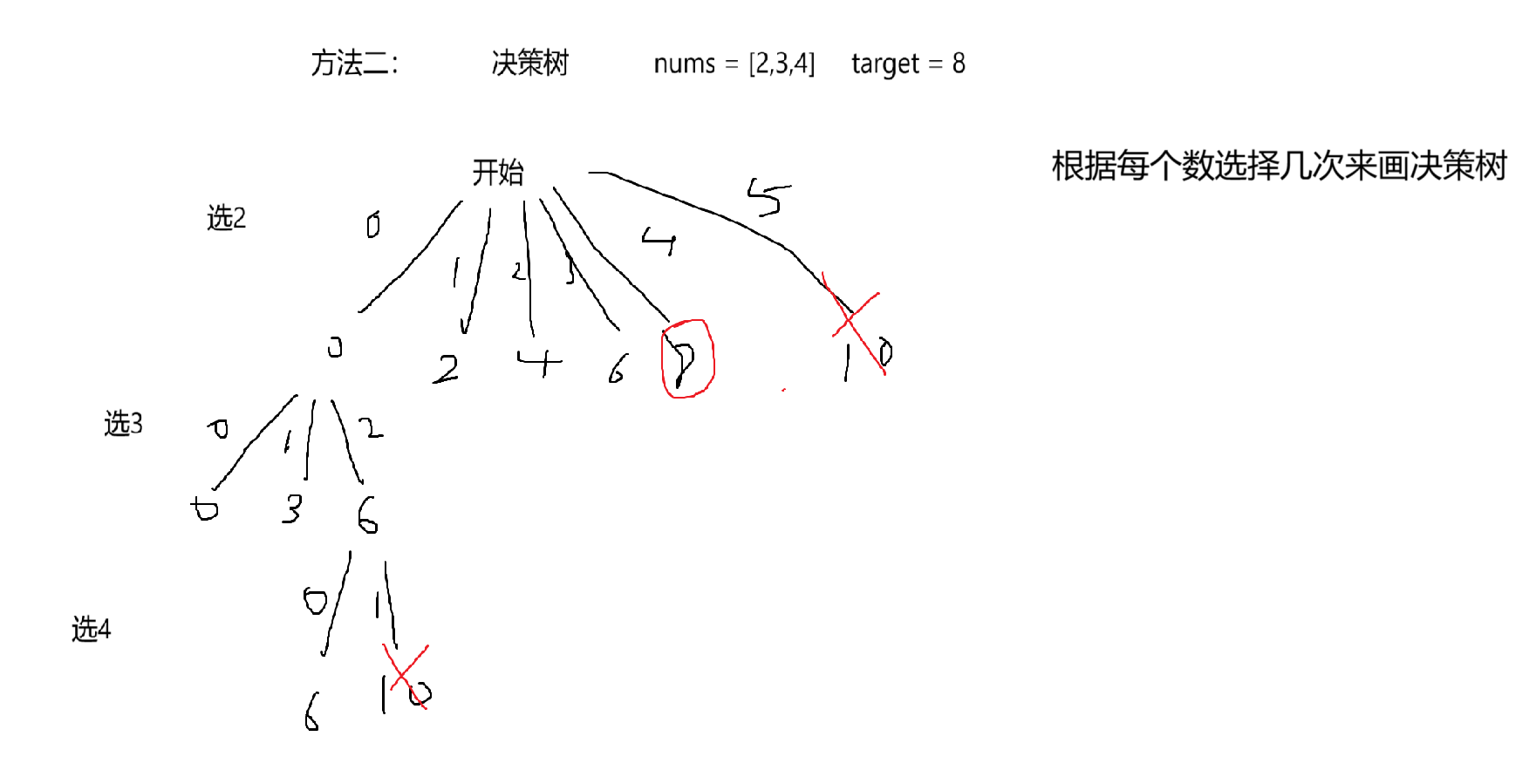
15.1 解题思路

方法一:
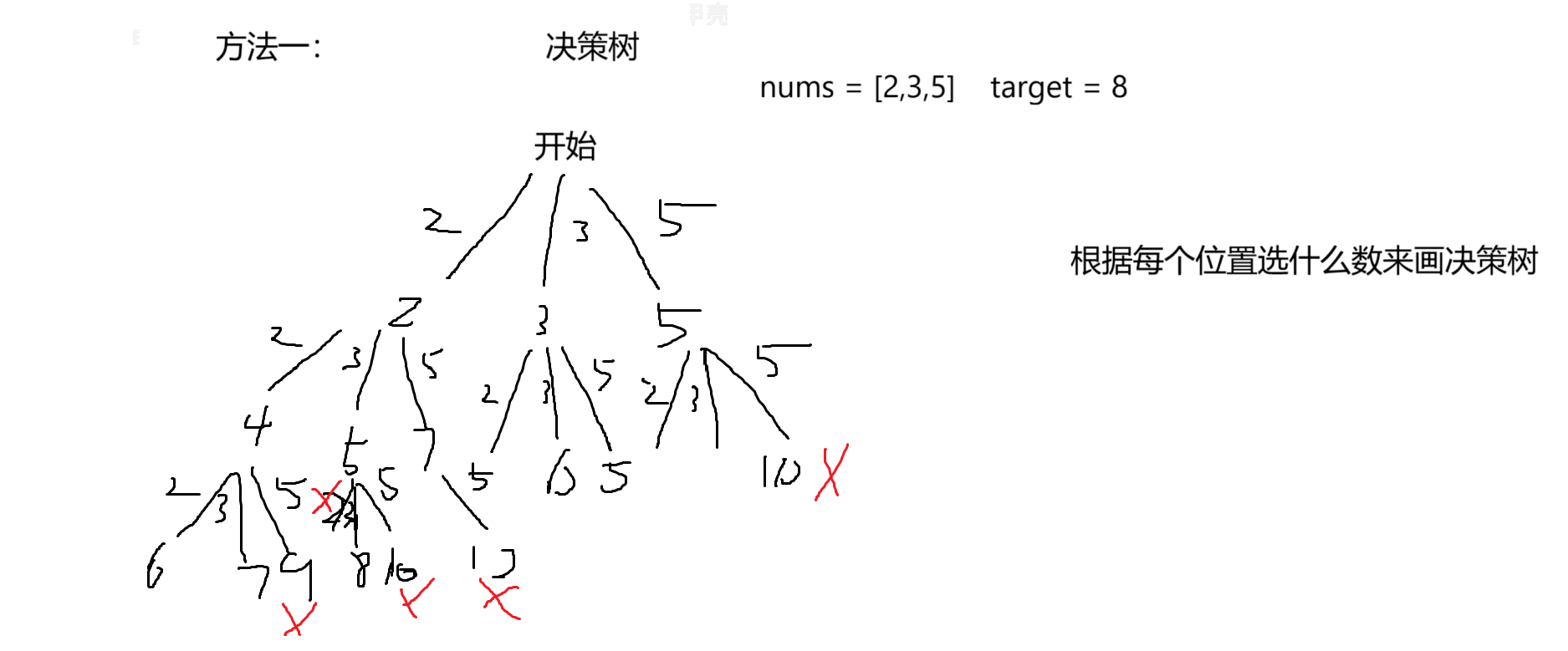
方法二:
15.2 代码实现
方法一:
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
dfs(candidates,target,0,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] candidates, int target, int pos, int sum) {
if(sum >= target || pos == candidates.length) {
if(sum == target) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return;
}
for(int i = pos; i < candidates.length; i++) {
path.add(candidates[i]);
dfs(candidates,target,i,sum + candidates[i]);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}方法二:
java
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
dfs(candidates,target,0,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int[] nums, int target, int pos, int sum) {
if(sum >= target || pos == nums.length) {
if(sum == target) {
ret.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
return;
}
//nums[pos] 表示这个数
for(int i = 0; i * nums[pos] <= target; i++) {
if(i != 0) {
path.add(nums[pos]);
}
dfs(nums,target,pos + 1,sum + i * nums[pos]);
}
//回溯时候恢复原来状况
for(int i = 1; i * nums[pos] <= target; i++) {
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}16. 字母大小写全排列
16.1 解题思路
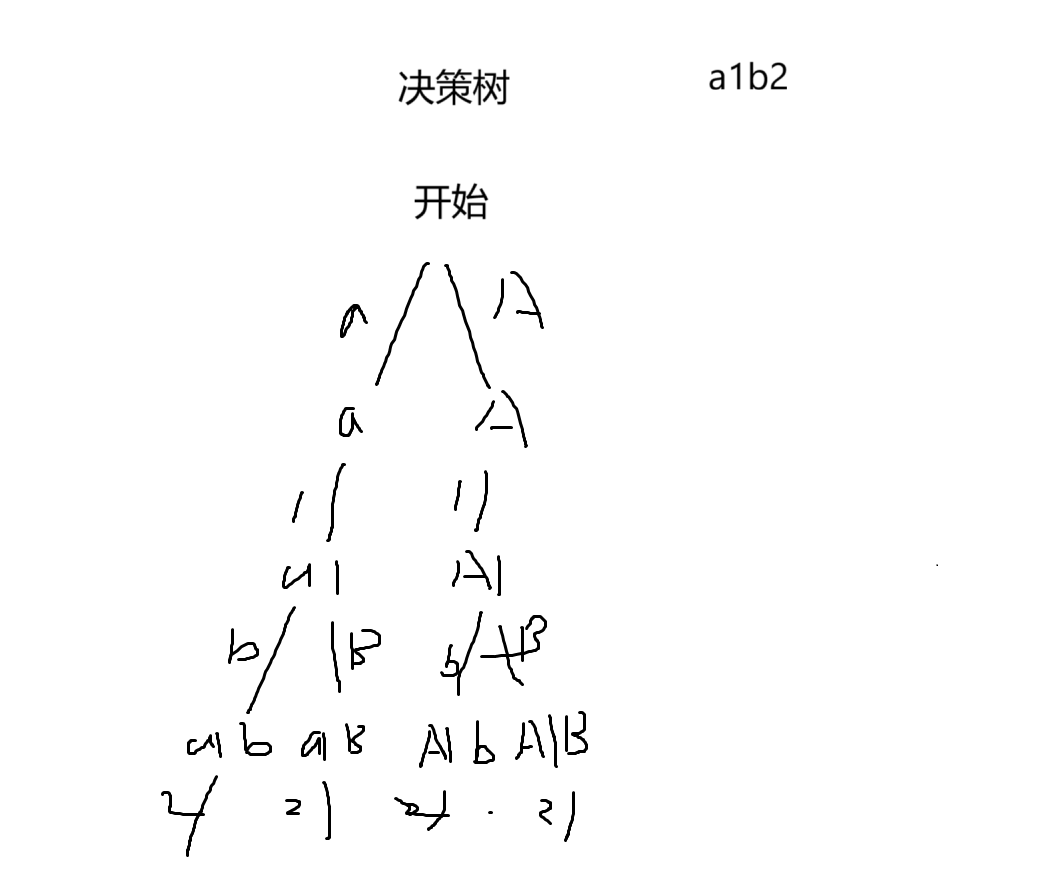
16.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
List<String> ret;
StringBuffer path;
public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s) {
ret = new ArrayList<>();
path = new StringBuffer();
dfs(s,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(String s, int pos) {
if(pos == s.length()) {
ret.add(path.toString());
return;
}
char c = s.charAt(pos);
//不改变字符
path.append(c);
dfs(s,pos+1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
//改变字符
if(c < '0' || c > '9') {
char tmp = change(c);
path.append(tmp);
dfs(s,pos+1);
path.deleteCharAt(path.length() - 1);
}
}
public char change(char c) {
if(c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') {
return c -= 32;
}else {
return c += 32;
}
}
}17. 优美的排列
17.1 解题思路
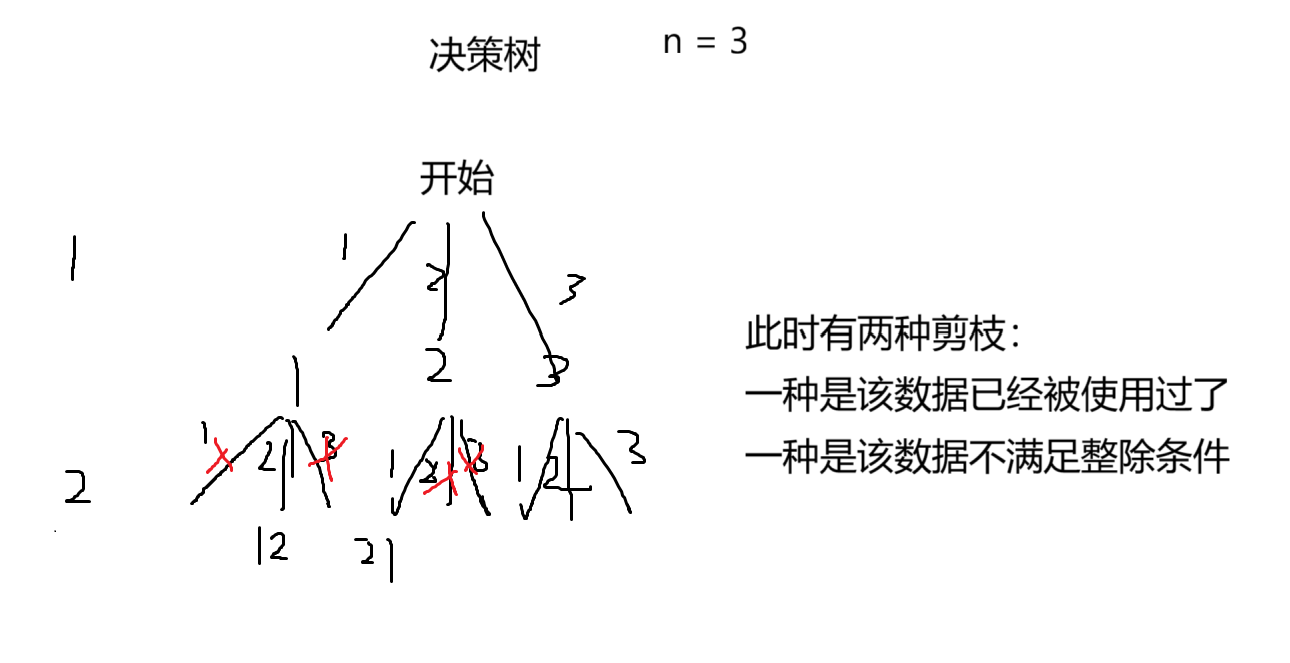
17.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
int ret = 0;
boolean[] check;
public int countArrangement(int n) {
check = new boolean[n+1];
dfs(n,1);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int n, int pos) {
if(pos == n+1) {
ret++;
return;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if((check[i] == false) && (i % pos == 0 || pos % i == 0)) {
check[i] = true;
dfs(n,pos+1);
check[i] = false;
}
}
}
}18. N皇后
18.1 解题思路
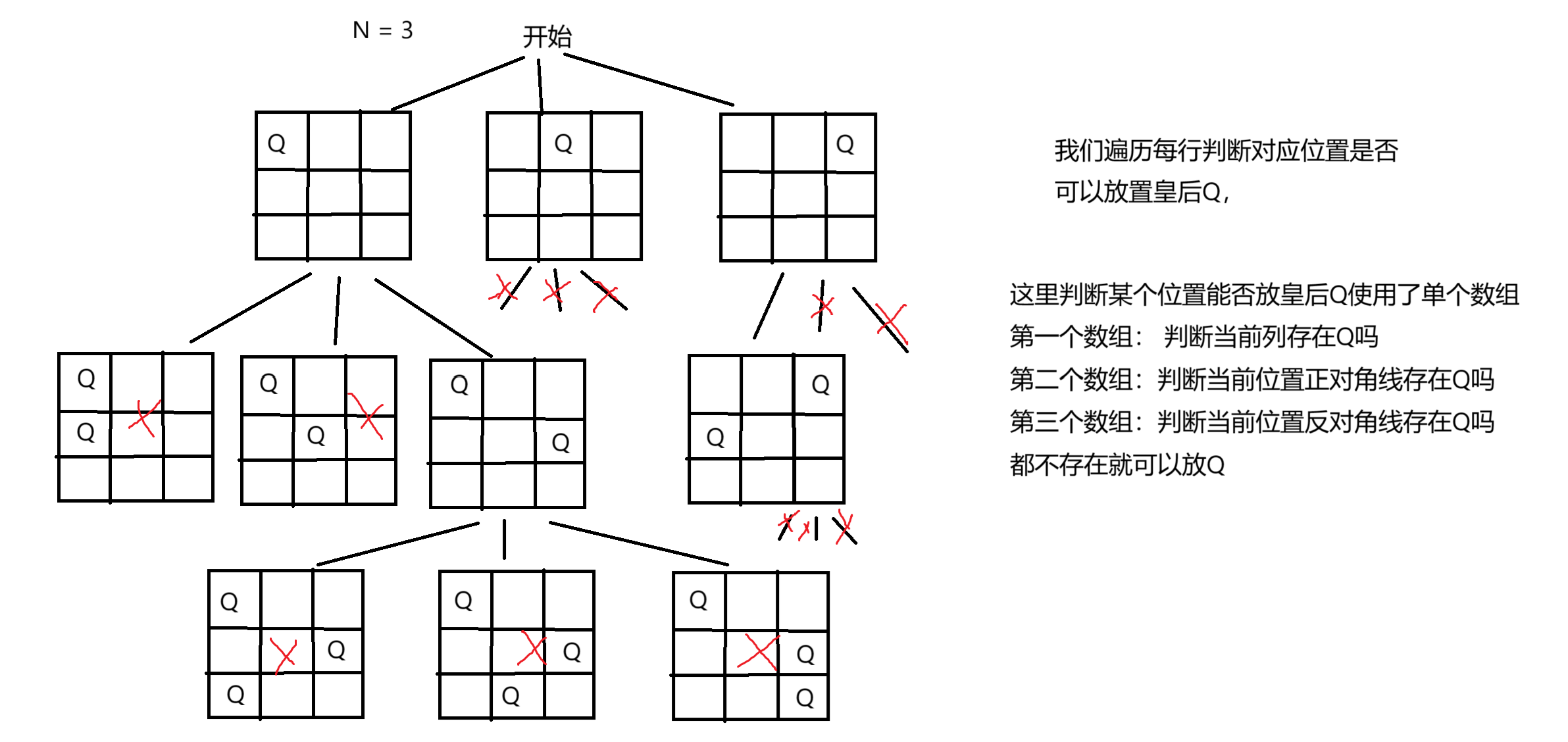
18.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
List<List<String>> ret;
//表示列是否存在皇后
boolean[] checkCol;
//表示主对角线是否存在皇后
boolean[] dig1;
//表示副对角线是否存在皇后
boolean[] dig2;
char[][] path;
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
ret = new ArrayList<>();
checkCol = new boolean[n];
dig1 = new boolean[2 * n];// y - x + n = b + n
dig2 = new boolean[2 * n];//y + x = b
path = new char[n][n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Arrays.fill(path[i],'.');
}
dfs(n,0);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(int n, int row) {
if(row == n) {
List<String> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
tmp.add(new String(path[i]));
}
ret.add(new ArrayList<String>(tmp));
return;
}
//列数
for(int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
//判断能不能放
if(checkCol[col] == false && dig1[row - col + n] == false &&
dig2[row + col] == false) {
path[row][col] = 'Q';
checkCol[col] = true; dig1[row - col + n] = true; dig2[row + col] = true;
dfs(n,row + 1);
path[row][col] = '.';
checkCol[col] = false; dig1[row - col + n] = false; dig2[row + col] = false;
}
}
}
}19. 有效数独
19.1 解题思路

19.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
//代表第几行是否存在某个数字
boolean[][] row = new boolean[9][10];
//代表第几列是否存在某个数字
boolean[][] col = new boolean[9][10];
//表示某个九宫小格子是否存在某个数字
boolean[][][] grid = new boolean[3][3][10];
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if(board[i][j] != '.') {
int tmp = board[i][j] - '0';
if(row[i][tmp] == false && col[j][tmp] == false &&
grid[i/3][j/3][tmp] == false) {
row[i][tmp] = true;
col[j][tmp] = true;
grid[i/3][j/3][tmp] = true;
}else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}20. 解数独
20.1 解题思路
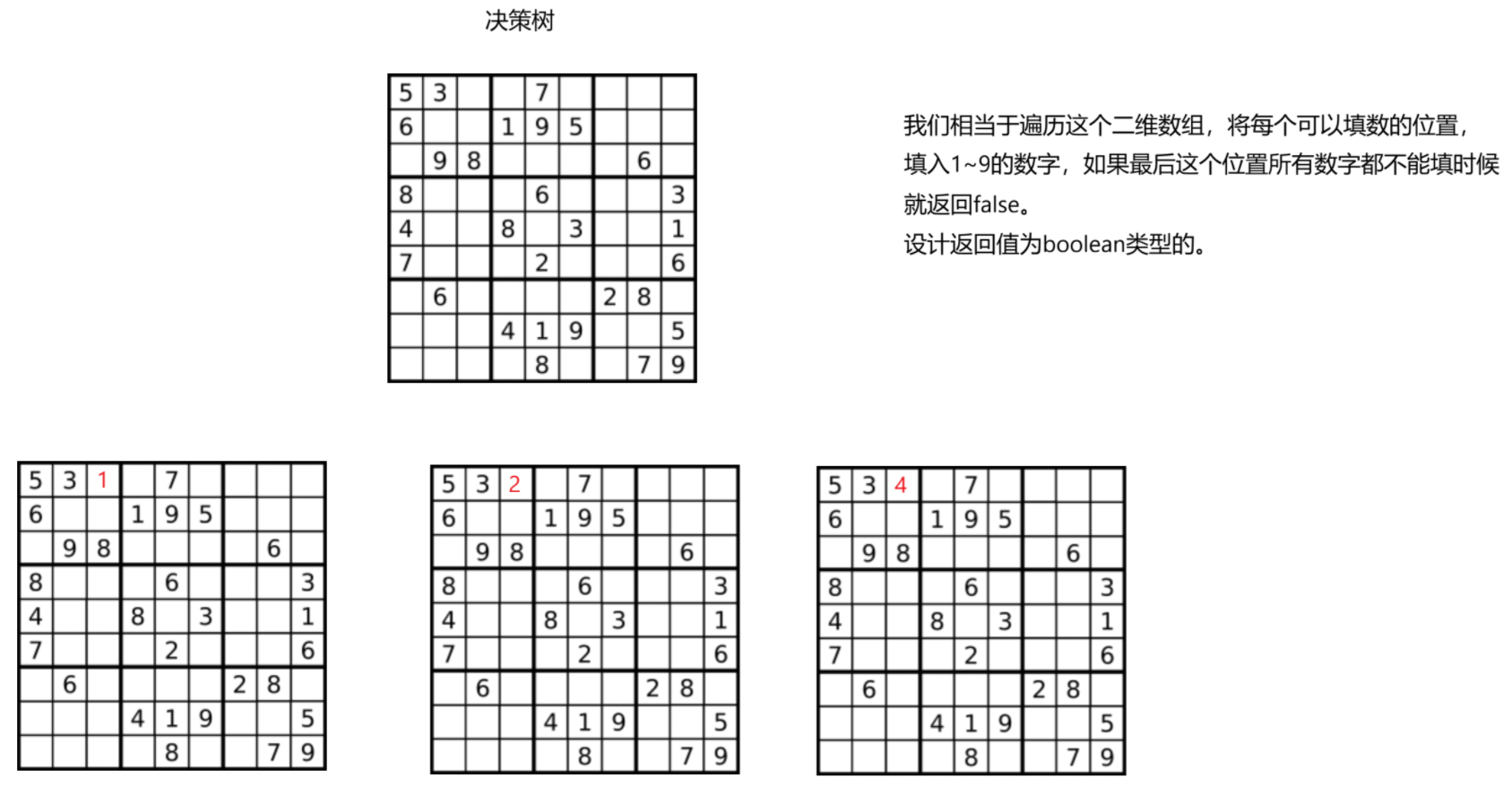
20.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
boolean[][] row = new boolean[9][10];
boolean[][] col = new boolean[9][10];
boolean[][][] grid = new boolean[3][3][10];
public void solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] != '.') {
int tmp = board[i][j] - '0';
row[i][tmp] = col[j][tmp] = grid[i / 3][j / 3][tmp] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(board);
}
public boolean dfs(char[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
if (board[i][j] == '.') {
//空位置填数
for (int k = 1; k <= 9; k++) {
//剪枝
if (row[i][k] == false && col[j][k] == false &&
grid[i / 3][j / 3][k] == false) {
board[i][j] = (char) ('0' + k);
row[i][k] = col[j][k] = grid[i / 3][j / 3][k] = true;
//这里要检查是否成功的填入成功
if (dfs(board) == true) {
return true;
}
//恢复原来状态
board[i][j] = '.';
row[i][k] = col[j][k] = grid[i / 3][j / 3][k] = false;
}
}
//如果没有返回true,说明没有填入成功
return false;
}
}
}
//数独遍历完成之后,说明此时数独已经填完了
return true;
}
}21. 单词搜索
21.1 解题思路
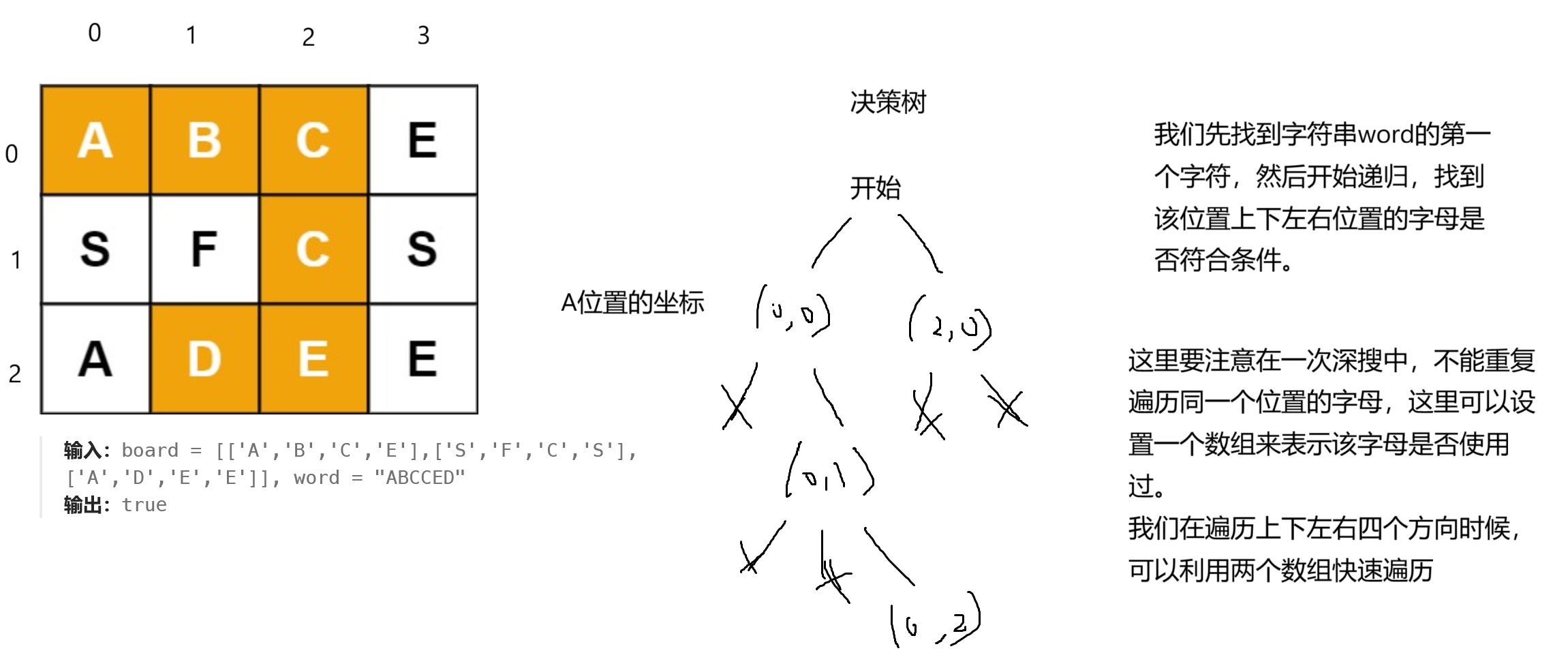
21.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
//判断原数组某个位置是否遍历过
boolean[][] check = null;
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
check = new boolean[board.length][board[0].length];
for(int i = 0; i < board.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < board[0].length; j++) {
if(board[i][j] == word.charAt(0)) {
//找到第一个字母
check[i][j] = true;
if(dfs(board,word,i,j,1)) {
return true;
}
check[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//利用两个数组来表示一个位置的上下左右四个位置
int[] dx = {-1,1,0,0};
int[] dy = {0,0,-1,1};
public boolean dfs(char[][] board, String word, int i, int j, int pos) {
//结束条件
if(pos == word.length()) {
return true;
}
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
//判断下一个位置是否合法
if(x >= 0 && x < board.length && y >= 0 && y < board[0].length &&
check[x][y] == false && board[x][y] == word.charAt(pos)) {
check[x][y] = true;
if(dfs(board,word,x,y,pos+1)) {
return true;
}
check[x][y] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
}22. 黄金矿工
22.1 解题思路
这道题跟上道题类似,需要注意的是,如何获取最后的结果,我们可以定义一个全局变量max来记录最后的结果。
22.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
boolean[][] check = null;
int max = 0;
int m = 0;
int n = 0;
public int getMaximumGold(int[][] grid) {
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
check = new boolean[m][n];
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] != 0) {
check[i][j] = true;
dfs(grid,i,j,grid[i][j]);
check[i][j] = false;
}
}
}
return max;
}
int[] dx = {-1,1,0,0};
int[] dy = {0,0,-1,1};
public void dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j, int tmp) {
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n &&
check[x][y] == false && grid[x][y] != 0) {
tmp += grid[x][y];
max = Math.max(max,tmp);
check[x][y] = true;
dfs(grid,x,y,tmp);
check[x][y] = false;
tmp -= grid[x][y];
}
}
}
}23. 不同路径3
23.1 解题思路
这道题跟前面两道题类似,起点为1,终点为2,通过0的个数+2来作为正确结果的步数。
23.2 代码实现
java
class Solution {
//最后的结果
int count = 0;
boolean[][] check = null;
int m = 0;
int n = 0;
//数组中0的个数
int zeroCount = 0;
int[] dx = {-1,1,0,0};
int[] dy = {0,0,-1,1};
public int uniquePathsIII(int[][] grid) {
m = grid.length;
n = grid[0].length;
check = new boolean[m][n];
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if(grid[i][j] == 0) {
zeroCount++;
}
if(grid[i][j] == 1) {
x = i;
y = j;
}
}
}
check[x][y] = true;
dfs(grid,x,y,1);
return count;
}
public void dfs(int[][] grid, int i, int j, int path) {
if(grid[i][j] == 2) {
if(path == zeroCount + 2) {
count++;
}
return;
}
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int x = i + dx[k];
int y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 0 && x < m && y >= 0 && y < n &&
check[x][y] == false && grid[x][y] != -1) {
check[x][y] = true;
dfs(grid,x,y,path + 1);
check[x][y] = false;
}
}
}
}