多态反序列化是处理继承结构对象序列化的常见需求,但不同 JSON 序列化库的实现机制差异会带来显著的安全风险。微软 CA2326 规则明确警示:避免使用非安全的 JsonSerializerSettings 配置(如 Newtonsoft.Json 的 TypeNameHandling 非 None 值),否则可能引发类型注入攻击。本文将对比 Newtonsoft.Json 与 System.Text.Json 在多态反序列化中的实现差异,重点分析安全性问题,并通过代码实例验证两者的安全表现。
多态反序列化的实现机制差异
Newtonsoft.Json:基于TypeNameHandling 的灵活设计
Newtonsoft.Json 通过 TypeNameHandling 配置项控制是否在 JSON 中嵌入类型元数据。当设置 TypeNameHandling 支持多态时,JSON 会携带 $type 字段(包含类型的完全限定名和程序集信息),反序列化时直接根据该字段实例化对应类型。这种设计虽然灵活支持多态,但缺乏默认的类型校验机制,攻击者可构造包含恶意类型的 JSON,触发敏感类型实例化。
System.Text.Json:多态配置的安全设计
System.Text.Json 默认不支持多态反序列化,需通过 [JsonDerivedType] 特性或 DerivedTypes 显式声明允许的派生类型。反序列化时仅处理配置过的类型,拒绝未授权的类型注入,从机制上规避了安全风险。
CA2326 规则的警示
CA2326 规则的核心是禁止使用 TypeNameHandling 非 None 值的配置 ------ 攻击者可利用 $type 字段构造恶意 JSON,实例化如 ProcessStartInfo(执行系统命令)、FileStream(读写文件)等敏感类型,引发远程代码执行或数据泄露。
代码实例验证
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Serialization;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization.Metadata;
namespace NewtonsoftSecurityDemo
{
[JsonPolymorphic(TypeDiscriminatorPropertyName = "CustomerType")]
[JsonDerivedType(typeof(PaymentCompletedEvent), "PaymentCompletedEvent")]
[JsonDerivedType(typeof(OrderCreatedEvent), "OrderCreatedEvent")]
public class TransactionEvent
{
public string EventId { get; set; } = Guid.NewGuid().ToString();
public DateTime EventTime { get; set; } = DateTime.Now;
public string OrderId { get; set; }
// 业务扩展字段(攻击者利用的入口)
public object ExtData { get; set; }
}
public class PaymentCompletedEvent : TransactionEvent
{
public decimal Amount { get; set; }
public string PaymentMethod { get; set; }
}
public class OrderCreatedEvent : TransactionEvent
{
public string UserId { get; set; }
public int ItemCount { get; set; }
}
// Newtonsoft.Json 安全绑定器(演示白名单校验)
public class EventSerializationBinder : ISerializationBinder
{
// 仅允许的安全类型白名单
private readonly HashSet<string> _allowedTypes = new()
{
"NewtonsoftSecurityDemo.PaymentCompletedEvent",
"NewtonsoftSecurityDemo.OrderCreatedEvent",
//"System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo"
};
public Type BindToType(string assemblyName, string typeName)
{
// 仅允许白名单内的类型
if (!_allowedTypes.Contains(typeName))
{
throw new NotSupportedException($"禁止反序列化未授权类型:{typeName}");
}
return Type.GetType($"{typeName}, {assemblyName}") ?? typeof(TransactionEvent);
}
public void BindToName(Type serializedType, out string? assemblyName, out string? typeName)
{
assemblyName = serializedType.Assembly.FullName;
typeName = serializedType.FullName;
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("=== Newtonsoft.Json 命令执行攻击演示 ===");
Newtonsoft_Attack_ProcessStartInfo();
Console.WriteLine("\n=== Newtonsoft.Json 文件读取攻击演示 ===");
Newtonsoft_Attack_FileStream();
Console.WriteLine("\n=== Newtonsoft.Json 启用 SerializationBinder:安全防护演示 ===");
Newtonsoft_Secure_WithBinder();
Console.WriteLine("\n=== System.Text.Json 安全防护演示 ===");
SystemTextJson_Defense();
Console.ReadKey();
}
/// <summary>
/// 模拟:注入ProcessStartInfo执行系统命令
/// </summary>
static void Newtonsoft_Attack_ProcessStartInfo()
{
string maliciousCallbackJson = @$"
{{
""$type"": ""NewtonsoftSecurityDemo.PaymentCompletedEvent, NewtonsoftSecurityDemo"",
""EventId"": ""{Guid.NewGuid()}"",
""OrderId"": ""ORD_{new Random().Next(1000, 9999)}"",
""Amount"": 999.00,
""PaymentMethod"": ""Alipay"",
""ExtData"": {{
""$type"": ""System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo,System.Diagnostics.Process"",
""FileName"": ""cmd.exe"",
""Arguments"": ""/c echo 'some scripts' > C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt && echo 'doing' >> C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt"",
""UseShellExecute"": true
}}
}}";
var settings = new JsonSerializerSettings
{
TypeNameHandling = TypeNameHandling.Auto,
};
var eventData = Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TransactionEvent>(maliciousCallbackJson, settings);
Console.WriteLine($"处理订单事件:{eventData.OrderId}");
if (eventData.ExtData is ProcessStartInfo psi)
{
Directory.CreateDirectory("C:\\temp");
Process.Start(psi);
Console.WriteLine($" [攻击成功] 执行命令:{psi.Arguments}");
Console.WriteLine($" [攻击结果] 生成文件:C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt 文件内容:");
if (File.Exists("C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt"))
{
string content = File.ReadAllText("C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt");
Console.WriteLine($"{content}");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 模拟:注入FileInfo读取敏感文件
/// </summary>
static void Newtonsoft_Attack_FileStream()
{
string targetFile = Path.Combine(Environment.GetFolderPath(Environment.SpecialFolder.Desktop), "appsettings.json");
if (!File.Exists(targetFile))
{
File.WriteAllText(targetFile, "ConnectionString: 123456");
}
string maliciousExportJson = @$"
{{
""$type"": ""NewtonsoftSecurityDemo.OrderCreatedEvent, NewtonsoftSecurityDemo"",
""OrderId"": ""ORD_{new Random().Next(1000, 9999)}"",
""UserId"": ""user_{new Random().Next(100, 999)}"",
""ExtData"": {{
""$type"": ""System.IO.FileInfo"",
""FileName"": ""{targetFile.Replace("\\", "\\\\")}""
}}
}}";
var settings = new JsonSerializerSettings
{
TypeNameHandling = TypeNameHandling.Auto
};
var eventData = Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TransactionEvent>(maliciousExportJson, settings);
Console.WriteLine($"处理订单导出:{eventData.OrderId}");
// 通过FileInfo读取文件内容(模拟攻击逻辑)
if (eventData.ExtData is FileInfo fileInfo)
{
using (var sr = new StreamReader(fileInfo.OpenRead()))
{
string sensitiveContent = sr.ReadToEnd();
Console.WriteLine($" [攻击成功] 读取敏感文件内容:\n{sensitiveContent}");
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Newtonsoft.Json 启用SerializationBinder:拦截恶意类型
/// </summary>
static void Newtonsoft_Secure_WithBinder()
{
string maliciousCallbackJson = @$"
{{
""$type"": ""NewtonsoftSecurityDemo.PaymentCompletedEvent, NewtonsoftSecurityDemo"",
""EventId"": ""{Guid.NewGuid()}"",
""OrderId"": ""ORD_{new Random().Next(1000, 9999)}"",
""Amount"": 999.00,
""PaymentMethod"": ""Alipay"",
""ExtData"": {{
""$type"": ""System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo,System.Diagnostics.Process"",
""FileName"": ""cmd.exe"",
""Arguments"": ""/c echo 'some scripts' > C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt && echo 'doing' >> C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt"",
""UseShellExecute"": true
}}
}}";
var settings = new JsonSerializerSettings
{
TypeNameHandling = TypeNameHandling.Auto,
SerializationBinder = new EventSerializationBinder() // 启用白名单校验
};
try
{
var eventData = Newtonsoft.Json.JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<TransactionEvent>(maliciousCallbackJson, settings);
if (eventData.ExtData is ProcessStartInfo)
{
Console.WriteLine(" [防护失效] 恶意类型未被拦截(异常)");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($" [防护成功] 拦截未授权类型:{ex.Message}");
}
}
/// <summary>
/// System.Text.Json 安全防护验证
/// </summary>
static void SystemTextJson_Defense()
{
string maliciousCallbackJson = @$"
{{
""CustomerType"": ""PaymentCompletedEvent"",
""EventId"": ""{Guid.NewGuid()}"",
""OrderId"": ""ORD_{new Random().Next(1000, 9999)}"",
""Amount"": 999.00,
""PaymentMethod"": ""Alipay"",
""ExtData"": {{
""$type"": ""System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo,System.Diagnostics.Process"",
""FileName"": ""cmd.exe"",
""Arguments"": ""/c echo 'some scripts' > C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt && echo 'doing' >> C:\\temp\\attack_log.txt"",
""UseShellExecute"": true
}}
}}";
var eventData = System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Deserialize<TransactionEvent>(maliciousCallbackJson);
Console.WriteLine($" 主对象类型:{eventData.GetType().FullName}");
Console.WriteLine($" ExtData 实际类型:{eventData.ExtData.GetType().FullName}");
if (eventData.ExtData is JsonElement)
{
Console.WriteLine(" [防护成功] 恶意类型ProcessStartInfo被拦截,ExtData仅保留原始JSON结构,未反序列化为恶意对象");
}
else if (eventData.ExtData is ProcessStartInfo)
{
Console.WriteLine(" [防护失效] 恶意类型解析成功");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($" [正常业务] 解析到合法类型:{eventData.ExtData.GetType().FullName}");
}
Console.WriteLine("\n尝试转换ExtData为ProcessStartInfo:");
try
{
var psi = (ProcessStartInfo)eventData.ExtData;
Console.WriteLine(" [防护失效] 恶意类型解析成功");
}
catch (InvalidCastException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($" [防护成功] 强制转换失败,原因:{ex.Message}");
}
}
}
}运行结果为:
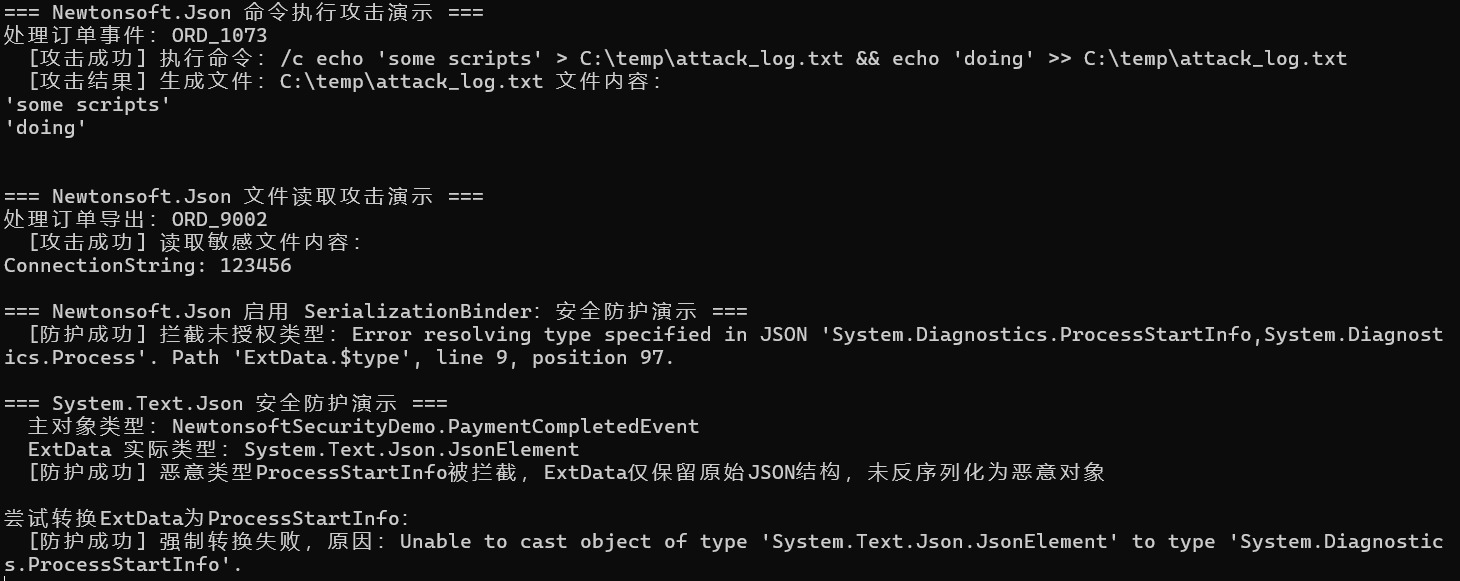
通过 Demo 可以发现:
- Newtonsoft 无防护时攻击成功;
- Newtonsoft 启用 SerializationBinder 后拦截了恶意类型;
- System.Text.Json 始终拦截恶意类型,ExtData 为 JsonElement,无法转换为 ProcessStartInfo。
为什么 Newtonsoft.Json 启用 SerializationBinder 可降低风险?
先看代码:
public class EventSerializationBinder : ISerializationBinder
{
// 仅允许的安全类型白名单
private readonly HashSet<string> _allowedTypes = new()
{
"NewtonsoftSecurityDemo.PaymentCompletedEvent",
"NewtonsoftSecurityDemo.OrderCreatedEvent",
//"System.Diagnostics.ProcessStartInfo"
};
public Type BindToType(string assemblyName, string typeName)
{
// 仅允许白名单内的类型
if (!_allowedTypes.Contains(typeName))
{
throw new NotSupportedException($"禁止反序列化未授权类型:{typeName}");
}
return Type.GetType($"{typeName}, {assemblyName}") ?? typeof(TransactionEvent);
}
public void BindToName(Type serializedType, out string? assemblyName, out string? typeName)
{
assemblyName = serializedType.Assembly.FullName;
typeName = serializedType.FullName;
}
}SerializationBinder 的核心作用是:接管从 JSON 中的 $type 字符串 到实际 Type 类型的映射过程,强制校验类型合法性。简单说:
- 无 SerializationBinder:反序列化器会无条件反射创建 $type 指定的任意类型,包括危险类型;
- 有 SerializationBinder:反序列化器必须经过你的自定义校验逻辑,仅允许白名单内的类型被实例化,直接阻断恶意类型的创建。
小结
Newtonsoft.Json 的 TypeNameHandling 机制虽灵活,但易被利用触发安全漏洞;System.Text.Json 通过显式多态配置白名单的设计,规避了类型注入风险。
在实际开发中,针对多态场景,建议优先使用 System.Text.Json。若必须使用 Newtonsoft.Json,需遵循以下安全实践:
- 避免使用 TypeNameHandling 非 None 值。
- 若必须启用,需严格校验 $type 字段类型的合法性,仅允许安全类型。
我希望您喜欢这篇文章,并一如既往地感谢您阅读并与朋友和同事分享我的文章。
