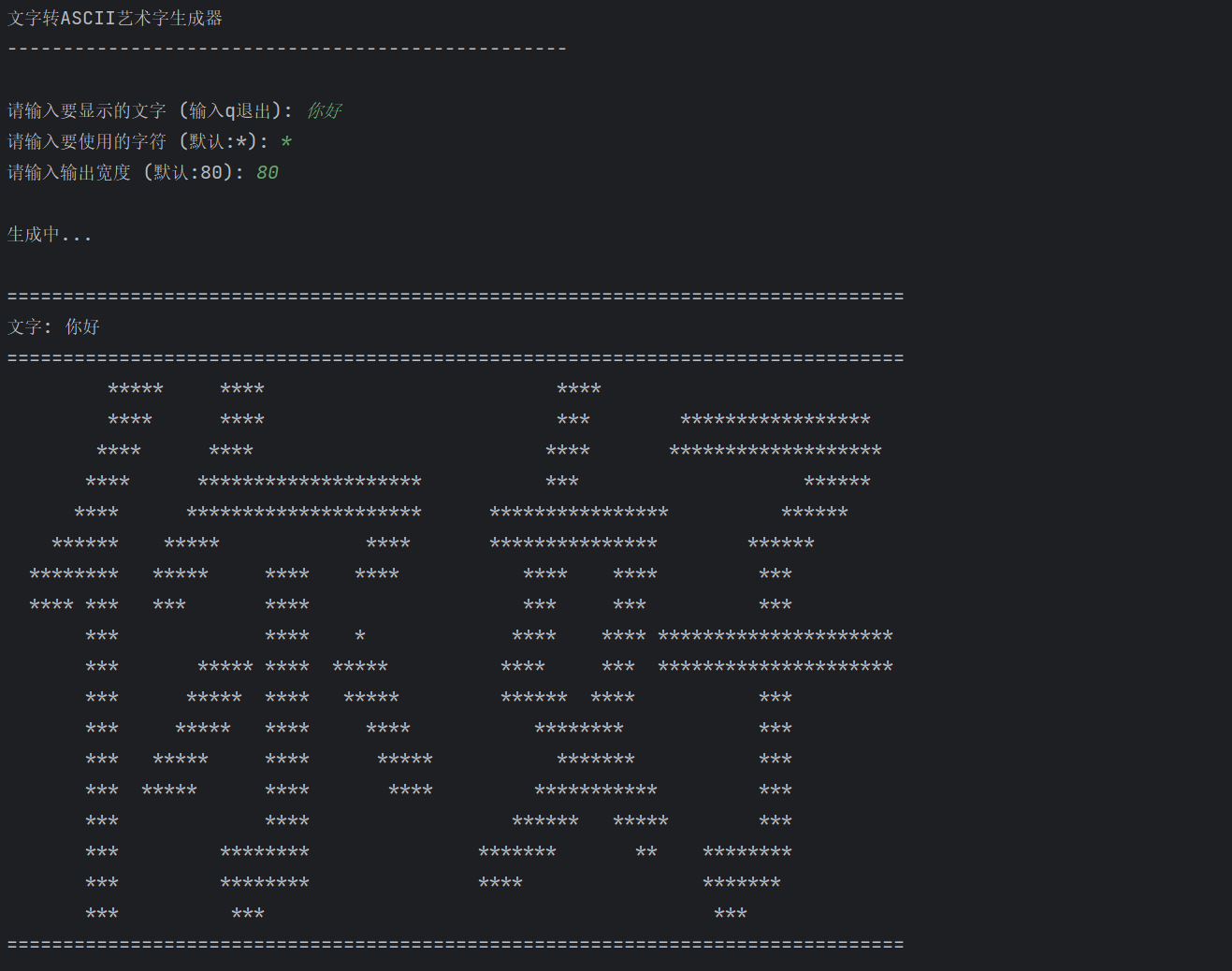
1. 简介
作为一个程序员,经常看到console里面有很多使用各种字符构建的文字,一直以为是自己拼出来的,但是这样老麻烦了,所以就想着用python的图像处理看看能不能实现这样的功能。
2. 具体依赖
- Python 3.x
- PIL (Pillow) - 图像处理
- NumPy - 数组操作
- 跨平台字体检测
3. 核心实现
3.1跨平台字体检测
python
def get_system_font():
"""获取系统可用的字体"""
font_paths = []
# Windows 字体路径
if os.name == 'nt':
font_dirs = [
os.path.join(os.environ['WINDIR'], 'Fonts'),
os.path.join(os.environ['SYSTEMROOT'], 'Fonts'),
]
for font_dir in font_dirs:
if os.path.exists(font_dir):
# 中文常用字体
chinese_fonts = [
'simhei.ttf', # 黑体
'msyh.ttc', # 微软雅黑
'simsun.ttc', # 宋体
'msjh.ttc', # 微软正黑体
'kaiu.ttf', # 标楷体
]
for font in chinese_fonts:
font_path = os.path.join(font_dir, font)
if os.path.exists(font_path):
return font_path3.2 文字到ASCII转换算法
python
def text_to_ascii_simple(text, char='*', width=60):
"""
简化的版本,兼容性更好
"""
# 创建图片
font_size = 80
img_width = font_size * len(text) + 100
img_height = font_size + 50
img = Image.new('RGB', (img_width, img_height), 'white')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# 获取字体
font_path = get_system_font()
try:
if font_path:
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
else:
font = ImageFont.load_default()
except:
font = ImageFont.load_default()3.3 字体检测机制
- Windows系统:检测C:\Windows\Fonts目录下的中文字体
- macOS系统:检测/System/Library/Fonts等目录
- Linux系统:检测/usr/share/fonts等目录
python
# Linux 字体路径
font_dirs = [
'/usr/share/fonts',
'/usr/local/share/fonts',
os.path.expanduser('~/.fonts'),
]3.4 图像处理
- 创建图像:根据文字长度创建适当大小的图像
- 文字绘制:使用检测到的字体绘制文字
- 灰度转换:将彩色图像转换为灰度图像
- 字符映射:根据灰度值映射为ASCII字符
python
# 转换为灰度
img_gray = img.convert('L')
img_array = np.array(img_gray)
# 转换为字符
lines = []
for y in range(new_h):
line = ''.join([' ' if resized.getpixel((x, y)) > 200 else char for x in range(width)])
lines.append(line)3.5 智能裁剪算法
主要是为了将字符转成图片的时候去掉上部和下部的空白
python
# 找到文字边界
non_white_rows = np.where(np.any(arr < 250, axis=1))[0]
non_white_cols = np.where(np.any(arr < 250, axis=0))[0]
if len(non_white_rows) == 0 or len(non_white_cols) == 0:
return [f"无法显示: {text}"]
top, bottom = non_white_rows[0], non_white_rows[-1]
left, right = non_white_cols[0], non_white_cols[-1]4. 完整实现
python
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
import numpy as np
import os
def get_system_font():
"""获取系统可用的字体"""
font_paths = []
# Windows 字体路径
if os.name == 'nt':
font_dirs = [
os.path.join(os.environ['WINDIR'], 'Fonts'),
os.path.join(os.environ['SYSTEMROOT'], 'Fonts'),
]
for font_dir in font_dirs:
if os.path.exists(font_dir):
# 中文常用字体
chinese_fonts = [
'simhei.ttf', # 黑体
'msyh.ttc', # 微软雅黑
'simsun.ttc', # 宋体
'msjh.ttc', # 微软正黑体
'kaiu.ttf', # 标楷体
]
for font in chinese_fonts:
font_path = os.path.join(font_dir, font)
if os.path.exists(font_path):
return font_path
# 如果没找到中文字体,找第一个ttf文件
for file in os.listdir(font_dir):
if file.lower().endswith(('.ttf', '.ttc', '.otf')):
return os.path.join(font_dir, file)
# macOS 字体路径
elif os.name == 'posix':
font_dirs = [
'/System/Library/Fonts',
'/Library/Fonts',
os.path.expanduser('~/Library/Fonts'),
]
for font_dir in font_dirs:
if os.path.exists(font_dir):
# macOS 中文字体
chinese_fonts = [
'PingFang.ttc',
'STHeiti.ttc',
'Hiragino Sans GB.ttc',
'Apple SD Gothic Neo.ttc',
]
for font in chinese_fonts:
font_path = os.path.join(font_dir, font)
if os.path.exists(font_path):
return font_path
# 找第一个支持中文的字体
for file in os.listdir(font_dir):
if file.lower().endswith(('.ttf', '.ttc', '.otf')):
return os.path.join(font_dir, file)
# Linux 字体路径
font_dirs = [
'/usr/share/fonts',
'/usr/local/share/fonts',
os.path.expanduser('~/.fonts'),
]
for font_dir in font_dirs:
if os.path.exists(font_dir):
# Linux 中文字体
chinese_fonts = [
'wqy-microhei.ttc', # 文泉驿微米黑
'wqy-zenhei.ttc', # 文泉驿正黑
'droid-sans-fallback.ttf',
]
for font in chinese_fonts:
font_path = os.path.join(font_dir, font)
if os.path.exists(font_path):
return font_path
# 找第一个字体文件
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(font_dir):
for file in files:
if file.lower().endswith(('.ttf', '.ttc', '.otf')):
return os.path.join(root, file)
return None
def text_to_custom_ascii(text, char='*', width=80, font_size=100):
"""
将任意文字转换为自定义字符的ASCII艺术,自动去除上下空白
参数:
- text: 要转换的文字
- char: 使用的字符
- width: 输出宽度
- font_size: 字体大小
"""
# 获取字体
font_path = get_system_font()
if font_path:
try:
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
print(f"使用字体: {os.path.basename(font_path)}")
except:
print("警告: 字体加载失败,使用默认字体")
font = ImageFont.load_default()
else:
print("警告: 未找到系统字体,使用默认字体")
font = ImageFont.load_default()
# 创建图片(根据文字长度自适应)
# 对于中文字符,每个字符需要更多空间
img_width = max(len(text.encode('utf-8')) * font_size // 2, width * 10)
img_height = font_size * 2
img = Image.new('RGB', (img_width, img_height), 'white')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# 对于默认字体,使用不同的方法
if font.path is None: # 默认字体
# 使用textsize替代textbbox(兼容旧版本)
try:
# 尝试使用textsize
text_width, text_height = font.getsize(text)
x = (img_width - text_width) // 2
y = (img_height - text_height) // 2
draw.text((x, y), text, fill='black', font=font)
except:
# 如果还不行,简化处理
print("警告: 字体可能不支持中文,尝试简化处理")
x = img_width // 4
y = img_height // 4
draw.text((x, y), text, fill='black', font=font)
else:
# 使用textbbox(新版本PIL)
try:
text_bbox = draw.textbbox((0, 0), text, font=font)
text_width = text_bbox[2] - text_bbox[0]
text_height = text_bbox[3] - text_bbox[1]
x = (img_width - text_width) // 2
y = (img_height - text_height) // 2
draw.text((x, y), text, fill='black', font=font)
except Exception as e:
print(f"警告: textbbox失败 ({e}),使用备用方法")
# 备用方法
x = img_width // 4
y = img_height // 4
draw.text((x, y), text, fill='black', font=font)
# 转换为灰度
img_gray = img.convert('L')
img_array = np.array(img_gray)
# 自动检测文字区域(去除上下空白)
# 找到非白色(灰度值<250)的行
rows_with_content = np.where(np.any(img_array < 250, axis=1))[0]
if len(rows_with_content) > 0:
top = max(0, rows_with_content[0] - 2) # 留一点边距
bottom = min(img_height, rows_with_content[-1] + 3)
# 裁剪图片,只保留文字部分
img_cropped = img_gray.crop((0, top, img_width, bottom + 1))
cropped_height = bottom - top + 1
else:
# 如果没有找到内容,使用原始图片
img_cropped = img_gray
cropped_height = img_height
# 计算新的高度,保持宽高比
aspect_ratio = cropped_height / img_width
new_height = max(1, int(aspect_ratio * width))
# 调整大小
img_resized = img_cropped.resize((width, new_height))
# 转换为字符(简化版本,更清晰)
output_lines = []
for y in range(new_height):
line = ""
for x in range(width):
gray = img_resized.getpixel((x, y))
# 简单的阈值处理
if gray > 220: # 较亮的部分
line += " "
else:
line += char
output_lines.append(line)
# 再次去除结果中的空白行(可选)
# 移除顶部空白行
while output_lines and all(c == ' ' for c in output_lines[0]):
output_lines.pop(0)
# 移除底部空白行
while output_lines and all(c == ' ' for c in output_lines[-1]):
output_lines.pop()
return output_lines
def text_to_ascii_simple(text, char='*', width=60):
"""
简化的版本,兼容性更好
"""
# 创建图片
font_size = 80
img_width = font_size * len(text) + 100
img_height = font_size + 50
img = Image.new('RGB', (img_width, img_height), 'white')
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(img)
# 获取字体
font_path = get_system_font()
try:
if font_path:
font = ImageFont.truetype(font_path, font_size)
else:
font = ImageFont.load_default()
except:
font = ImageFont.load_default()
# 使用try-except处理字体绘制
try:
# 尝试绘制文字
x = 50
y = 25
draw.text((x, y), text, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
except Exception as e:
print(f"警告: 文字绘制失败 ({e}),使用英文模式")
# 如果失败,使用ASCII字符
text = text.encode('ascii', 'ignore').decode('ascii')
if not text:
text = "TEXT"
draw.text((x, y), text, fill=(0, 0, 0), font=font)
# 转换为灰度并裁剪
gray = img.convert('L')
arr = np.array(gray)
# 找到文字边界
non_white_rows = np.where(np.any(arr < 250, axis=1))[0]
non_white_cols = np.where(np.any(arr < 250, axis=0))[0]
if len(non_white_rows) == 0 or len(non_white_cols) == 0:
return [f"无法显示: {text}"]
top, bottom = non_white_rows[0], non_white_rows[-1]
left, right = non_white_cols[0], non_white_cols[-1]
# 裁剪,加一点边距
margin = 3
cropped = gray.crop((
max(0, left - margin),
max(0, top - margin),
min(gray.width, right + margin),
min(gray.height, bottom + margin)
))
# 调整大小
cw, ch = cropped.size
new_h = max(1, int(ch / cw * width * 0.5))
resized = cropped.resize((width, new_h))
# 转换为字符
lines = []
for y in range(new_h):
line = ''.join([' ' if resized.getpixel((x, y)) > 200 else char for x in range(width)])
lines.append(line)
# 去除结果中的空白行
while lines and all(c == ' ' for c in lines[0]):
lines.pop(0)
while lines and all(c == ' ' for c in lines[-1]):
lines.pop()
return lines
def main():
print("文字转ASCII艺术字生成器")
print("-" * 50)
while True:
text = input("\n请输入要显示的文字 (输入q退出): ")
if text.lower() == 'q':
break
char = input("请输入要使用的字符 (默认:*): ").strip() or "*"
width = input("请输入输出宽度 (默认:80): ").strip()
width = int(width) if width.isdigit() else 80
print("\n生成中...")
try:
# 使用简化版本
result = text_to_ascii_simple(text, char=char, width=width)
# 计算输出宽度
output_width = max(len(line) for line in result) if result else width
print("\n" + "=" * output_width)
print(f"文字: {text}")
print("=" * output_width)
for line in result:
print(line)
print("=" * output_width)
# 保存选项
save = input("\n是否保存到文件? (y/n): ").lower()
if save == 'y':
filename = input("文件名 (默认: text_art.txt): ").strip() or "text_art.txt"
with open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(result))
print(f"已保存到 {filename}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"生成失败: {e}")
print("尝试使用更简单的版本...")
# 最简单的回退方案
print("\n简单版本:")
print("=" * width)
for i in range(5):
spaces = (width - len(text) * 3) // 2
if i == 2:
print(" " * spaces + text)
else:
print(" " * spaces + char * (len(text) * 3))
print("=" * width)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()5. 实现效果