文章目录
一、进程替换
fork() 之后,⽗⼦各⾃执⾏⽗进程代码的⼀部分,如果⼦进程就想执⾏⼀个全新的程序呢?进程的程序替换来完成这个功能!
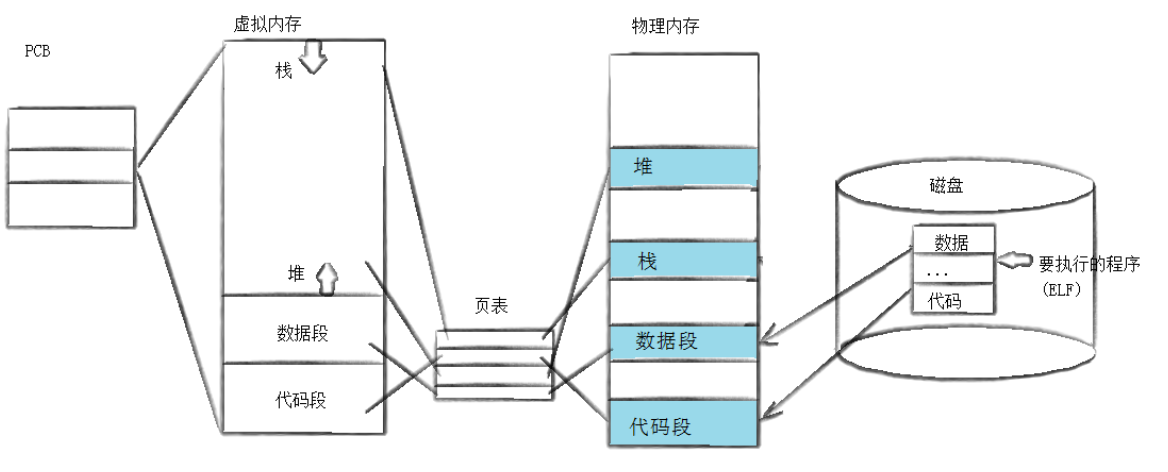
程序替换是通过特定的接⼝,加载磁盘上的⼀个全新的程序(代码和数据),加载到调⽤进程的地址空间中!
1、替换原理
⽤ fork 创建⼦进程后执⾏的是和⽗进程相同的程序(但有可能执⾏不同的代码分⽀),进程往往要调⽤⼀种exec函数以执⾏另⼀个程序。当进程调⽤⼀种exec函数时,该进程的⽤户空间代码和数据完全被新程序替换,从新程序的启动例程开始执⾏。调⽤exec并不创建新进程,所以调⽤exec前后该进程的id并未改变。
2、替换函数
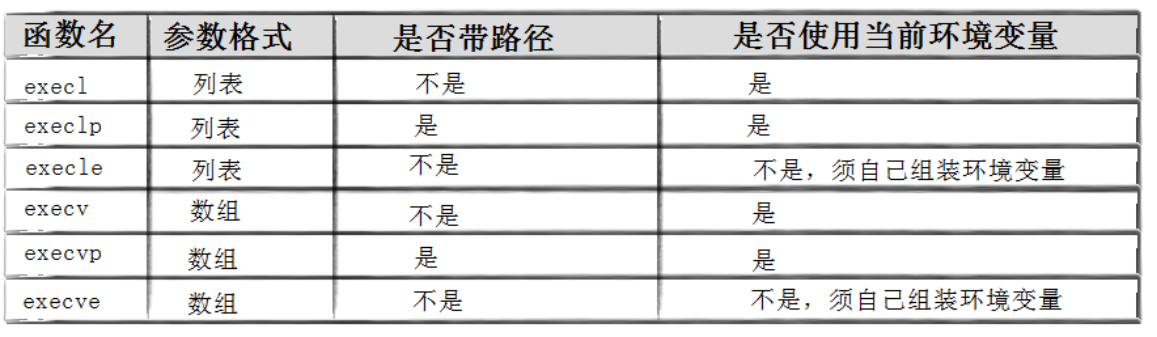
其实有六种以exec开头的函数,统称为exec函数:
cpp
#include <unistd.h>
int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ...,char *const envp[]);
int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execve(const char *path, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);函数解释:
- 这些函数如果调⽤成功则加载新的程序从启动代码开始执⾏,不再返回。
- 如果调⽤出错则返回 -1。
- 所以exec函数只有出错的返回值⽽没有成功的返回值。
命令理解:
这些函数原型看起来很容易混,但只要掌握了规律就很好记。
- l(list):表⽰参数采⽤列表
- v(vector):参数⽤数组
- p(path):有p⾃动搜索环境变量PATH
- e(env):表⽰⾃⼰维护环境变量
exec调⽤举例如下:
1)execl
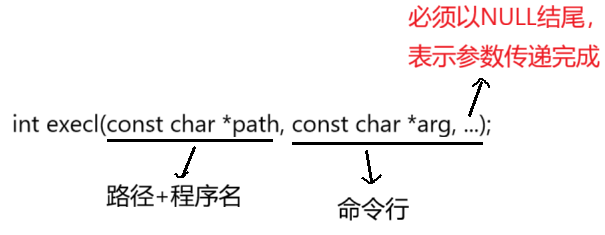
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了!\n");
if(fork() == 0)
{
// child
sleep(1);
execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-ln", "-a", NULL);
exit(1);
}
waitpid(-1, NULL, 0);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
} 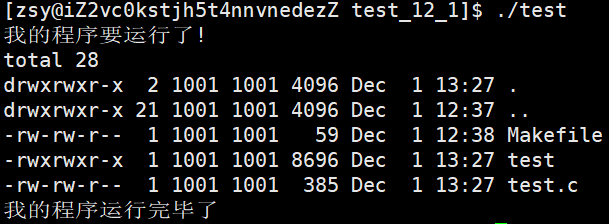
我们发现进程替换并没有影响父进程,原因有二,其一是进程具有独立性,其二是因为数据代码发生了写时拷贝!
同理也可以替换我们自己写的程序:
cpp
// other.c
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
printf("hello world!\n");
return 0;
}
cpp
// test.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
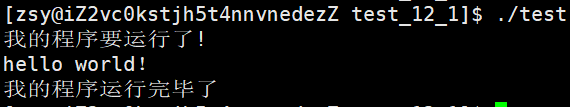
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了!\n");
if(fork() == 0)
{
// child
sleep(1);
execl("./other", "other", NULL);
exit(1);
}
waitpid(-1, NULL, 0);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
} 
2)execlp

cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
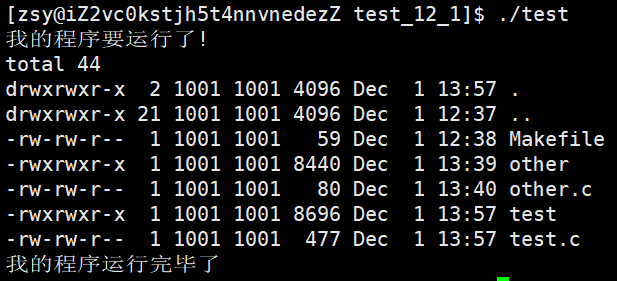
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了!\n");
if(fork() == 0)
{
// child
sleep(1);
execlp("ls", "ls", "-ln", "-a", NULL);
exit(1);
}
waitpid(-1, NULL, 0);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
} 
3)execv

cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
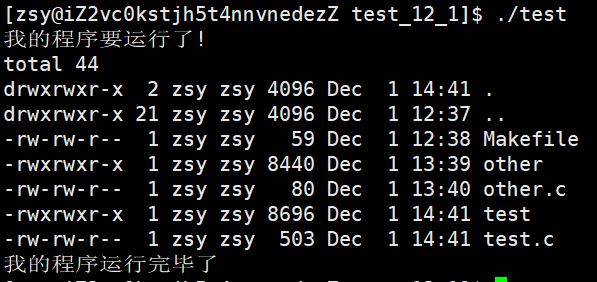
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了!\n");
if(fork() == 0)
{
sleep(1);
char* const argv[] = {
(char* const)"ls",
(char* const)"-l",
(char* const)"-a",
NULL
};
execv("/usr/bin/ls", argv);
exit(1);
}
waitpid(-1, NULL, 0);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
}
4)execvp

cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了!\n");
if(fork() == 0)
{
sleep(1);
char* const argv[] = {
(char* const)"ls",
(char* const)"-l",
(char* const)"-a",
NULL
};
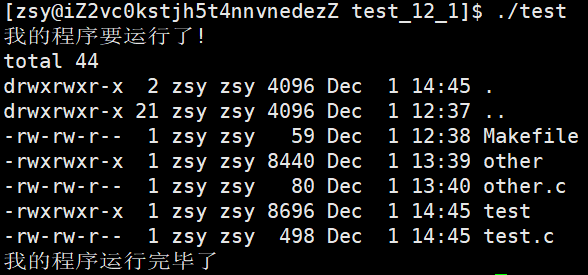
execvp(argv[0], argv);
exit(1);
}
waitpid(-1, NULL, 0);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
}
5)execvpe

cpp
// other.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[], char *env[])
{
printf("hello C++, My Pid Is: %d\n", getpid());
for(int i = 0; i < argc; i++)
{
printf("argv[%d]: %s\n", i, argv[i]);
}
printf("\n");
for(int i = 0; env[i]; i++)
{
printf("env[%d]: %s\n", i, env[i]);
}
return 0;
}
cpp
// test.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了!\n");
if(fork() == 0)
{
// child
sleep(1);
char* const argv[] = {
(char* const)"other",
(char* const)"-a",
(char* const)"-b",
(char* const)"-c",
(char* const)"-d",
NULL
};
char* const env[] = {
(char* const)"MYENV=123456789",
NULL
};
execvpe("./other", argv, env);
exit(1);
}
waitpid(-1, NULL, 0);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
} 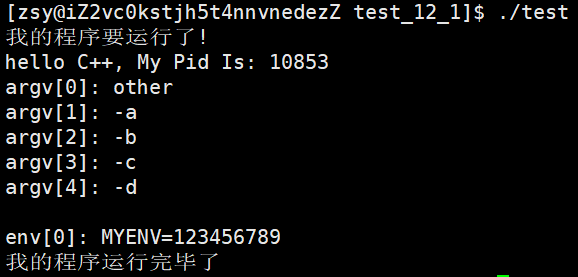
我们发现这里是直接将原有的环境变量所覆盖,从而导成新的环境变量,在实际运用中,如果我们只想将新的环境变量增加到原有的环境变量中,那么该如何实现呢?
6)putenv
那么这里就得引入一个导入环境变量的函数:putenv
cpp
#include <stdlib.h>
int putenv(char *string);有了这个函数,我们就有两种方式直接导入环境变量给子进程:
- 直接使用putenv函数
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
char* newenv = (char*)"MyEnv=666666";
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了!\n");
if(fork() == 0)
{
// child
sleep(1);
char* const argv[] = {
(char* const)"other",
(char* const)"-a",
(char* const)"-b",
(char* const)"-c",
(char* const)"-d",
NULL
};
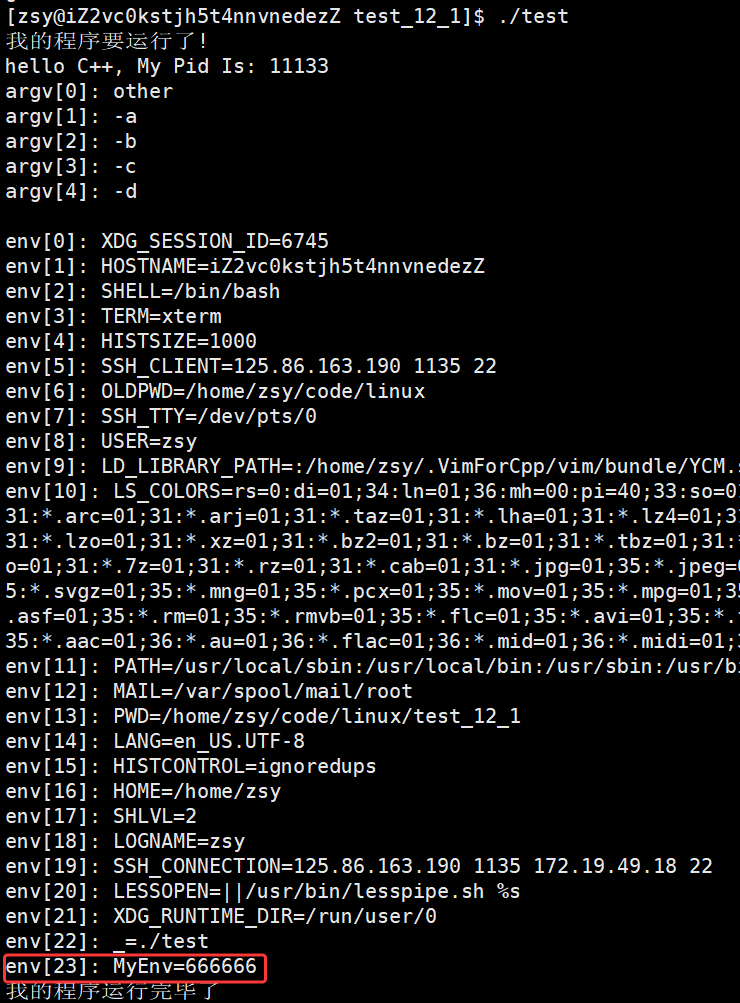
putenv(newenv);// 导入环境变量
execvp("./other", argv);
exit(1);
}
waitpid(-1, NULL, 0);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
} 
- 使用exec*e的替换函数,结合putenv(),environ
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
char* const addenv[] = {
(char* const)"MYVAL=123456789",
NULL
};
int main()
{
printf("我的程序要运行了!\n");
if(fork() == 0)
{
// child
printf("I am Child, My Pid is: %d\n", getpid());
sleep(1);
char* const argv[] = {
(char* const)"other",
(char* const)"-a",
(char* const)"-b",
(char* const)"-c",
(char* const)"-d",
NULL
};
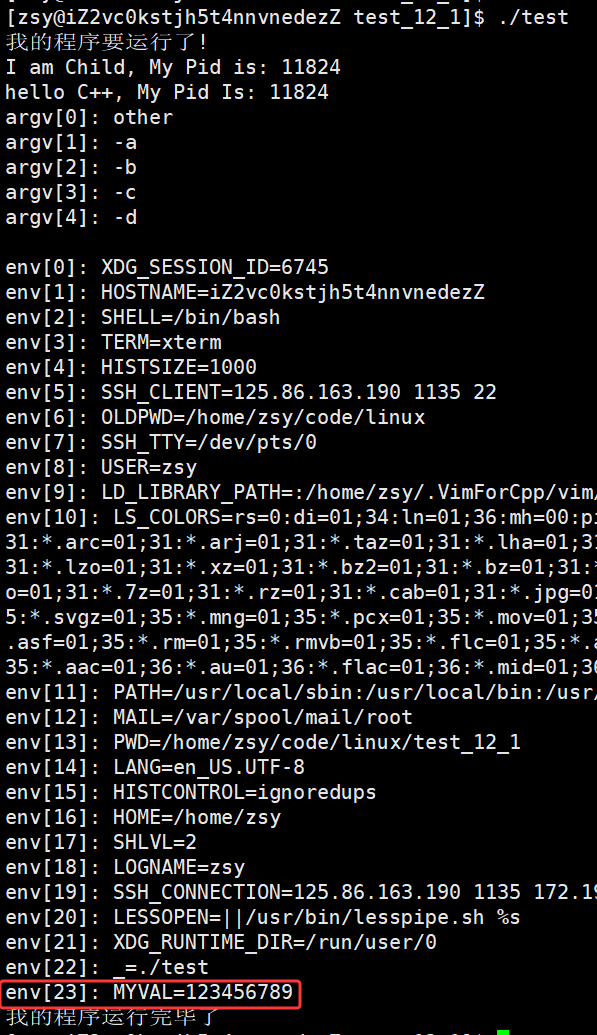
for(int i = 0; addenv[i]; i++)
{
putenv(addenv[i]);
}
extern char** environ;
execvpe("./other", argv, environ);
exit(1);
}
waitpid(-1, NULL, 0);
printf("我的程序运行完毕了\n");
return 0;
} 
7)总结
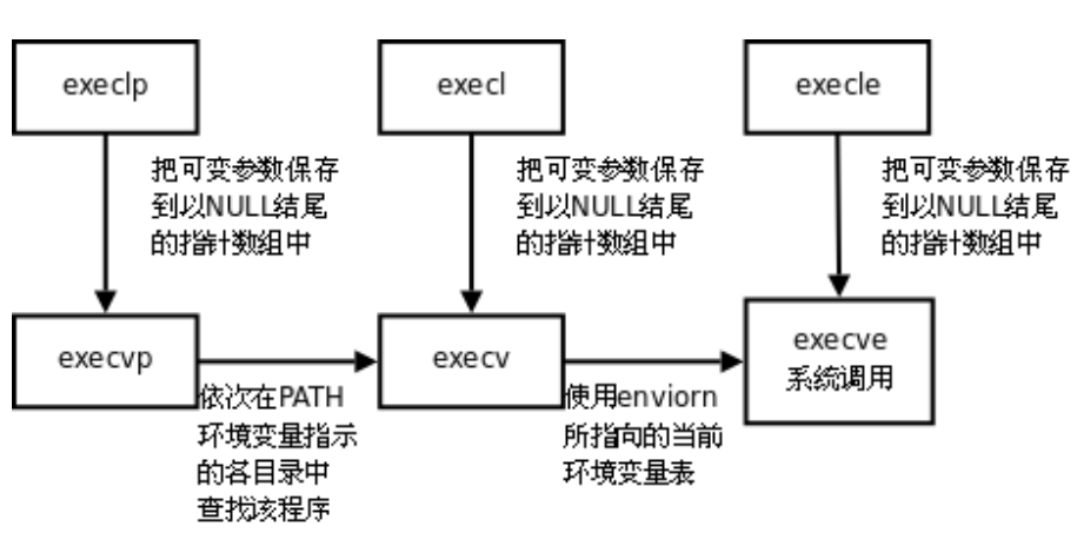
事实上,只有execve是真正的系统调⽤,其它五个函数最终都调⽤execve,所以execve在man⼿册第2节,其它函数在man⼿册第3节。
这些函数之间的关系如下图所⽰。
二、⾃主Shell命令⾏解释器
1、⽬标
- 要能处理普通命令
- 要能处理内建命令
- 要能帮助我们理解内建命令/本地变量/环境变量这些概念
- 要能帮助我们理解shell的允许原理
2、实现原理
考虑下⾯这个与shell典型的互动:
⽤下图的时间轴来表⽰事件的发⽣次序。其中时间从左向右。shell由标识为sh的⽅块代表,它随着时间的流逝从左向右移动。shell从⽤户读⼊字符串"ls"。shell建⽴⼀个新的进程,然后在那个进程中运⾏ls程序并等待那个进程结束。
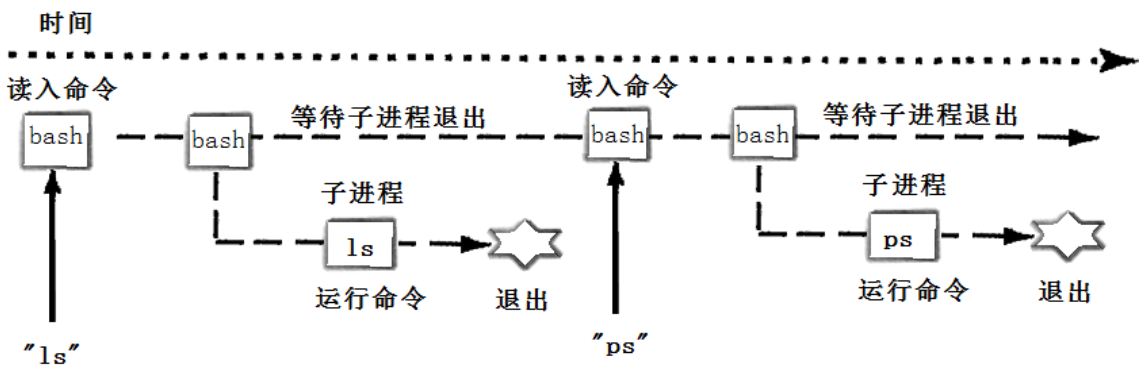
然后shell读取新的⼀⾏输⼊,建⽴⼀个新的进程,在这个进程中运⾏程序并等待这个进程结束。
所以要写⼀个shell,需要循环以下过程:
- 获取命令⾏
- 解析命令⾏
- 建⽴⼀个⼦进程(fork)
- 替换⼦进程(execvp)
- ⽗进程等待⼦进程退出(wait)
3、源码
实现代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#include<cstring>
#include<unordered_map>
#define COMMAND_SIZE 1024
#define FORMAT "[%s@%s %s]# "
// 下面是shell定义的全局数据
// 1. 命令行参数表
#define MAXARGC 128
char* g_argv[MAXARGC];
int g_argc = 0;
// 2. 环境变量表
#define MAX_ENVS 100
char* g_env[MAX_ENVS];
int g_envs = 0;
// 3. 别名映射表
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> alias_list;
// for test
char cwd[1024];
char cwdenv[1024];
// last exit code
int lastcode = 0;
const char* GetUserName()
{
const char* name = getenv("USER");
return name == NULL ? "None" : name;
}
const char* GetHostName()
{
const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME");
return hostname == NULL ? "None" : hostname;
}
const char* GetPwd()
{
//const char* pwd = getenv("PWD");
const char* pwd = getcwd(cwd, sizeof(cwd));
if(pwd != NULL)
{
snprintf(cwdenv, sizeof(cwdenv), "PWD=%s", cwd);
putenv(cwdenv);
}
return pwd == NULL ? "None" : pwd;
}
const char* GetHome()
{
const char* home = getenv("HOME");
return home == NULL ? "None" : home;
}
void InitEnv()
{
extern char** environ;
memset(g_env, 0, sizeof(g_env));
g_envs = 0;
// 1. 获取环境变量
for(int i = 0; environ[i]; i++)
{
// 申请空间
g_env[i] = (char*)malloc(strlen(environ[i])+1);
strcpy(g_env[i], environ[i]);
g_envs++;
}
g_env[g_envs++] = (char*)"HELLO=ENV"; // for test
g_env[g_envs] = NULL;
// 2. 导成环境变量
for(int i = 0; g_env[i]; i++)
{
putenv(g_env[i]);
}
environ = g_env;
}
// /a/b/c
std::string DirName(const char* pwd)
{
#define SLASH "/"
std::string dir = pwd;
if(dir == SLASH) return SLASH;
auto pos = dir.rfind(SLASH);
if(pos == std::string::npos) return "BUG?";
return dir.substr(pos+1);
}
void MakeCommandLine(char cmd_prompt[], int size)
{
// 将获取的信息存入cmd_prompt数组中
snprintf(cmd_prompt, size, FORMAT, GetUserName(), GetHostName(), DirName(GetPwd()).c_str());
//snprintf(cmd_prompt, size, FORMAT, GetUserName(), GetHostName(), GetPwd());
}
void PrintCommandPrompt()
{
char prompt[COMMAND_SIZE];
MakeCommandLine(prompt, sizeof(prompt));
printf("%s", prompt);
fflush(stdout);
}
bool GetCommandLine(char* out, int size)
{
// ls -a -l -> "ls -a -l\n" 字符串
char* c = fgets(out, size, stdin);
if(c == NULL) return false;
out[strlen(out)-1] = 0; // 清理\n
if(strlen(out) == 0) return false;
return true;
}
// 3. 命令行分析 "ls -a -l" -> "ls" "-a" "-l"
bool CommandParse(char* commandline)
{
#define SEP " "
g_argc = 0;
g_argv[g_argc++] = strtok(commandline, SEP);
while((bool)(g_argv[g_argc++] = strtok(nullptr, SEP)));
g_argc--;
return g_argc > 0 ? true:false;
}
void PrintArgv()
{
for(int i = 0; g_argv[i]; i++)
{
printf("argv[%d]->%s\n", i, g_argv[i]);
}
printf("argc: %d\n", g_argc);
}
bool Cd()
{
// cd不带参数(等价于 cd ~) 家目录
if(g_argc == 1)
{
std::string home = GetHome();
if(home.empty()) return true;
chdir(home.c_str());
}
else
{
std::string where = g_argv[1];
// cd - 切换到上一次目录
if(where == "-")
{
const char* old_pwd = getenv("OLDPWD");
if(old_pwd != nullptr)
{
chdir(old_pwd);
printf("%s\n", old_pwd);
}
}
else if(where == "~")
{
std::string home = GetHome();
if(!home.empty())
{
chdir(home.c_str());
}
}
else // 其他路径, 直接切换
{
chdir(where.c_str());
}
}
return true;
}
void Echo()
{
if(g_argc == 2)
{
// echo "hello world"
// echo $?
// echo $PATH
std::string opt = g_argv[1];
if (opt == "$?")
{
std::cout << lastcode << std::endl;
lastcode = 0;
}
else if (opt[0] == '$')
{
std::string env_name = opt.substr(1);
const char* env_value = getenv(env_name.c_str());
if (env_value)
std::cout << env_value << std::endl;
}
else
{
std::cout << opt << std::endl;
}
}
}
// 内建命令: 不能由子进程执行,要由shell自己执行
bool CheckAndExecBuiltin()
{
std::string cmd = g_argv[0];
if(cmd == "cd")
{
Cd();
return true;
}
else if(cmd == "echo")
{
Echo();
return true;
}
else if(cmd == "export")
{
}
else if(cmd == "alias")
{
//std::string nickname = g_argv[1];
//alias_list.insert(k,v);
}
return false;
}
int Execute()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0)
{
// child
execvp(g_argv[0], g_argv);
exit(1);
}
// father
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(id, nullptr, 0);
if(rid > 0)
{
lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
}
return 0;
}
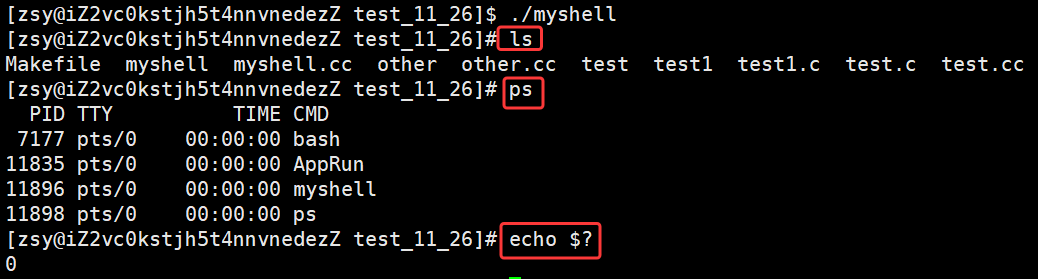
int main()
{
// 从父shell中获取环境变量
InitEnv();
while(true)
{
// 1. 输出命令行提示符
PrintCommandPrompt();
// 2. 获取用户输入的命令
char commandline[COMMAND_SIZE];
if(!GetCommandLine(commandline, sizeof(commandline)))
continue;
// 3. 命令行分析 "ls -a -l" -> "ls" "-a" "-l"
CommandParse(commandline);
//PrintArgv();
// 4. 检测并处理内建命令
if(CheckAndExecBuiltin())
continue;
// 5. 执行命令
Execute();
}
return 0;
} 实现效果: