摘要
软件开发工具包(Software Development Kit,SDK)是现代软件开发生态系统的核心组成部分,它通过提供预构建的工具、库和文档,显著降低了开发复杂性并加速了应用交付。本文将深入探讨SDK的核心概念、架构设计、开发实践以及未来发展趋势,为开发者提供全面理解SDK技术内涵和实践应用的权威参考。
1 SDK概述与演进历程
1.1 SDK的基本定义
SDK(Software Development Kit)是一套软件开发工具集合 ,旨在帮助开发者为特定平台、框架或服务创建应用程序。一个完整的SDK通常包含编译器、调试器、代码库、文档、示例代码和API等组件,为开发者提供"开箱即用"的开发体验。
从本质上讲,SDK是技术能力的封装和抽象,它将复杂的技术实现细节隐藏起来,暴露简单易用的接口,使开发者能够专注于业务逻辑而非底层技术细节。正如建筑工人使用预制构件而非从零开始制造砖块一样,SDK让开发者能够站在巨人的肩膀上构建应用。
1.2 SDK的历史演进
SDK的概念和实践随着软件开发范式的演变而不断发展:
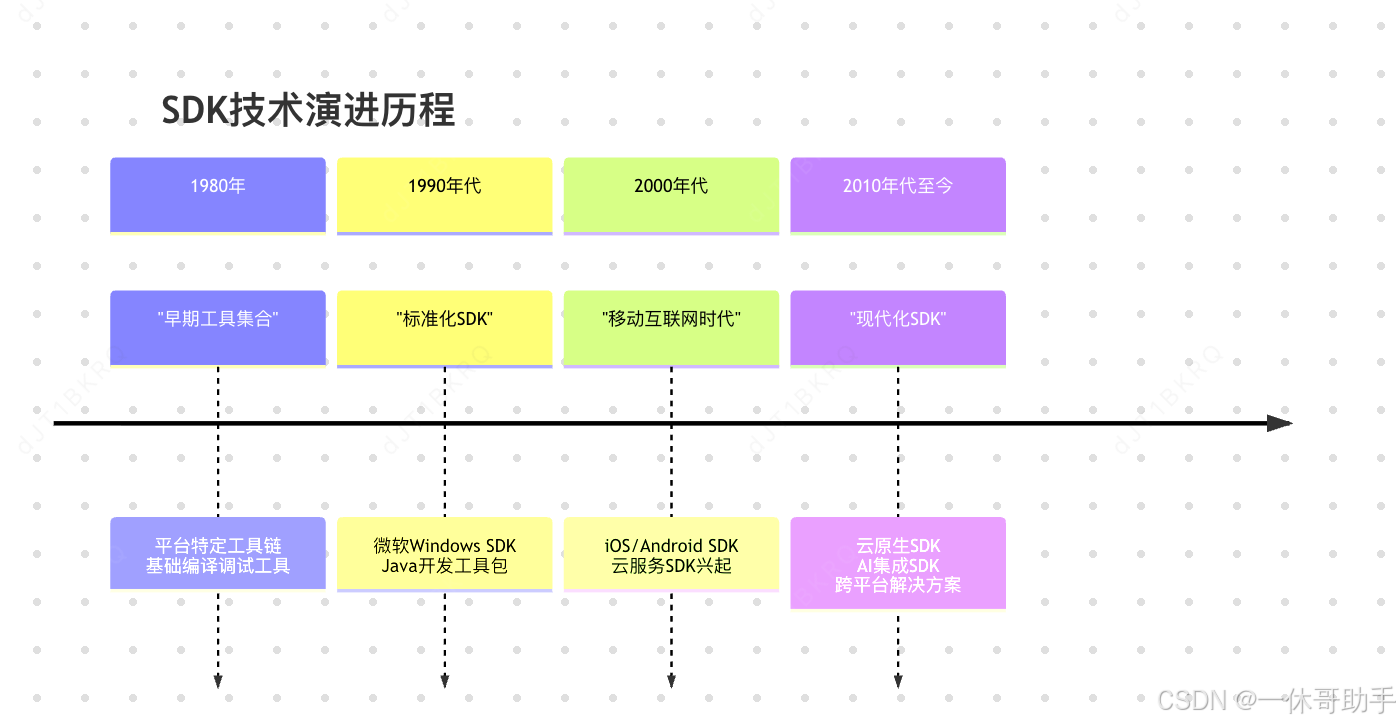
1.3 SDK与API的关系辨析
虽然SDK和API经常被同时提及,但两者有着本质区别:
- API(应用程序编程接口) :定义了软件组件之间的交互协议,是一组明确的规则和规范,说明如何与其他软件通信
- SDK(软件开发工具包) :是实现API的工具集合,包含使API调用更便捷的代码库、文档和其他资源
简单来说,API是"菜单",描述了可点的菜品;而SDK是"厨房工具",帮助你更高效地准备这些菜品。一个SDK通常会实现一个或多个API,但API可以不依赖特定SDK而独立存在。
2 SDK的核心架构与组成
2.1 SDK的层次化架构
现代SDK通常采用分层架构设计,各层职责分明,协同工作:
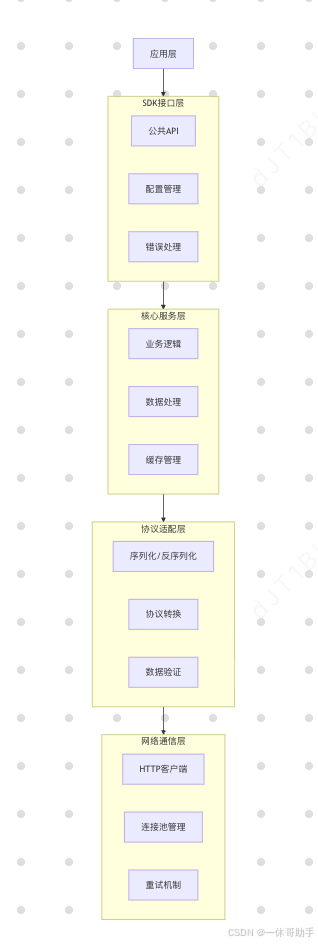
2.2 SDK的核心组件
2.2.1 API客户端
API客户端是SDK的核心组件,负责与服务端进行通信。它封装了网络请求的细节,包括认证、序列化、错误处理等:
java
// SDK API客户端示例
public class PaymentSDKClient {
private final String apiKey;
private final HttpClient httpClient;
private final ObjectMapper mapper;
public PaymentSDKClient(String apiKey) {
this.apiKey = apiKey;
this.httpClient = HttpClient.newBuilder()
.connectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.build();
this.mapper = new ObjectMapper();
}
public PaymentResult processPayment(PaymentRequest request) {
try {
String jsonBody = mapper.writeValueAsString(request);
HttpRequest httpRequest = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://api.payments.com/v1/charge"))
.header("Authorization", "Bearer " + apiKey)
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.POST(HttpRequest.BodyPublishers.ofString(jsonBody))
.build();
HttpResponse<String> response = httpClient.send(
httpRequest, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString());
return mapper.readValue(response.body(), PaymentResult.class);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SDKException("Payment processing failed", e);
}
}
}2.2.2 配置管理
配置管理组件负责处理SDK的初始化配置,包括认证信息、超时设置、重试策略等:
yaml
# SDK配置示例
sdk:
payment:
base_url: "https://api.payments.com/v1"
timeout: 30000
retry:
max_attempts: 3
backoff_multiplier: 2.0
logging:
level: "INFO"
format: "JSON"2.2.3 错误处理机制
健壮的错误处理是高质量SDK的关键特征。SDK应该定义清晰的错误类型和异常层次结构:
java
// SDK错误处理示例
public class SDKException extends RuntimeException {
private final String errorCode;
private final String requestId;
public SDKException(String message, String errorCode, String requestId) {
super(message);
this.errorCode = errorCode;
this.requestId = requestId;
}
// 特定错误类型
public static class AuthenticationException extends SDKException {
public AuthenticationException(String message, String requestId) {
super(message, "AUTH_ERROR", requestId);
}
}
public static class NetworkException extends SDKException {
public NetworkException(String message, String requestId) {
super(message, "NETWORK_ERROR", requestId);
}
}
}2.2.4 文档和示例
完善的文档和实用的示例代码是SDK不可或缺的组成部分。好的文档应该包括:
- 快速入门指南:5分钟内上手的教程
- API参考文档:详细的类和方法说明
- 概念解释:核心概念和工作原理说明
- 最佳实践:推荐的使用模式和避坑指南
3 SDK的类型与分类
3.1 按目标平台分类
不同的运行环境需要特定设计的SDK:
3.1.1 移动端SDK
针对iOS和Android平台的SDK,通常需要考虑移动网络环境、电池消耗和数据使用量:
swift
// iOS SDK使用示例
let analyticsSDK = AnalyticsSDK(configuration: config)
analyticsSDK.trackEvent("purchase_completed",
properties: ["amount": 99.99, "currency": "USD"])3.1.2 Web端SDK
基于JavaScript的SDK,通常通过CDN分发或npm包管理:
javascript
// Web SDK使用示例
import { Analytics } from 'web-analytics-sdk';
const analytics = new Analytics({
apiKey: 'your-api-key',
endpoint: 'https://analytics.example.com'
});
analytics.pageView('homepage');3.1.3 服务端SDK
用于后端服务的SDK,支持多种编程语言,注重性能和高并发:
python
# Python服务端SDK示例
from payment_sdk import Client
client = Client(api_key='sk_test_...')
payment = client.payment.create(
amount=1000,
currency='usd',
source='tok_visa'
)3.1.4 桌面端SDK
针对Windows、macOS和Linux桌面应用的SDK,通常提供原生系统集成能力。
3.2 按功能领域分类
3.2.1 支付SDK
如Stripe、支付宝、微信支付等,提供安全的支付处理能力:
表:主流支付SDK特性对比
| 特性 | Stripe | 支付宝 | 微信支付 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 支付方式 | 信用卡、银行转账 | 余额、花呗、银行卡 | 余额、银行卡 |
| 国际支持 | 全球覆盖 | 主要亚洲市场 | 主要中国市场 |
| 费率结构 | 每笔交易2.9%+$0.30 | 0.55%-1.2% | 0.6%-1% |
| SDK语言 | 多语言支持 | Java/Python/PHP等 | 多语言支持 |
3.2.2 分析SDK
如Google Analytics、Mixpanel等,提供用户行为追踪和分析:
java
// 移动分析SDK示例
Analytics.logEvent("search_completed", Bundle().apply {
putString("search_query", query)
putInt("result_count", results.size)
})3.2.3 身份验证SDK
如Auth0、Firebase Authentication等,简化用户认证流程:
javascript
// 身份验证SDK示例
const auth0 = new auth0.WebAuth({
domain: 'your-domain.auth0.com',
clientID: 'your-client-id'
});
auth0.loginWithRedirect({
redirectUri: 'http://localhost:3000/callback'
});3.2.4 云服务SDK
如AWS SDK、Azure SDK等,提供云资源的管理和操作接口。
4 SDK的设计原则与最佳实践
4.1 核心设计原则
4.1.1 易用性优先
SDK应该遵循"约定优于配置"的原则,提供合理的默认值,减少必要的配置步骤:
java
// 好的设计:简单初始化
AnalyticsSDK analytics = AnalyticsSDK.init("YOUR_API_KEY");
// 不好的设计:复杂配置
AnalyticsSDK analytics = new AnalyticsSDK.Builder()
.setApiKey("YOUR_API_KEY")
.setEndpoint("https://api.analytics.com")
.setMaxBatchSize(50)
.setFlushInterval(30000)
.setRetryPolicy(RetryPolicy.EXPONENTIAL_BACKOFF)
.build();4.1.2 一致性原则
SDK的API设计应该在整个SDK中保持一致的模式和命名约定:
python
# 一致的设计模式
client.users.create(...)
client.users.get(...)
client.users.update(...)
client.users.delete(...)
client.products.create(...)
client.products.get(...)
# ... 同样的模式4.1.3 向后兼容性
保持API的向后兼容性是SDK长期成功的关键。应该通过版本策略和弃用机制来管理变更:
java
// 通过版本管理兼容性
@Deprecated(since = "2.0.0", forRemoval = true)
public void oldMethod(String param) {
// 老实现
}
public void newMethod(String param, Config options) {
// 新实现
}4.2 性能优化策略
4.2.1 异步操作
对于可能阻塞的操作,提供异步接口避免影响主线程:
javascript
// 异步SDK操作示例
// 同步方式(不推荐)
const result = sdk.processData(data); // 可能阻塞
// 异步方式(推荐)
sdk.processDataAsync(data)
.then(result => {
console.log('Processing completed', result);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Processing failed', error);
});
// 或者使用async/await
async function processData() {
try {
const result = await sdk.processDataAsync(data);
console.log('Processing completed', result);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Processing failed', error);
}
}4.2.2 批量处理
对于高频小操作,提供批量处理接口减少网络开销:
java
// 批量操作示例
public class AnalyticsSDK {
private final List<Event> eventBatch = new ArrayList<>();
private final ScheduledExecutorService executor;
public void trackEvent(Event event) {
eventBatch.add(event);
if (eventBatch.size() >= BATCH_SIZE) {
flushEvents();
}
}
private void flushEvents() {
List<Event> batchToSend = new ArrayList<>(eventBatch);
eventBatch.clear();
executor.submit(() -> {
sendBatchToServer(batchToSend);
});
}
}4.2.3 缓存策略
合理使用缓存减少重复计算和网络请求:
python
class CachingSDKClient:
def __init__(self, api_key):
self.api_key = api_key
self.cache = {}
self.ttl = 300 # 5分钟缓存
def get_user(self, user_id):
cache_key = f"user_{user_id}"
# 检查缓存
if cache_key in self.cache:
cached_data, timestamp = self.cache[cache_key]
if time.time() - timestamp < self.ttl:
return cached_data
# 缓存未命中,调用API
user_data = self.call_api(f"/users/{user_id}")
# 更新缓存
self.cache[cache_key] = (user_data, time.time())
return user_data4.3 安全最佳实践
4.3.1 安全认证
安全地处理认证信息,避免在日志或错误信息中泄露敏感数据:
java
public class SecureSDKClient {
private final String apiKey;
public SecureSDKClient(String apiKey) {
validateApiKey(apiKey);
this.apiKey = apiKey;
}
private void validateApiKey(String apiKey) {
if (apiKey == null || apiKey.trim().isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("API key cannot be null or empty");
}
if (!apiKey.startsWith("sk_") && !apiKey.startsWith("pk_")) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid API key format");
}
}
// 安全地记录API密钥(只显示部分字符)
@Override
public String toString() {
return "SecureSDKClient{apiKey='" +
maskApiKey(apiKey) + "'}";
}
private String maskApiKey(String apiKey) {
if (apiKey.length() <= 8) return "***";
return apiKey.substring(0, 4) + "..." +
apiKey.substring(apiKey.length() - 4);
}
}4.3.2 数据传输安全
确保所有网络通信都使用加密协议:
java
public class SecureHttpClient {
private final HttpClient httpClient;
public SecureHttpClient() {
this.httpClient = HttpClient.newBuilder()
.version(HttpClient.Version.HTTP_2)
.followRedirects(HttpClient.Redirect.NORMAL)
.connectTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.sslContext(createSecureSSLContext())
.sslParameters(createSecureSSLParameters())
.build();
}
private SSLContext createSecureSSLContext() {
try {
SSLContext sslContext = SSLContext.getInstance("TLSv1.3");
sslContext.init(null,
new TrustManager[] { createTrustManager() },
new SecureRandom());
return sslContext;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new SDKException("Failed to create SSL context", e);
}
}
}5 SDK的开发与发布流程
5.1 SDK开发流程
现代化的SDK开发应该遵循系统化的流程:
需求分析 架构设计 接口定义 实现核心功能 编写测试 文档编写 打包发布 持续维护
5.2 自动化测试策略
全面的测试覆盖是SDK质量的保证:
python
# SDK测试示例
import pytest
from unittest.mock import Mock, patch
from my_sdk import PaymentClient
class TestPaymentSDK:
@pytest.fixture
def client(self):
return PaymentClient(api_key='test_key')
def test_successful_payment(self, client):
"""测试成功支付场景"""
with patch('my_sdk.http_client') as mock_client:
mock_client.post.return_value = {
'status': 'success',
'transaction_id': 'txn_123'
}
result = client.charge(amount=1000, currency='usd')
assert result.status == 'success'
assert result.transaction_id == 'txn_123'
def test_network_failure(self, client):
"""测试网络故障场景"""
with patch('my_sdk.http_client') as mock_client:
mock_client.post.side_effect = ConnectionError('Network issue')
with pytest.raises(SDKNetworkError):
client.charge(amount=1000, currency='usd')
def test_invalid_input(self, client):
"""测试输入验证"""
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
client.charge(amount=-100, currency='usd')5.3 版本管理与发布
采用语义化版本控制(SemVer)管理SDK版本:
yaml
# 版本发布配置示例
version: 2.1.0
release_notes:
added:
- 支持新的支付方式
- 新增批量操作API
changed:
- 优化网络请求性能
deprecated:
- 旧认证方法将在3.0.0移除
fixed:
- 修复内存泄漏问题
- 修复重试逻辑缺陷6 SDK的集成与使用模式
6.1 典型集成模式
6.1.1 直接集成模式
最简单的集成方式,直接引入SDK依赖并初始化:
javascript
// Web应用中的SDK集成
import { Analytics } from 'web-analytics-sdk';
// 初始化
const analytics = new Analytics({
apiKey: 'your-api-key',
endpoint: 'https://analytics.example.com'
});
// 使用
analytics.trackPageView('homepage');
analytics.trackEvent('button_click', { button_id: 'cta-primary' });6.1.2 依赖注入模式
在大型应用中使用依赖注入框架管理SDK实例:
java
// Spring Boot应用中的SDK集成
@Configuration
public class SDKConfiguration {
@Value("${payment.api.key}")
private String apiKey;
@Bean
@Primary
public PaymentSDK paymentSDK() {
return PaymentSDK.builder()
.apiKey(apiKey)
.timeout(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.build();
}
}
@Service
public class OrderService {
private final PaymentSDK paymentSDK;
public OrderService(PaymentSDK paymentSDK) {
this.paymentSDK = paymentSDK;
}
public PaymentResult processPayment(Order order) {
return paymentSDK.charge(
order.getAmount(),
order.getCurrency(),
order.getPaymentMethod()
);
}
}6.1.3 适配器模式
当需要兼容多个类似SDK或进行SDK迁移时使用:
python
# 支付SDK适配器示例
class PaymentAdapter:
def __init__(self, provider='stripe'):
if provider == 'stripe':
self.sdk = StripeSDK(api_key='sk_stripe_...')
elif provider == 'paypal':
self.sdk = PayPalSDK(client_id='...', client_secret='...')
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported provider: {provider}")
def charge(self, amount, currency, source):
# 统一接口,隐藏不同SDK的差异
if isinstance(self.sdk, StripeSDK):
return self.sdk.create_charge(
amount=amount,
currency=currency,
source=source
)
elif isinstance(self.sdk, PayPalSDK):
return self.sdk.payment.create(
amount={'total': amount, 'currency': currency},
payment_method=source
)6.2 性能监控与调试
6.2.1 集成监控
在SDK中集成性能监控和日志记录:
java
public class MonitoredSDKClient {
private final MetricsCollector metrics;
private final Logger logger;
public MonitoredSDKClient(MetricsCollector metrics, Logger logger) {
this.metrics = metrics;
this.logger = logger;
}
public ApiResponse callApi(ApiRequest request) {
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
logger.debug("Making API request: {}", request);
ApiResponse response = executeRequest(request);
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
metrics.recordSuccess(duration);
logger.debug("API request completed in {}ms", duration);
return response;
} catch (Exception e) {
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
metrics.recordError(duration, e.getClass().getSimpleName());
logger.error("API request failed after {}ms", duration, e);
throw e;
}
}
}6.2.2 调试支持
为开发环境提供详细的调试信息:
javascript
class DebuggableSDK {
constructor(config) {
this.config = config;
this.debug = config.debug || false;
}
log(level, message, data) {
if (!this.debug && level === 'debug') return;
const timestamp = new Date().toISOString();
const logEntry = {
timestamp,
level,
message,
data,
sdkVersion: this.config.version
};
if (this.config.logger) {
this.config.logger(logEntry);
} else if (this.debug) {
console[level](JSON.stringify(logEntry, null, 2));
}
}
trackEvent(event, properties) {
this.log('debug', 'Tracking event', { event, properties });
// 实际的事件跟踪逻辑
return this.sendToServer({ event, properties });
}
}7 SDK的未来发展趋势
7.1 AI增强的SDK
随着AI技术的发展,SDK正在变得更加智能:
python
# AI增强的SDK示例
class AISmartSDK:
def __init__(self):
self.ai_helper = AIHelper()
def suggest_optimizations(self, usage_patterns):
"""基于使用模式智能推荐优化"""
suggestions = self.ai_helper.analyze_patterns(usage_patterns)
return suggestions
def predict_errors(self, configuration):
"""基于配置预测潜在错误"""
risk_analysis = self.ai_helper.assess_risk(configuration)
return risk_analysis.warnings
def auto_retry_with_ai(self, operation, max_retries=3):
"""AI指导的智能重试"""
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
return operation()
except Exception as e:
if self.ai_helper.should_retry(e, attempt):
delay = self.ai_helper.calculate_backoff(attempt)
time.sleep(delay)
else:
raise7.2 低代码/无代码集成
SDK正在向更易用的方向发展,支持可视化集成:
传统SDK 可视化配置 低代码平台 无代码集成
7.3 边缘计算SDK
随着边缘计算的兴起,SDK需要适应分布式边缘环境:
java
public class EdgeEnabledSDK {
private final EdgeManager edgeManager;
private final SyncService syncService;
public EdgeEnabledSDK(EdgeConfig config) {
this.edgeManager = new EdgeManager(config);
this.syncService = new SyncService(config);
}
public void processWithEdgeFallback(Data data) {
// 优先尝试边缘处理
if (edgeManager.isEdgeAvailable()) {
try {
edgeManager.processLocally(data);
return;
} catch (EdgeProcessingException e) {
// 边缘处理失败,回退到云端
syncService.syncToCloud(data);
}
} else {
// 直接发送到云端
syncService.syncToCloud(data);
}
}
}8 结论
SDK作为现代软件开发的基础构建块,已经从简单的工具集合演变为复杂的技术能力抽象层。优秀的SDK设计不仅需要考虑功能完整性,更要关注开发者体验、性能、安全性和可维护性。
随着云原生、AI和边缘计算等技术的发展,SDK将继续演进,呈现以下趋势:
- 智能化:集成AI能力,提供更智能的调试、优化和建议
- 一体化:提供从开发到运维的完整工具链支持
- 平台化:跨越不同环境和设备的统一开发体验
- 生态化:构建围绕核心SDK的插件和扩展生态系统
对于开发者而言,掌握SDK的设计原理和使用模式,能够显著提高开发效率和应用质量。对于技术决策者,选择和维护合适的SDK组合,将成为构建稳健技术架构的关键能力。
在日益复杂的技术环境中,SDK将继续扮演"技术加速器"的角色,通过抽象复杂性、标准化实践和促进协作,推动整个软件行业向前发展。