文章目录
- [1. inline hook 机器码](#1. inline hook 机器码)
-
- [1.1 什么是Frida中的inline hook](#1.1 什么是Frida中的inline hook)
- [1.2 inline hook的检测原理](#1.2 inline hook的检测原理)
- [2. 检测源码(基于上一章的扩展)](#2. 检测源码(基于上一章的扩展))
-
- [2.1 核心检测函数](#2.1 核心检测函数)
- [3. Hook 思路(绕过inline hook检测)](#3. Hook 思路(绕过inline hook检测))
- [4. 本章总结](#4. 本章总结)
-
- [4.1 inline hook检测与绕过核心](#4.1 inline hook检测与绕过核心)
- [4.2 动态调整](#4.2 动态调整)
⚠️本博文所涉安全渗透测试技术、方法及案例,仅用于网络安全技术研究与合规性交流,旨在提升读者的安全防护意识与技术能力。任何个人或组织在使用相关内容前,必须获得目标网络 / 系统所有者的明确且书面授权,严禁用于未经授权的网络探测、漏洞利用、数据获取等非法行为。
1. inline hook 机器码
1.1 什么是Frida中的inline hook
在Frida的动态调试中,inline hook是Native层钩子(如Interceptor.attach)实现的核心机制。其本质是通过修改目标函数的开头指令,将函数的执行流程劫持到Frida的钩子逻辑中,具体过程如下:
- 指令替换 :Frida会在目标函数(如系统库
libc.so中的strstr、strcmp)的开头,替换前N字节指令为跳转指令; - 执行流劫持 :当目标函数被调用时,跳转指令会将执行流程导向Frida的钩子函数(
onEnter/onLeave),从而实现参数监控、修改或逻辑篡改; - 原函数恢复:钩子函数执行完成后,Frida通过"跳板(Trampoline)"恢复被替换的原始指令,并跳回原函数继续执行剩余逻辑。
1.2 inline hook的检测原理
由于Frida的inline hook必然会篡改函数开头的指令,因此检测逻辑的核心是:检查目标函数开头的机器码是否包含异常跳转指令 。
当应用检测到函数开头存在Frida特征的跳转指令时,即可判定该函数被inline hook,进而推断可能存在Frida注入。
2. 检测源码(基于上一章的扩展)
本章节使用的示例 APK、相关源码如下:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1dpbagjFPJVouisb2_AW3eg?pwd=b4e6
提取码: b4e6
上一章的检测逻辑主要通过扫描进程线程的status文件,识别与Frida相关的线程名(如frida、gmain等)。本章在此基础上,新增了对inline hook的检测,核心代码逻辑如下:
2.1 核心检测函数
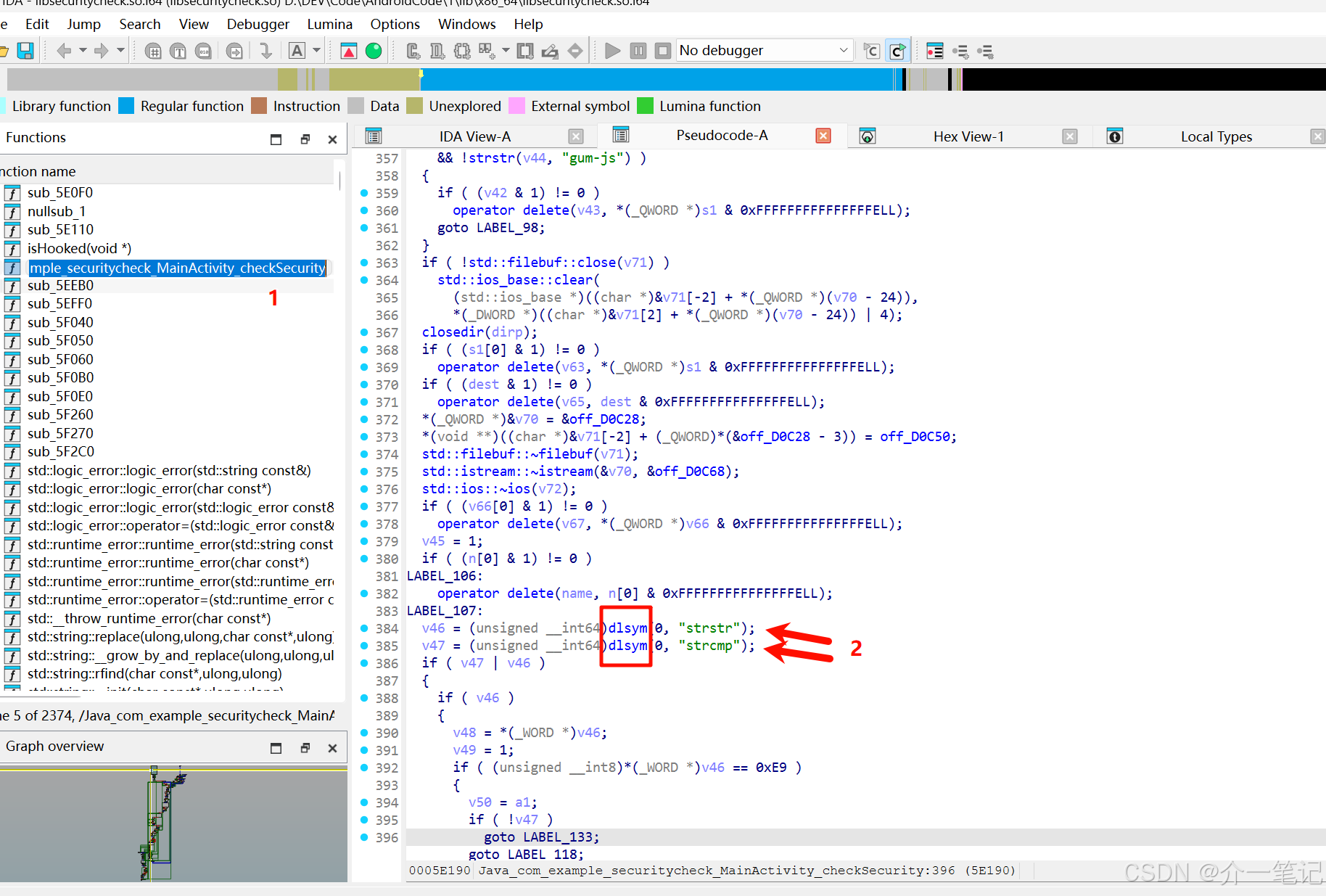
isHooked函数 :根据架构(ARM64/x86_64)检查函数开头的机器码是否包含Frida特征的跳转指令(如ARM64的0x14000000、0x94000000等跳转指令掩码,x86_64的0xE9(jmp)、0xFF(间接跳转)等);checkInlineHooks函数 :通过dlsym获取strstr和strcmp(高频被Hook的系统函数)的地址,调用isHooked检查这两个函数是否被篡改;checkFrida函数 :保留上一章的线程名检测逻辑,通过扫描/proc/[pid]/task/[tid]/status中的Name字段识别Frida相关线程;Java_com_example_securitycheck_MainActivity_checkSecurity函数 :综合checkFrida(线程名检测)和checkInlineHooks(inline hook检测)的结果,返回最终检测结论。
c++
#include <jni.h>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <dlfcn.h>
#if defined(__aarch64__)
bool isHooked(void* func) {
if (!func) {
return false;
}
uint32_t* instructions = (uint32_t*)func;
uint32_t instruction = *instructions;
if ((instruction & 0xFC000000) == 0x14000000) {
return true;
}
if ((instruction & 0xFC000000) == 0x94000000) {
return true;
}
if ((instruction & 0xFFFF001F) == 0xD61F0000) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
#elif defined(__x86_64__)
bool isHooked(void* func) {
if (!func) {
return false;
}
unsigned char* bytes = (unsigned char*)func;
unsigned char buffer[2] = {0};
memcpy(buffer, bytes, sizeof(buffer));
if (buffer[0] == 0xE9) {
return true;
}
if (buffer[0] == 0xFF) {
unsigned char modrm = buffer[1];
if (((modrm >> 3) & 0x7) == 0x4) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
#else
// 默认实现,防止未定义错误
bool isHooked(void* func) {
(void)func;
return false;
}
#endif
static bool checkInlineHooks() {
void* strstr_addr = dlsym(RTLD_DEFAULT, "strstr");
void* strcmp_addr = dlsym(RTLD_DEFAULT, "strcmp");
if (!strstr_addr && !strcmp_addr) {
return false;
}
bool strstr_hooked = strstr_addr != nullptr && isHooked(strstr_addr);
bool strcmp_hooked = strcmp_addr != nullptr && isHooked(strcmp_addr);
return strstr_hooked || strcmp_hooked;
}
static bool checkFrida() {
DIR* taskDir;
struct dirent* entry;
// 获取当前进程ID并构建task目录路径
pid_t pid = getpid();
std::string taskPath = "/proc/" + std::to_string(pid) + "/task";
taskDir = opendir(taskPath.c_str());
if (!taskDir) {
return false;
}
// 遍历task目录中的每个线程
while ((entry = readdir(taskDir)) != nullptr) {
// 跳过.和..目录项
if (strcmp(entry->d_name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(entry->d_name, "..") == 0) {
continue;
}
// 构建线程status文件路径
std::string statusPath = taskPath + "/" + std::string(entry->d_name) + "/status";
std::ifstream statusFile(statusPath);
if (statusFile.is_open()) {
std::string line;
// 读取status文件中的每一行,查找Name字段
while (std::getline(statusFile, line)) {
if (line.find("Name:") != std::string::npos) {
// 提取Name字段的值
size_t colonPos = line.find(':');
if (colonPos != std::string::npos) {
std::string name = line.substr(colonPos + 1);
// 去除前导空格
name.erase(0, name.find_first_not_of(" \t"));
// 使用strcmp进行精确匹配
if (strcmp(name.c_str(), "gmain") == 0 ||
strcmp(name.c_str(), "gdbus") == 0 ||
strcmp(name.c_str(), "frida") == 0 ||
strcmp(name.c_str(), "gum-js-loop") == 0) {
statusFile.close();
closedir(taskDir);
return true;
}
// 使用strstr进行子字符串检测
if (strstr(name.c_str(), "gmain") != nullptr ||
strstr(name.c_str(), "gdbus") != nullptr ||
strstr(name.c_str(), "frida") != nullptr ||
strstr(name.c_str(), "gum-js") != nullptr) {
statusFile.close();
closedir(taskDir);
return true;
}
}
break; // 只需要检查Name行
}
}
statusFile.close();
}
}
closedir(taskDir);
return false;
}
extern "C" JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL
Java_com_example_securitycheck_MainActivity_checkSecurity(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz) {
bool fridaDetected = checkFrida();
bool inlineHookDetected = checkInlineHooks();
if (fridaDetected && inlineHookDetected) {
return env->NewStringUTF("检测到status、inline hook");
} else if (fridaDetected) {
return env->NewStringUTF("检测到status");
} else if (inlineHookDetected) {
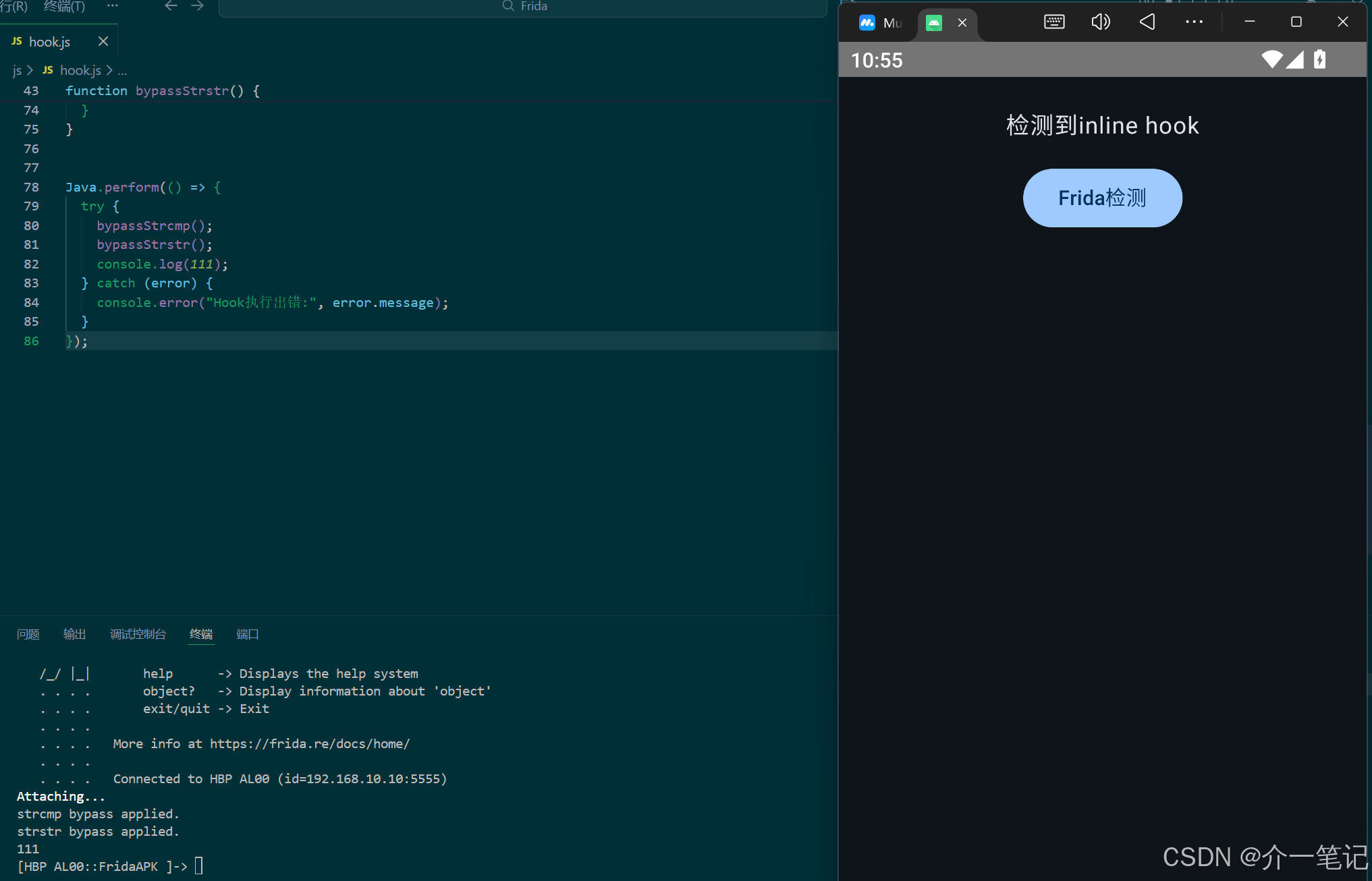
return env->NewStringUTF("检测到inline hook");
} else {
return env->NewStringUTF("未检测到frida");
}
}若仅使用上一章的线程名绕过脚本,会被本章新增的inline hook检测拦截,效果如下:
3. Hook 思路(绕过inline hook检测)
3.1 分析基础:为何需要Hook dlsym?
通过IDA反编译后对比源码分析可知(IDA的伪代码可以使用AI辅助分析),应用通过dlsym(RTLD_DEFAULT, "strstr")和dlsym(RTLD_DEFAULT, "strcmp")获取函数地址,再对地址处的机器码进行校验。因此,绕过的核心是干预dlsym返回的地址或该地址对应的机器码,使检测逻辑判断为"未被Hook"。
3.2 方法一:动态恢复原始机器码
核心逻辑
- 预先保存原始机器码 :在对
strstr和strcmp应用Hook前,保存这两个函数开头的原始字节(根据架构保存8字节或16字节); - 正常Hook目标函数 :对
strstr和strcmp应用常规Hook(如过滤Frida相关关键字); - 拦截dlsym调用并恢复 :当
dlsym被调用以获取strstr或strcmp地址时,立即将预先保存的原始机器码写回函数开头,使检测逻辑读取到未被篡改的指令;检测完成后,Frida的钩子仍能正常工作(因Frida会自动维护钩子状态)。
实现脚本
javascript
const FRIDA_KEYWORDS = ['frida', 'gmain', 'gdbus', 'gum-js-loop'];
const STRSTR_KEYWORDS = ['frida', 'gum-js', 'gmain', 'gdbus', 'tmp'];
// 存储原始函数机器码
const originalCode = new Map();
function saveOriginalCode() {
try {
const libc = Module.load('libc.so');
if (!libc) {
console.log('[!] 未找到 libc.so');
return;
}
const byteCount = Process.arch === 'arm64' ? 8 : 16;
console.log(`[+] 当前架构${Process.arch},保存${byteCount}字节机器码`);
const strstrAddr = libc.getExportByName('strstr');
const strcmpAddr = libc.getExportByName('strcmp');
// 保存原始机器码
if (strstrAddr) {
originalCode.set('strstr', {
address: strstrAddr,
bytes: strstrAddr.readByteArray(byteCount)
});
console.log('[+] 保存strstr原始机器码');
}
if (strcmpAddr) {
originalCode.set('strcmp', {
address: strcmpAddr,
bytes: strcmpAddr.readByteArray(byteCount)
});
console.log('[+] 保存strcmp原始机器码');
}
} catch (e) {
console.log('[!] 保存原始代码出错: ' + e.message);
}
}
// hook strstr/strcmp
function hookStr() {
try {
const libc = Module.load('libc.so');
if (!libc) return;
const strstrAddr = libc.getExportByName('strstr');
const strcmpAddr = libc.getExportByName('strcmp');
if (strstrAddr) {
Interceptor.attach(strstrAddr, {
onEnter: function (args) {
this.haystack = args[0].readCString();
this.needle = args[1].readCString();
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
if (STRSTR_KEYWORDS.includes(this.needle)) {
if (retval !== NULL) {
retval.replace(NULL);
}
}
}
});
console.log('strstr hook applied.');
}
if (strcmpAddr) {
Interceptor.attach(strcmpAddr, {
onEnter: function (args) {
this.str1 = args[0].readCString();
this.str2 = args[1].readCString();
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
if (FRIDA_KEYWORDS.includes(this.str2)) {
if (this.str1?.includes(this.str2)) {
retval.replace(ptr(1));
}
}
}
});
console.log('strcmp hook applied.');
}
} catch (e) {
console.log('[!] 应用hook出错: ' + e.message);
}
}
// Hook dlsym函数
function hookDlsym() {
try {
const libc = Module.load('libc.so');
if (!libc) {
console.log('[!] 未找到 libc.so');
return;
}
const dlsymAddr = libc.getExportByName('dlsym');
if (!dlsymAddr) {
console.log('[!] 未找到 dlsym 函数');
return;
}
Interceptor.attach(dlsymAddr, {
onEnter: function (args) {
this.symbolName = args[1].readCString();
console.log(`[+] dlsym 被调用,查找符号: ${this.symbolName}`);
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
// 检查是否在查找我们的目标函数
if (this.symbolName === 'strstr' || this.symbolName === 'strcmp') {
// 使用writeByteArray还原函数原始的机器码
const funcInfo = originalCode.get(this.symbolName);
funcInfo.address.writeByteArray(funcInfo.bytes);
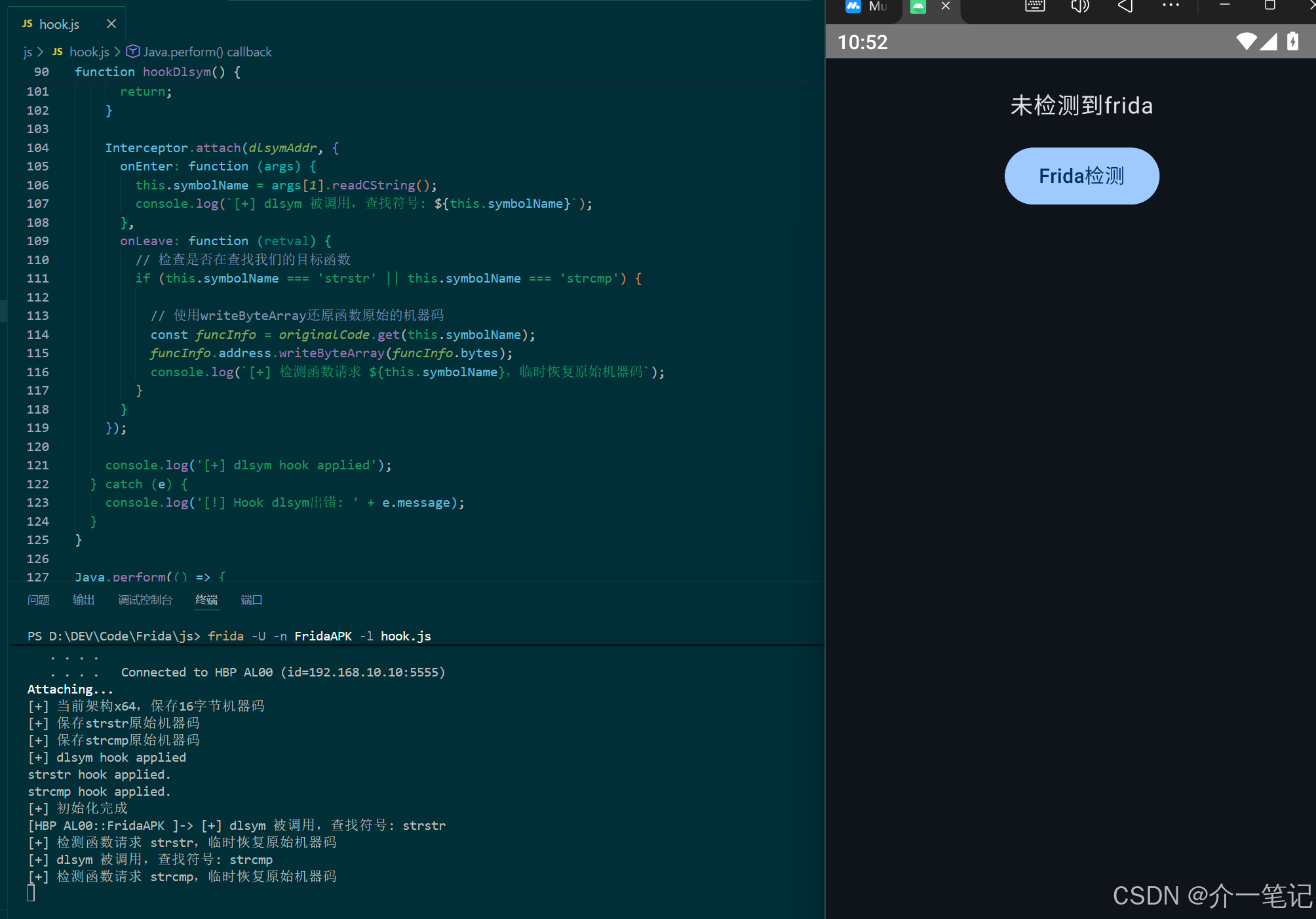
console.log(`[+] 检测函数请求 ${this.symbolName},临时恢复原始机器码`);
}
}
});
console.log('[+] dlsym hook applied');
} catch (e) {
console.log('[!] Hook dlsym出错: ' + e.message);
}
}
Java.perform(() => {
try {
// 保存原始代码
saveOriginalCode();
// Hook dlsym
hookDlsym();
// 初始应用hook
hookStr();
console.log('[+] 初始化完成');
} catch (e) {
console.log('[!] 初始化出错: ' + e.message);
}
});执行效果:成功绕过线程名和inline hook检测。
3.3 方法二:伪造函数地址
核心逻辑
- 保存原始机器码 :同方法一,记录
strstr和strcmp开头的原始字节; - 创建伪造函数:在内存中分配新的可执行区域,将原始机器码复制到该区域,形成与原始函数开头指令一致的"伪造函数";
- 正常Hook目标函数 :对真实的
strstr和strcmp应用常规Hook; - 拦截dlsym调用并返回伪造地址 :当
dlsym被调用以获取strstr或strcmp地址时,不返回真实地址,而是返回伪造函数的地址。由于伪造函数的机器码未被Hook,检测逻辑会判定为"未被篡改"。
实现脚本
javascript
const FRIDA_KEYWORDS = ['frida', 'gmain', 'gdbus', 'gum-js-loop'];
const STRSTR_KEYWORDS = ['frida', 'gum-js', 'gmain', 'gdbus', 'tmp'];
// 存储原始函数地址和伪造函数地址
const originalCode = new Map();
const fakeFunctions = new Map();
let hooksAttached = false;
function saveOriginalCode() {
try {
const libc = Module.load('libc.so');
if (!libc) {
console.log('[!] 未找到 libc.so');
return;
}
const strstrAddr = libc.getExportByName('strstr');
const strcmpAddr = libc.getExportByName('strcmp');
// 保存对应架构的原始字节(ARM64:8字节,X86_64:16字节)
if (strstrAddr) {
originalCode.set('strstr', {
address: strstrAddr,
bytes: strstrAddr.readByteArray(Process.arch === 'arm64' ? 8 : 16)
});
console.log('[+] 保存strstr原始地址');
}
if (strcmpAddr) {
originalCode.set('strcmp', {
address: strcmpAddr,
bytes: strcmpAddr.readByteArray(Process.arch === 'arm64' ? 8 : 16)
});
console.log('[+] 保存strcmp原始地址');
}
} catch (e) {
console.log('[!] 保存原始地址出错: ' + e.message);
}
}
// 创建伪造的函数(复制原始函数地址)
function createFakeFunction(funcName) {
try {
const libc = Module.load('libc.so');
if (!libc) return null;
let originalAddr = null;
if (funcName === 'strstr') {
originalAddr = libc.getExportByName('strstr');
} else if (funcName === 'strcmp') {
originalAddr = libc.getExportByName('strcmp');
}
if (!originalAddr) return null;
// 分配内存来存储伪造函数
const fakeFuncMemory = Memory.alloc(Process.pageSize);
if (!fakeFuncMemory) return null;
// 复制原始函数代码到伪造函数
const funcBytes = originalCode.get(funcName).bytes;
fakeFuncMemory.writeByteArray(funcBytes);
// 设置内存保护为可执行
Memory.protect(fakeFuncMemory, Process.pageSize, 'rwx');
console.log(`[+] 创建伪造的${funcName}地址: ${fakeFuncMemory}`);
return fakeFuncMemory;
} catch (e) {
console.log(`[!] 创建伪造${funcName}地址出错: ` + e.message);
return null;
}
}
// hook strstr/strcmp
function hookStr() {
try {
const libc = Module.load('libc.so');
if (!libc) return;
const strstrAddr = libc.getExportByName('strstr');
const strcmpAddr = libc.getExportByName('strcmp');
if (strstrAddr) {
Interceptor.attach(strstrAddr, {
onEnter: function (args) {
this.haystack = args[0].readCString();
this.needle = args[1].readCString();
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
if (STRSTR_KEYWORDS.includes(this.needle)) {
if (retval !== NULL) {
retval.replace(NULL);
}
}
}
});
console.log('strstr hook finished.');
}
if (strcmpAddr) {
Interceptor.attach(strcmpAddr, {
onEnter: function (args) {
this.str1 = args[0].readCString();
this.str2 = args[1].readCString();
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
if (FRIDA_KEYWORDS.includes(this.str2)) {
if (this.str1?.includes(this.str2)) {
retval.replace(ptr(1));
}
}
}
});
console.log('strcmp hook finished.');
}
hooksAttached = true;
} catch (e) {
console.log('[!] hook str 出错: ' + e.message);
}
}
// Hook dlsym函数
function hookDlsym() {
try {
const libc = Module.load('libc.so');
if (!libc) {
console.log('[!] 未找到 libc.so');
return;
}
const dlsymAddr = libc.getExportByName('dlsym');
if (!dlsymAddr) {
console.log('[!] 未找到 dlsym 函数');
return;
}
Interceptor.attach(dlsymAddr, {
onEnter: function (args) {
// args[0] = handle, args[1] = symbol name
this.symbolName = args[1].readCString();
console.log(`[+] dlsym 被调用,查找符号: ${this.symbolName}`);
},
onLeave: function (retval) {
// 检查是否在查找我们的目标函数
if (this.symbolName === 'strstr' || this.symbolName === 'strcmp') {
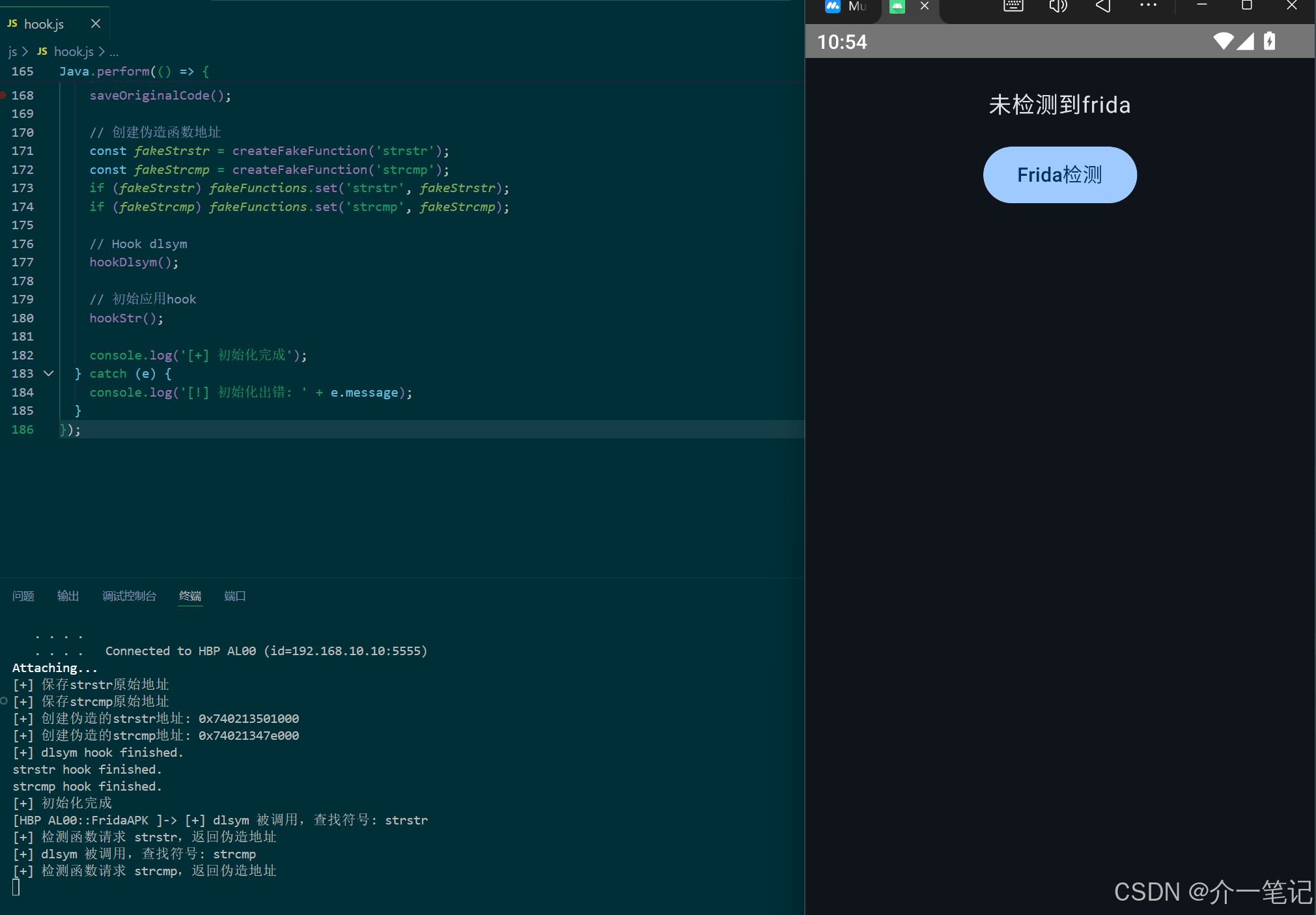
console.log(`[+] 检测函数请求 ${this.symbolName},返回伪造地址`);
// 返回伪造函数地址
if (fakeFunctions.has(this.symbolName)) {
retval.replace(fakeFunctions.get(this.symbolName));
}
}
}
});
console.log('[+] dlsym hook finished.');
} catch (e) {
console.log('[!] Hook dlsym出错: ' + e.message);
}
}
Java.perform(() => {
try {
// 保存函数原始地址
saveOriginalCode();
// 创建伪造函数地址
const fakeStrstr = createFakeFunction('strstr');
const fakeStrcmp = createFakeFunction('strcmp');
if (fakeStrstr) fakeFunctions.set('strstr', fakeStrstr);
if (fakeStrcmp) fakeFunctions.set('strcmp', fakeStrcmp);
// Hook dlsym
hookDlsym();
// 初始应用hook
hookStr();
console.log('[+] 初始化完成');
} catch (e) {
console.log('[!] 初始化出错: ' + e.message);
}
});执行效果:同样可绕过inline hook检测。
3.4 两种方法的核心区别
| 维度 | 方法一(动态恢复原始机器码) | 方法二(伪造函数地址) |
|---|---|---|
| 地址真实性 | 使用函数真实地址,临时恢复原始机器码 | 使用全新的伪造地址,与真实地址无关 |
| 适用场景 | 检测逻辑依赖函数真实地址(如后续调用需真实函数) | 检测逻辑仅校验地址处的机器码,不依赖后续函数调用 |
| 实现复杂度 | 较低(仅需保存和恢复字节) | 较高(需分配可执行内存并复制指令) |
4. 本章总结
4.1 inline hook检测与绕过核心
- 检测方式 :通过检查函数开头的机器码是否包含Frida特征的跳转指令,判断函数是否被
inline hook; - 绕过思路:干预检测逻辑获取的函数地址或地址对应的机器码,使其看到"未被Hook"的状态。具体可通过动态恢复原始机器码(临时还原真实地址的指令)或提供伪造函数地址(返回未被篡改的指令副本)实现。
4.2 动态调整
实际场景中,应用的检测逻辑可能更复杂(如检测更多函数、校验完整指令而非仅开头等)。因此,需根据具体检测手段灵活调整绕过策略:
- 若检测函数范围扩大(如新增
memcpy、ptrace),需同步扩展Hook和恢复/伪造的目标; - 若检测逻辑不仅校验
dlsym返回的地址,还直接读取函数内存(如通过固定地址),需额外Hook内存读取函数(如memcpy)以返回原始指令,但是总体思路是一模一样的; - 避免僵化使用脚本,需结合逆向分析(如IDA反编译)理解检测逻辑的细节,针对性设计绕过方案。