进程间通信分类
管道
System V进程间通信
POSIX进程间通信管道
匿名管道
命名管道System V IPC
System V 消息队列
System V 共享内存
System V 信号量POSIX IPC
消息队列
共享内存
信号量
互斥量
条件变量
读写锁管道
是Unix中最古老的进程间通信的形式。
把从一个进程连接到另一个进程的一个数据流称为一个"管道"。
匿名管道
#include <unistd.h>
功能:创建一个匿名管道
int pipe(int fd[2]);
参数:
fd:文件描述符数组,其中fd[0]表示读端,fd[1]表示写端。
返回值:成功返回0,失败返回-1,错误码被设置。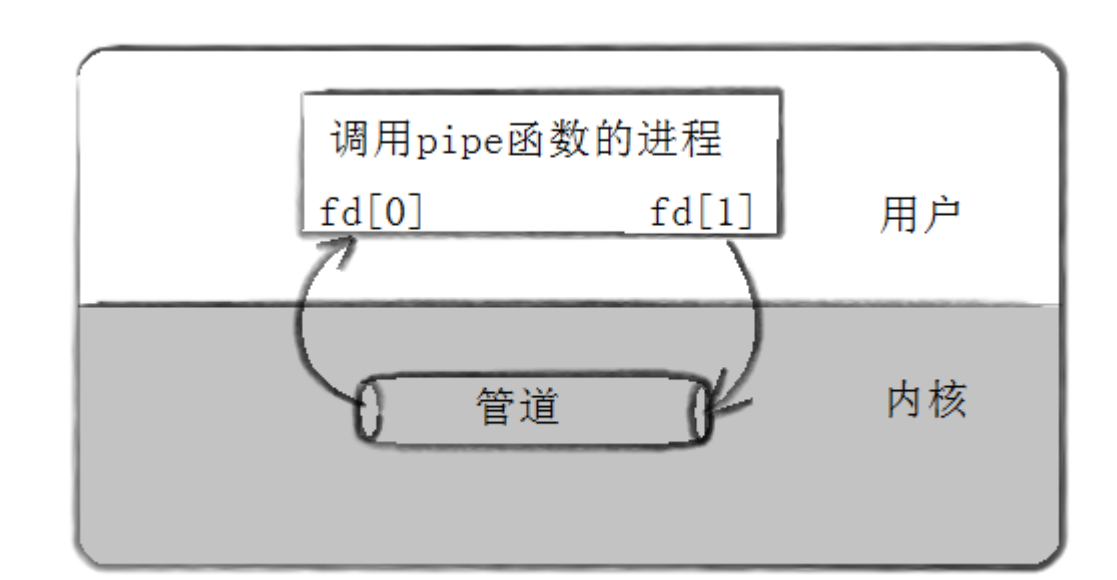
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#define N 2
#define NUM 1024
using namespace std;
void Writer(int wfd)
{
string s="hello,I am a child";
pid_t self=getpid();
int number=0;
char buffer[NUM];
while(true)
{
sleep(1);
buffer[0]=0;//字符串清空
snprintf(buffer,sizeof(buffer),"%s-%d-%d",s.c_str(),self,number++);
cout<<buffer<<endl;
//发送/写入给父进程
write(wfd,buffer,strlen(buffer));
}
}
void Reader(int rfd)
{
char buffer[NUM];
while(true)
{
buffer[0]=0;
ssize_t n=read(rfd,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
if(n>0)
{
buffer[n]=0;
cout<<"father get a message["<<getpid()<<"]#"<<buffer<<endl;
}
else if(n==0)
{
cout<<"father process read file done!"<<endl;
break;
}
else break;
}
}
int main()
{
int pipefd[N]={0};
int n=pipe(pipefd);
if(n<0) return 1;
pid_t id=fork();
if(id<0)
{
return 2;
}
else if(id==0)
{
//child
close(pipefd[0]);//关闭读
//IPC code
Writer(pipefd[1]);
close(pipefd[1]);
exit(0);
}
//father
close(pipefd[1]);
Reader(pipefd[0]);
pid_t rid=waitpid(id,nullptr,0);
if(rid<0)
return 3;
close(pipefd[0]);
sleep(5);
return 0;
}
注意:
管道就是文件(内存级文件)
特点:
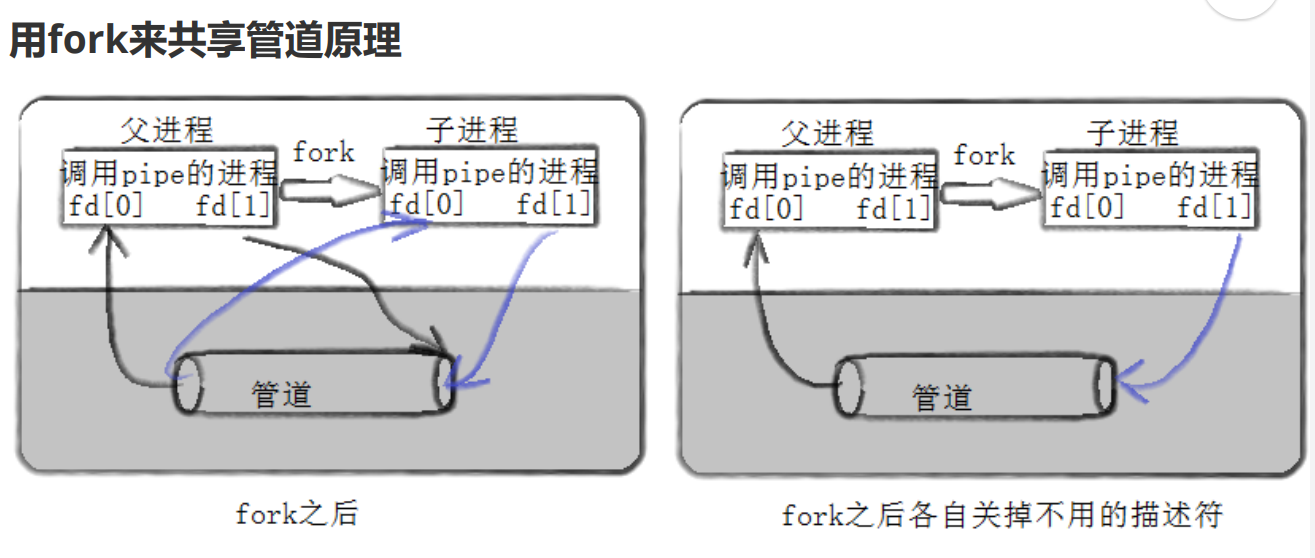
1.用管道通信时,通信的进程间需要有血缘关系,常用于父子。
2.单向通行。
3.父子进程是会进程协同的。同步与互斥------保护管道文件的数据安全。
4.管道是面向字节流的。
5.管道是基于文件的。而文件的生命周期是随进程的。
管道中的四种情况:
1.读写端正常,管道如果为空,读端就要阻塞。
2.读写端正常,管道如果被写满,写端就要阻塞。
3.读端正常,写端关闭,读端就会读到0,表示读到了管道文件的结尾,不会被阻塞。
4.写端正常写入,读端关闭了,操作系统要通过信号杀掉正在写入的进程。
命名管道
可用于毫不相关的进程间通信。
创建一个命名管道:
mkfifo filename也可以从程序里创建:
int mkfifo(const char* filename,mode_t mode);
int n=mkfifo(FIFO_FILE,0664);匿名管道和命名管道的区别:
1.匿名管道由pipe函数创建并打开。
2.命名管道由mkfifo函数创建,打开用open
3.FIFO和pipe唯一区别是它们创建和打开的方式不同,一旦这些过程完成后,它们具有相同的语义。例子:
common.hpp
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cerrno>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define FIFO_FILE "./myfifo"
#define MODE 0664
enum
{
FIFO_CREATE_ERR = 1,
FIFO_DELETE_ERR,
FIFO_OPEN_ERR
};
class Init
{
public:
Init()
{
//创建管道
int n=mkfifo(FIFO_FILE,MODE);
if(n==-1)
{
perror("mkfifo");
exit(FIFO_CREATE_ERR);
}
}
~Init()
{
int m=unlink(FIFO_FILE);
if(m==-1)
{
perror("unlink");
exit(FIFO_DELETE_ERR);
}
}
};
cpp
#include "common.hpp"
#include "log.hpp"
using namespace std;
// 管理管道文件
int main()
{
Init init;
Log log;
log.Enable(Onefile);
// 打开管道
int fd = open(FIFO_FILE, O_RDONLY); // 等待写入方打开后自己才会打开并向后执行
// 所以open可能会阻塞。
if (fd < 0)
{
log(Fatal, "error string:%s,error code:%d", strerror(errno), errno);
exit(FIFO_OPEN_ERR);
}
while(true)
{
char buffer[1024]={0};
int x=read(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
if(x>0)
{
buffer[x]=0;
cout<<"client say# "<<buffer<<endl;
}
else if(x==0)
{
log(Debug,"client quit,me too!,error string:%s,errno code:%d",strerror(errno),errno);
break;
}
else break;
}
close(fd);//关闭管道
return 0;
}
cpp
#include "common.hpp"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int fd=open(FIFO_FILE,O_WRONLY);
if(fd<0)
{
perror("open");
exit(FIFO_OPEN_ERR);
}
cout<<"client open file done"<<endl;
string line;
while(true)
{
cout<<"Please Enter@ ";
getline(cin,line);
write(fd,line.c_str(),line.size());
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}log.hpp
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define SIZE 1024
#define Info 0
#define Debug 1
#define Warning 2
#define Error 3
#define Fatal 4
#define Screen 1
#define Onefile 2
#define Classfile 3
#define LogFile "log.txt"
class Log
{
public:
Log()
{
printMethod = Screen;
path = "./log/";
}
void Enable(int method)
{
printMethod = method;
}
std::string levelToString(int level)
{
switch (level)
{
case Info:
return "Info";
case Debug:
return "Debug";
case Warning:
return "Warning";
case Error:
return "Error";
case Fatal:
return "Fatal";
default:
return "None";
}
}
void printLog(int level, const std::string &logtxt)
{
switch (printMethod)
{
case Screen:
std::cout << logtxt << std::endl;
break;
case Onefile:
printOneFile(LogFile, logtxt);
break;
case Classfile:
printClassFile(level, logtxt);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
void printOneFile(const std::string& logname,const std::string& logtxt)
{
std::string _logname=path+logname;
int fd=open(_logname.c_str(),O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_APPEND,0666);
if(fd<0) return;
write(fd,logtxt.c_str(),logtxt.size());
close(fd);
}
void printClassFile(int level,const std::string& logtxt)
{
std::string filename=LogFile;
filename+=".";
filename+=levelToString(level);
printOneFile(filename,logtxt);
}
~Log()
{}
void operator()(int level,const char* format,...)
{
time_t t=time(nullptr);
struct tm* ctime=localtime(&t);
char leftbuffer[SIZE];
snprintf(leftbuffer,sizeof(leftbuffer),"[%s][%d-%d-%d %d:%d:%d]",levelToString(level).c_str(),
ctime->tm_year+1900,ctime->tm_mon+1,ctime->tm_mday,ctime->tm_hour,
ctime->tm_min,ctime->tm_sec);
va_list s;
va_start(s,format);
char rightbuffer[SIZE];
vsnprintf(rightbuffer,sizeof(rightbuffer),format,s);
va_end(s);
//格式:默认部分+自定义部分
char logtxt[SIZE*2];
snprintf(logtxt,sizeof(logtxt),"%s %s\n",leftbuffer,rightbuffer);
printLog(level,logtxt);
}
private:
int printMethod;
std::string path;
};