文章目录
一、栈的基本概念
栈(Stack)是一种后进先出(LIFO, Last In First Out)的线性数据结构。通俗地说:最后放进去的元素最先被取出来,就像一叠盘子,最后放上去的盘子最先拿出来。
栈的主要特点:

栈的基本操作:

二、数组版本的栈实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 顺序栈
class SeqStack {
public:
SeqStack(int size = 10)
: mtop(0)
, mcap(size) {
mpStack = new int[mcap];
}
~SeqStack() {
delete[] mpStack;
mpStack = nullptr;
}
public:
// 入栈
void push(int val) {
if (mtop == mcap) {
// 栈扩容
expand(2 * mcap);
}
mpStack[mtop++] = val;
}
// 出栈
void pop() {
if (mtop == 0) {
throw "stack is empty";
}
mtop--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
int top() const {
if (mtop == 0) {
throw "stack is empty";
}
return mpStack[mtop - 1];
}
// 栈空
bool empty() {
return mtop == 0;
}
int size() const {
return mtop;
}
private:
void expand(int size) {
int* p = new int[size];
memcpy(p, mpStack, mtop * sizeof(int));
delete[] mpStack;
mpStack = p;
mcap = size;
}
private:
int* mpStack;
int mtop; // 栈顶位置
int mcap; // 栈空间大小
};
int main() {
int array[] = { 12, 4, 56, 7, 89, 31, 53, 75 };
SeqStack s;
for (int v : array) {
s.push(v);
}
while (!s.empty()) {
std::cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop();
}
return 0;
}输出结果:

三、链表版的栈实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 链式栈
class LinkStack {
public:
LinkStack() : size_(0) {
head_ = new Node;
}
~LinkStack() {
Node* p = head_;
while (p != nullptr) {
head_ = head_->next_;
delete p;
p = head_;
}
}
public:
// 入栈 O(1) 把链表头节点后面,第一个有笑点的位置,当作栈顶位置
void push(int val) {
Node* node = new Node(val);
node->next_ = head_->next_;
head_->next_ = node;
size_++;
}
// 出栈 O(1)
void pop() {
if (head_->next_ == nullptr) {
throw "stack is empty!";
}
Node* p = head_->next_;
head_->next_ = p->next_;
delete p;
size_--;
}
// 获取栈顶操作
int top() const {
if (head_->next_ == nullptr) {
throw "stack is empty!";
}
return head_->next_->data_;
}
// 判空
bool empty() const {
return head_->next_ == nullptr;
}
// 返回栈元素个数 O(1)
int size() const {
return size_;
}
private:
struct Node {
Node(int data = 0) : data_(data), next_(nullptr) {}
int data_;
Node* next_;
};
Node* head_;
int size_;
};
int main() {
int array[] = { 12, 4, 56, 7, 89, 31, 53, 75 };
LinkStack s;
for (int v : array) {
s.push(v);
}
while (!s.empty()) {
std::cout << s.top() << " ";
s.pop();
}
return 0;
}输出结果:

四、括号匹配
问题描述:
给定一个只包含括号的字符串,如:
cpp
"([]){}"要求判断这个字符串的括号是否匹配正确。
匹配规则如下:
- 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合;
- 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合;
- 每个右括号都有一个对应的相同类型的左括号。
为什么使用栈?
栈是一种后进先出(LIFO) 的数据结构。括号匹配的逻辑恰好与栈的特性吻合:
- 每当遇到一个左括号 ( [ {,就压入栈;
- 每当遇到一个右括号 ) ] },就弹出栈顶元素进行匹配;
- 如果不匹配或者栈为空,就表示错误;
- 最后,栈为空则表示匹配完全正确。
算法步骤:
实现代码:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
bool isMatching(char left, char right) {
return (left == '(' && right == ')') ||
(left == '[' && right == ']') ||
(left == '{' && right == '}');
}
bool isValidParentheses(const string& s) {
stack<char> st;
for (char c : s) {
// 左括号 -> 入栈
if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') {
st.push(c);
} else if (c == ')' || c == ']' || c == '}') {
// 右括号 -> 检查匹配
if (st.empty()) return false; // 没有可匹配的左括号
char top = st.top();
st.pop();
if (!isMatching(top, c)) return false; // 类型不匹配
}
}
// 最后栈应为空
return st.empty();
}
int main() {
string test1 = "{[()]}";
string test2 = "([)]";
string test3 = "((()))";
string test4 = "{[()]}[";
cout << test1 << " -> " << (isValidParentheses(test1) ? "匹配正确" : "匹配错误") << endl;
cout << test2 << " -> " << (isValidParentheses(test2) ? "匹配正确" : "匹配错误") << endl;
cout << test3 << " -> " << (isValidParentheses(test3) ? "匹配正确" : "匹配错误") << endl;
cout << test4 << " -> " << (isValidParentheses(test4) ? "匹配正确" : "匹配错误") << endl;
return 0;
}输出结果:

五、逆波兰表达式(RPN)
逆波兰表达式(Reverse Polish Notation, RPN) 又称为后缀表达式。
它的特点是:
- 操作符在操作数之后 出现;
- 不需要括号,计算顺序由表达式本身决定。
例如:
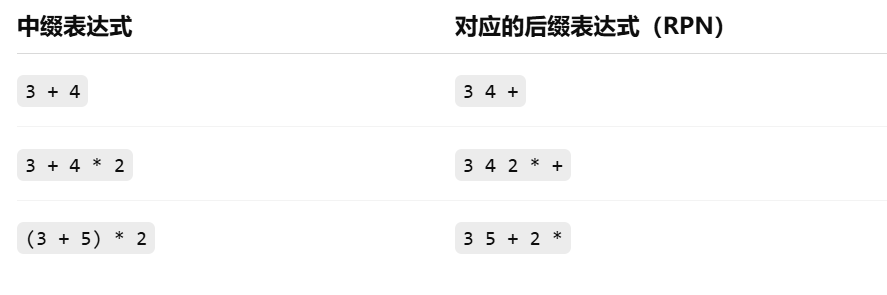
为什么用栈?
逆波兰表达式求值的核心思想是:
- 从左到右扫描表达式
- 遇到操作数(数字) → 入栈
- 遇到运算符 → 从栈中弹出两个操作数,计算结果再入栈
- 扫描结束时,栈顶的值就是最终结果
算法步骤
- 创建一个空栈;
- 从左到右扫描逆波兰表达式:
- 如果是数字 → 入栈;
- 如果是运算符(如 + - * /):
- 弹出两个操作数(注意顺序:先弹出的为右操作数 b,后弹出的为左操作数 a)
- 计算 a op b
- 将结果压回栈;
- 扫描结束 → 栈顶元素即为最终结果。
实现示例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <stdexcept>
using namespace std;
// 判断字符串是否为数字
bool isNumber(const string& s) {
if (s[0] == '+' || s[0] == '-' ||
s[0] == '*' || s[0] == '/') {
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 执行一次运算
double applyOp(double a, double b, const string& op) {
if (op == "+") return a + b;
if (op == "-") return a - b;
if (op == "*") return a * b;
if (op == "/") {
if (b == 0) throw runtime_error("除零错误");
return a / b;
}
throw runtime_error("未知运算符:" + op);
}
// 计算逆波兰表达式(后缀表达式)
double evalRPN(const string& expr) {
stack<double> st;
stringstream ss(expr);
string token;
while (ss >> token) {
if (isNumber(token)) {
st.push(stod(token));
} else {
if (st.size() < 2) throw runtime_error("表达式错误,操作数不足");
double b = st.top(); st.pop();
double a = st.top(); st.pop();
st.push(applyOp(a, b, token));
}
}
if (st.size() != 1) throw runtime_error("表达式错误:栈中剩余元素不为1");
return st.top();
}
int main() {
try {
string expr1 = "3 4 +"; // => 7
string expr2 = "3 4 2 * +"; // => 11
string expr3 = "3 5 + 2 *"; // => 16
string expr4 = "10 2 8 * + 3 -"; // => 23
cout << expr1 << " = " << evalRPN(expr1) << endl;
cout << expr2 << " = " << evalRPN(expr2) << endl;
cout << expr3 << " = " << evalRPN(expr3) << endl;
cout << expr4 << " = " << evalRPN(expr4) << endl;
}
catch (const exception& e) {
cout << "错误: " << e.what() << endl;
}
return 0;
}输出结果:
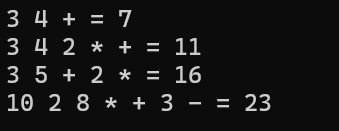
六、中缀表达式转为后缀表达式
基本思想(使用栈 Stack)
使用两个序列:
- 输出序列:存放生成的后缀表达式
- 运算符栈:存放操作符(+ − * / ( ) 等)
核心规则:
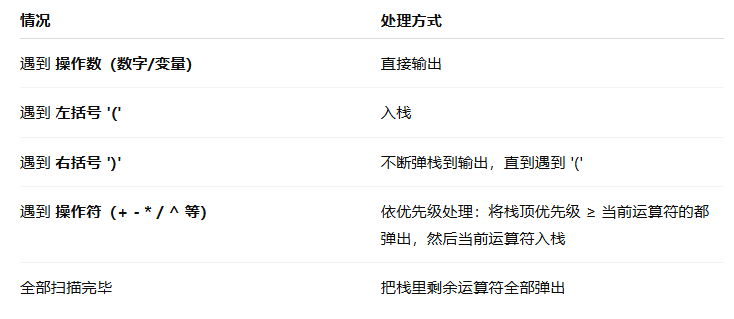
运算符优先级
设定一个函数:
cpp
^ // 最高,幂
* / // 其次
+ - // 最低举例说明
中缀表达式:
cpp
A + B * C - (D - E) * F转换过程(略),最终后缀表达式:
cpp
A B C * + D E - F * -实现代码:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// 返回运算符优先级
int precedence(char op) {
if (op == '^') return 3;
if (op == '*' || op == '/') return 2;
if (op == '+' || op == '-') return 1;
return 0;
}
// 中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式
string infixToPostfix(const string& exp) {
stack<char> st;
string output;
for (char c : exp) {
// 1. 操作数:直接输出
if (isalnum(c)) {
output += c;
}
// 2. 左括号:入栈
else if (c == '(') {
st.push(c);
}
// 3. 右括号:弹出直到 '('
else if (c == ')') {
while (!st.empty() && st.top() != '(') {
output += st.top();
st.pop();
}
st.pop(); // 弹出 '('
}
// 4. 运算符:依优先级处理
else {
while (!st.empty() && precedence(st.top()) >= precedence(c)) {
output += st.top();
st.pop();
}
st.push(c);
}
}
// 5. 剩余运算符全部弹出
while (!st.empty()) {
output += st.top();
st.pop();
}
return output;
}
int main() {
string exp = "A+B*C-(D-E)*F";
cout << "中缀: " << exp << endl;
cout << "后缀: " << infixToPostfix(exp) << endl;
return 0;
}输出结果:
