文章目录

clone()
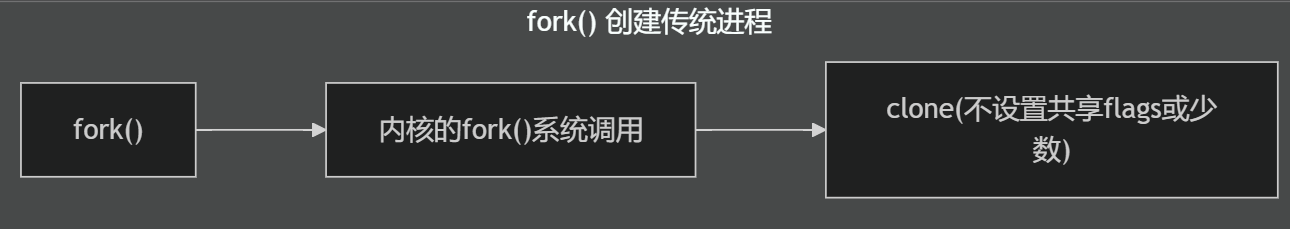
- 进程的创建可以使用
fork(),除了fork()以外还有一些系统调用可以实现进程的创建 clone是Linux特有的系统调用,功能比fork()更强大、更灵活- 早期LinuxThreads线程库就是用clone()创建独立进程来模拟线程
c
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#include <sched.h>
int clone(int (*fn)(void *), void *stack, int flags, void *arg, ...
/* pid_t *parent_tid, void *tls, pid_t *child_tid */ );- 通过flags参数精确控制新创建的"执行流"与父进程共享哪些资源
- CLONE_VM:共享内存空间(即创建线程)
- CLONE_FILES:共享文件描述符表
- CLONE_FS:共享文件系统信息(如根目录、当前工作目录)
- CLONE_SIGHAND:共享信号处理程序表
clone()并不是一个被广泛使用的函数接口,是特定于 Linux 的,不应用于旨在可移植的程序中- 可移植性差:是Linux特有的,可能无法在其他类Unix系统上编译
- 接口复杂:需要手动管理栈空间(stack参数)、线程本地存储(tls)等,容易出错
- 抽象层次低:pthread_create()对clone()进行了封装,提供了更安全、更符合POSIX标准的抽象
pthread_create()
- 创建一个新线程并启动执行
函数原型
c
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);参数(按重要顺序)
| 参数 | 类型 | 作用 | 注意事项 |
|---|---|---|---|
**start_routine** |
void *(*)(void *) |
线程入口函数 新线程从这个函数开始执行 | 1. 函数签名必须严格匹配:接收一个void* 参数,返回一个void*值 2. 线程正常结束时,应调用pthread_exit()或return一个值 |
**arg** |
void * |
传递给start_routine的唯一参数 |
如果需要传递多个参数,需要将它们打包到一个struct里,然后传递这个结构的指针 |
**thread** |
pthread_t * |
输出参数 。用于存储新创建线程的标识符(ID) | 成功返回后,*thread中会填入有效的线程ID,可用于pthread_join, pthread_detach等操作。 |
**attr** |
pthread_attr_t * |
线程属性对象。用于设置新线程的栈大小、调度策略、分离状态等 | 最常用的情况是传入 **NULL**,表示使用所有默认属性。需要非默认设置时才需要创建和配置pthread_attr_t 对象 |
返回值
- 成功:返回 0。
- 失败:返回一个正的错误号(如 EAGAIN, EINVAL, EPERM)
pthread_create() 不会设置全局变量 errno,错误信息直接通过返回值给出
错误处理
| 方式 | 代码示例 | 是否正确 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 错误方式 | if (ret < 0) { perror("..."); } |
错误 | 1. 错误判断条件错(应该!=0)2. perror依赖于errno,但errno未被设置。 |
| 移植方式 | errno = ret; perror("..."); |
可用 但不推荐 | 人为将错误号赋给errno,再利用perror。这增加了步骤,且perror的输出格式固定。 |
| 推荐方式 | fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", strerror(ret)); |
最佳实践 | 使用strerror()函数将错误号ret直接转换为可读的字符串。这是处理Pthreads函数错误的标准方法 |
- 推荐 strerror方式:
- 意图清晰:明确表示在处理Pthreads的错误
- 线程安全:strerror的线程安全版本(strerror_r)在多线程环境下更安全
- 格式化灵活:可以自由控制错误信息的输出格式
- 常见错误码:
EAGAIN:资源不足,无法创建另一个线程。EINVAL:attr中的设置无效。EPERM: 没有权限设置attr中指定的调度策略和参数
例程
- perror()方式
c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
void *func (void *arg) {
printf("Hello thread!\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, func, NULL);
if(ret != 0){
errno = ret;
perror("pthread_create");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("tid=%lu\n", tid);
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
return 0;
}- strerror()方式
c
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
void *func (void *arg) {
printf("Hello thread!\n");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
int ret = pthread_create(&tid, NULL, func, NULL);
if(ret != 0){
fprintf(stderr, "pthread_create:%s\n", strerror(ret) );
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("tid=%lu\n", tid);
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
return 0;
}编译命令
bash
gcc -o my_program my_program.c -pthread必须使用 -pthread 选项(注意是 -pthread,不是 -lpthread,虽然后者通常也行)
-pthread会正确设置必要的宏定义和链接库