Color and Depth Textures
https://catlikecoding.com/unity/tutorials/custom-srp/particles/
-
Support flipbook, near fade, soft, and distortion particles.
-
Determine fragment depth, for orthographic and perspective projections.
-
Copy and sample the color and depth buffers.
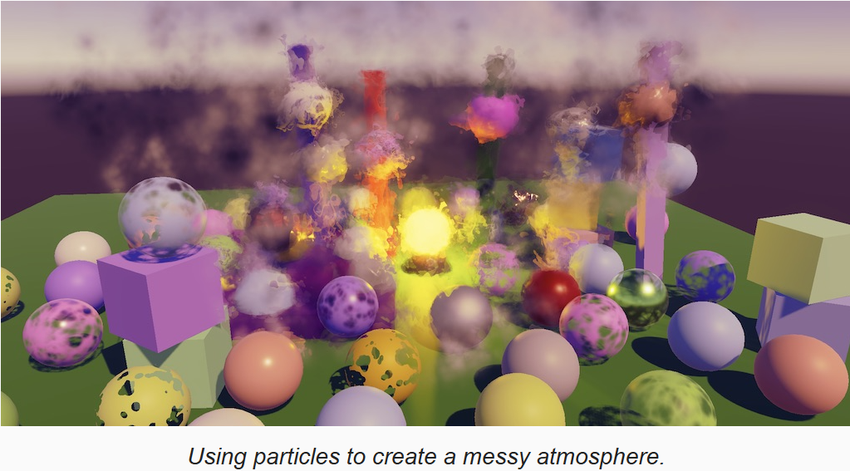

1 Unlit Particles
特效系统可以用任意的材质渲染,也包括我们自己的 RP,当然也有一些限制。我们接下来实现 unlit particles,lit particles 是类似的,只是多一些属性和光照计算。
首先构建一个场景,里面有一些垂直的立方体,和一个亮黄色的灯泡,作为粒子系统的背景

1.1 Particle System
通过 GameObject/Effects/Particle System 菜单项创建一个粒子,并将其放置在比地面略低的位置。假定你已经学会了如何配置粒子,如果不会参考文档: Unity's documentation
粒子系统默认向上喷射粒子,填充到一个锥形区域。如果将我们的 unlit 材质赋值给粒子,那么就会渲染成对齐到摄像机平面的白色的方片。

1.2 Unlit Particles Shader
从 unlit.shader 复制,为粒子创建专门的 shader,改名为 UnlitParticle.shader,定义菜单为 Custom RP/Particles/Unlit。粒子总是动态的,因此不可以被烘焙,所以我们将 meta pass 删除。
然后用这个 shader 创建专门的材质,应用到粒子系统。我们还没有改动 shader,因此效果还和之前一样。可以设置粒子系统让其发射 mesh 粒子,如果粒子系统和材质都开启了阴影,还可以渲染粒子的阴影。由于粒子系统使用过程化的绘制,因此 GPU instancing 没有工作,实际上粒子的 mesh 被合并成一个 mesh 进行渲染,就像粒子片一样。
后面我们只考虑 billboard 粒子,不渲染阴影。下面的链接提供了一个平滑淡出的粒子图片:https://catlikecoding.com/unity/tutorials/custom-srp/particles/unlit-particles/particles-single.png

为材质应用该贴图,模式改为 Fade 后,粒子效果如下图。为了让效果更明显,把粒子发射率改为100
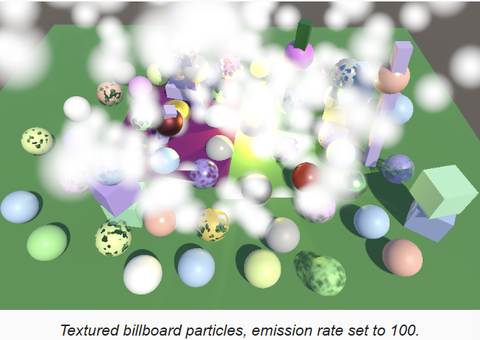
如果渲染结果与上图有差异,为 MainCamera 添加 CustomRenderPipelineCamera 组件,激活 Override Post FX,并设置 Post FX Settings 为 null,就可以在 Game 视图看到符合效果的画面了。我们无法改变 Scene,是因为 Scene 的 Camera 无法添加组件,只能使用管线的 Post FX Settings。
1.3 Vertex Colors
每个粒子可以使用不同的颜色,可以通过设置粒子系统的 starting color 为黑色和白色之间的随机颜色,来看到效果。但是我们的 shader 还不支持顶点颜色,因此看不到效果,下面增加顶点颜色的支持。
首先,修改 InputConfig,增加颜色属性。如果之前 InputConfig 是定义在 common.hlsl 中的,把相关定义和函数移到 LitInput.hlsl 中,然后在 UnlitInput.hlsl 中重新定义:
cs
struct InputConfig
{
float4 color;
float2 baseUV;
};
InputConfig GetInputConfig(float2 baseUV)
{
InputConfig input;
input.baseUV = baseUV;
input.color = 1.0;
return input;
}
float4 GetBase(InputConfig c)
{
float4 map = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_BaseMap, sampler_BaseMap, c.baseUV);
float4 color = UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _BaseColor);
return map * color * c.color;
}为了支持顶点颜色,在 UnlitParticle.shader 中,增加 _VERTEX_COLORS 属性。定义对应的 shader feature。也可以对 Unlit.shader 做同样的修改以支持顶点颜色。
cs
Properties
{
[HDR]_BaseColor("Color", Color) = (1.0,1.0,1.0,1.0)
[Toggle(_VERTEX_COLORS)] _VertexColors ("Vertex Colors", Float) = 0
...
}
CustomEditor "CustomShaderGUI"
SubShader
{
...
Pass
{
...
#pragma shader_feature _CLIPPING
#pragma shader_feature _VERTEX_COLORS
...
}
...
}在 Unlit.hlsl 中,为顶点属性,增加颜色语义,传递到片段着色器,并应用颜色:
cs
struct Attributes
{
float3 positionOS : POSITION;
float4 color : COLOR;
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
UNITY_VERTEX_INPUT_INSTANCE_ID
};
struct Varyings
{
float4 positionCS : SV_POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXTCOORD0;
#if defined(_VERTEX_COLORS)
float4 color : VAR_COLOR;
#endif
UNITY_VERTEX_INPUT_INSTANCE_ID
};
Varyings UnlitPassVertex(Attributes input)
{
Varyings output;
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
UNITY_TRANSFER_INSTANCE_ID(input, output);
float3 positionWS = TransformObjectToWorld(input.positionOS);
output.positionCS = TransformWorldToHClip(positionWS);
#if defined(_VERTEX_COLORS)
output.color = input.color;
#endif
output.uv = TransformBaseUV(input.uv);
return output;
}
float4 UnlitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
InputConfig config = GetInputConfig(input.uv);
#if defined(_VERTEX_COLORS)
config.color = input.color;
#endif
float4 base = GetBase(config);
#if defined(_CLIPPING)
clip(base.a - GetCutoff(input.uv));
#endif
return float4(base.rgb, GetAlpha(base.a));
}在粒子材质中开启 vertex color,可以看到每个粒子的颜色都不同了,但是现在粒子排序就有问题了。之前所有粒子颜色都是一样的,因此看不太出来,现在颜色不同,就需要根据距离进行排序,才能得到正确的结果。值得注意的是,当摄像机位置发生变化时,基于距离的排序会出现顺序突然改变的现象,其它半透明物体的渲染也有同样问题。
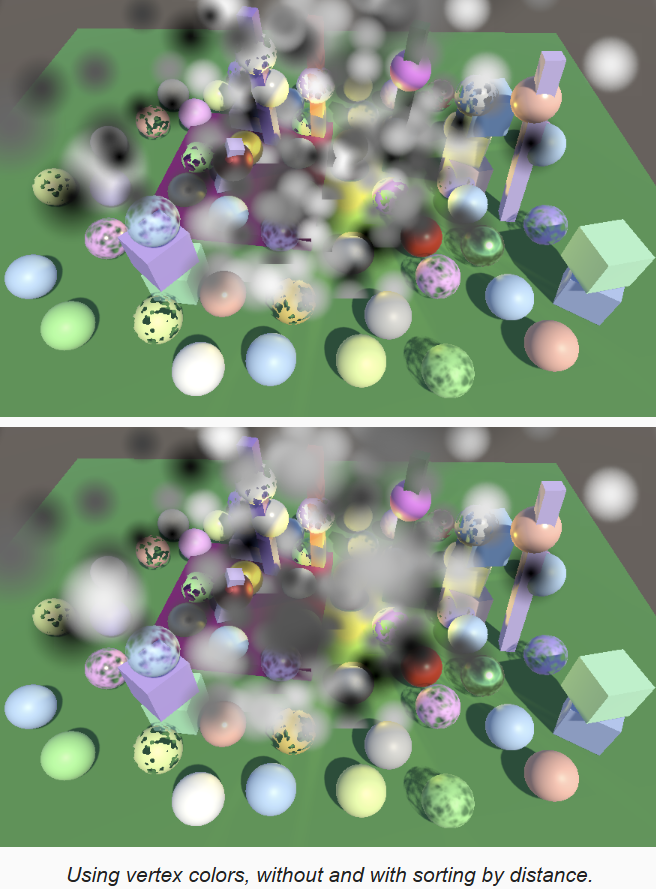
1.4 Flipbooks
通过 flipbook ,Billboard 粒子可以播放序列帧动画,需要指定一个图集贴图,如下:
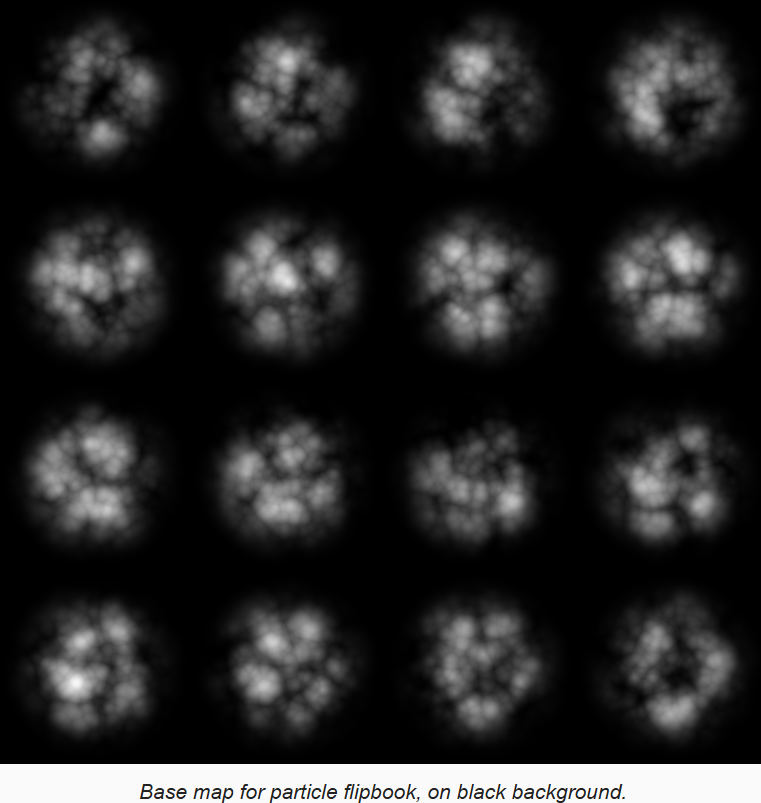
用上面的图,创建一个新的 unlit 材质,然后在场景中已有的粒子系统复制一个,使用新的材质进行渲染。启用粒子系统的 Texture Sheet Animation 模块,配置为 4x4 flipbook,让其从随机帧开始,基于粒子的生命周期播放一个循环。
通过让粒子在X和Y轴上以50%的概率反转,以任意旋转开始,以随机的速度渲染等,增加粒子多样性。

1.5 Flipbook Blending
可以看到粒子的帧动画的帧率很低,能够很容易的看出动画帧(类似卡顿),如果粒子的声明周期是5秒,那么帧率就只有3.2帧/秒。可以通过混合相邻帧来进行平滑,这需要我们向 shader 传递第二组 UV 坐标,以及混合参数。通过在粒子系统的 Renderer 模块中启用 custom vertex stream 来实现,增加 UV2 和 AnimBlend,同时移除不需要的 normal。
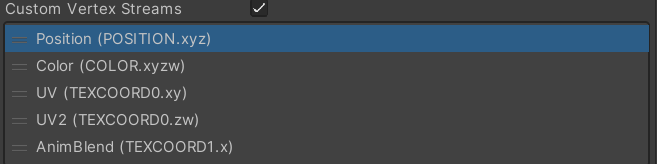
向 UnlitPartile 增加一个开关属性来控制是否支持 flipbook 混合,以及 shader feature
cs
[Toggle(_VERTEX_COLORS)] _VertexColors ("Vertex Colors", Float) = 0
[Toggle(_FLIPBOOK_BLENDING)]_FlipbookBlending("Flipbook Blending", Float) = 0
...
#pragma shader_feature _VERTEX_COLORS
#pragma shader_feature _FLIPBOOK_BLENDING如果 flipbook blending 启用,通过 TEXCOORD0 将两组UV传递进去,因此要用 float4,混合参数是一个 float,用 TEXCOORD1 传递。同时将混合用的 UV 和参数,用 float3 传递到像素着色器。
cs
struct Attributes
{
float3 positionOS : POSITION;
float4 color : COLOR;
#if defined(_FLIPBOOK_BLENDING)
float4 uv : TEXCOORD0;
float flipbookBlend : TEXCOORD1;
#else
float2 uv : TEXCOORD0;
#endif
UNITY_VERTEX_INPUT_INSTANCE_ID
};
Varyings UnlitPassVertex(Attributes input)
{
Varyings output;
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
UNITY_TRANSFER_INSTANCE_ID(input, output);
float3 positionWS = TransformObjectToWorld(input.positionOS);
output.positionCS = TransformWorldToHClip(positionWS);
#if defined(_VERTEX_COLORS)
output.color = input.color;
#endif
output.uv.xy = TransformBaseUV(input.uv.xy);
#if defined(_FLIPBOOK_BLENDING)
output.flipbookUVB.xy = TransformBaseUV(input.uv.zw);
output.flipbookUVB.z = input.flipbookBlend;
#endif
return output;
}
struct Varyings
{
float4 positionCS : SV_POSITION;
float2 uv : TEXTCOORD0;
#if defined(_FLIPBOOK_BLENDING)
float3 flipbookUVB : VAR_FLIPBOOK;
#endif
#if defined(_VERTEX_COLORS)
float4 color : VAR_COLOR;
#endif
UNITY_VERTEX_INPUT_INSTANCE_ID
};在 InputConfig 加入混合参数,以及是否启用的开关,并在 GetInputConfig 中填充默认值为 false。然后在 GetBase 中,如果需要,进行第二次采样并进行混合
cs
struct InputConfig
{
float4 color;
float2 baseUV;
float3 flipbookUVB;
bool flipbookBlending;
};
InputConfig GetInputConfig(float2 baseUV)
{
InputConfig input;
input.baseUV = baseUV;
input.color = 1.0;
input.flipbookUVB = 0;
input.flipbookBlending = false;
return input;
}
float4 GetBase(InputConfig c)
{
float4 map = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_BaseMap, sampler_BaseMap, c.baseUV);
if (c.flipbookBlending)
{
float4 map2 = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_BaseMap, sampler_BaseMap, c.flipbookUVB.xy);
map = lerp(map, map2, c.flipbookUVB.z);
}
float4 color = UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _BaseColor);
return map * color * c.color;
}最后,在像素着色器中,调用 GetBase 时,根据需要填充 InputConfig 中的混合相关参数
cs
float4 UnlitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
InputConfig config = GetInputConfig(input.uv);
#if defined(_FLIPBOOK_BLENDING)
config.flipbookUVB = input.flipbookUVB;
config.flipbookBlending = true;
#endif
#if defined(_VERTEX_COLORS)
config.color = input.color;
#endif
float4 base = GetBase(config);
#if defined(_CLIPPING)
clip(base.a - GetCutoff(input.uv));
#endif
return float4(base.rgb, GetAlpha(base.a));
}2 Fading Near Camera
当摄像机在粒子系统内部时,粒子可能会非常靠近摄像机的近平面,甚至会穿过近平面。粒子系统提供了 Renderer/Max Particle Size 属性,来避免单个粒子覆盖过大的窗口区域。当粒子靠近近平面时,如果粒子达到了最大尺寸,它们看起来像是滑倒旁边去了,而不是继续变大。
另一种处理方式是基于深度淡出靠近近平面的粒子,在表现穿过由粒子系统模拟的大气环境时,这种效果会更好。
2.1 Fragment Data
在顶点着色器中,SV_POSITION 表示的是顶点的裁剪空间的4D其次坐标,在片段着色器中则是片段的屏幕空间坐标,这个转换是由GPU完成的。为了更加明确,将 Varyings 结构体中的 positionCS 改名为 positionCS_SS,并在顶点着色器中做相应的调整。
cs
struct Varyings
{
float4 positionCS_SS : SV_POSITION;
...
};
Varyings UnlitPassVertex(Attributes input)
{
...
float3 positionWS = TransformObjectToWorld(input.positionOS);
output.positionCS_SS = TransformWorldToHClip(positionWS);
...
}然后我们新建 Fragment.hlsl 文件,在里面定义 Fragment 结构和获取的函数,根据给定的 float4 类型的屏幕空间的位置返回结果。现在 Fragment 只有2D的位置,由屏幕空间位置的 xy 分量进行赋值。这是带有 0.5 偏移的图素坐标,(0.5,0.5) 是屏幕的左下角,(1.5,0.5) 是右下角。
cs
// fragment.hlsl
#ifndef FRAGMENT_INCLUDED
#define FRAGMENT_INCLUDED
struct Fragment
{
// 屏幕空间位置
float2 positionSS;
};
Fragment GetFragment(float4 positionSS)
{
Fragment f;
f.positionSS = positionSS.xy;
return f;
}在 Common 中,unity include 之后包含上面的文件,然后调整 ClipLOD 使用 Fragment 作为参数。同时,在 common 中定义点采样器和线性采样器,然后移除在 PostFXStackPasses.hlsl 中重复的定义:
cs
SAMPLER(sampler_linear_wrap);
SAMPLER(sampler_point_wrap);
#include "Fragment.hlsl"
// 执行 lod fade 裁剪
void ClipLOD(Fragment fragment, float fade)
{
#if defined(LOD_FADE_CROSSFADE)
// unity dither 生成函数
float dither = InterleavedGradientNoise(fragment.positionSS, 0);
// 淡入时,fade 时负的,因此需要 + dither
clip(fade + (fade < 0 ? dither : -dither));
#endif
}将 Fragment 添加到 LitInput 和 UnlitInput 的 InputConfig 结构体中,并在 GetInputConfig 时进行初始化,
cs
struct InputConfig
{
Fragment fragment;
...
};
InputConfig GetInputConfig(float4 positionSS, float2 baseUV, float2 detailUV = 0)
{
InputConfig input;
input.fragment = GetFragment(positionSS);
...
}然后调整 LitPassFragment,在 GetInputConfig 之后,调用 ClipLOD。同时调用 InterleavedGradientNoise 时,也使用 fragment.positionSS。
cs
float4 LitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
InputConfig config = GetInputConfig(input.positionCS_SS, input.uv);
ClipLOD(config.fragment, unity_LODFade.x);
...
surface.dither = InterleavedGradientNoise(config.fragment.positionSS, 0);
...
}ShadowCasterPassFragment 也需要类似的调整:
cs
void ShadowCasterPassFragment(Varyings input)
{
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
InputConfig config = GetInputConfig(input.positionCS_SS, input.uv);
ClipLOD(config.fragment, unity_LODFade.x);
...
}2.2 Fragment Depth
想要淡出靠近近平面的粒子,我们需要知道片段的深度,因此向 Fragment 结构中加入 depth 字段。片段深度存储在屏幕空间位置向量的最后一个分量上,该值是用来进行透视除法,将3D位置投影到屏幕上。这是视口空间的深度,因此是到摄像机 XY 平面的距离,而不是到近平面的距离。
cs
struct Fragment
{
// 屏幕空间位置
float2 positionSS;
// 摄像机空间,到摄像机 XY 平面的距离
float depth;
};
Fragment GetFragment(float4 positionSS)
{
Fragment f;
f.positionSS = positionSS.xy;
f.depth = positionSS.w;
return f;
}2.3 正交深度
上面的方法适用于透视相机,而正交摄像机的深度需要另外获取。对于正交相机,其不需要透视除法,因此屏幕空间位置向量的 w 分量总是 1。
向 UnityInput 中添加 float4 unity_OrthoParams 字段,Unity 通过该字段向GPU提交正交相机的数据。
如果是正交相机,该值的最后一个分量就会是1,否则是0.据此我们在 Common 中实现判断是否是正交相机的函数。因为要在 Fragment 中使用,因此定义在包含 Fragment 之前。
cs
// UnityInput.hlsl
...
float4 unity_OrthoParams;
float4 _ProjectionParams;
// Common.hlsl
bool IsOrthographicCamera()
{
return unity_OrthoParams.w;
}
#include "Fragment.hlsl"对于正交相机,屏幕空间位置向量的 z 分量包含了变换过的裁剪空间的深度。该深度是用来比较并在允许时写入深度缓冲区的原始值,是范围 0-1 的线性变化的值。为了将其变换到视口空间的深度,需要根据摄像机的 near-far 范围进行缩放,并加上 near 。near far 数据存储在 _ProjectionParams 的 Y Z 分量上。如果开启了 reverse Z,则深度也需要反转。将获取深度的逻辑实现在专门的函数中,同样在包含 Fragment.hlsl 之前:
cs
float OrthographicDepthBufferToLinear(float rawDepth)
{
#if UNITY_REVERSED_Z
rawDepth = 1.0f - rawDepth;
#endif
return (_ProjectionParams.z - _ProjectionParams.y) * rawDepth + _ProjectionParams.y;
}
#include "Fragment.hlsl"现在,可以在 GetFragment 中正确的获取深度值了:
cs
Fragment GetFragment(float4 positionSS)
{
Fragment f;
f.positionSS = positionSS.xy;
f.depth = IsOrthographicCamera() ?
OrthographicDepthBufferToLinear(positionSS.z) : positionSS.w;
return f;
}在 LitPassFragment 和 UnlitPassFragment 中,可以返回该深度值以进行验证。记得验证完后删除:
cs
float4 UnlitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
InputConfig config = GetInputConfig(input.positionCS_SS, input.uv);
// 验证深度计算
//return float4(config.fragment.depth.xxx / 20.0, 1.0);
...
}2.4 Distance-Bassed Fading
向 UnlitParticles.shader 中,添加 Near Fade 开关,随后定义 Near Fade Distance 表示距离摄像机平面多远时开始淡出,1 是比较合适的值,也就是距离摄像机 1 单位距离。定义 Near Fade Range 表示淡出的变化区间,在该范围内,粒子会线性的淡出。这里 1也是一个不错的选择,其最小值必须是一个小的整数。同时定义 shader feature:
cs
...
[Toggle(_FLIPBOOK_BLENDING)]_FlipbookBlending("Flipbook Blending", Float) = 0
[Toggle(_NEAR_FADE)]_NearFade("Near Fade", Float) = 0
_NearFadeDistance("Near Fade Distance", Range(0.0,10.0)) = 1
_NearFadeRange("Near Fade Range", Range(0.01,10.0)) = 1
...
#pragma shader_feature _FLIPBOOK_BLENDING
#pragma shader_feature _NEAR_FADE
...在 UnlitInput 的 UnityPerMaterial 中加入两个控制参数:
cs
...
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float4, _BaseColor)
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _NearFadeDistance)
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _NearFadeRange)
...在 InputConfig 添加一个 bool 来记录是否启用 near fade,默认是 false
cs
struct InputConfig
{
...
bool flipbookBlending;
bool nearFade;
};
InputConfig GetInputConfig(float4 positionSS, float2 baseUV)
{
...
input.nearFade = false;
return input;
}我们通过降低片段的 base alpha 来完成淡出,用片段深度减去淡出距离,然后除以淡出范围作为衰减。因为可能产生负值,因此需要 saturate。在 GetBase 执行该逻辑
cs
float4 GetBase(InputConfig c)
{
float4 map = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_BaseMap, sampler_BaseMap, c.baseUV);
if (c.flipbookBlending)
{
float4 map2 = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_BaseMap, sampler_BaseMap, c.flipbookUVB.xy);
map = lerp(map, map2, c.flipbookUVB.z);
}
if (c.nearFade)
{
float nearAttenuation = c.fragment.depth - UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _NearFadeDistance);
nearAttenuation = nearAttenuation / UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _NearFadeRange);
nearAttenuation = saturate(nearAttenuation);
map.a *= nearAttenuation;
}
float4 color = UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _BaseColor);
return map * color * c.color;
}最后,根据 _NEAR_FADE 来为 InputConfig.nearFade 进行赋值。
cs
float4 UnlitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
InputConfig config = GetInputConfig(input.positionCS_SS, input.uv);
// 验证深度计算
//return float4(config.fragment.depth.xxx / 20.0, 1.0);
#if defined(_FLIPBOOK_BLENDING)
config.flipbookUVB = input.flipbookUVB;
config.flipbookBlending = true;
#endif
#if defined(_NEAR_FADE)
config.nearFade = true;
#endif
...
}3 Soft Particles
当粒子根场景中的面穿插时,会发现明显的交线,解决方法是使用软粒子,即在交叉的地方,根据到面的距离进行淡出。这就需要在粒子的片段着色器中比较粒子的深度和深度缓冲区的深度,因此需要对深度缓冲区进行采样。
3.1 Separate Depth Buffer
首先,在 CamerarRenderer 中,添加深度缓冲区的 ID,修改引用处的代码。同时正确的处理深度缓冲区的创建和释放:
cs
//static int frameBufferId = Shader.PropertyToID("_CameraFrameBuffer");
static int colorAttachmentId = Shader.PropertyToID("CameraColorAttachment");
static int depthAttachmentId = Shader.PropertyToID("CameraDepthAttachment");
...
void Setup(){
buffer.GetTemporaryRT(colorAttachmentId,
camera.pixelWidth, camera.pixelHeight,
32, FilterMode.Bilinear,
useHDR ? RenderTextureFormat.DefaultHDR : RenderTextureFormat.Default);
buffer.GetTemporaryRT(depthAttachmentId, camera.pixelWidth, camera.pixelHeight,
32, FilterMode.Point, RenderTextureFormat.Depth);
buffer.SetRenderTarget(
colorAttachmentId, RenderBufferLoadAction.DontCare, RenderBufferStoreAction.Store,
depthAttachmentId, RenderBufferLoadAction.DontCare, RenderBufferStoreAction.Store
);
...
}
...
void Cleanup()
{
lighting.Cleanup();
if (postFXStack.IsActive)
{
buffer.ReleaseTemporaryRT(colorAttachmentId);
buffer.ReleaseTemporaryRT(depthAttachmentId);
}
}3.2 Copying Depth
在我们采样深度时,深度缓冲区正用于渲染,不能直接采样,因此需要将其拷贝出来。声明新的 _CameraDepthTexture 并进行拷贝。同时声明一个 bool 用来跟踪是否需要拷贝深度,目前总是 true。
cs
static int depthTextureId = Shader.PropertyToID("_CameraDepthTexture");
bool useDepthTexture = false;
bool useHDR = false;
...
void Render(...)
{
...
CameraSettings cameraSettings = crpCamera ? crpCamera.Settings : defaultCameraSettings;
useDepthTexture = true;
...
}
...
void DrawVisibleGeometry(...)
{
...
context.DrawSkybox(camera);
CopyAttachments();
...
}
...
void CopyAttachments()
{
if(useDepthTexture)
{
buffer.GetTemporaryRT(depthTextureId, camera.pixelWidth, camera.pixelHeight,
32, FilterMode.Point, RenderTextureFormat.Depth);
buffer.CopyTexture(depthAttachmentId, depthTextureId);
ExecuteBuffer();
}
}3.3 Copying Depth Without Post FX
执行深度拷贝的前提是有 depth attachment,目前只有在 Post FX 启用时,才会创建它。为了在不启用 Post FX 时也可以拷贝,当用到深度图时,就需要使用中间的 frame buffer。定义 useIntermediateBuffer 标识,在 setup 中,访问 attachment 之前进行初始化,当 postFX 启用,或者需要访问 depth buffer 时就使用中间 frame buffer。同时在 Cleanup 中正确的释放。
cs
bool useDepthTexture = false;
bool useIntermediateBuffer = false;
bool useHDR = false;
...
void Setup()
{
context.SetupCameraProperties(camera);
CameraClearFlags clearFlags = camera.clearFlags;
useIntermediateBuffer = useDepthTexture || postFXStack.IsActive;
// 如果开启了后处理,则渲染到临时 RT 上
if (useIntermediateBuffer)
{
// 获取的 RenderTexture 数据是随机的,因此要清除
if (clearFlags > CameraClearFlags.Color)
clearFlags = CameraClearFlags.Color;
...
}
...
void Cleanup()
{
lighting.Cleanup();
if (useIntermediateBuffer)
{
buffer.ReleaseTemporaryRT(colorAttachmentId);
buffer.ReleaseTemporaryRT(depthAttachmentId);
if (useDepthTexture)
buffer.ReleaseTemporaryRT(depthTextureId);
}
}当 post FX 未启用时,由于我们只渲染到中间 buffer 上了,因此渲染结果不会在屏幕上显示,我们需要在最后执行拷贝到摄像机 target 的操作。不幸的是 CopyTexture 只能以 render texture 为拷贝的目标,不能拷贝到 frame buffer。我们可以用 post FX 的 copy pass 方法,专门写一个 CameraRenderer.shader 来实现,可以从 PostFX.shader 中拷贝并修改
cs
Shader "Hidden/Custom RP/Camera Renderer"
{
SubShader
{
Cull Off
ZTest Always
ZWrite Off
HLSLINCLUDE
#include "../ShaderLibrary/Common.hlsl"
#include "CameraRendererPasses.hlsl"
ENDHLSL
Pass
{
Name "Copy"
HLSLPROGRAM
#pragma target 3.5
#pragma vertex DefaultPassVertex
#pragma fragment CopyPassFragment
ENDHLSL
}
}
}CameraRendererPasses.hlsl 的定义与 PostFXStackPasses 类似,所以拷贝,并删除不需要的内容
cs
#ifndef CAMERA_RENDERER_PASSES_INCLUDED
#define CAMERA_RENDERER_PASSES_INCLUDED
TEXTURE2D(_SourceTexture);
struct Varyings
{
float4 positionCS : SV_POSITION;
float2 screenUV : VAR_SCREEN_UV;
};
Varyings DefaultPassVertex(uint vertexID : SV_VertexID)
{
Varyings output;
output.positionCS = float4(
vertexID <= 1 ? -1.0 : 3.0,
vertexID == 1 ? 3.0 : -1.0,
0.0, 1.0);
output.screenUV = float2(
vertexID <= 1 ? 0.0 : 2.0,
vertexID == 1 ? 2.0 : 0.0);
// 处理Y轴翻转
if (_ProjectionParams.x < 0.0)
{
output.positionCS.y = -output.positionCS.y;
}
return output;
}
float4 CopyPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
return SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_LOD(_SourceTexture, sampler_linear_clamp, input.screenUV, 0.0);
}
#endif然后,为 CameraRenderer 创建材质,在其构造函数中,用构造函数指定的 shader 名字调用 CoreUtils.CreateEngineMaterial,该接口创建材质并确保不会被存储为 asset。
同时实现 Dispose 接口,销毁材质。该接口可能正常销毁(有延迟),也可能立即销毁,这取决于是否是播放模式。因为当我们修改了我们 RP,就会重新创建 RP 实例,如果不实现 dispose,那么材质就会得不到释放,从而创建很多材质。
cs
bool useIntermediateBuffer = false;
// 用于将 render texture 渲染到屏幕
Material material;
bool useHDR = false;
...
public CameraRenderer(Shader shader)
{
material = CoreUtils.CreateEngineMaterial(shader);
}
public void Dispose()
{
CoreUtils.Destroy(material);
}修改 CustomRenderPipeline 的构造函数,接收 shader 参数,用改参数创建 CameraRenderer。之前的 Dispose 仅在编辑器下定义,也需要改为运行时,并调用 camera renderer 的 dispose,然后将之前编辑器的 dispose 改名为 DisposeForEditor
CustomRenderPipeline.cs:
cs
public CustomRenderPipeline(..., Shader cameraRendererShader)
{
cameraRenderer = new CameraRenderer(cameraRendererShader);
...
}
...
partial void DisposeForEditor();
protected override void Dispose(bool disposing)
{
base.Dispose(disposing);
DisposeForEditor();
cameraRenderer.Dispose();
}CustomRenderPipeline.Editor.cs
cs
partial void DisposeForEditor()
{
Lightmapping.ResetDelegate();
}然后在 CustomRenderPipelineAsset 中声明 CameraRenderer Shader 并在创建CustomRenderPipeline时作为参数
cs
[SerializeField] Shader cameraRendererShader = default;
protected override RenderPipeline CreatePipeline()
{
var rp = new CustomRenderPipeline(
...
cameraRendererShader
);
rp.EnableHDR(allowHDR);
return rp;
}最后,在 CameraRenderer 中,定义 _SourceTexture,并实现 Draw 方法,并在检测到 postFXStack 未启用时,调用 Draw 拷贝到屏幕上
3.4 Reconstructing View-Space Depth
我们需要片段在屏幕上的UV坐标来采样深度图,可以用片段位置除以屏幕像素尺寸来计算该UV坐标,shader 中,屏幕尺寸由 Unity 提供的 _ScreenParams 提供,因此添加到 UnityInput 中
cs
float4 _ProjectionParams;
// xy 屏幕像素宽高
float4 _ScreenParams;在 Fragments.hlsl 增加屏幕UV,并采样深度
cs
TEXTURE2D(_CameraDepthTexture)
struct Fragment
{
// 屏幕空间位置
float2 positionSS;
// 屏幕片段的UV
float2 screenUV;
// 摄像机空间,到摄像机 XY 平面的距离
float depth;
// 深度缓冲区中的深度
float bufferDepth;
};
Fragment GetFragment(float4 positionSS)
{
Fragment f;
f.positionSS = positionSS.xy;
f.depth = IsOrthographicCamera() ? OrthographicDepthBufferToLinear(positionSS.z) : positionSS.w;
f.screenUV = positionSS.xy / _ScreenParams.xy;
// 采样深度。SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE_LOD 功能同 SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_LOD 一样,但是只返回 R 通道
f.bufferDepth = SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE_LOD(_CameraDepthTexture, sampler_point_clamp, f.screenUV, 0);
return f;
}从深度缓冲区获取的是0-1的深度,需要转换成视口空间的深度。如果是正交相机,可以调用 OrthographicDepthBufferToLinear 来计算。透视深度通过 LinearEyeDepth 来计算得到,该函数需要 _ZBufferParams,因此在 UnityInput.hlsl 声明它。
透视摄像机下计算的深度:
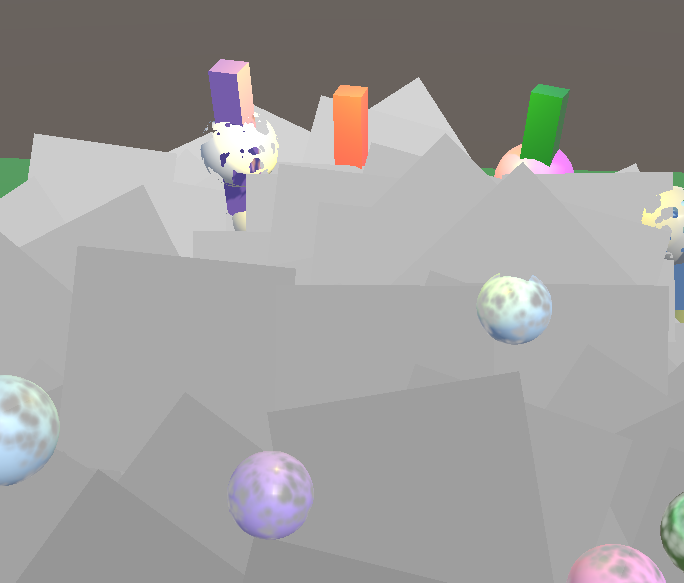

正交摄像机下的深度

记得在 LitPassFragment 和 UnlitPassFragment 中,删除调试深度输出的代码:
cs
float4 UnlitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
...
// 验证深度计算
//return float4(config.fragment.depth.xxx / 20.0, 1.0);
....
}3.5 Optional Depth Texture
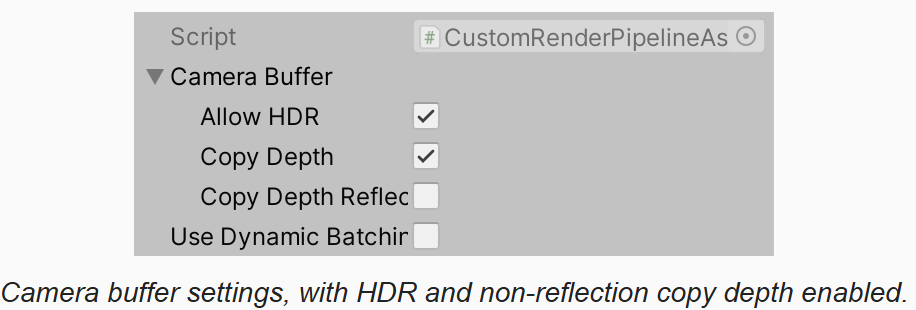
拷贝深度需要额外的工作,尤其是 post FX 没有启用时,还需要中间 buffer 和额外的拷贝到摄像机 target 的操作。因此增加一个配置来决定 RP 是否支持拷贝深度,为此我们定义 CameraBufferSettings 结构体,并将跟摄像机 buffer 相关的设置组织起来。包括是否拷贝深度的开关,是否启用 HDR,渲染反射时是否拷贝了深度。在渲染反射时,通常不开后效,粒子系统可能也不会渲染,因为反射拷贝深度代价太高,而且可能没有用。但是也可能其它的一些在反射渲染中的效果需要深度。而且,对于 cube map 的每个面,depth buffer 都是不同的,因此在 cube map 的边缘处会有接缝。
cs
[System.Serializable]
public class CameraBufferSettings
{
public bool allowHDR;
public bool copyDepth;
public bool copyDepthReflection;
}在管线 asset 中,替换掉 allowHDR,改用 CameraBufferSettings
cs
public partial class CustomRenderPipelineAsset : RenderPipelineAsset
{
...
[SerializeField] bool _usePerObjectLights = false;
[SerializeField] CameraBufferSettings cameraBuffer = new CameraBufferSettings() {
allowHDR = true
};
...
protected override RenderPipeline CreatePipeline()
{
var rp = new CustomRenderPipeline(
cameraBuffer,
...
);
return rp;
}
}管线实例对象也记录 CameraBufferSettings,并删除 allowHDR 替换为 CameraBufferSettings。同时CameraRenderer 接受该配置作为参数,基于该配置来决定是否拷贝深度图
cs
public void Render(ScriptableRenderContext context,
Camera camera,
CameraBufferSettings cameraBufferSettings,
...
)
{
...
if (camera.cameraType == CameraType.Reflection)
useDepthTexture = cameraBufferSettings.copyDepthReflection;
else
useDepthTexture = cameraBufferSettings.copyDepth;
useHDR = cameraBufferSettings.allowHDR && camera.allowHDR;
...
}
除了 RP,也需要为 CameraSettings 增加 copy depth 开关
cs
[Serializable]
public class CameraSettings
{
...
public bool copyDepth = true;
}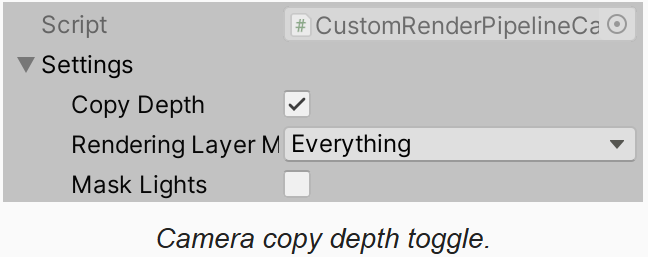
对于正常相机,只有 RP 和摄像机都开启了深度拷贝,才会在渲染中开启深度拷贝:
cs
if (camera.cameraType == CameraType.Reflection)
useDepthTexture = cameraBufferSettings.copyDepthReflection;
else
useDepthTexture = cameraBufferSettings.copyDepth && cameraSettings.copyDepth;3.6 Missing Texture
现在深度图是可选的,因此就可能不存在深度图。当在 shader 中采样时,结果就是随机的,可能是空贴图,或另一个摄像机的拷贝。我们可以确保当深度图无效时,其结果是确定的,通过在 CameraRenderer 的构造函数中,创建一个默认的 missing texture 来实现。创建一个 1x1 的贴图,设置其颜色为灰色。设置其 hideFlags,并设置其名字为 missing以便能看到该错误。在 Dispose 中释放贴图,在 setup 中应用该贴图,如果后面有有效的深度图,则会覆盖。
cs
// missing depth texture
Texture2D missingTexture;
public CameraRenderer(Shader shader)
{
material = CoreUtils.CreateEngineMaterial(shader);
missingTexture = new Texture2D(1, 1)
{
hideFlags = HideFlags.HideAndDontSave,
name = "Missing"
};
missingTexture.SetPixel(0, 0, Color.white * 0.5f);
missingTexture.Apply();
}
public void Dispose()
{
CoreUtils.Destroy(material);
CoreUtils.Destroy(missingTexture);
}
...
void Setup()
{
...
buffer.BeginSample(SampleName);
buffer.SetGlobalTexture(depthTextureId, missingTexture);
ExecuteBuffer();
}3.7 Fading Particles Nearby Background
有了深度图,就可以继续实现软粒子了。首先向 UnlitParticles.shader 中添加 soft particle 关键字开关,距离,范围三个属性。距离是测量的从粒子向后(远处)的距离,默认设置为0。
cs
Properties
{
...
_NearFadeRange("Near Fade Range", Range(0.01,10.0)) = 1
[Toggle(_SOFT_PARTICLES)]_SoftParticles("Soft Particles", Float) = 0
_SoftParticlesDistance("Soft Particles Distance", Range(0.0, 10.0) =0
_SoftParticlesRange("Soft Particles Range", Range(0.01, 10.0))=0
....
}
...
#pragma shader_feature _NEAR_FADE
#pragma shader_feature _SOFT_PARTICLES
...在 UnlitInput 中,定义相关常量。同时在 InputConfig 中增加 softParticles ,并默认返回 false
cs
UNITY_INSTANCING_BUFFER_START(UnityPerMaterial)
...
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _SoftParticlesDistance)
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _SoftParticlesRange)
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _Cutoff)
...
UNITY_INSTANCING_BUFFER_END(UnityPerMaterial)
struct InputConfig
{
...
bool softParticles;
};
InputConfig GetInputConfig(float4 positionSS, float2 baseUV)
{
...
input.softParticles = false;
return input;
}在 UnlitPassFragment 中,如果定义了 _SOFT_PARTICLES 则设置 config 标记
cs
float4 UnlitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
...
#if defined(_SOFT_PARTICLES)
config.softParticles = true;
#endif
...
}在 GetBase 中,如果开启了 soft particles,用当前的 buffer 深度减去像素的深度
cs
float4 GetBase(InputConfig c)
{
...
if (c.softParticles)
{
float deltaDepth = c.fragment.bufferDepth - c.fragment.depth;
float distance = UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _SoftParticlesDistance);
float nearAttenuation = (deltaDepth - distance) / UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _SoftParticlesRange);
map.a *= saturate(nearAttenuation);
}
...3.8 No Copy Texture Support
现在的软粒子,依赖 CopyTexture ,但是某些情况下,如 WebGL2.0 是不支持的。因此如果要在 WebGL2.0下支持软粒子,就需要我们自己用 shader 完成拷贝,虽然效率不高,但至少是可以工作的。
首先在 CameraRenderer.shader 中实现 copy depth pass,不写颜色,仅写深度
cs
Pass
{
Name "Copy Depth"
ColorMask 0
ZWrite On
HLSLPROGRAM
#pragma target 3.5
#pragma vertex DefaultPassVertex
#pragma fragment CopyDepthPassFragment
ENDHLSL
}在 CameraRendererPasses.hlsl 中实现 CopyDepthPassFragment,采样深度并返回
cs
float CopyDepthPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_DEPTH
{
return SAMPLE_DEPTH_TEXTURE_LOD(_SourceTexture, sampler_linear_clamp, input.screenUV, 0.0);
}在 CameraRenderer 中用一个静态变量来跟踪是否支持 CopyTexture。先将值设置为 false ,方便我们实现 shader 完成拷贝。
在 CopyAttachments 中,如果支持 copyTexture ,则调用 copy 接口,否则用我们自己的 Draw 来进行拷贝。Draw 过程中修改了 render target,因此要在调用后改回来。同时 draw 增加是否是拷贝深度的参数,根据该参数使用正确的 pass id
cs
void Draw(RenderTargetIdentifier from, RenderTargetIdentifier to, bool isDepth)
{
buffer.SetGlobalTexture(sourceTextureId, from);
buffer.SetRenderTarget(to);
buffer.DrawProcedural(Matrix4x4.identity, material, isDepth?1:0, MeshTopology.Triangles, 3);
}
void CopyAttachments()
{
if(useDepthTexture)
{
buffer.GetTemporaryRT(depthTextureId, camera.pixelWidth, camera.pixelHeight,
32, FilterMode.Point, RenderTextureFormat.Depth);
if (copyTextureSupported)
{
buffer.CopyTexture(depthAttachmentId, depthTextureId);
}
else
{
Draw(depthAttachmentId, depthTextureId, true);
buffer.SetRenderTarget(colorAttachmentId, RenderBufferLoadAction.Load, RenderBufferStoreAction.Store,
depthAttachmentId, RenderBufferLoadAction.Load, RenderBufferStoreAction.Store);
}
ExecuteBuffer();
}
}测试 depth copy shader 没问题后,正确的判断 copy texture 的支持情况:
cs
static bool copyTextureSupported =
SystemInfo.copyTextureSupport > CopyTextureSupport.None;3.9 Gizmos and Depth
现在我们可以绘制/拷贝深度了,因此可以在绘制 gizmos 前,将深度先绘制/拷贝过去,这样绘制 gizmos 时就有有效的深度值作为参考了,分别在 before/afterFX 中,绘制前拷贝深度:
cs
partial void DrawGizmosBeforeFX()
{
if(Handles.ShouldRenderGizmos())
{
// 如果有中间 buffer,则先将深度拷贝到 target,这样 gizmos 渲染便有深度了
if (useIntermediateBuffer)
{
Draw(depthAttachmentId, BuiltinRenderTextureType.CameraTarget, true);
ExecuteBuffer();
}
context.DrawGizmos(camera, GizmoSubset.PreImageEffects);
}
}
partial void DrawGizmosAfterFX()
{
if(Handles.ShouldRenderGizmos())
{
// 如果有中间 buffer,则先将深度拷贝到 target,这样 gizmos 渲染便有深度了
if (useIntermediateBuffer)
{
Draw(depthAttachmentId, BuiltinRenderTextureType.CameraTarget, true);
ExecuteBuffer();
}
context.DrawGizmos(camera, GizmoSubset.PostImageEffects);
}
}
4 Distortion
接下来,我们添加对粒子扰动的支持,用来模拟被加热的大气折射现象。这需要采样颜色缓冲区,就像采样深度一样,不过要用对UV进行偏移(扰动)。
4.1 Color Copy Texture
首先向 CameraBufferSettings 中添加拷贝颜色缓冲区的两个开关,一个用于正常渲染,一个用于反射渲染。
cs
public class CameraBufferSettings
{
...
public bool copyColor;
public bool copyColorReflection;
}同时向 CameraSettings 添加拷贝颜色的开关
cs
public class CameraSettings
{
...
public bool copyColor = true;
}CameraRenderer 中定义 color texture 标识,并检查跟踪是否使用 color texture
cs
bool useIntermediateBuffer = false;
// 用于采样屏幕颜色
static int colorTextureId = Shader.PropertyToID("_CameraColorTexture");
bool useColorTexture = false;
public void Render(...)
{
if (camera.cameraType == CameraType.Reflection)
{
useDepthTexture = cameraBufferSettings.copyDepthReflection;
useColorTexture = cameraBufferSettings.copyColorReflection;
}
else
{
useDepthTexture = cameraBufferSettings.copyDepth && cameraSettings.copyDepth;
useColorTexture = cameraBufferSettings.copyColor && cameraSettings.copyColor;
}如果使用 color texture,那么也需要中间缓冲区。同时也需要为 color texture 指定 missing texture。并在销毁时,释放RT:
cs
void Setup()
{
...
useIntermediateBuffer = useDepthTexture || useColorTexture || postFXStack.IsActive;
...
buffer.BeginSample(SampleName);
buffer.SetGlobalTexture(depthTextureId, missingTexture);
buffer.SetGlobalTexture(colorTextureId, missingTexture);
ExecuteBuffer();
}
void Cleanup()
{
...
if (useIntermediateBuffer)
{
...
if (useColorTexture)
buffer.ReleaseTemporaryRT(colorTextureId);
}
}在 CopyAttachments 中,加入拷贝颜色缓冲区的逻辑,并在调用的地方判断,只要启用深度,颜色贴图中的一个,就执行拷贝:
cs
void CopyAttachments()
{
if(useColorTexture)
{
buffer.GetTemporaryRT(colorTextureId, camera.pixelWidth, camera.pixelHeight,
0, FilterMode.Bilinear, useHDR ? RenderTextureFormat.DefaultHDR : RenderTextureFormat.Default);
if (copyTextureSupported)
buffer.CopyTexture(colorAttachmentId, colorTextureId);
else
Draw(colorAttachmentId, colorTextureId, false);
}
if(useDepthTexture)
{
buffer.GetTemporaryRT(depthTextureId, camera.pixelWidth, camera.pixelHeight,
32, FilterMode.Point, RenderTextureFormat.Depth);
if (copyTextureSupported)
buffer.CopyTexture(depthAttachmentId, depthTextureId);
else
Draw(depthAttachmentId, depthTextureId, true);
}
if (!copyTextureSupported)
{
buffer.SetRenderTarget(colorAttachmentId, RenderBufferLoadAction.Load, RenderBufferStoreAction.Store,
depthAttachmentId, RenderBufferLoadAction.Load, RenderBufferStoreAction.Store);
}
ExecuteBuffer();
}
void DrawVisibleGeometry(...)
{
...
context.DrawSkybox(camera);
if(useColorTexture || useDepthTexture)
CopyAttachments();
...
}4.2 Sampling the Buffer Color
在 Fragment.hlsl 中添加缓冲区颜色贴图。因为我们并不需要确定位置处的颜色,因此没有向 Fragment 结构体中增加成员,而是实现方法,以 Fragment 和 uv 偏移为参数,完成采样并返回:
cs
TEXTURE2D(_CameraDepthTexture);
TEXTURE2D(_CameraColorTexture);
...
float4 GetBufferColor(Fragment fragment, float2 uvOffset = float2(0.0,0.0))
{
floa2 uv = fragment.screenUV + uvOffset;
return SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_LOD(_CameraColorTexture, sampler_linear_clamp, uv, 0);
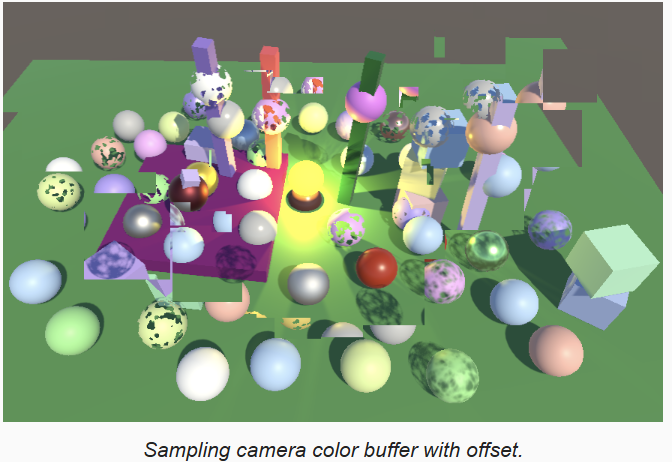
}为了测试,在 UnlitPassFragment.hlsl 中,以5%的偏移采样,并直接返回:
cs
float4 UnlitPassFragment(Varyings input) : SV_TARGET
{
UNITY_SETUP_INSTANCE_ID(input);
InputConfig config = GetInputConfig(input.positionCS_SS, input.uv);
// 测试采样 buffer color
return GetBufferColor(config.fragment, 0.05);
}
4.3 Distortion Vectors
我们需要一个变化平滑的扰动向量来实现扰动效果。下面是一张简单的圆形粒子的扰动图,下载并导入我们的项目中。

在我们的 UnlitParticles.shader 中,添加材质属性:扰动开关,扰动图,扰动强度。扰动应用的是屏幕空间的UV偏移,值不能太大,因此扰动强度定义范围为 0-0.2,默认0.1。同时声明 shader_feature:
cs
Properties
{
...
_SoftParticlesRange("Soft Particles Range", Range(0.01, 10.0))=0
[Toggle(_DISTORTION)]_Distortion("Distortion", Float) = 0
[NoOffsetScale]_DistortionMap("Distortion map", 2D) = "bump"{}
_DistortionStrength("Distortion Strength", Range(0,0.2)) = 0.1
...
}
...
#pragma shader_feature _SOFT_PARTICLES
#pragma shader_feature _DISTORTION
...
在 UnlitInput.hlsl 定义扰动图,及扰动强度。实现 GetDistortion 函数返回扰动的 uv offset。采样扰动图,并像 base map 一样,如果启用 flipbookBlending 则进行混合,然后用强度作为缩放解码法线,并使用 xy 分量。
cs
UNITY_INSTANCING_BUFFER_START(UnityPerMaterial)
...
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _SoftParticlesRange)
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _DistortionStrength)
...
UNITY_INSTANCING_BUFFER_END(UnityPerMaterial)
TEXTURE2D(_BaseMap);
TEXTURE2D(_DistortionMap);
float2 GetDistortion(InputConfig c)
{
float4 map = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_DistortionMap, sampler_BaseMap, c.baseUV);
if (c.flipbookBlending)
{
float4 map2 = SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D(_DistortionMap, sampler_BaseMap, c.flipbookUVB.xy);
map = lerp(map, map2, c.flipbookUVB.z);
}
return DecodeNormal(map, UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _DistortionStrength)).xy;
}在 UnlitPassFragment 中,如果启用了扰动,则在 clipping 后,获取扰动后,采样缓冲区颜色。
扰动应该跟粒子的视觉效果相关,也就是粒子越透明的地方,扰动越弱,因此,将扰动乘以粒子颜色的 alpha 值。
同时扰动值影响颜色值,不影响 alpha 值,因此只要 buffer color 的 rgb:
cs
float4 base = GetBase(config);
#if defined(_CLIPPING)
clip(base.a - GetCutoff(input.uv));
#endif
#if defined(_DISTORTION)
float2 distortion = GetDistortion(config) * base.a;
base.rgb = GetBufferColor(config.fragment, distortion).rgb;
#endif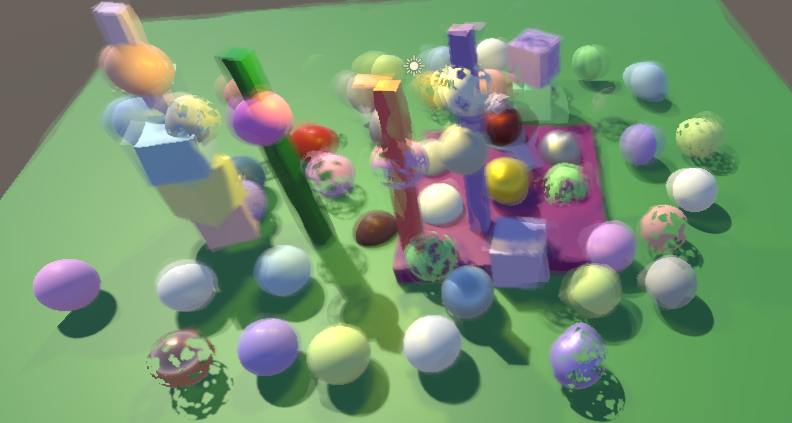
4.4 Distortion Blend
现在的扰动,粒子只显示了 buffer color,现在我们要混合上粒子本身的颜色。
添加一个控制混合的 shader 属性
cs
_DistortionStrength("Distortion Strength", Range(0,0.2)) = 0.1
_DistortionBlend("Distortion Blend", Range(0,1.0)) = 1在 UnlitInput.hlsl 中,声明属性,并实现一个获取混合参数的函数:
cs
UNITY_DEFINE_INSTANCED_PROP(float, _DistortionBlend)
...
float GetDistortionBlend(InputConfig c)
{
return UNITY_ACCESS_INSTANCED_PROP(UnityPerMaterial, _DistortionBlend);
}混合思想是,当混合参数为 1 时,只看到扰动效果,随着值变小,显示粒子的颜色,但是扰动不会彻底消失,因此我们用粒子颜色的 alpha 减去混合参数作为插值参数,执行从 buffer color 到粒子颜色的插值。这样当启用扰动时,粒子的颜色总是会弱一些,并且看起来比没有扰动时小一些,除非粒子是不透明的。
cs
#if defined(_DISTORTION)
float2 distortion = GetDistortion(config) * base.a;
float3 bufferColor = GetBufferColor(config.fragment, distortion).rgb;
float blendFactor = saturate(base.a - GetDistortionBlend(config));
base.rgb = lerp(bufferColor, base.rgb, blendFactor);
#endif用下面的图作为我们的 flipbook 特效的扰动图,效果会更好些:
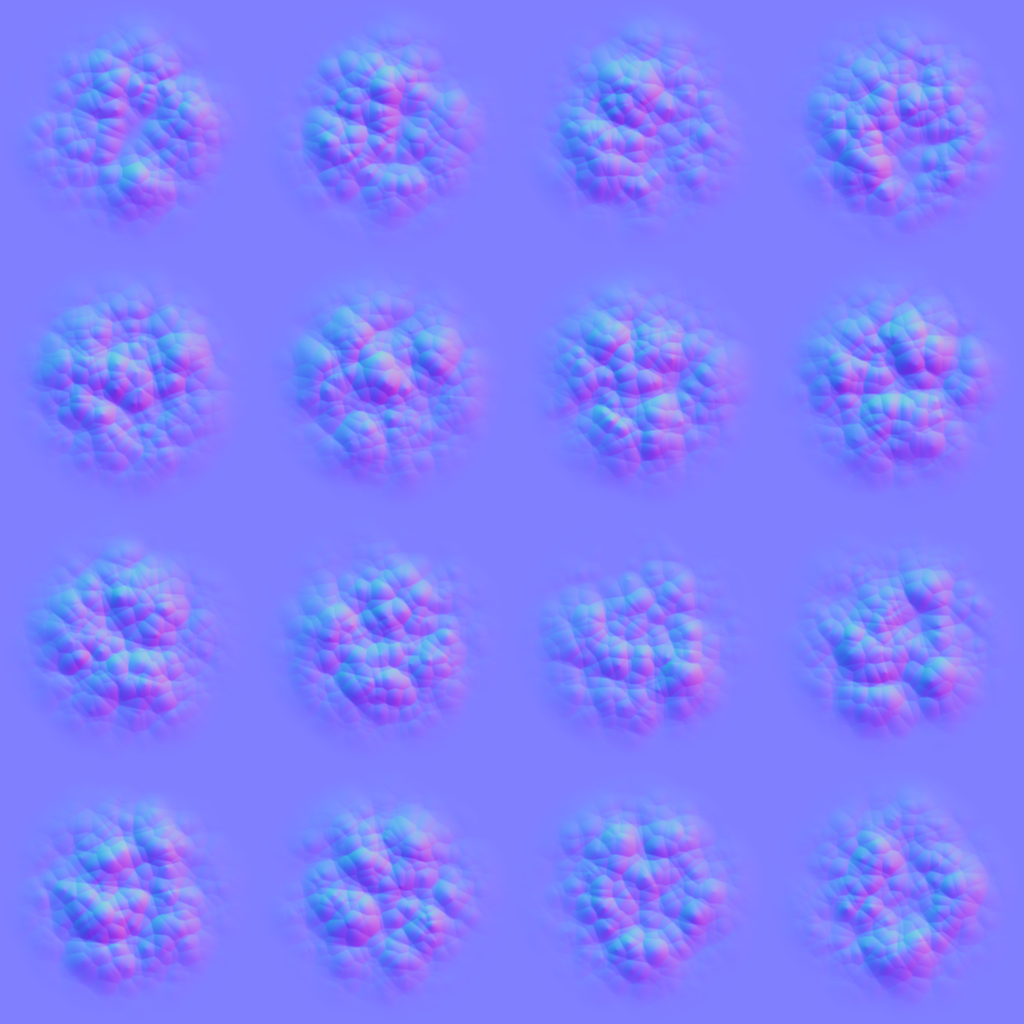

4.5 Fixing Nonstandard Cameras
我们现在的方法,在只有一个摄像机时才能正常工作,同时如果没有开启 post FX时,会渲染到中间缓冲区,也导致会失效。这是因为我们执行的是普通的拷贝到摄像机 target,忽略了 viewport 和混合模式,所以 CameraRenderer 也需要一个 FinalPass 方法来正确的完成拷贝。从 PostFXStack.FinalPass 拷贝该方法,不过我们要用正常的 copy pass,因此要在完成后将混合模式设置为 one-zero,避免影响其它的拷贝行为。源贴图是 color attachment,用 final blend mode 作为参数。
cs
public void Render(...)
{
...
// 后处理
if (postFXStack.IsActive)
{
postFXStack.Render(colorAttachmentId, colorLUTResolution);
}
else if (useIntermediateBuffer)
{
//Draw(colorAttachmentId, BuiltinRenderTextureType.CameraTarget, false);
DrawFinal(cameraSettings.finalBlendMode);
ExecuteBuffer();
}
...
}
static Rect fullViewPort = new Rect(0f, 0f, 1f, 1f);
static int srcBlendId = Shader.PropertyToID("_CameraSrcBlend");
static int dstBlendId = Shader.PropertyToID("_CameraDstBlend");
void DrawFinal(CameraSettings.FinalBlendMode finalBlendMode)
{
buffer.SetGlobalFloat(srcBlendId, (float)finalBlendMode.source);
buffer.SetGlobalFloat(dstBlendId, (float)finalBlendMode.destination);
buffer.SetGlobalTexture(sourceTextureId, colorAttachmentId);
RenderBufferLoadAction loadAction = RenderBufferLoadAction.Load;
if (finalBlendMode.destination == BlendMode.Zero && camera.pixelRect == fullViewPort)
{
loadAction = RenderBufferLoadAction.DontCare;
}
buffer.SetRenderTarget(BuiltinRenderTextureType.CameraTarget,
loadAction,
RenderBufferStoreAction.Store);
buffer.SetViewport(camera.pixelRect);
buffer.DrawProcedural(Matrix4x4.identity, material, 0, MeshTopology.Triangles, 3);
}修改CameraRenderer.shader,为 Copy Pass 增加 blend mode
cs
Pass
{
Name "Copy"
Blend [_CameraSrcBlend] [_CameraDstBlend]
...
}