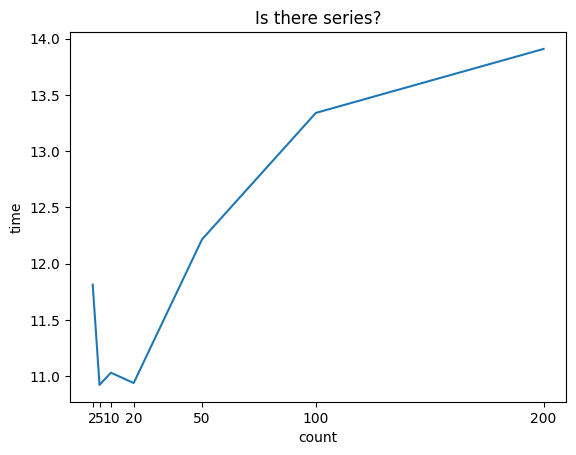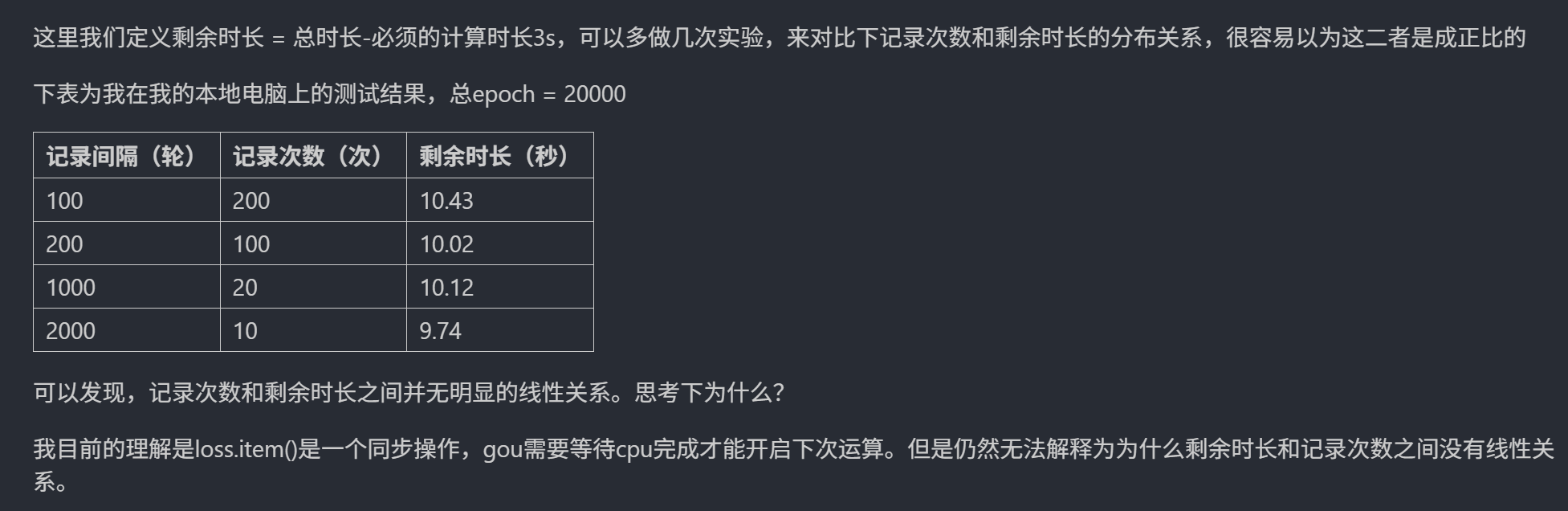
我感觉这个问题产生的原因是GPU和CPU在实际运行时候是异步的,可能存在很多别的线程占用资源,导致每次运行的结果并不是完全按照一定顺序进行的。但可能在进行很多次训练之后再对时间取平均值就有一个近似线性的关系了。以及内存的压力也很有可能对结果有影响。
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 设置GPU设备
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"使用设备: {device}")
# 加载鸢尾花数据集
iris = load_iris()
X = iris.data # 特征数据
y = iris.target # 标签数据
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 归一化数据
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
# 将数据转换为PyTorch张量并移至GPU
X_train = torch.FloatTensor(X_train).to(device)
y_train = torch.LongTensor(y_train).to(device)
X_test = torch.FloatTensor(X_test).to(device)
y_test = torch.LongTensor(y_test).to(device)
class MLP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MLP, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(4, 10) # 输入层到隐藏层
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(10, 3) # 隐藏层到输出层
def forward(self, x):
out = self.fc1(x)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
return out
# 实例化模型并移至GPU
# 训练模型
num_epochs = 20000 # 训练的轮数
# 用于存储每100个epoch的损失值和对应的epoch数
losses = []
avgs = []
counts = [2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200]
for count in counts:
times = []
for i in range(10):
print(count, i)
interval = 20000 // count
start_time = time.time() # 记录开始时间
model = MLP().to(device)
# 分类问题使用交叉熵损失函数
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 使用随机梯度下降优化器
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
losses = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 前向传播
outputs = model(X_train) # 隐式调用forward函数
loss = criterion(outputs, y_train)
# 反向传播和优化
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 记录损失值
if (epoch + 1) % interval == 0:
losses.append(loss.item()) # item()方法返回一个Python数值,loss是一个标量张量
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
# 打印训练信息
# if (epoch + 1) % 100 == 0: # range是从0开始,所以epoch+1是从当前epoch开始,每100个epoch打印一次
# print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {loss.item():.4f}')
time_all = time.time() - start_time # 计算训练时间
# print(f'Training time: {time_all:.2f} seconds')
times.append(time_all)
average = sum(times)/len(times)
avgs.append(average)
plt.plot(counts, avgs)
plt.xlabel('count')
plt.ylabel('time')
plt.xticks(counts)
plt.title('Is there series?')
plt.show()
# 可视化损失曲线
# plt.plot(range(len(losses)), losses)
# plt.xlabel('Epoch')
# plt.ylabel('Loss')
# plt.title('Training Loss over Epochs')
# plt.show()