单链表和哈希表题目练习
单链表
常用技巧和操作
技巧:1.使用虚拟头节点,这样方便处理边界和方便操作
2.有效开辟空间来简化代码
3.使用快慢双指针
操作:
1.new一个新节点
2.尾插和头插
两数相加
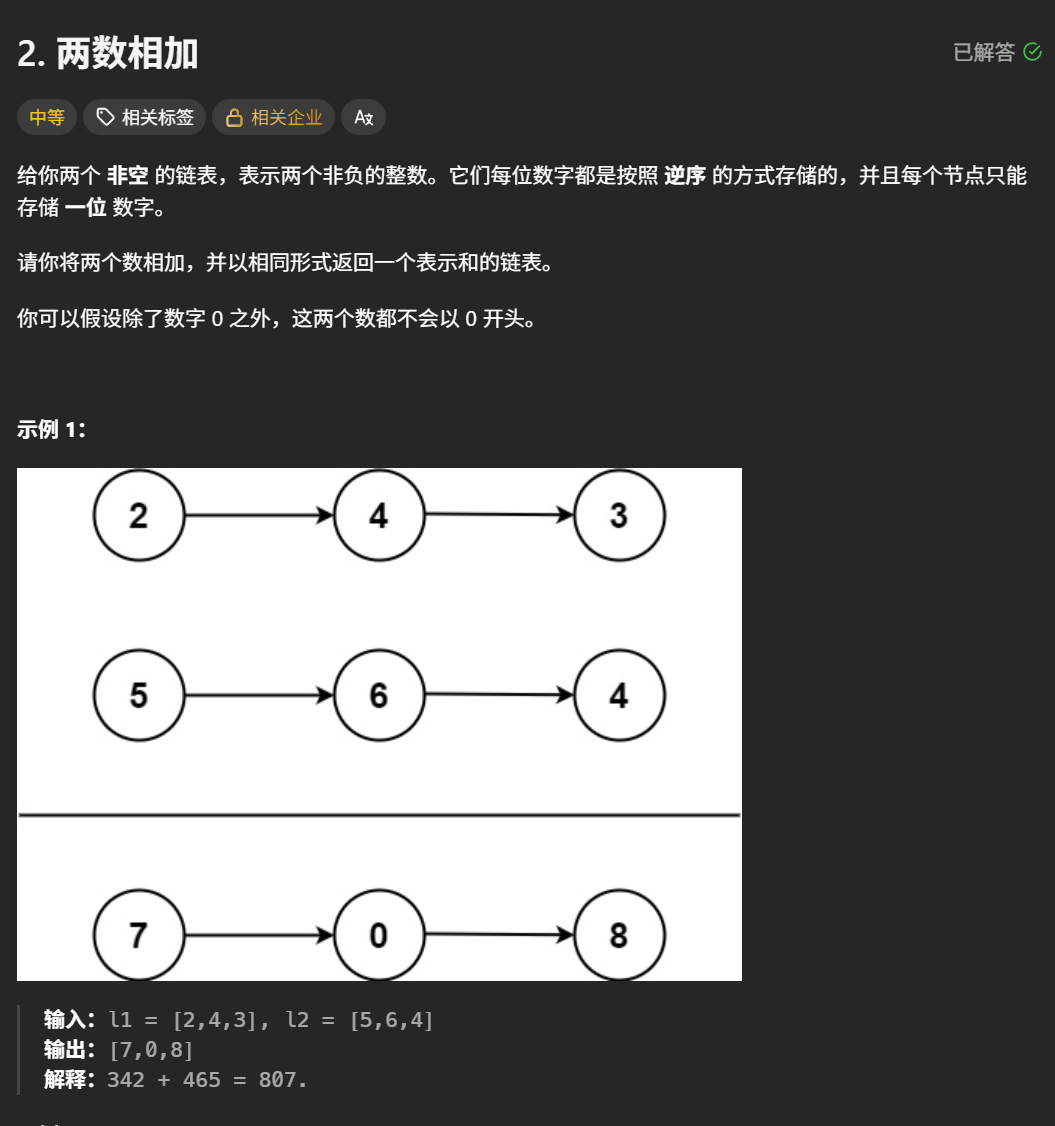
题目解析 :使用链表返回两个链表相加的结果,并且此时的链表对应的数是逆序的,结果也要返回逆序的
模拟:直接将l1和l2两个链表遍历完,并且对应的求和就行,循环结束,最后可能还有没有进位的数字

java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);//引用一个虚拟头节点存放结果
ListNode cur = newHead;
ListNode cur1 = l1;
ListNode cur2 = l2;
//两个都为空才结束
int carry = 0;//表示进位
while (cur1 != null || cur2 != null) {
if (cur1 != null) {
carry += cur1.val;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
if (cur2 != null) {
carry += cur2.val;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur.next = new ListNode(carry % 10);
carry = carry / 10;//算出进位
cur = cur.next;
}
//最后判断是否还有进位
if (carry != 0) {
cur.next = new ListNode(carry % 10);
}
return newHead.next;
}
}两两交换链表中的节点
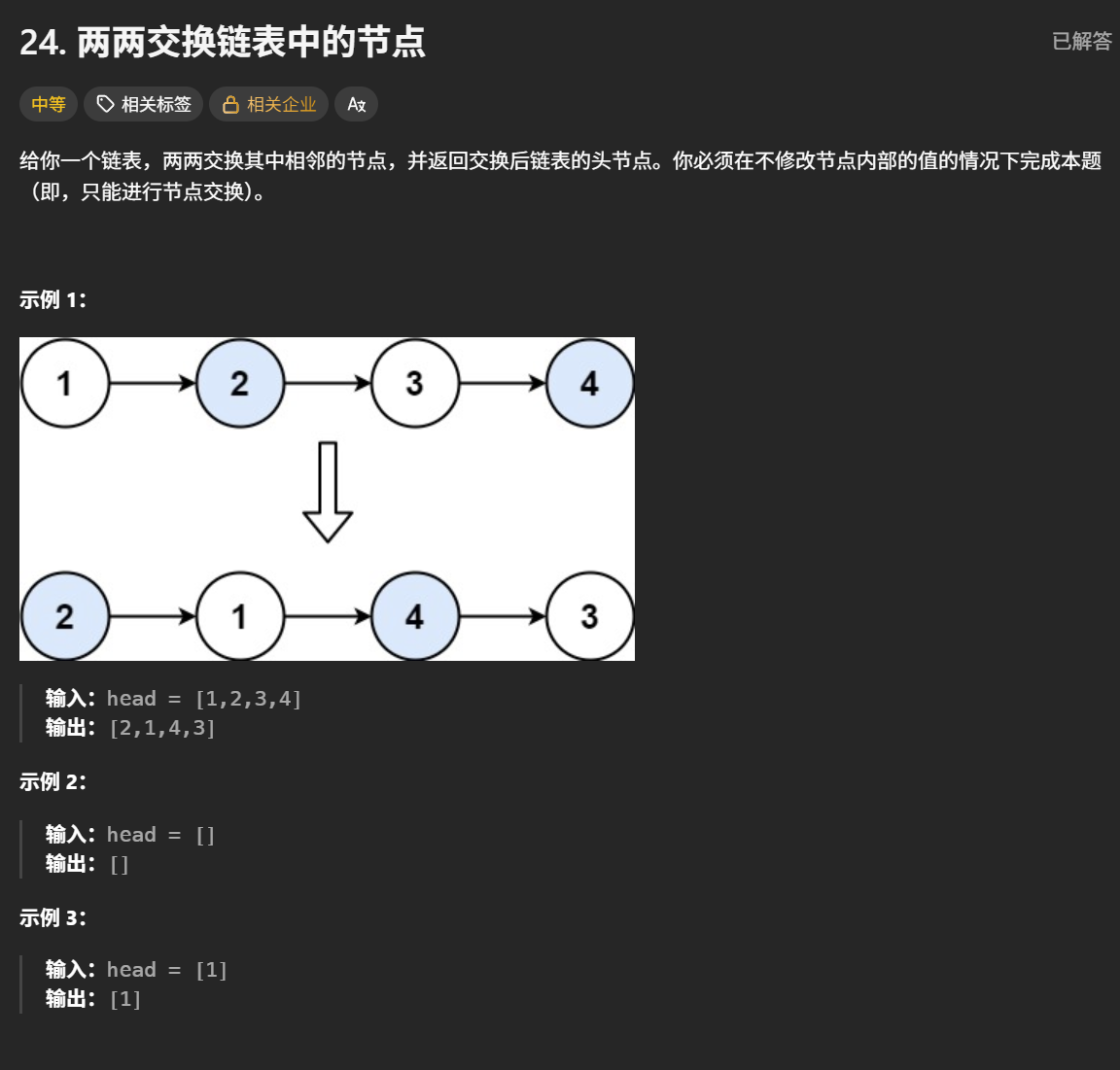
题目解析 :将相邻的两个节点进行交换,节点交换,不是简单值交换
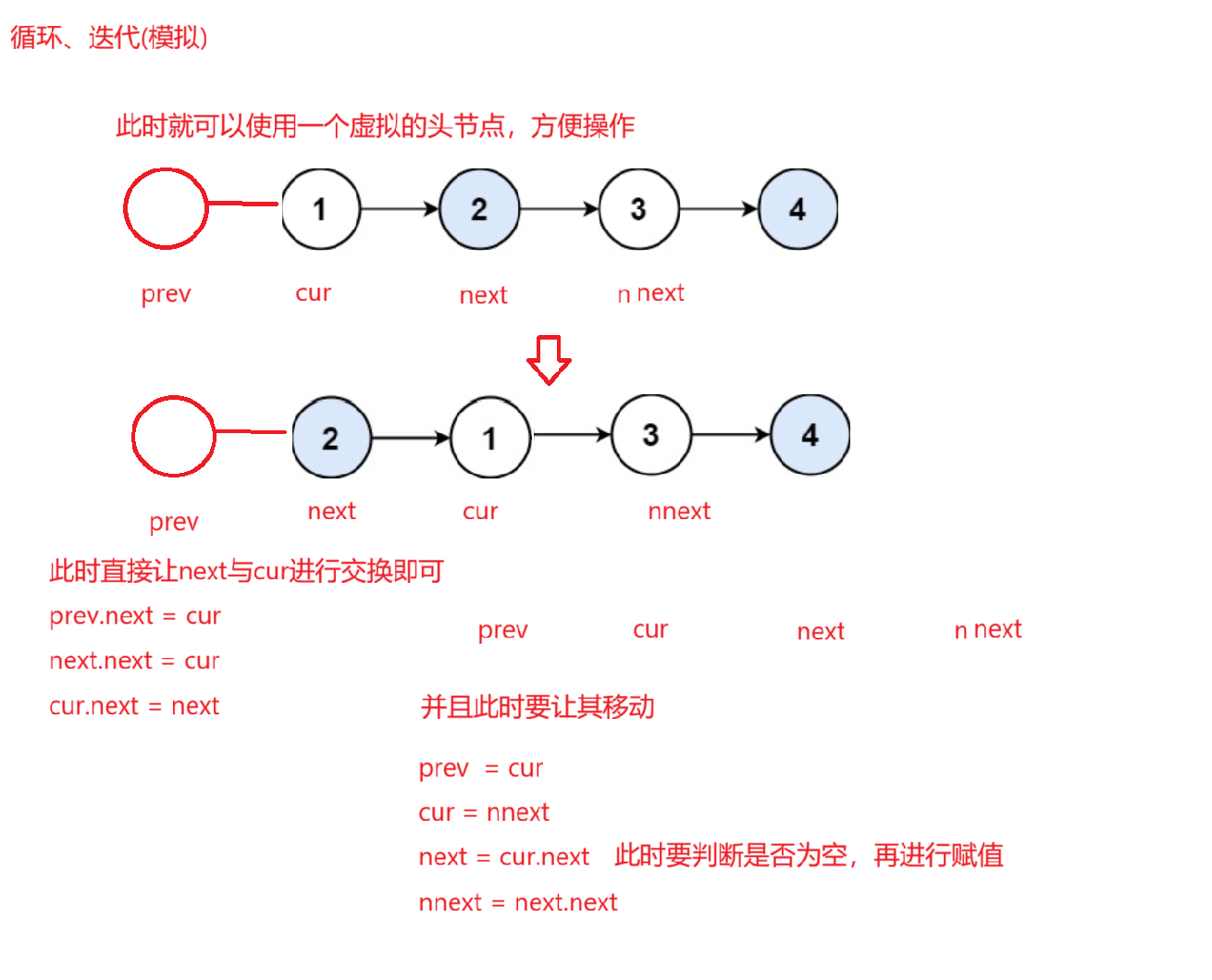
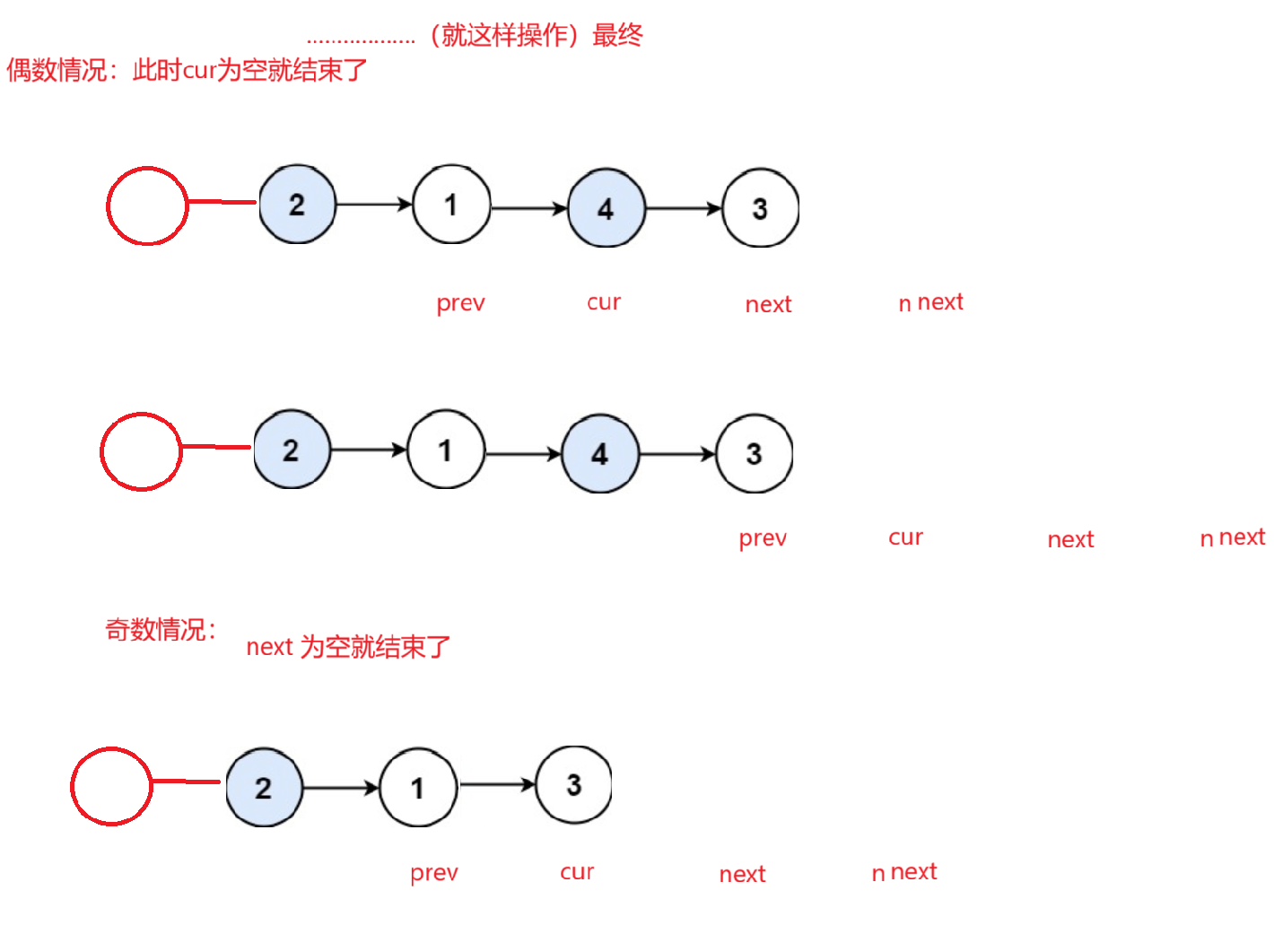
循环:使用四个变量方便进行交换
prev:虚拟头节点
cur:当前要交换节点
next:当前交换节点的下一个节点
nnext:当前交换节点的下一个节点的下一个节点
此时交换就让cur 和 next进行交换即可,都后让其向后移动即可,重复操作,但是要注意截止条件
java
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode Nhead = new ListNode(-1);
Nhead.next = head;
ListNode prev = Nhead;//虚拟头节点
ListNode cur = head;//当前节点
ListNode next = head.next;//后一个
ListNode nnext = next.next;//后一个的后一个
while(cur != null && next != null){
prev.next = next;
next.next = cur;
cur.next = nnext;
prev = cur;
cur = nnext;
if(cur != null){
next = cur.next;
}
if(next != null){
nnext = next.next;
}
}
return Nhead.next;
}
}重拍链表
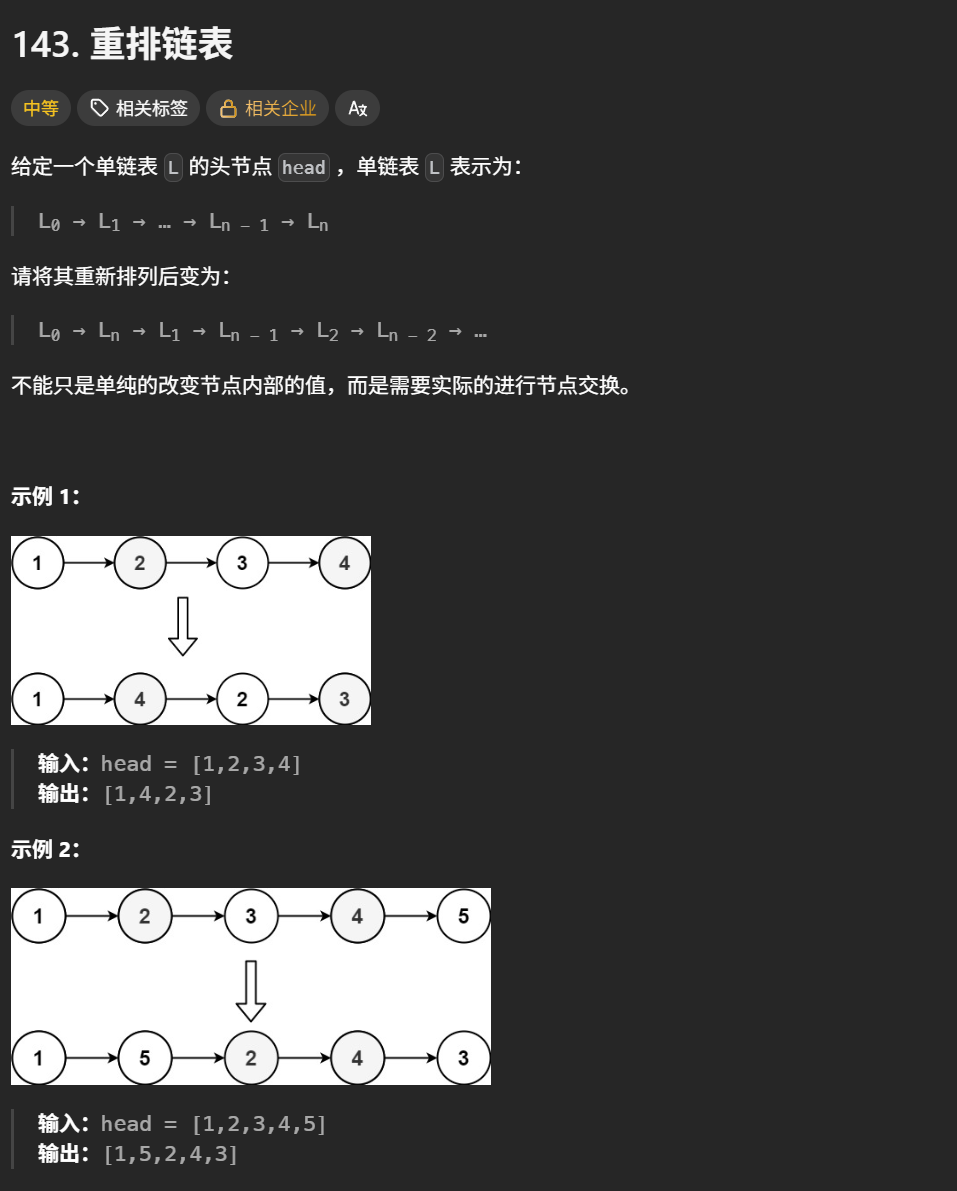
思路 :此时要从后面进行选择元素
1.找到中间节点(快慢双指针)
2.逆序中间节点的后面节点(可以包括中间节点,也可以不包括)
3.合并两个链表
java
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return;
}
//1.找到中间节点
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while(fast != null && fast.next != null){
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//2.逆序slow后面节点
ListNode head2 = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = slow.next;//将slow后面的节点逆序放入一个新的链表中
slow.next = null;//将两个链表进行分离
while(cur != null){
//采用头插法
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = head2.next;
head2.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
//2.合并两个链表
ListNode cur1 = head;
ListNode cur2 = head2.next;
ListNode Nhead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = Nhead;
while(cur1 != null){
//先放第一个
prev.next = cur1;
prev = cur1;
cur1 = cur1.next;
//合并第二个
if(cur2 != null){
prev.next = cur2;
prev = cur2;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
}
}
}K个一组翻转链表
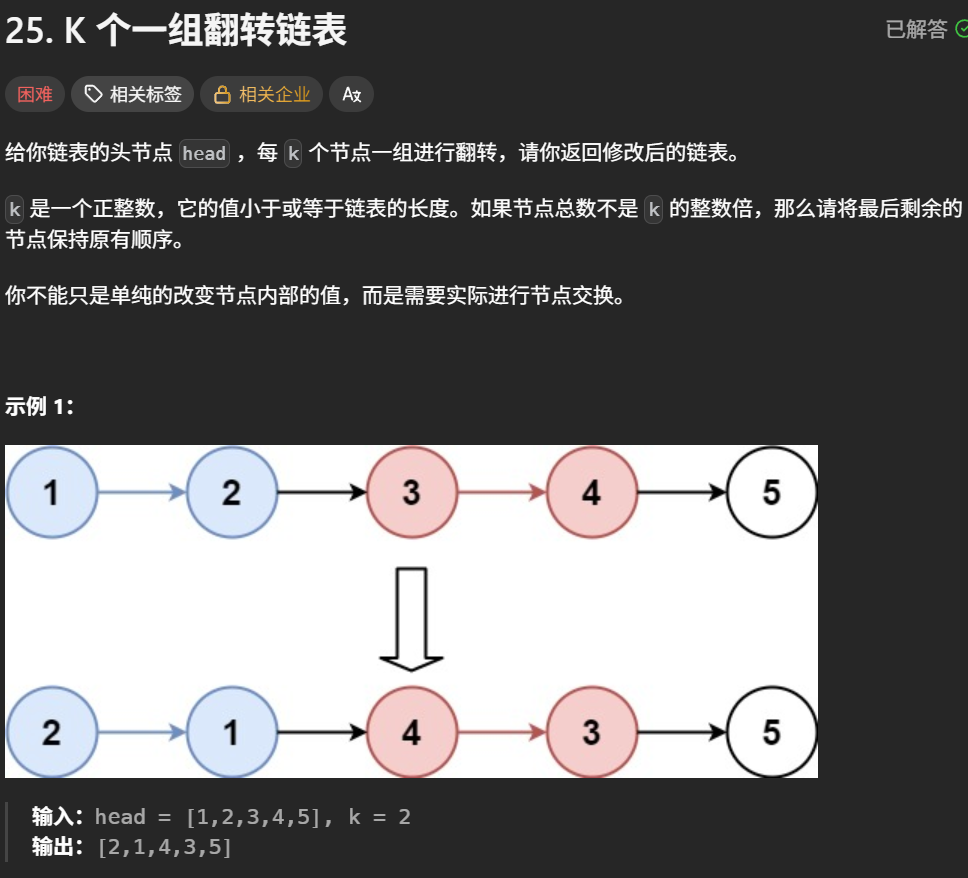
题目解析 :就是每K个元素进行分开逆序,不满足k个的元素不需要逆序
思路:我们找出需要逆序多少组,分组进行逆序即可
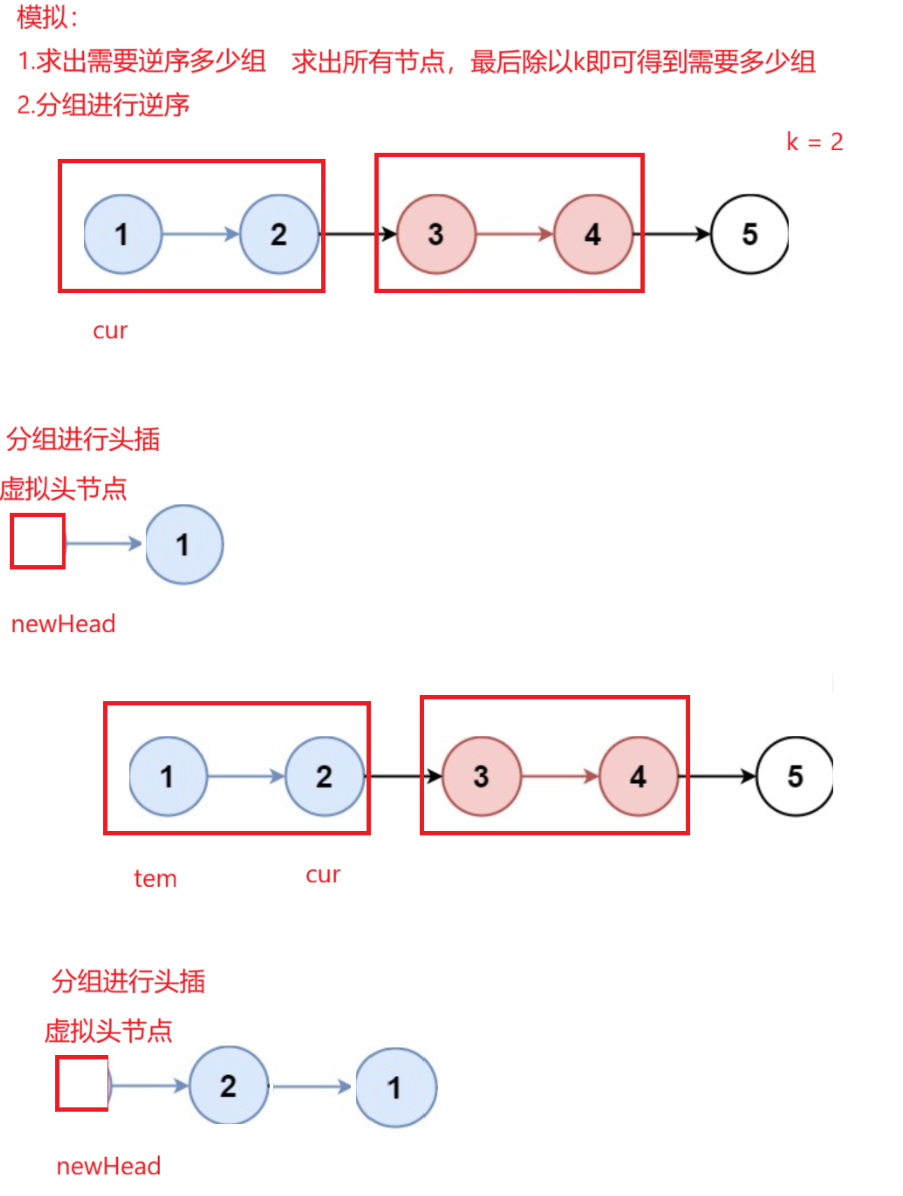
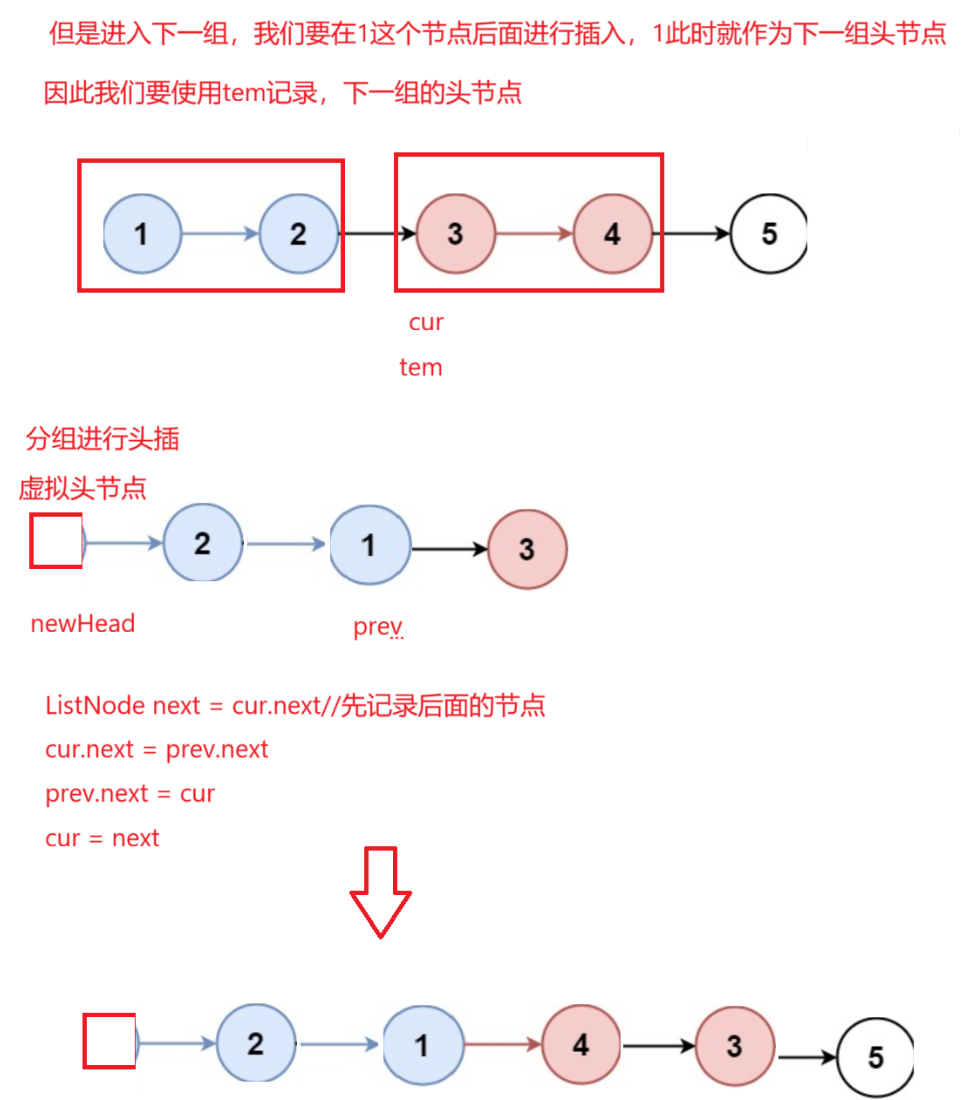

java
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
//让其k个为一组进行翻转
ListNode cur = head;
int n = 0;//统计有多少组需要逆序
while(cur != null){
n++;
cur = cur.next;
}
n/=k;
cur = head;
ListNode Nhead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = Nhead;
for(int i = 0;i < n;i++){
//此时使用一个变量记录当前第一个节点
//为了后面链表翻转插入这个位置
ListNode tem = cur;
//进行这一组的翻转
for(int j = 0; j < k; j++){
//先记录cur后面的节点,因为头插就找不到后面的节点了
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev.next;
prev.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
//更新prev,让其变成相当于下一组头节点
prev = tem;
}
//将剩余不需要逆序的放进来
prev.next = cur;
return Nhead.next;
}
}合并K个升序链表

题目解析 :将k个升序链表合并
思路一 :将这个问题转化为合并两个有序链表,不断操作,这样最终也可以得到结果,时间复杂度:O(k^2 * n),n表示每一个链表平均节点个数
思路二 :使用优先级队列(堆),这里我们可以让k个链表同时操作 ,现将所有链表头节点放入小根堆中,将堆顶元素放入拼接到虚拟头节点上 ,将这个被放入元素的下一个节点放入小根堆 中,就这样不断操作,直到堆为空,时间复杂度:O(K * n * log K)
思路三:分治思想(递归),这里可以将这个看成归并排序,将左边进行排序,将右边进行排序,最后合并这两个链表即可,时间复杂度:O(K * n * log K)
java
//将问题转化为合并两个升序链表
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode Nhead = null;
for(int i=0;i<lists.length;i++){
Nhead = mergeTwoLists(Nhead,lists[i]);
}
return Nhead;
}
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
//定义一个新的头进行存放
//比较
//拼接剩余的
ListNode Nhead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tem = Nhead;
ListNode l1 = list1;
ListNode l2 = list2;
while(l1!=null&&l2!=null){
if(l1.val<l2.val){
tem.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
tem.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
tem = tem.next;
}
if(l1!=null){
tem.next = l1;
}
if(l2!=null){
tem.next = l2;
}
return Nhead.next;
}
}
java
//使用小根堆
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
//使用小根堆,每次将三个元素放入进去,进行判断
PriorityQueue<ListNode> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((v1,v2) -> (v1.val - v2.val ));
//先将所有头放进去
for(ListNode list : lists){
if(list != null){
heap.offer(list);
}
}
ListNode ret = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode Nhead = ret;
//堆为空就结束
while(!heap.isEmpty()){
ListNode tem = heap.poll();
Nhead.next = tem;
Nhead = tem;
if(tem.next != null){
heap.offer(tem.next);
}
}
return ret.next;
}
}
java
//使用归并排序
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
//采用分治递归思想
return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
public ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return null;
}
if (left == right) {
return lists[left];
}
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
//分为[left,mid] 和 [mid + 1 , right]
ListNode list1 = merge(lists, left, mid);
ListNode list2 = merge(lists, mid + 1, right);
//合并两个有序链表
return mergerTwoList(list1, list2);
}
public ListNode mergerTwoList(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode Nhead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tem = Nhead;
ListNode l1 = list1;
ListNode l2 = list2;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
tem.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
tem.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
tem = tem.next;
}
if (l1 != null) {
tem.next = l1;
}
if (l2 != null) {
tem.next = l2;
}
return Nhead.next;
}
}哈希表
两数之和

题目解析 :找出两个数相加等于target,这两个数下标不同
解法 :
暴力解法一 :确定前一个数,不断从这个数后面找一个其相加之和等于target
暴力解法二 :确定后一个数,从这个位置前找一个数其两数之和等于target优化:可以使用哈希表,到了nums[i],我们直接在哈希表中找是否有targert - nums[i]即可

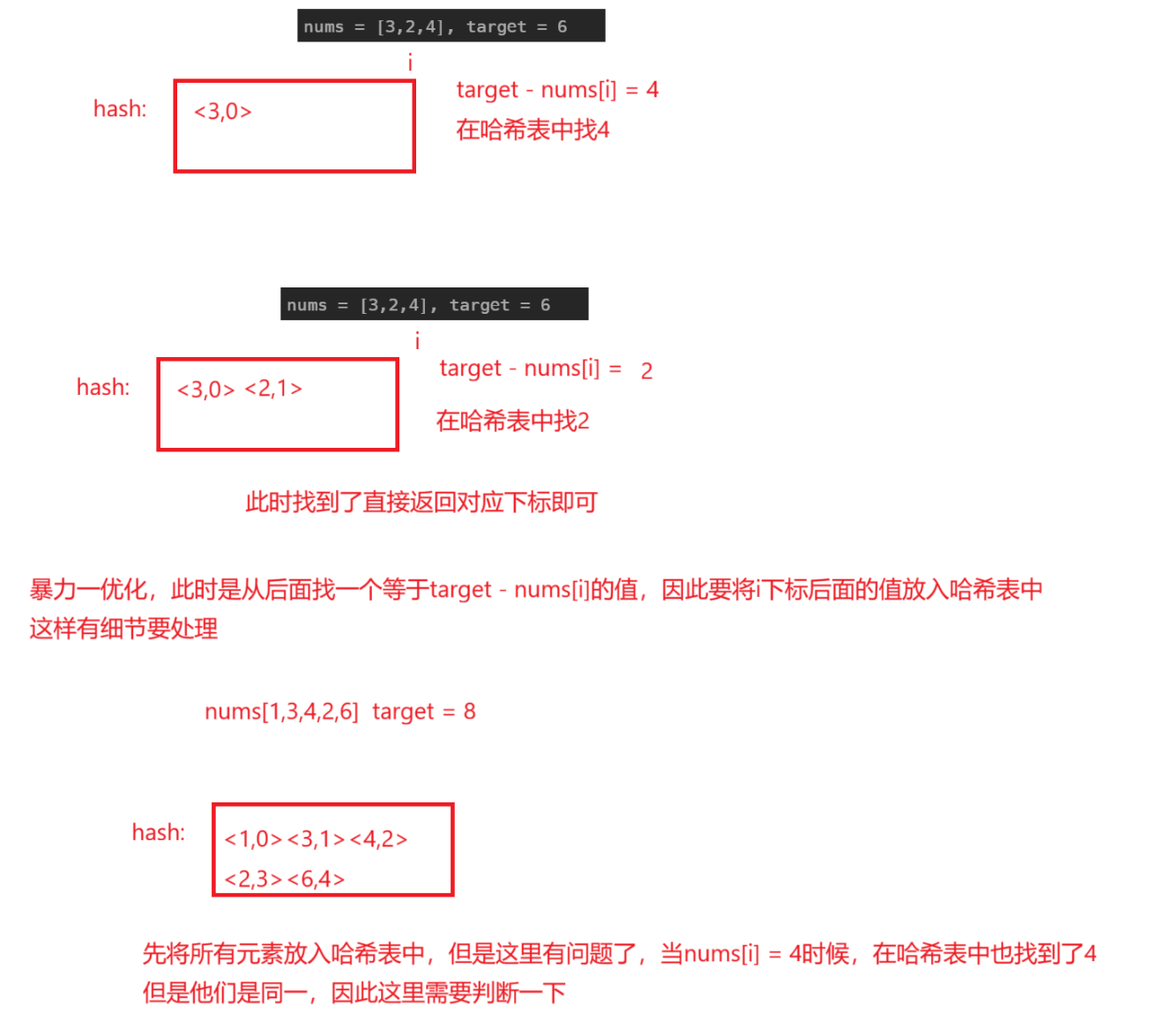
java
//暴力二
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target){
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
return new int[0];
}
}
java
//暴力二优化
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
//存储其对应值及其下标
Map<Integer, Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
//直接每次从这个数前面找出一个等于 targer - nums[i]的值即可
int x = target - nums[i];
if(hash.containsKey(x)){
return new int[]{hash.get(x),i};
}
hash.put(nums[i],i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}判定是否互为字符重排

题目解析 :就是判断两个字符串是否只是元素的位置不同,元素个数相同
解法 :
暴力解法 :直接根据s1将他的所有情况列举出来,看s2是否在里面
优化一 :使用两个哈希表,一个哈希表放s1的所有字符,一个哈希表放s2的所有字符,最后判断两个哈希表中对应字符个数是否相同即可
优化二:只使用一个哈希表,先将s1的所有字符放入进去,放入s2时候直接将对应的**哈希值进行--**即可,如果存在<0,说明肯定不满足
java
class Solution {
public boolean CheckPermutation(String s1, String s2) {
//使用数组模拟哈希表,这样直接判断对应下标的值是否符合条件即可
int len1 = s1.length();
int len2 = s2.length();
if(len1 != len2){
return false;
}
int[] hash1 = new int[26];
int[] hash2 = new int[26];
//将s1放入hash1
for(char ch : s1.toCharArray()){
hash1[ch - 'a']++;
}
//将s2放入hash2
for(char ch : s2.toCharArray()){
hash2[ch - 'a']++;
}
for(int i = 0;i < 26;i++){
if(hash1[i] != hash2[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
java
//使用一个哈希
class Solution {
public boolean CheckPermutation(String s1, String s2) {
//使用数组模拟哈希表,这样直接判断对应下标的值是否符合条件即可
int len1 = s1.length();
int len2 = s2.length();
if(len1 != len2){
return false;
}
int[] hash = new int[26];
//将s1放入hash
for(char ch : s1.toCharArray()){
hash[ch - 'a']++;
}
//直接遍历s2将其对应hash1中的值进行相减即可
for(char ch : s2.toCharArray()){
hash[ch - 'a']--;
//这里只需要判断其是否<0即可
//此时s1和s2长度一样
//如果不完全相同,其肯定有的元素多了,有的元素少了
if(hash[ch - 'a'] < 0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}存在重复元素
题目解析 :判断这个数组是否有重复元素
解法 :这个题目和两数之和类似,就是遍历数组,遍历过程中将元素放入哈希表中,每次都是向前判断是否有相同元素
java
class Solution {
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
//
Set<Integer> hash = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(hash.contains(nums[i])){
return true;
}else{
hash.add(nums[i]);
}
}
return false;
}
}存在重复元素||

题目解析 :找出数组中是存在重复元素并且其对应下标差值<=k才符合条件
解法:依旧是固定后面一个数,判断前面元素是否有符合条件的,可以使用一个哈希表来解决,并且当遇到一个存在元素,但不符合条件也要将这个元素放入哈希表中进行覆盖原本元素
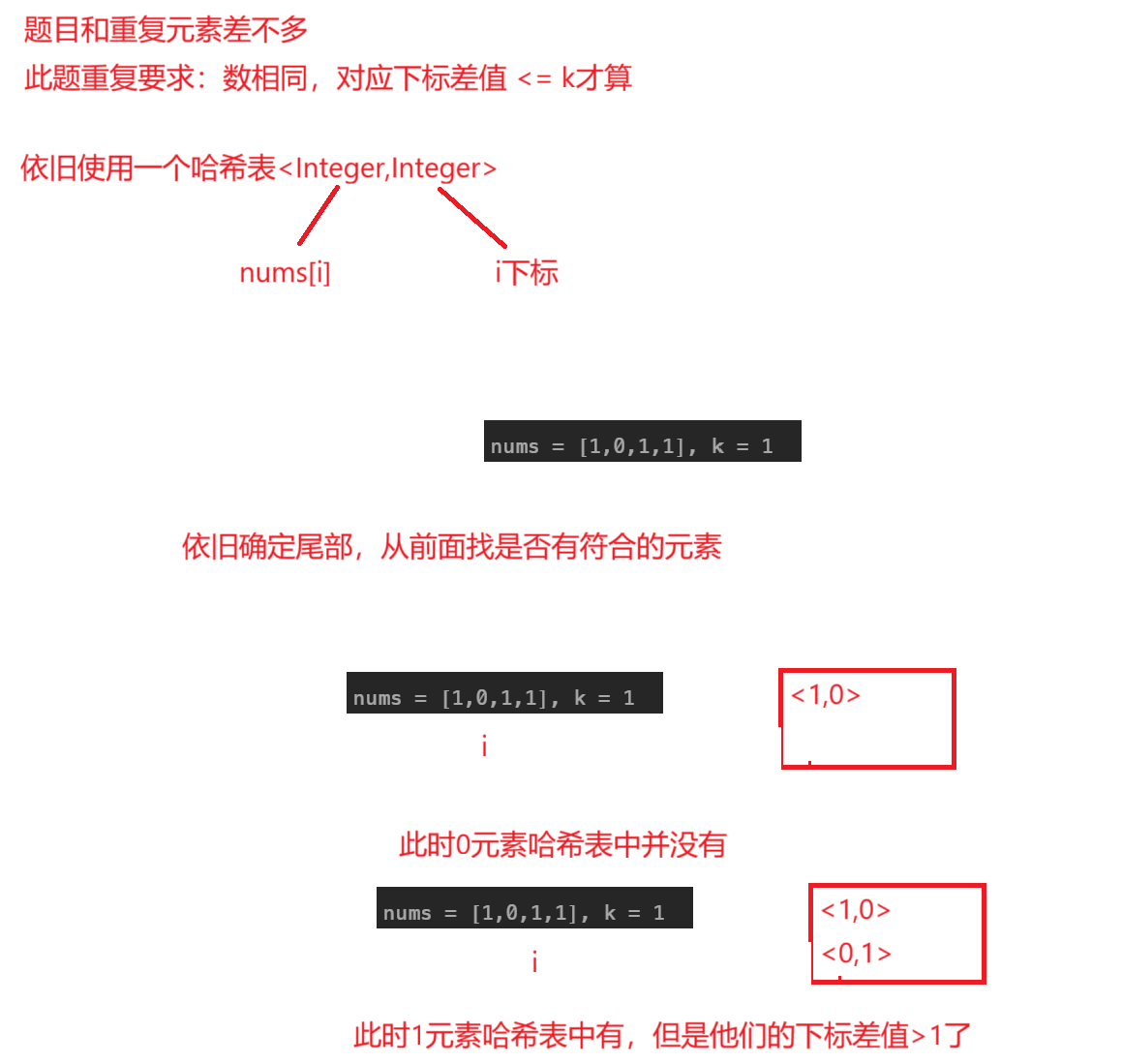

java
class Solution {
public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
//和重复数字一样,只不过这里对下标的差值有要求
Map<Integer,Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length ; i++){
if(hash.containsKey(nums[i]) && (i - hash.get(nums[i]) <= k)){
return true;
}
hash.put(nums[i],i);
}
return false;
}
}字母异位词分组

题目解析 :就是将一些互为异位词的放在一起,最终一起返回
解法:首先想的是每次都判断其是否是异位词,这样比较麻烦,
因此使用一个哈希表放入其排好序及其对应异位词的字符串,不断进行拼接,最终将其哈希表中的值返回即可

java
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
//直接使用哈希表
Map<String , List<String>> hash = new HashMap<>();
for(String str : strs){
char[] tem = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(tem);
String key = new String(tem);
if(!hash.containsKey(key)){
//不存在就将这个其对应关系进行创建
hash.put(key,new ArrayList<>());
}
//将这放入哈希表中进行拼接
hash.get(key).add(str);
}
return new ArrayList<>(hash.values());
}
}