day33 Agent 错误恢复与回退策略
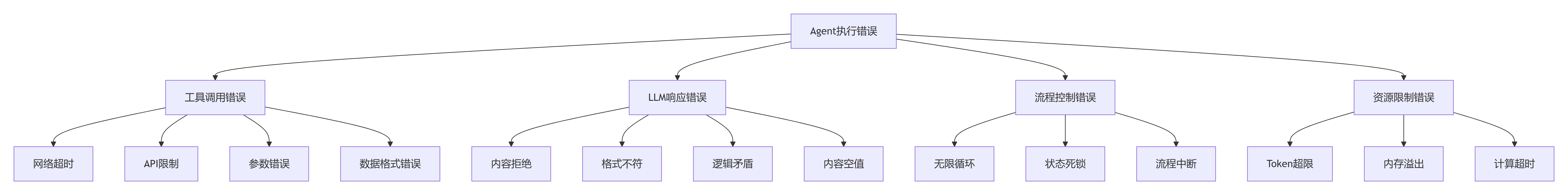
错误类型分类与处理策略
错误分类体系
核心恢复策略矩阵
| 策略类型 | 适用场景 | 实现复杂度 | 恢复成功率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 重试机制 | 临时性错误(网络、API限流) | 低 | 60-80% |
| 降级处理 | 工具不可用、功能缺失 | 中 | 70-90% |
| 熔断机制 | 服务持续故障 | 中 | 90-95% |
| 旁路策略 | 主路径失败 | 高 | 80-95% |
| 人工干预 | 复杂逻辑错误 | 低 | 95-100% |
多层级防御架构
第1层:预防层(Prevention)
python
class PreventiveMeasures:
"""预防性措施"""
@staticmethod
def validate_input(user_input: str, max_length: int = 1000) -> ValidationResult:
"""输入验证"""
checks = [
("长度检查", len(user_input) <= max_length),
("恶意代码检查", not any(keyword in user_input.lower()
for keyword in ["system(", "exec(", "eval("])),
("敏感信息检查", not any(pattern in user_input
for pattern in ["密码", "token:", "apikey"])),
("编码检查", user_input.isprintable())
]
failures = [name for name, passed in checks if not passed]
return ValidationResult(
valid=len(failures) == 0,
failures=failures
)
@staticmethod
def sanitize_tool_parameters(params: Dict) -> Dict:
"""参数消毒"""
sanitized = {}
for key, value in params.items():
if isinstance(value, str):
# 移除潜在的注入代码
sanitized[key] = value.replace(";", "").replace("`", "").replace("$(", "")
else:
sanitized[key] = value
return sanitized第2层:检测层(Detection)
python
class ErrorDetector:
"""错误检测器"""
def __init__(self):
self.error_patterns = {
"timeout": [
"timeout", "timed out", "请求超时",
"operation timeout", "连接超时"
],
"rate_limit": [
"rate limit", "quota", "limit exceeded",
"API调用次数超限", "429"
],
"authentication": [
"unauthorized", "forbidden", "invalid token",
"authentication failed", "401", "403"
],
"validation": [
"invalid parameter", "bad request", "validation failed",
"参数错误", "400"
],
"server_error": [
"internal server error", "server unavailable",
"服务器错误", "500", "503"
],
"llm_error": [
"content policy", "cannot fulfill", "refused",
"抱歉,我无法", "根据我的使用条款"
]
}
def classify_error(self, error_message: str) -> ErrorType:
"""错误分类"""
error_message_lower = error_message.lower()
for error_type, patterns in self.error_patterns.items():
for pattern in patterns:
if pattern.lower() in error_message_lower:
return ErrorType(
type=error_type,
pattern=pattern,
confidence=0.9
)
return ErrorType(type="unknown", pattern="", confidence=0.0)
def detect_infinite_loop(self, execution_history: List[Dict]) -> bool:
"""检测无限循环"""
if len(execution_history) < 3:
return False
# 检查最近三次操作是否相同
recent_ops = [step.get("tool_name", "") for step in execution_history[-3:]]
if len(set(recent_ops)) == 1 and recent_ops[0]:
return True
# 检查状态是否重复
recent_states = [
hash(str(step.get("parameters", {})))
for step in execution_history[-5:]
]
return len(set(recent_states)) < 3第3层:恢复层(Recovery)
python
class RecoveryStrategies:
"""恢复策略集合"""
def __init__(self, llm_client, fallback_tools: Dict):
self.llm = llm_client
self.fallback_tools = fallback_tools
self.circuit_breakers = {}
def retry_with_backoff(self,
func: Callable,
max_retries: int = 3,
initial_delay: float = 1.0) -> Any:
"""指数退避重试"""
delay = initial_delay
for attempt in range(max_retries):
try:
return func()
except Exception as e:
if attempt == max_retries - 1:
raise
error_type = self.detector.classify_error(str(e))
# 对于某些错误不重试
if error_type.type in ["authentication", "validation"]:
raise
logger.warning(f"重试 {attempt + 1}/{max_retries}: {str(e)}")
time.sleep(delay)
delay *= 2 # 指数退避
def fallback_to_simpler_tool(self,
failed_tool: str,
original_params: Dict,
context: Dict) -> Any:
"""降级到更简单的工具"""
fallback_chain = {
"web_search": [
("local_knowledge_base", 0.8),
("cached_search_results", 0.6),
("llm_general_knowledge", 0.4)
],
"calculator": [
("simple_math_parser", 0.9),
("llm_calculation", 0.7),
("approximate_estimation", 0.5)
],
"weather_api": [
("historical_weather", 0.8),
("seasonal_average", 0.6),
("manual_input", 0.3)
]
}
if failed_tool not in fallback_chain:
return None
for fallback_tool, confidence in fallback_chain[failed_tool]:
if fallback_tool in self.fallback_tools:
try:
result = self.fallback_tools[fallback_tool](original_params)
logger.info(f"使用降级工具 {fallback_tool} (置信度: {confidence})")
return {
"result": result,
"source": fallback_tool,
"confidence": confidence,
"is_fallback": True
}
except:
continue
return None
def circuit_breaker(self, tool_name: str, failure_threshold: int = 5) -> bool:
"""熔断器模式"""
if tool_name not in self.circuit_breakers:
self.circuit_breakers[tool_name] = {
"failures": 0,
"last_failure": None,
"state": "closed"
}
cb = self.circuit_breakers[tool_name]
if cb["state"] == "open":
# 检查是否应该进入半开状态
if (cb["last_failure"] and
time.time() - cb["last_failure"] > 60): # 60秒后重试
cb["state"] = "half-open"
return True
return False
if cb["state"] == "half-open":
# 半开状态只允许一次尝试
cb["state"] = "open" # 假设这次会失败
return True
# closed状态,检查失败次数
if cb["failures"] >= failure_threshold:
cb["state"] = "open"
cb["last_failure"] = time.time()
logger.warning(f"熔断器触发: {tool_name}")
return False
return True
def update_circuit_state(self, tool_name: str, success: bool):
"""更新熔断器状态"""
if tool_name not in self.circuit_breakers:
return
cb = self.circuit_breakers[tool_name]
if success:
cb["failures"] = 0
if cb["state"] == "half-open":
cb["state"] = "closed" # 成功,关闭熔断器
else:
cb["failures"] += 1
cb["last_failure"] = time.time()
if cb["state"] == "half-open":
cb["state"] = "open" # 失败,保持打开第4层:旁路层(Bypass)
python
class BypassStrategies:
"""旁路策略"""
@staticmethod
def semantic_approximation(query: str, available_data: List) -> str:
"""语义近似:当无法获取精确数据时提供近似答案"""
approximation_rules = {
r".*多少.*钱.*": [
"根据市场行情,类似产品价格在XXX-XXX元之间",
"价格因地区和时间而异,通常范围是...",
"我无法获取实时价格,但可以参考历史数据..."
],
r".*天气.*": [
"当前季节该地区通常天气是...",
"根据天气预报模型,预计...",
"可以参考邻近城市的天气情况..."
],
r".*时间.*": [
"通常需要XXX小时,具体取决于...",
"历史平均时间是...",
"根据类似情况估计..."
]
}
for pattern, responses in approximation_rules.items():
if re.match(pattern, query):
return random.choice(responses)
return "虽然无法提供精确答案,但根据一般情况..."
@staticmethod
def stepwise_refinement(problem: str, max_steps: int = 3) -> List[str]:
"""逐步细化:将复杂问题分解为简单问题"""
refinement_prompt = f"""
将以下复杂问题分解为不超过{max_steps}个简单问题:
原问题:{problem}
分解步骤(每个步骤应该是独立可回答的问题):
1. """
# 调用LLM进行分解
decomposed = llm_call(refinement_prompt)
return decomposed.split("\n")
@staticmethod
def alternative_paths(main_path: List[str],
available_tools: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
"""生成替代执行路径"""
alternatives = []
# 1. 工具替换路径
tool_mapping = {
"web_search": ["local_search", "knowledge_base_query"],
"calculator": ["llm_calculation", "rule_based_estimation"],
"weather_api": ["historical_data", "seasonal_pattern"]
}
for tool in main_path:
if tool in tool_mapping:
for alt in tool_mapping[tool]:
if alt in available_tools:
alt_path = main_path.copy()
alt_path[alt_path.index(tool)] = alt
alternatives.append(alt_path)
# 2. 顺序调整路径(如果顺序不重要)
if len(main_path) > 1:
for perm in itertools.permutations(main_path):
if list(perm) != main_path:
alternatives.append(list(perm))
return alternatives[:5] # 返回前5个替代路径第5层:修复层(Repair)
python
class AutoRepairMechanisms:
"""自动修复机制"""
def __init__(self, llm_client):
self.llm = llm_client
self.repair_history = []
def repair_invalid_response(self,
invalid_response: str,
expected_format: str) -> str:
"""修复无效的LLM响应"""
repair_prompt = f"""
以下LLM响应不符合预期格式。请修复它。
预期格式:{expected_format}
无效响应:{invalid_response}
问题分析:
1. 格式错误(如缺少字段、错误分隔符)
2. 内容错误(如逻辑矛盾、事实错误)
3. 结构错误(如嵌套错误、类型错误)
修复后的响应:
"""
try:
repaired = self.llm.call(repair_prompt)
self.repair_history.append({
"original": invalid_response,
"repaired": repaired,
"timestamp": datetime.now()
})
return repaired
except:
# 如果修复失败,返回默认结构
return self._create_default_response(expected_format)
def recover_from_deadlock(self,
agent_state: Dict,
execution_history: List) -> Dict:
"""从死锁状态恢复"""
# 策略1:回退到最后一个稳定状态
stable_states = [
state for state in execution_history
if state.get("status") == "success"
]
if stable_states:
last_stable = stable_states[-1]
logger.info(f"回退到稳定状态: {last_stable.get('step_id')}")
return {
**agent_state,
"current_step": last_stable.get("step_id"),
"context": last_stable.get("context", {}),
"recovery_action": "rollback_to_stable"
}
# 策略2:重置并重新开始
logger.warning("无稳定状态可用,执行软重置")
return {
**agent_state,
"current_step": 0,
"context": {},
"execution_path": self._find_simpler_path(agent_state["goal"]),
"recovery_action": "soft_reset"
}
def fix_data_inconsistency(self, data_sources: List[Dict]) -> Dict:
"""修复数据不一致问题"""
# 策略1:多数投票
values = [source.get("value") for source in data_sources]
if values:
value_counts = Counter(values)
most_common = value_counts.most_common(1)
if most_common[0][1] > len(values) / 2:
return {"value": most_common[0][0], "confidence": 0.8}
# 策略2:加权平均(对于数值)
numeric_values = []
weights = []
for source in data_sources:
try:
val = float(source.get("value", 0))
numeric_values.append(val)
weights.append(source.get("confidence", 0.5))
except:
continue
if numeric_values:
weighted_avg = np.average(numeric_values, weights=weights)
return {"value": weighted_avg, "confidence": 0.7}
# 策略3:让LLM仲裁
arbitration_prompt = f"""
以下数据源提供的信息不一致,请分析并给出最可能正确的值:
数据源:
{json.dumps(data_sources, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)}
请综合考虑数据源的可信度、时间戳和内在逻辑。
输出格式:{{"value": "最可能的值", "reasoning": "推理过程"}}
"""
return self.llm.call(arbitration_prompt)