文章目录
- [1 基本介绍](#1 基本介绍)
- [2 公式](#2 公式)
-
- [2.1 决策变量](#2.1 决策变量)
- [2.2 目标函数](#2.2 目标函数)
- [2.3 约束条件](#2.3 约束条件)
-
- a) 等式约束 - 潮流方程 等式约束 - 潮流方程)
- b) 不等式约束 - 安全运行限制 不等式约束 - 安全运行限制)
- [2.4 完整OPF数学模型](#2.4 完整OPF数学模型)
- [3 项目实战](#3 项目实战)
- [4 问题特性](#4 问题特性)
1 基本介绍
最优化潮流问题,一般来说就是指一个优化问题,在特定的条件限制下需要实现最优分布潮流。从本质上讲,最优潮流是对电力系统潮流的扩展,它将描述系统稳态运行的非线性潮流方程作为必须满足的等式约束,从而将问题构建为一个大规模、非凸、非线性的约束优化问题。由于其数学上的复杂性,寻求OPF问题的全局最优解极具挑战,因此在工程实践中,大量研究集中于开发高效的数值计算方法,例如非线性规划的内点法、线性规划或二次规划的顺序逼近、以及近年来兴起的基于人工智能的求解方法,以在可接受的时间内获得满足工程精度要求的局部最优解。
2 公式
任何一个优化问题都包含三个基本要素:决策变量、目标函数和约束条件,OPF也不例外。
2.1 决策变量
- 发电机有功出力 : P G i P_{Gi} PGi( i ∈ G i \in G i∈G,G为发电机节点集合)
- 发电机机端电压幅值 : V i V_i Vi( i ∈ G i \in G i∈G)
- 节点电压相角 : θ i \theta_i θi( i ∈ N i \in N i∈N,N为节点集合,通常设参考节点相角为0)
决策变量向量表示为:
x = [ ... , P G i , ... , V i , ... , θ i , ... ] T \mathbf{x} = [\ldots, P_{Gi}, \ldots, V_{i}, \ldots, \theta_{i}, \ldots]^{T} x=[...,PGi,...,Vi,...,θi,...]T
2.2 目标函数
最经典的目标是总发电成本最小化,采用二次成本函数:
min F ( x ) = ∑ i ∈ G ( a i P G i 2 + b i P G i + c i ) \min F(\mathbf{x}) = \sum_{i \in G} (a_i P_{Gi}^2 + b_i P_{Gi} + c_i) minF(x)=i∈G∑(aiPGi2+biPGi+ci)
其中 a i > 0 a_i > 0 ai>0, b i b_i bi, c i c_i ci为发电机成本系数。
2.3 约束条件
a) 等式约束 - 潮流方程
描述电力网络物理定律,每个节点 i i i满足:
有功功率平衡 :
P G i − P D i = V i ∑ j = 1 N V j ( G i j cos θ i j + B i j sin θ i j ) P_{Gi} - P_{Di} = V_i \sum_{j=1}^{N} V_j (G_{ij} \cos \theta_{ij} + B_{ij} \sin \theta_{ij}) PGi−PDi=Vij=1∑NVj(Gijcosθij+Bijsinθij)
无功功率平衡 :
Q G i − Q D i = V i ∑ j = 1 N V j ( G i j sin θ i j − B i j cos θ i j ) Q_{Gi} - Q_{Di} = V_i \sum_{j=1}^{N} V_j (G_{ij} \sin \theta_{ij} - B_{ij} \cos \theta_{ij}) QGi−QDi=Vij=1∑NVj(Gijsinθij−Bijcosθij)
其中:
- θ i j = θ i − θ j \theta_{ij} = \theta_i - \theta_j θij=θi−θj
- G i j + j B i j G_{ij} + jB_{ij} Gij+jBij为节点导纳矩阵元素
- P D i P_{Di} PDi, Q D i Q_{Di} QDi为负荷功率(已知)
b) 不等式约束 - 安全运行限制
发电机出力限制 :
P G i min ≤ P G i ≤ P G i max , ∀ i ∈ G P_{Gi}^{\min} \le P_{Gi} \le P_{Gi}^{\max}, \quad \forall i \in G PGimin≤PGi≤PGimax,∀i∈G
Q G i min ≤ Q G i ≤ Q G i max , ∀ i ∈ G Q_{Gi}^{\min} \le Q_{Gi} \le Q_{Gi}^{\max}, \quad \forall i \in G QGimin≤QGi≤QGimax,∀i∈G
节点电压限制 :
V i min ≤ V i ≤ V i max , ∀ i ∈ N V_{i}^{\min} \le V_{i} \le V_{i}^{\max}, \quad \forall i \in N Vimin≤Vi≤Vimax,∀i∈N
线路容量限制 :
∣ S l ( x ) ∣ ≤ S l max , ∀ l ∈ L |S_l(\mathbf{x})| \le S_l^{\max}, \quad \forall l \in L ∣Sl(x)∣≤Slmax,∀l∈L
其中 S l = P l 2 + Q l 2 S_l = \sqrt{P_l^2 + Q_l^2} Sl=Pl2+Ql2 为线路视在功率。
2.4 完整OPF数学模型
minimize x F ( x ) = ∑ i ∈ G ( a i P G i 2 + b i P G i + c i ) subject to g i P ( x ) = P G i − P D i − V i ∑ j V j ( G i j cos θ i j + B i j sin θ i j ) = 0 g i Q ( x ) = Q G i − Q D i − V i ∑ j V j ( G i j sin θ i j − B i j cos θ i j ) = 0 P ‾ G i ≤ P G i ≤ P ‾ G i Q ‾ G i ≤ Q G i ≤ Q ‾ G i V ‾ i ≤ V i ≤ V ‾ i ∣ S l ( x ) ∣ ≤ S ‾ l \begin{aligned} & \underset{\mathbf{x}}{\text{minimize}} & & F(\mathbf{x}) = \sum_{i \in G} (a_i P_{Gi}^2 + b_i P_{Gi} + c_i) \\ & \text{subject to} & & g^P_i(\mathbf{x}) = P_{Gi} - P_{Di} - V_i \sum_{j} V_j (G_{ij}\cos\theta_{ij} + B_{ij}\sin\theta_{ij}) = 0 \\ & & & g^Q_i(\mathbf{x}) = Q_{Gi} - Q_{Di} - V_i \sum_{j} V_j (G_{ij}\sin\theta_{ij} - B_{ij}\cos\theta_{ij}) = 0 \\ & & & \underline{P}{Gi} \le P{Gi} \le \overline{P}{Gi} \\ & & & \underline{Q}{Gi} \le Q_{Gi} \le \overline{Q}{Gi} \\ & & & \underline{V}{i} \le V_{i} \le \overline{V}_{i} \\ & & & |S_l(\mathbf{x})| \le \overline{S}_l \end{aligned} xminimizesubject toF(x)=i∈G∑(aiPGi2+biPGi+ci)giP(x)=PGi−PDi−Vij∑Vj(Gijcosθij+Bijsinθij)=0giQ(x)=QGi−QDi−Vij∑Vj(Gijsinθij−Bijcosθij)=0PGi≤PGi≤PGiQGi≤QGi≤QGiVi≤Vi≤Vi∣Sl(x)∣≤Sl
3 项目实战
python
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.optimize import minimize, BFGS
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif']=['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
class StableOPF:
"""
数值稳定的最优潮流实现
"""
def __init__(self):
# 3节点系统
self.n_buses = 3
self.slack_bus = 0
# 发电机参数
self.generators = [
{'bus': 0, 'pmin': 0.1, 'pmax': 3.0, 'a': 0.11, 'b': 5.0, 'c': 0.0},
{'bus': 1, 'pmin': 0.1, 'pmax': 2.0, 'a': 0.085, 'b': 1.2, 'c': 0.0}
]
# 负荷参数(进一步简化)
self.loads = {
1: {'pd': 0.8, 'qd': 0.3},
2: {'pd': 0.6, 'qd': 0.2}
}
# 线路参数
self.lines = [
{'from': 0, 'to': 1, 'r': 0.02, 'x': 0.06, 'b': 0.0, 'rate': 2.0},
{'from': 1, 'to': 2, 'r': 0.03, 'x': 0.08, 'b': 0.0, 'rate': 1.5},
{'from': 2, 'to': 0, 'r': 0.04, 'x': 0.10, 'b': 0.0, 'rate': 2.5}
]
# 电压限制
self.v_min = 0.95
self.v_max = 1.05
def build_ybus(self):
"""构建矩阵"""
Ybus = np.zeros((self.n_buses, self.n_buses), dtype=complex)
for line in self.lines:
i, j, r, x, b = line['from'], line['to'], line['r'], line['x'], line['b']
z = r + 1j * x
y = 1.0 / z
Ybus[i, j] = Ybus[j, i] = -y
Ybus[i, i] += y + 1j * b / 2
Ybus[j, j] += y + 1j * b / 2
return Ybus
def calculate_power_flow(self, V, theta):
"""计算潮流方程"""
Ybus = self.build_ybus()
P_calc = np.zeros(self.n_buses)
Q_calc = np.zeros(self.n_buses)
for i in range(self.n_buses):
for j in range(self.n_buses):
theta_ij = theta[i] - theta[j]
G, B = Ybus[i,j].real, Ybus[i,j].imag
P_calc[i] += V[i] * V[j] * (G * np.cos(theta_ij) + B * np.sin(theta_ij))
Q_calc[i] += V[i] * V[j] * (G * np.sin(theta_ij) - B * np.cos(theta_ij))
return P_calc, Q_calc
def parse_variables(self, x):
"""解析变量"""
# x = [V1, V2, theta1, theta2, Pg0, Pg1]
V = np.array([1.0, x[0], x[1]]) # 平衡节点V0=1.0
theta = np.array([0.0, x[2], x[3]]) # 平衡节点theta0=0.0
Pg = np.array([x[4], x[5], 0.0]) # 节点2无发电机
return Pg, V, theta
def objective(self, x):
"""目标函数"""
Pg, _, _ = self.parse_variables(x)
cost = 0.0
for gen in self.generators:
bus, a, b, c = gen['bus'], gen['a'], gen['b'], gen['c']
cost += a * Pg[bus]**2 + b * Pg[bus] + c
return cost
def power_balance(self, x):
"""功率平衡约束(简化版)"""
Pg, V, theta = self.parse_variables(x)
P_calc, Q_calc = self.calculate_power_flow(V, theta)
# 负荷
Pd = np.zeros(self.n_buses)
Qd = np.zeros(self.n_buses)
for bus, load in self.loads.items():
Pd[bus] = load['pd']
Qd[bus] = load['qd']
constraints = []
# 有功平衡(所有节点)
for i in range(self.n_buses):
constraints.append(Pg[i] - Pd[i] - P_calc[i])
# 无功平衡(PQ节点)
for i in [1, 2]: # PQ节点
constraints.append(-Qd[i] - Q_calc[i])
return np.array(constraints)
def constraints_ineq(self, x):
"""不等式约束(简化版)"""
Pg, V, theta = self.parse_variables(x)
constraints = []
# 发电机限制
for gen in self.generators:
bus, pmin, pmax = gen['bus'], gen['pmin'], gen['pmax']
constraints.extend([Pg[bus] - pmin, pmax - Pg[bus]])
# 电压限制
for i in range(self.n_buses):
constraints.extend([V[i] - self.v_min, self.v_max - V[i]])
return np.array(constraints)
def solve_stable(self):
"""稳定的优化求解"""
# 更好的初始猜测
total_load = sum(load['pd'] for load in self.loads.values())
x0 = np.array([1.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, total_load*0.6, total_load*0.4])
bounds = [
(0.98, 1.02), (0.98, 1.02), # V1, V2
(-0.2, 0.2), (-0.2, 0.2), # theta1, theta2
(0.1, 3.0), (0.1, 2.0) # Pg0, Pg1
]
constraints = [
{'type': 'eq', 'fun': self.power_balance},
{'type': 'ineq', 'fun': self.constraints_ineq}
]
# 使用更稳健的优化方法
result = minimize(
self.objective, x0,
method='trust-constr', # 更稳健的方法
bounds=bounds,
constraints=constraints,
options={'verbose': 1, 'gtol': 1e-6, 'maxiter': 200}
)
return result
def print_simple_results(self, result):
"""简化结果输出"""
print("="*60)
print("简化OPF结果")
print("="*60)
if hasattr(result, 'x'):
x_opt = result.x
Pg, V, theta = self.parse_variables(x_opt)
print(f"状态: {'成功' if result.success else '优化困难'}")
print(f"成本: {result.fun:.4f} $/h")
print(f"信息: {result.message}")
print()
# 节点结果
Pd = np.zeros(self.n_buses)
for bus, load in self.loads.items():
Pd[bus] = load['pd']
print("节点结果:")
for i in range(self.n_buses):
print(f"节点{i}: Pg={Pg[i]:.3f}MW, Pd={Pd[i]:.3f}MW, "
f"V={V[i]:.3f}pu, θ={np.degrees(theta[i]):.2f}°")
# 功率平衡
total_pg = sum(Pg)
total_pd = sum(Pd)
loss = total_pg - total_pd
print(f"\n功率平衡:")
print(f"发电: {total_pg:.3f}MW, 负荷: {total_pd:.3f}MW, "
f"网损: {loss:.3f}MW ({loss/total_pg*100:.1f}%)")
# 约束检查
power_eq = self.power_balance(x_opt)
ineq = self.constraints_ineq(x_opt)
print(f"\n约束检查:")
print(f"功率平衡误差: {max(abs(power_eq)):.6f}")
print(f"不等式约束裕度: {min(ineq):.6f}")
return True
return False
def main():
"""主函数 - 简化版本"""
print("创建简化OPF实例...")
opf = StableOPF()
print("开始优化求解...")
result = opf.solve_stable()
print("\n" + "="*60)
if opf.print_simple_results(result):
print("\n优化完成!")
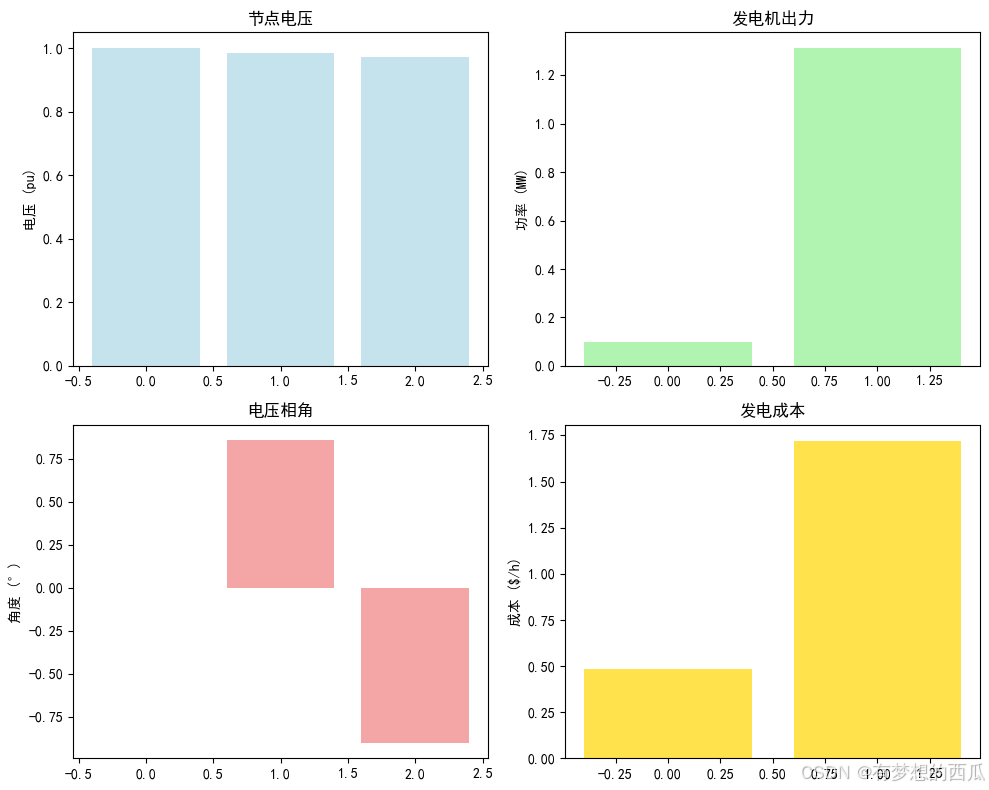
# 简单可视化
x_opt = result.x
Pg, V, theta = opf.parse_variables(x_opt)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(10, 8))
# 电压分布
axes[0,0].bar(range(3), V, color='lightblue', alpha=0.7)
axes[0,0].set_title('节点电压')
axes[0,0].set_ylabel('电压 (pu)')
# 发电机出力
gen_power = [Pg[0], Pg[1]]
axes[0,1].bar([0, 1], gen_power, color='lightgreen', alpha=0.7)
axes[0,1].set_title('发电机出力')
axes[0,1].set_ylabel('功率 (MW)')
# 相角分布
angles_deg = np.degrees(theta)
axes[1,0].bar(range(3), angles_deg, color='lightcoral', alpha=0.7)
axes[1,0].set_title('电压相角')
axes[1,0].set_ylabel('角度 (°)')
# 成本分布
costs = []
for gen in opf.generators:
bus, a, b, c = gen['bus'], gen['a'], gen['b'], gen['c']
costs.append(a * Pg[bus]**2 + b * Pg[bus] + c)
axes[1,1].bar([0, 1], costs, color='gold', alpha=0.7)
axes[1,1].set_title('发电成本')
axes[1,1].set_ylabel('成本 ($/h)')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
else:
print("优化失败!")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()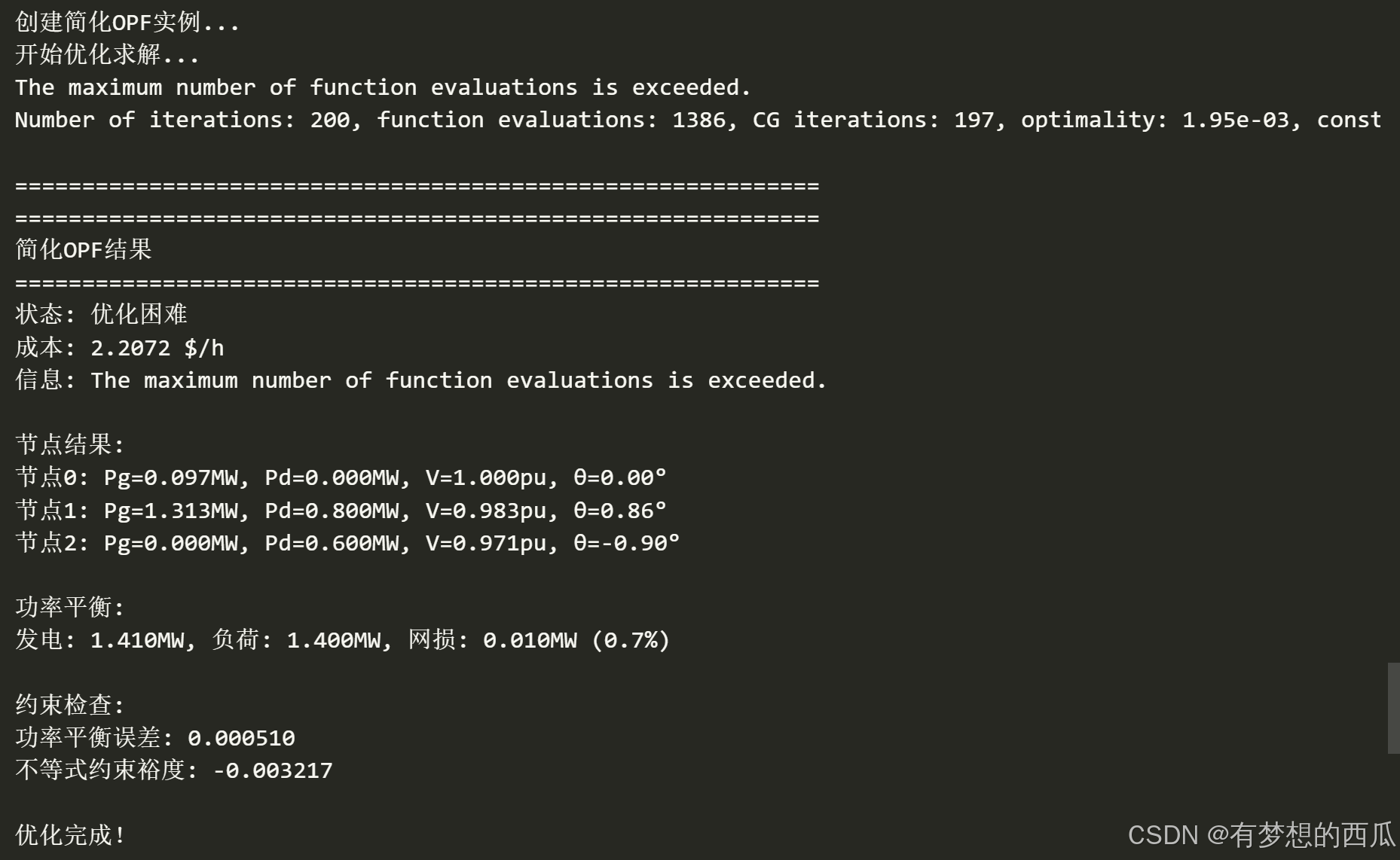
4 问题特性
该模型是典型的大规模、非线性、非凸优化问题:
- 大规模:实际电网节点数众多,变量和约束数量庞大
- 非线性:潮流方程包含电压乘积和三角函数项
- 非凸:可行域非凸,存在多个局部最优解
这一数学模型是OPF理论研究与算法开发的基础。