- 矩形 (Rect):这是所有 UI 组件(按钮、卡片、背景)的基础。
- 文本 (Text):这是信息展示的核心。
相较于圆,文本的难点在于"包围盒计算"(为了支持点击检测),因为 Canvas 只有画图命令,没有直接告诉我们字有多高。
我们将分两步实现。
1. 实现矩形 (src/graphic/shape/Rect.ts)
矩形的逻辑比较标准,重点是实现 buildPath 和 containLocal。
typescript
// src/graphic/shape/Rect.ts
import { Displayable, DisplayableProps } from '../Displayable';
export interface RectShape {
x?: number;
y?: number;
width?: number;
height?: number;
r?: number; // 圆角半径 (简单起见,暂只支持统一圆角)
}
interface RectProps extends DisplayableProps {
shape?: RectShape;
}
export class Rect extends Displayable {
shape: Required<RectShape>; // 确保内部使用时都有值
constructor(opts?: RectProps) {
super(opts);
this.shape = {
x: 0, y: 0, width: 0, height: 0, r: 0,
...opts?.shape
};
}
buildPath(ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D) {
const shape = this.shape;
const x = shape.x;
const y = shape.y;
const width = shape.width;
const height = shape.height;
const r = shape.r;
if (!r) {
// 普通矩形
ctx.rect(x, y, width, height);
} else {
// 圆角矩形 (使用 arcTo 或者 roundRect)
// 这里使用通用的 arcTo 模拟
ctx.moveTo(x + r, y);
ctx.lineTo(x + width - r, y);
ctx.arcTo(x + width, y, x + width, y + r, r);
ctx.lineTo(x + width, y + height - r);
ctx.arcTo(x + width, y + height, x + width - r, y + height, r);
ctx.lineTo(x + r, y + height);
ctx.arcTo(x, y + height, x, y + height - r, r);
ctx.lineTo(x, y + r);
ctx.arcTo(x, y, x + r, y, r);
ctx.closePath();
}
}
/**
* 矩形的包含检测
*/
containLocal(x: number, y: number): boolean {
const shape = this.shape;
// 简单矩形检测
// 如果要做圆角检测比较复杂,通常这里简化为矩形包围盒
return x >= shape.x && x <= shape.x + shape.width &&
y >= shape.y && y <= shape.y + shape.height;
}
}2. 实现文本 (src/graphic/Text.ts)
文本比较特殊。
- 绘制方式不同 :它不用
beginPath/fill流程,而是直接fillText。 - 样式属性多:字号、字体、对齐方式。
- 碰撞检测难 :需要用
measureText算宽度,用字号估算高度。
我们需要先在 Displayable 或 Style 中补充文本相关的样式定义。
更新 src/graphic/Style.ts:
typescript
export interface CommonStyle {
// ... 原有属性 ...
// 文本相关
text?: string;
fontSize?: number;
fontFamily?: string;
fontWeight?: string; // 'bold', 'normal'
// 对齐
textAlign?: CanvasTextAlign; // 'left' | 'right' | 'center' | 'start' | 'end'
textBaseline?: CanvasTextBaseline; // 'top' | 'middle' | 'bottom' ...
}创建 src/graphic/Text.ts:
注意:为了能在 brush 中使用特殊的绘制逻辑,我们这里覆盖 brush 方法,或者复用基类逻辑但重写 buildPath 实际上不太合适(因为 fillText 不是 path)。
ZRender 的做法是 Text 也是 Displayable,但绘制逻辑独立。为了 MiniRender 架构简单,我们重写 brush。
typescript
// src/graphic/Text.ts
import { Displayable, DisplayableProps } from './Displayable';
// 默认字体
const DEFAULT_FONT_FAMILY = 'sans-serif';
export class Text extends Displayable {
constructor(opts?: DisplayableProps) {
super(opts);
}
/**
* 重写 brush,因为文本不是 Path
*/
brush(ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D) {
const style = this.style;
if (!style.text) return;
ctx.save();
// 1. 设置常规样式
if (style.fill) ctx.fillStyle = style.fill;
if (style.stroke) ctx.strokeStyle = style.stroke;
if (style.opacity != null) ctx.globalAlpha = style.opacity;
// 2. 设置字体样式
const fontSize = style.fontSize || 12;
const fontFamily = style.fontFamily || DEFAULT_FONT_FAMILY;
const fontWeight = style.fontWeight || '';
ctx.font = `${fontWeight} ${fontSize}px ${fontFamily}`.trim();
ctx.textAlign = style.textAlign || 'left';
ctx.textBaseline = style.textBaseline || 'alphabetic';
// 3. 应用变换
const m = this.globalTransform;
ctx.setTransform(m[0], m[1], m[2], m[3], m[4], m[5]);
// 4. 绘制文本
// 这里的 0, 0 是相对于 Text 元素自身的原点
if (style.stroke) ctx.strokeText(style.text, 0, 0);
if (style.fill) ctx.fillText(style.text, 0, 0);
ctx.restore();
}
// 文本不需要 buildPath,因为我们在 brush 里直接画了
buildPath(ctx: CanvasRenderingContext2D) {}
/**
* 文本的碰撞检测
* 难点:计算文本的包围盒
*/
containLocal(x: number, y: number): boolean {
const style = this.style;
if (!style.text) return false;
// 借用一个辅助 canvas 来测量文本宽度(或者用全局单一实例)
// 在真实项目中,应该缓存 measureText 的结果
const ctx = document.createElement('canvas').getContext('2d')!;
const fontSize = style.fontSize || 12;
const fontFamily = style.fontFamily || DEFAULT_FONT_FAMILY;
const fontWeight = style.fontWeight || '';
ctx.font = `${fontWeight} ${fontSize}px ${fontFamily}`.trim();
// 1. 计算宽
const width = ctx.measureText(style.text).width;
// 2. 估算高 (Canvas API 不直接提供高度,通常用 fontSize 估算)
const height = fontSize;
// 3. 根据对齐方式计算左上角 (Bounding Box 的 x, y)
// 默认原点在 (0,0)
let bx = 0;
let by = 0;
// 水平对齐修正
const align = style.textAlign || 'left';
if (align === 'center') {
bx -= width / 2;
} else if (align === 'right' || align === 'end') {
bx -= width;
}
// 垂直对齐修正
const baseline = style.textBaseline || 'alphabetic';
if (baseline === 'top') {
by = 0;
} else if (baseline === 'middle') {
by -= height / 2;
} else if (baseline === 'bottom') {
by -= height;
} else {
// alphabetic (基线) 大概在 bottom 偏上一点,这里简单按 bottom 处理或忽略
by -= height;
}
// 4. 判断点是否在矩形内
return x >= bx && x <= bx + width &&
y >= by && y <= by + height;
}
}3. 验证
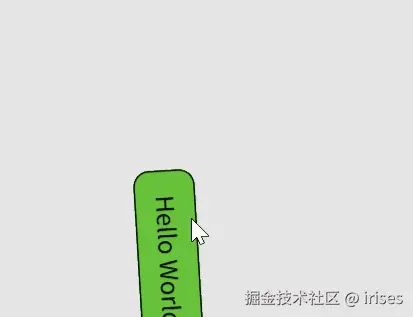
现在我们可以在 index.ts 中同时使用圆形、矩形和文本,构建一个简单的 UI 按钮。
index.ts (测试代码)
typescript
import { init } from './core/MiniRender';
import { Group } from './graphic/Group';
import { Circle } from './graphic/shape/Circle';
import { Rect } from './graphic/shape/Rect'; // 新增
import { Text } from './graphic/Text'; // 新增
const miniRender = init(document.getElementById('main')!);
// --- 示例 1: 创建一个简单的按钮 (Group + Rect + Text) ---
const button = new Group({
position: [100, 100], // 按钮整体位置
// scale: [1.5, 1.5] // 测试父级缩放对文本点击是否有效
});
// 1. 按钮背景
const bg = new Rect({
shape: {
x: 0,
y: 0,
width: 120,
height: 40,
r: 10 // 圆角
},
style: {
fill: '#409EFF',
stroke: '#000',
lineWidth: 1
}
});
// 2. 按钮文字
const label = new Text({
style: {
text: 'Hello World',
fill: '#fff',
fontSize: 16,
textAlign: 'center', // 水平居中
textBaseline: 'middle' // 垂直居中
},
// 将文字放到按钮中心
position: [60, 20], // 120/2, 40/2
z: 1 // 确保文字在背景上面
});
button.add(bg);
button.add(label);
miniRender.add(button);
// --- 交互测试 ---
// 点击背景变色
bg.on('click', () => {
console.log('Background clicked');
bg.style.fill = bg.style.fill === '#409EFF' ? '#67C23A' : '#409EFF';
miniRender.refresh();
});
// 点击文字变色
label.on('click', () => {
console.log('Text clicked');
label.style.fill = label.style.fill === '#fff' ? '#000' : '#fff';
miniRender.refresh();
});
// --- 动画测试 ---
// 让按钮慢慢旋转,测试 Rect 和 Text 的点击区域是否跟着旋转
let angle = 0;
function loop() {
angle += 0.01;
button.rotation = angle;
// 如果想要看旋转效果,取消下面注释
miniRender.refresh();
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
}
loop();