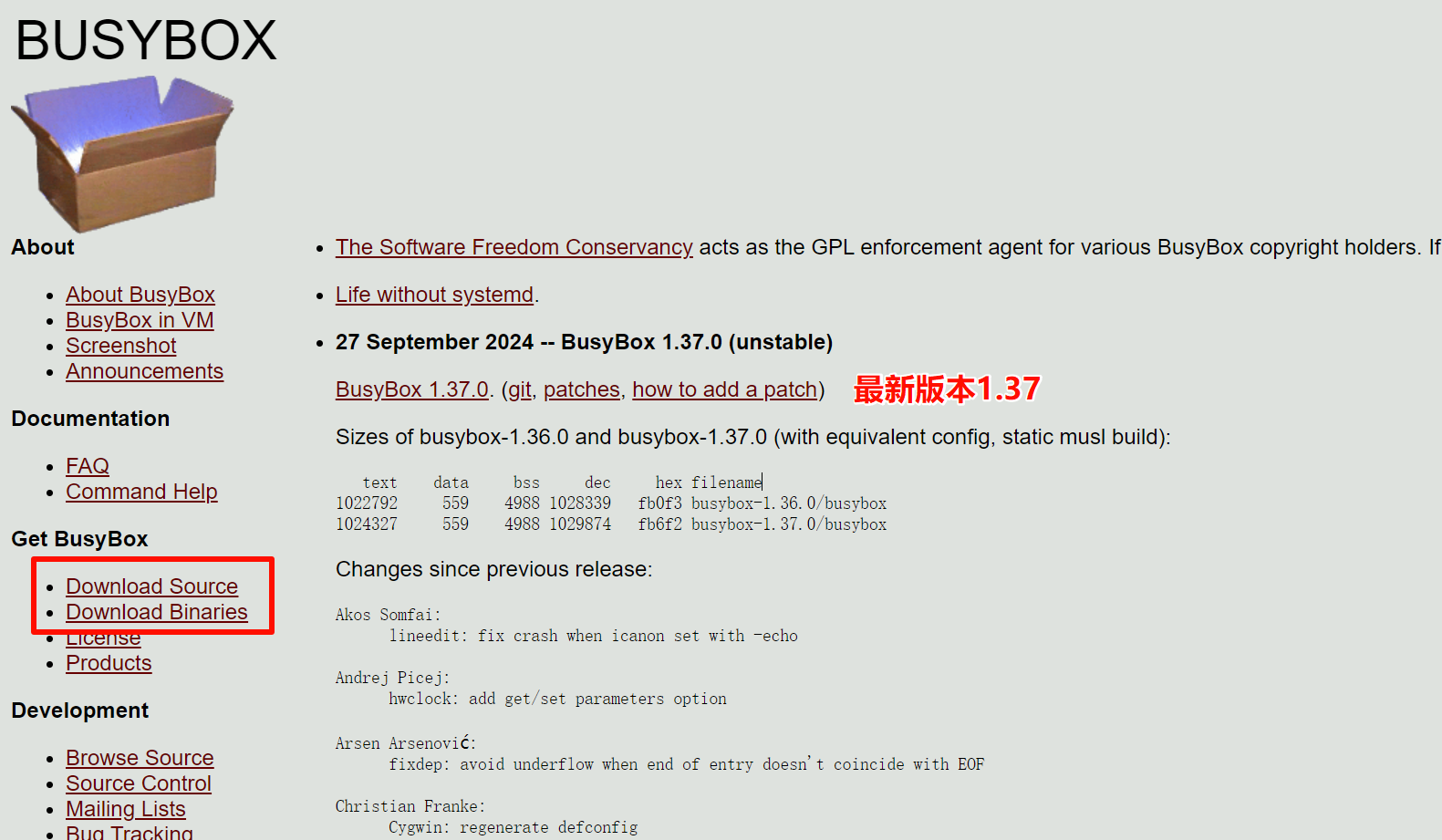
一、busybox介绍
BusyBox 是一个集成了三百多个最常用Linux命令和工具的软件。BusyBox 包含了一些简单的工具,例如ls、cat和echo等等,还包含了一些更大、更复杂的工具,例grep、find、mount以及telnet。有些人将BusyBox称为Linux工具里的瑞士军刀。简单的说BusyBox就好像是个大工具箱,它集成压缩了Linux的许多工具和命令,也包含了Linux系统的自带的shell。\
二、busybox移植
解压源码
cpp
linux@linux-virtual-machine:~/imx6ull_dev/nfs$ ls
busybox-1.35.0.tar.bz2 rootfs rootfs.tar.bz2
linux@linux-virtual-machine:~/imx6ull_dev/nfs$ tar -xvf busybox-1.35.0.tar.bz2支持中文
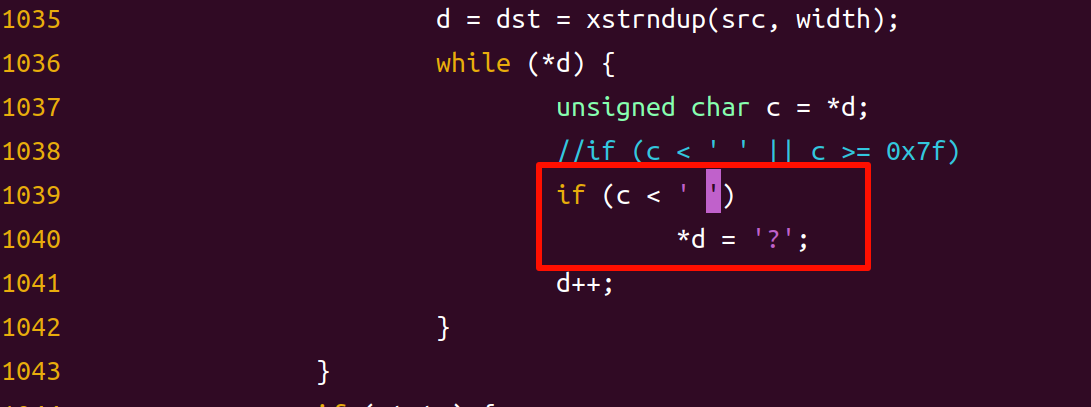
从busybox1.17.0以上之后,对ls命令不做修改是无法显示中文的,就算是内核设置了支持中文, 在 shell 下用ls 命令也是无法显示中文的,这是因为 busybox1.17.0 以后版本对中文的支持进行了限制。要想让busybox1.17.0 以上支持中文,需要修改 libbb/printable_string.c 和 libbb/unicode.c 文件。
printable_string.c文件的修改:
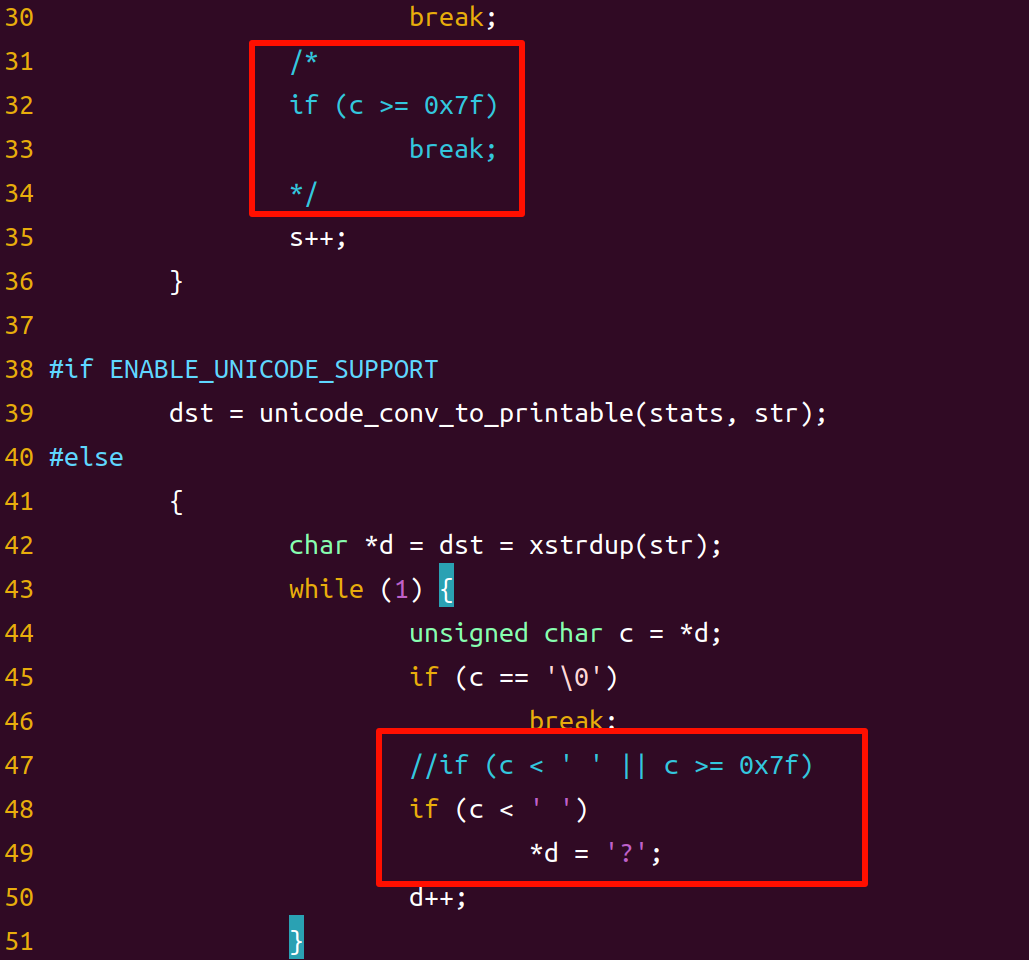
unicode.c文件修改
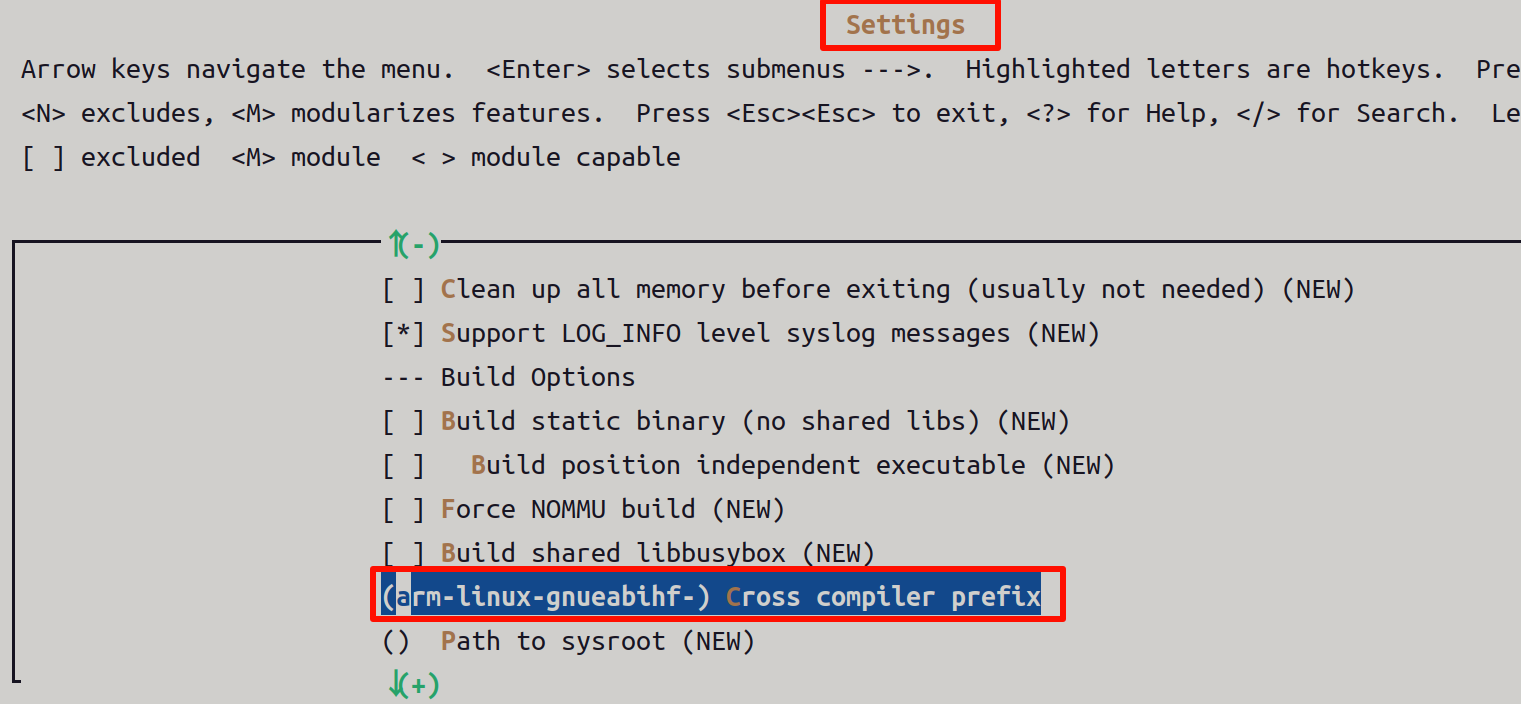
配置
指定交叉编译工具链前缀,
输入使用的交叉编译工具的前缀: arm-linux-gnueabihf-,如下图所示
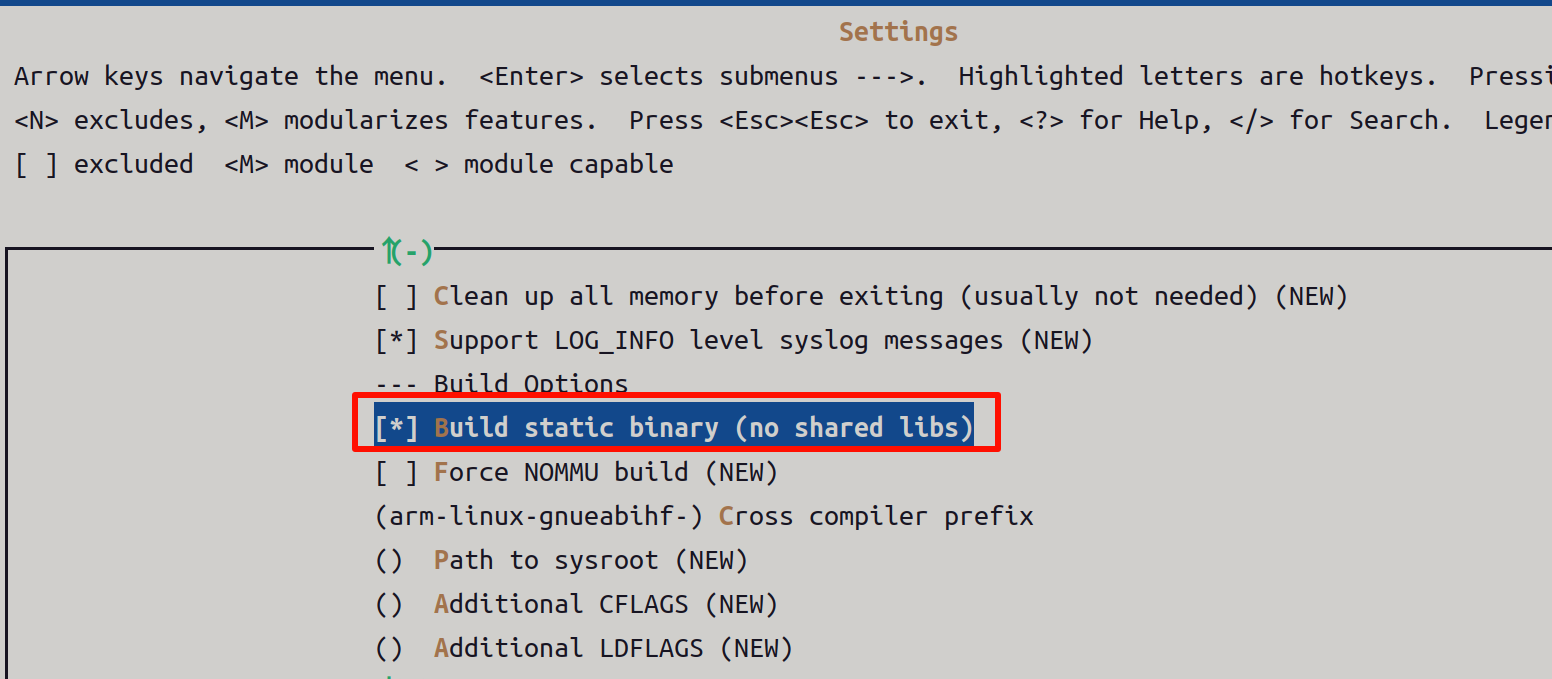
使用静态库链接
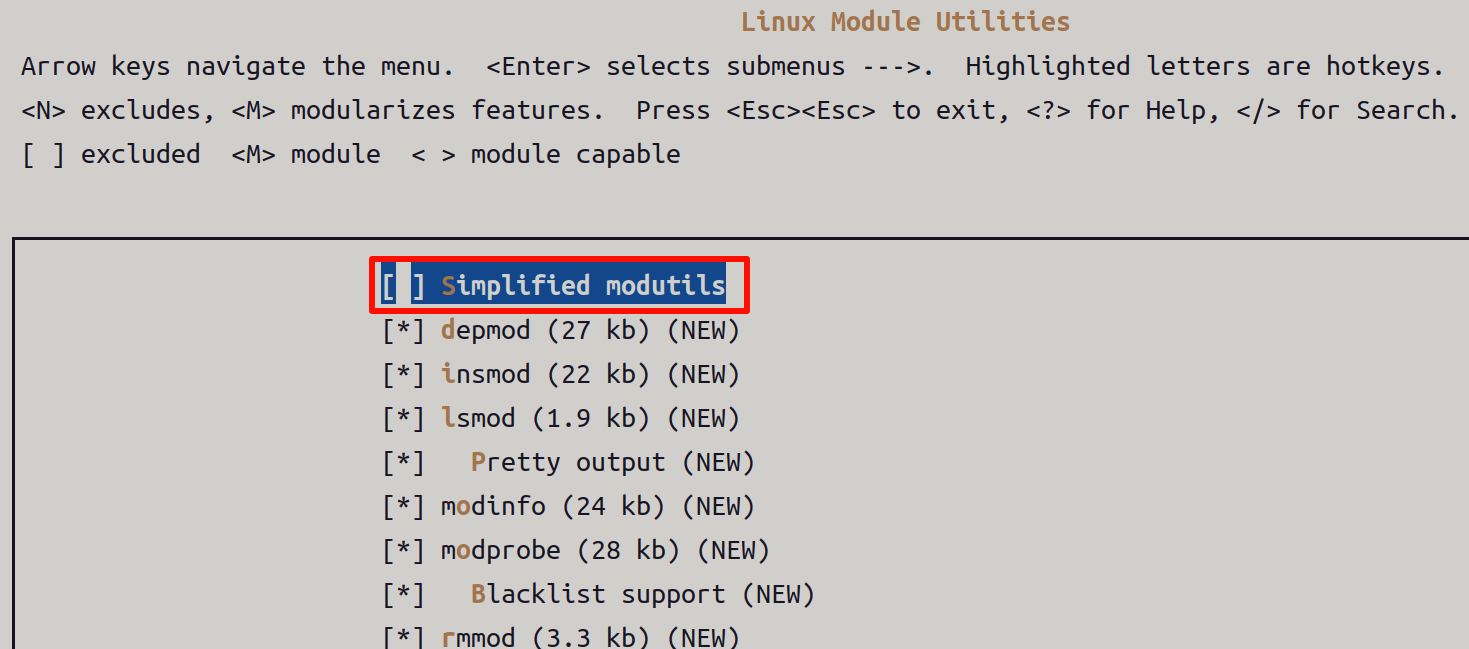
支持驱动模块相关命令
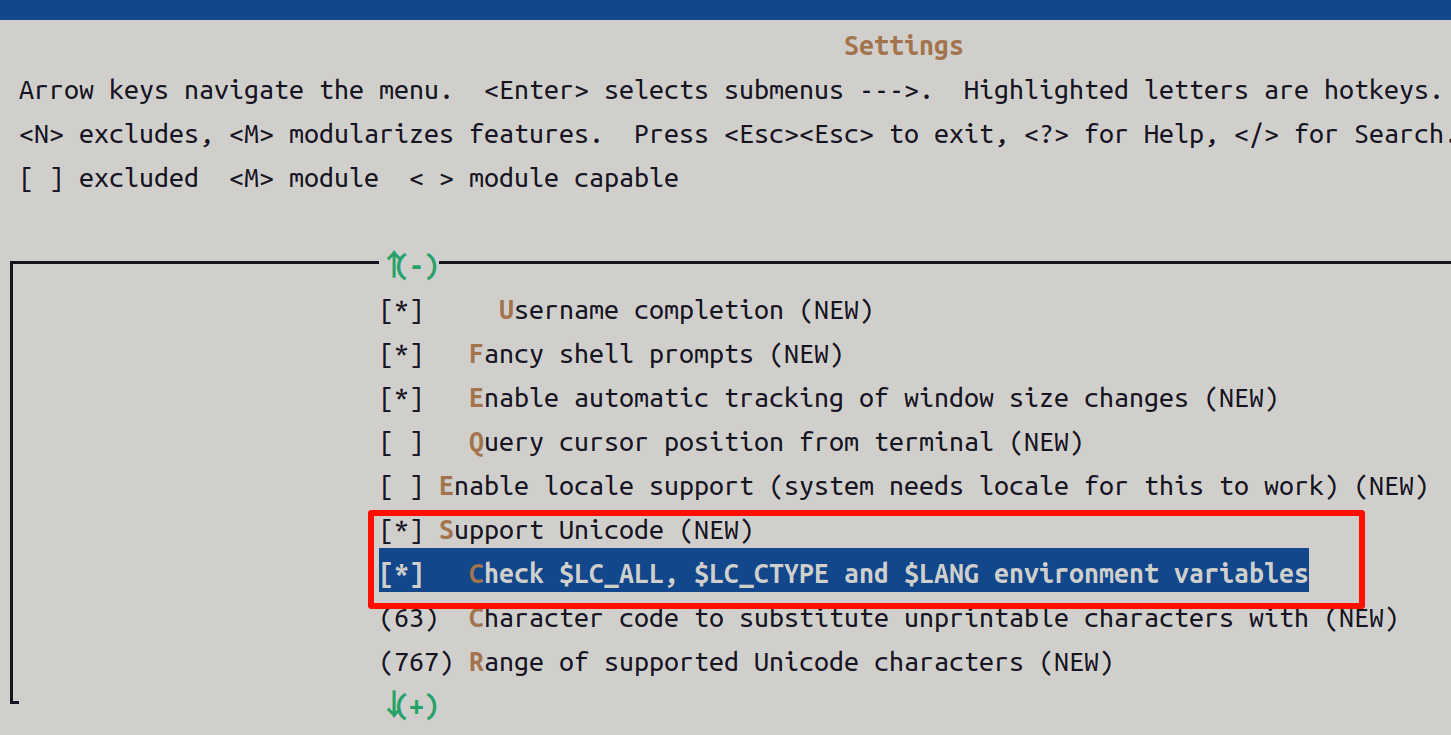
中文支持
最后安装编译,会出现__install的目录
三、根文件系统制作
拷贝busybox源码目录下的_install目录为rootfs目录
向根文件系统添加libc库
在交叉编译工具链的路径下有编译器默认链接的动态库,我们需要把这些动态库拷贝到rootfs目录下。在编译器gcclinaro-4.9.4-2017.01-x86_64_arm-linux-gnueabihf/arm-linux-gnueabihf/libc的路径下有一个lib目录,这个目录下包含了编译器默认链接的C库
添加其它文件夹
**添加rcS文件,**下面有解释,在创建好脚本文件之后还要增加可执行权限
创建/etc/fstab文件
在rootfs中创建/etc/fstab文件,fstab在linux开机后自动挂载的文件系统。
创建/etc/inittab文件
创建/etc/profile文件
四、根文件系统测试
NFS挂载网络文件系统测试
cpp
setenv bootcmd 'tftp 80010000 zImage; tftp 83800000 imx6ull-14x14-emmc-mini.dtb;
bootz 80010000 - 83800000'
setenv bootargs console=ttymxc0,115200 root=/dev/nfs rw ip=dhcp
nfsroot=192.168.0.105:/home/linux/imx6ull_dev/nfs/rootfs,v3,tcp五、解析文件创建和命令
mkdir -p etc/init.d-----------这条命令是构建 imx6ull 根文件系统(rootfs)时的基础操作,用于创建启动脚本存放目录。srC文件
存放启动脚本 :开发板开机后,init 进程(系统第一个进程)会读取
etc/init.d中的脚本(如rcS、network),执行系统初始化操作 ------ 比如你之前配置的 NFS 根文件系统,若需开机自动挂载额外目录、启动应用程序,都需将脚本放在该目录
创建/etc/fstab文件,fstab在linux开机后自动挂载的文件系统
创建/etc/inittab文件,会启动init进程,init程序会读取/etc/inittab这个文件来启动一些进程,系统初始化进程管理
创建/etc/profile文件,用户环境全局配置
六、读取并解析
/etc/inittab文件
init 进程会读取并执行系统的初始化脚本(如 /etc/inittab 等),这些脚本包含了一系列的配置和命令,用于设置系统环境变量、挂载文件系统(例如挂载根文件系统以及其他必要的文件系统,如 /proc 、 /sys 等虚拟文件系统)、加载设备驱动等操作,为后续进程的运行准备好基础环境
cpp
# /etc/inittab init(8) configuration for BusyBox
#
# Copyright (C) 1999-2004 by Erik Andersen <andersen@codepoet.org>
# #
注意,BusyBox的init的程序是不支持运行级别的。 这里的运行级别域
#Note, BusyBox init doesn't support runlevels. The runlevels field is
#会被BusyBox的init程序完全忽略 如果你想使用运行级别,可以使用sysvinit
#completely ignored by BusyBox init. If you want runlevels, use sysvinit.
#
# /etc/inittab文件中每个条目的格式
# Format for each entry:
<id>:<runlevels>:<action>:<process>
#
# 警告:<id>的这个域,对于BusyBox的init进程而言,它的含义和传统的含义不一样
# 即不是ID的意思,这里的ID表示它后面跟的程序运行的时候使用的控制台,如果这个字段忽略,则使
用和init进程一样的控制台
# <id>: WARNING: This field has a non-traditional meaning for BusyBox init!
#
# The id field is used by BusyBox init to specify the controlling tty for
# the specified process to run on.The contents of this field are
# appended to "/dev/" and used as-is. There is no need for this field to
# be unique, although if it isn't you may have strange results. If this
# field is left blank, it is completely ignored. Also note that if
# BusyBox detects that a serial console is in use, then all entries
# containing non-empty id fields will be ignored. BusyBox init does
# nothing with utmp. We don't need no stinkin' utmp.
#
# 运行级别 :运行级别域被完成忽略
# <runlevels>: The runlevels field is completely ignored.
#
# <action> Valid actions include: 【action表示后面的程序或脚本执行的时机】
# sysinit : 表示<process>在系统启动后最先执行,只执行一次,init进程等待它结束才继续执行其
他动作
# wait : 表示<process>在执行sysinit进程后执行,只执行一次,init进程等待它结束才继续执
行其他动作
# once : 表示<process>在执行wait进程后执行,只执行一次,init进程不等待它结束
# respawn : 表示<process>在启动once进程后执行,init进程一旦发现<process>死掉,就会重新启
动它
# askfirst: 表示<process>在启动完respawn进程后执行,与respawn类似,不过init进程先输
出"Please
# press Enter to activate this console",等用户输入回车键之后才启动子进程。
#
# restart : 如果BusyBox中配置了CONFIG_FEATURE_USE_INITTAB,并且init进程接收SIGHUP信号,
此时init进程会重新读取并解析/etc/inittab文件,将restart的程序重新执行
# shutdown: 在系统关机时,init进程会执行标记为shutdown的进程或脚本。这些脚本通常用于执行
一些清理操作,如卸载文件系统等。
# ctrlaltdel:当用户按下 Ctrl + Alt + Del 组合键时,init 进程会执行被标记为 ctrlaltdel
的进程或脚本。一般用于定义系统的重启操作。
# #
# Note: askfirst acts just like respawn, but before running the specified
# process it displays the line "Please press Enter to activate this
# console." and then waits for the user to press enter before starting
# the specified process.
#
# Note: unrecognized actions (like initdefault) will cause init to emit
# an error message, and then go along with its business.
#
# <process>可以是可执行的程序,也可以是脚本
# <process>: Specifies the process to be executed and it's command line.
# #
# init进程在读取/etc/inittab后,做的事情可以总结如下:
# <1>在系统启动前,init进程首先启动<action>为sysinit,wait,once三类进程
# <2>在系统正常运行期间,init进程首先启动<action>为respawn,askfirst的两类子进程,并监视他
们,如果发现某个进程退出时就重新启动它
# <3>在系统退出时,执行<action>为shutdown,restart,ctrlaltdel三类进程
# #
# 注意:如果BusyBox的init进程没有发现/etc/inittab文件,它的默认行为如下
# Note: BusyBox init works just fine without an inittab. If no inittab is
# found, it has the following default behavior:
# ::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS
# ::askfirst:/bin/sh
# ::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot
# ::shutdown:/sbin/swapoff -a
# ::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
# ::restart:/sbin/init
#
# 如果它发现/dev/console不是一个串口控制台时,它还会干以下事情
# if it detects that /dev/console is _not_ a serial console, it will
# also run:
# tty2::askfirst:/bin/sh
# tty3::askfirst:/bin/sh
# tty4::askfirst:/bin/sh
#
# Boot-time system configuration/initialization script.
# This is run first except when booting in single-user mode.
#
::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS
# /bin/sh invocations on selected ttys
#
# 在 shell 命令前添加 "-" 符号,是为了告知shell应作为登录shell来运行【当用户通过终端登录
系统时,登录程序会启动一个登录shell,它会自动处理读取配置文件等操作,用户无需手动指定。】
# Note below that we prefix the shell commands with a "-" to indicate to the shell
that it is supposed to be a login shell.
# 通常情况下,登录shell的处理是由登录程序(如 login)完成的,在当前这种情况下绕过了登录程
序,所以借助BusyBox提供的功能手动添加 "-" 符号来实现登录shell的效果。
# Normally this is handled by login, but since we are bypassing login in this case,
BusyBox lets you do
# this yourself...
#
# Start an "askfirst" shell on the console (whatever that may be)
::askfirst:-/bin/sh
# Start an "askfirst" shell on /dev/tty2-4
tty2::askfirst:-/bin/sh
tty3::askfirst:-/bin/sh
tty4::askfirst:-/bin/sh
# /sbin/getty invocations for selected ttys
tty4::respawn:/sbin/getty 38400 tty5
tty5::respawn:/sbin/getty 38400 tty6
# Example of how to put a getty on a serial line (for a terminal)
#::respawn:/sbin/getty -L ttyS0 9600 vt100
#::respawn:/sbin/getty -L ttyS1 9600 vt100
#
# Example how to put a getty on a modem line.
#::respawn:/sbin/getty 57600 ttyS2
# Stuff to do when restarting the init process
::restart:/sbin/init
# Stuff to do before rebooting
::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot
::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
#/bin/umount 是用于卸载文件系统的命令,-a 选项表示卸载所有已挂载的文件系统,-r 选项表示如
果卸载失败,则尝试以只读模式重新挂载文件系#统,以保证文件系统的一致性。
::shutdown:/sbin/swapoff -a
# /sbin/swapoff 是用于关闭交换空间(swap space)的命令,-a 选项表示关闭所有已启用的交换
空间/etc/init.d/rcS脚本
cpp
#!/bin/sh
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:$PATH
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/lib:/usr/lib
export PATH LD_LIBRARY_PATH
#This is the first script called by init process
# #
挂载/etc/fstab指定的文件系统
mount -a
mkdir /dev/pts
#用于挂载devpts文件系统,-t devpts用于指定要挂载的文件系统类型,第二个devpts表示要挂载的文
件系统源,/dev/pts这是挂载点。
#devpts挂载成功后,系统能够管理和使用伪终端设备,以实现与伪终端的交互(远程登录)
mount -t devpts devpts /dev/pts
#告诉内核mdev程序的路径,当系统有热插拔设备时,内核会调用mdev程序新建或删除对应设备文件节点
echo /sbin/mdev>/proc/sys/kernel/hotplug
#启动mdev程序,扫描系统识别的设备,并且新建设备文件节点
mdev -s/etc/fstab
文件指定的设备及文件系统
cpp
#device mount-point type options dump fsck order
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
tmpfs /tmp tmpfs defaults 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0
tmpfs /dev tmpfs defaults 0 0
<1>device:要挂载的设备
比如/dev/hda2,/dev/mtdbloc1等设备文件;也可以是文件系统,比如proc,tmpfs,sysfs ,对于NFS文
件系统,这个字段为<host>:<dir>。
<2>mount-point:挂载点
<3>type:文件系统类型
比如proc,jffs2,yaffs,ext2,nfs等;也可以是auto,表示自动检测文件系统类型
<4>options :挂载参数,多个参数以逗号隔开
常用的参数有
auto : 执行"mount -a"时,自动挂载
noauto : 执行"mount -a"时,不挂载
user : 允许普通挂载设备
nouser : 只允许root用户挂载设备
exec : 允许执行设备上的程序
noexec : 不允许执行设备上的程序
Ro : 以只读方式挂载文件系统
rw : 以读写方式挂载文件系统
sync : 修改文件时,它会同时写入设备中
async : 修改文件时,不会同时写入设备
defaults : rw,exec,auto,nouser,async等组合
<5>dump : dump程序根据这个字段来决定这个文件系统是否需要备份
0-> 表示忽略dump程序忽略这个文件系统
<3>fsck order : fsck程序根据这个字段来决定是否对磁盘做检查
0-> 表示fsck程序忽略这个文件系统init=/linuxrc是 Linux 内核启动参数(通常写在bootargs中),用于指定系统启动后内核要执行的第一个用户态进程(init 进程),是嵌入式 Linux(如 imx6ull)根文件系统启动的核心配置