文章目录
问题引入
在SpringBoot自动配置原理我们介绍了SpringBoot怎么自动加载配置类。
自动配置,通常需要读取配置文件,SpringBoot有没有提供什么便捷的方法来获取配置吗?
答案是有的,SpringBoot提供了@ConfigurationProperties注解。
可以把@ConfigurationProperties看做是对@Value的增强,可以处理很多复杂的配置,支持复杂类型和全套。
例如,Spring Gateway的路由配置这种比较复杂的配置。
理解属性自动配置,就不用遇到这类问题我们就能轻松搞定。
对于,一些复杂配置,我们也能快速通过源码来看怎么配置。
使用模式
定制属性类,通过前缀来避免混淆,也容易分组。
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mybatis")
public class MybatisProperties {
private String configLocation;
private String[] mapperLocations;
}还有我们常用的spring.datasource:
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware, InitializingBean {
}在自动配置类中导入配置属性类:
java
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class)
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
private final MybatisProperties properties;
} @ConfigurationProperties对复杂类型的支持
完整示例
先来看完整示例,后面再单独介绍。
配置文件application.yaml:
yaml
config:
color: RED
list:
- "a"
- "a"
- "b"
set:
- "a"
- "b"
- "b"
map:
a: 1
b: 2
c: 3
birthday: 2050-01-01
nest:
name: "nest"
age: 20
custom-list:
- Path=/api/normal/**
- Header=Authorization=Bearer
complex-nest:
- name: "c1"
nodes:
- name: "node-1"
port: 8080
host: "192.168.12.10"
- name: "node-2"
port: 8081
host: "192.168.12.11"
- name: "c2"
nodes:
- name: "node-2"
port: 8080
host: "192.168.10.11"
- name: "node-2"
port: 8081
host: "192.168.10.12"配置类:
java
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class CustomProperties {
private Color color;
private List<String> list;
private Set<String> set;
private Map<String, Integer> map;
private LocalDate birthday;
private Nest nest;
private List<NameValue> customList;
private List<ComplexNest> complexNest;
public static enum Color {
RED, BLUE
}
@Data
public static class Nest {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Data
public static class Node {
private String name;
private Integer port;
private String host;
}
@Data
public static class ComplexNest {
private String name;
private List<Node> nodes;
}
@Data
public static class NameValue{
private String name;
private String value;
}
}枚举
yaml
config:
color: RED这类为了方便看,枚举定义成了内部类,不是必须为内部类,通常是定义在外部。
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class CustomProperties {
private Color color;
public static enum Color {
RED, BLUE
}
}list set
list set配置中用数组就可以:
yaml
config:
list:
- "a"
- "a"
- "b"
set:
- "a"
- "b"
- "b"会自动处理为对应的类型:
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class CustomProperties {
private List<String> list;
private Set<String> set;
}map
注意,map在yaml配置中不是数组,而是对象,使用的是:没有-
yaml
config:
map:
a: 1
b: 2
c: 3
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class CustomProperties {
private Map<String, Integer> map;
}嵌套类型
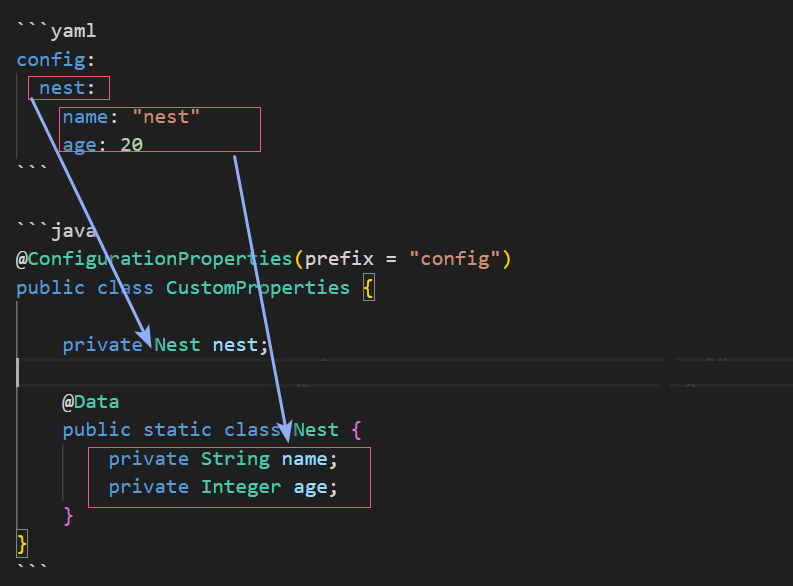
对象可以嵌套,例如Spring发现nest是一个对象,就会自动用nest的下一级属性去装配Nest对象的属性
yaml
config:
nest:
name: "nest"
age: 20
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class CustomProperties {
private Nest nest;
@Data
public static class Nest {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
}
复杂嵌套
对于复杂的嵌套,清楚它的层级就可以,每个层级的属性对应就没有问题。
yaml
config:
complex-nest:
- name: "c1"
nodes:
- name: "node-1"
port: 8080
host: "192.168.12.10"
- name: "node-2"
port: 8081
host: "192.168.12.11"
- name: "c2"
nodes:
- name: "node-2"
port: 8080
host: "192.168.10.11"
- name: "node-2"
port: 8081
host: "192.168.10.12"complexNest是一个List,每个元素都是ComplexNest
每一个ComplexNest都有一个name和一个Node List
每一个Node层级又有一个name,port,host属性
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class CustomProperties {
private List<ComplexNest> complexNest;
@Data
public static class Node {
private String name;
private Integer port;
private String host;
}
@Data
public static class ComplexNest {
private String name;
private List<Node> nodes;
}
}@ConfigurationProperties原理
@ConfigurationProperties处理逻辑非常复杂,这里简单说一下关键点:
@ConfigurationProperties的核心处理逻辑在ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor中。
ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor有Binder(org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.Binder),它会可以做格式化话和数据类型转换。
其中数据转换主要有下面几个类型:
- Converter<S,T>
- ConverterFactory<S,R>
- GenericConverter
- PropertyEditor
实际上是通过多个ConversionService统一管理:
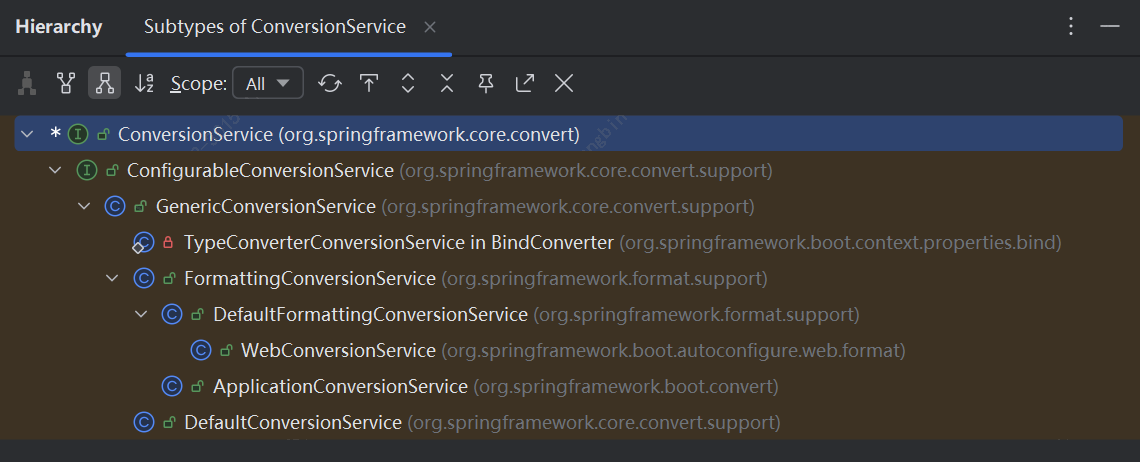
我们能把配置文件中一个简单的String转换为对应的类型,就是类型转换系统的功劳。
例如🎂 2050-01-01(String)-->private LocalDate birthday;
执行String到LocalDate转换的转换器为:org.springframework.format.support.FormattingConversionService.ParserConverter
自定义类型转换器
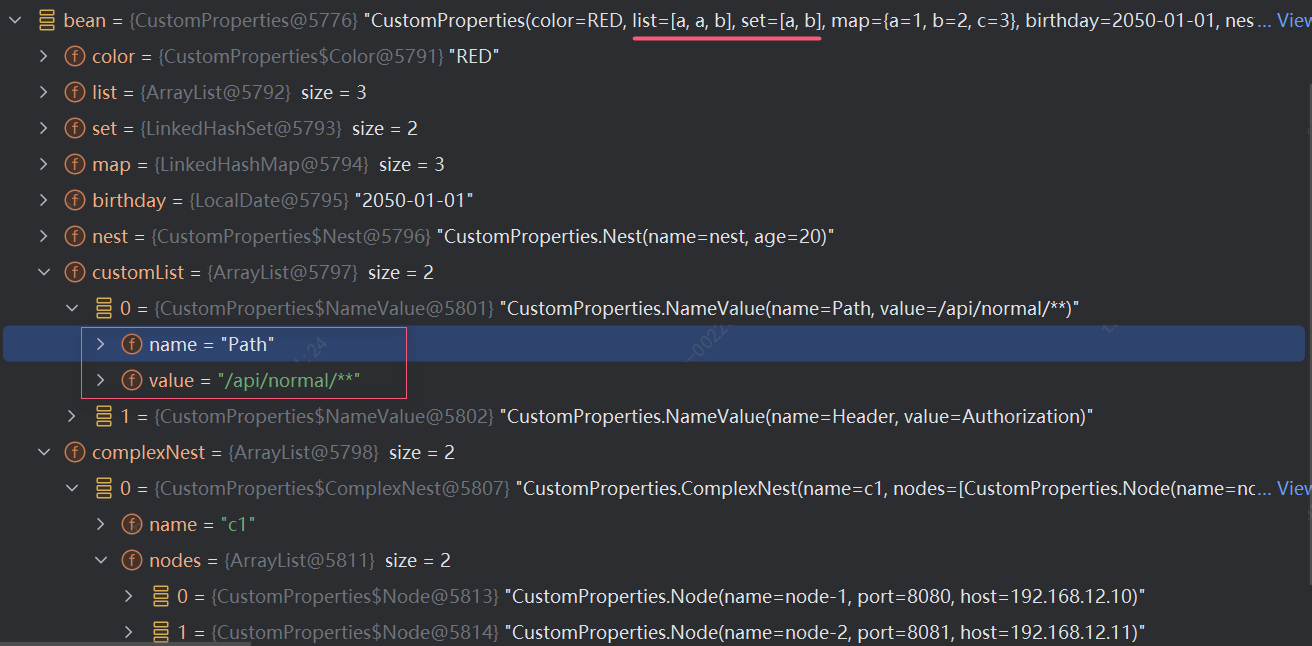
如果有朋友尝试过上面的我们的测试代码,大概率会得到一个如下异常:
txt
Failed to bind properties under 'config.custom-list[0]' to vip.oschool.property.CustomProperties$NameValue:
Reason: org.springframework.core.convert.ConverterNotFoundException: No converter found capable of converting from type [java.lang.String] to type [vip.oschool.property.CustomProperties$NameValue]为什么呢?
因为Spring默认带有的转换器,不能把Path=/api/normal/**这样的String转换为NameValue类型。
yaml
config:
custom-list:
- Path=/api/normal/**
- Header=Authorization=Bearer
java
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "config")
public class CustomProperties {
private List<NameValue> customList;
@Data
public static class NameValue{
private String name;
private String value;
}
}怎么办呢?
我们可以自定义类型转换器。
这里是一个简单的转换,我们实现Converter就可以:
java
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationPropertiesBinding;
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@ConfigurationPropertiesBinding
public class StringToNameValueConverter implements Converter<String, CustomProperties.NameValue> {
@Override
public CustomProperties.NameValue convert(String source) {
String[] split = source.split("=");
CustomProperties.NameValue nameValue = new CustomProperties.NameValue();
nameValue.setName(split[0]);
nameValue.setValue(split[1]);
return nameValue;
}
}@ConfigurationPropertiesBinding是说明这个转换器就是用于属性绑定的转换器。
注意,如果只有@ConfigurationProperties,需要EnableConfigurationProperties注解,否则无法生效。
java
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigurationProperties({CustomProperties.class, DataProperties.class})
public class BaseServiceApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(BaseServiceApp.class, args);
}
}属性配置实践
查找配置项
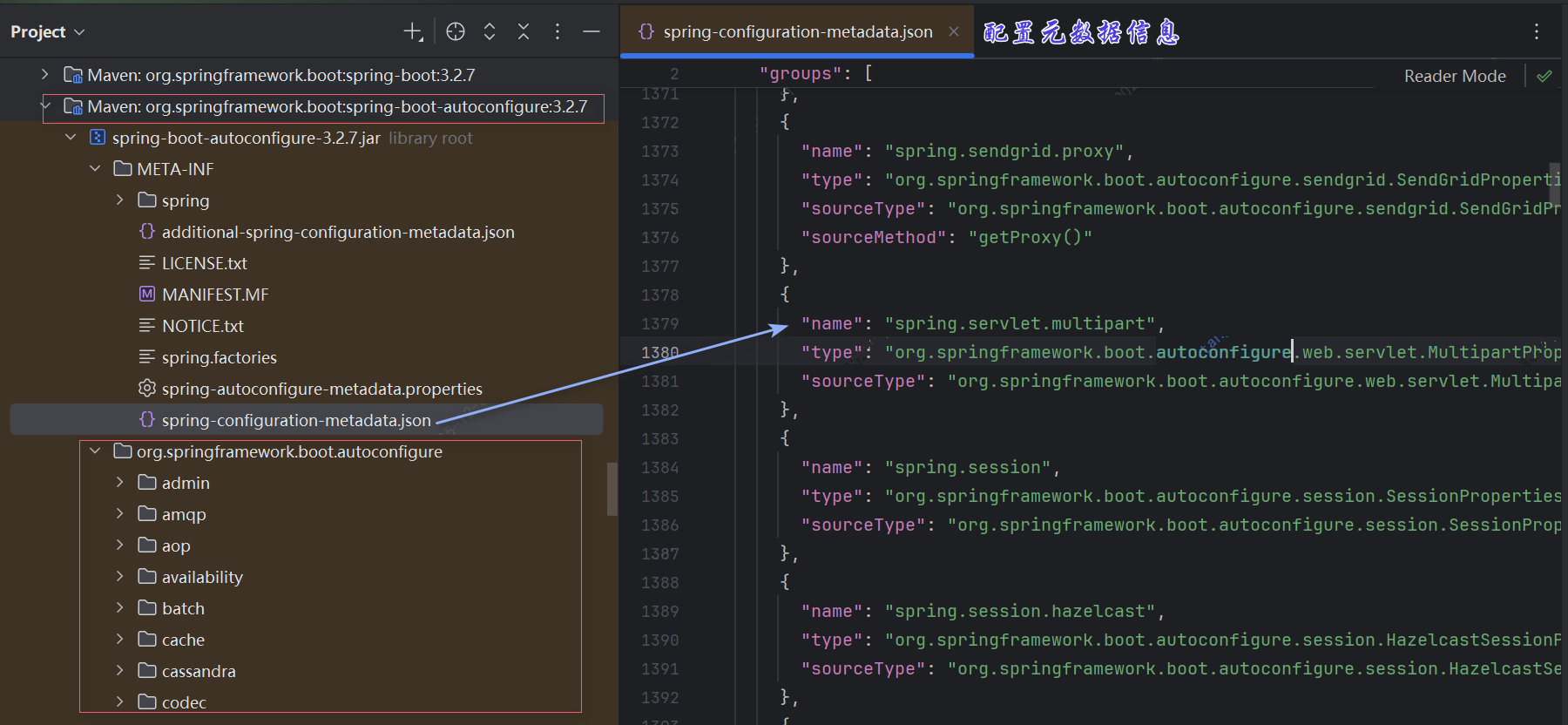
因为属性配置非常多,很多时候,我们根本记不完,怎么办呢?
只要我们自动自动配置原理,结合本会的属性自动配置,我们就能轻松的查找配置项。
不清楚自动配置原理的,可以看看:SpringBoot自动配置原理
找@EnableConfigurationProperties、@ConfigurationProperties
另外通常会有一个自动配置的项目:autoconfigure,去搜索对应的配置项,就能找到对应的配置类。
问题排查
有些自定义的转换,我们不知道规则,试了出错了,怎么排查错误呢?
例如:
yaml
spring:
servlet:
multipart:
max-file-size: 10M
max-request-size: 30M
txt
Failed to bind properties under 'spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size' to org.springframework.util.unit.DataSize:
Property: spring.servlet.multipart.max-file-size
Value: "10M"
Origin: class path resource [application.yaml] - 45:22
Reason: failed to convert java.lang.String to org.springframework.util.unit.DataSize (caused by java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Unknown data unit suffix 'M')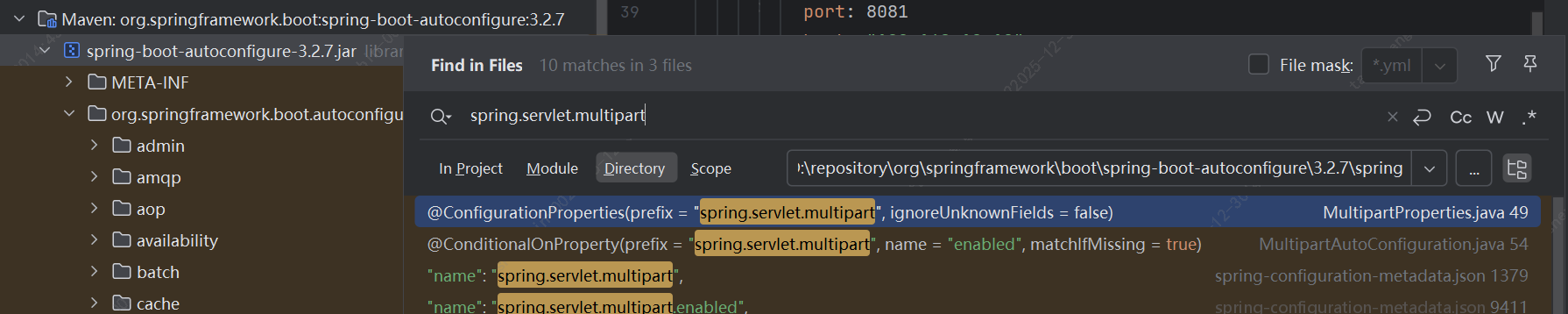
找到对应属性类型:
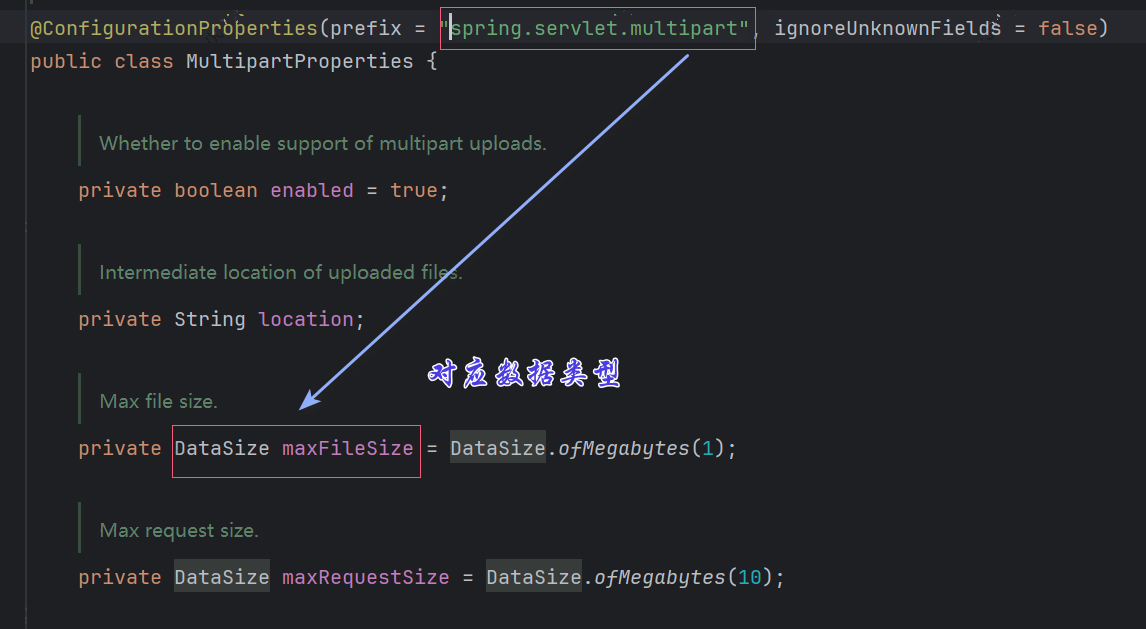
例如,上面,我们知道了是DataSize类型,那么我们就去找对应的转换器
去找Converter<S,T>、GenericConverter等的具体实现类。
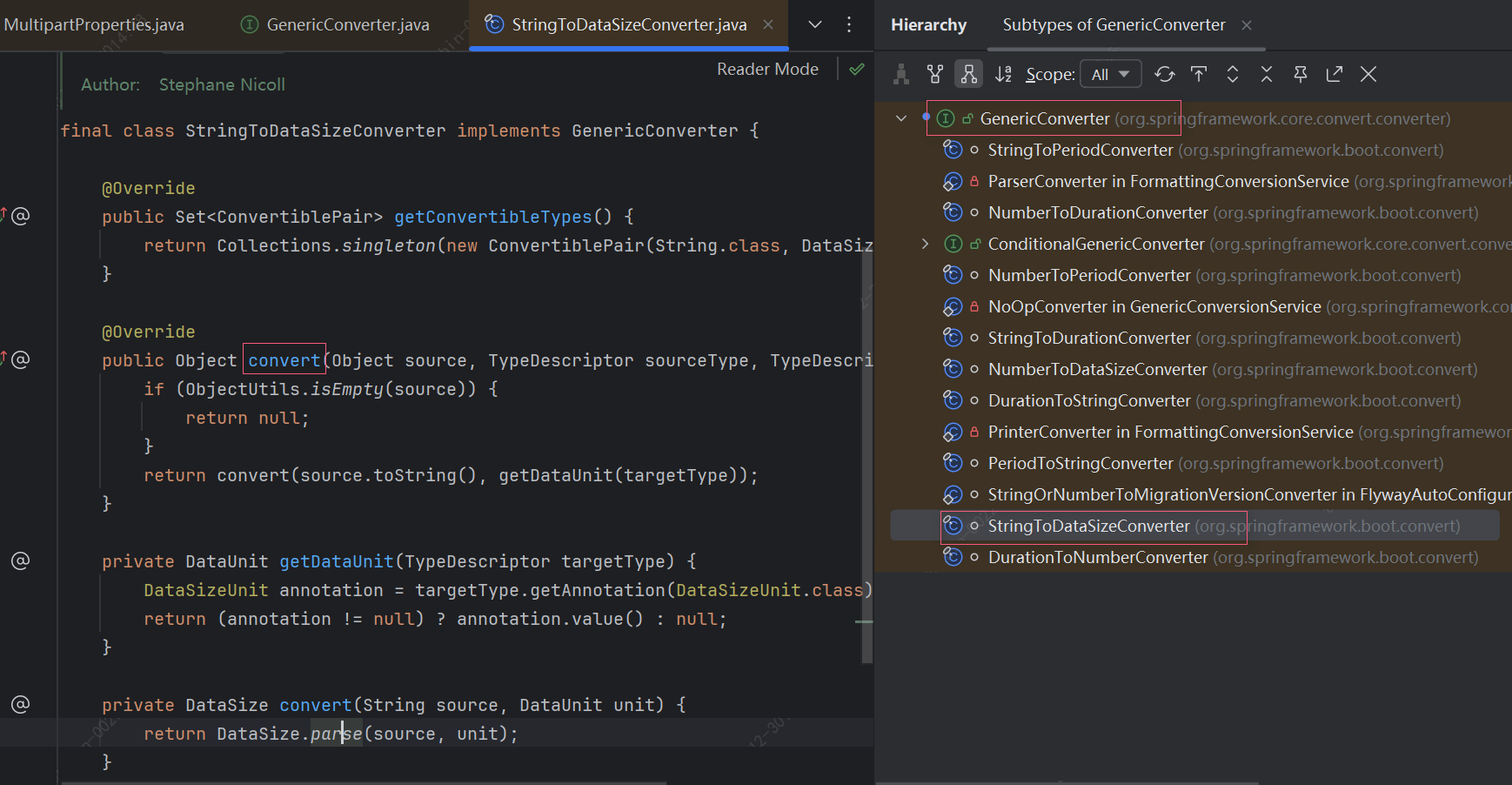
看到具体的逻辑org.springframework.util.unit.DataSize#parse(java.lang.CharSequence, org.springframework.util.unit.DataUnit)我们都不用看代码,看一下注释就知道,原来不支持M,只支持MB。
这样,我们就学到了,以后如果我们自己需要数据大小限制就可以不使用long类型,直接使用DataSize类型,这样配置就非常灵活了,Spring直接就帮我们支持了。