进行本实验前需要具备如下能力:
具备linux操作系统运维能力,熟练使用Linux运维命令,包括但不限top、iostat等;
熟练使用GaussDB数据库,具有理解和分析GaussDB数据库执行计划的能力;
熟悉GaussDB数据库的SQL优化方法。
实验环境准备
1.确定sysbench等压测工具安装成功。
sql
[root@gs01 lib64]# sysbench --version
sysbench 1.0.17-71abd99
[root@gs01 lib64]# 2.GaussDB中创建用户,之后sysbench压测使用。
sql
gsql -d postgres -p 8000 -r
create user sysbench with sysadmin password 'Huawei@1234';3.验证sysbench用户是否可以登录。
sql
[Ruby@gs01 cm_agent]$ gsql -d postgres -p 8000 -U sysbench -W Huawei@1234 -h 192.168.3.60 -r
gsql ((GaussDB Kernel 505.2.1.SPC0800 build 85996fbb) compiled at 2025-07-03 01:15:58 commit 10558 last mr 24271 release)
SSL connection (cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256, bits: 128)
Type "help" for help.
gaussdb=>
gaussdb=> \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+-------+-----------+---------+-------+-------------------
postgres | Ruby | SQL_ASCII | C | C |
template0 | Ruby | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/Ruby +
| | | | | Ruby=CTc/Ruby
template1 | Ruby | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/Ruby +
| | | | | Ruby=CTc/Ruby
templatea | Ruby | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/Ruby +
| | | | | Ruby=CTc/Ruby
templatem | Ruby | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/Ruby +
| | | | | Ruby=CTc/Ruby
(5 rows)4.创建测试库。
sql
[Ruby@gs01 cm_agent]$ gsql -d postgres -p 8000 -U sysbench -W Huawei@1234 -c "create database db_test;"
CREATE DATABASE
[Ruby@gs01 cm_agent]$ 5.初始化数据。
sql
[root@gs01 share]# sysbench oltp_read_write --tables=1 --table-size=5000000 --threads=8 --time=600 --db-driver=pgsql --pgsql-db=db_test --pgsql-user=sysbench --pgsql-password=Huawei@1234 --pgsql-host=192.168.3.60 --pgsql-port=8000 --report-interval=5 prepare
sysbench 1.0.17-71abd99 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta2)
Initializing worker threads...
FATAL: Connection to database failed: none of the server's SASL authentication mechanisms are supported
FATAL: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: ./oltp_common.lua:88: connection creation failed
FATAL: Connection to database failed: none of the server's SASL authentication mechanisms are supported
FATAL: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: ./oltp_common.lua:88: connection creation failed
FATAL: Connection to database failed: none of the server's SASL authentication mechanisms are supported
FATAL: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: ./oltp_common.lua:88: connection creation failed
FATAL: Connection to database failed: none of the server's SASL authentication mechanisms are supported
FATAL: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: ./oltp_common.lua:88: connection creation failed
FATAL: Connection to database failed: none of the server's SASL authentication mechanisms are supported
FATAL: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: ./oltp_common.lua:88: connection creation failed
FATAL: Connection to database failed: none of the server's SASL authentication mechanisms are supported
FATAL: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: ./oltp_common.lua:88: connection creation failed
FATAL: Connection to database failed: none of the server's SASL authentication mechanisms are supported
FATAL: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: ./oltp_common.lua:88: connection creation failed
FATAL: Connection to database failed: none of the server's SASL authentication mechanisms are supported
FATAL: `sysbench.cmdline.call_command' function failed: ./oltp_common.lua:88: connection creation failed解决办法:
sql
[Ruby@gs01 cm_agent]$ gs_guc reload -Z datanode -N all -I all -c "password_encryption_type=0"
The gs_guc run with the following arguments: [gs_guc -Z datanode -N all -I all -c password_encryption_type=0 reload ].
Begin to perform the total nodes: 1.
Popen count is 1, Popen success count is 1, Popen failure count is 0.
Begin to perform gs_guc for datanodes.
Command count is 1, Command success count is 1, Command failure count is 0.
Total instances: 1. Failed instances: 0.
ALL: Success to perform gs_guc!
[Ruby@gs01 cm_agent]$ gs_guc reload -Z datanode -N all -I all -h "host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5"
The gs_guc run with the following arguments: [gs_guc -Z datanode -N all -I all -h host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5 reload ].
Begin to perform the total nodes: 1.
Popen count is 1, Popen success count is 1, Popen failure count is 0.
Begin to perform gs_guc for datanodes.
Command count is 1, Command success count is 1, Command failure count is 0.
Total instances: 1. Failed instances: 0.
ALL: Success to perform gs_guc!删除sysbench用户重新创建:
sql
gsql -d postgres -p 8000 -r
drop database db_test;
drop user sysbench;
create database db_test;
create user sysbench with sysadmin password 'Huawei@1234';6.重新执行数据初始化。
sql
[root@gs01 share]# sysbench oltp_read_write --tables=1 --table-size=5000000 --threads=8 --time=600 --db-driver=pgsql --pgsql-db=db_test --pgsql-user=sysbench --pgsql-password=Huawei@1234 --pgsql-host=192.168.3.60 --pgsql-port=8000 --report-interval=5 prepare
sysbench 1.0.17-71abd99 (using bundled LuaJIT 2.1.0-beta2)
Initializing worker threads...
Creating table 'sbtest1'...
Inserting 5000000 records into 'sbtest1'
Creating a secondary index on 'sbtest1'...
[root@gs01 share]# 7.登录GaussDB数据库,查询数据库参数synchronous_commit
sql
gaussdb=# show synchronous_commit;
synchronous_commit
--------------------
off
(1 row)8.重新设置 synchronous_commit 参数。
sql
[Ruby@gs01 cm_agent]$ gs_guc reload -Z datanode -N all -I all -c "synchronous_commit=local"
The gs_guc run with the following arguments: [gs_guc -Z datanode -N all -I all -c synchronous_commit=local reload ].
Begin to perform the total nodes: 1.
Popen count is 1, Popen success count is 1, Popen failure count is 0.
Begin to perform gs_guc for datanodes.
Command count is 1, Command success count is 1, Command failure count is 0.
Total instances: 1. Failed instances: 0.
ALL: Success to perform gs_guc!9.手动进行环境检测。
sql
sysbench oltp_read_write --tables=1 --table-size=500000000 --threads=8 --time=600 --db-driver=pgsql --pgsql-db=db_test --pgsql-user=sysbench --pgsql-password=Huawei@1234 --pgsql-host=192.168.3.60 --pgsql-port=8000 --report-interval=5 run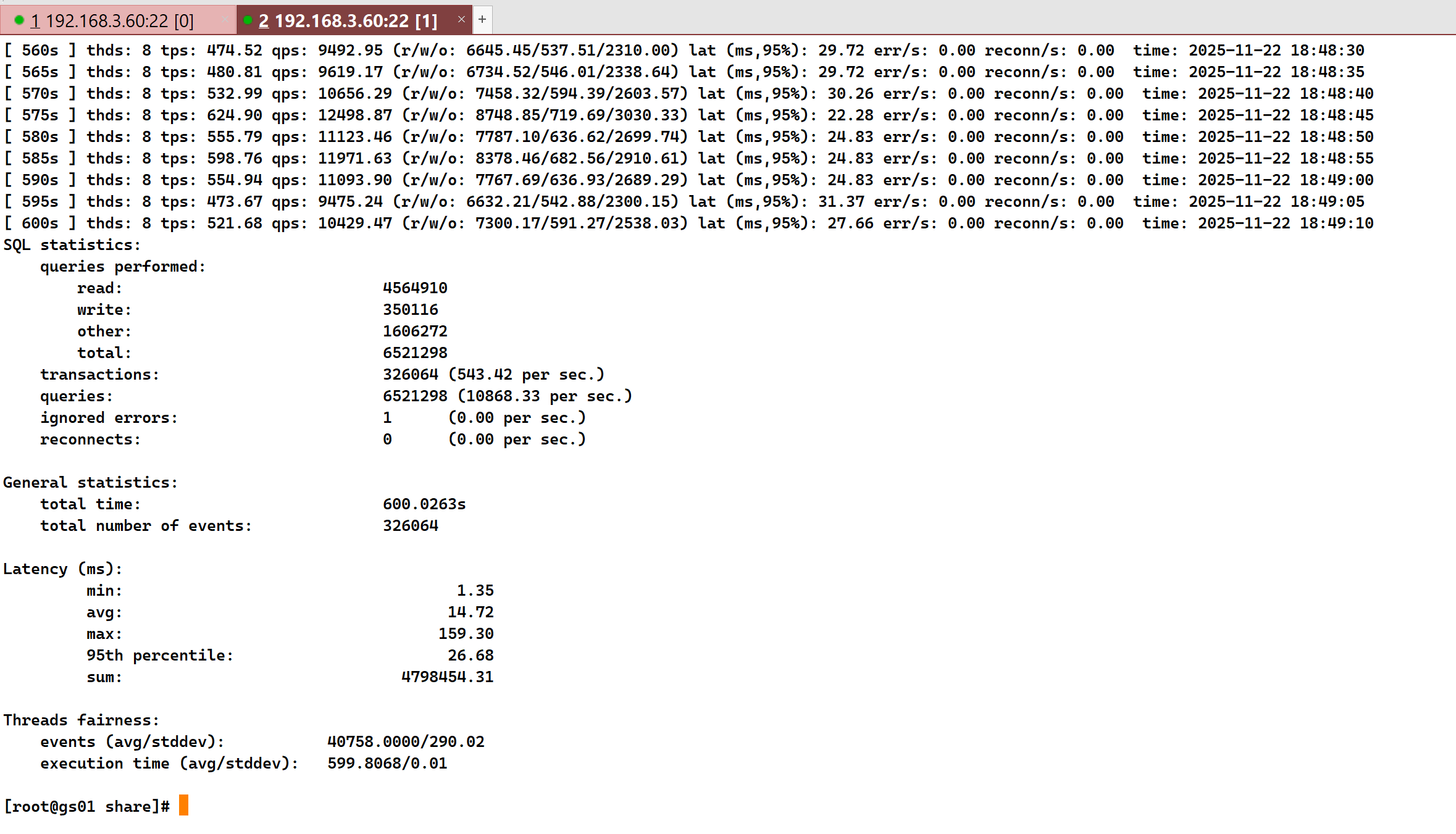
磁盘IO压力大造成的性能劣化实验模拟
1.使用如下脚本模拟常规IO压力下业务的性能情况。
sql
sysbench oltp_read_write --tables=1 --table-size=5000000 --threads=8 --time=600 --db-driver=pgsql --pgsql-db=db_test --pgsql-user=sysbench --pgsql-password=Huawei@1234 --pgsql-host=192.168.3.60 --pgsql-port=8000 --report-interval=5 --percentile=99 run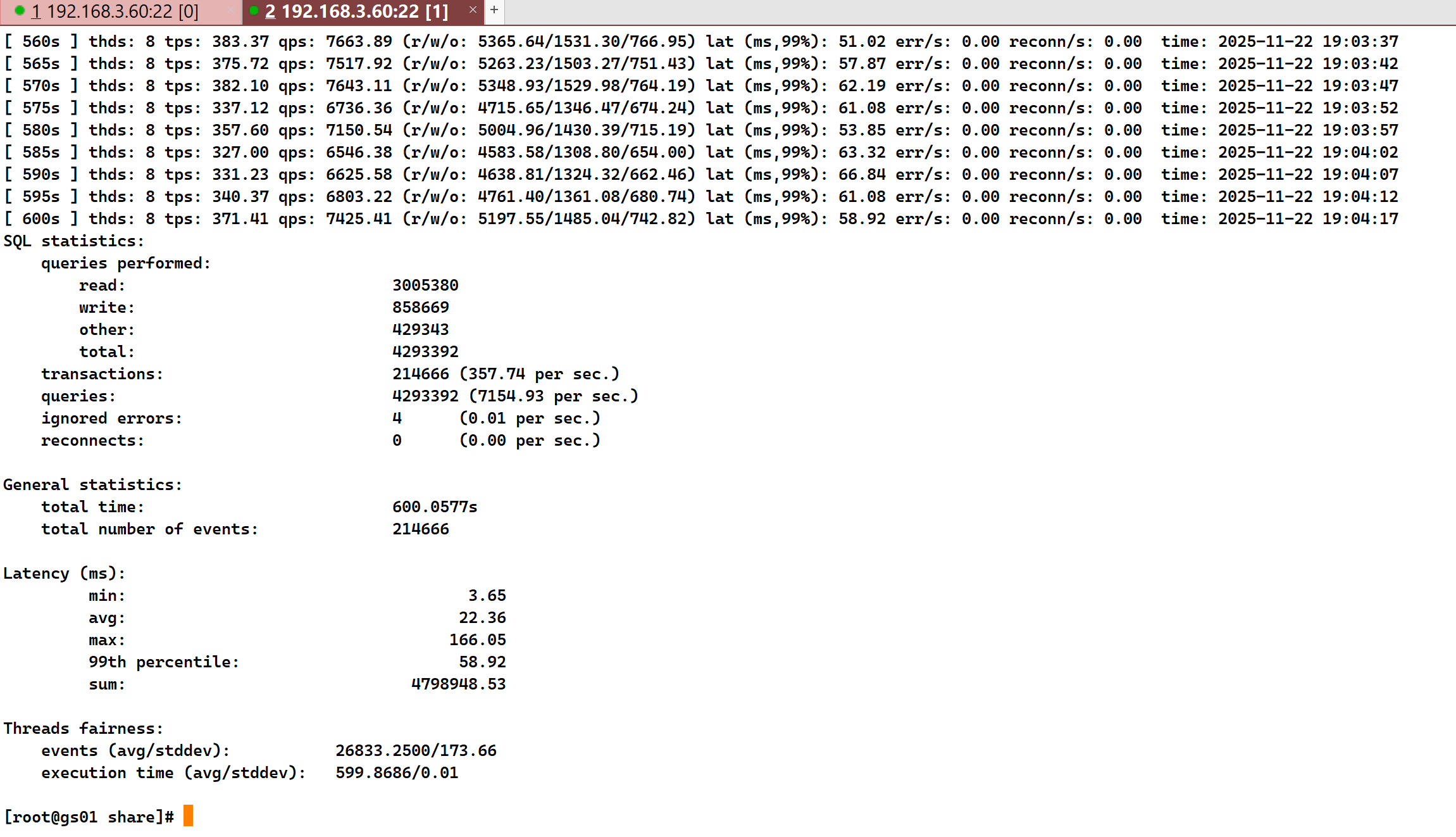
2.执行如下脚本,构建数据盘IO压力高场景。
sql
touch /data/cluster/master/datanode1/test_in
touch /data/cluster/master/datanode1/test_out
dd if=/dev/zero of="/data/cluster/master/datanode1/test_in" bs=3G count=10 iflag=fullblock
while true;
do
dd if="/data/cluster/master/datanode1/test_in" of="/data/cluster/master/datanode1/test_out" bs=3G count=10 iflag=fullblock
done;3.再次执行sysbench压测。
sql
sysbench oltp_read_write --tables=1 --table-size=5000000 --threads=8 --time=600 --db-driver=pgsql --pgsql-db=db_test --pgsql-user=sysbench --pgsql-password=Huawei@1234 --pgsql-host=192.168.3.60 --pgsql-port=8000 --report-interval=5 --percentile=99 run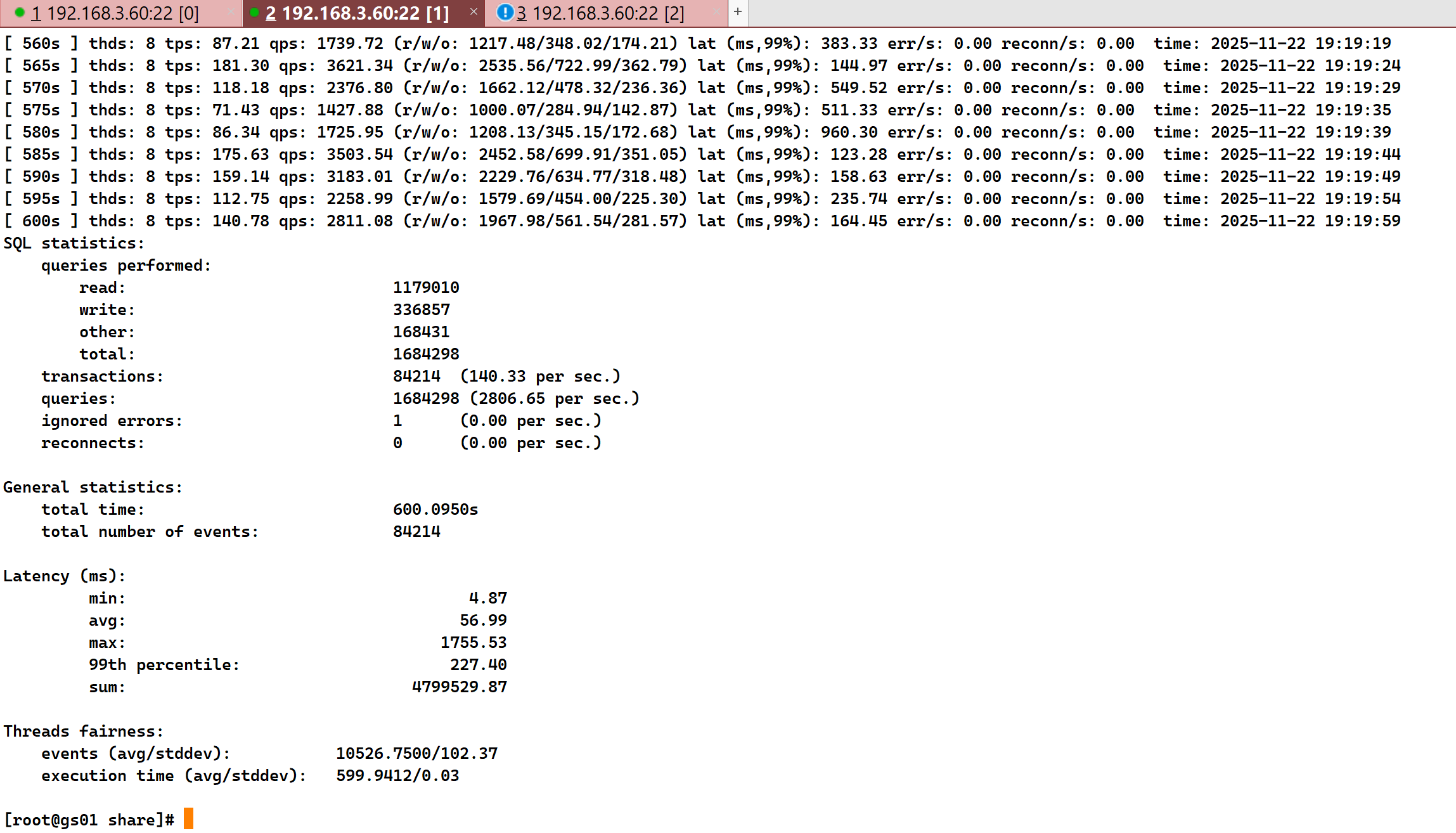
通过实验得知,没有IO读写压力的情况下TPS为357,QPS为7154;有IO读写压力的情况下,TPS为140,QPS为 2806。