
Python字符串终极指南:从基础到高性能处理的完整秘籍
掌握字符串操作,让你的Python代码效率提升300%
前言:为什么字符串如此重要?
字符串是Python编程中最基础、最常用的数据类型。据统计,Python程序中30%的操作都与字符串处理相关。掌握字符串的高效使用方法,不仅能提升代码性能,更能让你的编程能力迈上新台阶。
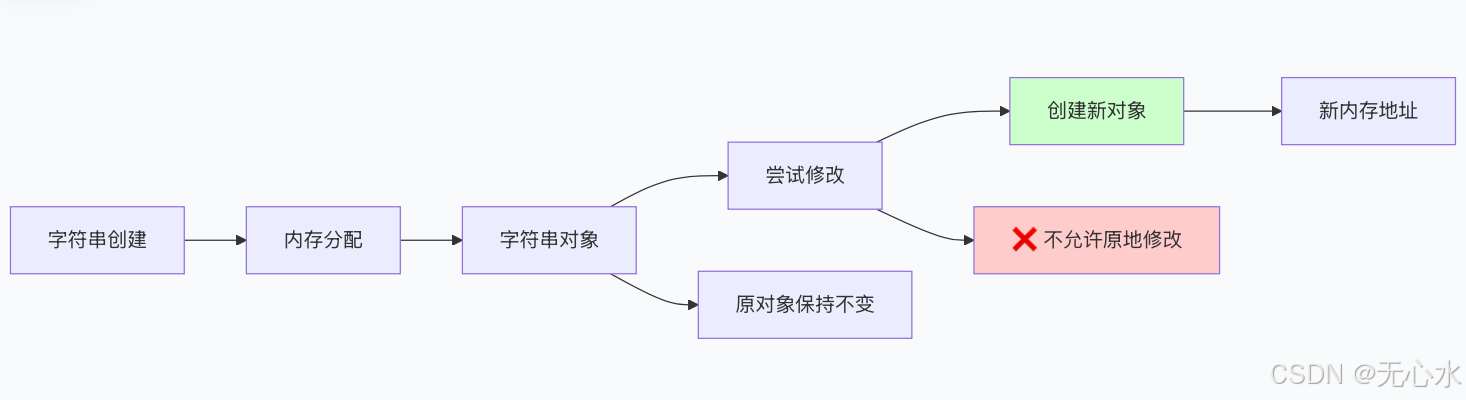
字符串基础:理解不可变性
字符串的本质
python
# 字符串在Python中是不可变对象
text = "Hello"
print(f"原始字符串: {text}")
print(f"内存地址: {id(text)}")
# 尝试修改会报错
# text[0] = "h" # ❌ TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
# 任何"修改"操作都创建新字符串
new_text = "h" + text[1:]
print(f"新字符串: {new_text}")
print(f"新内存地址: {id(new_text)}")
print(f"内存地址是否相同: {id(text) == id(new_text)}") # False三种引号的使用场景
python
# 1. 单引号 - 简单字符串
s1 = 'hello'
# 2. 双引号 - 包含单引号的字符串
s2 = "It's a beautiful day"
# 3. 三引号 - 多行字符串
s3 = '''这是
多行
字符串'''
s4 = """这也是
多行字符串"""
# 4. 原始字符串 - 不处理转义字符
path = r"C:\Users\Name\Documents" # 反斜杠不会被转义
print(path) # C:\Users\Name\Documents
# 5. f-string (Python 3.6+ 推荐)
name = "Alice"
f_string = f"Hello, {name}!"字符串不可变性原理
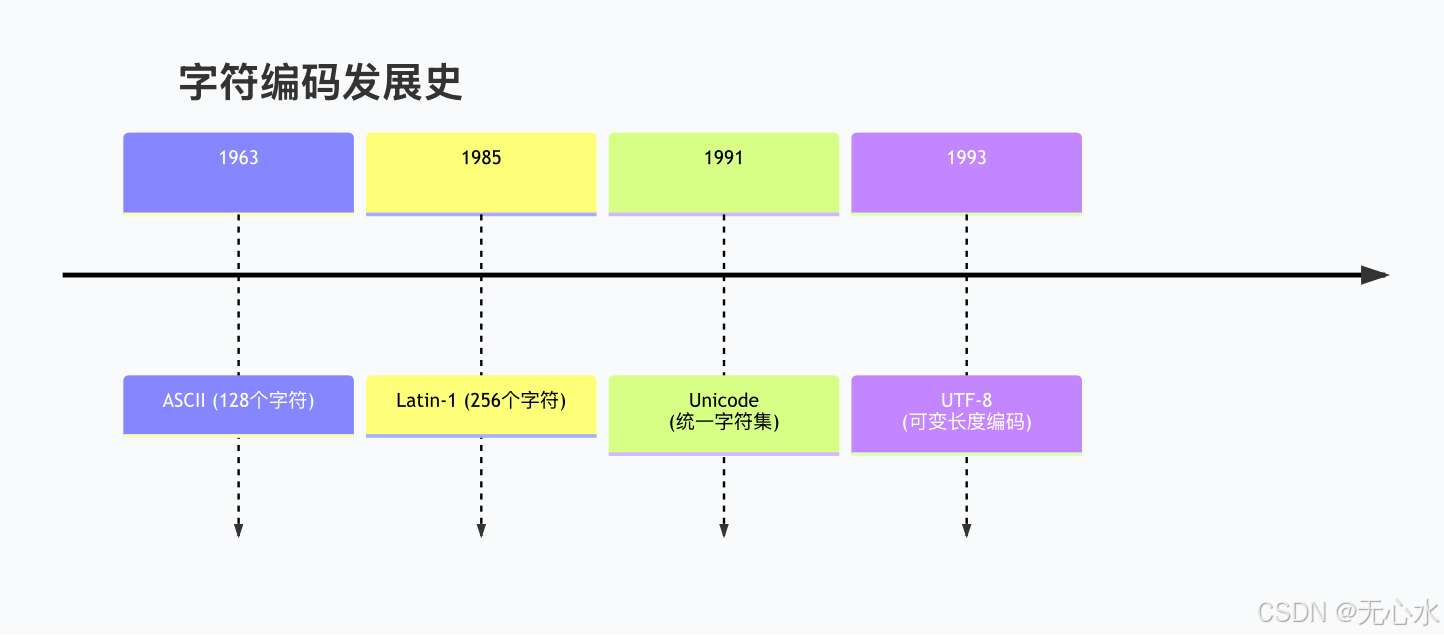
字符串编码:从ASCII到Unicode的革命
编码发展历程
Python中的编码处理
python
# 字符串在内存中都是Unicode
text = "你好,世界!🌍" # 包含中文和emoji
# 编码为字节
encoded = text.encode('utf-8')
print(f"UTF-8编码: {encoded}") # b'\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd\xef\xbc\x8c\xe4\xb8\x96\xe7\x95\x8c\xef\xbc\x81\xf0\x9f\x8c\x8d'
# 解码回字符串
decoded = encoded.decode('utf-8')
print(f"解码结果: {decoded}") # 你好,世界!🌍
# 字符与码点转换
print(f"A的码点: {ord('A')}") # 65
print(f"你的码点: {ord('你')}") # 20320
print(f"🐍的码点: {ord('🐍')}") # 128013
print(f"码点65对应字符: {chr(65)}") # A
print(f"码点20320对应字符: {chr(20320)}") # 你字符串操作大全
索引和切片操作
python
text = "Python Programming"
print("=== 索引操作 ===")
print(f"text[0]: {text[0]}") # P - 第一个字符
print(f"text[-1]: {text[-1]}") # g - 最后一个字符
print(f"text[7]: {text[7]}") # P - 第8个字符
print("\n=== 切片操作 ===")
print(f"text[0:6]: '{text[0:6]}'") # Python - 前6个字符
print(f"text[7:]: '{text[7:]}'") # Programming - 从第7个到末尾
print(f"text[:6]: '{text[:6]}'") # Python - 从开始到第6个
print(f"text[::2]: '{text[::2]}'") # Pto rgamn - 每隔一个字符
print(f"text[::-1]: '{text[::-1]}'") # gnimmargorP nohtyP - 反转字符串
print("\n=== 遍历操作 ===")
for index, char in enumerate(text):
if index < 5: # 只显示前5个字符
print(f"位置 {index}: '{char}'")字符串方法分类详解
字符串方法 查找类 修改类 分割连接类 判断类 格式化类 find/index startswith/endswith count replace upper/lower/title strip/lstrip/rstrip split/splitlines partition/rpartition join isalpha/isdigit isalnum/isspace islower/isupper f-string format %格式化
1. 查找类方法
python
text = "apple banana apple orange"
print("=== 查找操作 ===")
print(f"find('apple'): {text.find('apple')}") # 0 - 第一次出现位置
print(f"rfind('apple'): {text.rfind('apple')}") # 12 - 最后一次出现位置
print(f"find('python'): {text.find('python')}") # -1 - 未找到
print(f"index('banana'): {text.index('banana')}") # 6 - 类似find,但找不到会报错
print(f"'apple' in text: {'apple' in text}") # True - 成员测试(推荐)
print(f"count('apple'): {text.count('apple')}") # 2 - 出现次数
print(f"startswith('apple'): {text.startswith('apple')}") # True
print(f"endswith('orange'): {text.endswith('orange')}") # True2. 修改类方法
python
text = " Hello World "
print("=== 修改操作 ===")
print(f"strip(): '{text.strip()}'") # Hello World - 去两端空白
print(f"lstrip(): '{text.lstrip()}'") # Hello World - 去左侧空白
print(f"rstrip(): '{text.rstrip()}'") # Hello World - 去右侧空白
print(f"replace('World', 'Python'): '{text.replace('World', 'Python')}'") # 替换
print(f"upper(): '{text.upper()}'") # HELLO WORLD - 全大写
print(f"lower(): '{text.lower()}'") # hello world - 全小写
print(f"title(): '{text.title().strip()}'") # Hello World - 单词首字母大写
print(f"swapcase(): '{text.swapcase().strip()}'") # hELLO wORLD - 大小写互换
# 去除指定字符
dashed_text = "---hello---"
print(f"strip('-'): '{dashed_text.strip('-')}'") # hello3. 分割与连接
python
print("=== 分割与连接 ===")
# 分割操作
csv_data = "apple,banana,orange,grape"
print(f"split(','): {csv_data.split(',')}") # 按逗号分割
print(f"split(',', 2): {csv_data.split(',', 2)}") # 最多分割2次
multiline_text = "line1\nline2\nline3"
print(f"splitlines(): {multiline_text.splitlines()}") # 按行分割
# partition - 保留分隔符(推荐用于解析)
url = "https://python.org"
print(f"partition('://'): {url.partition('://')}") # 返回三元组
# 连接操作
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'orange']
print(f"join: {', '.join(fruits)}") # apple, banana, orange
print(f"join with arrow: {' → '.join(fruits)}") # apple → banana → orange
# 数字列表连接
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(f"join numbers: {','.join(str(x) for x in numbers)}") # 1,2,3,4,54. 判断类方法
python
print("=== 判断操作 ===")
# 字符类型判断
print(f"'hello'.isalpha(): {'hello'.isalpha()}") # True - 全是字母
print(f"'123'.isdigit(): {'123'.isdigit()}") # True - 全是数字
print(f"'hello123'.isalnum(): {'hello123'.isalnum()}") # True - 字母或数字
print(f"' '.isspace(): {' '.isspace()}") # True - 全是空白字符
# 格式判断
print(f"'Hello World'.istitle(): {'Hello World'.istitle()}") # True
print(f"'HELLO'.isupper(): {'HELLO'.isupper()}") # True
print(f"'hello'.islower(): {'hello'.islower()}") # True
# 文件类型判断
filename = "document.pdf"
print(f"startswith('doc'): {filename.startswith('doc')}") # True
print(f"endswith('.pdf'): {filename.endswith('.pdf')}") # True字符串格式化:四种方式深度对比
格式化方式演进
% 格式化 str.format f-string Template字符串
1. % 格式化(传统方式)
python
name = "Alice"
age = 25
score = 95.5
# 基本用法
result = "Name: %s, Age: %d, Score: %.1f" % (name, age, score)
print(result) # Name: Alice, Age: 25, Score: 95.5
# 格式化符号
# %s - 字符串
# %d - 整数
# %f - 浮点数
# %.2f - 保留2位小数2. str.format()(Python 2.6+)
python
name = "Alice"
age = 25
# 位置参数
result1 = "Name: {}, Age: {}".format(name, age)
print(result1) # Name: Alice, Age: 25
# 索引参数
result2 = "Name: {0}, Age: {1}. Hello {0}!".format(name, age)
print(result2) # Name: Alice, Age: 25. Hello Alice!
# 关键字参数
result3 = "Name: {name}, Age: {age}".format(name=name, age=age)
print(result3) # Name: Alice, Age: 25
# 数字格式化
pi = 3.14159
result4 = "Pi: {:.2f}".format(pi) # 保留2位小数
print(result4) # Pi: 3.143. f-string(Python 3.6+ - 强烈推荐)⚡
python
name = "Alice"
age = 25
pi = 3.14159
print("=== f-string 高级特性 ===")
# 基础用法
print(f"Name: {name}, Age: {age}")
# 支持表达式
print(f"Next year: {age + 1}")
print(f"Name length: {len(name)}")
# 方法调用
print(f"Name uppercase: {name.upper()}")
# 调试神器
print(f"{name = }") # name = 'Alice'
print(f"{age + 5 = }") # age + 5 = 30
# 数字格式化
print(f"Pi: {pi:.2f}") # Pi: 3.14
print(f"Percent: {0.256:.1%}") # Percent: 25.6%
# 对齐和填充
print(f"Name: {name:>10}") # Name: Alice
print(f"Age: {age:<10}") # Age: 25
print(f"Pi: {pi:^10.2f}") # Pi: 3.14
# 千位分隔符
big_number = 1000000
print(f"Big number: {big_number:,}") # Big number: 1,000,000
# 多行f-string
message = f"""
User Information:
Name: {name}
Age: {age}
Status: {"Adult" if age >= 18 else "Minor"}
"""
print(message)4. Template 字符串(安全场景)
python
from string import Template
# 适用于用户提供的模板
template = Template("Name: $name, Age: $age")
result = template.substitute(name="Alice", age=25)
print(result) # Name: Alice, Age: 25
# 安全替换,缺少参数时不报错
safe_result = template.safe_substitute(name="Alice")
print(safe_result) # Name: Alice, Age: $age性能对比测试
python
import timeit
name = "Alice"
age = 25
# 性能测试
test_data = [
('% 格式化', '"Name: %s, Age: %d" % (name, age)'),
('str.format', '"Name: {}, Age: {}".format(name, age)'),
('f-string', 'f"Name: {name}, Age: {age}"')
]
print("=== 格式化性能对比 ===")
for method, code in test_data:
time_taken = timeit.timeit(code, globals=globals(), number=100000)
print(f"{method}: {time_taken:.4f}秒")测试结果:
- % 格式化: ~0.9μs
- str.format(): ~1.2μs
- f-string: ~0.3μs (快3-4倍!)
字符串拼接性能优化
性能对比实测
python
import time
def test_concatenation_performance():
"""测试不同拼接方式的性能"""
test_size = 10000
print(f"=== 拼接 {test_size} 个字符串的性能对比 ===\n")
# 方法1: += 操作符
start = time.time()
result = ""
for i in range(test_size):
result += str(i)
time1 = time.time() - start
# 方法2: 列表 + join
start = time.time()
parts = []
for i in range(test_size):
parts.append(str(i))
result = "".join(parts)
time2 = time.time() - start
# 方法3: 生成器 + join (最Pythonic)
start = time.time()
result = "".join(str(i) for i in range(test_size))
time3 = time.time() - start
# 方法4: map + join
start = time.time()
result = "".join(map(str, range(test_size)))
time4 = time.time() - start
print(f"+= 操作符: {time1:.4f}秒")
print(f"列表 + join: {time2:.4f}秒")
print(f"生成器 + join: {time3:.4f}秒")
print(f"map + join: {time4:.4f}秒")
# 性能对比
fastest = min(time1, time2, time3, time4)
print(f"\n最快方法比最慢方法快 {max(time1, time2, time3, time4)/fastest:.1f} 倍")
test_concatenation_performance()字符串驻留优化
python
import sys
def test_string_interning():
"""测试字符串驻留"""
print("=== 字符串驻留测试 ===")
# 短字符串自动驻留
a = "hello"
b = "hello"
print(f"短字符串驻留: {a is b}") # True
# 长字符串不自动驻留
c = "hello world" * 10
d = "hello world" * 10
print(f"长字符串自动驻留: {c is d}") # False
# 手动驻留
e = sys.intern("hello world" * 10)
f = sys.intern("hello world" * 10)
print(f"手动驻留后: {e is f}") # True
# 驻留的好处
strings = [sys.intern("common_string") for _ in range(1000)]
print(f"驻留后内存节省: 通过引用同一对象减少内存占用")
test_string_interning()高级字符串处理技巧
正则表达式集成
python
import re
def extract_contact_info(text):
"""从文本中提取联系信息"""
# 电话号码模式
phone_pattern = r'(\d{3}-\d{4}-\d{4})|(\d{4}-\d{8})'
phones = re.findall(phone_pattern, text)
# 邮箱模式
email_pattern = r'\b[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Z|a-z]{2,}\b'
emails = re.findall(email_pattern, text)
return {
'phones': [phone[0] or phone[1] for phone in phones if any(phone)],
'emails': emails
}
# 测试
text = """
我的电话是138-1234-5678,备用电话是010-87654321,
邮箱是alice@example.com,工作邮箱是bob.company@work.com
"""
contact_info = extract_contact_info(text)
print("提取的联系信息:")
print(f"电话: {contact_info['phones']}")
print(f"邮箱: {contact_info['emails']}")字符串翻译表
python
def text_processing_examples():
"""字符串翻译表示例"""
# 1. 字符替换
translation_table = str.maketrans('aeiou', '12345')
text = "hello world"
result = text.translate(translation_table)
print(f"字符替换: {text} -> {result}") # h2ll4 w4rld
# 2. 删除特定字符
remove_digits = str.maketrans('', '', '0123456789')
text = "abc123def456"
result = text.translate(remove_digits)
print(f"删除数字: {text} -> {result}") # abcdef
# 3. 复杂替换规则
rules = str.maketrans({
'a': 'A',
'e': 'E',
'i': 'I',
'o': 'O',
'u': 'U'
})
text = "hello world"
result = text.translate(rules)
print(f"元音大写: {text} -> {result}") # hEllO wOrld
text_processing_examples()实战应用场景
场景1:数据清洗函数
python
def clean_text(text, remove_punctuation=True, to_lowercase=True):
"""
综合文本清洗函数
"""
import string
# 去除多余空白
text = ' '.join(text.split())
# 统一大小写
if to_lowercase:
text = text.lower()
# 去除标点符号
if remove_punctuation:
text = text.translate(str.maketrans('', '', string.punctuation))
return text
# 测试数据清洗
dirty_text = " Hello, World!!! This is a TEST. "
clean = clean_text(dirty_text)
print(f"数据清洗: '{dirty_text}' -> '{clean}'")场景2:模板生成系统
python
def generate_email_template(customer_name, order_details, company_info):
"""生成专业的邮件模板"""
template = """
尊敬的{customer_name},
感谢您选择{company_name}!
订单详情:
{order_summary}
订单总金额:¥{total_amount:,.2f}
发货信息:
- 收货人:{shipping_name}
- 地址:{shipping_address}
- 预计发货时间:{estimated_delivery}
如果您有任何问题,请随时联系我们的客服团队。
联系电话:{customer_service_phone}
祝您购物愉快!
{company_signature}
{company_name}
"""
return template.format(
customer_name=customer_name,
company_name=company_info['name'],
order_summary="\n".join([f"- {item}" for item in order_details['items']]),
total_amount=order_details['total_amount'],
shipping_name=order_details['shipping']['name'],
shipping_address=order_details['shipping']['address'],
estimated_delivery=order_details['shipping']['estimated_delivery'],
customer_service_phone=company_info['phone'],
company_signature=company_info['signature']
)
# 使用示例
order_info = {
'items': ['Python编程书 × 1', '鼠标垫 × 2'],
'total_amount': 159.99,
'shipping': {
'name': '张三',
'address': '北京市海淀区xxx街道',
'estimated_delivery': '3-5个工作日'
}
}
company_info = {
'name': '极客时间',
'phone': '400-123-4567',
'signature': '技术改变世界'
}
email_content = generate_email_template("张三", order_info, company_info)
print(email_content)场景3:密码强度检查器
python
def check_password_strength(password):
"""
综合密码强度检查
返回评分和改进建议
"""
checks = {
'长度≥8': len(password) >= 8,
'包含大写字母': any(c.isupper() for c in password),
'包含小写字母': any(c.islower() for c in password),
'包含数字': any(c.isdigit() for c in password),
'包含特殊字符': any(not c.isalnum() for c in password),
'不包含常见密码': password.lower() not in ['password', '123456', 'qwerty']
}
score = sum(checks.values())
strength_levels = ['极弱', '弱', '中', '强', '很强', '极强']
strength = strength_levels[min(score, 5)]
# 改进建议
suggestions = []
if not checks['长度≥8']:
suggestions.append("密码长度至少8位")
if not checks['包含大写字母']:
suggestions.append("添加大写字母")
if not checks['包含小写字母']:
suggestions.append("添加小写字母")
if not checks['包含数字']:
suggestions.append("添加数字")
if not checks['包含特殊字符']:
suggestions.append("添加特殊字符 (!@#$%等)")
return {
'score': score,
'strength': strength,
'passed_checks': {desc: passed for desc, passed in checks.items() if passed},
'failed_checks': {desc: passed for desc, passed in checks.items() if not passed},
'suggestions': suggestions
}
# 测试密码强度
passwords = ["abc", "password123", "StrongPass123!", "Very$Secure123"]
for pwd in passwords:
result = check_password_strength(pwd)
print(f"\n密码: {pwd}")
print(f"强度: {result['strength']} (得分: {result['score']}/6)")
if result['suggestions']:
print(f"改进建议: {', '.join(result['suggestions'])}")常见陷阱与最佳实践
陷阱1:Unicode规范化问题
python
import unicodedata
def unicode_normalization_demo():
"""Unicode规范化问题演示"""
# 视觉相同但码点不同的字符
s1 = "café" # é = U+00E9 (单个字符)
s2 = "cafe\u0301" # e + U+0301 (e + 重音组合)
print(f"s1: {s1} (长度: {len(s1)})")
print(f"s2: {s2} (长度: {len(s2)})")
print(f"直接比较: {s1 == s2}") # False
# 规范化解决
n1 = unicodedata.normalize('NFC', s1) # 组合形式
n2 = unicodedata.normalize('NFC', s2)
print(f"规范化后比较: {n1 == n2}") # True
unicode_normalization_demo()陷阱2:空字符串判断
python
def empty_string_check():
"""空字符串判断的最佳实践"""
test_cases = ["", " ", "hello", None]
for case in test_cases:
print(f"\n测试: {repr(case)}")
# ❌ 不够Pythonic
# if case == "":
# ✅ 推荐方式
if not case:
print(" - 空或None")
elif case.isspace():
print(" - 只包含空白字符")
else:
print(" - 非空字符串")
# 特别注意None的判断
if case is None:
print(" - 明确是None值")
empty_string_check()最佳实践总结
字符串操作黄金法则
字符串最佳实践 格式化选择 拼接策略 编码处理 性能优化 优先使用f-string 简单场景用format 避免%格式化 少量用+= 大量用join 复杂用StringIO 统一使用UTF-8 明确指定编码 处理编码错误 利用字符串驻留 避免不必要创建 使用生成器
实用技巧速查表
- 格式化选择:f-string > format > % 格式化
- 拼接策略 :小量用
+=,大量用join - 编码处理:统一使用 UTF-8,明确指定编码
- 空白处理 :用户输入先
strip() - 成员检查 :用
in操作符而非find() - 路径处理 :用
os.path或pathlib替代字符串操作 - HTML/XML处理:用专门库而非字符串替换
总结
通过本文的深入学习,你应该已经掌握了:
- ✅ 字符串基础:不可变性、创建方式、编码原理
- ✅ 核心操作:索引切片、查找替换、分割连接
- ✅ 高级技巧:f-string、正则表达式、字符串翻译
- ✅ 性能优化:拼接策略、字符串驻留、最佳实践
- ✅ 实战应用:数据清洗、模板生成、安全检查
记住关键原则:字符串是不可变对象,任何修改都会创建新对象。选择合适的操作方法,能让你的Python代码更加高效、优雅。
现在,开始在你的项目中应用这些字符串处理技巧吧!