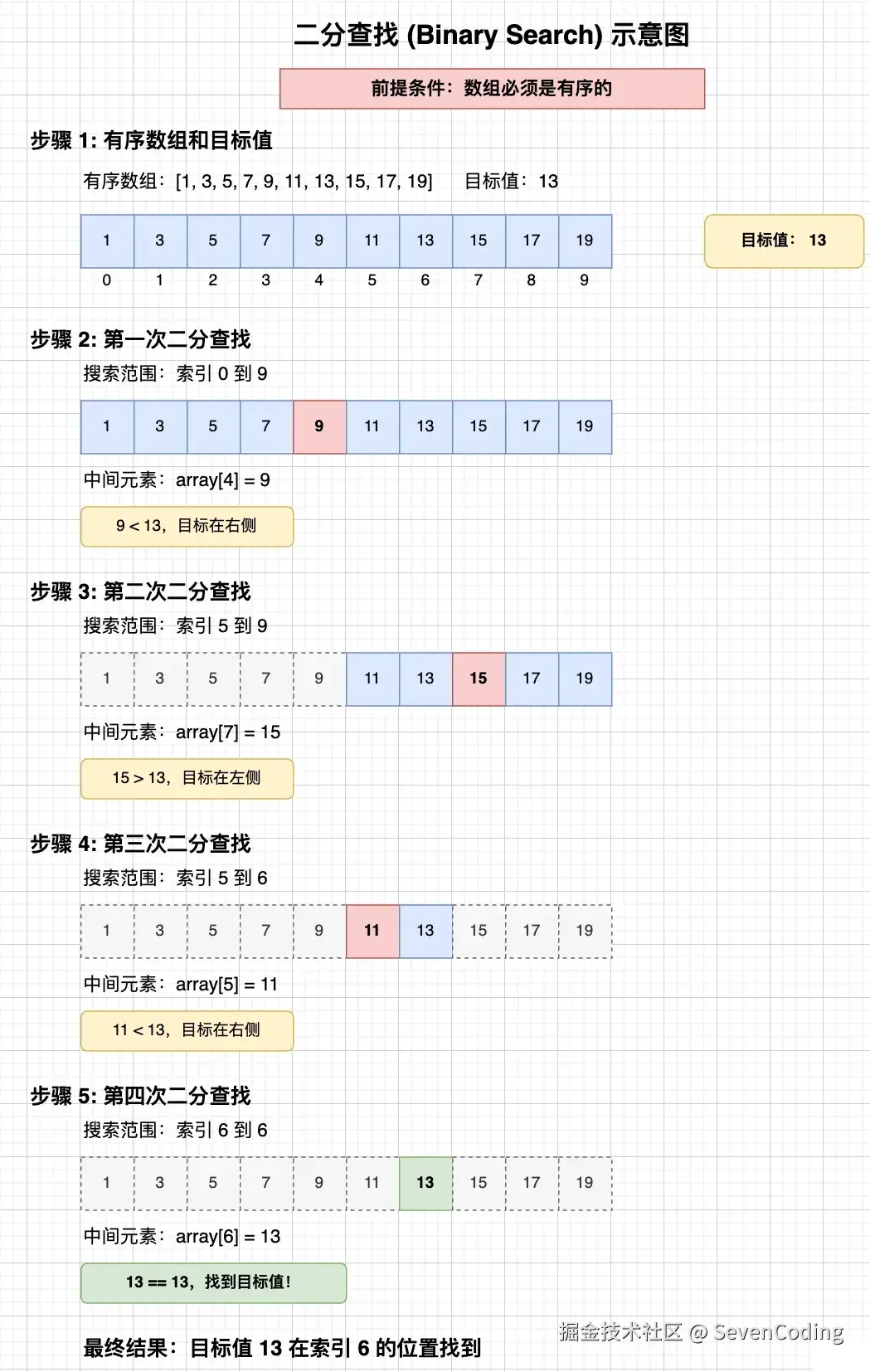
二分查找
二分查找(Binary Search)是一种高效的查找算法,也叫折半查找。核心思想:对于一个有序的数据集合,每次查找都将查找范围缩小为原来的一半,直到找到目标值或确定目标值不存在。二分查找要求数据必须是有序的,经常应用于数组等支持随机访问的数据结构里。跟线性查找相比,二分查找的效率要高得多,特别是对于大规模数据集。
算法步骤
- 确定查找范围的左边界 left 和右边界 right
- 计算中间位置 mid = (left + right) / 2(注意整数溢出问题,更安全的做法是 mid = left + (right - left) / 2)
- 将中间位置的元素与目标值比较
- 如果中间元素等于目标值,查找成功,返回中间元素的位置
- 如果中间元素大于目标值,目标值可能在左半部分,将右边界调整为 mid - 1
- 如果中间元素小于目标值,目标值可能在右半部分,将左边界调整为 mid + 1
- 重复步骤2-3,直到找到目标值或者左边界大于右边界(此时表示目标值不存在)
核心特性:
- 要求有序:二分查找只适用于有序数据集合
- 时间复杂度:O(log n),在大规模数据集上非常高效
- 空间复杂度:迭代实现为O(1),递归实现为O(log n)(因为递归调用栈的深度)
- 随机访问:要求数据结构支持O(1)时间复杂度的随机访问(比如数组)
基础实现
下面是二分查找算法在各种主流编程语言中的实现:
java
public class BinarySearch {
// 迭代实现
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
// 避免整数溢出
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 找到目标值
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
// 在左半部分继续查找
else if (arr[mid] > target) {
right = mid - 1;
}
// 在右半部分继续查找
else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
// 未找到目标值
return -1;
}
// 递归实现
public static int binarySearchRecursive(int[] arr, int target, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return -1;
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] > target) {
return binarySearchRecursive(arr, target, left, mid - 1);
} else {
return binarySearchRecursive(arr, target, mid + 1, right);
}
}
// 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {2, 3, 4, 10, 40, 50, 70, 80};
int target = 10;
// 迭代方法
int result = binarySearch(arr, target);
if (result == -1) {
System.out.println("元素 " + target + " 不存在于数组中");
} else {
System.out.println("元素 " + target + " 在数组中的索引为 " + result);
}
// 递归方法
result = binarySearchRecursive(arr, target, 0, arr.length - 1);
if (result == -1) {
System.out.println("元素 " + target + " 不存在于数组中");
} else {
System.out.println("元素 " + target + " 在数组中的索引为 " + result);
}
}
}优点
- 查找效率非常高,时间复杂度为 O(log n)
- 在大规模数据集上表现优异
- 实现相对简单
- 不需要额外的空间(迭代实现)
缺点
- 要求数据必须是有序的
- 只适用于支持随机访问的数据结构(如数组)
- 对于频繁插入和删除的数据结构,维护有序性的成本很高
- 不适合小数据量的查找(这种情况下线性查找可能更快)
应用场景
二分查找在很多场景中都有广泛的应用:
- 数据库索引的实现(如 B 树和 B+ 树的查找过程)
- 查找最接近某个值的元素(下界查找和上界查找)
- 计算平方根等数值计算中(二分法求解)
- 猜数字游戏(每次猜测中间值)
- 在旋转排序数组中查找元素
- 查找数组中第一个或最后一个满足某条件的元素
相关的 LeetCode 热门题目
- 704. 二分查找 - 二分查找的基础应用
- 35. 搜索插入位置 - 查找元素应该插入的位置(下界)
- 34. 在排序数组中查找元素的第一个和最后一个位置 - 查找目标值的第一次和最后一次出现位置
- 69. x 的平方根 - 使用二分查找求解平方根
- 33. 搜索旋转排序数组 - 在旋转过的有序数组中用二分查找
- 153. 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 - 在旋转数组中查找最小值
- 74. 搜索二维矩阵
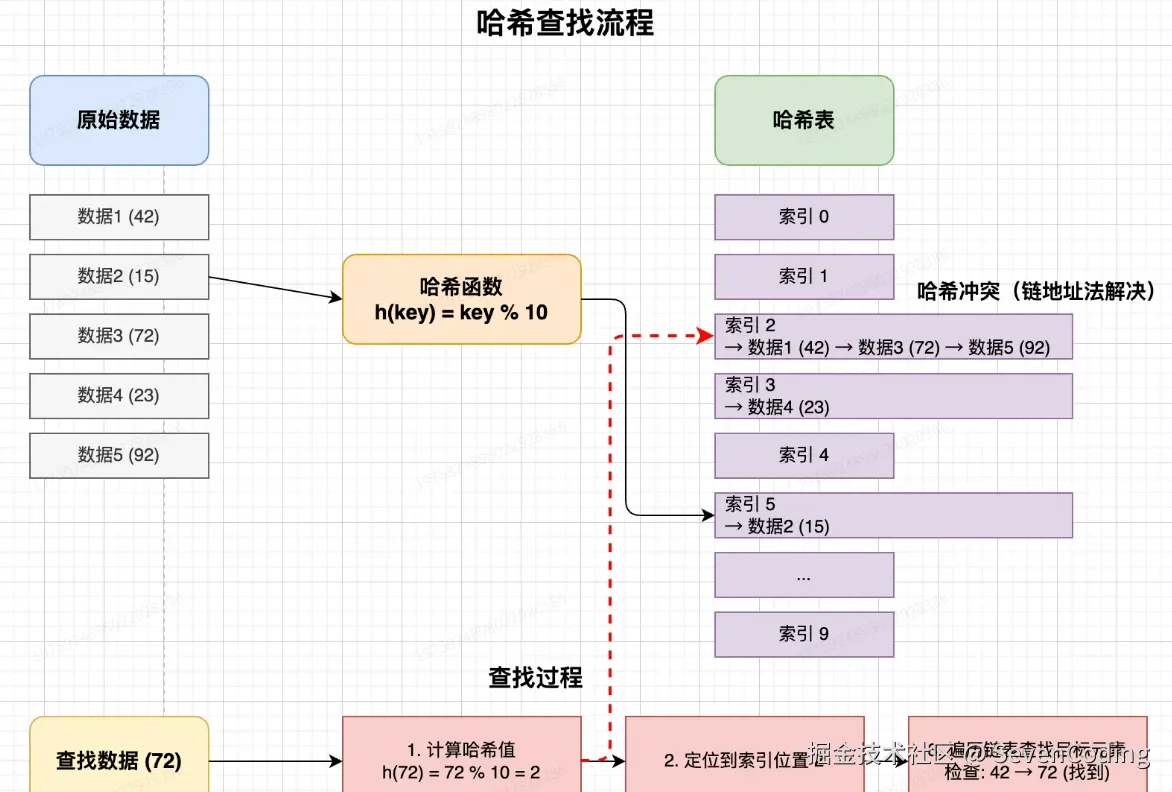
哈希查找
哈希查找(Hash Search),又称散列查找,是一种高效的查找算法,它用哈希函数将数据转换为数组下标,然后直接访问数组中的元素。哈希查找的核心思想是将数据元素通过哈希函数映射到哈希表中的位置,实现快速查找。
在理想情况下,哈希查找的时间复杂度为 O(1),这就意味着无论数据规模多大,查找操作都能在常数时间内完成,这是哈希查找相比其他查找算法(如二分查找、线性查找)的最大优势。
不过使用哈希查找必须要考虑哈希冲突(不同的数据被映射到相同的位置)问题。
算法步骤
- 设计一个适合数据特点的哈希函数,将数据映射到哈希表的索引位置
- 构建哈希表,将所有元素通过哈希函数映射、存储到相应位置
- 解决可能出现的哈希冲突(通常采用链地址法或开放寻址法)
- 查找时,通过同样的哈希函数计算目标数据的哈希值
- 根据哈希值定位到哈希表中的位置
- 如果存在冲突,则按照解决冲突的方法查找目标元素
核心特性:
- 快速访问:理想情况下查找时间复杂度为 O(1)
- 哈希函数:哈希查找的核心,将数据映射到数组索引的函数
- 哈希冲突:不同数据映射到相同位置的情况,需要特殊处理
- 空间换时间:通过额外的内存空间换取查找时间的提升
- 负载因子:表示哈希表的填充程度,影响查找效率和冲突概率
- 动态扩容 :负载因子过高时,需要扩大哈希表并重新哈希所有元素
基础实现
java
public class HashSearch {
// 哈希表节点类
static class Node {
String key;
int value;
Node next;
public Node(String key, int value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
// 哈希表类
static class HashTable {
private Node[] buckets;
private int capacity;
private int size;
private final float LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; // 负载因子阈值
public HashTable(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.buckets = new Node[capacity];
this.size = 0;
}
// 哈希函数
private int hash(String key) {
int hash = 0;
for (char c : key.toCharArray()) {
hash = (hash * 31 + c) % capacity;
}
return Math.abs(hash);
}
// 插入键值对
public void put(String key, int value) {
if ((float)size / capacity >= LOAD_FACTOR) {
resize(2 * capacity);
}
int index = hash(key);
Node newNode = new Node(key, value);
// 如果桶为空,直接插入
if (buckets[index] == null) {
buckets[index] = newNode;
size++;
return;
}
// 处理哈希冲突,使用链地址法
Node current = buckets[index];
// 检查是否已存在相同的键
while (current != null) {
if (current.key.equals(key)) {
current.value = value; // 更新值
return;
}
if (current.next == null) {
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
// 在链表末尾添加新节点
current.next = newNode;
size++;
}
// 查找键对应的值
public Integer get(String key) {
int index = hash(key);
Node current = buckets[index];
// 遍历链表查找匹配的键
while (current != null) {
if (current.key.equals(key)) {
return current.value;
}
current = current.next;
}
// 未找到
return null;
}
// 删除键值对
public boolean remove(String key) {
int index = hash(key);
Node current = buckets[index];
Node prev = null;
// 查找目标节点
while (current != null) {
if (current.key.equals(key)) {
break;
}
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
// 未找到目标节点
if (current == null) {
return false;
}
// 删除节点
if (prev == null) {
buckets[index] = current.next;
} else {
prev.next = current.next;
}
size--;
return true;
}
// 扩容并重新哈希
private void resize(int newCapacity) {
Node[] oldBuckets = buckets;
// 创建新的哈希表
buckets = new Node[newCapacity];
capacity = newCapacity;
size = 0;
// 重新哈希所有元素
for (Node bucket : oldBuckets) {
Node current = bucket;
while (current != null) {
put(current.key, current.value);
current = current.next;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTable hashTable = new HashTable(10);
// 插入数据
hashTable.put("apple", 5);
hashTable.put("banana", 10);
hashTable.put("orange", 15);
hashTable.put("grape", 20);
// 查找数据
System.out.println("apple: " + hashTable.get("apple"));
System.out.println("banana: " + hashTable.get("banana"));
System.out.println("orange: " + hashTable.get("orange"));
System.out.println("grape: " + hashTable.get("grape"));
System.out.println("watermelon: " + hashTable.get("watermelon"));
// 删除数据
hashTable.remove("orange");
System.out.println("After removing orange: " + hashTable.get("orange"));
}
}优点
- 查找、插入和删除操作的平均时间复杂度为 O(1)
- 适用于快速查找
- 不要求数据有序,更灵活
- 支持动态数据集,高效地添加和删除元素
- 通过合适的哈希函数和解决冲突策略,能实现非常优秀的性能
缺点
- 哈希冲突会降低查找效率,最坏情况下时间复杂度可能退化到 O(n)
- 需要额外的空间存储哈希表
- 不支持范围查询,不适合按顺序遍历场景
- 负载因子过高会导致性能下降,过低会浪费空间
应用场景
哈希查找适用于以下场景:
- 需要快速查找、插入和删除操作的数据结构,如字典或映射
- 实现缓存系统,比如LRU缓存、内存缓存等
- 数据库索引,特别是等值查询
- 符号表实现,如编译器和解释器中的变量表
- 去重操作,判断元素是否已存在
- 网页爬虫的URL去重
一致性哈希
一致性哈希是分布式系统中的重要概念,目的是尽可能少地重新分配数据
详情可以看一致性哈希算法
布隆过滤器
布隆过滤器是一种空间效率高的概率型数据结构,判断一个元素是否在集合中
详情可以看布隆过滤器
相关的 LeetCode 热门题目
- 1. 两数之和 - 使用哈希表记录已遍历元素,查找目标值的补数
- 3. 无重复字符的最长子串 - 使用哈希表记录字符最后出现的位置
- 136. 只出现一次的数字 - 可以用哈希表记录每个数字的出现次数
- 146. LRU 缓存 - 结合哈希表和双向链表实现LRU缓存
- 217. 存在重复元素 - 使用哈希表检查重复元素
- 349. 两个数组的交集
- 387. 字符串中的第一个唯一字符 - 使用哈希表统计字符出现次数