B站:【黑马程序员Java零基础视频教程_上部(Java入门,含斯坦福大学练习题+力扣算法题和大厂java面试题)】https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV17F411T7Ao?vd_source=902cae974409091c868112996a85ad70
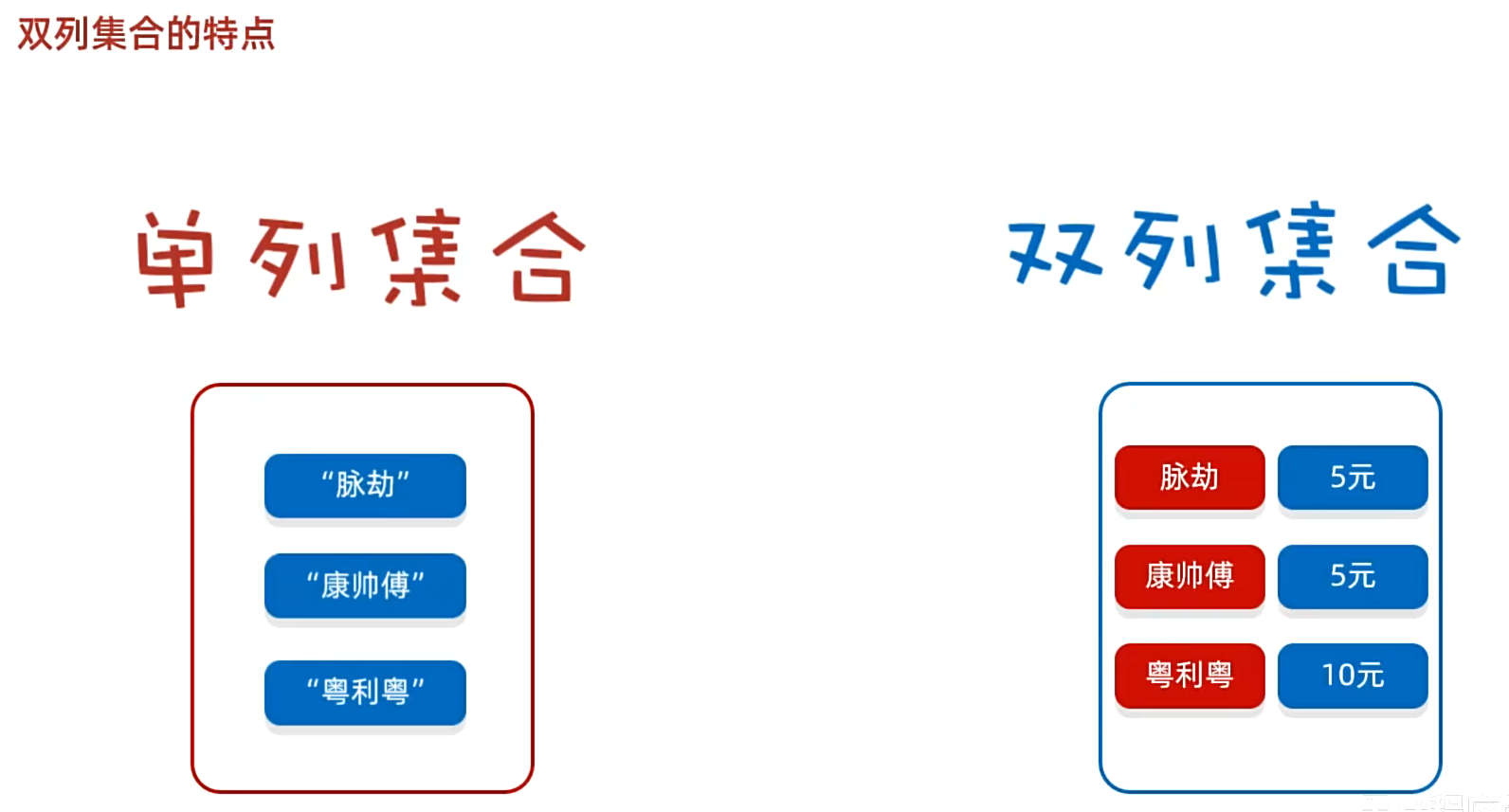
一. 双列集合
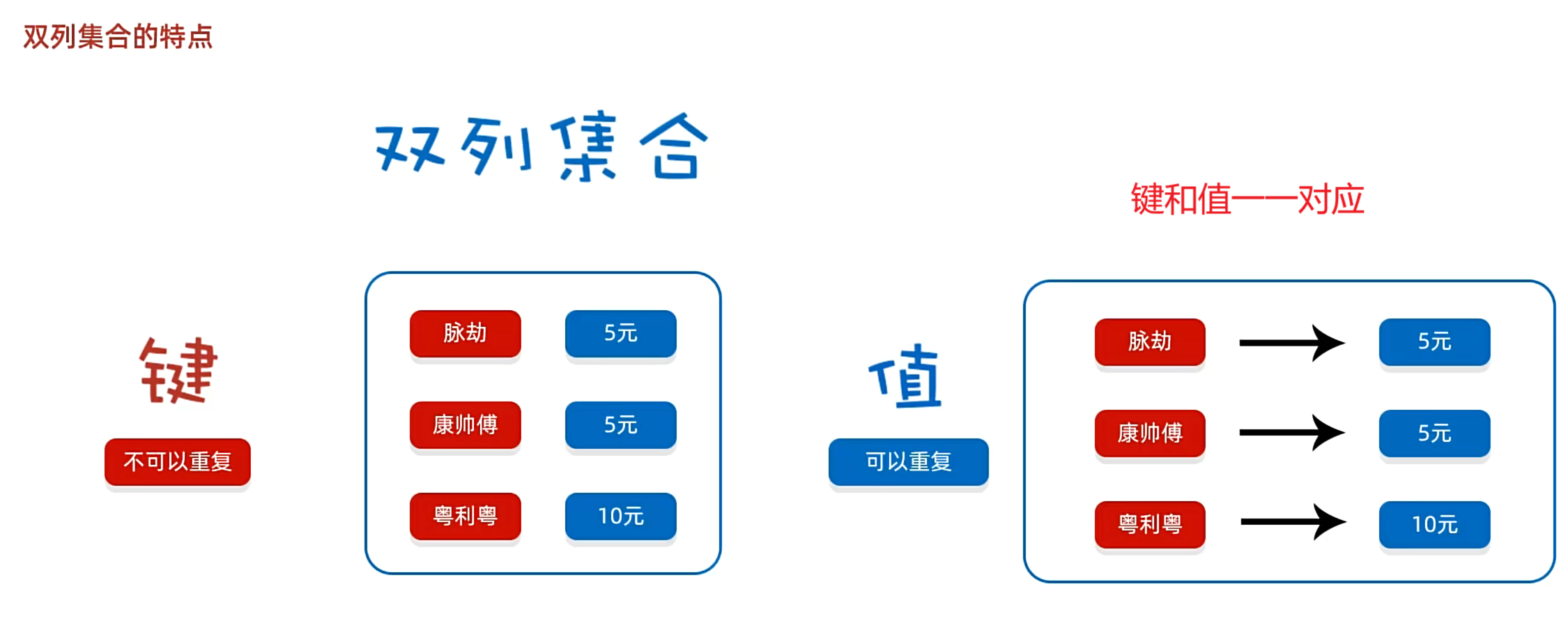
1. 双列集合的特点
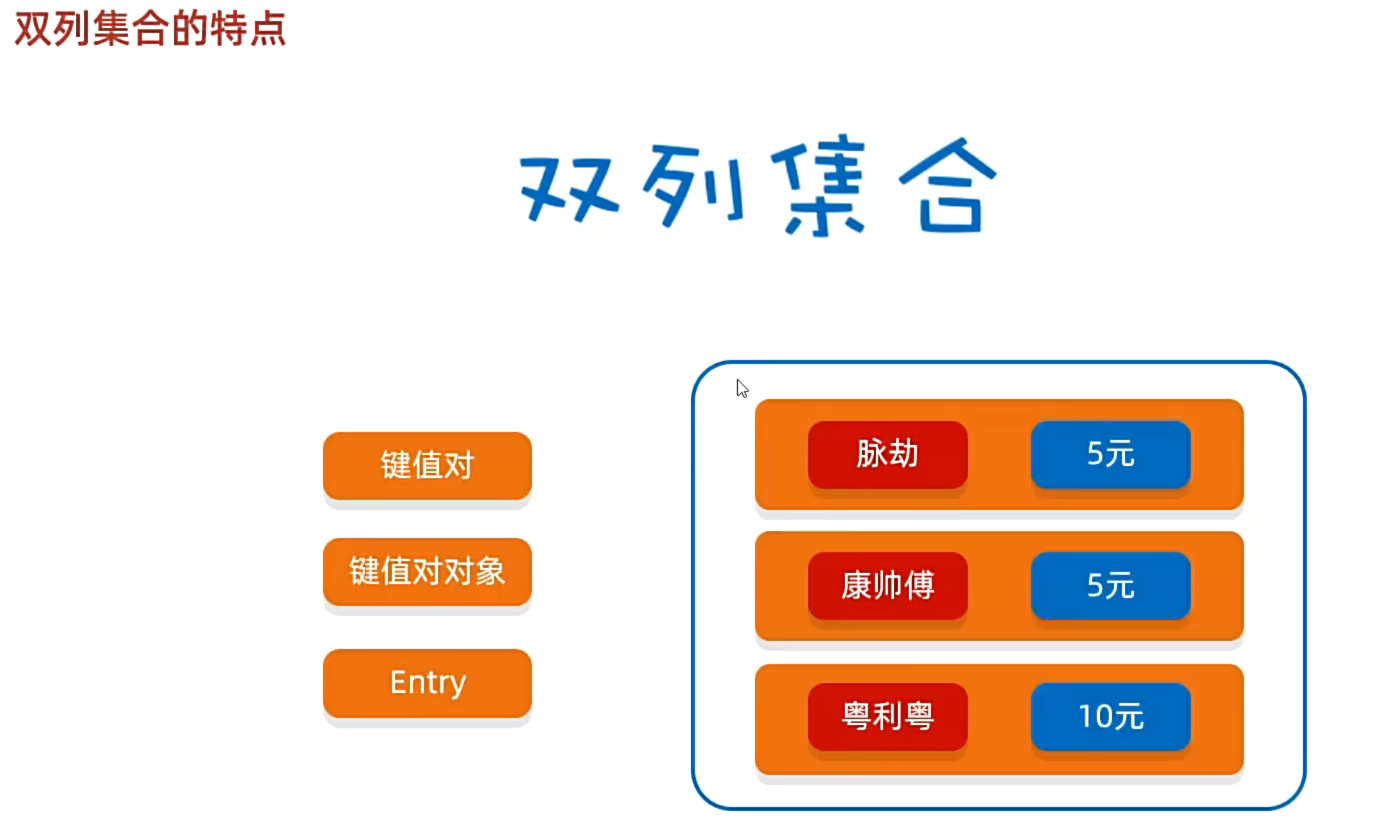
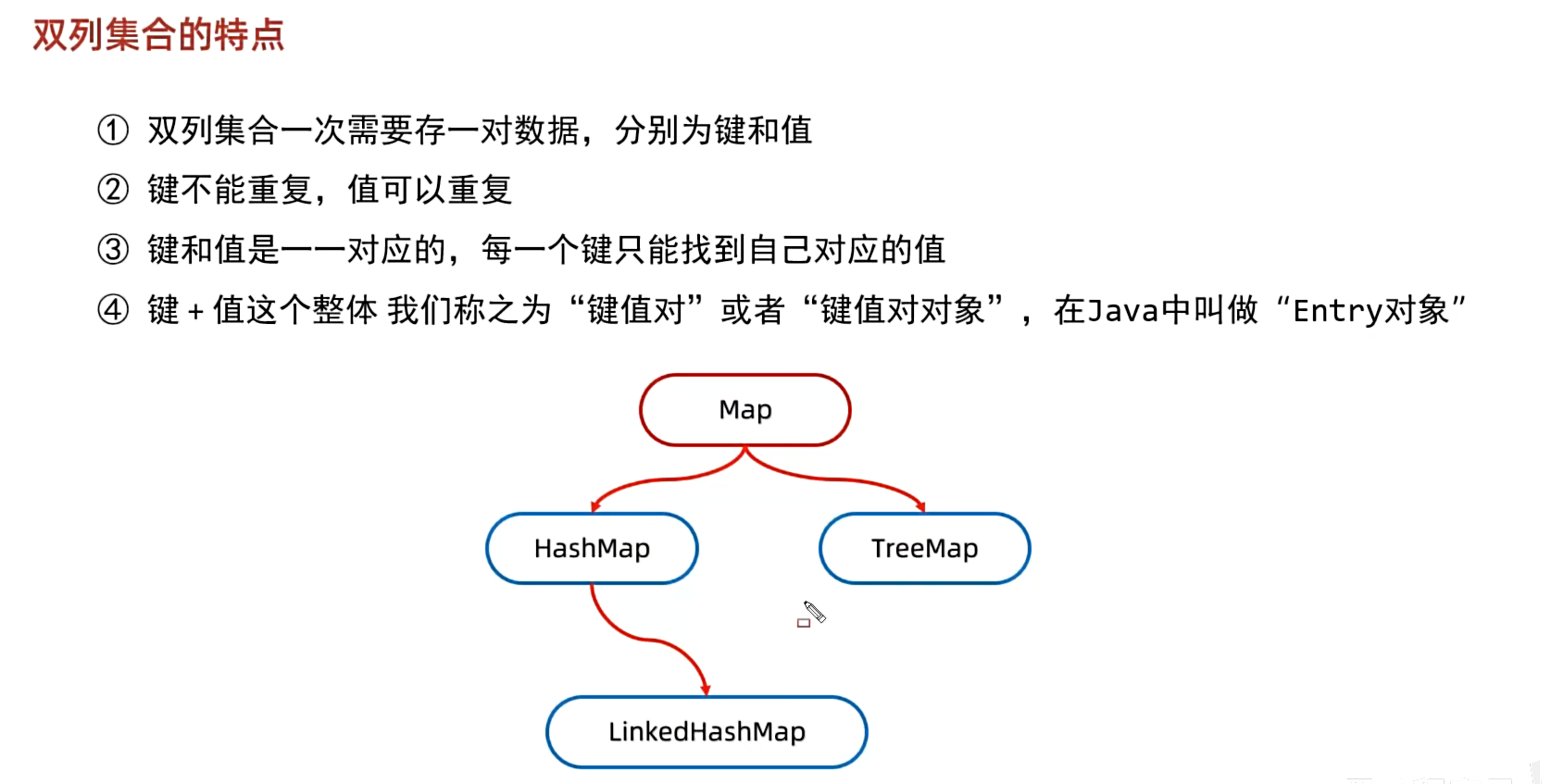
2. Map
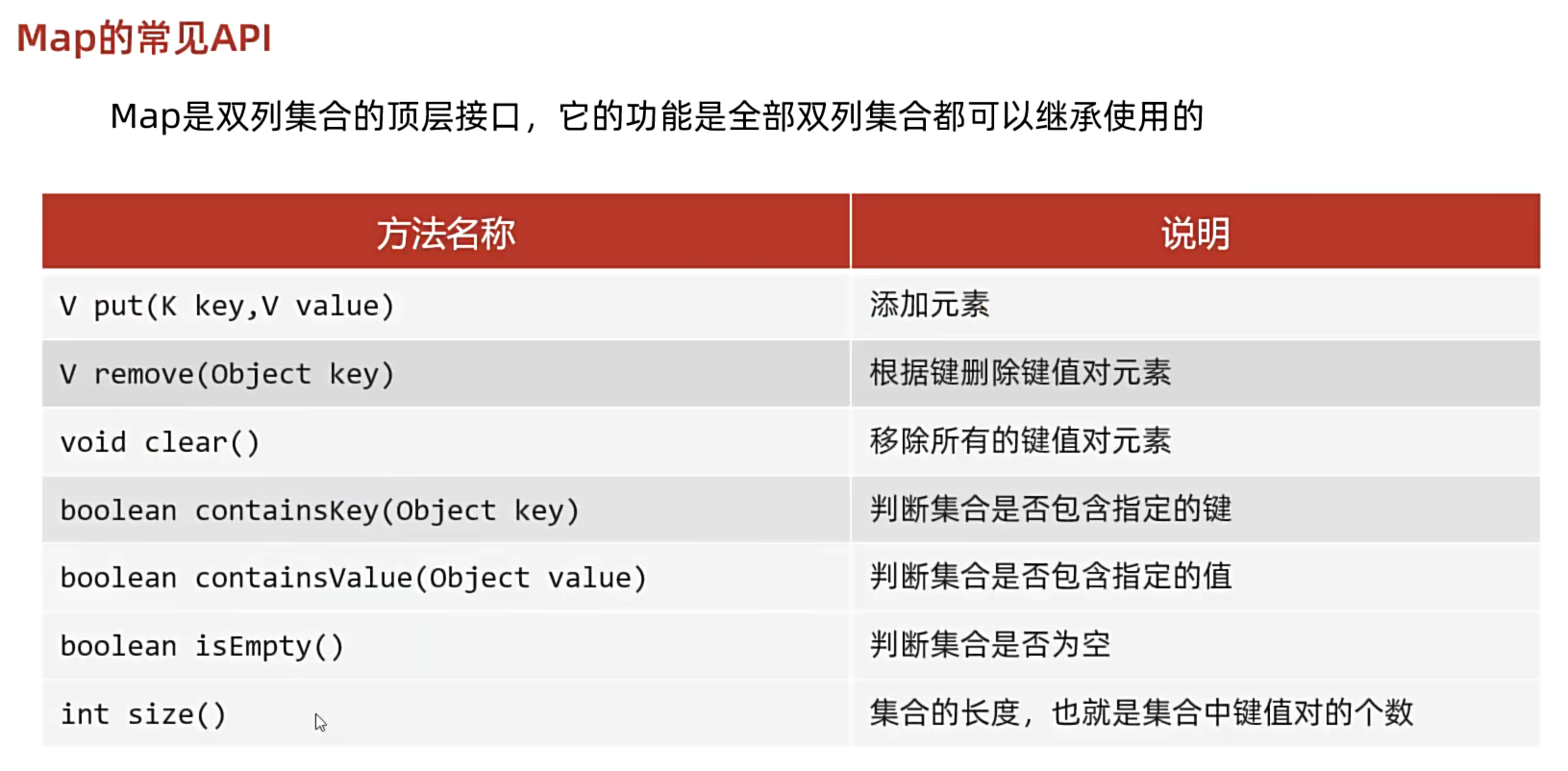
2.1 Map的常见 API
java
package pracitce2.daily.test1;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* V put(K key,V value) 添加元素
* remove(Object key) 根据键删除键值对元素
* void clear() 移除所有的键值对元素
* boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合是否包含指定的键
* boolean containsValue(Object value) 判断集合是否包含指定的值
* boolean isEmpty() 判断集合是否为空
* int size() 集合的长度,也就是集合中键值对的个数
* */
//1. 创建Map集合的对象
Map<String, String> m = new HashMap<>();
//2.添加元素
//put方法的细节:
//添加/覆盖
//在添加数据的时候,如果键不存在,那么直接把键值对对象添加到map集合当中,方法返回null
//在添加数据的时候,如果键存在,那么会把原有的键值对对象覆盖,会把被覆盖的值进行返回
String value1 = m.put("郭靖", "黄蓉");//null
System.out.println(value1);
m.put("韦小宝", "沐剑英");
m.put("尹志平", "小龙女");
String value2 = m.put("韦小宝", "双儿");
System.out.println(value2);//沐剑英
//删除
//String result = m.remove("郭靖");
//System.out.println(result);//黄蓉
//清空
//m.clear();//{}
//判断是否包含
//boolean keyResult = m.containsKey("郭靖");
//System.out.println(keyResult);//true
//boolean valueResult = m.containsValue("小明");
//System.out.println(valueResult);//false
//判断是否为空
boolean result = m.isEmpty();
System.out.println(result);//false
//集合长度
int size = m.size();
System.out.println(size);//3
//3.打印集合
System.out.println(m);//{韦小宝=双儿, 尹志平=小龙女, 郭靖=黄蓉}
}
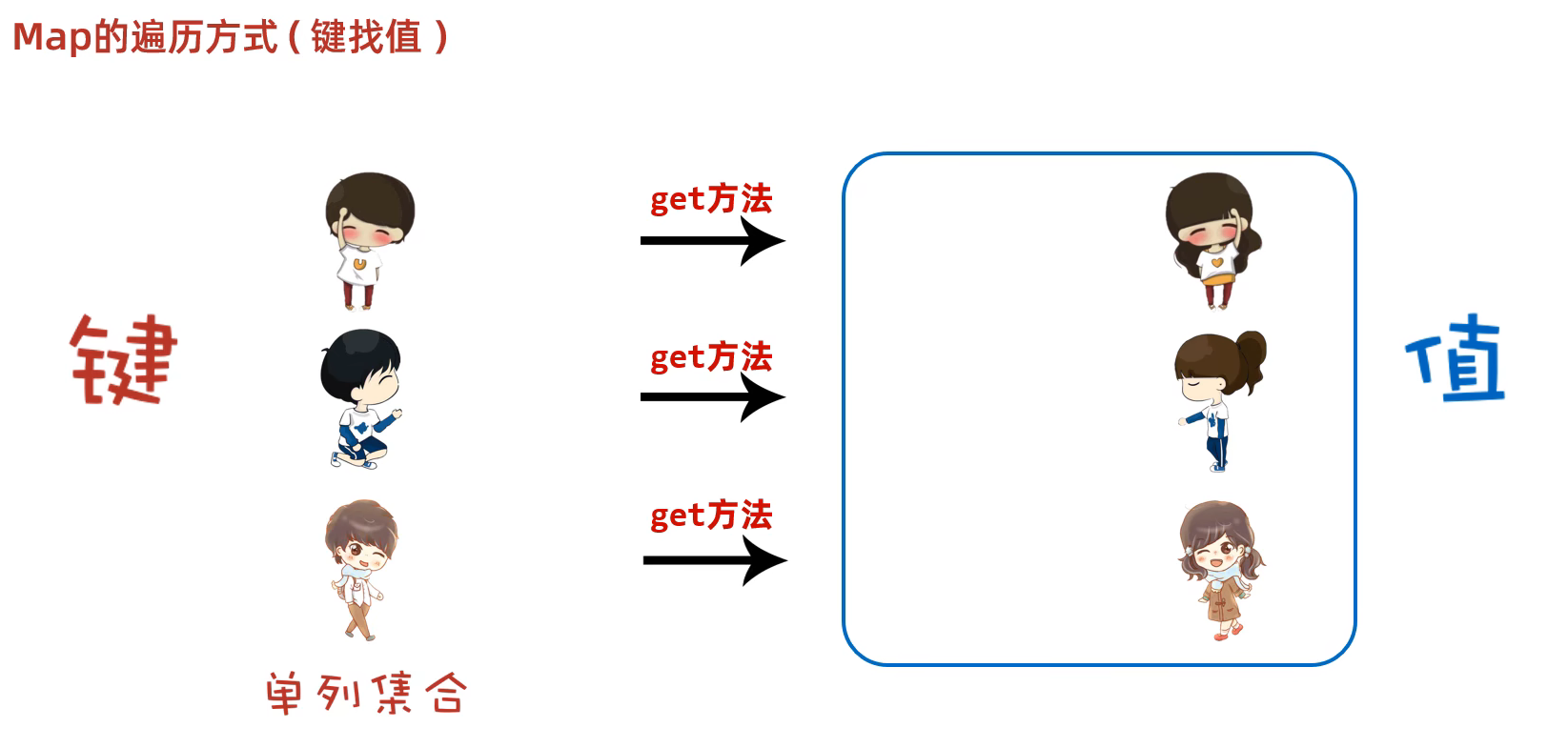
}2.2 Map 的遍历方式

键找值:
键不可以重复,值可以重复
java
package pracitce2.daily.test1;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Map集合的第一种遍历方式:键找值
//1.创建Mao集合的对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
//2.添加元素
map.put("郭靖", "黄蓉");
map.put("韦小宝", "沐剑英");
map.put("尹志平", "小龙女");
//3.通过键找值
//3.1 获取所有的键,把这些键放到一个单列集合当中
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
//3.2 遍历单列集合,得到每一个键
//增强for循环遍历
/*for (String key : keys) {
//System.out.println(key);
//3.3 利用ma集合中的键获取对应的值,用get方法
String values = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + values);
}*/
//迭代器遍历
/*Iterator<String> it = keys.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String key = it.next();
String values = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + values);
}*/
//lambda表达式遍历
keys.forEach(key -> System.out.println(key + " = " + map.get(key)));
}
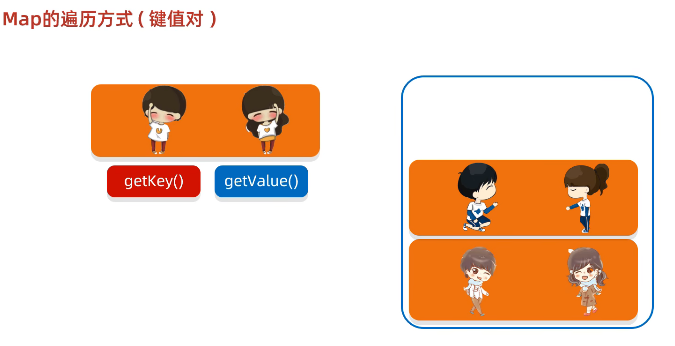
}键值对:
java
package pracitce2.daily.test1;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class MapDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Map集合的第二种遍历方式:键值对
//1.创建Map集合的对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
//2.添加元素
map.put("郭靖", "黄蓉");
map.put("韦小宝", "沐剑英");
map.put("尹志平", "小龙女");
//3.键值对
//3.1 通过一个方法获取所有的键值对对象,返回一个Set集合
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> entries = map.entrySet();
//3.2 遍历entries这个集合,得到里面每一个键值对对象
//增强for循环遍历
/*for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : entries) {
//System.out.println(entry);
//3.3 利用entry调用get方法获取键和值
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}*/
//迭代器遍历
/*Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = entries.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry<String, String> next = it.next();
String key = next.getKey();
String value = next.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}*/
//lambda表达式遍历
entries.forEach(entry -> System.out.println(entry.getKey() + " = " + entry.getValue()));
}
}Lambda表达式:

java
package pracitce2.daily.test1;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.function.BiConsumer;
public class MapDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Map集合的第三种遍历方式:Lambda表达式
//1.创建Map集合的对象
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
//2.添加元素
map.put("1001", "张三");
map.put("1002", "李四");
map.put("1003", "王五");
//3.利用lambda表达式进行遍历
//匿名内部类
/*map.forEach(new BiConsumer<String, String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String key, String value) {
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
});*/
//将匿名内部类改写为lambda的方式
map.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + " = " + value));
}
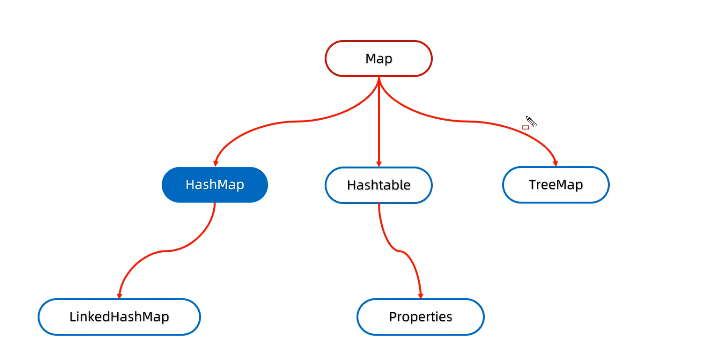
}二. HashMap

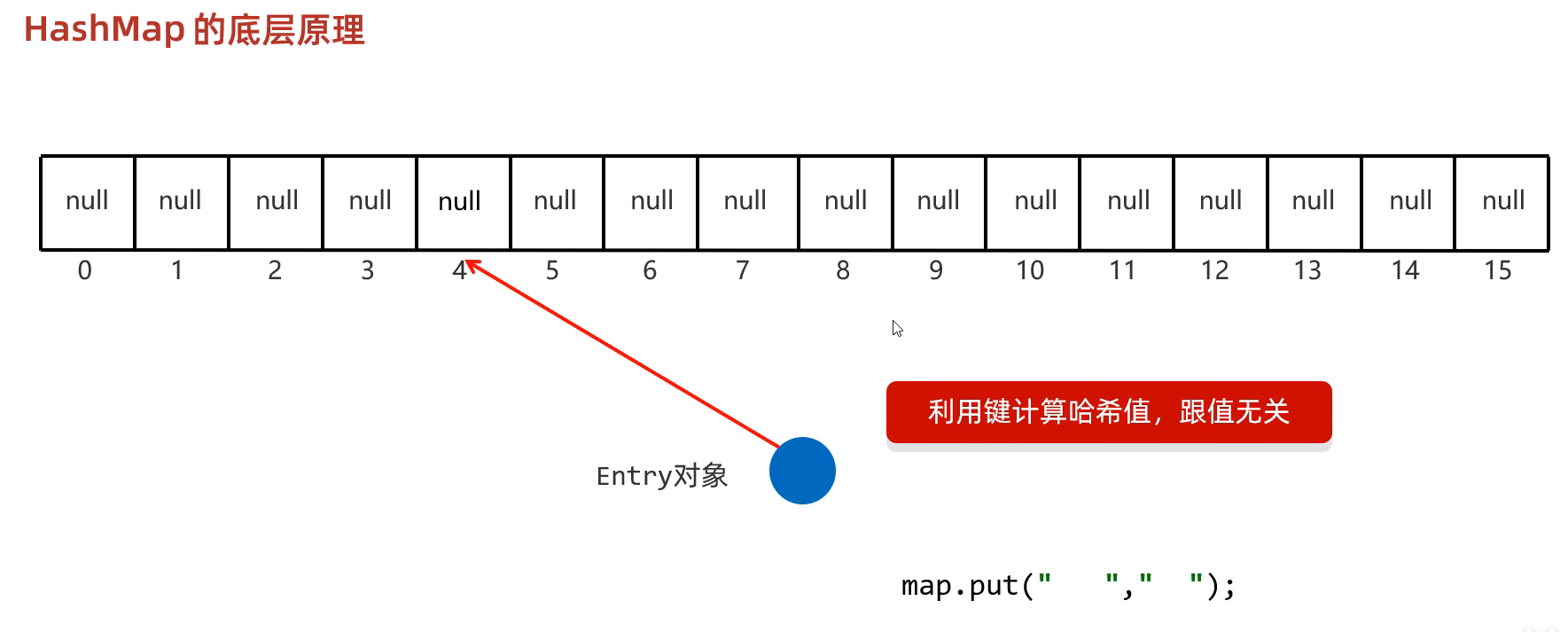
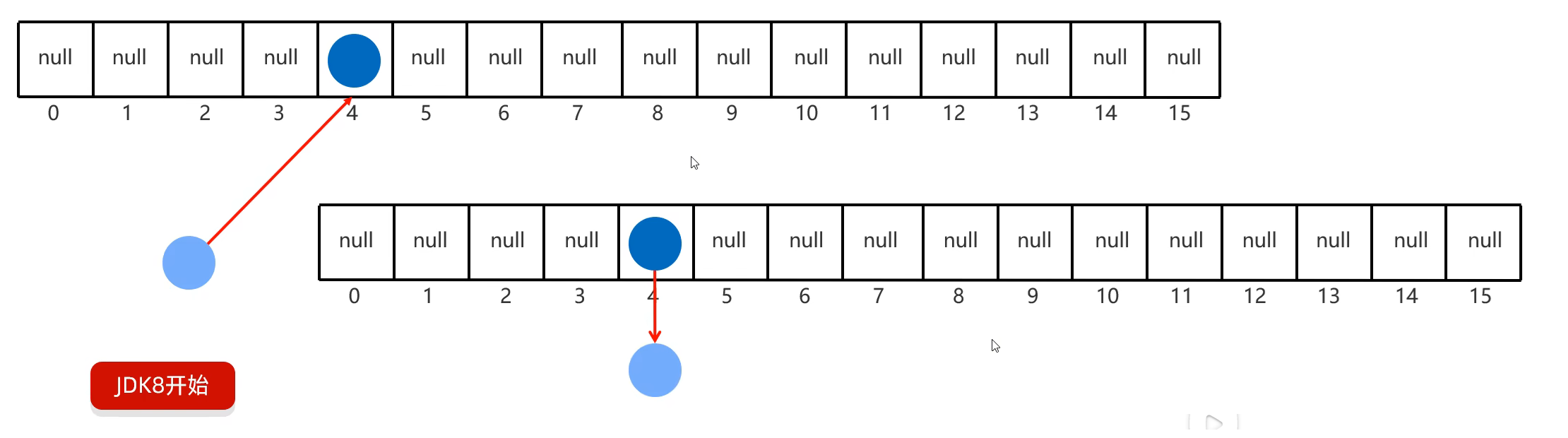
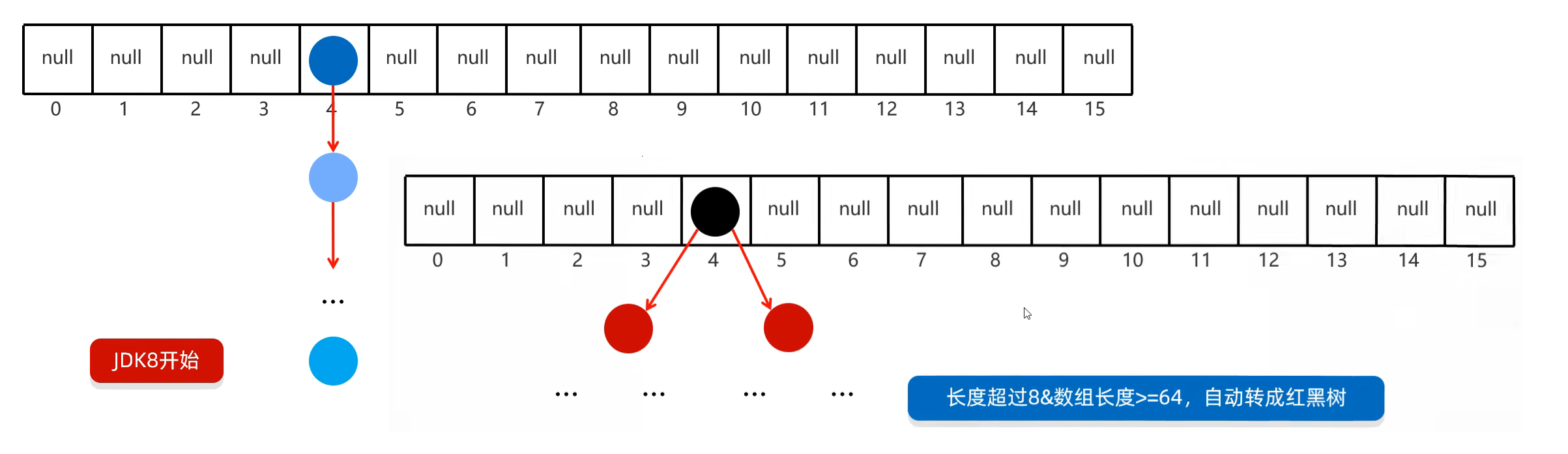

练习一:

java
package pracitce2.daily.test1;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class HashMapDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//核心点;
//HashMapde的键位置如果存储的是自定义对象,需要重写hashCode和equals方法
//1.创建HashMap对象
HashMap<Student, String> hm = new HashMap<>();
//2.创建三个学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan", 23);
Student s2 = new Student("lisi", 24);
Student s3 = new Student("wangwu", 25);
Student s4 = new Student("wangwu", 25);
//3.添加元素
hm.put(s1, "北京");
hm.put(s2, "上海");
hm.put(s3, "广州");
hm.put(s4, "山东");
//4.遍历集合
//键找值
Set<Student> keys = hm.keySet();
for (Student key : keys) {
String value = hm.get(key);
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
//键值对
Set<Map.Entry<Student, String>> entries = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<Student, String> entry : entries) {
Student key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key + " = " + value);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
//Lambda表达式
hm.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.println(key + " = " + value));
}
}练习二:
java
package pracitce2.daily.test1;
import java.util.*;
public class HashMapDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.先让同学们投票
//定义一个数组,存储4个景点
String[] arr = {"A", "B", "C", "D"};
//利用随机数模拟80个同学的投票,并把投票结果存储起来
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 80; i++) {
int index = r.nextInt(arr.length);
list.add(arr[index]);
}
//System.out.println(list);
//2.利用集合进行统计
//如果要统计的东西比较多,不方便使用计数器思想,就可以定义map集合,利用集合进行统计
HashMap<String, Integer> hm = new HashMap<>();
for (String name : list) {
//判断当前景点在map集合中是否存在
if (hm.containsKey(name)) {
//存在
//获取当前景点已经被投票的次数
int count = hm.get(name);
//次数加1,表示当前景点又被投了一次
count++;
//把新的次数再次添加到集合中
hm.put(name, count);
} else {
//不存在
//添加至map集合
hm.put(name, 1);
}
}
System.out.println(hm);
//3.求最大值
//遍历集合
int max = 0;
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = hm.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
int count = entry.getValue();
//max = count > max ? count : max;
if (count > max) {
max = count;
}
}
System.out.println(max);
//4.判断哪个景点的次数跟最大值一样,如果一样,就打印
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : entries) {
int count = entry.getValue();
//max = count > max ? count : max;
if (count == max) {
System.out.println(entry.getKey());
}
}
}
}三. LinkedHashMap
java
package pracitce2.daily.test1;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class LinkedHashMapDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建集合
LinkedHashMap<String, Integer> lhm = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//2.添加元素
lhm.put("a", 234);
lhm.put("b", 123);
lhm.put("a", 456);
lhm.put("d", 789);
//3.打印集合
System.out.println(lhm);//{a=456, b=123, d=789}
}
}四. TreeMap

练习:

需求1:
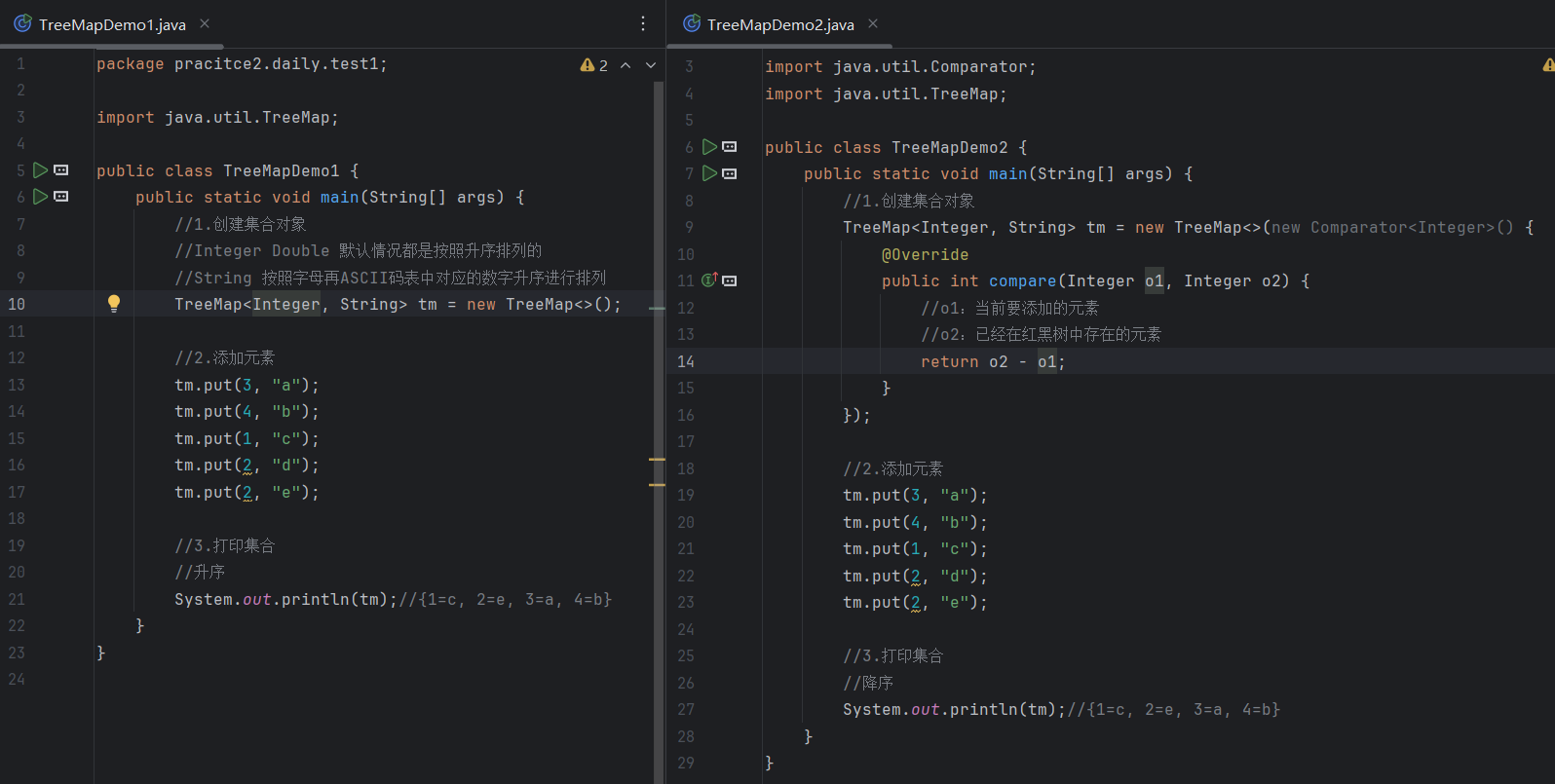
需求2:
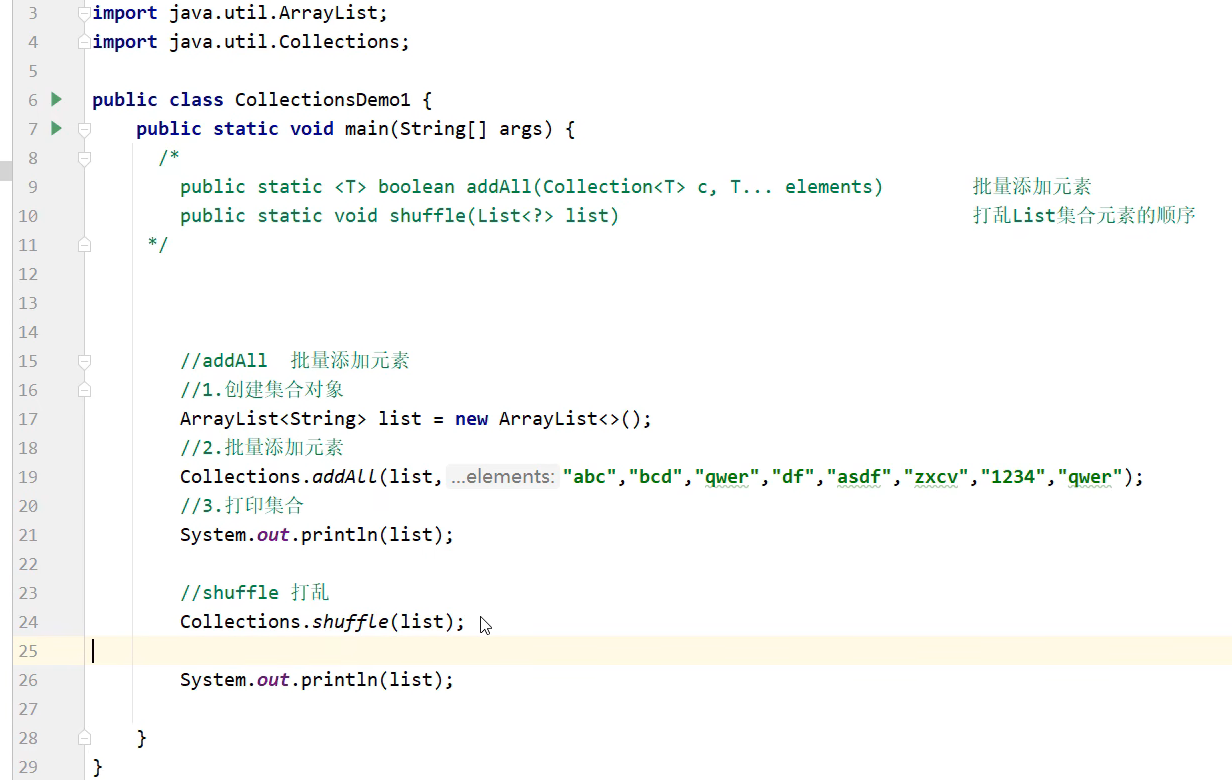
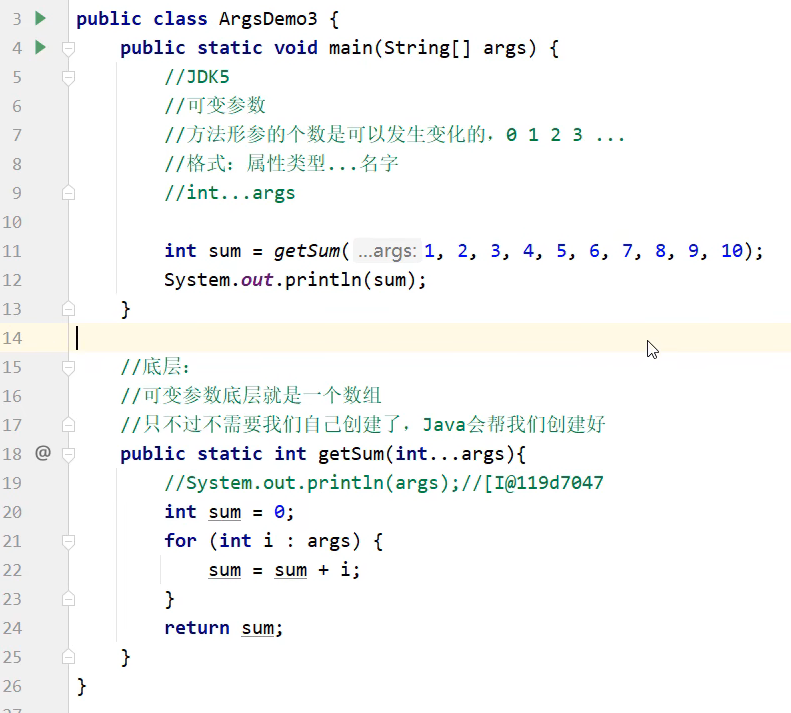
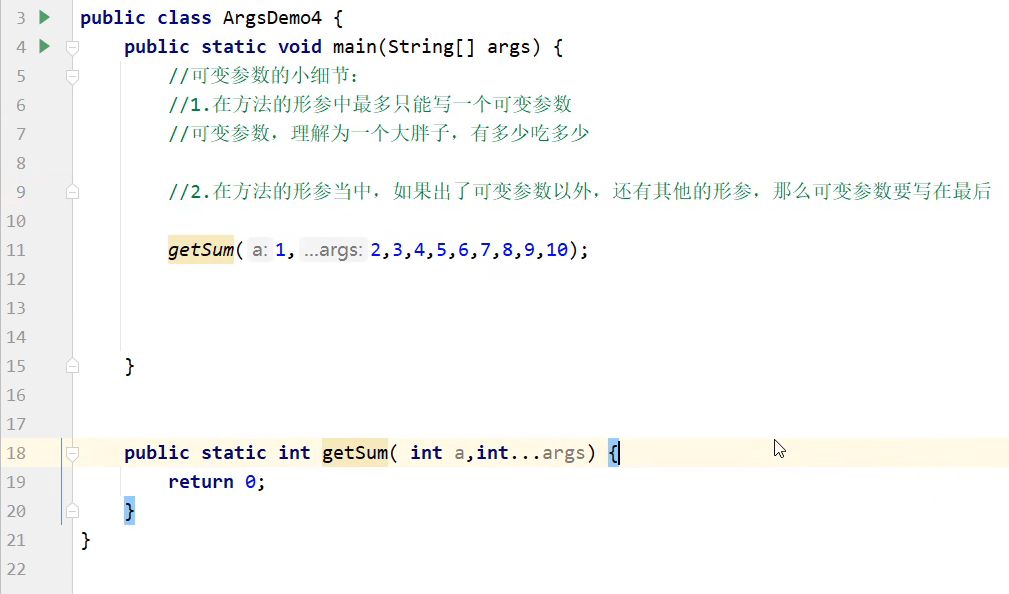
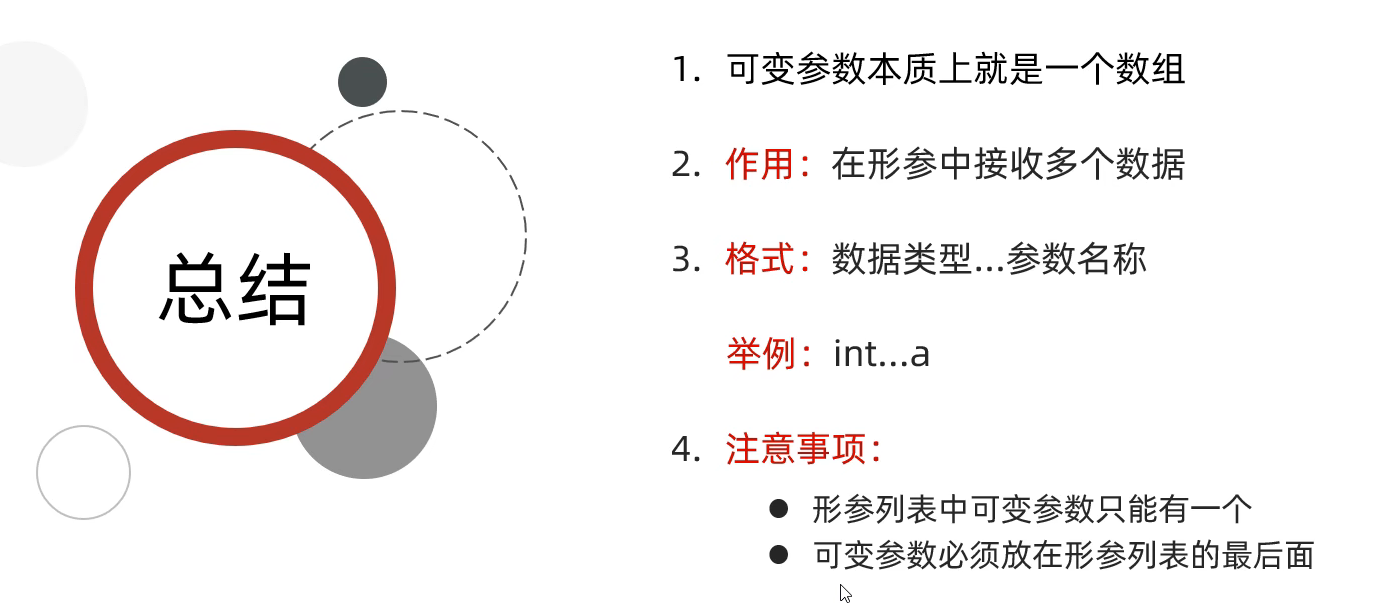
五. 可变参数
六. 集合工具类 Collections