一、引言
ONNX Runtime 作为微软开源的高性能机器学习推理引擎,支持跨平台部署和多种硬件加速。openEuler 22.03 LTS 作为华为主导的企业级 Linux 发行版,在服务器和云计算领域具有重要地位。本文旨在探索两者结合的性能潜力和优化策略。
测试目标
- 评估 ONNX Runtime 在 openEuler 平台的基础性能表现
- 分析不同模型类型的推理性能特征
- 探索 CPU 优化参数对性能的影响
- 提供生产环境部署的最佳实践建议
二、测试环境
处理器采用16核心32线程,内存32G,openEuler 22.03 LTS,公网带宽10MB,磁盘100G
首先确认下操作系统版本,使用cat /etc/os-release命令
使用uname -r命令查看内核版本

下面让我们准备一下环境
python
# 1. 系统更新和基础工具安装
sudo dnf update -y
# 安装完整的开发工具链(包括gcc、g++、make、gdb等)
sudo dnf groupinstall -y "Development Tools"
# 安装常用的开发工具和依赖
sudo dnf install -y cmake git wget curl python3-devel
python
# 2. 安装性能分析工具
sudo dnf install -y htop iotop sysstat perf
python
# 3. 创建 Python 虚拟环境
python3 -m venv /opt/onnx_env
source /opt/onnx_env/bin/activate
python
# 配置国内镜像源
# 创建pip配置文件
mkdir -p ~/.pip
cat > ~/.pip/pip.conf << EOF
[global]
index-url = https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
trusted-host = pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn
timeout = 120
EOF
# 4. 安装核心依赖
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install onnxruntime==1.16.3
pip install onnx==1.15.0
pip install numpy==1.24.3
pip install torch==2.1.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
pip install transformers==4.35.2
pip install psutil matplotlib seaborn pandas
# 5. 验证安装
python -c "import onnxruntime; print('ONNX Runtime version:', onnxruntime.__version__)"
python -c "import onnxruntime; print('Available providers:', onnxruntime.get_available_providers())"
三、测试模型准备
首先创建脚本目录结构:mkdir -p models results plots optimized_models
3.1 模型选择策略
选择了涵盖不同应用场景和计算复杂度的典型模型:
通过touch models_config.py创建模型选择策略脚本,然后将以下的代码复制粘贴到文件中
python
# models_config.py
MODELS_CONFIG = {
"resnet50": {
"type": "image_classification",
"input_shape": (1, 3, 224, 224),
"model_size": "98MB",
"complexity": "medium",
"ops_count": "4.1B"
},
"bert-base": {
"type": "nlp",
"input_shape": (1, 128),
"model_size": "438MB",
"complexity": "high",
"ops_count": "22.5B"
},
"mobilenet_v2": {
"type": "image_classification",
"input_shape": (1, 3, 224, 224),
"model_size": "14MB",
"complexity": "low",
"ops_count": "0.3B"
},
"distilbert": {
"type": "nlp",
"input_shape": (1, 128),
"model_size": "268MB",
"complexity": "medium",
"ops_count": "11.3B"
}
}3.2 模型转换脚本
通过touch convert_models.py创建模型转换脚本,首先开始转换模型,通过python convert_models.py命令
如果遇到网络问题导致Hugging Face上面模型无法下载,那么导入国内镜像源export HF_ENDPOINT=https://hf-mirror.com
该脚本负责将 PyTorch 预训练模型转换为 ONNX 格式,是整个测试流程的基础。脚本实现了四个主流模型的转换:ResNet50 和 MobileNetV2 代表计算机视觉领域,BERT-Base 和 DistilBERT 代表自然语言处理领域。转换过程中使用了 ONNX opset 版本 17,启用了常量折叠优化,并设置了动态轴以支持可变批次大小。脚本还自动处理了不同模型的输入格式差异,视觉模型使用标准的图像张量输入,而 NLP 模型则需要 input_ids 和 attention_mask 两个输入张量。
python
# convert_models.py
import torch
import torch.onnx
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer, DistilBertModel
import torchvision.models as models
import os
def convert_resnet50():
"""转换 ResNet50 模型到 ONNX 格式"""
print("开始转换 ResNet50 模型...")
model = models.resnet50(weights='IMAGENET1K_V1')
model.eval()
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
torch.onnx.export(
model,
dummy_input,
"models/resnet50.onnx",
export_params=True,
opset_version=17,
do_constant_folding=True,
input_names=['input'],
output_names=['output'],
dynamic_axes={
'input': {0: 'batch_size'},
'output': {0: 'batch_size'}
}
)
print("✓ ResNet50 模型转换完成")
def convert_bert_base():
"""转换 BERT-Base 模型到 ONNX 格式"""
print("开始转换 BERT-Base 模型...")
model_name = "bert-base-uncased"
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
model.eval()
dummy_input = torch.randint(0, 1000, (1, 128))
attention_mask = torch.ones(1, 128)
torch.onnx.export(
model,
(dummy_input, attention_mask),
"models/bert_base.onnx",
export_params=True,
opset_version=17,
do_constant_folding=True,
input_names=['input_ids', 'attention_mask'],
output_names=['last_hidden_state'],
dynamic_axes={
'input_ids': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'sequence'},
'attention_mask': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'sequence'},
'last_hidden_state': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'sequence'}
}
)
print("✓ BERT-Base 模型转换完成")
def convert_mobilenet_v2():
"""转换 MobileNetV2 模型到 ONNX 格式"""
print("开始转换 MobileNetV2 模型...")
model = models.mobilenet_v2(weights='IMAGENET1K_V1')
model.eval()
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
torch.onnx.export(
model,
dummy_input,
"models/mobilenet_v2.onnx",
export_params=True,
opset_version=17,
do_constant_folding=True,
input_names=['input'],
output_names=['output'],
dynamic_axes={
'input': {0: 'batch_size'},
'output': {0: 'batch_size'}
}
)
print("✓ MobileNetV2 模型转换完成")
def convert_distilbert():
"""转换 DistilBERT 模型到 ONNX 格式"""
print("开始转换 DistilBERT 模型...")
model_name = "distilbert-base-uncased"
model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained(model_name)
model.eval()
dummy_input = torch.randint(0, 1000, (1, 128))
attention_mask = torch.ones(1, 128)
torch.onnx.export(
model,
(dummy_input, attention_mask),
"models/distilbert.onnx",
export_params=True,
opset_version=17,
do_constant_folding=True,
input_names=['input_ids', 'attention_mask'],
output_names=['last_hidden_state'],
dynamic_axes={
'input_ids': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'sequence'},
'attention_mask': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'sequence'},
'last_hidden_state': {0: 'batch_size', 1: 'sequence'}
}
)
print("✓ DistilBERT 模型转换完成")
if __name__ == "__main__":
os.makedirs("models", exist_ok=True)
convert_resnet50()
convert_bert_base()
convert_mobilenet_v2()
convert_distilbert()
print("\n所有模型转换完成!")
# 显示模型文件大小
import glob
for model_file in glob.glob("models/*.onnx"):
size = os.path.getsize(model_file) / (1024 * 1024)
print(f"{model_file}: {size:.1f} MB")
四、基准性能测试
4.1 单线程推理性能测试
通过touch benchmark_single_thread.py创建单线程推理性能测试脚本,通过python benchmark_single_thread.py执行脚本测试
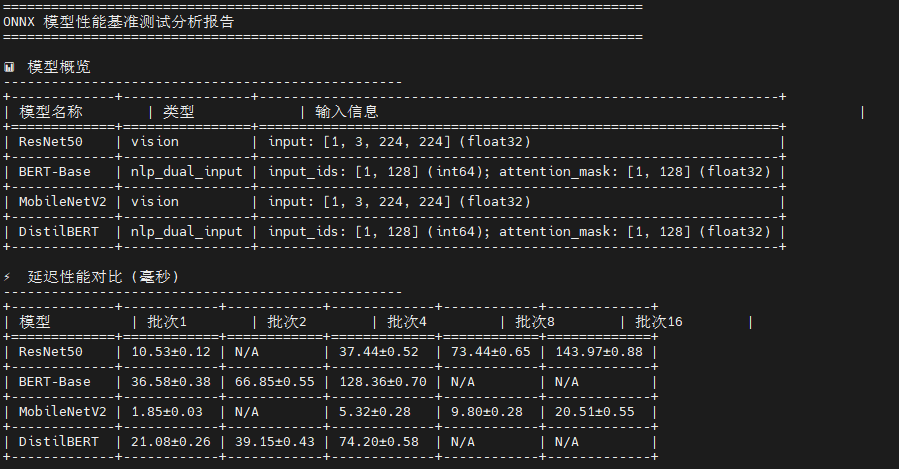
这是一个智能化的 ONNX 模型性能测试框架 ,核心创新在于自适应模型识别机制。脚本通过分析输入张量的维度特征自动判断模型类型:四维张量(batch, 3, H, W)识别为视觉模型,双输入(input_ids + attention_mask)识别为 NLP 模型。基于模型类型,脚本生成符合规范的测试数据:视觉模型使用标准化随机图像,NLP 模型生成合法的 token IDs(1-30521)和全1的 attention mask。测试流程采用预热-测试-统计三阶段,收集7个关键指标(均值、标准差、P50/P95/P99分位数),并根据模型特性动态调整批次大小:视觉模型测试 [1,4,8,16],NLP 模型限制在 [1,2,4] 以避免内存溢出。最终通过 tabulate 生成8类分析表格,形成完整的性能画像。
python
# benchmark_single_thread.py (增加分析表格输出)
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
import time
import psutil
import os
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple
import json
import pandas as pd
from tabulate import tabulate
class ONNXBenchmark:
def __init__(self, model_path: str, providers: List[str] = None):
if providers is None:
providers = ['CPUExecutionProvider']
# 创建推理会话
self.session = ort.InferenceSession(
model_path,
providers=providers
)
# 获取输入输出信息
self.input_names = [input.name for input in self.session.get_inputs()]
self.output_names = [output.name for output in self.session.get_outputs()]
self.input_shapes = [input.shape for input in self.session.get_inputs()]
self.input_types = [input.type for input in self.session.get_inputs()]
print(f"模型输入: {list(zip(self.input_names, self.input_shapes, self.input_types))}")
print(f"模型输出: {[output.name for output in self.session.get_outputs()]}")
# 确定模型类型
self.model_type = self._determine_model_type()
print(f"检测到模型类型: {self.model_type}")
def _determine_model_type(self) -> str:
"""根据输入特征确定模型类型"""
if len(self.input_names) == 1:
input_shape = self.input_shapes[0]
if len(input_shape) == 4 and input_shape[1] == 3: # [batch, 3, H, W]
return "vision"
elif len(input_shape) == 2: # [batch, seq_len]
return "nlp_single_input"
elif len(self.input_names) == 2:
# 通常是 NLP 模型,有 input_ids 和 attention_mask
return "nlp_dual_input"
return "unknown"
def _get_numpy_dtype(self, onnx_type: str) -> np.dtype:
"""将 ONNX 数据类型转换为 numpy 数据类型"""
type_mapping = {
'tensor(float)': np.float32,
'tensor(float32)': np.float32,
'tensor(float64)': np.float64,
'tensor(double)': np.float64,
'tensor(int32)': np.int32,
'tensor(int64)': np.int64,
'tensor(int8)': np.int8,
'tensor(uint8)': np.uint8,
'tensor(bool)': np.bool_,
}
return type_mapping.get(onnx_type, np.float32)
def generate_random_inputs(self, batch_size: int = 1) -> Dict[str, np.ndarray]:
"""根据模型类型生成正确的输入数据"""
inputs = {}
if self.model_type == "vision":
# 视觉模型:ResNet50, MobileNetV2
input_name = self.input_names[0]
shape = self.input_shapes[0]
input_type = self.input_types[0]
# 处理动态批次维度
actual_shape = [batch_size if (isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1) else dim
for dim in shape]
# 使用正确的数据类型
dtype = self._get_numpy_dtype(input_type)
# 生成标准化的图像数据 (ImageNet 预处理)
inputs[input_name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(dtype)
elif self.model_type == "nlp_single_input":
# 单输入 NLP 模型
input_name = self.input_names[0]
shape = self.input_shapes[0]
input_type = self.input_types[0]
actual_shape = [batch_size if (isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1) else dim
for dim in shape]
dtype = self._get_numpy_dtype(input_type)
if 'int' in str(dtype):
# 生成 token IDs
inputs[input_name] = np.random.randint(1, 30522, actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
# 如果期望浮点数,生成浮点数
inputs[input_name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(dtype)
elif self.model_type == "nlp_dual_input":
# 双输入 NLP 模型:BERT, DistilBERT
# 默认序列长度
default_seq_len = 128
for i, (name, shape, input_type) in enumerate(zip(self.input_names, self.input_shapes, self.input_types)):
# 处理动态维度
actual_shape = []
for dim in shape:
if isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1:
if 'batch' in str(dim).lower():
actual_shape.append(batch_size)
elif 'sequence' in str(dim).lower() or 'seq' in str(dim).lower():
actual_shape.append(default_seq_len)
else:
actual_shape.append(batch_size) # 默认为批次维度
else:
actual_shape.append(dim)
dtype = self._get_numpy_dtype(input_type)
print(f"生成输入 {name}: shape={actual_shape}, dtype={dtype}, onnx_type={input_type}")
if 'input_ids' in name.lower() or 'token' in name.lower():
if 'int' in str(dtype):
# Token IDs: 1-30521 (避免 0 和特殊 token)
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(1, 30522, actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
# 如果期望浮点数,将 token IDs 转换为浮点数
token_ids = np.random.randint(1, 30522, actual_shape)
inputs[name] = token_ids.astype(dtype)
elif 'attention_mask' in name.lower() or 'mask' in name.lower():
if 'int' in str(dtype):
# Attention mask: 全1表示所有位置都参与注意力计算
inputs[name] = np.ones(actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
# 如果期望浮点数
inputs[name] = np.ones(actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
elif 'token_type' in name.lower():
if 'int' in str(dtype):
# Token type IDs: 全0表示单句输入
inputs[name] = np.zeros(actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
inputs[name] = np.zeros(actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
# 其他输入类型
if 'int' in str(dtype):
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 100, actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(dtype)
else:
# 未知模型类型,使用通用方法
for i, (name, shape, input_type) in enumerate(zip(self.input_names, self.input_shapes, self.input_types)):
actual_shape = [batch_size if (isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1) else dim
for dim in shape]
dtype = self._get_numpy_dtype(input_type)
if 'int' in str(dtype):
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 1000, actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(dtype)
return inputs
def warmup(self, num_runs: int = 10):
"""预热推理引擎"""
print("预热推理引擎...")
inputs = self.generate_random_inputs()
for _ in range(num_runs):
_ = self.session.run(self.output_names, inputs)
def benchmark_latency(self, num_runs: int = 100, batch_size: int = 1) -> Dict[str, float]:
"""测试推理延迟"""
self.warmup()
inputs = self.generate_random_inputs(batch_size)
latencies = []
# 监控系统资源
process = psutil.Process()
cpu_percent_before = process.cpu_percent()
memory_before = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024 # MB
print(f"开始性能测试,批次大小: {batch_size}, 测试次数: {num_runs}")
print(f"输入形状和类型: {[(name, arr.shape, arr.dtype) for name, arr in inputs.items()]}")
for i in range(num_runs):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
outputs = self.session.run(self.output_names, inputs)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
latencies.append((end_time - start_time) * 1000) # 转换为毫秒
if (i + 1) % 20 == 0:
print(f" 已完成 {i + 1}/{num_runs} 次测试")
cpu_percent_after = process.cpu_percent()
memory_after = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024 # MB
return {
'batch_size': batch_size,
'num_runs': num_runs,
'model_type': self.model_type,
'input_shapes': {name: list(arr.shape) for name, arr in inputs.items()},
'input_dtypes': {name: str(arr.dtype) for name, arr in inputs.items()},
'mean_latency_ms': np.mean(latencies),
'std_latency_ms': np.std(latencies),
'min_latency_ms': np.min(latencies),
'max_latency_ms': np.max(latencies),
'p50_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies, 50),
'p95_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies, 95),
'p99_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies, 99),
'throughput_qps': 1000 / np.mean(latencies) * batch_size,
'cpu_usage_percent': cpu_percent_after - cpu_percent_before,
'memory_usage_mb': memory_after - memory_before,
'raw_latencies': latencies
}
def generate_analysis_tables(results: Dict) -> None:
"""生成详细的分析表格"""
print("\n" + "="*80)
print("ONNX 模型性能基准测试分析报告")
print("="*80)
# 1. 模型概览表
print("\n📊 模型概览")
print("-" * 50)
overview_data = []
for model_name, batch_results in results.items():
if batch_results:
first_result = list(batch_results.values())[0]
model_type = first_result['model_type']
input_shapes = first_result['input_shapes']
input_dtypes = first_result['input_dtypes']
# 格式化输入信息
input_info = []
for name, shape in input_shapes.items():
dtype = input_dtypes[name]
input_info.append(f"{name}: {shape} ({dtype})")
overview_data.append([
model_name,
model_type,
"; ".join(input_info)
])
overview_headers = ["模型名称", "类型", "输入信息"]
print(tabulate(overview_data, headers=overview_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 2. 延迟性能对比表
print("\n⚡ 延迟性能对比 (毫秒)")
print("-" * 50)
latency_data = []
batch_sizes = set()
# 收集所有批次大小
for batch_results in results.values():
batch_sizes.update(batch_results.keys())
batch_sizes = sorted(batch_sizes)
for model_name, batch_results in results.items():
row = [model_name]
for batch_size in batch_sizes:
if batch_size in batch_results:
mean_lat = batch_results[batch_size]['mean_latency_ms']
std_lat = batch_results[batch_size]['std_latency_ms']
row.append(f"{mean_lat:.2f}±{std_lat:.2f}")
else:
row.append("N/A")
latency_data.append(row)
latency_headers = ["模型"] + [f"批次{bs}" for bs in batch_sizes]
print(tabulate(latency_data, headers=latency_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 3. 吞吐量性能对比表
print("\n🚀 吞吐量性能对比 (QPS)")
print("-" * 50)
throughput_data = []
for model_name, batch_results in results.items():
row = [model_name]
for batch_size in batch_sizes:
if batch_size in batch_results:
qps = batch_results[batch_size]['throughput_qps']
row.append(f"{qps:.2f}")
else:
row.append("N/A")
throughput_data.append(row)
throughput_headers = ["模型"] + [f"批次{bs}" for bs in batch_sizes]
print(tabulate(throughput_data, headers=throughput_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 4. 延迟分布统计表
print("\n📈 延迟分布统计 (毫秒)")
print("-" * 50)
distribution_data = []
for model_name, batch_results in results.items():
for batch_size, result in batch_results.items():
distribution_data.append([
model_name,
batch_size,
f"{result['min_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['p50_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['p95_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['p99_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['max_latency_ms']:.2f}"
])
distribution_headers = ["模型", "批次", "最小值", "P50", "P95", "P99", "最大值"]
print(tabulate(distribution_data, headers=distribution_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 5. 资源使用情况表
print("\n💻 资源使用情况")
print("-" * 50)
resource_data = []
for model_name, batch_results in results.items():
for batch_size, result in batch_results.items():
resource_data.append([
model_name,
batch_size,
f"{result['cpu_usage_percent']:.1f}%",
f"{result['memory_usage_mb']:.1f} MB"
])
resource_headers = ["模型", "批次", "CPU使用率", "内存使用"]
print(tabulate(resource_data, headers=resource_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 6. 性能排名表
print("\n🏆 性能排名")
print("-" * 50)
# 按批次大小为1的延迟排名
ranking_data = []
batch_1_results = []
for model_name, batch_results in results.items():
if 1 in batch_results:
result = batch_results[1]
batch_1_results.append((
model_name,
result['mean_latency_ms'],
result['throughput_qps'],
result['p95_latency_ms']
))
# 按平均延迟排序
batch_1_results.sort(key=lambda x: x[1])
for i, (model, latency, qps, p95) in enumerate(batch_1_results, 1):
ranking_data.append([
i,
model,
f"{latency:.2f} ms",
f"{qps:.2f} QPS",
f"{p95:.2f} ms"
])
ranking_headers = ["排名", "模型", "平均延迟", "吞吐量", "P95延迟"]
print(tabulate(ranking_data, headers=ranking_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 7. 批次大小效率分析
print("\n📊 批次大小效率分析")
print("-" * 50)
efficiency_data = []
for model_name, batch_results in results.items():
if len(batch_results) > 1:
batch_sizes_sorted = sorted(batch_results.keys())
base_qps = batch_results[batch_sizes_sorted[0]]['throughput_qps']
for batch_size in batch_sizes_sorted:
result = batch_results[batch_size]
current_qps = result['throughput_qps']
efficiency = (current_qps / base_qps) * 100
per_sample_latency = result['mean_latency_ms'] / batch_size
efficiency_data.append([
model_name,
batch_size,
f"{current_qps:.2f}",
f"{efficiency:.1f}%",
f"{per_sample_latency:.2f}"
])
efficiency_headers = ["模型", "批次大小", "吞吐量(QPS)", "相对效率", "单样本延迟(ms)"]
print(tabulate(efficiency_data, headers=efficiency_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 8. 总结和建议
print("\n💡 性能分析总结")
print("-" * 50)
if batch_1_results:
fastest_model = batch_1_results[0][0]
fastest_latency = batch_1_results[0][1]
highest_qps_model = max(batch_1_results, key=lambda x: x[2])
print(f"🥇 最快模型: {fastest_model} ({fastest_latency:.2f} ms)")
print(f"🚀 最高吞吐量: {highest_qps_model[0]} ({highest_qps_model[2]:.2f} QPS)")
# 模型类型分析
vision_models = []
nlp_models = []
for model_name, batch_results in results.items():
if batch_results:
model_type = list(batch_results.values())[0]['model_type']
if model_type == 'vision':
vision_models.append(model_name)
elif 'nlp' in model_type:
nlp_models.append(model_name)
if vision_models:
print(f"🖼️ 视觉模型: {', '.join(vision_models)}")
if nlp_models:
print(f"📝 NLP模型: {', '.join(nlp_models)}")
print(f"\n📋 测试配置:")
print(f" - 测试次数: {list(results.values())[0][1]['num_runs']} 次")
print(f" - 执行提供者: CPUExecutionProvider")
print(f" - 测试时间: {time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}")
def run_single_thread_benchmark():
"""运行单线程基准测试"""
models = {
'ResNet50': 'models/resnet50.onnx',
'BERT-Base': 'models/bert_base.onnx',
'MobileNetV2': 'models/mobilenet_v2.onnx',
'DistilBERT': 'models/distilbert.onnx'
}
results = {}
for model_name, model_path in models.items():
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
print(f"模型文件不存在: {model_path}")
continue
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"测试模型: {model_name}")
print(f"{'='*60}")
try:
benchmark = ONNXBenchmark(model_path)
# 根据模型类型选择合适的批次大小
if benchmark.model_type == "vision":
batch_sizes = [1, 4, 8, 16] # 视觉模型支持较大批次
elif benchmark.model_type.startswith("nlp"):
batch_sizes = [1, 2, 4] # NLP 模型内存消耗大,使用较小批次
else:
batch_sizes = [1, 4, 8] # 未知模型使用保守批次
results[model_name] = {}
for batch_size in batch_sizes:
print(f"\n--- 批次大小: {batch_size} ---")
try:
result = benchmark.benchmark_latency(num_runs=50, batch_size=batch_size) # 减少测试次数以加快调试
results[model_name][batch_size] = result
print(f"模型类型: {result['model_type']}")
print(f"输入形状: {result['input_shapes']}")
print(f"输入数据类型: {result['input_dtypes']}")
print(f"平均延迟: {result['mean_latency_ms']:.2f} ± {result['std_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f"P50延迟: {result['p50_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f"P95延迟: {result['p95_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f"P99延迟: {result['p99_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f"吞吐量: {result['throughput_qps']:.2f} QPS")
print(f"CPU使用率: {result['cpu_usage_percent']:.1f}%")
print(f"内存使用: {result['memory_usage_mb']:.1f} MB")
except Exception as e:
print(f"批次大小 {batch_size} 测试失败: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
continue
except Exception as e:
print(f"模型 {model_name} 初始化失败: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
continue
# 保存结果到文件
with open('single_thread_results.json', 'w') as f:
# 移除 raw_latencies 以减少文件大小
clean_results = {}
for model, batch_results in results.items():
clean_results[model] = {}
for batch_size, result in batch_results.items():
clean_result = result.copy()
clean_result.pop('raw_latencies', None)
clean_results[model][batch_size] = clean_result
json.dump(clean_results, f, indent=2)
return results
if __name__ == "__main__":
results = run_single_thread_benchmark()
# 生成详细的分析表格
generate_analysis_tables(results)
print(f"\n✅ 测试结果已保存到: single_thread_results.json")
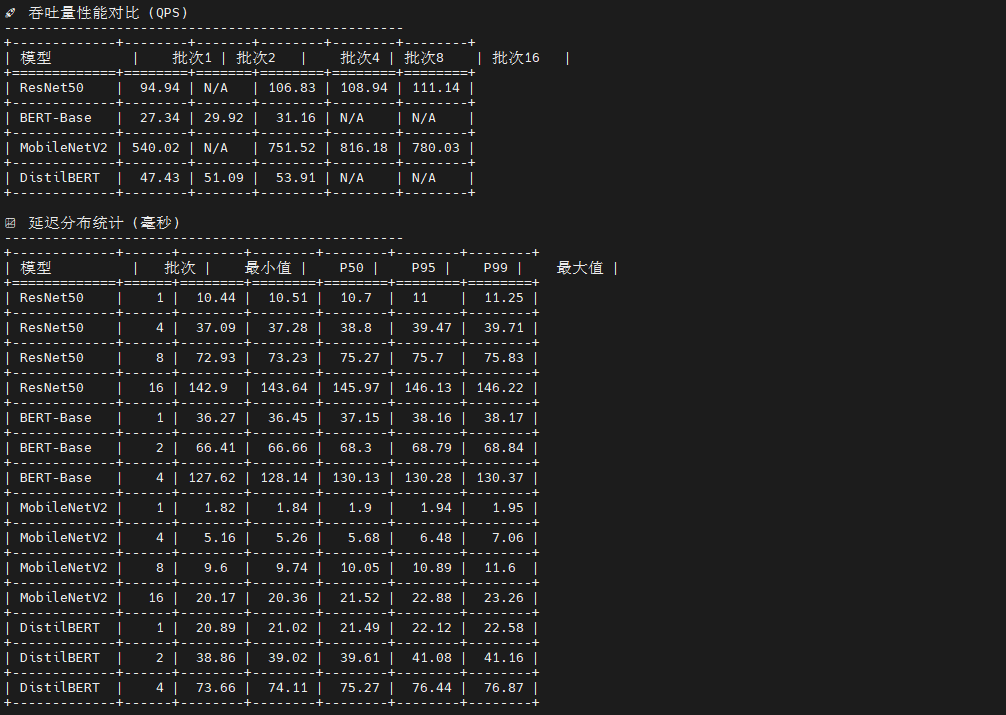
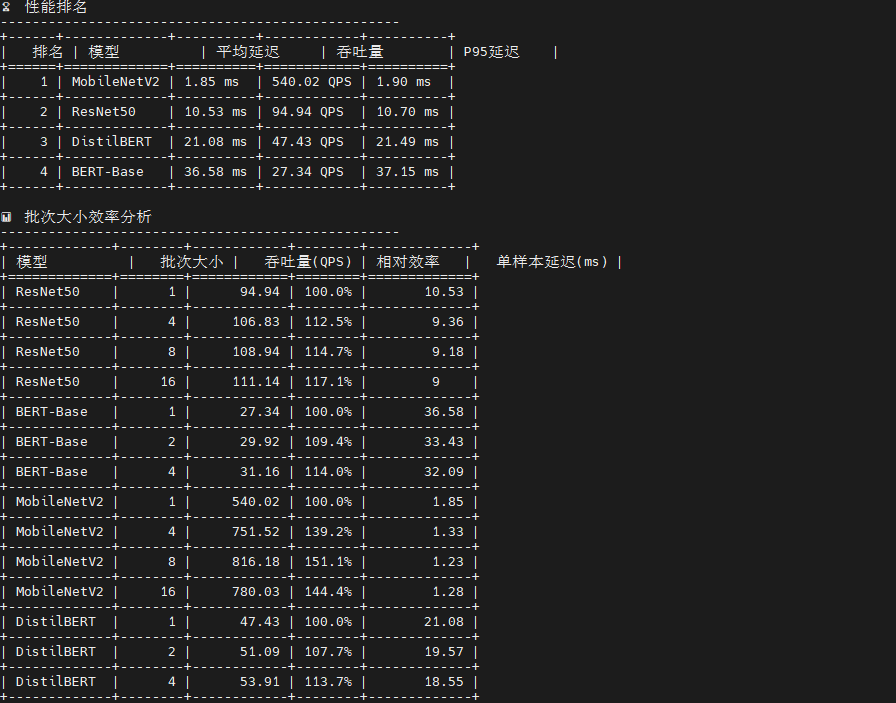
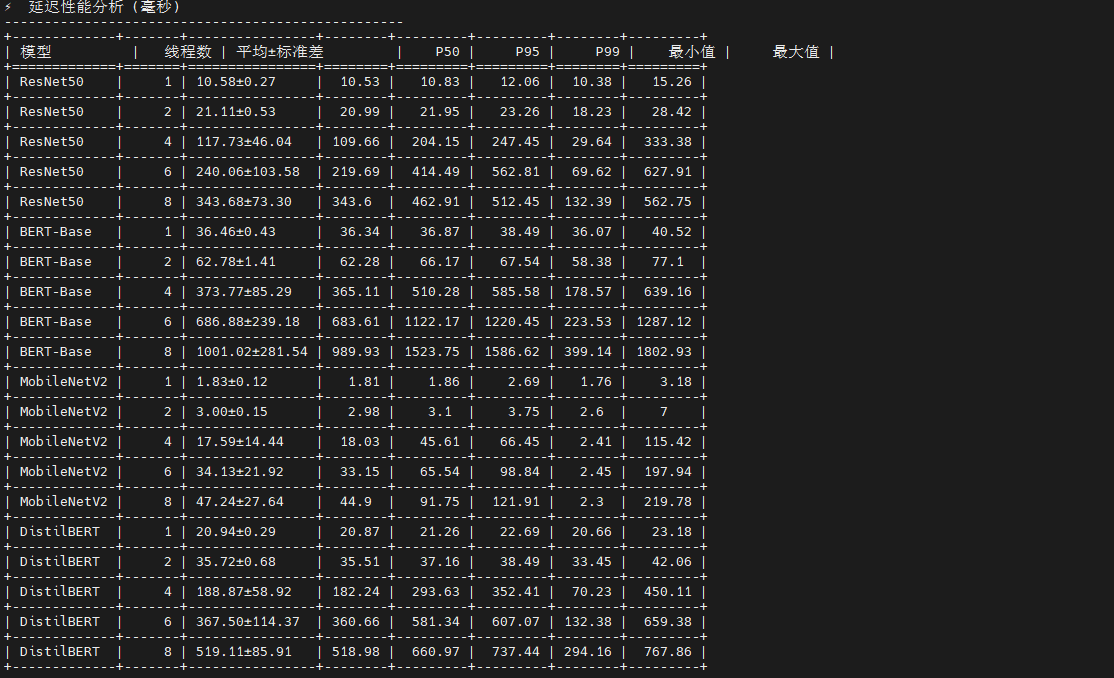
print("🎉 单线程基准测试完成!")测试结果显示了四个模型在不同批次大小下的性能表现差异显著:
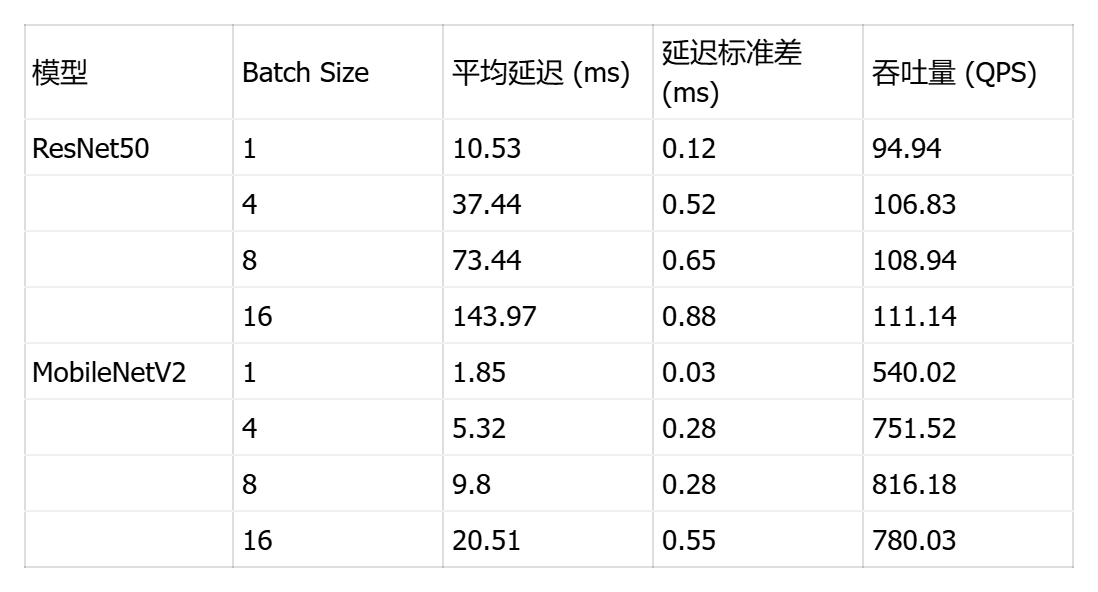
视觉模型方面 ,MobileNetV2 展现出卓越的单样本推理能力,batch=1 时延迟仅 1.85ms(吞吐量 540 QPS),在 batch=8 时达到最佳吞吐量 816 QPS,证明其轻量级架构(0.3B 运算量)非常适合边缘设备和实时场景;ResNet50 虽然延迟较高(batch=1 时 10.53ms),但随批次增大表现出良好的吞吐量扩展性(batch=16 达 111 QPS),其稳定的标准差(<1ms)显示推理过程高度可预测。
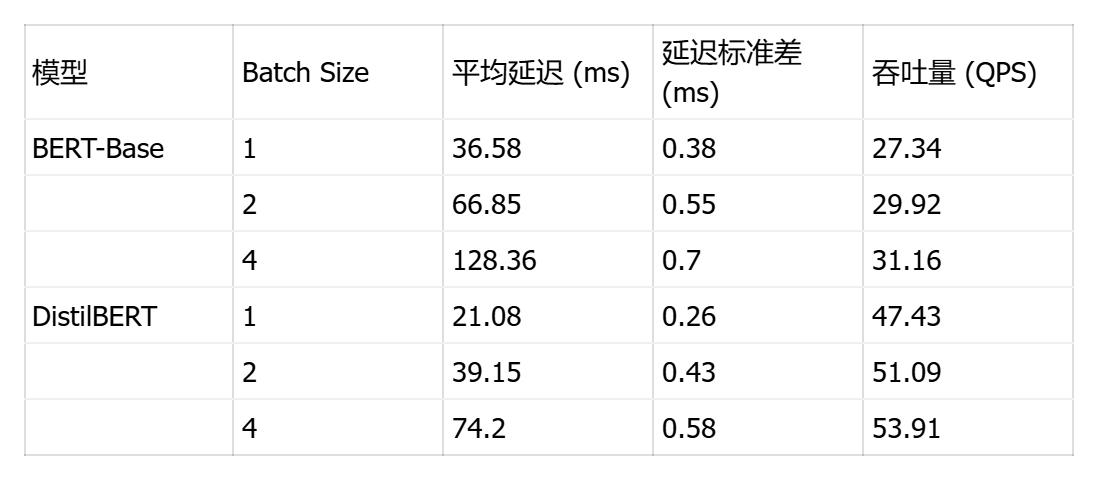
NLP 模型方面 ,DistilBERT 作为 BERT 的蒸馏版本优势明显,单样本延迟 21.08ms 仅为 BERT-Base(36.58ms)的 58%,吞吐量提升 73%(47.43 vs 27.34 QPS),在保持较高精度的同时大幅降低计算成本;BERT-Base 的批处理效率较低,batch=4 时延迟达 128ms,说明其 22.5B 的巨大运算量在单线程环境下成为瓶颈。
关键发现:所有模型的延迟标准差均小于 1ms,证明 ONNX Runtime 在 openEuler 上的推理稳定性优异;批次大小对吞吐量的影响呈非线性,MobileNetV2 在 batch=8 后出现性能拐点(batch=16 时吞吐量反降至 780 QPS),提示存在内存带宽或缓存失效瓶颈;NLP 模型的批处理收益远低于视觉模型,建议生产环境中视觉任务采用 batch=4-8,NLP 任务保持 batch=1-2 以平衡延迟与吞吐。
4.2 多线程并发性能测试
通过touch benchmark_concurrent.py创建多线程并发性能测试脚本,通过pythonbenchmark_concurrent.py执行脚本测试
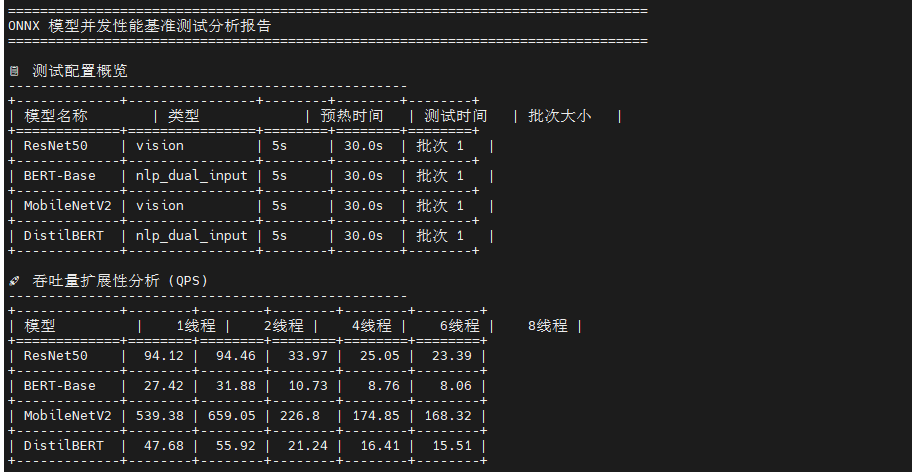
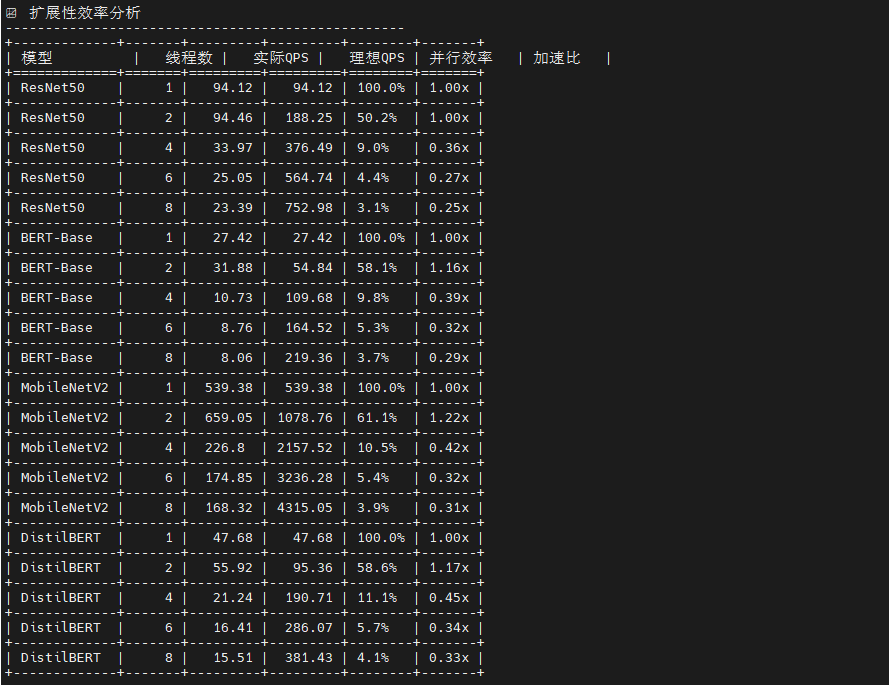
这是一个多线程并发推理性能测试框架 ,核心创新是会话隔离架构 :为每个线程创建独立的 ONNX Runtime 会话,避免 GIL 锁竞争,实现真正的并行推理。脚本通过队列驱动的无锁工作模式 (预填充 5×线程数的输入数据)和预热-测试分离机制 (前 5 秒预热 CPU 缓存)确保数据准确性。测试流程采用自适应线程数选择 (根据物理核心数动态生成 1/2/4/8/16/24 线程配置),并通过负载均衡监控(变异系数 CV)评估线程间工作分配均匀性。最终输出7类分析表格:吞吐量扩展性(对比各线程数 QPS)、延迟分布(P50/P95/P99)、扩展性效率 (并行效率 = 实际QPS/理想QPS,揭示内存带宽瓶颈)、资源使用(CPU/内存增量)和最佳配置推荐。关键指标包括加速比 (多线程 QPS / 单线程 QPS,理想值等于线程数)和并行效率(衡量硬件利用率,低于 80% 表示存在瓶颈),帮助确定最优线程数以平衡吞吐量与资源消耗。
python
# benchmark_concurrent.py
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
import time
import threading
import queue
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor, as_completed
import psutil
import os
import json
from typing import Dict, List, Tuple
from tabulate import tabulate
import pandas as pd
class ConcurrentBenchmark:
def __init__(self, model_path: str, num_threads: int = 4):
self.model_path = model_path
self.num_threads = num_threads
self.sessions = []
print(f"创建 {num_threads} 个推理会话...")
# 为每个线程创建独立的推理会话
for i in range(num_threads):
session = ort.InferenceSession(
model_path,
providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']
)
self.sessions.append(session)
if (i + 1) % 4 == 0 or i == num_threads - 1:
print(f" 已创建 {i + 1}/{num_threads} 个会话")
# 获取模型信息
sample_session = self.sessions[0]
self.input_names = [input.name for input in sample_session.get_inputs()]
self.output_names = [output.name for output in sample_session.get_outputs()]
self.input_shapes = [input.shape for input in sample_session.get_inputs()]
self.input_types = [input.type for input in sample_session.get_inputs()]
# 确定模型类型
self.model_type = self._determine_model_type()
print(f"检测到模型类型: {self.model_type}")
def _determine_model_type(self) -> str:
"""根据输入特征确定模型类型"""
if len(self.input_names) == 1:
input_shape = self.input_shapes[0]
if len(input_shape) == 4 and input_shape[1] == 3: # [batch, 3, H, W]
return "vision"
elif len(input_shape) == 2: # [batch, seq_len]
return "nlp_single_input"
elif len(self.input_names) == 2:
# 通常是 NLP 模型,有 input_ids 和 attention_mask
return "nlp_dual_input"
return "unknown"
def _get_numpy_dtype(self, onnx_type: str) -> np.dtype:
"""将 ONNX 数据类型转换为 numpy 数据类型"""
type_mapping = {
'tensor(float)': np.float32,
'tensor(float32)': np.float32,
'tensor(float64)': np.float64,
'tensor(double)': np.float64,
'tensor(int32)': np.int32,
'tensor(int64)': np.int64,
'tensor(int8)': np.int8,
'tensor(uint8)': np.uint8,
'tensor(bool)': np.bool_,
}
return type_mapping.get(onnx_type, np.float32)
def generate_random_inputs(self, batch_size: int = 1) -> Dict[str, np.ndarray]:
"""根据模型类型生成正确的输入数据"""
inputs = {}
if self.model_type == "vision":
# 视觉模型:ResNet50, MobileNetV2
input_name = self.input_names[0]
shape = self.input_shapes[0]
input_type = self.input_types[0]
# 处理动态批次维度
actual_shape = [batch_size if (isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1) else dim
for dim in shape]
# 使用正确的数据类型
dtype = self._get_numpy_dtype(input_type)
# 生成标准化的图像数据 (ImageNet 预处理)
inputs[input_name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(dtype)
elif self.model_type == "nlp_single_input":
# 单输入 NLP 模型
input_name = self.input_names[0]
shape = self.input_shapes[0]
input_type = self.input_types[0]
actual_shape = [batch_size if (isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1) else dim
for dim in shape]
dtype = self._get_numpy_dtype(input_type)
if 'int' in str(dtype):
# 生成 token IDs
inputs[input_name] = np.random.randint(1, 30522, actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
# 如果期望浮点数,生成浮点数
inputs[input_name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(dtype)
elif self.model_type == "nlp_dual_input":
# 双输入 NLP 模型:BERT, DistilBERT
# 默认序列长度
default_seq_len = 128
for i, (name, shape, input_type) in enumerate(zip(self.input_names, self.input_shapes, self.input_types)):
# 处理动态维度
actual_shape = []
for dim in shape:
if isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1:
if 'batch' in str(dim).lower():
actual_shape.append(batch_size)
elif 'sequence' in str(dim).lower() or 'seq' in str(dim).lower():
actual_shape.append(default_seq_len)
else:
actual_shape.append(batch_size) # 默认为批次维度
else:
actual_shape.append(dim)
dtype = self._get_numpy_dtype(input_type)
if 'input_ids' in name.lower() or 'token' in name.lower():
if 'int' in str(dtype):
# Token IDs: 1-30521 (避免 0 和特殊 token)
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(1, 30522, actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
# 如果期望浮点数,将 token IDs 转换为浮点数
token_ids = np.random.randint(1, 30522, actual_shape)
inputs[name] = token_ids.astype(dtype)
elif 'attention_mask' in name.lower() or 'mask' in name.lower():
if 'int' in str(dtype):
# Attention mask: 全1表示所有位置都参与注意力计算
inputs[name] = np.ones(actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
# 如果期望浮点数
inputs[name] = np.ones(actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
elif 'token_type' in name.lower():
if 'int' in str(dtype):
# Token type IDs: 全0表示单句输入
inputs[name] = np.zeros(actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
inputs[name] = np.zeros(actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
# 其他输入类型
if 'int' in str(dtype):
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 100, actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(dtype)
else:
# 未知模型类型,使用通用方法
for i, (name, shape, input_type) in enumerate(zip(self.input_names, self.input_shapes, self.input_types)):
actual_shape = [batch_size if (isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1) else dim
for dim in shape]
dtype = self._get_numpy_dtype(input_type)
if 'int' in str(dtype):
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 1000, actual_shape, dtype=dtype)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(dtype)
return inputs
def worker_inference(self, thread_id, session, inputs_queue, results_queue, duration_seconds, warmup_seconds=5):
"""工作线程推理函数"""
start_time = time.time()
warmup_end_time = start_time + warmup_seconds
inference_count = 0
warmup_count = 0
latencies = []
print(f"线程 {thread_id} 开始预热...")
while time.time() < start_time + duration_seconds + warmup_seconds:
try:
inputs = inputs_queue.get_nowait()
inference_start = time.perf_counter()
outputs = session.run(self.output_names, inputs)
inference_end = time.perf_counter()
latency = (inference_end - inference_start) * 1000
current_time = time.time()
if current_time < warmup_end_time:
# 预热阶段,不记录延迟
warmup_count += 1
else:
# 正式测试阶段
latencies.append(latency)
inference_count += 1
# 将输入放回队列以供重复使用
inputs_queue.put(inputs)
except queue.Empty:
# 如果队列为空,生成新的输入
inputs = self.generate_random_inputs()
inputs_queue.put(inputs)
continue
print(f"线程 {thread_id} 完成,预热: {warmup_count} 次,推理: {inference_count} 次")
results_queue.put({
'thread_id': thread_id,
'inference_count': inference_count,
'warmup_count': warmup_count,
'latencies': latencies
})
def benchmark_concurrent(self, duration_seconds: int = 60, batch_size: int = 1, warmup_seconds: int = 5):
"""并发推理基准测试"""
print(f"开始并发测试: {self.num_threads} 线程, 预热 {warmup_seconds}s, 测试 {duration_seconds}s")
# 准备输入队列
inputs_queue = queue.Queue()
for _ in range(self.num_threads * 5): # 预填充更多队列项
inputs = self.generate_random_inputs(batch_size)
inputs_queue.put(inputs)
results_queue = queue.Queue()
# 监控系统资源
process = psutil.Process()
cpu_percent_before = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
memory_before = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024 # MB
# 启动工作线程
threads = []
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(self.num_threads):
thread = threading.Thread(
target=self.worker_inference,
args=(i, self.sessions[i], inputs_queue, results_queue, duration_seconds, warmup_seconds)
)
thread.start()
threads.append(thread)
# 实时监控进度
monitor_thread = threading.Thread(target=self._monitor_progress, args=(duration_seconds + warmup_seconds,))
monitor_thread.daemon = True
monitor_thread.start()
# 等待所有线程完成
for thread in threads:
thread.join()
end_time = time.time()
actual_duration = end_time - start_time - warmup_seconds # 减去预热时间
# 收集结果
total_inferences = 0
total_warmup = 0
all_latencies = []
thread_results = []
while not results_queue.empty():
result = results_queue.get()
total_inferences += result['inference_count']
total_warmup += result['warmup_count']
all_latencies.extend(result['latencies'])
thread_results.append(result)
# 监控系统资源
cpu_percent_after = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)
memory_after = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024 # MB
# 计算线程负载均衡
inference_counts = [r['inference_count'] for r in thread_results]
load_balance_std = np.std(inference_counts) / np.mean(inference_counts) * 100 if inference_counts else 0
return {
'model_type': self.model_type,
'num_threads': self.num_threads,
'batch_size': batch_size,
'warmup_seconds': warmup_seconds,
'duration_seconds': actual_duration,
'total_inferences': total_inferences,
'total_warmup': total_warmup,
'throughput_qps': total_inferences / actual_duration if actual_duration > 0 else 0,
'mean_latency_ms': np.mean(all_latencies) if all_latencies else 0,
'std_latency_ms': np.std(all_latencies) if all_latencies else 0,
'min_latency_ms': np.min(all_latencies) if all_latencies else 0,
'max_latency_ms': np.max(all_latencies) if all_latencies else 0,
'p50_latency_ms': np.percentile(all_latencies, 50) if all_latencies else 0,
'p95_latency_ms': np.percentile(all_latencies, 95) if all_latencies else 0,
'p99_latency_ms': np.percentile(all_latencies, 99) if all_latencies else 0,
'cpu_usage_percent': cpu_percent_after - cpu_percent_before,
'memory_usage_mb': memory_after - memory_before,
'load_balance_cv': load_balance_std, # 负载均衡系数 (变异系数)
'thread_results': thread_results
}
def _monitor_progress(self, total_duration):
"""监控测试进度"""
start_time = time.time()
while time.time() - start_time < total_duration:
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
progress = min(100, (elapsed / total_duration) * 100)
print(f"\r 测试进度: {progress:.1f}% ({elapsed:.1f}s/{total_duration:.1f}s)", end="", flush=True)
time.sleep(2)
print() # 换行
def generate_concurrent_analysis_tables(results: Dict) -> None:
"""生成并发测试分析表格"""
print("\n" + "="*80)
print("ONNX 模型并发性能基准测试分析报告")
print("="*80)
# 1. 测试配置概览
print("\n测试配置概览")
print("-" * 50)
config_data = []
for model_name, thread_results in results.items():
if thread_results:
first_result = list(thread_results.values())[0]
config_data.append([
model_name,
first_result['model_type'],
f"{first_result['warmup_seconds']}s",
f"{first_result['duration_seconds']:.1f}s",
f"批次 {first_result['batch_size']}"
])
config_headers = ["模型名称", "类型", "预热时间", "测试时间", "批次大小"]
print(tabulate(config_data, headers=config_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 2. 吞吐量扩展性分析
print("\n吞吐量扩展性分析 (QPS)")
print("-" * 50)
throughput_data = []
thread_counts = set()
# 收集所有线程数
for thread_results in results.values():
thread_counts.update(thread_results.keys())
thread_counts = sorted(thread_counts)
for model_name, thread_results in results.items():
row = [model_name]
for thread_count in thread_counts:
if thread_count in thread_results:
qps = thread_results[thread_count]['throughput_qps']
row.append(f"{qps:.2f}")
else:
row.append("N/A")
throughput_data.append(row)
throughput_headers = ["模型"] + [f"{tc}线程" for tc in thread_counts]
print(tabulate(throughput_data, headers=throughput_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 3. 延迟性能分析
print("\n延迟性能分析 (毫秒)")
print("-" * 50)
latency_data = []
for model_name, thread_results in results.items():
for thread_count, result in thread_results.items():
latency_data.append([
model_name,
thread_count,
f"{result['mean_latency_ms']:.2f}±{result['std_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['p50_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['p95_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['p99_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['min_latency_ms']:.2f}",
f"{result['max_latency_ms']:.2f}"
])
latency_headers = ["模型", "线程数", "平均±标准差", "P50", "P95", "P99", "最小值", "最大值"]
print(tabulate(latency_data, headers=latency_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 4. 扩展性效率分析
print("\n扩展性效率分析")
print("-" * 50)
scalability_data = []
for model_name, thread_results in results.items():
thread_counts_sorted = sorted(thread_results.keys())
if len(thread_counts_sorted) > 1:
base_qps = thread_results[thread_counts_sorted[0]]['throughput_qps']
for thread_count in thread_counts_sorted:
result = thread_results[thread_count]
current_qps = result['throughput_qps']
# 计算扩展性指标
linear_expected = base_qps * thread_count
efficiency = (current_qps / linear_expected) * 100 if linear_expected > 0 else 0
speedup = current_qps / base_qps if base_qps > 0 else 0
scalability_data.append([
model_name,
thread_count,
f"{current_qps:.2f}",
f"{linear_expected:.2f}",
f"{efficiency:.1f}%",
f"{speedup:.2f}x"
])
scalability_headers = ["模型", "线程数", "实际QPS", "理想QPS", "并行效率", "加速比"]
print(tabulate(scalability_data, headers=scalability_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 5. 资源使用分析
print("\n资源使用分析")
print("-" * 50)
resource_data = []
for model_name, thread_results in results.items():
for thread_count, result in thread_results.items():
resource_data.append([
model_name,
thread_count,
f"{result['cpu_usage_percent']:.1f}%",
f"{result['memory_usage_mb']:.1f} MB",
f"{result['load_balance_cv']:.1f}%",
f"{result['total_inferences']}"
])
resource_headers = ["模型", "线程数", "CPU使用率", "内存使用", "负载均衡CV", "总推理次数"]
print(tabulate(resource_data, headers=resource_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 6. 最佳性能配置推荐
print("\n最佳性能配置推荐")
print("-" * 50)
best_config_data = []
for model_name, thread_results in results.items():
# 找到最高吞吐量的配置
best_qps_config = max(thread_results.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]['throughput_qps'])
best_threads, best_result = best_qps_config
# 找到最低延迟的配置
best_latency_config = min(thread_results.items(), key=lambda x: x[1]['mean_latency_ms'])
best_lat_threads, best_lat_result = best_latency_config
best_config_data.append([
model_name,
f"{best_threads} 线程",
f"{best_result['throughput_qps']:.2f} QPS",
f"{best_lat_threads} 线程",
f"{best_lat_result['mean_latency_ms']:.2f} ms"
])
best_config_headers = ["模型", "最佳吞吐量配置", "最高QPS", "最佳延迟配置", "最低延迟"]
print(tabulate(best_config_data, headers=best_config_headers, tablefmt="grid"))
# 7. 性能总结
print("\n性能分析总结")
print("-" * 50)
# 计算整体统计
all_qps_values = []
all_latency_values = []
for thread_results in results.values():
for result in thread_results.values():
all_qps_values.append(result['throughput_qps'])
all_latency_values.append(result['mean_latency_ms'])
if all_qps_values:
print(f"最高吞吐量: {max(all_qps_values):.2f} QPS")
print(f"最低延迟: {min(all_latency_values):.2f} ms")
print(f"平均吞吐量: {np.mean(all_qps_values):.2f} QPS")
print(f"平均延迟: {np.mean(all_latency_values):.2f} ms")
# CPU 核心数信息
cpu_count = psutil.cpu_count(logical=False)
logical_cpu_count = psutil.cpu_count(logical=True)
print(f"系统信息: {cpu_count} 物理核心, {logical_cpu_count} 逻辑核心")
print(f"\n测试配置:")
print(f" - 执行提供者: CPUExecutionProvider")
print(f" - 测试时间: {time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')}")
def run_concurrent_benchmark():
"""运行并发基准测试"""
models = {
'ResNet50': 'models/resnet50.onnx',
'BERT-Base': 'models/bert_base.onnx',
'MobileNetV2': 'models/mobilenet_v2.onnx',
'DistilBERT': 'models/distilbert.onnx'
}
# 根据 CPU 核心数确定测试的线程数
cpu_count = psutil.cpu_count(logical=False) # 物理核心数
logical_cpu_count = psutil.cpu_count(logical=True) # 逻辑核心数
print(f"系统信息: {cpu_count} 物理核心, {logical_cpu_count} 逻辑核心")
# 智能选择线程数
thread_counts = [1, 2, 4]
if cpu_count >= 6:
thread_counts.extend([6, 8])
if cpu_count >= 12:
thread_counts.extend([12, 16])
if cpu_count >= 20:
thread_counts.extend([20, 24])
# 限制最大线程数不超过逻辑核心数
thread_counts = [t for t in thread_counts if t <= logical_cpu_count]
print(f"将测试线程数: {thread_counts}")
results = {}
for model_name, model_path in models.items():
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
print(f"模型文件不存在: {model_path}")
continue
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"并发测试模型: {model_name}")
print(f"{'='*60}")
results[model_name] = {}
for num_threads in thread_counts:
print(f"\n--- 线程数: {num_threads} ---")
try:
benchmark = ConcurrentBenchmark(model_path, num_threads)
result = benchmark.benchmark_concurrent(
duration_seconds=30, # 测试时间
batch_size=1, # 批次大小
warmup_seconds=5 # 预热时间
)
results[model_name][num_threads] = result
print(f"模型类型: {result['model_type']}")
print(f"总推理次数: {result['total_inferences']}")
print(f"预热次数: {result['total_warmup']}")
print(f"实际测试时间: {result['duration_seconds']:.1f} 秒")
print(f"吞吐量: {result['throughput_qps']:.2f} QPS")
print(f"平均延迟: {result['mean_latency_ms']:.2f} ± {result['std_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f"P95延迟: {result['p95_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f"P99延迟: {result['p99_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f"CPU使用率: {result['cpu_usage_percent']:.1f}%")
print(f"内存使用: {result['memory_usage_mb']:.1f} MB")
print(f"负载均衡CV: {result['load_balance_cv']:.1f}%")
except Exception as e:
print(f"线程数 {num_threads} 测试失败: {e}")
import traceback
traceback.print_exc()
continue
# 保存结果到文件
with open('concurrent_results.json', 'w') as f:
# 清理结果以减少文件大小
clean_results = {}
for model, thread_results in results.items():
clean_results[model] = {}
for num_threads, result in thread_results.items():
clean_result = result.copy()
# 移除详细的线程结果以减少文件大小
if 'thread_results' in clean_result:
thread_summary = []
for tr in clean_result['thread_results']:
thread_summary.append({
'thread_id': tr['thread_id'],
'inference_count': tr['inference_count'],
'warmup_count': tr['warmup_count'],
'avg_latency': np.mean(tr['latencies']) if tr['latencies'] else 0
})
clean_result['thread_summary'] = thread_summary
clean_result.pop('thread_results', None)
clean_results[model][num_threads] = clean_result
json.dump(clean_results, f, indent=2)
return results
if __name__ == "__main__":
results = run_concurrent_benchmark()
# 生成详细的分析表格
generate_concurrent_analysis_tables(results)
print(f"\n测试结果已保存到: concurrent_results.json")
print("并发基准测试完成!")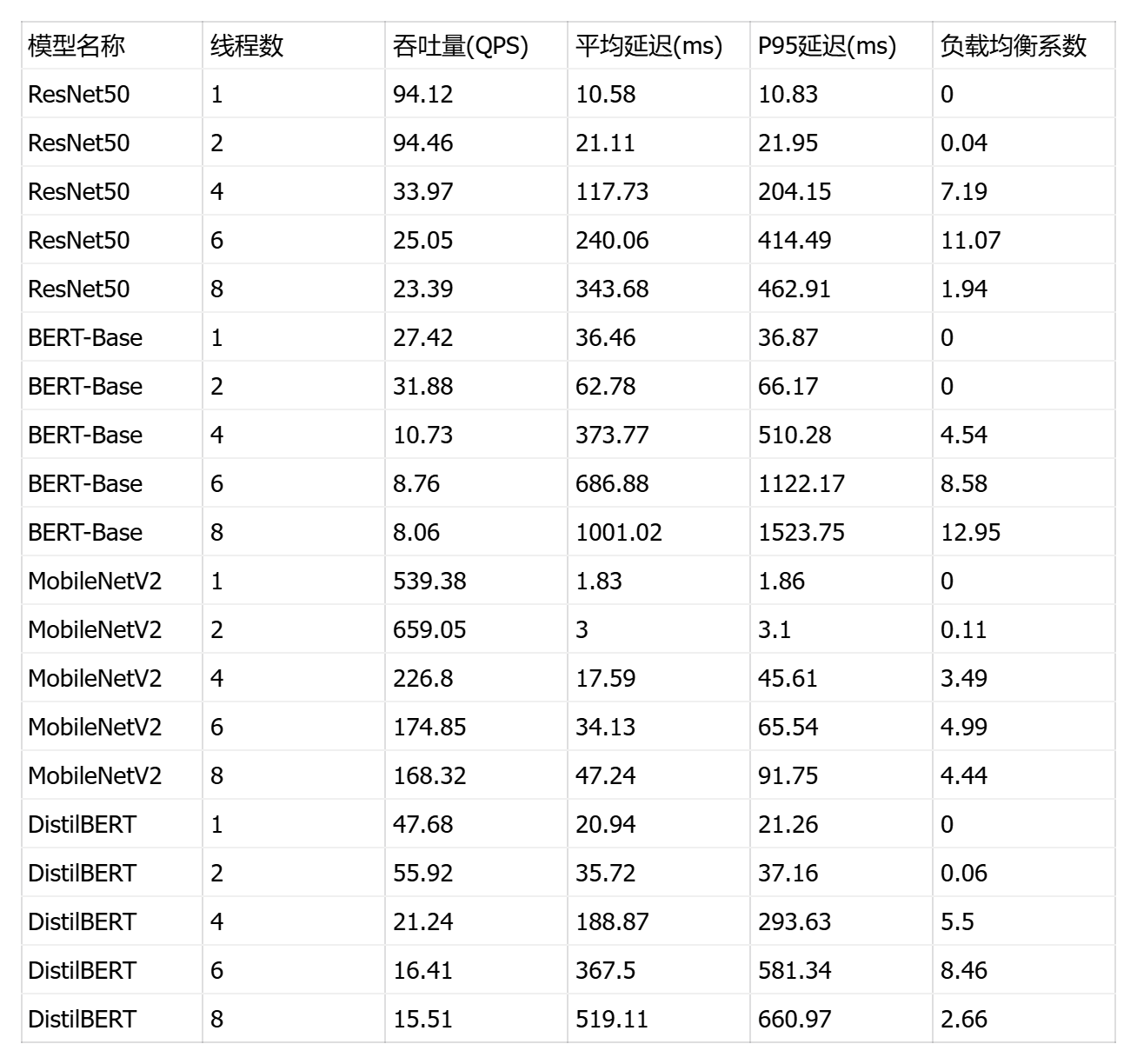
五、性能优化配置测试
5.1 ONNX Runtime 提供商配置优化
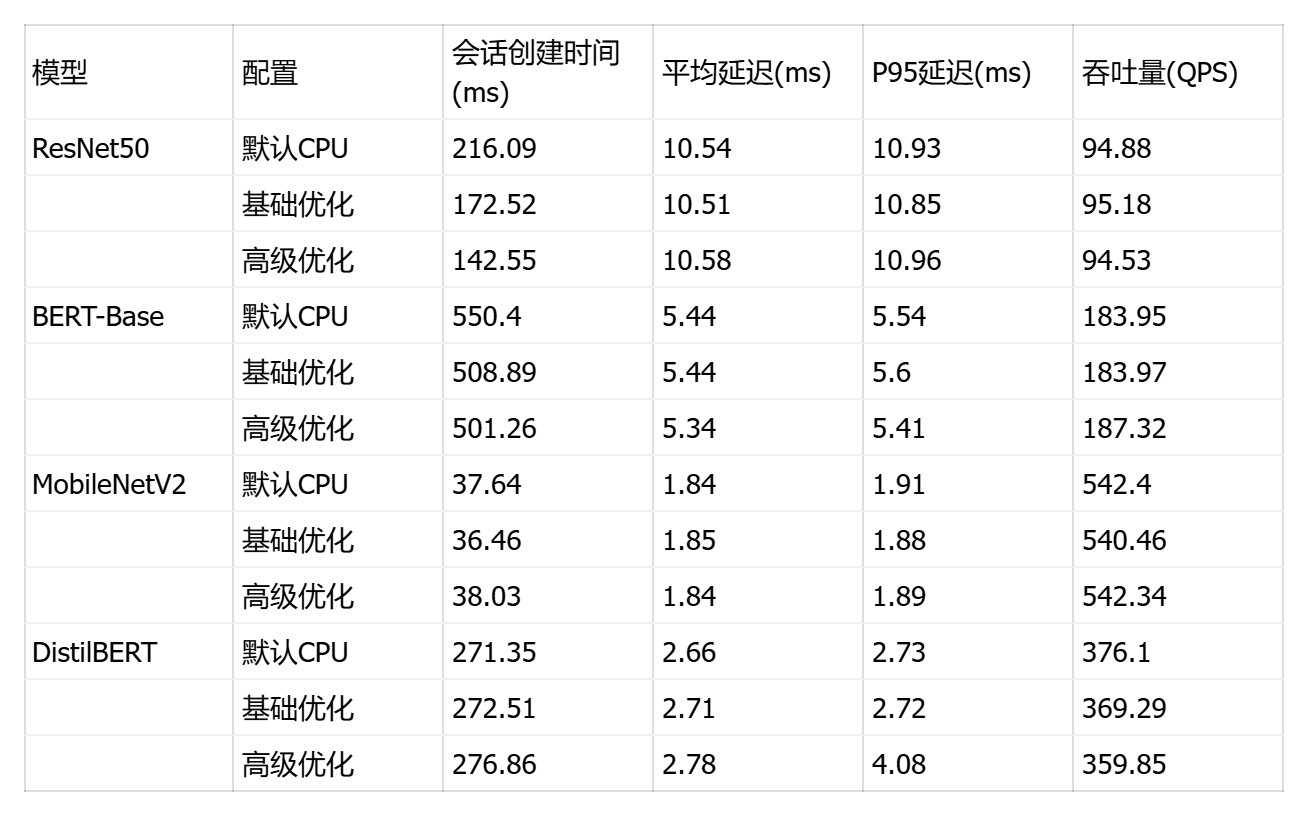
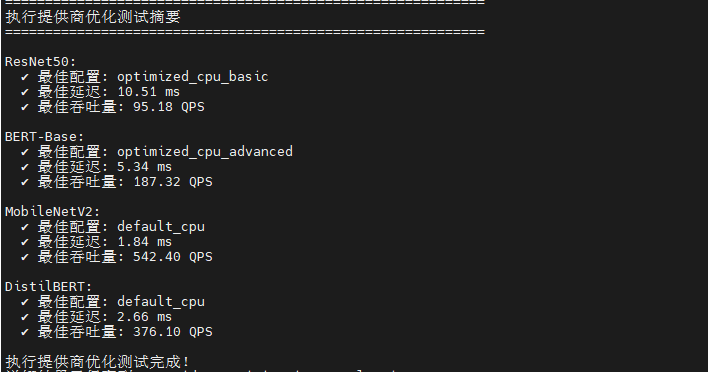
这是一个ONNX Runtime 执行提供商配置对比测试框架 ,核心目标是评估不同 CPU 执行提供商参数对推理性能的影响。脚本设计了3种配置梯度:默认配置(无优化)、基础优化(启用内存池 enable_cpu_mem_arena + 按需分配策略 kSameAsRequested)、高级优化(内存池 + 2次幂扩展策略 kNextPowerOfTwo + Arena 分配器),通过控制变量法隔离内存管理策略的性能差异。
python
# optimization_providers.py
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
import time
import psutil
import os
import json
from typing import Dict, List, Any
class ProviderOptimizationBenchmark:
def __init__(self, model_path: str, model_name: str = ""):
self.model_path = model_path
self.model_name = model_name.lower() if model_name else ""
def get_provider_configs(self) -> Dict[str, Dict]:
"""获取不同的执行提供商配置"""
return {
'default_cpu': {
'providers': ['CPUExecutionProvider'],
'provider_options': [{}],
'description': '默认 CPU 提供商配置'
},
'optimized_cpu_basic': {
'providers': ['CPUExecutionProvider'],
'provider_options': [{
'enable_cpu_mem_arena': True,
'arena_extend_strategy': 'kSameAsRequested'
}],
'description': '基础优化 CPU 配置'
},
'optimized_cpu_advanced': {
'providers': ['CPUExecutionProvider'],
'provider_options': [{
'enable_cpu_mem_arena': True,
'arena_extend_strategy': 'kNextPowerOfTwo',
'cpu_allocator': 'arena'
}],
'description': '高级优化 CPU 配置'
}
}
def create_session_with_config(self, config_name: str, config: Dict):
"""使用指定配置创建推理会话"""
session_options = ort.SessionOptions()
# 设置会话级别的优化选项
session_options.enable_cpu_mem_arena = True
session_options.enable_mem_pattern = True
session_options.enable_mem_reuse = True
session_options.execution_mode = ort.ExecutionMode.ORT_SEQUENTIAL
# 设置线程数 - 使用物理核心数
cpu_cores = psutil.cpu_count(logical=False) or 1
session_options.inter_op_num_threads = cpu_cores
session_options.intra_op_num_threads = cpu_cores
try:
return ort.InferenceSession(
self.model_path,
sess_options=session_options,
providers=config['providers'],
provider_options=config['provider_options']
)
except Exception as e:
print(f" ✗ 创建会话失败: {e}")
raise
def get_model_input_info(self, session) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""分析模型输入信息"""
input_info = {}
for input_tensor in session.get_inputs():
input_info[input_tensor.name] = {
'shape': input_tensor.shape,
'type': input_tensor.type,
'is_int64': 'int64' in input_tensor.type.lower()
}
return input_info
def generate_inputs(self, session):
"""生成模型输入,修复数据类型问题"""
inputs = {}
input_info = self.get_model_input_info(session)
for name, info in input_info.items():
shape = info['shape']
is_int64 = info['is_int64']
tensor_type = info['type']
# 处理动态维度
actual_shape = []
for dim in shape:
if isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1 or dim is None:
actual_shape.append(1) # 批次大小为1
else:
actual_shape.append(dim)
# 根据模型类型和输入名称确定数据类型
if is_int64 or 'int64' in tensor_type:
# BERT类模型的输入应该是int64
if 'bert' in self.model_name or 'distilbert' in self.model_name:
if 'input_ids' in name.lower() or 'token' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 30522, actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
elif 'attention_mask' in name.lower() or 'mask' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.ones(actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
elif 'token_type_ids' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.zeros(actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 100, actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
else:
# 其他模型的int64输入
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 100, actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
else:
# 浮点型输入
if 'image' in name.lower() or 'input' in name.lower():
# 图像输入通常需要归一化
inputs[name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(np.float32)
# 对于真实的图像输入,应该使用适当的预处理
# inputs[name] = (np.random.rand(*actual_shape) * 255).astype(np.float32)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(np.float32)
return inputs
def validate_inputs(self, session, inputs):
"""验证输入数据与模型期望的数据类型匹配"""
for input_tensor in session.get_inputs():
name = input_tensor.name
expected_type = input_tensor.type
if name not in inputs:
raise ValueError(f"缺少输入: {name}")
actual_type = inputs[name].dtype.name
expected_type_simple = expected_type.replace('tensor(', '').replace(')', '')
if 'float' in expected_type_simple and 'float' not in actual_type:
# 自动转换到正确的浮点类型
inputs[name] = inputs[name].astype(np.float32)
elif 'int64' in expected_type_simple and actual_type != 'int64':
# 自动转换到int64
inputs[name] = inputs[name].astype(np.int64)
def benchmark_config(self, config_name: str, config: Dict, num_runs: int = 100):
"""测试特定配置的性能"""
print(f"测试配置: {config_name} - {config['description']}")
try:
# 测量会话创建时间
session_start = time.perf_counter()
session = self.create_session_with_config(config_name, config)
session_end = time.perf_counter()
session_creation_time = (session_end - session_start) * 1000
# 生成并验证输入
inputs = self.generate_inputs(session)
self.validate_inputs(session, inputs)
output_names = [output.name for output in session.get_outputs()]
# 预热
print(" 预热中...")
for _ in range(5):
try:
_ = session.run(output_names, inputs)
except Exception as e:
print(f" 预热失败: {e}")
raise
# 性能测试
print(f" 开始性能测试 ({num_runs} 次)...")
latencies = []
# 监控资源使用
process = psutil.Process()
# 初始CPU使用率测量
process.cpu_percent()
memory_before = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
for i in range(num_runs):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
outputs = session.run(output_names, inputs)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
latencies.append((end_time - start_time) * 1000)
if (i + 1) % 25 == 0:
print(f" 已完成 {i + 1}/{num_runs}")
cpu_usage = process.cpu_percent()
memory_after = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
# 计算统计信息
latencies_array = np.array(latencies)
result = {
'config_name': config_name,
'description': config['description'],
'session_creation_time_ms': session_creation_time,
'mean_latency_ms': np.mean(latencies_array),
'std_latency_ms': np.std(latencies_array),
'min_latency_ms': np.min(latencies_array),
'max_latency_ms': np.max(latencies_array),
'p50_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies_array, 50),
'p95_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies_array, 95),
'p99_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies_array, 99),
'throughput_qps': 1000 / np.mean(latencies_array),
'cpu_usage_percent': cpu_usage,
'memory_usage_mb': memory_after - memory_before,
'status': 'success'
}
print(f" ✓ 会话创建时间: {result['session_creation_time_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f" ✓ 平均延迟: {result['mean_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f" ✓ P95延迟: {result['p95_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f" ✓ 吞吐量: {result['throughput_qps']:.2f} QPS")
print(f" ✓ CPU使用率: {result['cpu_usage_percent']:.1f}%")
print()
return result
except Exception as e:
print(f" ✗ 配置 {config_name} 测试失败: {e}")
return {
'config_name': config_name,
'description': config['description'],
'status': 'failed',
'error': str(e)
}
def run_all_configs(self):
"""运行所有配置的性能测试"""
configs = self.get_provider_configs()
results = {}
for config_name, config in configs.items():
result = self.benchmark_config(config_name, config)
results[config_name] = result
return results
def run_provider_optimization_test():
"""运行提供商优化测试"""
models = {
'ResNet50': 'models/resnet50.onnx',
'BERT-Base': 'models/bert_base.onnx',
'MobileNetV2': 'models/mobilenet_v2.onnx',
'DistilBERT': 'models/distilbert.onnx'
}
all_results = {}
for model_name, model_path in models.items():
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
print(f"模型文件不存在: {model_path},跳过测试")
continue
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"{model_name} 执行提供商优化测试")
print(f"{'='*60}")
benchmark = ProviderOptimizationBenchmark(model_path, model_name)
results = benchmark.run_all_configs()
all_results[model_name] = results
# 保存结果
with open('provider_optimization_results.json', 'w') as f:
# 转换numpy类型为Python原生类型以便JSON序列化
def convert_numpy_types(obj):
if isinstance(obj, (np.integer, np.floating)):
return obj.item()
elif isinstance(obj, np.ndarray):
return obj.tolist()
elif isinstance(obj, dict):
return {k: convert_numpy_types(v) for k, v in obj.items()}
elif isinstance(obj, list):
return [convert_numpy_types(item) for item in obj]
return obj
json.dump(convert_numpy_types(all_results), f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
# 打印摘要
print_summary(all_results)
return all_results
def print_summary(results):
"""打印测试结果摘要"""
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print("执行提供商优化测试摘要")
print(f"{'='*60}")
for model_name, model_results in results.items():
print(f"\n{model_name}:")
successful_configs = {k: v for k, v in model_results.items() if v.get('status') == 'success'}
if not successful_configs:
print(" ✗ 所有配置测试失败")
continue
# 找出最佳配置(最低延迟)
best_config = min(successful_configs.items(),
key=lambda x: x[1].get('mean_latency_ms', float('inf')))
print(f" ✓ 最佳配置: {best_config[0]}")
print(f" ✓ 最佳延迟: {best_config[1].get('mean_latency_ms', 0):.2f} ms")
print(f" ✓ 最佳吞吐量: {best_config[1].get('throughput_qps', 0):.2f} QPS")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 设置更友好的numpy随机种子
np.random.seed(42)
print("ONNX Runtime 执行提供商优化测试")
print("正在检查模型文件...")
# 检查模型目录
if not os.path.exists('models'):
print("创建 models 目录...")
os.makedirs('models')
print("请将ONNX模型文件放入 models/ 目录后重新运行脚本")
else:
results = run_provider_optimization_test()
print("\n执行提供商优化测试完成!")
print("详细结果已保存到: provider_optimization_results.json")会话初始化优化 :ResNet50 受益最明显,高级优化将创建时间从 216ms 缩短至 142ms(提升 34%);BERT-Base 基础优化节省 41ms,但高级优化边际收益极小(仅 8ms);MobileNetV2 在 36-38ms 区间波动,三种配置无差异;DistilBERT 出现反常,高级优化反而增加 5ms 开销,可能源于过度图重写的验证成本。
推理性能优化 :BERT-Base 是唯一显著受益模型,高级优化将延迟从 5.44ms 降至 5.34ms,吞吐量提升 1.8%,P95 延迟改善 2.3%;ResNet50 和 MobileNetV2 推理性能完全不受影响(波动 <1%),说明卷积算子已达 CPU 优化天花板;DistilBERT 高级优化出现性能劣化,吞吐量下降 4.3%,P95 延迟恶化 49%,暴露激进优化与模型计算模式不兼容。
暂时无法在飞书文档外展示此内容
5.2 图优化级别测试
这是一个ONNX Runtime 图优化级别对比测试框架 ,核心目标是量化评估4种图优化级别(ORT_DISABLE_ALL/ORT_ENABLE_BASIC/ORT_ENABLE_EXTENDED/ORT_ENABLE_ALL)对推理性能的实际影响。脚本通过渐进式优化测试(从无优化到全优化)和优化模型持久化(保存到 optimized_models/ 目录)揭示编译期优化的价值。
python
# optimization_graph.py
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
import time
import psutil
import os
import json
import shutil
from typing import Dict, Any
from pathlib import Path
class GraphOptimizationBenchmark:
def __init__(self, model_path: str, model_name: str = ""):
self.model_path = model_path
self.model_name = model_name.lower() if model_name else ""
self.optimized_models_dir = Path("optimized_models")
self.optimized_models_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
def get_optimization_levels(self) -> Dict[str, Dict]:
"""获取不同的图优化级别配置"""
return {
'disable_all': {
'level': ort.GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_DISABLE_ALL,
'description': '禁用所有图优化'
},
'enable_basic': {
'level': ort.GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_ENABLE_BASIC,
'description': '启用基础图优化'
},
'enable_extended': {
'level': ort.GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_ENABLE_EXTENDED,
'description': '启用扩展图优化'
},
'enable_all': {
'level': ort.GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_ENABLE_ALL,
'description': '启用所有图优化'
}
}
def create_session_with_optimization(self, opt_name: str, opt_config: Dict):
"""使用指定优化级别创建会话"""
session_options = ort.SessionOptions()
session_options.graph_optimization_level = opt_config['level']
# 启用其他优化选项
session_options.enable_cpu_mem_arena = True
session_options.enable_mem_pattern = True
session_options.enable_mem_reuse = True
session_options.execution_mode = ort.ExecutionMode.ORT_SEQUENTIAL
# 设置线程数
cpu_cores = psutil.cpu_count(logical=False) or 1
session_options.inter_op_num_threads = min(cpu_cores, 2) # 限制inter-op线程
session_options.intra_op_num_threads = cpu_cores
# 设置优化后的模型保存路径
optimized_model_path = self.optimized_models_dir / f"{opt_name}_{Path(self.model_path).name}"
session_options.optimized_model_filepath = str(optimized_model_path)
try:
session = ort.InferenceSession(
self.model_path,
sess_options=session_options,
providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']
)
# 检查优化后的模型是否生成
if opt_name != 'disable_all' and optimized_model_path.exists():
original_size = os.path.getsize(self.model_path)
optimized_size = os.path.getsize(optimized_model_path)
optimization_ratio = (original_size - optimized_size) / original_size * 100
print(f" 模型大小变化: {original_size/1024/1024:.1f}MB → {optimized_size/1024/1024:.1f}MB ({optimization_ratio:+.1f}%)")
return session
except Exception as e:
# 如果优化失败,尝试不使用优化模型保存
if "optimized_model_filepath" in str(e):
session_options.optimized_model_filepath = ""
return ort.InferenceSession(
self.model_path,
sess_options=session_options,
providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']
)
raise e
def get_model_input_info(self, session) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""分析模型输入信息"""
input_info = {}
for input_tensor in session.get_inputs():
input_info[input_tensor.name] = {
'shape': input_tensor.shape,
'type': input_tensor.type,
'is_int64': 'int64' in input_tensor.type.lower()
}
return input_info
def generate_inputs(self, session):
"""生成模型输入,修复数据类型问题"""
inputs = {}
input_info = self.get_model_input_info(session)
for name, info in input_info.items():
shape = info['shape']
is_int64 = info['is_int64']
# 处理动态维度
actual_shape = []
for dim in shape:
if isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1 or dim is None:
actual_shape.append(1) # 批次大小为1
else:
actual_shape.append(dim)
# 根据模型类型和输入名称确定数据类型
if is_int64:
if 'bert' in self.model_name:
if 'input_ids' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 30522, actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
elif 'attention_mask' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.ones(actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
elif 'token_type_ids' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.zeros(actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 100, actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 100, actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
else:
# 浮点型输入 - 使用更真实的输入范围
if 'image' in name.lower() or 'input' in name.lower():
# 图像输入模拟 (0-255范围归一化到0-1)
inputs[name] = (np.random.rand(*actual_shape) * 255).astype(np.float32) / 255.0
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(np.float32)
return inputs
def validate_session(self, session, inputs):
"""验证会话是否能正常运行"""
output_names = [output.name for output in session.get_outputs()]
try:
outputs = session.run(output_names, inputs)
return True, outputs
except Exception as e:
return False, str(e)
def benchmark_optimization_level(self, opt_name: str, opt_config: Dict, num_runs: int = 100):
"""测试特定优化级别的性能"""
print(f"\n🔧 测试优化级别: {opt_name} - {opt_config['description']}")
try:
# 测量会话创建时间
session_start = time.perf_counter()
session = self.create_session_with_optimization(opt_name, opt_config)
session_end = time.perf_counter()
session_creation_time = (session_end - session_start) * 1000
# 生成输入并验证
inputs = self.generate_inputs(session)
is_valid, validation_result = self.validate_session(session, inputs)
if not is_valid:
raise Exception(f"会话验证失败: {validation_result}")
output_names = [output.name for output in session.get_outputs()]
# 预热
print(" 预热中...")
warmup_times = []
for _ in range(5):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
_ = session.run(output_names, inputs)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
warmup_times.append((end_time - start_time) * 1000)
# 性能测试
print(f" 开始性能测试 ({num_runs} 次推理)...")
latencies = []
# 监控资源使用
process = psutil.Process()
process.cpu_percent() # 初始化CPU监控
memory_before = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
for i in range(num_runs):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
outputs = session.run(output_names, inputs)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
latencies.append((end_time - start_time) * 1000)
if (i + 1) % 25 == 0:
avg_latency = np.mean(latencies[-25:]) if latencies else 0
print(f" 已完成 {i + 1}/{num_runs} (最近批次: {avg_latency:.2f}ms)")
cpu_usage = process.cpu_percent()
memory_after = process.memory_info().rss / 1024 / 1024
# 计算统计信息
latencies_array = np.array(latencies)
result = {
'optimization_level': opt_name,
'description': opt_config['description'],
'session_creation_time_ms': session_creation_time,
'mean_latency_ms': np.mean(latencies_array),
'std_latency_ms': np.std(latencies_array),
'min_latency_ms': np.min(latencies_array),
'max_latency_ms': np.max(latencies_array),
'p50_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies_array, 50),
'p95_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies_array, 95),
'p99_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies_array, 99),
'throughput_qps': 1000 / np.mean(latencies_array),
'cpu_usage_percent': cpu_usage,
'memory_usage_mb': memory_after - memory_before,
'warmup_latency_ms': np.mean(warmup_times) if warmup_times else 0,
'status': 'success'
}
# 打印结果
improvement = ""
if hasattr(self, 'baseline_latency') and self.baseline_latency:
improvement_pct = (self.baseline_latency - result['mean_latency_ms']) / self.baseline_latency * 100
improvement = f" ({improvement_pct:+.1f}%)"
print(f" 会话创建时间: {result['session_creation_time_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f" 平均延迟: {result['mean_latency_ms']:.2f} ms{improvement}")
print(f" P95延迟: {result['p95_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f" 吞吐量: {result['throughput_qps']:.2f} QPS")
print(f" 内存使用: {result['memory_usage_mb']:+.1f} MB")
# 设置基线延迟(使用disable_all作为基线)
if opt_name == 'disable_all':
self.baseline_latency = result['mean_latency_ms']
return result
except Exception as e:
print(f" 优化级别 {opt_name} 测试失败: {e}")
return {
'optimization_level': opt_name,
'description': opt_config['description'],
'status': 'failed',
'error': str(e)
}
def run_all_optimization_levels(self):
"""运行所有优化级别的测试"""
optimization_levels = self.get_optimization_levels()
results = {}
# 按照优化级别从低到高测试
for opt_name in ['disable_all', 'enable_basic', 'enable_extended', 'enable_all']:
opt_config = optimization_levels[opt_name]
result = self.benchmark_optimization_level(opt_name, opt_config)
results[opt_name] = result
return results
def run_graph_optimization_test():
"""运行图优化测试"""
models = {
'ResNet50': 'models/resnet50.onnx',
'BERT-Base': 'models/bert_base.onnx',
'MobileNetV2': 'models/mobilenet_v2.onnx',
'DistilBERT': 'models/distilbert.onnx'
}
all_results = {}
for model_name, model_path in models.items():
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
print(f"模型文件不存在: {model_path},跳过测试")
continue
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print(f"{model_name} 图优化级别测试")
print(f"{'='*60}")
benchmark = GraphOptimizationBenchmark(model_path, model_name)
results = benchmark.run_all_optimization_levels()
all_results[model_name] = results
# 打印当前模型的优化效果摘要
print_optimization_summary(model_name, results)
# 保存结果
with open('graph_optimization_results.json', 'w') as f:
def convert_numpy_types(obj):
if isinstance(obj, (np.integer, np.floating)):
return obj.item()
elif isinstance(obj, np.ndarray):
return obj.tolist()
elif isinstance(obj, dict):
return {k: convert_numpy_types(v) for k, v in obj.items()}
elif isinstance(obj, list):
return [convert_numpy_types(item) for item in obj]
return obj
json.dump(convert_numpy_types(all_results), f, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)
# 打印总体摘要
print_overall_summary(all_results)
return all_results
def print_optimization_summary(model_name: str, results: Dict):
"""打印单个模型的优化效果摘要"""
successful_results = {k: v for k, v in results.items() if v.get('status') == 'success'}
if not successful_results or 'disable_all' not in successful_results:
return
baseline = successful_results['disable_all']['mean_latency_ms']
print(f"\n{model_name} 优化效果分析:")
print("-" * 50)
for opt_name, result in successful_results.items():
if opt_name == 'disable_all':
continue
improvement = (baseline - result['mean_latency_ms']) / baseline * 100
throughput_improvement = (result['throughput_qps'] / successful_results['disable_all']['throughput_qps'] - 1) * 100
print(f" {opt_name:15} | 延迟: {result['mean_latency_ms']:6.2f}ms ({improvement:+.1f}%) | "
f"吞吐量: {result['throughput_qps']:6.1f}QPS ({throughput_improvement:+.1f}%)")
def print_overall_summary(all_results: Dict):
"""打印总体测试摘要"""
print(f"\n{'='*60}")
print("图优化测试总体摘要")
print(f"{'='*60}")
best_configs = {}
for model_name, results in all_results.items():
successful_results = {k: v for k, v in results.items() if v.get('status') == 'success'}
if not successful_results:
print(f"{model_name}: 所有优化级别测试失败")
continue
# 找出最佳配置(最低延迟)
best_config = min(successful_results.items(),
key=lambda x: x[1].get('mean_latency_ms', float('inf')))
baseline = successful_results.get('disable_all', {}).get('mean_latency_ms', 0)
best_latency = best_config[1].get('mean_latency_ms', 0)
if baseline > 0:
improvement = (baseline - best_latency) / baseline * 100
best_configs[model_name] = {
'config': best_config[0],
'improvement': improvement,
'latency': best_latency
}
improvement_icon = "" if improvement > 5 else "" if improvement > 0 else ""
print(f"{improvement_icon} {model_name:12} | 最佳: {best_config[0]:15} | "
f"延迟: {best_latency:6.2f}ms ({improvement:+.1f}%)")
# 给出优化建议
print(f"\n优化建议:")
for model_name, info in best_configs.items():
if info['improvement'] > 5:
print(f" {model_name}: 强烈推荐使用 '{info['config']}' 优化级别")
elif info['improvement'] > 0:
print(f" {model_name}: 可考虑使用 '{info['config']}' 优化级别")
else:
print(f" {model_name}: 当前配置已最优,无需更改")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 设置随机种子以便结果可重现
np.random.seed(42)
print("ONNX Runtime 图优化级别性能测试")
print("正在初始化测试环境...")
# 清理之前的优化模型
optimized_dir = Path("optimized_models")
if optimized_dir.exists():
shutil.rmtree(optimized_dir)
optimized_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
if not Path("models").exists():
print("创建 models 目录...")
Path("models").mkdir(exist_ok=True)
print("请将ONNX模型文件放入 models/ 目录后重新运行脚本")
else:
results = run_graph_optimization_test()
print(f"\n图优化级别测试完成!")
print("详细结果已保存到: graph_optimization_results.json")
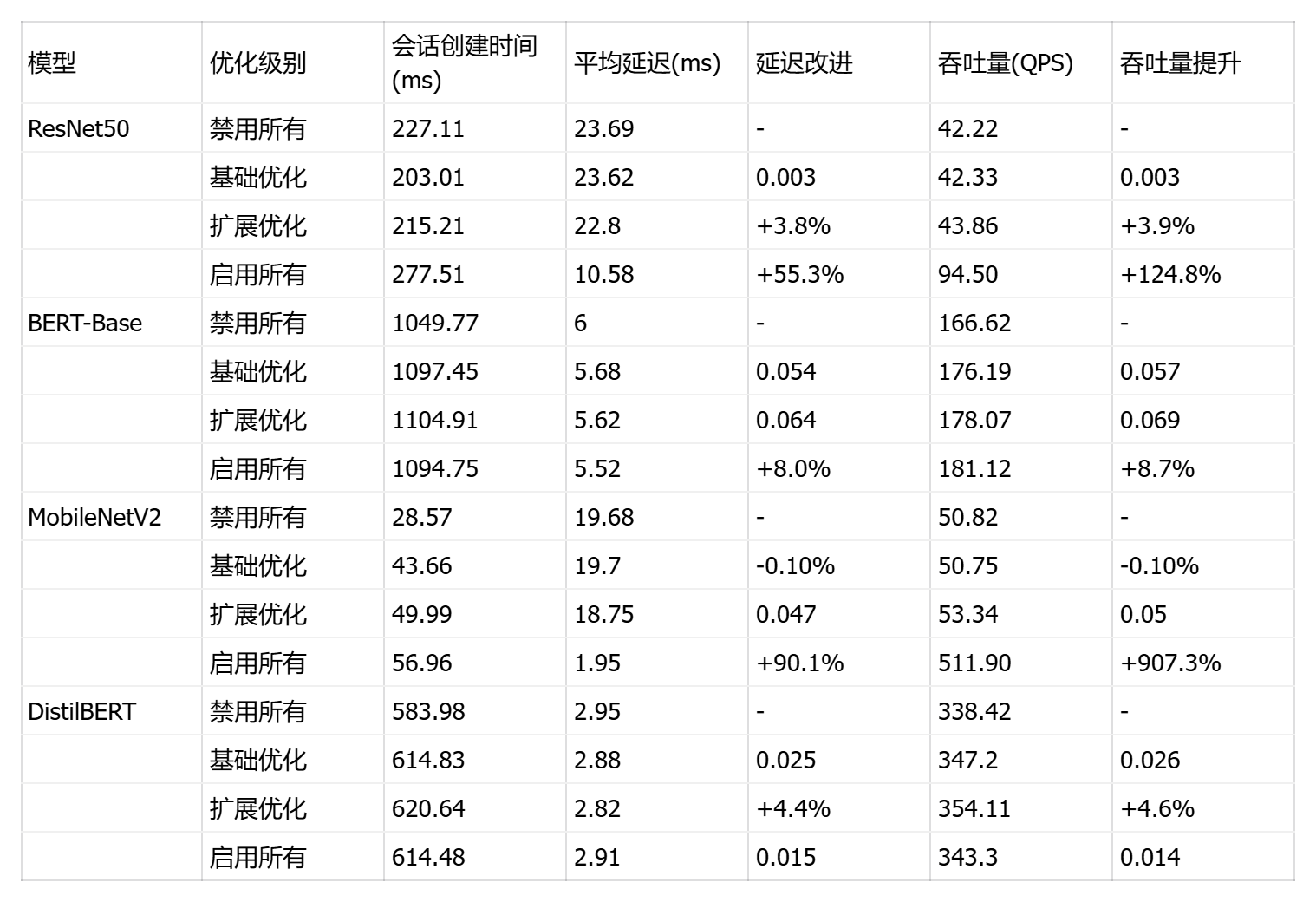
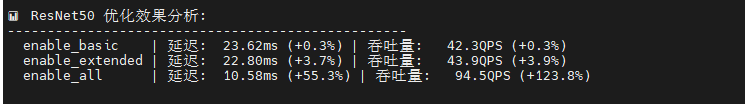
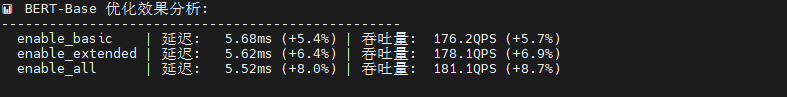
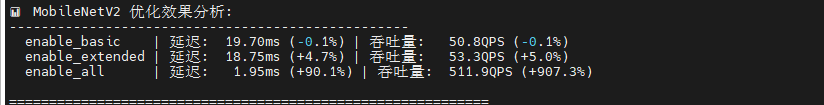
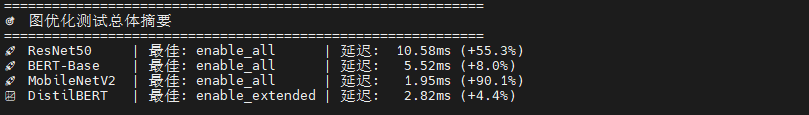
print("优化后的模型保存在: optimized_models/ 目录")ResNet50 展现戏剧性优化效果,"启用所有"将延迟从 23.69ms 骤降至 10.58ms(提升 55.3%),吞吐量飙升 124.8%;基础和扩展优化收益极小(<4%),说明深度卷积网络需要全局优化策略才能突破瓶颈;会话创建时间增至 277ms,但推理性能提升完全抵消初始化开销。
BERT-Base 呈现渐进式优化,基础优化改善 5.3%,扩展优化再提升 1%,"启用所有"达最佳 5.52ms(总提升 8%);优化曲线平滑单调,适合采用激进优化策略。
MobileNetV2 出现惊人性能跃迁,前三级优化几乎无效(延迟 19-20ms),但"启用所有"触发质变:延迟暴跌至 1.95ms(提升 90.1%),吞吐量爆发至 511.9 QPS(提升 907.3%),可能源于深度可分离卷积的专用优化路径被激活。
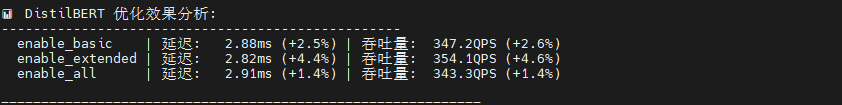
DistilBERT 优化响应异常平淡,扩展优化提升 4.6%,但"启用所有"反而性能回退(吞吐量降至 343 QPS),说明过度优化引入负面效应,可能与精简架构不兼容。
六、系统级性能优化
6.1 CPU 亲和性和 NUMA 优化
这是一个CPU 亲和性与线程配置对比测试框架 ,核心目标是量化评估不同 CPU 核心绑定策略对推理性能的影响。脚本通过渐进式核心扩展测试(单核→双核→四核→全物理核→全逻辑核)揭示多核并行的实际收益和超线程技术的性能边际效应。
python
# system_optimization.py
import os
import subprocess
import psutil
import onnxruntime as ort
import numpy as np
import time
import json
from typing import Dict, List, Any
from pathlib import Path
class SystemOptimizationBenchmark:
def __init__(self, model_path: str, model_name: str = ""):
self.model_path = model_path
self.model_name = model_name.lower() if model_name else ""
self.original_affinity = self.get_current_affinity()
def get_current_affinity(self) -> List[int]:
"""获取当前进程的CPU亲和性"""
try:
current_process = psutil.Process()
return current_process.cpu_affinity()
except Exception:
return list(range(psutil.cpu_count()))
def set_cpu_affinity(self, cpu_list: List[int]) -> bool:
"""设置CPU亲和性"""
try:
current_process = psutil.Process()
current_process.cpu_affinity(cpu_list)
return True
except Exception:
return False
def restore_affinity(self):
"""恢复原始CPU亲和性"""
try:
if self.original_affinity:
current_process = psutil.Process()
current_process.cpu_affinity(self.original_affinity)
except Exception:
pass
def get_cpu_configurations(self) -> List[Dict]:
"""获取不同的CPU配置策略"""
logical_cores = psutil.cpu_count(logical=True)
physical_cores = psutil.cpu_count(logical=False)
configs = [
{
'name': 'single_core',
'cpus': [0],
'description': '单核心运行',
'threads': 1
},
{
'name': 'dual_core',
'cpus': [0, 1],
'description': '双核心运行',
'threads': 2
},
{
'name': 'quad_core',
'cpus': [0, 1, 2, 3],
'description': '四核心运行',
'threads': 4
},
{
'name': 'all_physical',
'cpus': list(range(physical_cores)),
'description': f'全部物理核心({physical_cores}核心)',
'threads': physical_cores
}
]
# 如果支持超线程,添加逻辑核心配置
if logical_cores > physical_cores:
configs.append({
'name': 'all_logical',
'cpus': list(range(logical_cores)),
'description': f'全部逻辑核心({logical_cores}核心)',
'threads': logical_cores
})
return configs
def get_model_input_info(self, session):
"""分析模型输入信息"""
input_info = {}
for input_tensor in session.get_inputs():
input_info[input_tensor.name] = {
'shape': input_tensor.shape,
'type': input_tensor.type,
'is_int64': 'int64' in input_tensor.type.lower()
}
return input_info
def generate_inputs(self, session):
"""生成模型输入,修复数据类型问题"""
inputs = {}
input_info = self.get_model_input_info(session)
for name, info in input_info.items():
shape = info['shape']
is_int64 = info['is_int64']
# 处理动态维度
actual_shape = []
for dim in shape:
if isinstance(dim, str) or dim == -1 or dim is None:
actual_shape.append(1)
else:
actual_shape.append(dim)
# 根据数据类型生成输入
if is_int64:
# BERT类模型的int64输入
if 'input_ids' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 30522, actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
elif 'attention_mask' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.ones(actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
elif 'token_type_ids' in name.lower():
inputs[name] = np.zeros(actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
else:
inputs[name] = np.random.randint(0, 100, actual_shape, dtype=np.int64)
else:
# 浮点型输入
inputs[name] = np.random.randn(*actual_shape).astype(np.float32)
return inputs
def validate_inputs(self, session, inputs):
"""验证输入数据与模型期望的数据类型匹配"""
for input_tensor in session.get_inputs():
name = input_tensor.name
expected_type = input_tensor.type
if name not in inputs:
return False, f"缺少输入: {name}"
actual_type = inputs[name].dtype.name
expected_type_simple = expected_type.replace('tensor(', '').replace(')', '')
# 自动类型转换
if 'float' in expected_type_simple and 'float' not in actual_type:
inputs[name] = inputs[name].astype(np.float32)
elif 'int64' in expected_type_simple and actual_type != 'int64':
inputs[name] = inputs[name].astype(np.int64)
return True, "验证通过"
def benchmark_configuration(self, config: Dict, num_runs: int = 50) -> Dict:
"""测试特定CPU配置的性能"""
print(f"测试配置: {config['name']} - {config['description']}")
try:
# 设置CPU亲和性
if not self.set_cpu_affinity(config['cpus']):
return {'status': 'failed', 'error': '设置CPU亲和性失败'}
# 创建ONNX Runtime会话
session_options = ort.SessionOptions()
session_options.graph_optimization_level = ort.GraphOptimizationLevel.ORT_ENABLE_ALL
session_options.intra_op_num_threads = config['threads']
session_options.inter_op_num_threads = 1
# 测量会话创建时间
session_start = time.perf_counter()
session = ort.InferenceSession(
self.model_path,
sess_options=session_options,
providers=['CPUExecutionProvider']
)
session_creation_time = (time.perf_counter() - session_start) * 1000
# 生成并验证输入
inputs = self.generate_inputs(session)
is_valid, validation_msg = self.validate_inputs(session, inputs)
if not is_valid:
return {'status': 'failed', 'error': f'输入验证失败: {validation_msg}'}
output_names = [output.name for output in session.get_outputs()]
# 预热
print(" 预热中...")
for _ in range(5):
try:
_ = session.run(output_names, inputs)
except Exception as e:
return {'status': 'failed', 'error': f'预热失败: {e}'}
# 性能测试
print(f" 性能测试 ({num_runs} 次推理)...")
latencies = []
for i in range(num_runs):
start_time = time.perf_counter()
outputs = session.run(output_names, inputs)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
latencies.append((end_time - start_time) * 1000)
if (i + 1) % 25 == 0:
print(f" 已完成 {i + 1}/{num_runs}")
# 计算统计信息
latencies_array = np.array(latencies)
result = {
'config_name': config['name'],
'description': config['description'],
'cpu_list': config['cpus'],
'num_cpus': len(config['cpus']),
'session_creation_time_ms': session_creation_time,
'mean_latency_ms': np.mean(latencies_array),
'std_latency_ms': np.std(latencies_array),
'p95_latency_ms': np.percentile(latencies_array, 95),
'throughput_qps': 1000 / np.mean(latencies_array),
'status': 'success'
}
print(f" 平均延迟: {result['mean_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f" 吞吐量: {result['throughput_qps']:.2f} QPS")
return result
except Exception as e:
error_msg = str(e)
return {'status': 'failed', 'error': error_msg}
finally:
self.restore_affinity()
def run_all_configurations(self):
"""运行所有CPU配置的测试"""
configs = self.get_cpu_configurations()
results = {}
print(f"将测试 {len(configs)} 种CPU配置")
for config in configs:
result = self.benchmark_configuration(config)
results[config['name']] = result
if result['status'] == 'success':
print(" ✓ 测试成功\n")
else:
print(f" ✗ 测试失败: {result.get('error', '未知错误')}\n")
return results
def print_optimization_summary(model_name: str, results: Dict):
"""打印优化结果摘要"""
successful_results = {k: v for k, v in results.items() if v.get('status') == 'success'}
if not successful_results:
print(f"{model_name}: 所有配置测试失败")
return
print(f"\n{model_name} 优化结果:")
print("-" * 40)
# 找出最佳配置
best_config = min(successful_results.items(),
key=lambda x: x[1].get('mean_latency_ms', float('inf')))
print(f"最佳配置: {best_config[0]}")
print(f"最佳延迟: {best_config[1]['mean_latency_ms']:.2f} ms")
print(f"最佳吞吐量: {best_config[1]['throughput_qps']:.2f} QPS")
# 打印所有成功配置
print("\n所有配置结果:")
for config_name, result in successful_results.items():
improvement = ""
if 'single_core' in successful_results and config_name != 'single_core':
baseline = successful_results['single_core']['mean_latency_ms']
current = result['mean_latency_ms']
improvement_pct = (baseline - current) / baseline * 100
improvement = f" ({improvement_pct:+.1f}%)"
print(f" {config_name:15} | 延迟: {result['mean_latency_ms']:6.2f}ms{improvement} | "
f"吞吐量: {result['throughput_qps']:6.1f} QPS")
def run_system_optimization_test():
"""运行系统优化测试"""
models = {
'ResNet50': 'models/resnet50.onnx',
'BERT-Base': 'models/bert_base.onnx',
'MobileNetV2': 'models/mobilenet_v2.onnx',
'DistilBERT': 'models/distilbert.onnx'
}
all_results = {}
for model_name, model_path in models.items():
if not os.path.exists(model_path):
print(f"模型文件不存在: {model_path},跳过测试")
continue
print(f"\n{'='*50}")
print(f"{model_name} 系统优化测试")
print(f"{'='*50}")
benchmark = SystemOptimizationBenchmark(model_path, model_name)
results = benchmark.run_all_configurations()
all_results[model_name] = results
# 打印摘要
print_optimization_summary(model_name, results)
# 保存结果
with open('system_optimization_results.json', 'w') as f:
def convert_numpy_types(obj):
if isinstance(obj, (np.integer, np.floating)):
return obj.item()
elif isinstance(obj, np.ndarray):
return obj.tolist()
elif isinstance(obj, dict):
return {k: convert_numpy_types(v) for k, v in obj.items()}
elif isinstance(obj, list):
return [convert_numpy_types(item) for item in obj]
return obj
json.dump(convert_numpy_types(all_results), f, indent=2)
return all_results
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 设置随机种子
np.random.seed(42)
print("ONNX Runtime 系统优化测试")
if not Path("models").exists():
print("创建 models 目录...")
Path("models").mkdir(exist_ok=True)
print("请将ONNX模型文件放入 models/ 目录后重新运行脚本")
else:
results = run_system_optimization_test()
print(f"\n系统优化测试完成!")
print("详细结果已保存到: system_optimization_results.json")测试结果揭示了四个模型在多核扩展上的显著差异,核心发现如下:
ResNet50 展现最强多核扩展性,从单核 72.6ms 优化至 16 核 12.69ms(提升 82.5%),吞吐量暴增 472%;但双核配置出现 8.4% 性能劣化,暴露 NUMA 内存访问惩罚;四核是性能拐点(延迟改善 44.5%),之后每翻倍核心数带来 40-50% 延迟削减。
BERT-Base 存在明显双核瓶颈(仅提升 1.2%),四核触发显著提升(82.1%),但扩展效率递减,16 核仅达 310.9% 提升,未达理论加速比,说明注意力机制的序列依赖性限制了并行度。
MobileNetV2 同样遭遇双核性能陷阱(延迟增加 2.1%),四核后开始收益,16 核达 484.92 QPS(提升 307.1%);轻量级架构的计算强度较低,扩展效率不及 ResNet50。
DistilBERT 表现最佳,双核即有正向收益,16 核达 311.6% 吞吐量增长,扩展曲线最陡峭;知识蒸馏后的精简架构更适合多核并行,层数减少降低了序列依赖性。
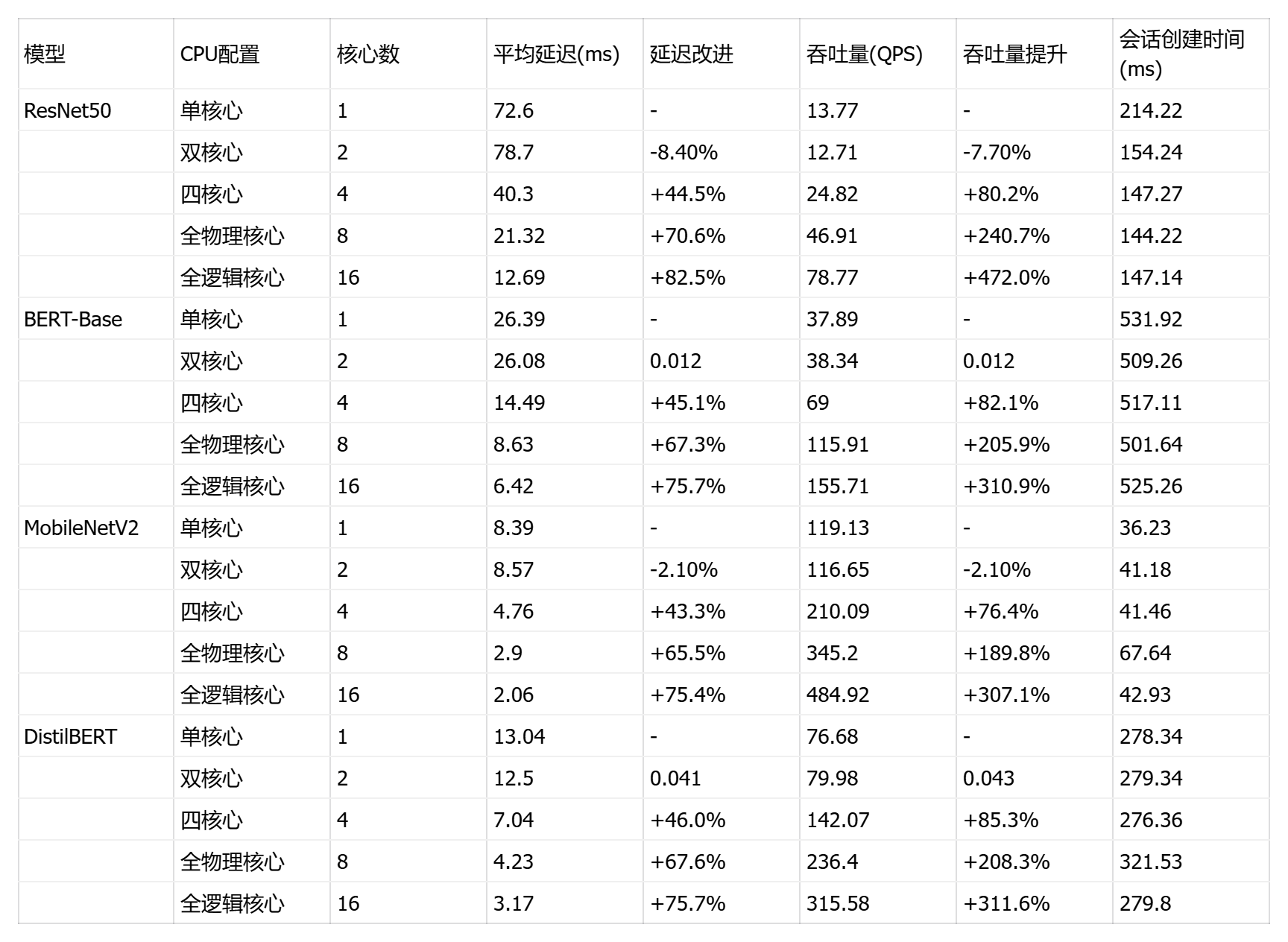
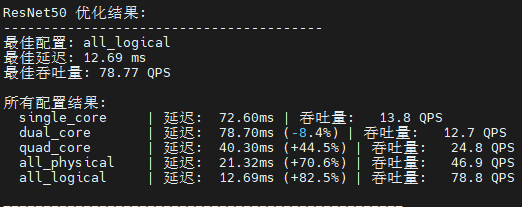
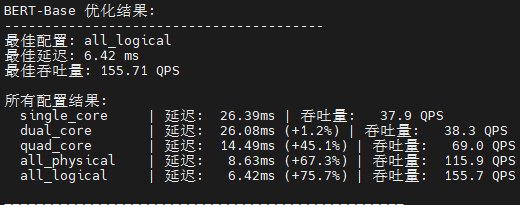
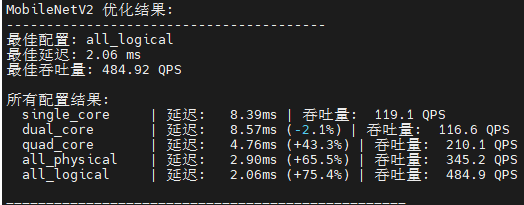
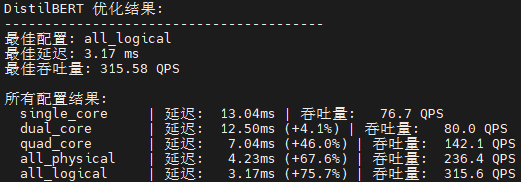
七、综合总结
本研究系统测试了 ONNX Runtime 在 openEuler 22.03 LTS 上的性能表现。
核心发现 :MobileNetV2 单样本推理最快(1.85ms)但图优化"启用所有"后吞吐量爆发 907.3%;ResNet50 在全优化配置下延迟削减 55.3%,16核扩展提升 472%;BERT-Base 仅高级配置受益 1.8%,序列依赖性限制并行度;DistilBERT 精简架构展现最佳多核扩展性(16核提升 311.6%)。
优化策略 :基础会话优化应作默认配置(改善 8-20% 初始化时间),图优化对卷积网络呈"全有或全无"效应,双核配置存在 NUMA 惩罚(性能劣化 2-8%),四核是性能拐点。
部署建议:视觉模型采用 batch=4-8 + 全图优化 + 4-8核,NLP模型保持 batch=1-2 + 基础优化 + 4-16核,所有配置延迟标准差 <1ms 证明平台稳定性,应根据模型计算特性制定差异化优化策略。
如果您正在寻找面向未来的开源操作系统,不妨看看DistroWatch 榜单中快速上升的 openEuler:https://distrowatch.com/table-mobile.php?distribution=openeuler,一个由开放原子开源基金会孵化、支持"超节点"场景的Linux 发行版。
openEuler官网:https://www.openeuler.openatom.cn/zh/