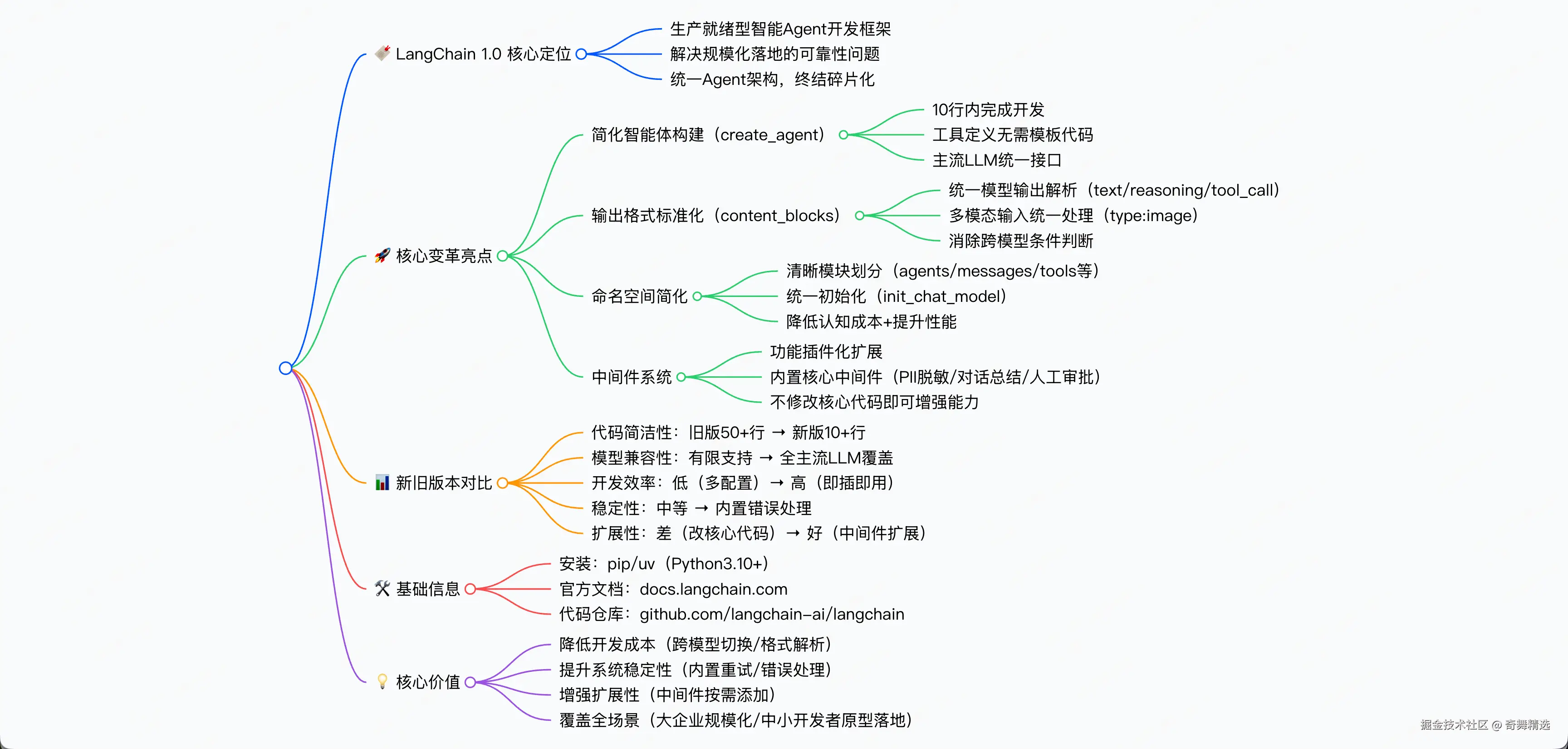
当大语言模型(LLM)的应用从原型验证走向规模化落地,开发人员面临的核心痛点已从"能否实现"转变为"如何可靠实现"。2025年10月23日,LangChain正式发布1.0版本,这一里程碑式的更新不仅终结了此前版本中Agent架构碎片化的局面,更以"生产就绪"为核心定位,重新定义了智能Agent开发框架的技术标准。
官方文档
docs.langchain.com/oss/python/...
安装
pip:
bash
pip install -U langchain
# Requires Python 3.10+Uv:
bash
uv add langchain
# Requires Python 3.10+主要内容
create_agent - 构建智能体简化
只需不到10行代码,你就可以连接到OpenAI、Anthropic、谷歌以及更多平台。
旧版本的问题
在 LangChain 1.0 之前,构建一个智能体需要编写大量模板代码:
ini
# 旧版本简单示例
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.tools import Tool
# 定义工具
def get_weather(city):
return f"{city}天气晴朗"
tools = [Tool(name="get_weather", func=get_weather, description="获取天气")]
# 配置提示词
system_prompt = """你是一个天气查询助手,使用工具获取实时天气..."""
# 创建 Agent
agent = create_react_agent(
model=ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4"),
tools=tools,
state_modifier=system_prompt
)
# 运行
result = agent.invoke({"messages": [("user", "北京天气怎么样?")]})新版本的简化
python
# LangChain 1.0
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
# 定义工具
def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
"""获取指定城市天气"""
return f"当前{city}天气晴朗,气温25℃"
# 创建智能体
agent = create_agent(
model=ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini"),
tools=[get_weather],
system_prompt="你是一个天气查询助手,使用工具获取实时天气"
)
# 运行智能体
response = agent.invoke({
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "深圳今天天气怎么样?"}]
})
print(response["messages"][-1]["content"])核心改进
-
自动化:自动处理工具调用、异常重试
-
简化工具:工具定义更简单,直接使用普通函数
-
统一接口:支持所有主流 LLM 模型,切换模型无需修改代码
content_blocks - 统一所有模型的输出格式
问题的根源
不同的 AI 模型返回结果的格式各不相同:
-
OpenAI:返回 function_call 字段
-
Anthropic Claude:使用 XML 标签包裹工具调用
......
这导致代码中充满了复杂的条件判断:
python
# 旧版本:处理不同模型的输出
def handle_response(response, model_type):
if model_type == "openai":
if response.function_call:
return handle_function_call(response.function_call)
else:
return response.content
elif model_type == "anthropic":
# 解析XML标签
if "<tool_call>" in response.content:
return parse_xml_tool_call(response.content)
else:
return response.content
# 其他模型的处理...不同模型对思考过程的标记也不同,(如 think 或 reason 标签),LangChain 1.0统一模型推理消息为type=="reasoning"
解决方案:content_blocks
python
# LangChain 1.0:统一处理所有模型输出
from langchain_anthropic import ChatAnthropic
model = ChatAnthropic(model="claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929")
response = model.invoke("解释什么是量子计算,并给出例子")
# 统一访问不同类型的内容块
for block in response.content_blocks:
if block["type"] == "reasoning":
print(f"推理过程: {block['reasoning']}")
elif block["type"] == "text":
print(f"回答内容: {block['text']}")
elif block["type"] == "tool_call":
print(f"工具调用: {block['name']}({block['args']})")不同的厂商会自己设计针对多模态大模型的图片输入,如下示例:

使用content_blocks之后:
bash
message = HumanMessage(
content=[
{
"type": "text",
"text": "根据这张图片写一下页面"
},
{
"type": "image",
"image_url": {"url": '图片链接'}
}
]
)通过type:image来统一处理
核心价值
-
标准接口:一套代码处理所有模型输出
-
成本节约:模型切换成本大幅度降低
-
开发效率:避免重复的格式解析代码
简化命名空间 - 甩掉历史包袱
旧版本的混乱
python
# 旧版本:复杂的导入路径
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.agents import AgentExecutor
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.tools import BaseTool
from langchain.utilities import SerpAPIWrapper新版本的清晰
| 模块 | 核心内容 |
|---|---|
langchain.agents |
create_agent, AgentState |
langchain.messages |
消息类型、内容块、trim_messages |
langchain.tools |
@tool, BaseTool, 注入工具类 |
langchain.chat_models |
init_chat_model, BaseChatModel |
langchain.embeddings |
Embeddings, init_embeddings |
下面以新版的init_chat_model为例子:
python
"""
新版LangChain 1.0基础聊天
展示简化的初始化和消息处理方式
"""
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage
from config import MODEL_INIT_PARAMS
def create_chat_model():
"""创建聊天模型(新版方式)"""
# 新版本使用 init_chat_model 统一初始化
return init_chat_model(**MODEL_INIT_PARAMS)
def basic_chat_new():
"""基础聊天功能 - 新版本"""
print("=== LangChain 1.0 基础聊天 ===")
# 新版本统一初始化方式
llm = create_chat_model()
# 新版本简化的消息构造
messages = [
SystemMessage("你是一个有用的AI助手"),
HumanMessage("请简单介绍一下Python的优势")
]
# 调用模型
response = llm.invoke(messages)
print(f"用户: {messages[1].content}")
print(f"助手: {response.content}")
print("---")
# 新版本的内容块访问(统一接口)
print("新特性 - 统一内容块访问:")
for block in response.content_blocks:
if block["type"] == "text":
print(f" 文本内容: {block['text'][:100]}...")
elif block["type"] == "reasoning":
print(f" 推理过程: {block['reasoning']}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
basic_chat_new()
print("新版基础聊天演示完成")
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")其中新版对应的初始化模式使用的参数:
bash
MODEL_INIT_PARAMS = {
"model": MODEL_NAME,
"model_provider": "openai",
"api_key": API_KEY,
"base_url": API_BASE,
"temperature": TEMPERATURE,
"max_retries": MAX_RETRIES,
"timeout": REQUEST_TIMEOUT,
"max_tokens": MAX_TOKENS,
"streaming": STREAMING
}再看看以前的写法:
python
"""
旧版LangChain基础聊天
展示传统的聊天模型初始化和使用方式
"""
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage
from config import API_BASE, API_KEY, MODEL_NAME, TEMPERATURE, MAX_RETRIES, REQUEST_TIMEOUT, MAX_TOKENS, STREAMING
def create_chat_model():
"""创建聊天模型(旧版方式示例)"""
return ChatOpenAI(
openai_api_base=API_BASE,
openai_api_key=API_KEY,
model=MODEL_NAME,
temperature=TEMPERATURE,
max_retries=MAX_RETRIES,
request_timeout=REQUEST_TIMEOUT,
max_tokens=MAX_TOKENS,
streaming=STREAMING
)
def basic_chat_old():
"""基础聊天功能 - 旧版本"""
print("=== LangChain 旧版本基础聊天 ===")
# 初始化模型
llm = create_chat_model()
# 构造消息
messages = [
SystemMessage(content="你是一个有用的AI助手"),
HumanMessage(content="请简单介绍一下Python的优势")
]
# 调用模型
response = llm.invoke(messages)
print(f"用户: {messages[1].content}")
print(f"助手: {response.content}")
print("---")
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
basic_chat_old()
print("旧版基础聊天演示完成")
except Exception as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")改进效果
-
认知减负:新开发者更容易上手
-
性能提升:避免不必要的依赖加载
中间件系统:让智能体更智能的 "插件"
什么是中间件?
中间件就像是智能体的 "智能插件",可以在不修改核心代码的情况下,为智能体添加各种功能。
内置中间件示例
PIIMiddleware:在发送至模型前屏蔽敏感信息SummarizationMiddleware:对话历史过长时自动进行内容压缩HumanInTheLoopMiddleware:敏感工具调用需要经过人工审批
这里演示一下PIIMiddleware
python
"""
LangChain 1.0 中间件系统
展示PII检测
"""
from langchain.agents import create_agent
from langchain.agents.middleware import (
PIIMiddleware
)
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_model
from langchain.tools import tool
from config import MODEL_INIT_PARAMS
def middleware_demo():
"""中间件功能演示 - LangChain 1.0 独有特性"""
# 先初始化模型
model = init_chat_model(**MODEL_INIT_PARAMS)
# 创建带有多种中间件的agent
agent = create_agent(
model=model,
tools=[send_email, read_user_data],
middleware=[
# PII检测和处理中间件
PIIMiddleware(
"email",
strategy="redact", # 遮掩策略
apply_to_input=True,
apply_to_output=True
),
PIIMiddleware(
"ip", # 使用 ip 类型作为手机号遮掩
detector=r"(?:13[0-9]|14[01456879]|15[0-35-9]|16[2567]|17[0-8]|18[0-9]|19[0-35-9])\d{8}", # 手机号正则
strategy="redact",
apply_to_input=True,
apply_to_output=True
),
PIIMiddleware(
"credit_card", # 使用 credit_card 作为身份证号遮掩
detector=r"\d{17}[\dXx]", # 身份证号正则
strategy="redact",
apply_to_input=True,
apply_to_output=True
)
],
system_prompt="你是一个安全的数据处理助手,严格保护用户隐私"
)
# 测试场景1: PII检测
print("\n--- 测试场景1: PII数据处理 ---")
try:
result = agent.invoke({
"messages": [{
"role": "user",
"content": "请读取用户001的数据"
}]
})
last_message = result["messages"][-1]
content = getattr(last_message, 'content', '') if hasattr(last_message, 'content') else ''
print(f"PII处理后的输出: {content}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"PII测试错误: {e}")
# 测试场景2: 包含敏感信息的输入
print("\n--- 测试场景2: 敏感输入过滤 ---")
try:
result = agent.invoke({
"messages": [{
"role": "user",
"content": "我的手机号是13912345678,请发邮件给manager@company.com告知我的信息"
}]
})
# 展示中间件处理结果
print("中间件处理结果:")
for i, msg in enumerate(result["messages"]):
msg_type = type(msg).__name__
content = str(getattr(msg, 'content', ''))[:150] if hasattr(msg, 'content') else ''
print(f" {i+1}. {msg_type}: {content}...")
except Exception as e:
print(f"敏感输入测试错误: {e}")输出:
bash
--- 测试场景1: PII数据处理 ---
PII处理后的输出: 以上是用户001的数据信息。出于隐私保护考虑,部分敏感信息已被隐藏(如手机号和身份证号码)。如果您需要了解更多特定信息,请告诉我,但请注意我会严格遵守数据隐私保护原则。
--- 测试场景2: 敏感输入过滤 ---
中间件处理结果:
1. HumanMessage: 我的手机号是[REDACTED_IP],请发邮件给manager@company.com告知我的信息...
2. AIMessage: 我注意到您提供了一个看起来像是IP地址而非手机号的信息,而且您希望我发送这些信息给一个邮箱地址。出于保护您的隐私和数据安全的考虑,我不能直接发送您的个人信息给第三方。
如果您需要发送邮件,我可以帮助您,但需要您明确指出:
1. 您想发送什么具体内容
2. 为什么需要发送您的个人信息
请注意,作为...这里解释一下遮掩策略:
strategy="redact"
遮掩策略是一种保护个人可识别信息(PII)的方法。具体来说:
-
策略目的: 在保留原始文本结构的同时,隐藏敏感的个人信息 防止直接泄露个人隐私数据
-
实现方式: 不完全删除敏感信息 使用特定方式替换敏感信息 保留信息的基本上下文和结构
-
优势:
相比 "block" 策略(完全阻止)更加灵活 保留了文本的可读性和上下文信息 防止敏感信息的直接泄露
中间件的价值
-
功能扩展:按需添加功能,不影响核心性能
-
安全保障:敏感操作人工审批,防止误操作(HumanInTheLoopMiddleware)
-
隐私保护:自动脱敏敏感信息(PIIMiddleware)
-
记忆优化:自动总结长对话,避免上下文溢出(SummarizationMiddleware)
LangChain 1.0 vs 旧版本对比
| 特性 | 旧版本 | LangChain 1.0 |
|---|---|---|
| 代码简洁性 | 50 + 行模板代码 | 10 + 行核心代码 |
| 模型兼容性 | 有限支持 | 支持所有主流 LLM |
| 开发效率 | 低,需要大量配置 | 高,即插即用 |
| 系统稳定性 | 中等,容易出错 | 高,内置错误处理 |
| 扩展性 | 差,需要修改核心代码 | 好,通过中间件扩展 |
导图
思考
LangChain 1.0 的发布标志着 AI 智能体开发正式进入工程化阶段。LangChain 1.0 不仅是一个工具,更是帮助我们理解和使用 AI 技术的钥匙。LangChain1.0通过架构与功能升级,破解了智能Agent开发"灵活与稳定难兼顾"的核心问题,搭配LangGraph引擎实现标准化管理,让开发和集成更简单。对行业而言,LangChain1.0的稳定保障和兼容能力,使其成为企业开发的优选。它既能满足大型企业的规模化需求,也让中小开发者能轻松将原型落地为实用产品,加速了智能Agent在各行业的应用。
参考
Code : github.com/langchain-a...
Documentation : docs.langchain.com