遇到的问题以及解决方式
配置如下:
yml
test:
test-time: 2025-12-31实体如下:
java
@Data
public class Test{
private LocalDate testTime;
}springBoot读取本地配置文件后,可以正常解析为LocalDate类型,而读取Consul中的配置后会报错如下:
log
Failed to bind properties under 'project.check-in-multiple-coin.test-time' to java.time.LocalDate:
Property: project.test.test-time
Value: "Wed Dec 31 08:00:00 CST 2025"
Origin: "project.test.test-time" from property source "config/demo/test/"
Reason: org.springframework.core.convert.ConverterNotFoundException: No converter found capable of converting from type [java.util.Date] to type [java.time.LocalDate]解决方法很简单,将配置改为如下:
yml
test:
test-time: '2025-12-31'探究两者差异的原因
二者都是通过YamlProcessor这个类来创建Ymal对象的。差异主要是创建Ymal的方式:
consul是直接调用YamlProcessor的createYaml方法,将日期标签转换成了Date,而springboot是通过OriginTrackedYamlLoader类重写了createYaml方法:
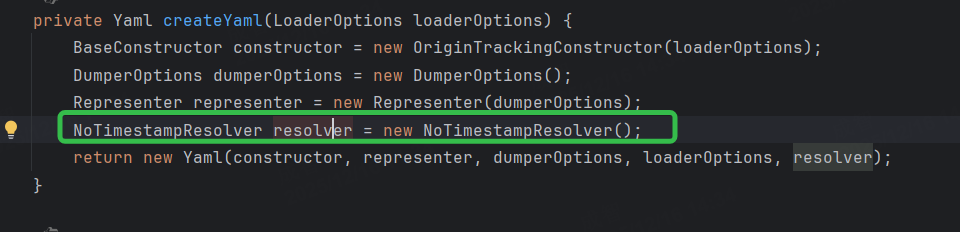
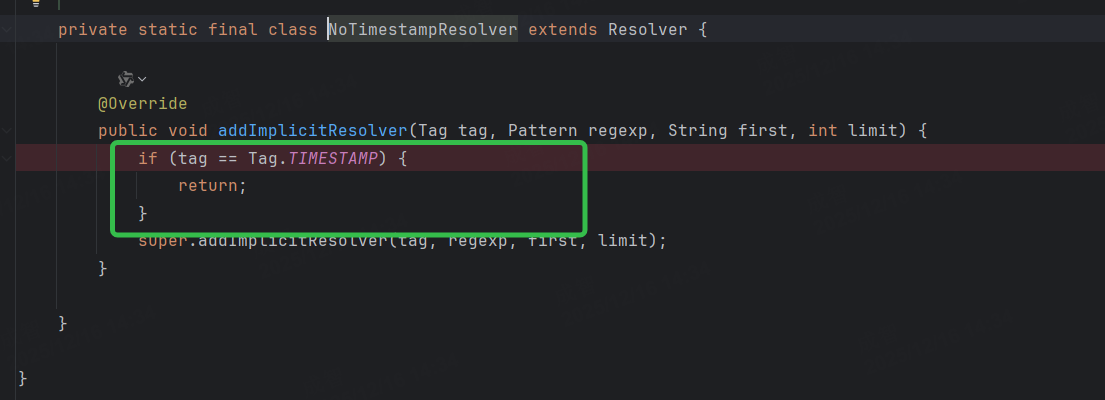
OriginTrackedYamlLoader类中的createYaml针对日期类标签做了特殊处理,不使用snakeyaml处理,而是将日期类的标签统一返回为字符串,然后在后续的操作中根据实体的属性类型进行了转换。
Consul处理流程如下:
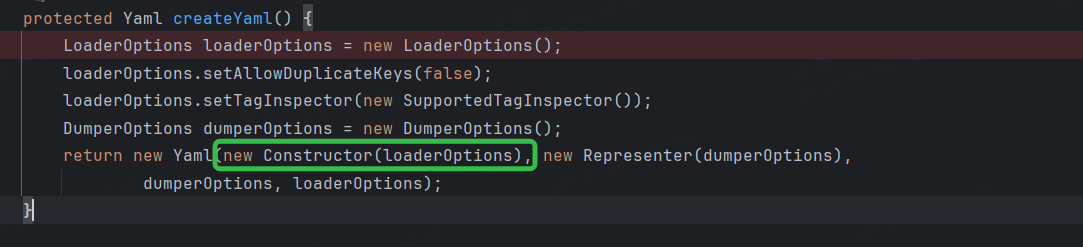
Constructor继承自SafeConstructor,SafeConstructor对以下标签规定了处理方式:
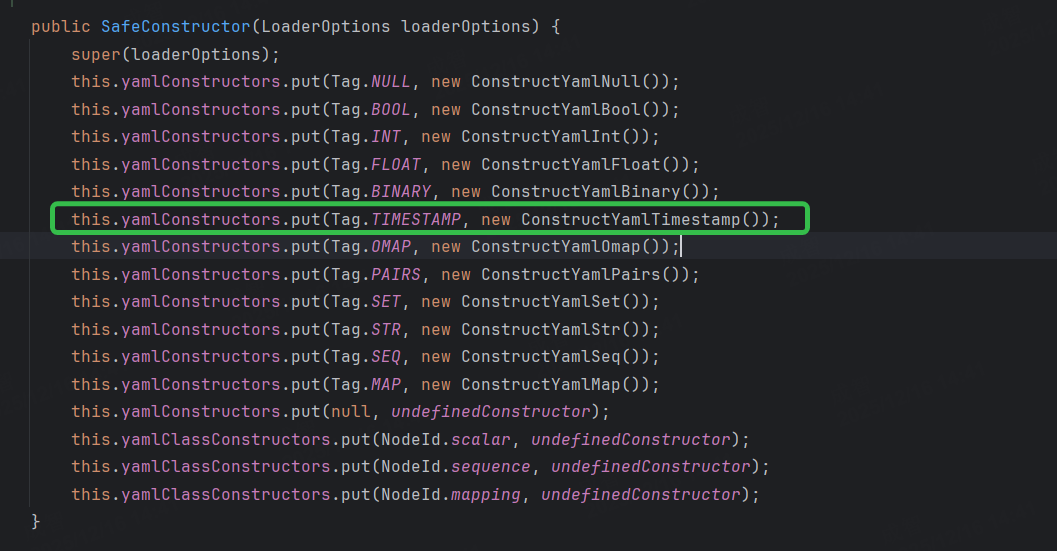
ConstructYamlTimestamp 类一顿操作之后返回了一个Date类型。
java
public static class ConstructYamlTimestamp extends AbstractConstruct {
private Calendar calendar;
public Calendar getCalendar() {
return calendar;
}
@Override
public Object construct(Node node) {
ScalarNode scalar = (ScalarNode) node;
String nodeValue = scalar.getValue();
Matcher match = YMD_REGEXP.matcher(nodeValue);
if (match.matches()) {
String year_s = match.group(1);
String month_s = match.group(2);
String day_s = match.group(3);
calendar = Calendar.getInstance(TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC"));
calendar.clear();
calendar.set(Calendar.YEAR, Integer.parseInt(year_s));
// Java's months are zero-based...
calendar.set(Calendar.MONTH, Integer.parseInt(month_s) - 1); // x
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, Integer.parseInt(day_s));
return calendar.getTime();
} else {
match = TIMESTAMP_REGEXP.matcher(nodeValue);
if (!match.matches()) {
throw new YAMLException("Unexpected timestamp: " + nodeValue);
}
String year_s = match.group(1);
String month_s = match.group(2);
String day_s = match.group(3);
String hour_s = match.group(4);
String min_s = match.group(5);
// seconds and milliseconds
String seconds = match.group(6);
String millis = match.group(7);
if (millis != null) {
seconds = seconds + "." + millis;
}
double fractions = Double.parseDouble(seconds);
int sec_s = (int) Math.round(Math.floor(fractions));
int usec = (int) Math.round((fractions - sec_s) * 1000);
// timezone
String timezoneh_s = match.group(8);
String timezonem_s = match.group(9);
TimeZone timeZone;
if (timezoneh_s != null) {
String time = timezonem_s != null ? ":" + timezonem_s : "00";
timeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone("GMT" + timezoneh_s + time);
} else {
// no time zone provided
timeZone = TimeZone.getTimeZone("UTC");
}
calendar = Calendar.getInstance(timeZone);
calendar.set(Calendar.YEAR, Integer.parseInt(year_s));
// Java's months are zero-based...
calendar.set(Calendar.MONTH, Integer.parseInt(month_s) - 1);
calendar.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, Integer.parseInt(day_s));
calendar.set(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY, Integer.parseInt(hour_s));
calendar.set(Calendar.MINUTE, Integer.parseInt(min_s));
calendar.set(Calendar.SECOND, sec_s);
calendar.set(Calendar.MILLISECOND, usec);
return calendar.getTime();
}
}
}总结
分析以上差异点并不是为了证明谁对谁错,而是要即知其然也要知其所以然。