背景
让我们按照 From Nand to Tetris 里 Project 2 的要求,来完成下列的设计。
- 实现半加器(
HalfAdder) - 实现全加器(
FullAdder) - 实现 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 16 16 </math>16 位加法器(
Add16) - 实现 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 16 16 </math>16 位自增器(
Inc16) - 实现算术逻辑单元(
ALU) (todo)
正文
1. 实现 HalfAdder
前往 Nand to Tetris Online IDE,选择 Project 2 里的 HalfAdder,效果如下图所示 ⬇️
我们的目标是用 Project 1 里已经实现的各种 chip 实现一个 HalfAdder。
- 输入是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a a </math>a
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b b </math>b
- 输出是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry
我们可以从它的真值表入手 ⬇️
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a a </math>a | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b b </math>b | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry |
|---|---|---|---|
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 |
可见
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m = ( ¬ a ∧ b ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ) = a ⊕ b sum=(\neg{a}\land b) \lor (a\land \neg{b})=a\oplus b </math>sum=(¬a∧b)∨(a∧¬b)=a⊕b
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y = a ∧ b carry=a\land b </math>carry=a∧b
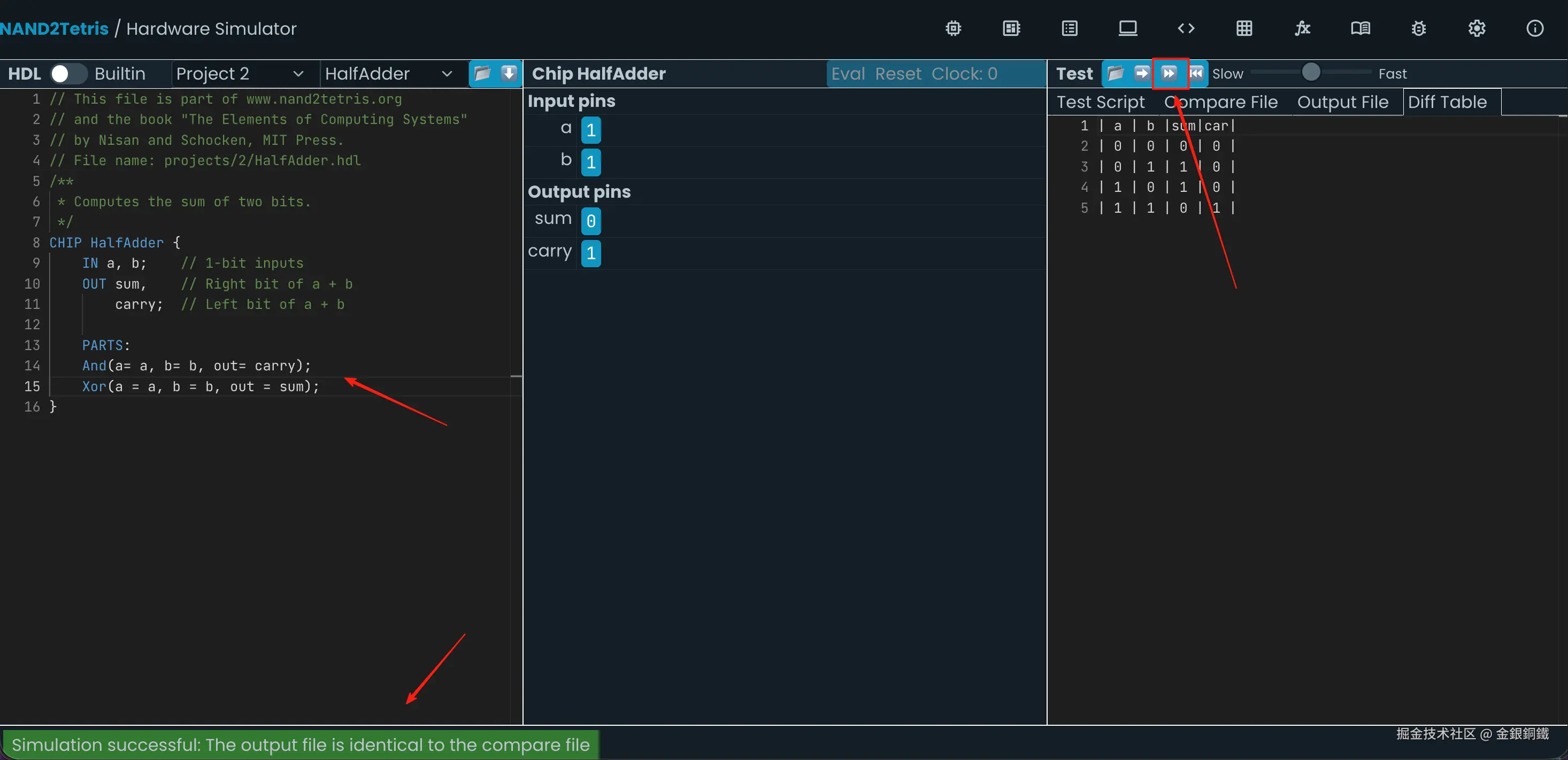
所以可以这样实现 ⬇️
hdl
CHIP HalfAdder {
IN a, b; // 1-bit inputs
OUT sum, // Right bit of a + b
carry; // Left bit of a + b
PARTS:
And(a= a, b= b, out= carry);
Xor(a = a, b = b, out = sum);
}这样的代码可以通过仿真测试,效果如下图所示 ⬇️
2. 实现 FullAdder
前往 Nand to Tetris Online IDE,选择 Project 2 里的 FullAdder,效果如下图所示 ⬇️
我们的目标是用 Project 1 里已经实现的各种 chip,以及刚才实现的 HalfAdder 来实现一个 FullAdder。
- 输入是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a a </math>a
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b b </math>b
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c c </math>c
- 输出是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry
我们还是从真值表入手 ⬇️
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a a </math>a | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b b </math>b | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c c </math>c | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 0 0 </math>0 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 |
| <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 | <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 1 1 </math>1 |
通过观察真值表,可以将 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry 写成对应的析取范式 DNF(Disjunctive Normal Form) 的形式
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m = ( ¬ a ∧ ¬ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( ¬ a ∧ b ∧ ¬ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ∧ ¬ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ b ∧ c ) sum=(\neg{a}\land \neg{b}\land c)\lor (\neg{a}\land b\land \neg{c})\lor(a\land\neg{b}\land \neg{c})\lor(a\land b\land c) </math>sum=(¬a∧¬b∧c)∨(¬a∧b∧¬c)∨(a∧¬b∧¬c)∨(a∧b∧c)
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y = ( ¬ a ∧ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ b ∧ ¬ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ b ∧ c ) carry=(\neg{a}\land b\land c)\lor(a\land \neg{b}\land c)\lor(a\land b\land \neg{c})\lor(a\land b\land c) </math>carry=(¬a∧b∧c)∨(a∧¬b∧c)∨(a∧b∧¬c)∨(a∧b∧c)
从上面的析取范式出发,我们可以只用 And/Or/Not 来实现 FullAdder。但有没有更简洁的实现方式呢? 我们回忆一下 HalfAdder 中的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry 是怎样的 ⬇️ (为了和 FullAdder 的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry 进行区分,我把 HalfAdder <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry 分别改写为的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a sum_{ha} </math>sumha 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y h a carry_{ha} </math>carryha)
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a = ( ¬ a ∧ b ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ) = a ⊕ b sum_{ha}=(\neg{a}\land b) \lor (a\land \neg{b})=a\oplus b </math>sumha=(¬a∧b)∨(a∧¬b)=a⊕b
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y h a = a ∧ b carry_{ha}=a\land b </math>carryha=a∧b
为了便于区分,我把 FullAdder 的 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry 分别改写为 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a sum_{fa} </math>sumfa 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y f a carry_{fa} </math>carryfa。 先看 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a sum_{fa} </math>sumfa 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a sum_{ha} </math>sumha 是否有关联。
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a = ( ¬ a ∧ ¬ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( ¬ a ∧ b ∧ ¬ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ∧ ¬ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ b ∧ c ) sum_{fa}=(\neg{a}\land \neg{b}\land c)\lor (\neg{a}\land b\land \neg{c})\lor(a\land\neg{b}\land \neg{c})\lor(a\land b\land c) </math>sumfa=(¬a∧¬b∧c)∨(¬a∧b∧¬c)∨(a∧¬b∧¬c)∨(a∧b∧c)
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a = a ⊕ b sum_{ha}=a\oplus b </math>sumha=a⊕b
如何表示 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m sum </math>sum
一个思路是看看能否将 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a sum_{fa} </math>sumfa 用 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a sum_{ha} </math>sumha 表示出来,我试了试,觉得有些繁琐,而且不容易想到。另一个思路是,我们从 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a sum_{fa} </math>sumfa 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a sum_{ha} </math>sumha 背后的含义入手。 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a sum_{ha} </math>sumha 表示 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a , b a,b </math>a,b 的和(忽略进位),所以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a = a ⊕ b sum_{ha}=a\oplus b </math>sumha=a⊕b。
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a = 0 sum_{ha}=0 </math>sumha=0 时,只有 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c = 1 c=1 </math>c=1, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a = 1 sum_{fa}=1 </math>sumfa=1 才会成立
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a = 1 sum_{ha}=1 </math>sumha=1 时,只有 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c = 0 c=0 </math>c=0, <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a = 1 sum_{fa}=1 </math>sumfa=1 才会成立
所以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a = s u m h a ⊕ c sum_{fa}=sum_{ha}\oplus c </math>sumfa=sumha⊕c
而 HalfAdder 的作用就是对输入 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a , b a,b </math>a,b 分别执行 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ⊕ \oplus </math>⊕ 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ∧ \land </math>∧ 运算,所以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a sum_{fa} </math>sumfa 可以通过拼接两个 HalfAdder 来实现 ⬇️
- 第一个
HalfAdder以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a , b a,b </math>a,b 为输入,其 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a 1 = a ⊕ b sum_{ha1}=a\oplus b </math>sumha1=a⊕b - 第二个
HalfAdder以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a 1 sum_{fa1} </math>sumfa1 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c c </math>c 为输入,其 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a 2 = s u m f a 1 ⊕ c = sum_{ha2}=sum_{fa1}\oplus c= </math>sumha2=sumfa1⊕c=
如何表示 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y carry </math>carry
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> c a r r y f a = ( ¬ a ∧ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ b ∧ ¬ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ b ∧ c ) carry_{fa}=(\neg{a}\land b\land c)\lor(a\land \neg{b}\land c)\lor(a\land b\land \neg{c})\lor(a\land b\land c) </math>carryfa=(¬a∧b∧c)∨(a∧¬b∧c)∨(a∧b∧¬c)∨(a∧b∧c)
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> = ( ¬ a ∧ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( ( a ∧ b ∧ ¬ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ b ∧ c ) ) =(\neg{a}\land b\land c)\lor(a\land \neg{b}\land c)\lor((a\land b\land \neg{c})\lor(a\land b\land c)) </math>=(¬a∧b∧c)∨(a∧¬b∧c)∨((a∧b∧¬c)∨(a∧b∧c))
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> = ( ¬ a ∧ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ b ) =(\neg{a}\land b\land c)\lor(a\land \neg{b}\land c)\lor(a\land b) </math>=(¬a∧b∧c)∨(a∧¬b∧c)∨(a∧b)
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> = ( ¬ a ∧ b ∧ c ) ∨ ( a ∧ ¬ b ∧ c ) ∨ c a r r y h a =(\neg{a}\land b\land c)\lor(a\land \neg{b}\land c)\lor carry_{ha} </math>=(¬a∧b∧c)∨(a∧¬b∧c)∨carryha
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> = ( ( a ⊕ b ) ∧ c ) ∨ c a r r y h a =((a\oplus b)\land c)\lor carry_{ha} </math>=((a⊕b)∧c)∨carryha
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> = ( s u m h a ∧ c ) ∨ c a r r y h a =(sum_{ha}\land c)\lor carry_{ha} </math>=(sumha∧c)∨carryha
考虑到 HalfAdder 的作用就是对输入 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a , b a,b </math>a,b 分别执行 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ⊕ \oplus </math>⊕ 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> ∧ \land </math>∧ 运算,所以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y f a carry_{fa} </math>carryfa 可以通过拼接两个 HalfAdder 再加上一个 Or 运算 来实现 ⬇️
- 第一个
HalfAdder以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a , b a,b </math>a,b 为输入,它的- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a 1 = a ⊕ b sum_{fa1}=a\oplus b </math>sumfa1=a⊕b
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y h a 1 = a ∧ b carry_{ha1}=a\land b </math>carryha1=a∧b
- 第二个
HalfAdder以 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m f a 1 sum_{fa1} </math>sumfa1 和 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c c </math>c 为输入,它的- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> s u m h a 2 = s u m f a 1 ⊕ c sum_{ha2}=sum_{fa1}\oplus c </math>sumha2=sumfa1⊕c
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> c a r r y h a 2 = s u m f a 1 ∧ c carry_{ha2}=sum_{fa1}\land c </math>carryha2=sumfa1∧c
那么
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> c a r r y f a = ( s u m h a 1 ∧ c ) ∨ c a r r y h a 1 = c a r r y h a 2 ∨ c a r r y h a 1 carry_{fa}=(sum_{ha1}\land c)\lor carry_{ha1}=carry_{ha2}\lor carry_{ha1} </math>carryfa=(sumha1∧c)∨carryha1=carryha2∨carryha1
至此我们可以用 HalfAdder 和 Or 来实现 FullAdder。具体的代码如下 ⬇️
hdl
CHIP FullAdder {
IN a, b, c; // 1-bit inputs
OUT sum, // Right bit of a + b + c
carry; // Left bit of a + b + c
PARTS:
HalfAdder(a= a, b= b, sum= sumHa, carry= carryHa);
HalfAdder(a= sumHa, b= c, sum= sum, carry= temp);
Or(a= carryHa, b= temp, out= carry);
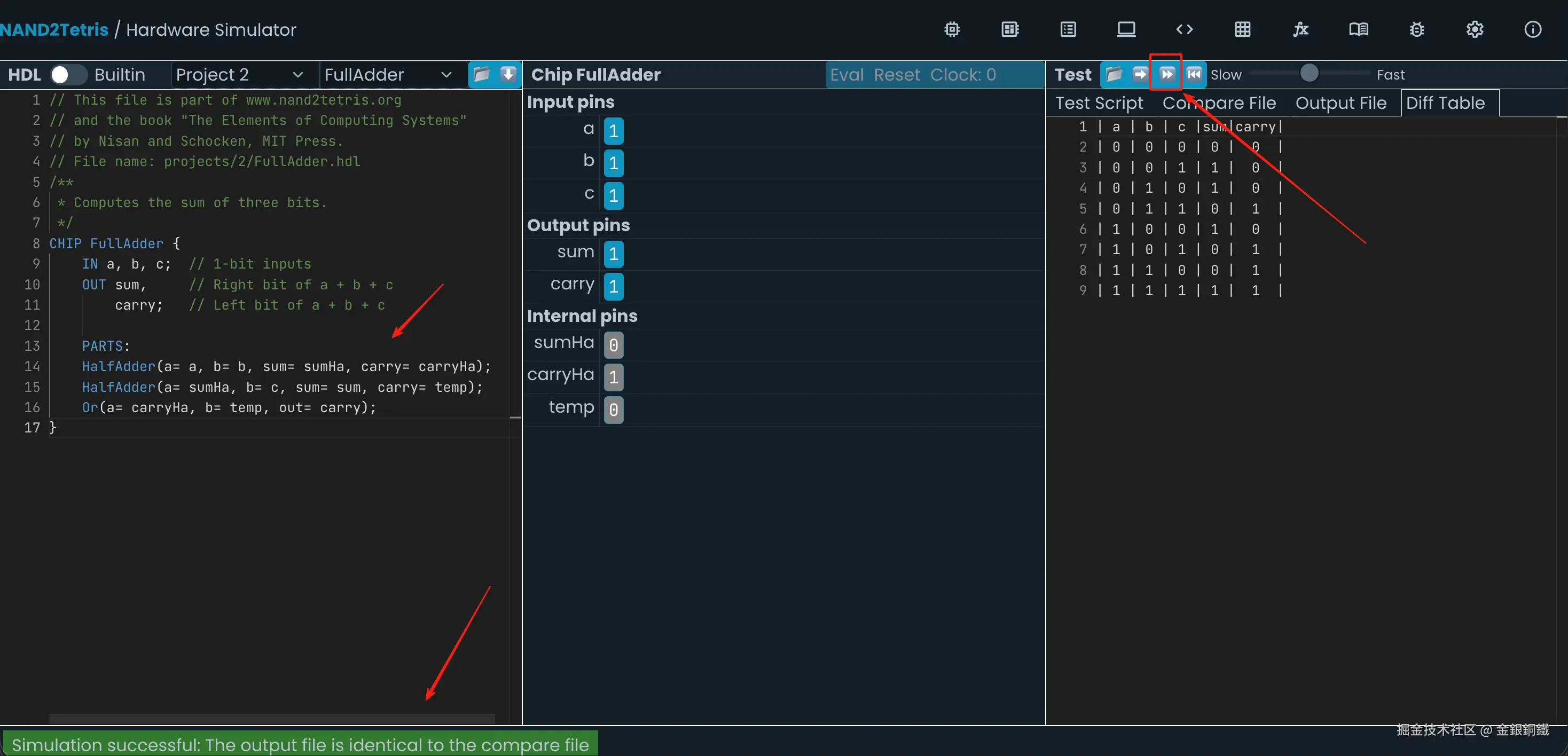
}这样的代码可以通过仿真测试,效果如下图所示 ⬇️
3. 实现 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 16 16 </math>16 位加法器(Add16)
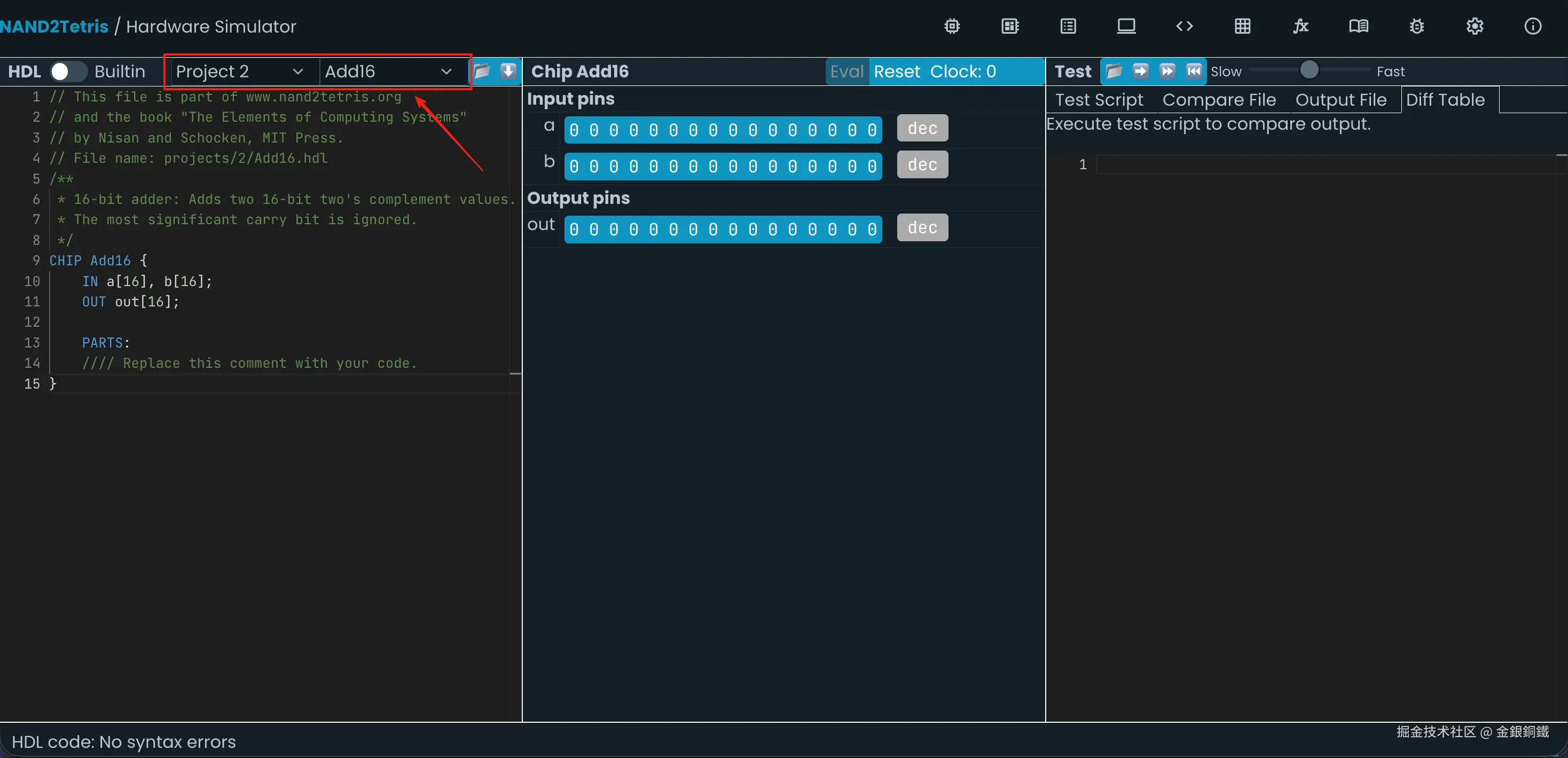
前往 Nand to Tetris Online IDE,选择 Project 2 里的 Add16,效果如下图所示 ⬇️
我们的目标是用 Project 1 里已经实现的各种 chip,以及刚才实现的 HalfAdder/FullAdder 来实现一个 Add16。
- 输入是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> a [ 16 ] a[16] </math>a[16]
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> b [ 16 ] b[16] </math>b[16]
- 输出是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> o u t [ 16 ] out[16] </math>out[16]
要实现的逻辑如下 ⬇️
text
16-bit adder: Adds two 16-bit two's complement values.
The most significant carry bit is ignored.我写了如下的 java 程序来生成对应的 HDL 代码
java
import java.util.StringJoiner;
public class Adder16HdlCodeGenerator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String template = """
CHIP Add16 {
IN a[16], b[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
%s
}
""";
StringJoiner joiner = new StringJoiner(System.lineSeparator());
joiner.add(" FullAdder(a= a[0], b= b[0], c= false, sum= out[0], carry= c0);");
for (int i = 1; i < 16; i++) {
String line = String.format(" FullAdder(a= a[%s], b= b[%s], c= c%s, sum= out[%s], carry= c%s);", i, i, i - 1, i, i);
joiner.add(line);
}
System.out.printf(template, joiner);
}
}请将以上 java 代码保存为 Adder16HdlCodeGenerator.java。用以下命令可以编译 Adder16HdlCodeGenerator.java 并运行其中的 main 方法。
bash
javac Adder16HdlCodeGenerator.java
java Adder16HdlCodeGenerator运行结果如下
hdl
CHIP Add16 {
IN a[16], b[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
FullAdder(a= a[0], b= b[0], c= false, sum= out[0], carry= c0);
FullAdder(a= a[1], b= b[1], c= c0, sum= out[1], carry= c1);
FullAdder(a= a[2], b= b[2], c= c1, sum= out[2], carry= c2);
FullAdder(a= a[3], b= b[3], c= c2, sum= out[3], carry= c3);
FullAdder(a= a[4], b= b[4], c= c3, sum= out[4], carry= c4);
FullAdder(a= a[5], b= b[5], c= c4, sum= out[5], carry= c5);
FullAdder(a= a[6], b= b[6], c= c5, sum= out[6], carry= c6);
FullAdder(a= a[7], b= b[7], c= c6, sum= out[7], carry= c7);
FullAdder(a= a[8], b= b[8], c= c7, sum= out[8], carry= c8);
FullAdder(a= a[9], b= b[9], c= c8, sum= out[9], carry= c9);
FullAdder(a= a[10], b= b[10], c= c9, sum= out[10], carry= c10);
FullAdder(a= a[11], b= b[11], c= c10, sum= out[11], carry= c11);
FullAdder(a= a[12], b= b[12], c= c11, sum= out[12], carry= c12);
FullAdder(a= a[13], b= b[13], c= c12, sum= out[13], carry= c13);
FullAdder(a= a[14], b= b[14], c= c13, sum= out[14], carry= c14);
FullAdder(a= a[15], b= b[15], c= c14, sum= out[15], carry= c15);
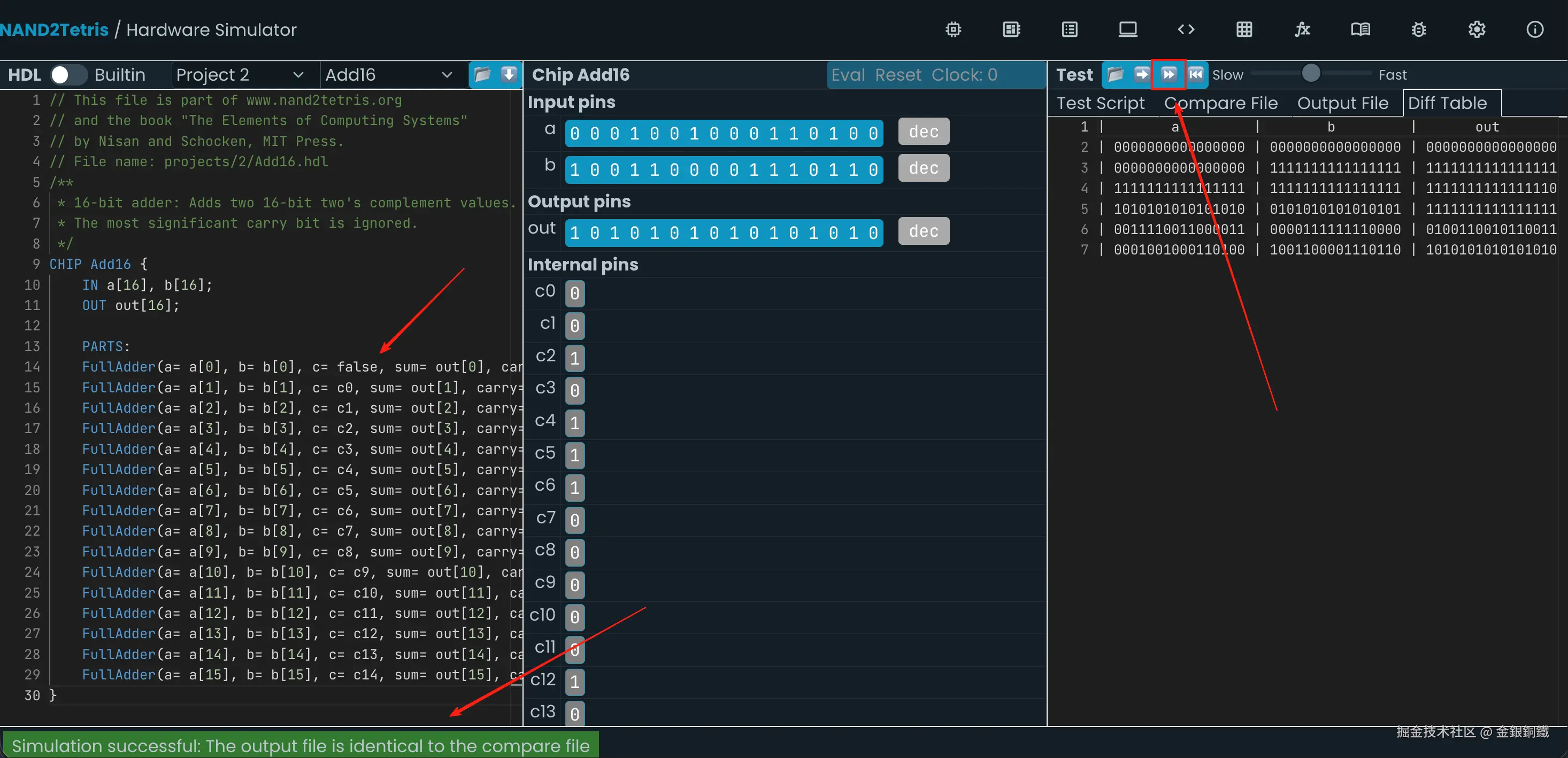
}这样的代码可以通过仿真测试,效果如下图所示 ⬇️
4. 实现 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> 16 16 </math>16 位自增器(Inc16)
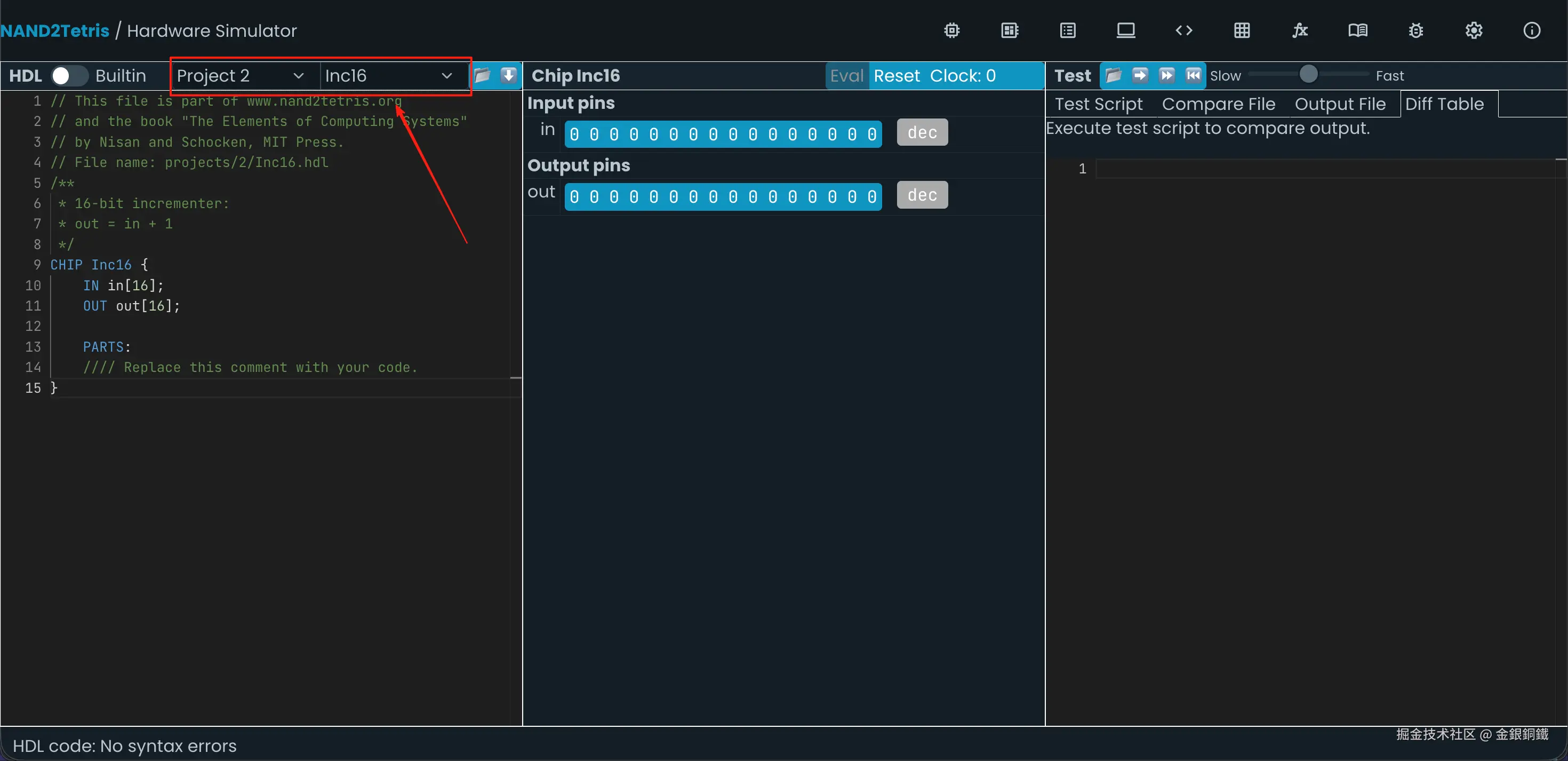
前往 Nand to Tetris Online IDE,选择 Project 2 里的 Inc16,效果如下图所示 ⬇️
我们的目标是用 Project 1 里已经实现的各种 chip,以及刚才实现的 HalfAdder/FullAdder/Add16 来实现一个 Inc16。
- 输入是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> i n [ 16 ] in[16] </math>in[16]
- 输出是
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> o u t [ 16 ] out[16] </math>out[16]
要实现的逻辑如下 ⬇️
text
16-bit incrementer:
out = in + 1一个直观的做法是使用上一步实现的 Add16,具体的代码如下 ⬇️
hdl
CHIP Inc16 {
IN in[16];
OUT out[16];
PARTS:
Add16(a = in, b[0]= true, b[1..15] = false, out = out);
}这样的代码可以通过仿真测试,效果如下图所示 ⬇️

5. 实现算术逻辑单元(ALU)
前往 Nand to Tetris Online IDE,选择 Project 2 里的 ALU,效果如下图所示 ⬇️