本系列介绍增强现代智能体系统可靠性的设计模式,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。本系列一共 14 篇文章,这是第 3 篇。原文:Building the 14 Key Pillars of Agentic AI
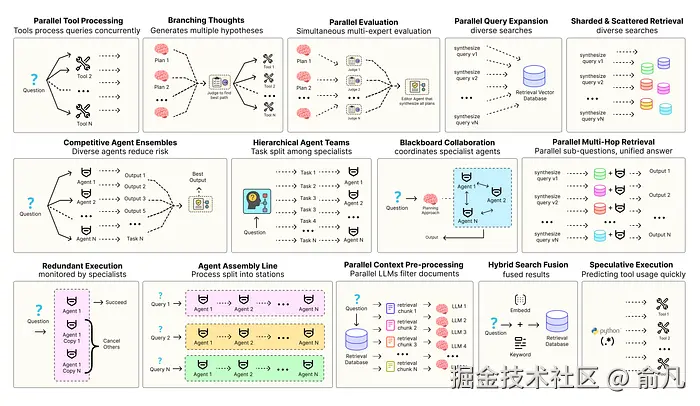
优化智能体解决方案需要软件工程确保组件协调、并行运行并与系统高效交互。例如预测执行,会尝试处理可预测查询以降低时延 ,或者进行冗余执行,即对同一智能体重复执行多次以防单点故障。其他增强现代智能体系统可靠性的模式包括:
- 并行工具:智能体同时执行独立 API 调用以隐藏 I/O 时延。
- 层级智能体:管理者将任务拆分为由执行智能体处理的小步骤。
- 竞争性智能体组合:多个智能体提出答案,系统选出最佳。
- 冗余执行:即两个或多个智能体解决同一任务以检测错误并提高可靠性。
- 并行检索和混合检索:多种检索策略协同运行以提升上下文质量。
- 多跳检索:智能体通过迭代检索步骤收集更深入、更相关的信息。
还有很多其他模式。
本系列将实现最常用智能体模式背后的基础概念,以直观方式逐一介绍每个概念,拆解其目的,然后实现简单可行的版本,演示其如何融入现实世界的智能体系统。
所有理论和代码都在 GitHub 仓库里:🤖 Agentic Parallelism: A Practical Guide 🚀
代码库组织如下:
erlang
agentic-parallelism/
├── 01_parallel_tool_use.ipynb
├── 02_parallel_hypothesis.ipynb
...
├── 06_competitive_agent_ensembles.ipynb
├── 07_agent_assembly_line.ipynb
├── 08_decentralized_blackboard.ipynb
...
├── 13_parallel_context_preprocessing.ipynb
└── 14_parallel_multi_hop_retrieval.ipynb强健治理的并行评估
在之前的模式中,即使产生多个想法,仍然依赖单一评估路径,意味着智能体解决方案仍然局限于单一评估视角......但对于复杂决策,需要从多个不同角度进行评估。
并行评估(Parallel Evaluation) 或多重批评反思(Multi-Critic Reflection)是一种结构模式,不再依赖单一评估......
- 创建一组 AI 评估器,一条内容会同时发送给所有评估器,每个评估器从独特、专家的视角进行评估。
- 这些并行反馈随后由最终编辑代理收集并综合,做出全面且明智的决策。
我们将建立一个内容审查系统,草稿先交给一组并行评估器,最终由编辑器根据集体反馈做出决定。
首先,为了确保评估器提供一致且机器可读的反馈,为输出定义 Pydantic 模式。
python
from langchain_core.pydantic_v1 import BaseModel, Field
from typing import Literal
class Critique(BaseModel):
"""A Pydantic model for a structured critique from a single, specialist critic."""
# 关于内容是否符合特定标准的明确的二元决定
is_compliant: bool = Field(description="Whether the content meets the specific criteria of this critic.")
# 详细、可操作的反馈,对决策做出解释
feedback: str = Field(description="Detailed feedback explaining why the content is or is not compliant. Provide actionable suggestions if non-compliant.")Critique 类是正式通信协议,确保每个评估器都能提供清晰的 is_compliant 裁定以及文本反馈 feedback,使输出可靠且易于被最终编辑器解析。
接下来定义 GraphState,跟踪正在审查的内容以及并行评估组的评估。
python
from typing import TypedDict, Annotated, Dict
import operator
class GraphState(TypedDict):
content_to_review: str
# 'critiques' 是字典,其中键是评估器名字,值是结构化的评估对象。
# 'operator.update' 归约函数对于合并来自并行分支的输出必不可少
critiques: Annotated[Dict[str, Critique], operator.update]
final_decision: dict # 简单起见,改为字典
performance_log: Annotated[List[str], operator.add]GraphState 中的 critiques 字典与 operator.update 归约函数结合,可以聚合并行反馈,自动将每个分支的结构化 Critique 对象收集成一个完整的对象,然后再传递给最终编辑器。
现在,定义系统的核心 ------ 评估节点,实现评估器(品牌声音分析师)和最终编辑器,不过 GitHub 上提供的 Jupyter Notebook 实现更深入更复杂。其他评估器(事实核查员、风险评估员)遵循相同模式,但提示不同。
python
import time
# 品牌声音分析师节点
def brand_voice_node(state: GraphState):
"""A simple critic that evaluates content against pre-defined brand voice guidelines."""
print("--- CRITIC: Brand Voice Analyst is reviewing... ---")
start_time = time.time()
# 一条简单链: 提示词 -> LLM -> 结构化输出
brand_chain = brand_voice_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(Critique)
critique = brand_chain.invoke({"content_to_review": state['content_to_review']})
execution_time = time.time() - start_time
log_entry = f"[BrandVoice] Completed in {execution_time:.2f}s."
print(log_entry)
return {"critiques": {"BrandVoice": critique}, "performance_log": [log_entry]}
# 总编辑节点(聚合和决策)
def chief_editor_node(state: GraphState):
"""The final node: aggregates all critiques and makes a final, justified decision."""
print("--- EDITOR: Chief Editor is making a decision... ---")
start_time = time.time()
# 将来自状态的结构化评论格式化为编辑器使用的单个字符串提升
critiques_str = ""
for critic_name, critique_obj in state['critiques'].items():
critiques_str += f"- {critic_name} Critique:\n - Compliant: {critique_obj.is_compliant}\n - Feedback: {critique_obj.feedback}\n\n"
# 创建编辑器链
editor_chain = chief_editor_prompt | llm.with_structured_output(dict) # Using dict for simplicity
final_decision = editor_chain.invoke({
"content_to_review": state['content_to_review'],
"critiques": critiques_str
})
execution_time = time.time() - start_time
log_entry = f"[ChiefEditor] Completed in {execution_time:.2f}s."
print(log_entry)
return {"final_decision": final_decision, "performance_log": [log_entry]}两个节点代表核心的扇出和扇入逻辑。brand_voice_node 是专业评估器模板,每个评估器独立运作。chief_editor_node 是汇总节点,将多方反馈综合成单一可执行决策。
就像之前的实现一样,组装完整的图,设置入口点,同时向三个评估器扇出。
python
from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
# 初始化新图
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
# 为评估器和编辑器定义节点
workflow.add_node("fact_checker", fact_checker_node)
workflow.add_node("brand_voice_analyst", brand_voice_node)
workflow.add_node("risk_assessor", risk_assessor_node)
workflow.add_node("chief_editor", chief_editor_node)
# 入口点是一个节点列表,告诉 LangGraph 并行运行
workflow.set_entry_point(["fact_checker", "brand_voice_analyst", "risk_assessor"])
# 在所有评估器节点完成后,合并结果,定义一个静态边来扇入主编辑器
workflow.add_edge(["fact_checker", "brand_voice_analyst", "risk_assessor"], "chief_editor")
# 编辑器的决定就是最后一步
workflow.add_edge("chief_editor", END)
# 编译成可运行应用程序
app = workflow.compile()
print("Graph constructed and compiled successfully.")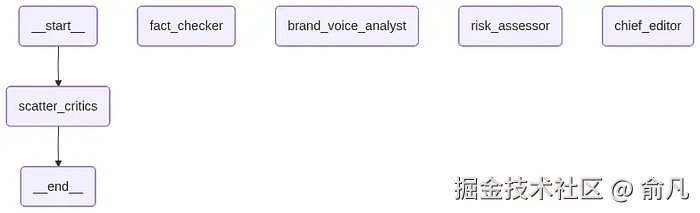
分析一下性能,看看这种并行工作流程的明显优势。
python
critic_times = []
editor_time = 0
# 解析性能日志,提取定时数据。
for log in final_state['performance_log']:
# 假设日志格式为 '[NodeName] Completed in X.XXs.'
time_val = float(log.split(' ')[-1].replace('s.', ''))
if "[ChiefEditor]" in log:
editor_time = time_val
else:
critic_times.append(time_val)
# 并行阶段的时间是执行时间最长的评估器的时间
parallel_critic_time = max(critic_times) if critic_times else 0
# 对于顺序模拟,将时间加起来
sequential_critic_time = sum(critic_times)
# 工作流的总时间
total_time = parallel_critic_time + editor_time
time_saved = sequential_critic_time - parallel_critic_time
print(f"Total Execution Time: {total_time:.2f} seconds\n")
print("Breakdown:")
print(f" - Parallel Critics (longest path): {parallel_critic_time:.2f} seconds")
print(f" - Chief Editor: {editor_time:.2f} seconds\n")看看评估结果......
python
#### 输出 ####
=============================================================
FINAL GOVERNANCE DECISION
=============================================================
Final Decision: Request Revisions
Editors Summary:
The post is non-compliant across the board. The Fact-Checker found unsupported claims, the Risk Assessor identified significant legal and reputational risks with the terms 'guaranteed' and 'cures procrastination', and the Brand Voice Analyst noted that the tone is overly hyped and exaggerated.
Revision Instructions:
Please remove the word 'guaranteed'. Rephrase the '500% faster' claim to be more specific and verifiable, for example, 'up to 5x faster in specific benchmarks'. Remove the unsupported claim about curing procrastination entirely. Tone down the language to be more professional and focus on the practical benefits for the user.
============================================================
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS
============================================================
Total Execution Time: 15.66 seconds
Breakdown:
- Parallel Critics (longest path): 9.21 seconds
- Chief Editor: 6.45 seconds三个评估节点并行运行。如果按顺序执行,该阶段将耗时 19.24s。通过并行运行,时间仅为 9.21s秒(最慢评估器的时间)。
评估阶段节省了 10.03s 的时间,时延减少了 52%。定量角度看,结果远优于单一评估。
我们从三个不同角度收到了深入且专业的反馈,这种多方面评估让主编辑器能够做出明智的决定。
Hi,我是俞凡,一名兼具技术深度与管理视野的技术管理者。曾就职于 Motorola,现任职于 Mavenir,多年带领技术团队,聚焦后端架构与云原生,持续关注 AI 等前沿方向,也关注人的成长,笃信持续学习的力量。在这里,我会分享技术实践与思考。欢迎关注公众号「DeepNoMind」,星标不迷路。也欢迎访问独立站 www.DeepNoMind.com,一起交流成长。