MyBatis插件模块详解
一、MyBatis整体架构与插件模块
在深入插件模块之前,我们先了解MyBatis的整体架构,以及插件模块在其中的重要地位。 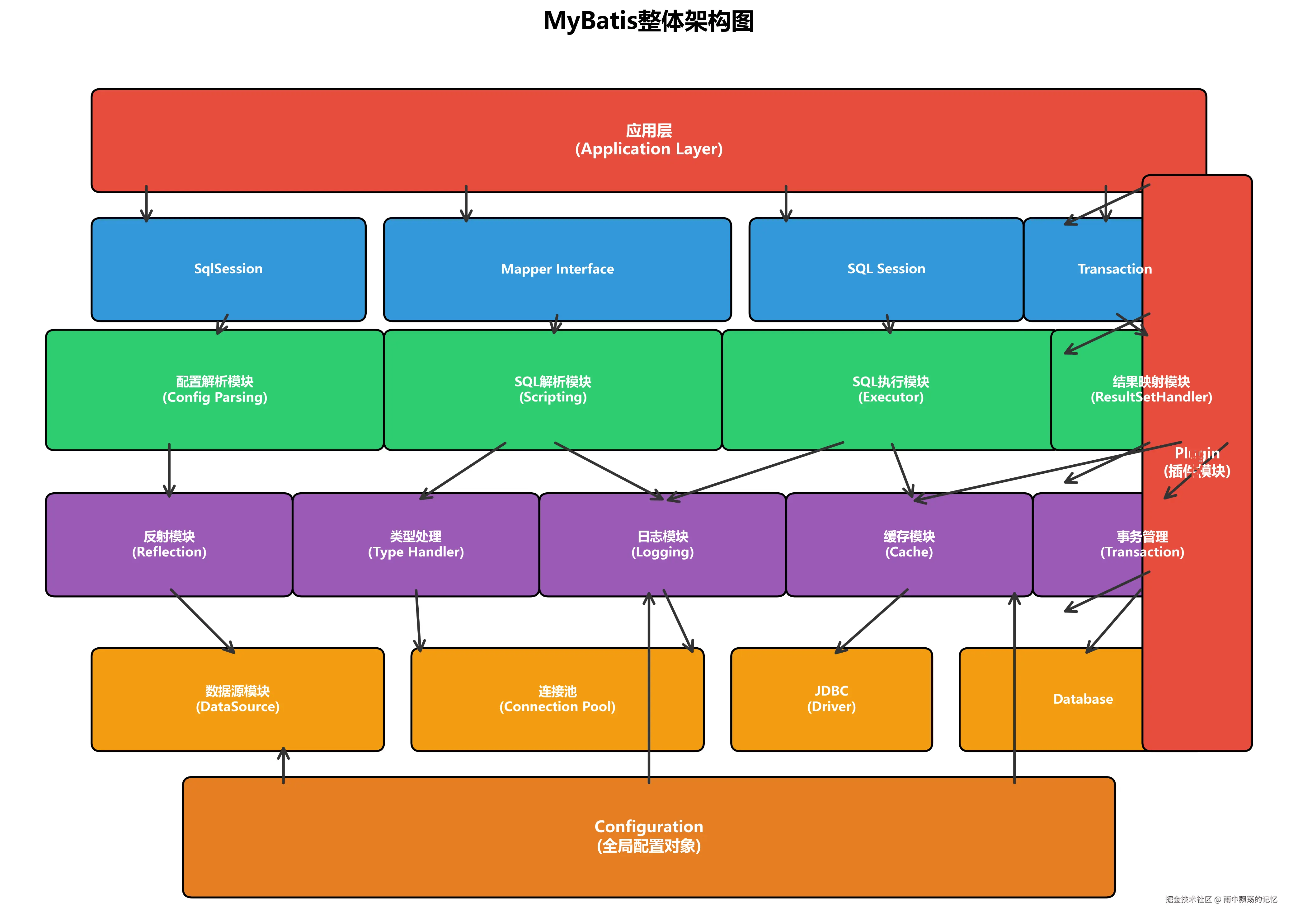
从上图可以看出,MyBatis采用了分层架构设计,而插件模块(Plugin)通过动态代理机制横切整个框架,能够在核心组件的执行过程中插入自定义逻辑。它为MyBatis提供了强大的扩展能力,使得开发者可以在不修改源码的情况下增强框架功能。
1.1 插件模块的核心职责
插件模块主要承担以下核心职责:
- 扩展框架功能:在不动源码的情况下增强MyBatis功能
- 拦截核心组件:拦截Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler
- 实现AOP功能:通过动态代理实现面向切面编程
- 统一权限控制:实现数据权限过滤
- 性能监控:记录SQL执行时间和性能指标
- 分页查询:实现物理分页功能
1.2 为什么需要插件
在实际开发中,我们经常有这些需求:
sql
需求场景:
├── SQL性能监控:记录慢查询
├── 数据权限控制:根据用户权限过滤数据
├── 分页查询:自动实现物理分页
├── 乐观锁:自动更新版本号
├── 审计日志:记录操作日志
└── 加密解密:敏感数据加密存储如果没有插件机制,我们需要修改MyBatis源码或编写大量重复代码。插件机制让我们可以优雅地实现这些功能。
1.3 插件的实现原理
MyBatis的插件基于动态代理实现:
scss
目标对象
↓
使用Plugin.wrap()包装
↓
生成代理对象
↓
调用intercept()方法
↓
执行自定义逻辑
↓
调用目标方法或继续传递二、插件拦截机制
MyBatis的插件机制基于Java动态代理和责任链模式。 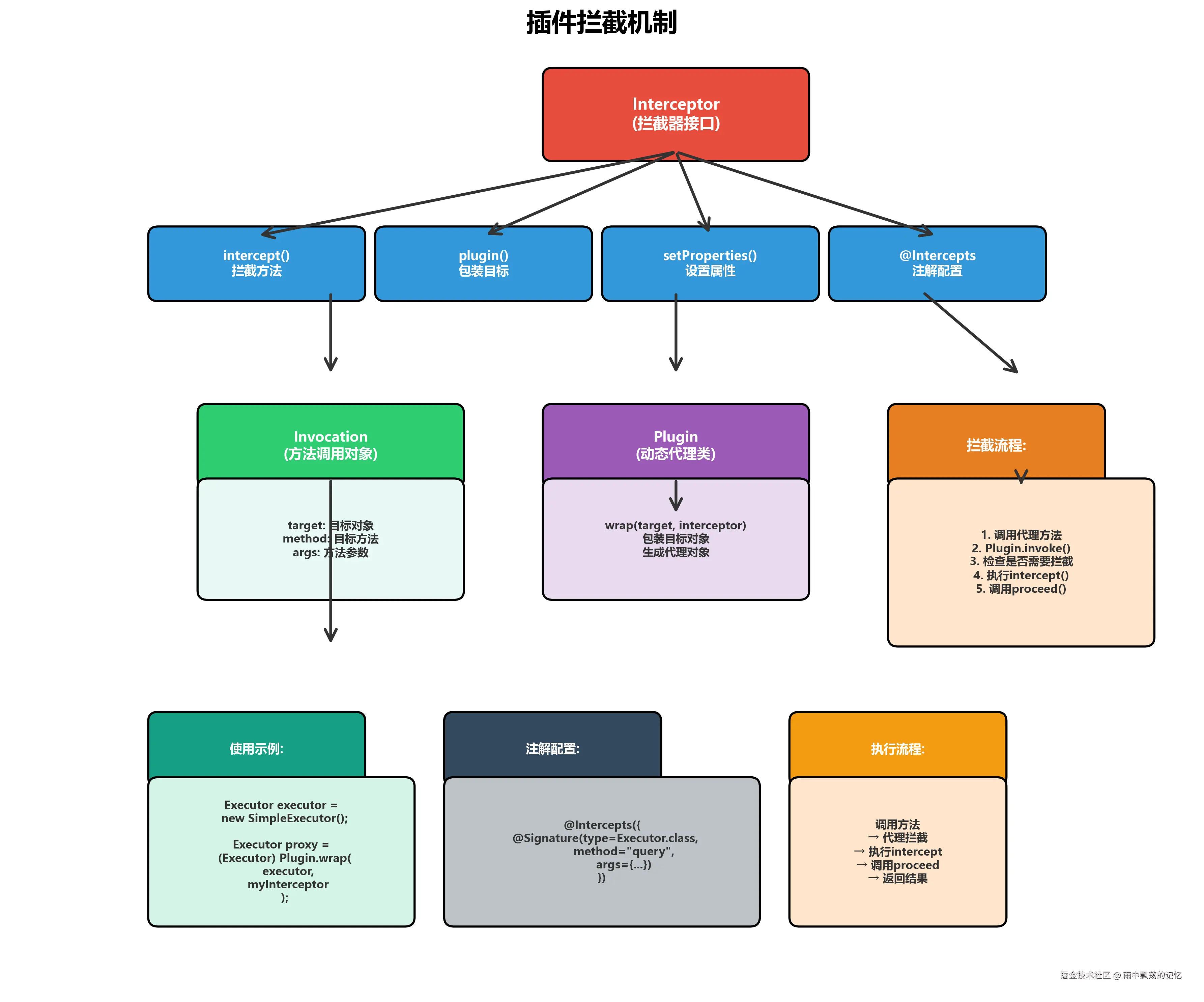
2.1 Interceptor接口
MyBatis插件的核心是Interceptor接口:
java
public interface Interceptor {
/**
* 拦截方法,在这里实现自定义逻辑
* @param invocation 代理调用对象
* @return 方法执行结果
* @throws Throwable 异常
*/
Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable;
/**
* 包装目标对象,生成代理对象
* @param target 目标对象
* @return 代理对象
*/
default Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
/**
* 设置插件属性
* @param properties 配置属性
*/
default void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// NOP
}
}2.2 Invocation类
Invocation封装了方法调用的相关信息:
java
public class Invocation {
private final Object target; // 目标对象
private final Method method; // 目标方法
private final Object[] args; // 方法参数
public Invocation(Object target, Method method, Object[] args) {
this.target = target;
this.method = method;
this.args = args;
}
// 执行目标方法
public Object proceed() throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
return method.invoke(target, args);
}
// Getter方法
public Object getTarget() { return target; }
public Method getMethod() { return method; }
public Object[] getArgs() { return args; }
}2.3 Plugin类
Plugin是代理对象的InvocationHandler:
java
public class Plugin implements InvocationHandler {
private final Object target;
private final Interceptor interceptor;
private final Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap;
private Plugin(Object target, Interceptor interceptor, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
this.target = target;
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.signatureMap = signatureMap;
}
// 静态工厂方法,包装目标对象
public static Object wrap(Object target, Interceptor interceptor) {
// 获取拦截的类和方法签名
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = getSignatureMap(interceptor);
Class<?> type = target.getClass();
// 获取需要拦截的接口
Class<?>[] interfaces = getAllInterfaces(type, signatureMap);
if (interfaces.length > 0) {
// 创建代理对象
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(
type.getClassLoader(),
interfaces,
new Plugin(target, interceptor, signatureMap)
);
}
return target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 获取需要拦截的方法集合
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.get(method.getDeclaringClass());
if (methods != null && methods.contains(method)) {
// 执行拦截器的intercept方法
return interceptor.intercept(new Invocation(target, method, args));
}
// 不需要拦截,直接执行
return method.invoke(target, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(e);
}
}
// 获取签名映射
private static Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> getSignatureMap(Interceptor interceptor) {
Intercepts interceptsAnnotation = interceptor.getClass().getAnnotation(Intercepts.class);
if (interceptsAnnotation == null) {
throw new PluginException("No @Intercepts annotation was found in interceptor " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
Signature[] sigs = interceptsAnnotation.value();
Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Signature sig : sigs) {
Set<Method> methods = signatureMap.computeIfAbsent(sig.type(), k -> new HashSet<>());
try {
Method method = sig.type().getMethod(sig.method(), sig.args());
methods.add(method);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new PluginException("Could not find method on " + sig.type() + " named " + sig.method() + ". Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
return signatureMap;
}
// 获取所有需要拦截的接口
private static Class<?>[] getAllInterfaces(Class<?> type, Map<Class<?>, Set<Method>> signatureMap) {
Set<Class<?>> interfaces = new HashSet<>();
while (type != null) {
for (Class<?> c : type.getInterfaces()) {
if (signatureMap.containsKey(c)) {
interfaces.add(c);
}
}
type = type.getSuperclass();
}
return interfaces.toArray(new Class<?>[interfaces.size()]);
}
}三、四大核心拦截点
MyBatis允许拦截四个核心组件。
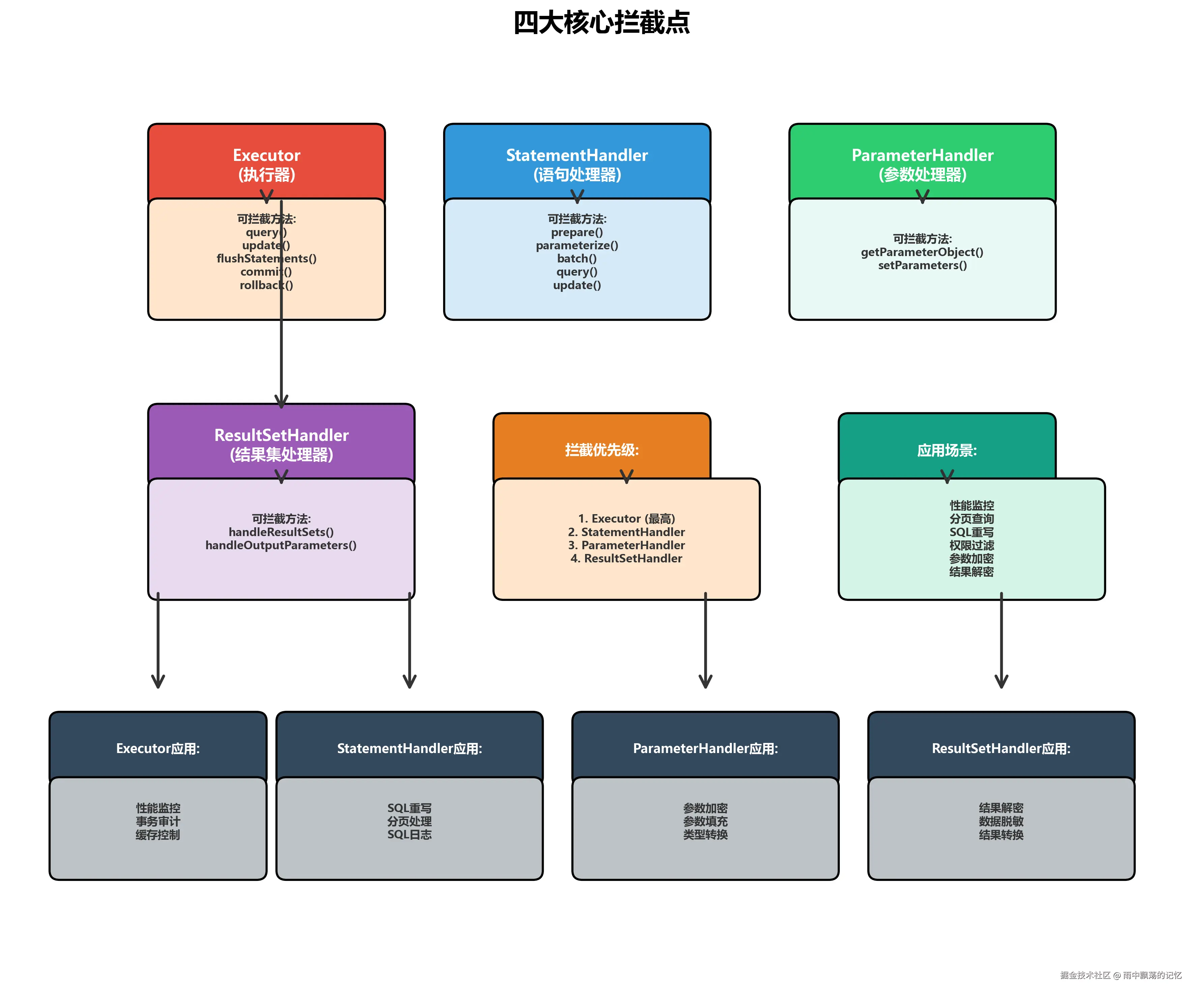
3.1 Executor(执行器)
Executor是MyBatis的核心执行器,负责SQL的执行。
可拦截方法:
update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter)- 执行增删改query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler)- 查询query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql)- 查询(带缓存)flushStatements()- 刷新批处理commit()- 提交事务rollback()- 回滚事务getTransaction()- 获取事务close()- 关闭会话isClosed()- 是否关闭
示例:性能监控插件
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "update",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class PerformanceMonitorPlugin implements Interceptor {
private long threshold; // 慢查询阈值
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 执行目标方法
return invocation.proceed();
} finally {
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
long time = end - start;
if (time > threshold) {
String sql = ms.getBoundSql(null).getSql();
System.out.println("慢查询警告: " + ms.getId() + " 耗时: " + time + "ms");
System.out.println("SQL: " + sql);
}
}
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.threshold = Long.parseLong(properties.getProperty("threshold", "1000"));
}
}3.2 StatementHandler(语句处理器)
StatementHandler负责创建Statement对象并设置参数。
可拦截方法:
prepare(Connection connection)- 准备Statementparameterize(Statement statement)- 设置参数batch(Statement statement)- 批处理update(Statement statement)- 执行更新query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler)- 执行查询getBoundSql()- 获取BoundSqlgetParameterHandler()- 获取ParameterHandlergetResultHandler()- 获取ResultSetHandler
示例:SQL重写插件
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class,
method = "prepare",
args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})
})
public class SQLRewritePlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
StatementHandler handler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 重写SQL:添加数据权限过滤
if (sql.toLowerCase().startsWith("select")) {
sql = rewriteSQL(sql);
// 使用反射修改sql字段
Field field = boundSql.getClass().getDeclaredField("sql");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(boundSql, sql);
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
private String rewriteSQL(String sql) {
// 添加数据权限过滤条件
return sql + " AND tenant_id = '" + getCurrentTenantId() + "'";
}
private String getCurrentTenantId() {
// 获取当前租户ID
return "1001";
}
}3.3 ParameterHandler(参数处理器)
ParameterHandler负责设置PreparedStatement的参数。
可拦截方法:
getParameterObject()- 获取参数对象setParameters(PreparedStatement ps)- 设置参数
示例:参数加密插件
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = ParameterHandler.class,
method = "setParameters",
args = {PreparedStatement.class})
})
public class ParameterEncryptPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
ParameterHandler handler = (ParameterHandler) invocation.getTarget();
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
// 获取参数对象
Object parameterObject = handler.getParameterObject();
if (parameterObject instanceof User) {
User user = (User) parameterObject;
// 加密敏感字段
if (user.getPassword() != null) {
user.setPassword(encrypt(user.getPassword()));
}
}
// 继续执行
return invocation.proceed();
}
private String encrypt(String plainText) {
// Base64简单加密
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(plainText.getBytes());
}
}3.4 ResultSetHandler(结果集处理器)
ResultSetHandler负责将ResultSet映射为Java对象。
可拦截方法:
handleResultSets(Statement stmt)- 处理结果集handleOutputParameters(CallableStatement cs)- 处理存储过程输出参数
示例:结果解密插件
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class,
method = "handleResultSets",
args = {Statement.class})
})
public class ResultDecryptPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 执行查询
Object result = invocation.proceed();
if (result instanceof List) {
List<?> list = (List<?>) result;
for (Object obj : list) {
if (obj instanceof User) {
User user = (User) obj;
// 解密敏感字段
if (user.getIdCard() != null) {
user.setIdCard(decrypt(user.getIdCard()));
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
private String decrypt(String cipherText) {
// Base64解密
byte[] decoded = Base64.getDecoder().decode(cipherText);
return new String(decoded);
}
}四、插件实现流程
理解插件的实现和配置流程非常重要。
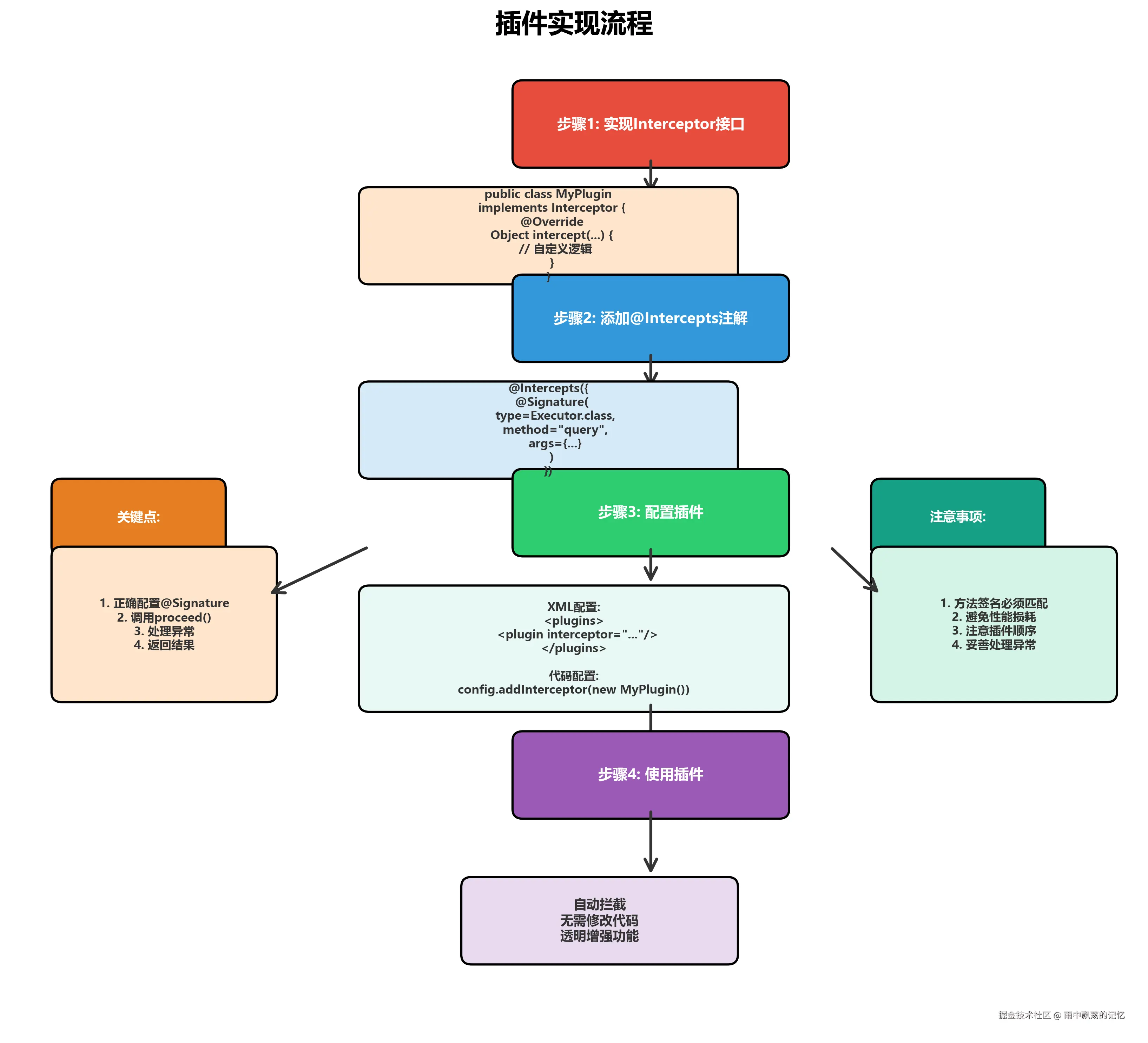
4.1 实现自定义插件
步骤1:实现Interceptor接口
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class CustomPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 前置逻辑
System.out.println("Before: " + invocation.getMethod().getName());
// 执行目标方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
// 后置逻辑
System.out.println("After: " + invocation.getMethod().getName());
return result;
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
// 使用Plugin.wrap包装目标对象
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
// 读取配置属性
String propertyName = properties.getProperty("propertyName");
System.out.println("Property: " + propertyName);
}
}4.2 配置插件
方式1:XML配置
xml
<configuration>
<plugins>
<!-- 性能监控插件 -->
<plugin interceptor="com.example.plugin.PerformanceMonitorPlugin">
<property name="threshold" value="1000"/>
</plugin>
<!-- 分页插件 -->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<property name="helperDialect" value="mysql"/>
</plugin>
<!-- 自定义插件 -->
<plugin interceptor="com.example.plugin.CustomPlugin">
<property name="propertyName" value="propertyValue"/>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</configuration>方式2:代码配置
java
// 创建Configuration
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
// 添加插件
configuration.addInterceptor(new PerformanceMonitorPlugin());
configuration.addInterceptor(new PageInterceptor());
configuration.addInterceptor(new CustomPlugin());
// 创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration);方式3:Spring配置
java
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public PerformanceMonitorPlugin performanceMonitorPlugin() {
PerformanceMonitorPlugin plugin = new PerformanceMonitorPlugin();
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("threshold", "1000");
plugin.setProperties(properties);
return plugin;
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource);
// 添加插件
sessionFactory.setPlugins(
new Interceptor[]{
performanceMonitorPlugin(),
new PageInterceptor()
}
);
return sessionFactory.getObject();
}
}4.3 插件链的执行顺序
当配置了多个插件时,它们会形成责任链:
markdown
原始Executor
↓
被Plugin1包装
↓
被Plugin2包装
↓
被Plugin3包装
↓
最终代理对象执行顺序:
java
// 配置顺序
<plugin interceptor="Plugin1"/>
<plugin interceptor="Plugin2"/>
<plugin interceptor="Plugin3"/>
// 执行顺序
Plugin3.intercept() → Plugin2.intercept() → Plugin1.intercept() → 目标方法
// 返回顺序
目标方法 → Plugin1处理 → Plugin2处理 → Plugin3处理 → 最终结果五、动态代理链
多个插件会形成多层代理。 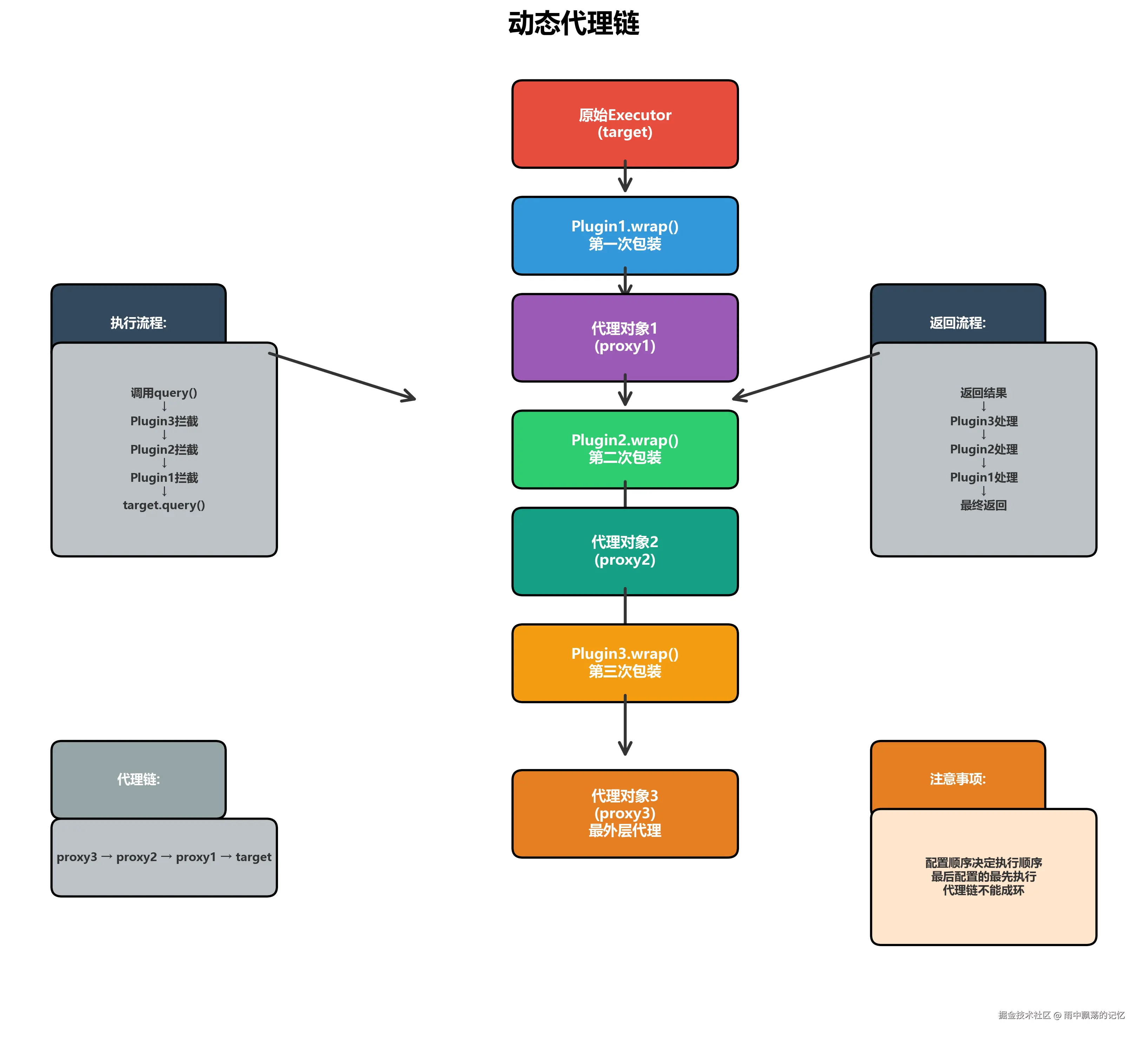
5.1 代理链的构建
java
// 原始对象
Executor target = new SimpleExecutor();
// 第一次包装
Executor proxy1 = (Executor) Plugin.wrap(target, plugin1);
// 第二次包装(包装的是代理对象)
Executor proxy2 = (Executor) Plugin.wrap(proxy1, plugin2);
// 第三次包装
Executor proxy3 = (Executor) Plugin.wrap(proxy2, plugin3);
// proxy3是最外层的代理5.2 代理链的执行
scss
调用 proxy3.query()
↓
Plugin3.invoke()
↓
Plugin3.intercept()
↓
invocation.proceed() 调用 proxy2.query()
↓
Plugin2.invoke()
↓
Plugin2.intercept()
↓
invocation.proceed() 调用 proxy1.query()
↓
Plugin1.invoke()
↓
Plugin1.intercept()
↓
invocation.proceed() 调用 target.query()
↓
执行真正的查询
↓
返回结果
↓
Plugin1处理返回值
↓
Plugin2处理返回值
↓
Plugin3处理返回值
↓
最终返回5.3 代理链示例代码
java
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}))
public class Plugin1 implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Plugin1 Before");
Object result = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("Plugin1 After");
return result;
}
}
@Intercepts(@Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}))
public class Plugin2 implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Plugin2 Before");
Object result = invocation.proceed();
System.out.println("Plugin2 After");
return result;
}
}
// 输出结果:
// Plugin2 Before
// Plugin1 Before
// 执行查询
// Plugin1 After
// Plugin2 After六、典型应用场景
插件在实际开发中有很多应用场景。 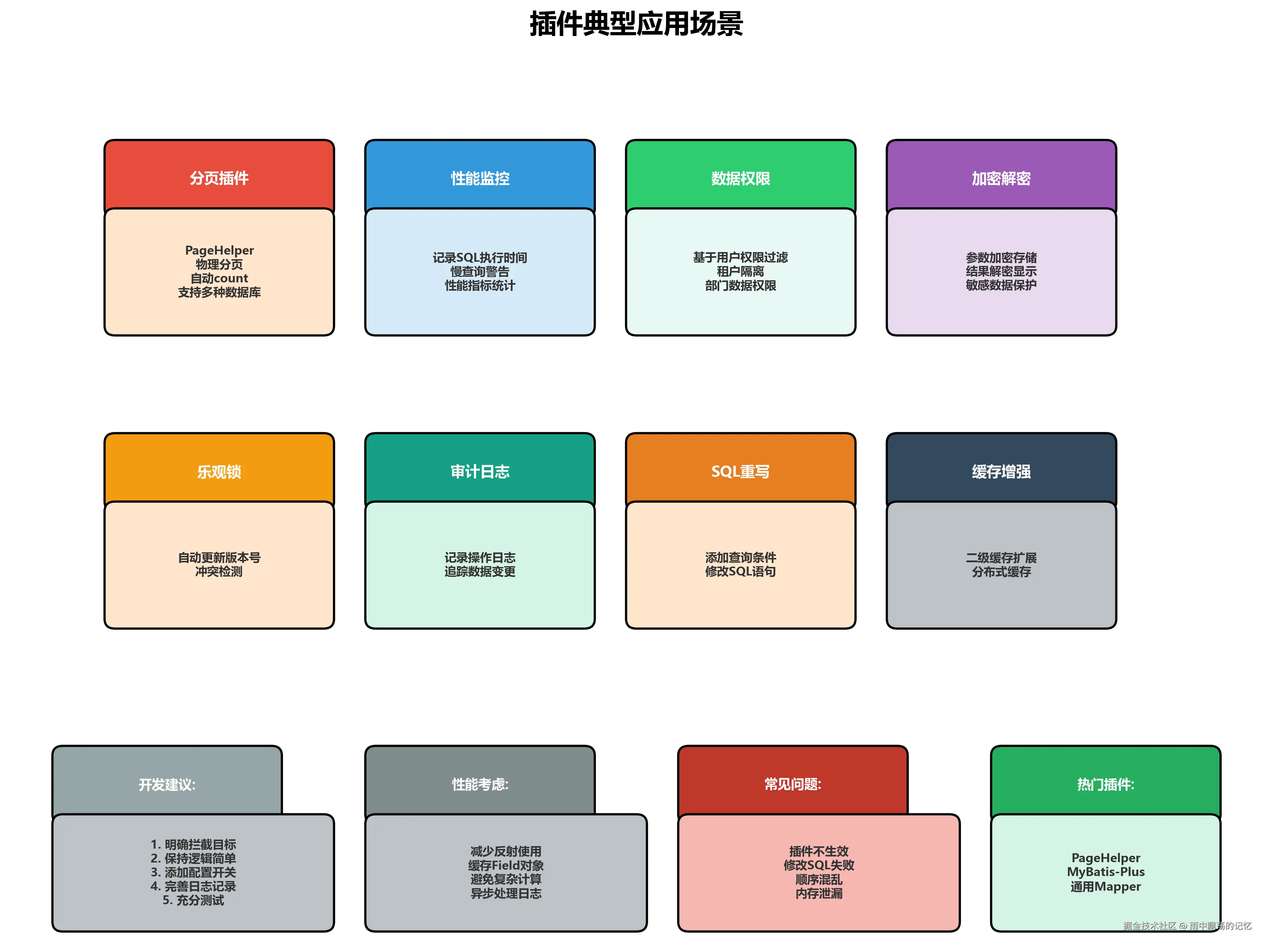
6.1 分页插件
PageHelper是最著名的MyBatis分页插件:
xml
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.3.2</version>
</dependency>配置:
xml
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<property name="helperDialect" value="mysql"/>
<property name="reasonable" value="true"/>
</plugin>使用:
java
// 查询前调用分页
PageHelper.startPage(1, 10);
List<User> users = userMapper.selectAll();
// 获取分页信息
PageInfo<User> pageInfo = new PageInfo<>(users);
System.out.println("总数: " + pageInfo.getTotal());
System.out.println("页数: " + pageInfo.getPages());6.2 性能监控插件
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "update",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}),
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class SlowQueryMonitorPlugin implements Interceptor {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SlowQueryMonitorPlugin.class);
private long slowQueryThreshold;
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
return invocation.proceed();
} finally {
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
if (cost > slowQueryThreshold) {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(invocation.getArgs()[1]);
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
logger.warn("慢查询: {} 耗时: {}ms\nSQL: {}", ms.getId(), cost, sql);
}
}
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.slowQueryThreshold = Long.parseLong(properties.getProperty("threshold", "1000"));
}
}6.3 数据权限插件
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = StatementHandler.class,
method = "prepare",
args = {Connection.class, Integer.class})
})
public class DataPermissionPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
StatementHandler handler = (StatementHandler) invocation.getTarget();
BoundSql boundSql = handler.getBoundSql();
String sql = boundSql.getSql();
// 获取当前用户的数据权限
Set<Long> deptIds = getCurrentUserDeptIds();
// 重写SQL,添加数据权限过滤
if (sql.toLowerCase().startsWith("select") && !deptIds.isEmpty()) {
String condition = "dept_id IN (" + String.join(",", deptIds.toString()) + ")";
sql = addDataPermission(sql, condition);
// 使用反射修改SQL
Field field = boundSql.getClass().getDeclaredField("sql");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(boundSql, sql);
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
private String addDataPermission(String sql, String condition) {
// 简单实现:在WHERE后添加条件
if (sql.toLowerCase().contains("where")) {
return sql + " AND " + condition;
} else {
return sql + " WHERE " + condition;
}
}
private Set<Long> getCurrentUserDeptIds() {
// 从上下文获取当前用户的数据权限
return SecurityContextHolder.getCurrentUserDataPermission();
}
}6.4 乐观锁插件
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "update",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class})
})
public class OptimisticLockPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object parameter = invocation.getArgs()[1];
if (parameter instanceof BaseEntity) {
BaseEntity entity = (BaseEntity) parameter;
// 自动设置版本号
if (entity.getVersion() == null) {
entity.setVersion(0);
} else {
entity.setVersion(entity.getVersion() + 1);
}
}
return invocation.proceed();
}
}6.5 审计日志插件
java
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "update",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class})
})
public class AuditLogPlugin implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
MappedStatement ms = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0];
Object parameter = invocation.getArgs()[1];
// 记录操作日志
String operation = ms.getId();
String operator = getCurrentUser();
Date operateTime = new Date();
System.out.println("操作人: " + operator);
System.out.println("操作时间: " + operateTime);
System.out.println("操作类型: " + operation);
System.out.println("操作数据: " + parameter);
// 执行目标方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
// 记录操作结果
System.out.println("影响行数: " + result);
return result;
}
private String getCurrentUser() {
// 获取当前登录用户
return SecurityContextHolder.getCurrentUser().getUsername();
}
}七、最佳实践
7.1 插件设计原则
- 最小侵入:尽量不修改原有逻辑
- 可配置性:通过属性配置开关
- 性能考虑:避免在插件中执行耗时操作
- 异常处理:妥善处理异常,避免影响正常流程
- 日志记录:记录关键操作日志
7.2 性能优化
- 减少反射使用:缓存Field/Method对象
- 避免复杂计算:插件逻辑要简单高效
- 使用缓存:缓存常用数据
- 异步处理:日志等操作异步执行
7.3 常见问题解决
问题1:插件不生效
java
// 原因:@Signature配置错误
// 错误:方法签名不匹配
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}) // 缺少参数
// 正确:完整的方法签名
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})问题2:修改SQL失败
java
// 原因:直接修改sql字段不生效
boundSql.setSql(newSql); // BoundSql没有setSql方法
// 正确:使用反射修改
Field field = boundSql.getClass().getDeclaredField("sql");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(boundSql, newSql);问题3:插件顺序混乱
xml
<!-- 建议:按执行顺序配置 -->
<!-- 分页插件应该先执行 -->
<plugin interceptor="PageInterceptor"/>
<!-- 数据权限插件后执行 -->
<plugin interceptor="DataPermissionPlugin"/>7.4 插件开发模板
java
/**
* 插件开发模板
*/
@Intercepts({
@Signature(type = Executor.class,
method = "query",
args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class})
})
public class TemplatePlugin implements Interceptor {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(TemplatePlugin.class);
// 配置属性
private String configProperty;
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
// 1. 前置处理
Object target = invocation.getTarget();
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
logger.debug("Before intercept: {}", method.getName());
try {
// 2. 执行目标方法
Object result = invocation.proceed();
// 3. 后置处理
logger.debug("After intercept: {}", method.getName());
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 4. 异常处理
logger.error("Plugin error", e);
throw e;
}
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.configProperty = properties.getProperty("configProperty", "defaultValue");
logger.info("Plugin initialized with property: {}", configProperty);
}
}八、总结
MyBatis的插件模块提供了强大的扩展能力,使得开发者可以在不修改源码的情况下增强框架功能。
核心要点
- Interceptor接口:定义插件的核心接口
- 四大拦截点:Executor、StatementHandler、ParameterHandler、ResultSetHandler
- 动态代理:基于JDK动态代理实现
- 责任链模式:多个插件形成责任链
- 应用场景:分页、监控、权限、加密、日志等