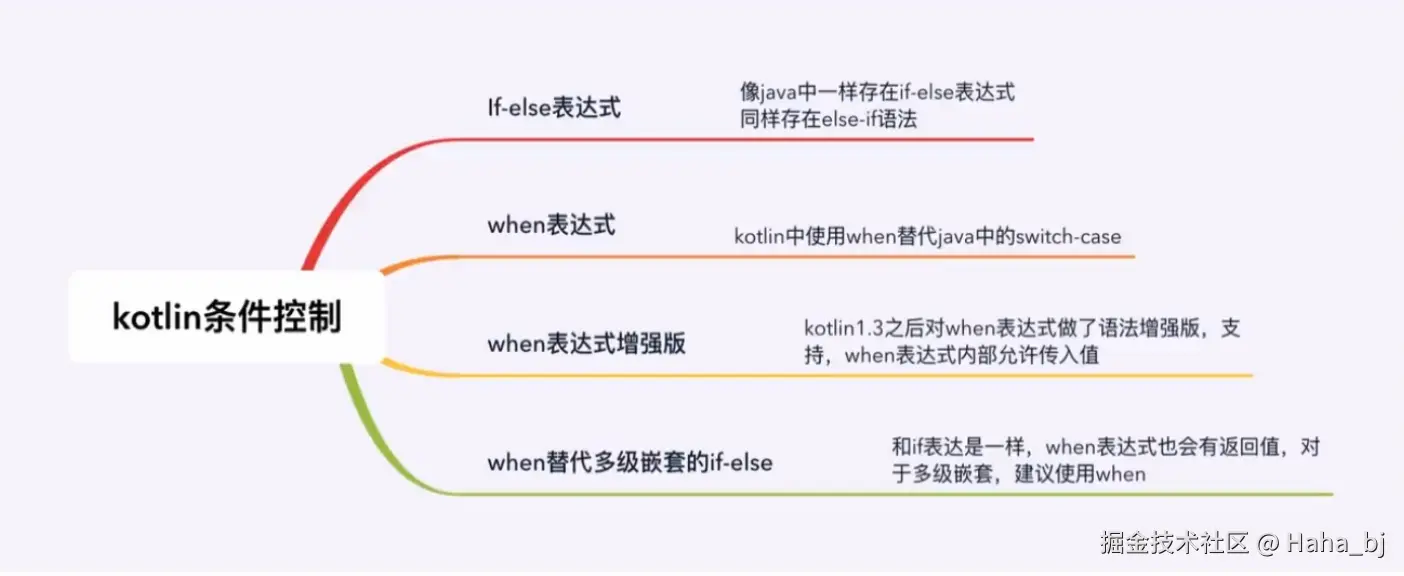
条件控制是每门编程语言中必不可少的,一般就是使用我们所熟知的if-else,来作为我们代码逻辑选择条件控制。在Java中一般使用 if-else和 switch-case 来作为条件控制,而在 Kotlin 中则是使用 if-else 和 when 来作为条件控制。 立
Tips:Kotlin中没有switch-case 。
一、if 表达式
1、带返回值 if 表达式
在 Kotlin 中,if是一个表达式所以它会返回一个值,表达式的值为表达式作用域内最后一行的值。这一点和Java 是不同的,在 Java 中 if 仅仅是语句。
Kotlin
fun maxOf(a: Int, b: Int): Int{
if (a > b){
return a
}else{
return b
}
}
fun main() {
val res = maxOf(10,22)
}2、 if 表达式替代三目运算符
因为在 Kotlin 中 if 表达式是带有返回值的、所以在 Kotlin 中是不需要三目运算符(xxx?xxx:xxx);因为 if 表达式这些都能做到。
而在 Kotlin 中则可以直接使用 if 表达式来使用:
kotlin
/// 返回if
fun maxOf(a: Int, b: Int): Int{
return if (a > b){
a
}else{
b
}
}
//简写
fun maxOf(a: Int,b: Int): Int{
return if (a>b) a else b
}二、when 表达式
在 Kotlin 中使用 when 表达式替代了类似C语言的 switch-case 语句。
when 将它的参数与所有的分支条件顺序比较,直到某个分支满足条件。 when 既可以被当做表达式使用也可以被当做语句使用。如果它被当做表达式,符合条件的分支的值就是整个表达式的值,如果当做语句使用,则忽略个别分支的值。(像 if一样,每一个分支可以是一个代码块,它的值是块中最后的表达式的值。)
Tips:如果其他分支都不满足条件将会求值 e/se 分支。如果 when 作为一个表达式使用,则必须有e/se 分支,除非编译器能够检测出所有的可能情况都已经覆盖了
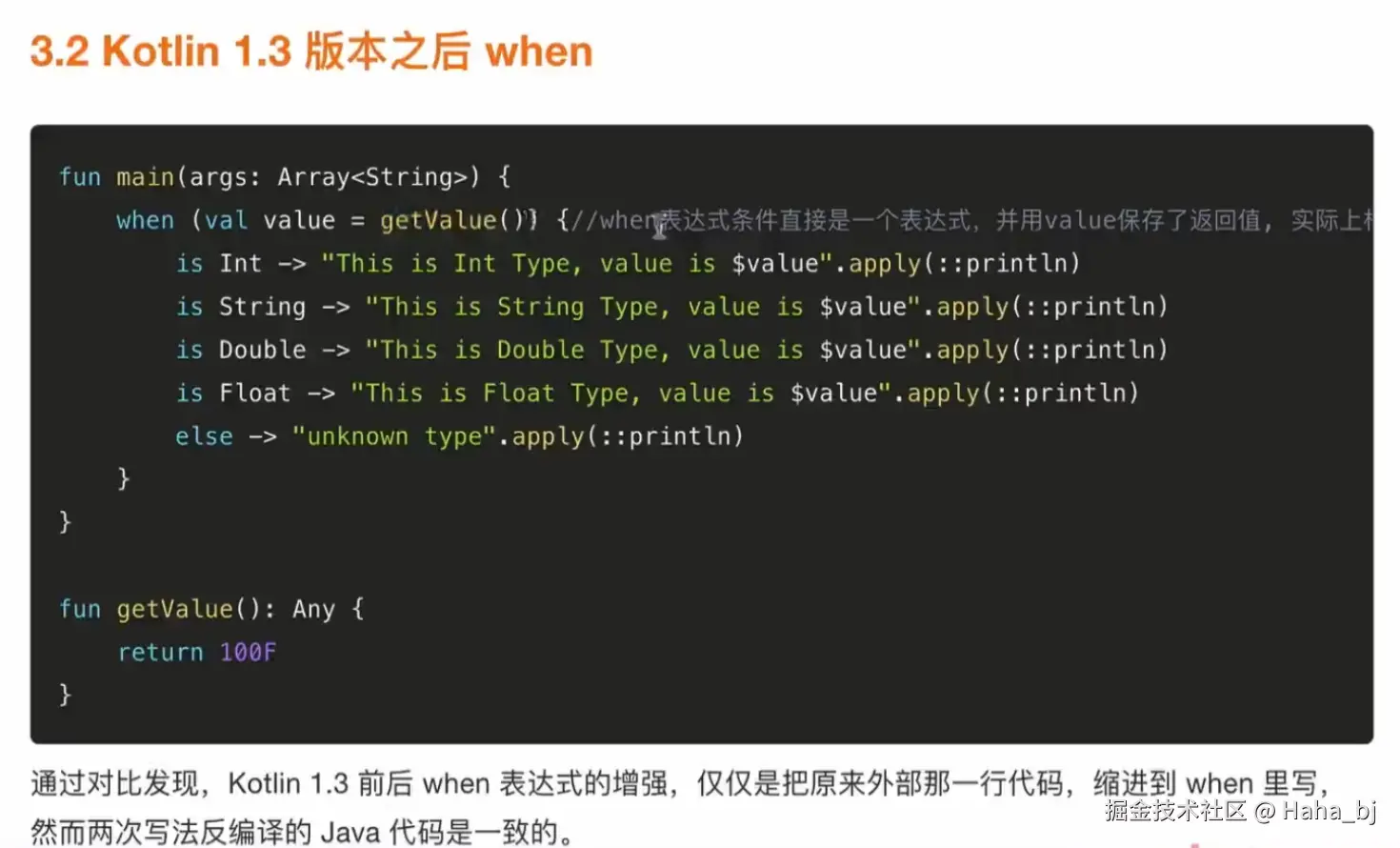
Kotlin
fun eval2(number: Number):String=when(number) {
is Int -> "this is int number"
is Double -> "this is double number"
is Float -> "ths is float number'
is Long -> "this is long number"
is Byte -> "this is byte number"
is Short -> "this is Short number"
else -> "invalid number"
}
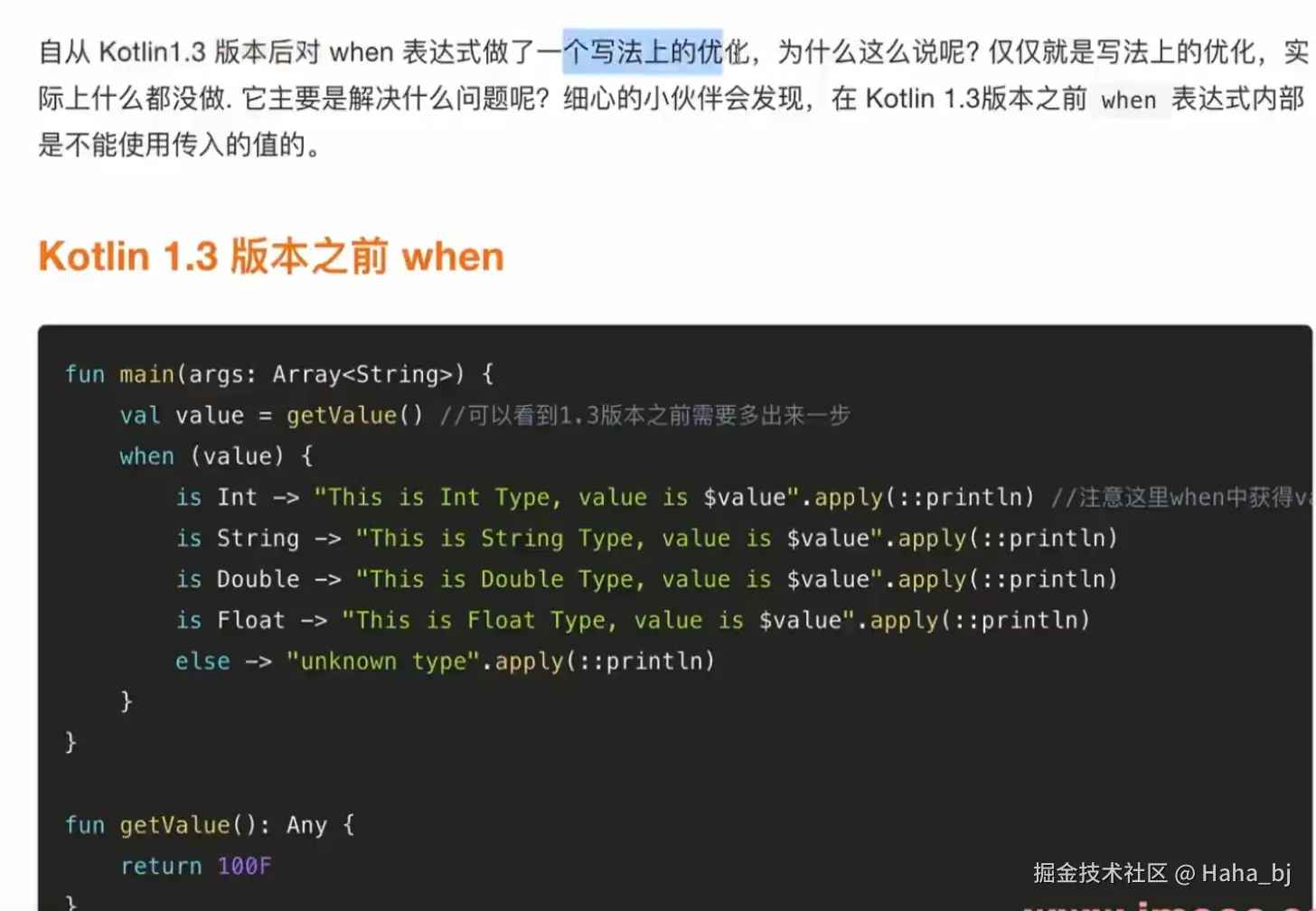
kotlin
// when 同样是带有返回值的// when 将它的参数与所有的分支条件顺序比较,直到某个分支满足条件
fun eval2(number:Number):String=when(number) {
is Int -> "this is int number"
is Double -> "this is double number'"
is Float -> {
println("the number is float")
"ths is float number"
}
is Byte -> "this is byte number"
is Short -> "this is Short number"
else -> "invalid number"
}
三、循环控制
循环控制语句也是每门语言不可缺少的一部分,一般就是我们所熟知的for、while、do-while 。 迟 Kotlin 循环其实几乎和 Java中 的一模一样。
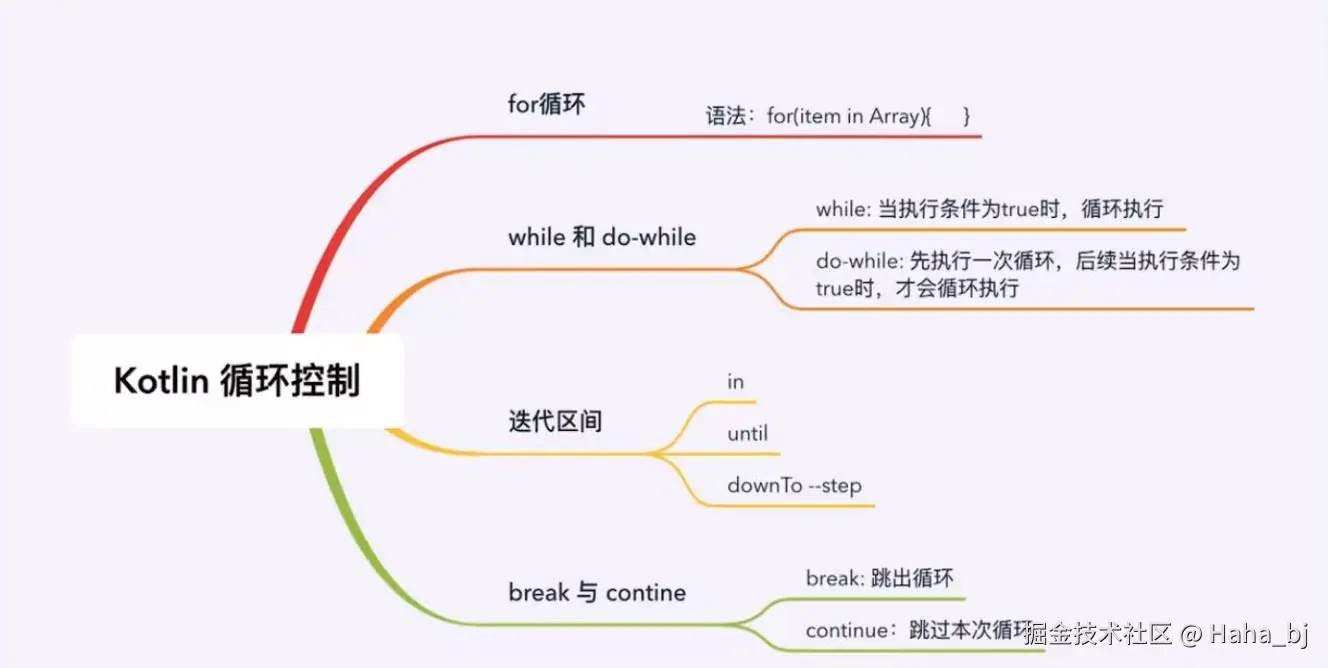
1、for 循环
for 循环 可以对任何提供迭代器(iterator)的对象进行遍历,for 循环仅以唯一一种形式存在,和 Java的 foreach循环一致。其写法 for item in elements 和 C# 一样。和 Java 类似。
Kotlin
val array = mutableListOf<Int>(1,2,3,4,5,6,8)
for (item in array){
println(item)
}2、while 和 do-while 循环
Kotlin 中 while 和 do-while 循环,它们的语法和 Java 中相应的循环没什么区别:
Kotlin
val array = mutableListOf<Int>(1,2,3,4,5,6,8)
var index = 0
while (index < array.size){
println("The $index element is ${array[index++]}")
}
println("空格")
// do - while 先执行 一次循环体,再看循环条件是否满足。满足继续执行,不满足则退
index = 0
do {
println("The $index element is ${array[index++]}")
}while (index < array.size)3、区间表达式
Kotlin
// .. 遍历区间,注意Kotlin的区间的包含或是闭合的。
for (i in 1 .. 10){
println("$i")
}
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
// until 不包括最后一个元素
for (i in 1 until 10){
println("$i")
}
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 6 7 8
Kotlin
// downTo //是指从10 ... 1
for ( i in 10 downTo 1){
println("$i")
}
// 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
// step 步长
for ( i in 10 downTo 1 step 2 ){
println("$i")
}
// 10 8 6 5 4 2