在参考文献1中下载AspNetCoreRateLimit源码,将测试项目的依赖项从Nuget包调整为项目依赖。
测试项目启动时启用的中间件为IpRateLimitMiddleware,其继承自: RateLimitMiddleware <IpRateLimitProcessor>,使用postman调用AddIpRule函数添加特定IP的限流规则后,再用postman调用GetString函数时,在RateLimitMiddleware.Invoke函数开头下断点,如下所示:
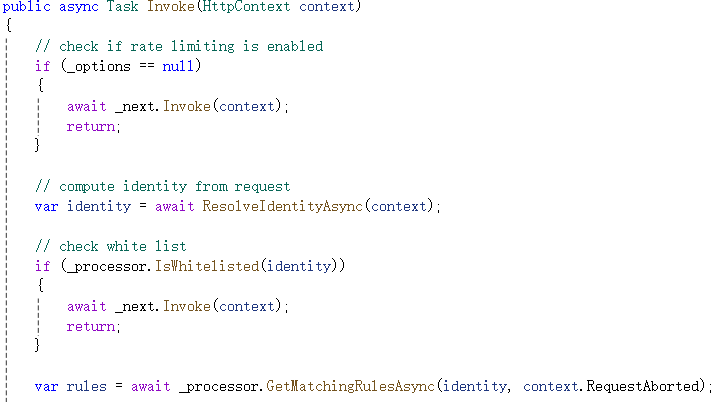
ResolveIdentityAsync函数从请求上下文中获取客户端ip或客户端id、请求方法、请求路径等信息用于后面的规则判断。

_processor.GetMatchingRulesAsync函数获取与客户端信息匹配的限流规则,其函数内部如下所示。GetMatchingRulesAsync函数开头查找与客户端IP相同的特定限流规则集合,并将查找结果传递给GetMatchingRules函数进一步匹配规则。

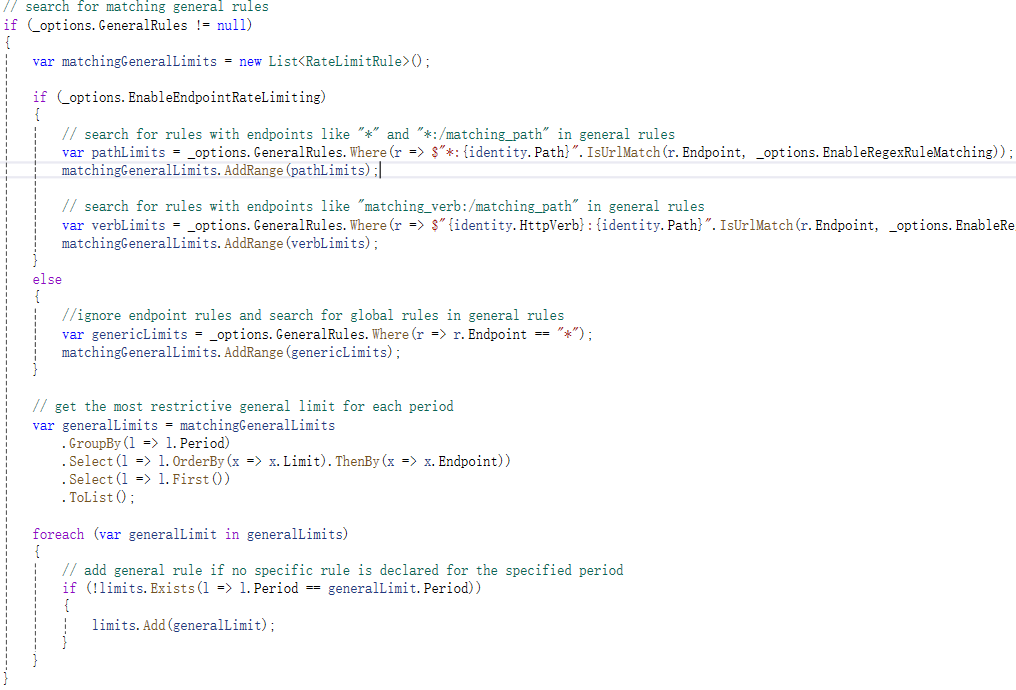
GetMatchingRules函数开头根据通用规则中的EnableEndpointRateLimiting属性,如果为true,则对特定规则中的endpoint值进行精确匹配,如果为false,则仅查找endpoint值为*的规则。上一篇文章中的测试代码,EnableEndpointRateLimiting值为false,但针对本机的特定限流规则中endpoint值为*:/RateLimit/GetString,因此在这一步就将特定限流规则跳过了。

匹配完特定规则后,还会在通用规则中查找endpoint满足当前客户端请求路径和方法的规则,如果能找到且特定规则中没有相同时间周期的规则,则将通用规则也添加到结果集合中。因此可以看出特定规则的优先级高于通用规则。
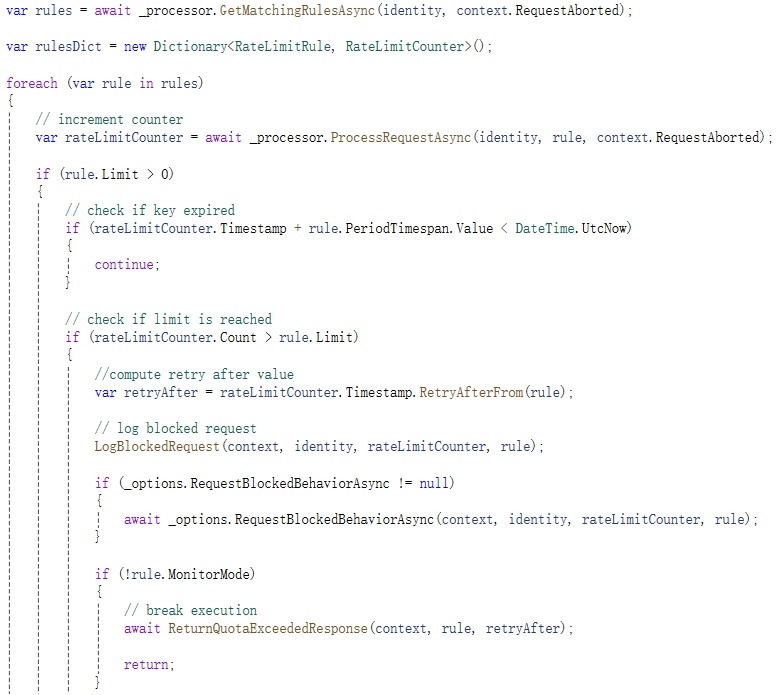
找到匹配的限流规则后,则逐规则判断当前请求是否满足规则要求,未超过规则要求的数量则放行,否则返回超过限流此时的错误码及错误信息。
通过上述源码分析,可以采用两种方式生效上一篇文章中的特定规则:
1)将通用规则中的EnableEndpointRateLimiting属性设置为true,如下面代码所示:
csharp
public async Task AddIpRule()
{
if (_options.GeneralRules == null)
{
_options.GeneralRules = new List<RateLimitRule>();
}
_options.EnableEndpointRateLimiting = true;
var policy = await _ipPolicyStore.GetAsync(_options.IpPolicyPrefix, HttpContext.RequestAborted);
if (policy == null)
{
await _ipPolicyStore.SeedAsync();
policy = _ipPolicyStore.GetAsync(_options.IpPolicyPrefix).Result;
}
policy.IpRules.AddRange(new IpRateLimitPolicy
{
Ip = "::1",
Rules = new List<RateLimitRule>(new RateLimitRule[] {
new RateLimitRule {
Endpoint = "get:/RateLimit/GetString",
Limit = 5,
Period = "30s" },
})
},
new IpRateLimitPolicy
{
Ip = "127.0.0.1",
Rules = new List<RateLimitRule>(new RateLimitRule[] {
new RateLimitRule {
Endpoint = "*:/RateLimit/GetString",
Limit = 5,
Period = "30s" },
})
});
await _ipPolicyStore.SetAsync(_options.IpPolicyPrefix, policy, cancellationToken: HttpContext.RequestAborted).ConfigureAwait(false);
}2)将本地IP规则中的endpoint设置为*;
csharp
public async Task AddIpRule()
{
var policy = await _ipPolicyStore.GetAsync(_options.IpPolicyPrefix, HttpContext.RequestAborted);
if (policy == null)
{
await _ipPolicyStore.SeedAsync();
policy = _ipPolicyStore.GetAsync(_options.IpPolicyPrefix).Result;
}
policy.IpRules.AddRange(new IpRateLimitPolicy
{
Ip = "::1",
Rules = new List<RateLimitRule>(new RateLimitRule[] {
new RateLimitRule {
Endpoint = "*",
Limit = 5,
Period = "30s" },
})
},
new IpRateLimitPolicy
{
Ip = "127.0.0.1",
Rules = new List<RateLimitRule>(new RateLimitRule[] {
new RateLimitRule {
Endpoint = "*:/RateLimit/GetString",
Limit = 5,
Period = "30s" },
})
});
await _ipPolicyStore.SetAsync(_options.IpPolicyPrefix, policy, cancellationToken: HttpContext.RequestAborted).ConfigureAwait(false);
}经过代码验证,上述两种方式均可生效特定IP限流规则。
参考文献:
1\]https://github.com/stefanprodan/AspNetCoreRateLimit \[2\]https://github.com/stefanprodan/AspNetCoreRateLimit/wiki/IpRateLimitMiddleware