Spring Bean的生命周期
1.实例化对象:通过反射生成对象。
首先准备一个实体类。
java
package com.example.springdemo.pojo;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.DisposableBean;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
public class Person implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean , ApplicationContextAware, EnvironmentAware {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private Environment environment;
public Person() {
System.out.println("new instance method");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("bean init method...");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("bean destroy method...");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
System.out.println("bean ApplicationContextAware method");
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
System.out.println("bean EnvironmentAware method");
}
}在准备一个xml文件,以xml文件的形式注册bean对象。
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="person" class="com.example.springdemo.pojo.Person" scope="singleton">
</bean>
<bean id="myBeanPostProcessor" class="com.example.springdemo.postporcesser.MyBeanPostProcessor" scope="singleton">
</bean>
</beans>实例化bean的过程涉及到容器的刷新流程,链路比较长,这里不做深究,只带着找到在哪里实现的。
给出一个大致的链路吧 getBean doGetBean createBean doCreateBean newInstance instantiateBean
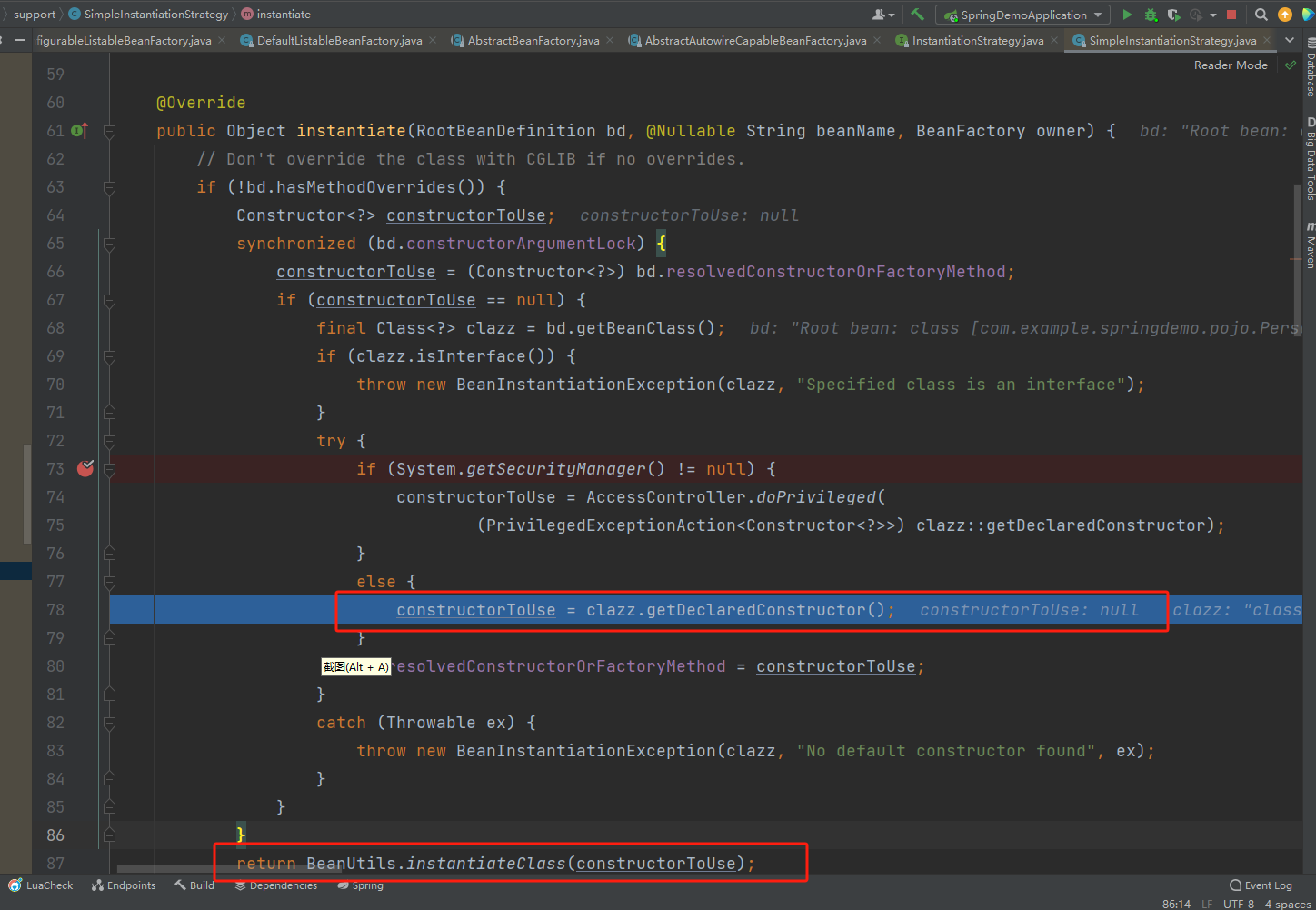
看到上图可知,实例化对象其实最终是通过反射来实现的。
2.填充bean的属性,populateBean(循环依赖的问题可在此处扩展)。
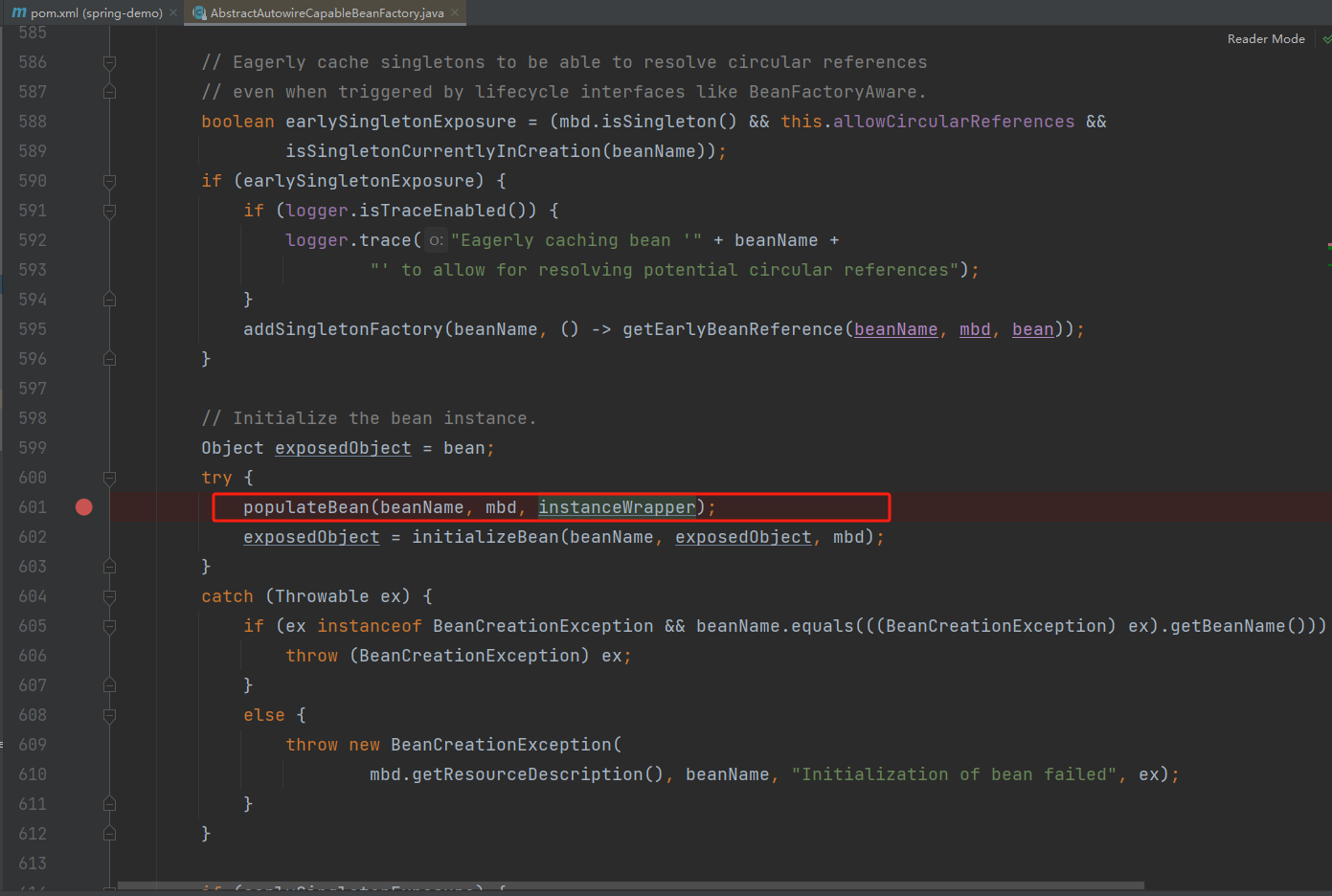
3.调用Aware接口。invokeAwareMethods。
4.执行BeanPostProcessors 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization
5.执行bean的init method方法
6.执行BeanPostProcessors 的 postProcessAfterInitialization
java
package org.springframework.beans.factory.support;
//AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//执行BeanPostProcessors 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//执行bean的init method方法
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//执行BeanPostProcessors 的 postProcessAfterInitialization
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
//其实就是判断bean对象是否实现了Aware接口 来设置BeanName BeanClassLoader BeanFactory
private void invokeAwareMethods(String beanName, Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
7.获取到完整的对象。
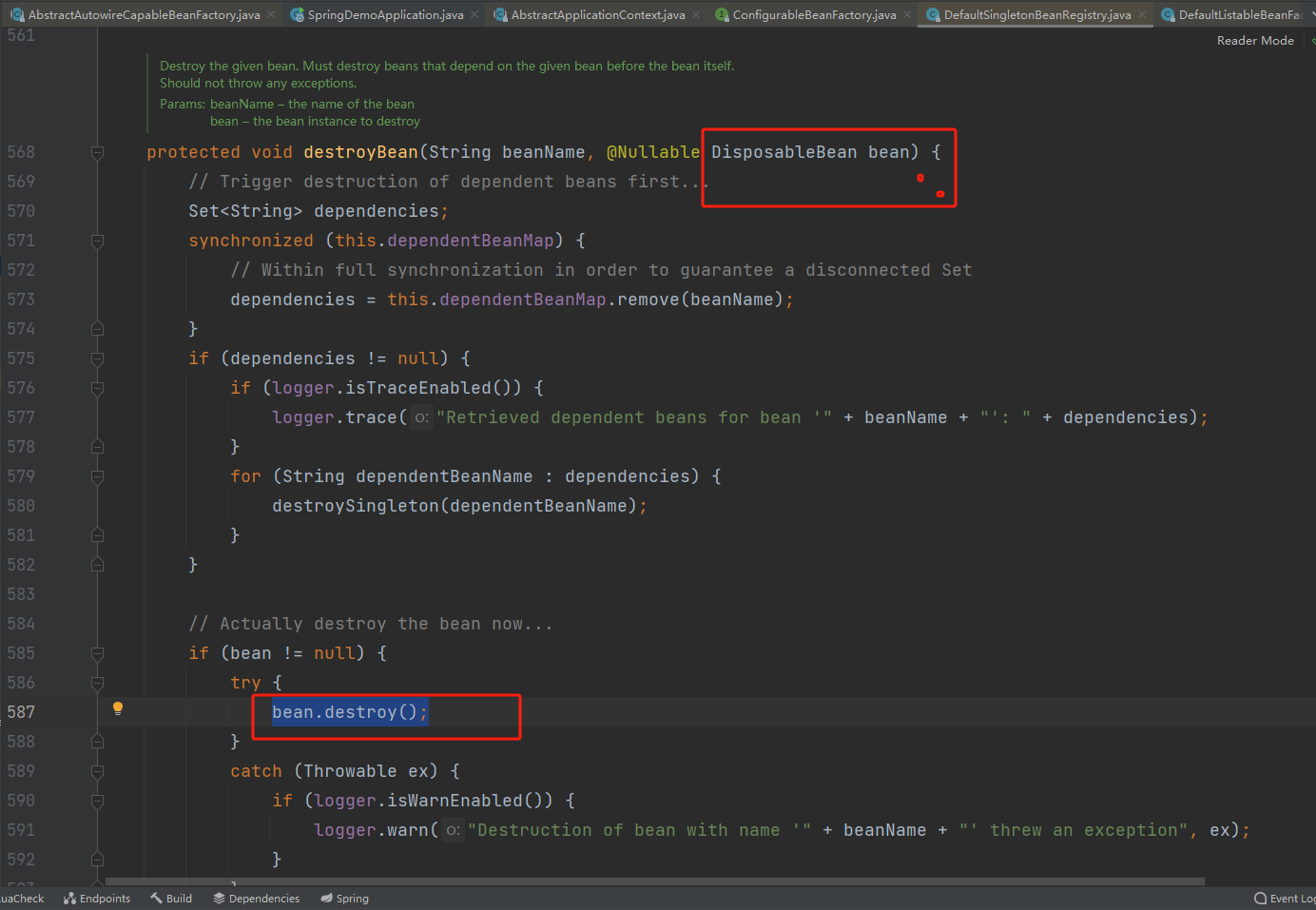
8.执行Disposable接口的destory方法。
可以看到 如果我们实现了DisposableBean接口后会执行DisposableBean.destroy()
最后我们依据person类验证下实现流程
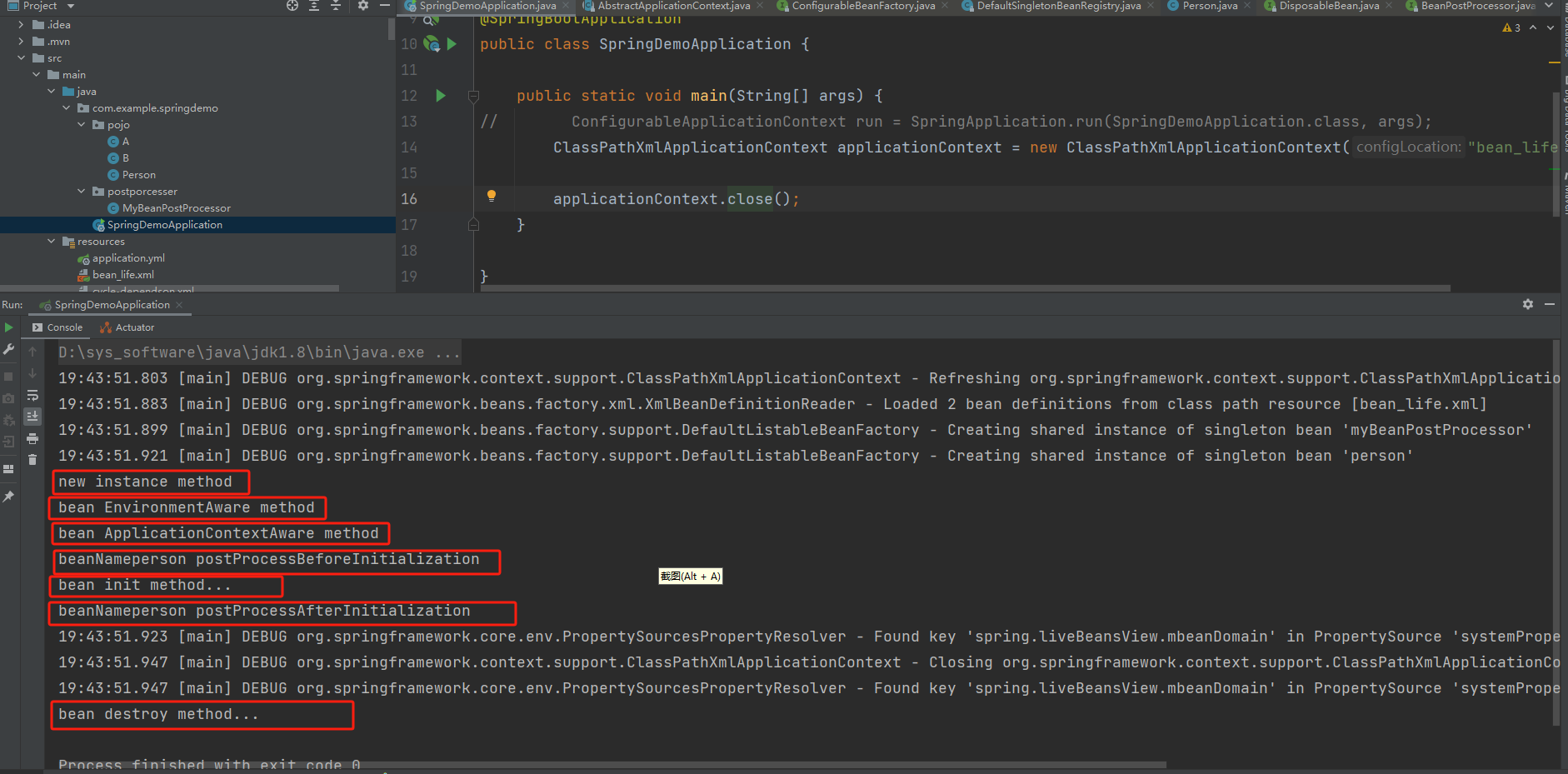
执行BeanPostProcessors 的 postProcessBeforeInitialization
以ApplicationContextAwareProcessor举例。
可以看到通过ApplicationContextAwareProcessor我们可以装配Environment、ApplicationContext,等系统对象。
java
@Override
@Nullable
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (!(bean instanceof EnvironmentAware || bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware ||
bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware || bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware ||
bean instanceof MessageSourceAware || bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware ||
bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware)) {
return bean;
}
AccessControlContext acc = null;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
acc = this.applicationContext.getBeanFactory().getAccessControlContext();
}
if (acc != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
return null;
}, acc);
}
else {
invokeAwareInterfaces(bean);
}
return bean;
}
private void invokeAwareInterfaces(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) bean).setEnvironment(this.applicationContext.getEnvironment());
}
if (bean instanceof EmbeddedValueResolverAware) {
((EmbeddedValueResolverAware) bean).setEmbeddedValueResolver(this.embeddedValueResolver);
}
if (bean instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) bean).setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationEventPublisherAware) {
((ApplicationEventPublisherAware) bean).setApplicationEventPublisher(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof MessageSourceAware) {
((MessageSourceAware) bean).setMessageSource(this.applicationContext);
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationStartupAware) {
((ApplicationStartupAware) bean).setApplicationStartup(this.applicationContext.getApplicationStartup());
}
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(this.applicationContext);
}
}