目录
[1.List 概述](#1.List 概述)
[list 的存储结构](#list 的存储结构)
[List 的优缺点](#List 的优缺点)
[2.1 list的常见构造(初始化)](#2.1 list的常见构造(初始化))
[2.2 List的遍历及迭代器(重点)](#2.2 List的遍历及迭代器(重点))
[List 遍历特点:](#List 遍历特点:)
[2.3 list 容器的常见容量操作](#2.3 list 容器的常见容量操作)
[2.4 list 容器的常见元素访问](#2.4 list 容器的常见元素访问)
[2.5 list 容器的常见修改操作(重点)](#2.5 list 容器的常见修改操作(重点))
[push_front - 头部插入](#push_front - 头部插入)
[pop_front - 头部删除](#pop_front - 头部删除)
[push_back - 尾部插入](#push_back - 尾部插入)
[pop_back - 尾部删除](#pop_back - 尾部删除)
[insert - 指定位置插入](#insert - 指定位置插入)
[erase - 指定位置删除](#erase - 指定位置删除)
[swap - 交换两个list](#swap - 交换两个list)
[clear - 清空list](#clear - 清空list)
[2.6 list 容器的常见操作函数](#2.6 list 容器的常见操作函数)
[splice - 将元素从列表转移到其它列表](#splice - 将元素从列表转移到其它列表)
[void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other);](#void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other);)
[void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other, const_iterator it);](#void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other, const_iterator it);)
[void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other, const_iterator first, const_iterator last);](#void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other, const_iterator first, const_iterator last);)
[remove - 删除具有特定值的元素](#remove - 删除具有特定值的元素)
[remove_if - 删除满足条件的元素](#remove_if - 删除满足条件的元素)
[unique - 删除重复值](#unique - 删除重复值)
[sort - 容器中的元素排序](#sort - 容器中的元素排序)
[merge - 合并排序列表](#merge - 合并排序列表)
[reverse - 反转元素的顺序](#reverse - 反转元素的顺序)
0.List文档介绍
1.List 概述
list 是C++的一个序列容器,允许在序列中的任意位置进行常数时间的插入和删除操作 ,并支持双向迭代。列表容器采用双向链表 实现,与其他基本标准序列容器(数组、向量和双端队列)相比,列表在插入、提取和移动容器内已获得迭代器的任何位置的元素方面通常表现更好,主要缺点是它们无法通过位置直接访问元素
主要特性
- 双向链表结构:每个节点包含数据、指向前一个节点的指针和指向后一个节点的指针。
- 不支持随机访问:不能像数组或 vector 那样通过下标直接访问元素。
- 在任何位置插入和删除高效:时间复杂度为 O(1),前提是已经获得了要操作的位置的迭代器。
- 不需要连续内存空间:相比 vector 和 array,list 在内存分配上更灵活。
list 的存储结构
list底层实现是一个带哨兵节点(头节点)的双向循环链表
基本节点结构:
cpp
struct ListNode {
T data; // 存储的数据
ListNode* prev; // 指向前一个节点
ListNode* next; // 指向后一个节点
};List 的优缺点
优点:
- 高效的插入删除:在任何位置插入删除都是 O(1)
- 不会使迭代器失效 :插入操作不会使其他元素的迭代器失效(删除只会使被删除元素的迭代器失效)因为list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代 器失效的,只有在删除时才会失效,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响。
- 动态大小:不需要预先分配内存
缺点:
- 不支持随机访问:访问特定元素需要 O(n) 时间
- 内存开销大:每个元素都需要额外的指针空间
- 缓存不友好:元素在内存中不连续,缓存命中率低
2.List常用接口的使用
注:advance 函数,用于将迭代器前进或后退指定步数
cpp#include <iterator> template <class InputIterator, class Distance> void advance(InputIterator& it, Distance n); //n为正数即向后移动迭代器,负数即向前移动迭代器
2.1 list的常见构造(初始化)
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------|
| 构造函数((constructor)) | 接口说明 |
| list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素 |
| list() | 构造空的list |
| list (const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
| list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list |
构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素
cpplist<int> lst2(3, 7);//构造含有3个7的int类型容器构造空的list
cpplist<int> lst1;//构造int类型的空容器拷贝构造函数
cpplist<int> lst3(lst2);//拷贝构造int类型的lt2容器的复制品用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list
cppvector<int> vec = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; list<int> lst4(vec.begin(), vec.end());完整代码测试
cpp#include <iostream> #include <list> #include <vector> using namespace std; void printList(const list<int>& lst) { for (auto it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); ++it) { cout << *it << " "; } cout << endl; } int main() { // 1. 默认构造 list<int> lst1; cout << "lst1 (default): "; printList(lst1); // 2. 数量+值构造 list<int> lst2(3, 7); cout << "lst2 (3,7): "; printList(lst2); // 3. 拷贝构造 list<int> lst3(lst2); cout << "lst3 (copy): "; printList(lst3); // 4. 迭代器范围构造 vector<int> vec = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; list<int> lst4(vec.begin(), vec.end()); cout << "lst4 (from vector): "; printList(lst4); // 5. 初始化列表构造 (C++11) list<int> lst5 = {2, 4, 6, 8, 10}; cout << "lst5 (initializer): "; printList(lst5); return 0; }输出结果
cpplst1 (default): lst2 (3,7): 7 7 7 lst3 (copy): 7 7 7 lst4 (from vector): 1 3 5 7 9 lst5 (initializer): 2 4 6 8 10
2.2 List的遍历及迭代器(重点)
List 遍历特点:
- 必须使用迭代器,不能使用下标 []
- 迭代器稳定:插入删除不会使其他迭代器失效
- 双向移动:支持 ++ 和 --,但不支持随机访问
- 多种迭代器:正向、反向、const 版本
迭代器:
|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| begin和end | 返回第一个元素的迭代器+返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin和rend | 返回第一个元素的reverse_iterator,即end位置,返回最后一个元素下一个位置的 reverse_iterator,即begin位置 |
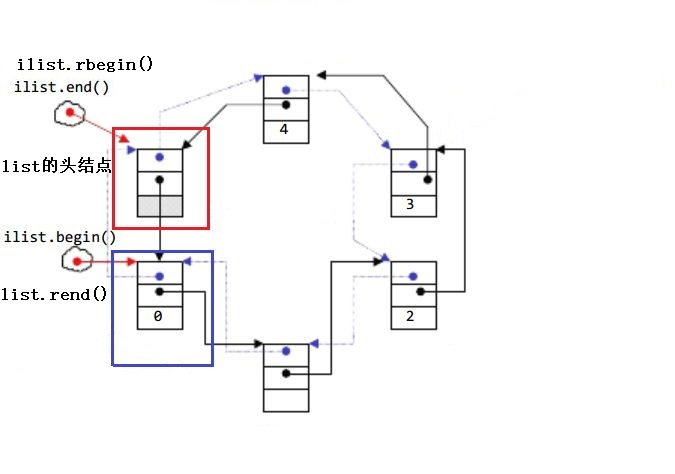
注:
- begin与end为正向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向后移动
- rbegin(end)与rend(begin)为反向迭代器,对迭代器执行++操作,迭代器向前移动
迭代器遍历(标准方式)
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // 正向遍历 cout << "正向遍历: "; for (auto it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); ++it) { cout << *it << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 } cout << endl;
反向迭代器遍历
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // 反向遍历 cout << "反向遍历: "; for (auto rit = lst.rbegin(); rit != lst.rend(); ++rit) { cout << *rit << " "; // 5 4 3 2 1 } cout << endl;
范围for:(底层迭代器)(C++11)
cppfor (range_declaration : range_expression) { // 循环体 } //range_declaration:声明一个变量,用于存储范围中的每个元素 //range_expression:任何可以返回序列的表达式(vector、array、string等)简单演示:
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // 只读遍历 cout << "范围for遍历: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 } cout << endl; // 可修改遍历 for (int& num : lst) { num *= 2; // 每个元素乘以2 } // 再次输出:2 4 6 8 10 cout << "修改后: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; } cout << endl;
2.3 list 容器的常见容量操作
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------|
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| empty | 检测list是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| size | 返回list中有效节点的个数 |
2.4 list 容器的常见元素访问
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------|
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| front | 返回list的第一个节点中值的引用 |
| back | 返回list的最后一个节点中值的引用 |
2.5 list 容器的常见修改操作(重点)
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------|
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| push_front | 在list首元素前插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_front | 删除list中第一个元素 |
| push_back | 在list尾部插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_back | 删除list中最后一个元素 |
| insert | 在list position 位置中插入值为val的元素 |
| erase | 删除list position位置的元素 |
| swap | 交换两个list中的元素 |
| clear | 清空两个list中的元素 |
push_front - 头部插入
cpplist<int> lst = {2, 3, 4}; lst.push_front(1); // 在头部插入1 // 现在 list: {1, 2, 3, 4} for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 1 2 3 4 }
pop_front - 头部删除
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4}; lst.pop_front(); // 删除头部元素1 // 现在 list: {2, 3, 4} cout << "删除后: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 2 3 4 }
push_back - 尾部插入
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3}; lst.push_back(4); // 在尾部插入4 lst.push_back(5); // 在尾部插入5 // 现在 list: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5} cout << "尾部插入后: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 }
pop_back - 尾部删除
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; lst.pop_back(); // 删除尾部元素5 // 现在 list: {1, 2, 3, 4} cout << "尾部删除后: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 1 2 3 4 }
insert - 指定位置插入
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 3, 5}; // 在第二个位置(值为3前面)插入2 auto it = lst.begin(); advance(it, 1); // 移动到第二个位置 lst.insert(it, 2); // 在it指向的位置前插入 // 现在 list: {1, 2, 3, 5} // 在末尾插入6 lst.insert(lst.end(), 6); // 现在 list: {1, 2, 3, 5, 6} cout << "插入后: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 1 2 3 5 6 } cout << endl;
erase - 指定位置删除
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // 删除第三个元素(值为3) auto it = lst.begin(); advance(it, 2); // 移动到第三个位置 it = lst.erase(it); // 删除并返回下一个位置的迭代器 // 现在 list: {1, 2, 4, 5} // it 现在指向4 cout << "删除后: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 1 2 4 5 } cout << endl; cout << "it现在指向: " << *it << endl; // 4
swap - 交换两个list
cpplist<int> lst1 = {1, 2, 3}; list<int> lst2 = {4, 5, 6}; cout << "交换前:" << endl; cout << "lst1: "; for (int num : lst1) cout << num << " "; // 1 2 3 cout << endl; cout << "lst2: "; for (int num : lst2) cout << num << " "; // 4 5 6 cout << endl; lst1.swap(lst2); // 交换两个list cout << "交换后:" << endl; cout << "lst1: "; for (int num : lst1) cout << num << " "; // 4 5 6 cout << endl; cout << "lst2: "; for (int num : lst2) cout << num << " "; // 1 2 3 cout << endl;
clear - 清空list
删除 list 中的所有元素,size() 变为 0,list 对象本身仍然存在,可以继续使用
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; cout << "清空前 size: " << lst.size() << endl; // 5 cout << "清空前: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 } cout << endl; lst.clear(); // 清空所有元素 cout << "清空后 size: " << lst.size() << endl; // 0 cout << "清空后: "; for (int num : lst) { cout << num << " "; // 无输出 } cout << "list已空" << endl;
2.6 list 容器的常见操作函数
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------|
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
| splice | 将元素从列表转移到其它列表 |
| remove | 删除具有特定值的元素 |
| remove_if | 删除满足条件的元素 |
| unique | 删除重复值 |
| sort | 容器中的元素排序 |
| merge | 合并排序列表 |
| reverse | 反转元素的顺序 |
splice - 将元素从列表转移到其它列表
cpp
list<int> lst1 = {1, 2, 3};
list<int> lst2 = {4, 5, 6};void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other);
转移整个list2到lst1末尾
cpp// 1. 转移整个list2到lst1末尾 lst1.splice(lst1.end(), lst2); cout << "转移整个list后:" << endl; cout << "lst1: "; for (int n : lst1) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 6 cout << endl; cout << "lst2: "; for (int n : lst2) cout << n << " "; // (空) cout << endl;
void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other, const_iterator it);
转移单个元素
cpp// 2. 转移单个元素 list<int> lst3 = {7, 8, 9}; auto it = lst3.begin(); lst1.splice(lst1.begin(), lst3, it); // 转移7到lst1开头 cout << "转移单个元素后:" << endl; cout << "lst1: "; for (int n : lst1) cout << n << " "; // 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 cout << endl; cout << "lst3: "; for (int n : lst3) cout << n << " "; // 8 9 cout << endl;
void splice(const_iterator pos, list& other, const_iterator first, const_iterator last);
转移元素范围
cpp// 3. 转移元素范围 list<int> lst4 = {10, 11, 12, 13}; auto first = lst4.begin(); auto last = lst4.begin(); advance(first, 1); // 指向11 advance(last, 3); // 指向13 lst1.splice(lst1.end(), lst4, first, last); // 转移11,12 cout << "转移范围后:" << endl; cout << "lst1: "; for (int n : lst1) cout << n << " "; // 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 11 12 cout << endl; cout << "lst4: "; for (int n : lst4) cout << n << " "; // 10 13 cout << endl;
remove - 删除具有特定值的元素
void remove(const T& value);
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 2, 4, 2, 5}; cout << "原始list: "; for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 3 2 4 2 5 cout << endl; // 删除所有值为2的元素 lst.remove(2); cout << "删除所有2后: "; for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 1 3 4 5 cout << endl; // 删除不存在的元素(无效果) lst.remove(99); cout << "删除99后: "; for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 1 3 4 5 cout << endl;
remove_if - 删除满足条件的元素
cpp
template <class Predicate>
void remove_if(Predicate pred);
cpp
list<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
cout << "原始list: ";
for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
cout << endl;使用lambda表达式删除偶数
cpplst.remove_if([](int n) { return n % 2 == 0; }); cout << "删除偶数后: "; for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 1 3 5 7 9 cout << endl;
使用函数对象删除大于5的数
cppstruct GreaterThan5 { bool operator()(int n) { return n > 5; } }; list<int> lst2 = {1, 6, 2, 7, 3, 8, 4, 9, 5}; lst2.remove_if(GreaterThan5()); cout << "删除大于5的数: "; for (int n : lst2) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 cout << endl;
使用普通函数
cpplist<int> lst3 = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50}; lst3.remove_if([](int n) { return n > 25; }); cout << "删除大于25的数: "; for (int n : lst3) cout << n << " "; // 10 20 cout << endl;
unique - 删除重复值
基本用法(需要先排序)
void unique();
cpplist<int> lst1 = {1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 4, 2, 1}; cout << "原始list: "; for (int n : lst1) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 2 3 3 3 4 2 1 cout << endl; lst1.sort(); // 必须先排序 cout << "排序后: "; for (int n : lst1) cout << n << " "; // 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 4 cout << endl; lst1.unique(); cout << "去重后: "; for (int n : lst1) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 3 4 cout << endl;
使用自定义条件
template <class BinaryPredicate>
void unique(BinaryPredicate binary_pred);
cpplist<int> lst2 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 10, 12, 15}; cout << "原始list: "; for (int n : lst2) cout << n << " "; // 1 3 5 7 9 10 12 15 cout << endl; // 删除与前一个元素差值小于3的元素 lst2.unique([](int a, int b) { return abs(a - b) < 3; }); cout << "自定义条件去重后: "; for (int n : lst2) cout << n << " "; // 1 5 9 12 15 cout << endl;
sort - 容器中的元素排序
cpp
list<int> lst = {5, 2, 8, 1, 9, 3};
cout << "原始list: ";
for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 5 2 8 1 9 3
cout << endl;默认升序排序
cpplst.sort(); cout << "升序排序: "; for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 3 5 8 9 cout << endl;
降序排序
cpplst.sort(greater<int>()); cout << "降序排序: "; for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 9 8 5 3 2 1 cout << endl;
自定义排序规则
cpplist<string> strList = {"apple", "banana", "cherry", "date"}; strList.sort([](const string& a, const string& b) { return a.length() < b.length(); // 按字符串长度排序 }); cout << "按长度排序: "; for (const auto& s : strList) cout << s << " "; // date apple banana cherry cout << endl;
merge - 合并排序列表
默认合并(升序)
void merge(list& other);
cpplist<int> lst1 = {1, 3, 5}; list<int> lst2 = {2, 4, 6}; cout << "合并前:" << endl; cout << "lst1: "; for (int n : lst1) cout << n << " "; // 1 3 5 cout << endl; cout << "lst2: "; for (int n : lst2) cout << n << " "; // 2 4 6 cout << endl; lst1.merge(lst2); // 两个list都必须已排序 cout << "合并后:" << endl; cout << "lst1: "; for (int n : lst1) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 6 cout << endl; cout << "lst2: "; for (int n : lst2) cout << n << " "; // (空) cout << endl;
自定义比较规则的合并
template <class Compare>
void merge(list& other, Compare comp);
cpplist<int> lst3 = {5, 3, 1}; // 降序 list<int> lst4 = {6, 4, 2}; // 降序 lst3.sort(greater<int>()); lst4.sort(greater<int>()); lst3.merge(lst4, greater<int>()); // 按降序合并 cout << "降序合并后: "; for (int n : lst3) cout << n << " "; // 6 5 4 3 2 1 cout << endl;
reverse - 反转元素的顺序
void reverse();
cpplist<int> lst = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; cout << "原始list: "; for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 1 2 3 4 5 cout << endl; lst.reverse(); cout << "反转后: "; for (int n : lst) cout << n << " "; // 5 4 3 2 1 cout << endl;字符串列表反转
cpplist<string> words = {"hello", "world", "c++", "programming"}; cout << "原始字符串: "; for (const auto& w : words) cout << w << " "; // hello world c++ programming cout << endl; words.reverse(); cout << "反转字符串: "; for (const auto& w : words) cout << w << " "; // programming c++ world hello cout << endl;