一、长列表性能问题的根源
长列表的性能问题本质是 "DOM 节点数量过多" 导致浏览器渲染过载,具体表现为:
1.渲染阶段耗时:
浏览器需为每个节点执行样式计算(Recalculate Style)、布局(Layout)、绘制(Paint)。若列表有 1000 条数据,每个节点平均触发 1ms 样式计算,总耗时就达 1 秒,直接导致页面加载慢、滚动卡顿。
2.内存占用过高:
每个DOM节点需存储大量属性(如 offsetTop、scrollHeight),1000 个节点可能占用数百MB内存,低端设备易触发内存不足。
二、性能问题优化方案
1.失效的方案
懒加载:滚动到底部时加载下一页数据。
缺点:数据加载后仍需渲染新DOM,列表越长,内存和渲染压力越大(如加载10 页后,DOM 节点数仍达数千)。
2.进化的方案
虚拟列表:只渲染可视区域的DOM。
content-visibility:浏览器自动判断元素是否在视口内,只渲染视口内的DOM。
三、方案具体实现(只实现进化方案)
1.虚拟列表
(1)计算可视区域参数
js
//设置每一项高度JavaScript
const itemHeight = 50;
//计算可视区域的项数
const visibleCount = Math.ceil(container.clientHeight / itemHeight);(2)定位数据与DOM
js
//添加滚动监听实时监听视口元素起始上标
container.addEventListener('scroll', () => {
//获取滚动高度
const scrollTop = container.scrollTop;
//计算视口元素起始上标
const startIndex = Math.floor(scrollTop / itemHeight);
//渲染视口元素
renderVisibleData(startIndex);
//同步偏移量
visibleArea.style.transform = `translateY(${scrollTop}px)`;
});
function renderVisibleData(startIndex) {
//计算视口元素终止下标
const endIndex = Math.min(data.length, startIndex + visibleCount + 2);//多获取两条缓冲
//截取视口元素
const visibleData = data.slice(startIndex, endIndex);
//插入DOM
let html = '';
visibleData.forEach((item, idx) => {
html += `<div class="virtual-item" >${item}</div>`;
});
visibleArea.innerHTML = html;
}(3)保持滚动条高度
js
//使用占位元素保持滚动条高度
placeholder.style.height = `${data.length * itemHeight}px`;思考1:不等高的列表项如何使用虚拟队列?
2.content-visibility
给列表项添加content-visibility:auto;
css
.normal-item {
padding: 16px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #f5f5f5;
background-color: #fff;
content-visibility: auto;
contain-intrinsic-size:50px;//如不加contain-intrinsic-size会出现滚动条抖动问题
}注意:content-visibility 支持 Chrome 85+、Edge 85+,Firefox 仅实验性支持(需配置)。
四、结果评估
1.普通长列表
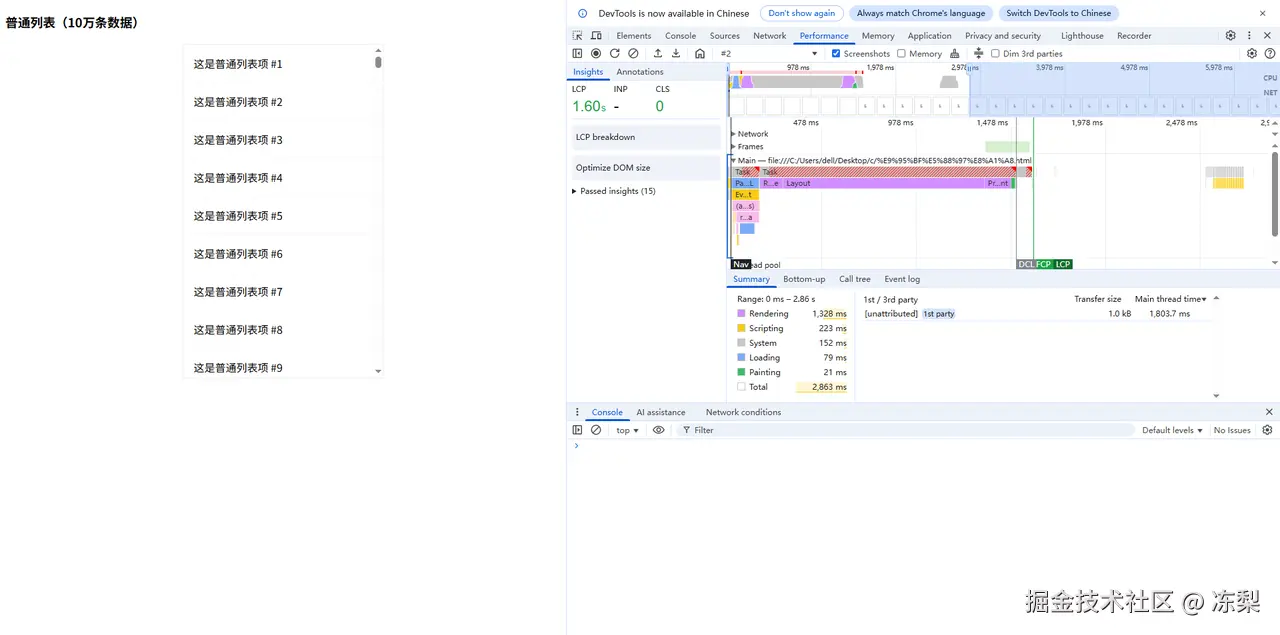 未进行优化的长列表Rendering耗时1328ms,Painting耗时21ms。
未进行优化的长列表Rendering耗时1328ms,Painting耗时21ms。
2.虚拟列表
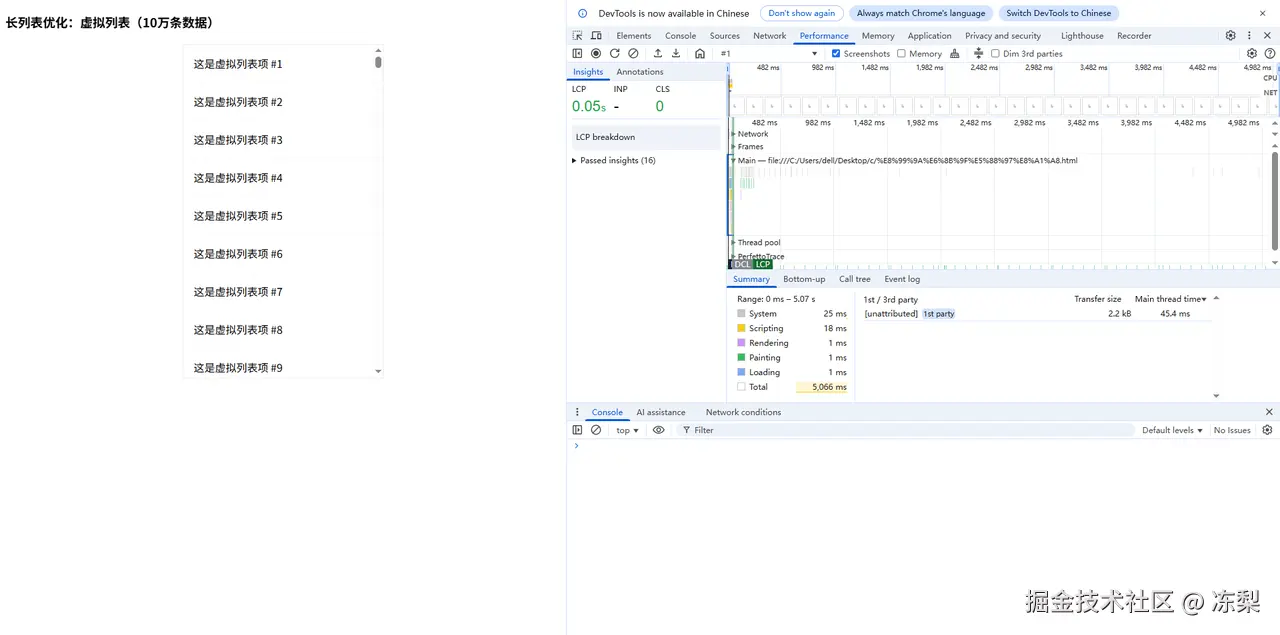 使用虚拟列表优化的长列表Rendering耗时1ms,Painting耗时1ms。大大缩短了渲染时间。
使用虚拟列表优化的长列表Rendering耗时1ms,Painting耗时1ms。大大缩短了渲染时间。
3.使用了content-visibility优化的长列表
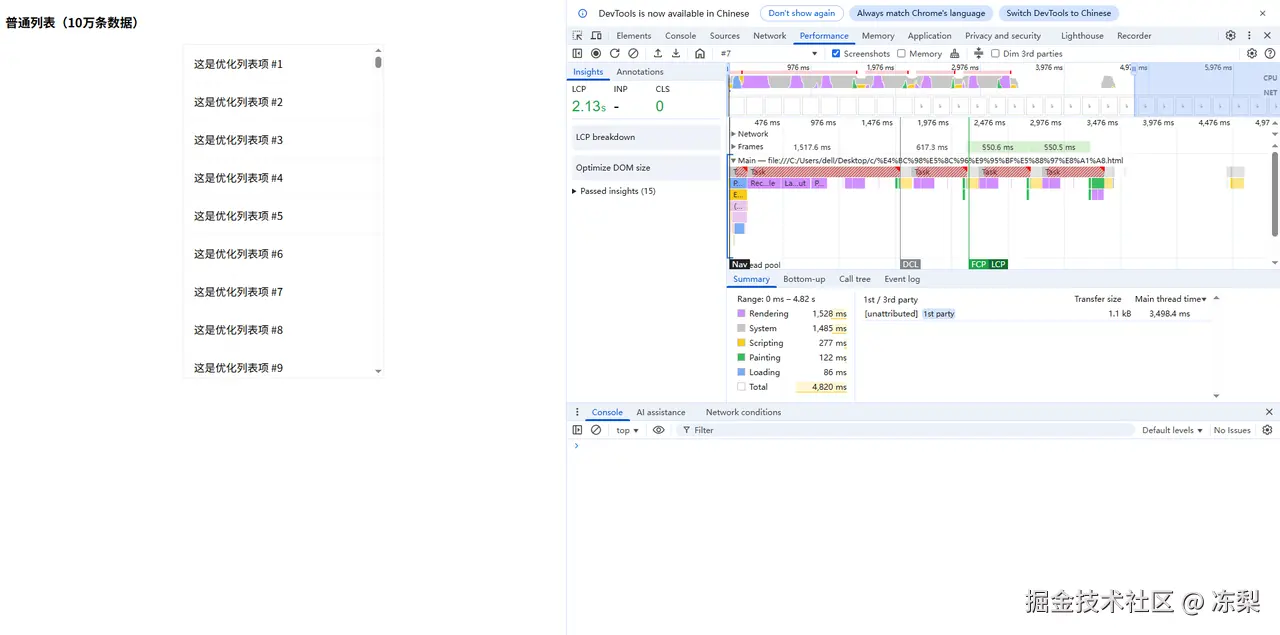 使用了content-visibility优化的长列表Rendering耗时1528ms,Painting耗时122ms。可以看到竟然变成了反向优化,渲染时间反而增加。
使用了content-visibility优化的长列表Rendering耗时1528ms,Painting耗时122ms。可以看到竟然变成了反向优化,渲染时间反而增加。
思考2:为什么content-visibility形成了反向优化?
五、思考复盘
1.不等高的列表项如何使用虚拟队列?
(1)为每个列表项设置一个预估高度
js
//根据内容预估列表项高度
function estimateHeight(item) {
const contentLines = item.content.split(" ").length;
return 40 + contentLines * 20;
}(2)基于预估高度构建一个位置映射数组,记录每个项的起始位置和高度
js
//基于预估高度构建位置映射数组
function initPositions() {
let currentOffsetTop = 0;
data.forEach((item, index) => {
const height = estimateHeight(item);
positions.push({
index,//下标
offsetTop: currentOffsetTop,//预估偏移高度
height,//预估高度
isMeasured: false,//实际高度是否被测量
});
currentOffsetTop += height;
});
placeholder.style.height = `${currentOffsetTop}px`;
}(3)根据当前滚动位置和容器高度,通过二分查找快速定位需要渲染的起始项
js
//二分查找起始项
function findFirstVisibleIndex(scrollTop) {
let low = 0,high = positions.length - 1;
let index = 0;
while (low <= high) {
const mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2);
if (positions[mid].offsetTop <= scrollTop) {
index = mid;
low = mid + 1;
}else{
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return index;
}(4)渲染可视区域内的项
js
//渲染函数
function renderVisibleData() {
//获取滚动高度和视口高度
const { scrollTop, clientHeight } = container;
const visibleStart = scrollTop;
const visibleEnd = scrollTop + clientHeight;
//获取起始下标
let startIndex = Math.max(
0,
findFirstVisibleIndex(visibleStart) - BUFFER_SIZE
);
//获取终止下标
let endIndex = startIndex;
while (
endIndex < data.length &&
positions[endIndex].offsetTop < visibleEnd
) {
endIndex++;
}
endIndex = Math.min(data.length, endIndex + BUFFER_SIZE);
//截取列表项
const visibleData = data.slice(startIndex, endIndex);
//插入DOM
let html = "";
visibleData.forEach((item, idx) => {
const realIndex = startIndex + idx;
const position = positions[realIndex];
html += `
<div
class="virtual-item"
style="top: ${position.offsetTop}px; height: ${position.height}px;"
data-index="${realIndex}"
>
<strong>${item.title}</strong>
<div>${item.content}</div>
<small>预估高度: ${estimateHeight(item)}px |
${
position.isMeasured
? `真实高度: ${position.height}px`
: "未测量"
}</small>
</div>
`;
});
visibleArea.innerHTML = html;
visibleArea.style.transform = "none";
}(5)渲染后,立即测量这些项的真实高度,将测量到的真实高度与预估高度进行比较,如果存在差异,更新位置映射数组
js
//测量真实高度
function measureAndUpdatePositions() {
//初始化变量
const renderedItems = visibleArea.querySelectorAll(".virtual-item");
let hasHeightChanged = false;
let totalHeightDiff = 0;
//遍历渲染的每一个DOM获取真实高度
renderedItems.forEach((element) => {
const index = parseInt(element.dataset.index);
const position = positions[index];
if (position.isMeasured) return;
const realHeight = element.offsetHeight;
//处理差异
if (realHeight !== position.height) {
//更新位置映射数组高度
hasHeightChanged = true;
const heightDiff = realHeight - position.height;
position.height = realHeight;
position.isMeasured = true;
//计算特殊情况造成的滚动条位置差值
if (position.offsetTop + heightDiff < container.scrollTop) {
totalHeightDiff += heightDiff;
}
//更新位置映射数组偏移高度
for (let i = index + 1; i < positions.length; i++) {
positions[i].offsetTop += heightDiff;
}
}
});
//更新容器总高度
if (hasHeightChanged) {
const totalHeight =
positions[positions.length - 1].offsetTop +
positions[positions.length - 1].height;
placeholder.style.height = `${totalHeight}px`;
//更新滚动条位置
if (totalHeightDiff !== 0) {
container.scrollTop += totalHeightDiff;
}
//渲染DOM
renderVisibleData();
}
}2.为什么content-visibility形成了反向优化?
对于本身渲染成本低的元素(如简单文本、小图标),添加content-visibility: auto可能不会提升性能,反而会增加浏览器的可见性判断成本。接下来比较包含图片和复杂样式的列表项。
(1)复杂长列表
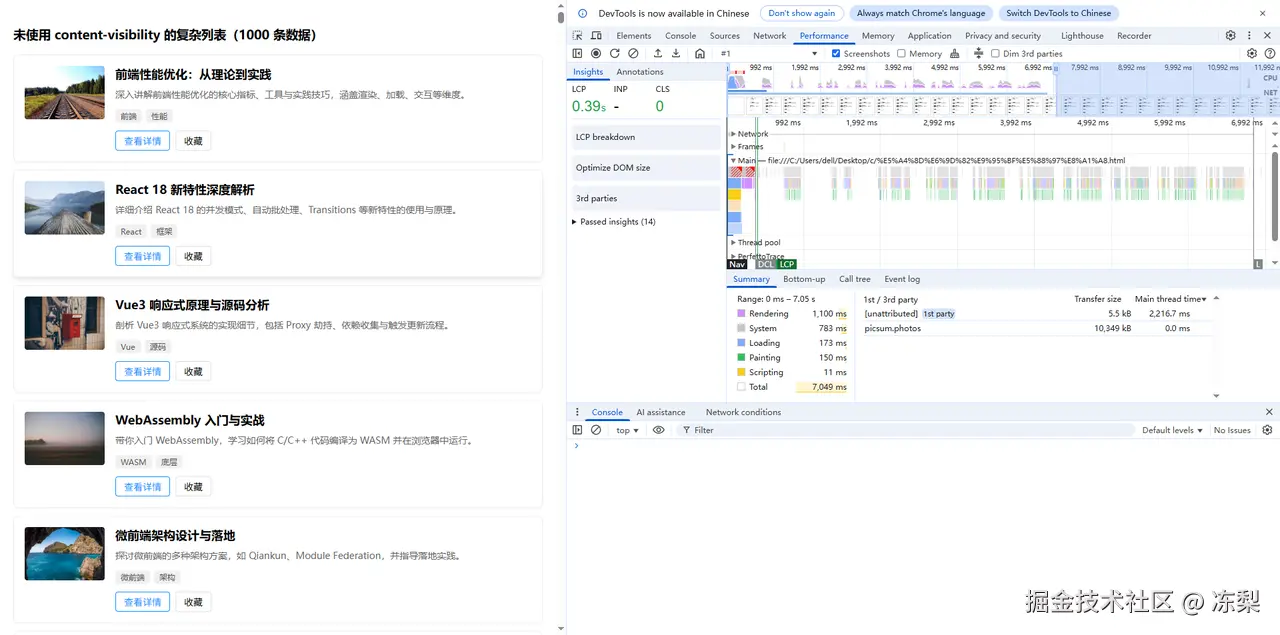 未进行优化的复杂长列表Rendering耗时1100ms,Painting耗时150ms。
未进行优化的复杂长列表Rendering耗时1100ms,Painting耗时150ms。
(2)复杂虚拟列表
 使用虚拟列表优化的复杂长列表Rendering耗时4ms,Painting耗时1ms。
使用虚拟列表优化的复杂长列表Rendering耗时4ms,Painting耗时1ms。
(3)使用了content-visibility优化的复杂长列表
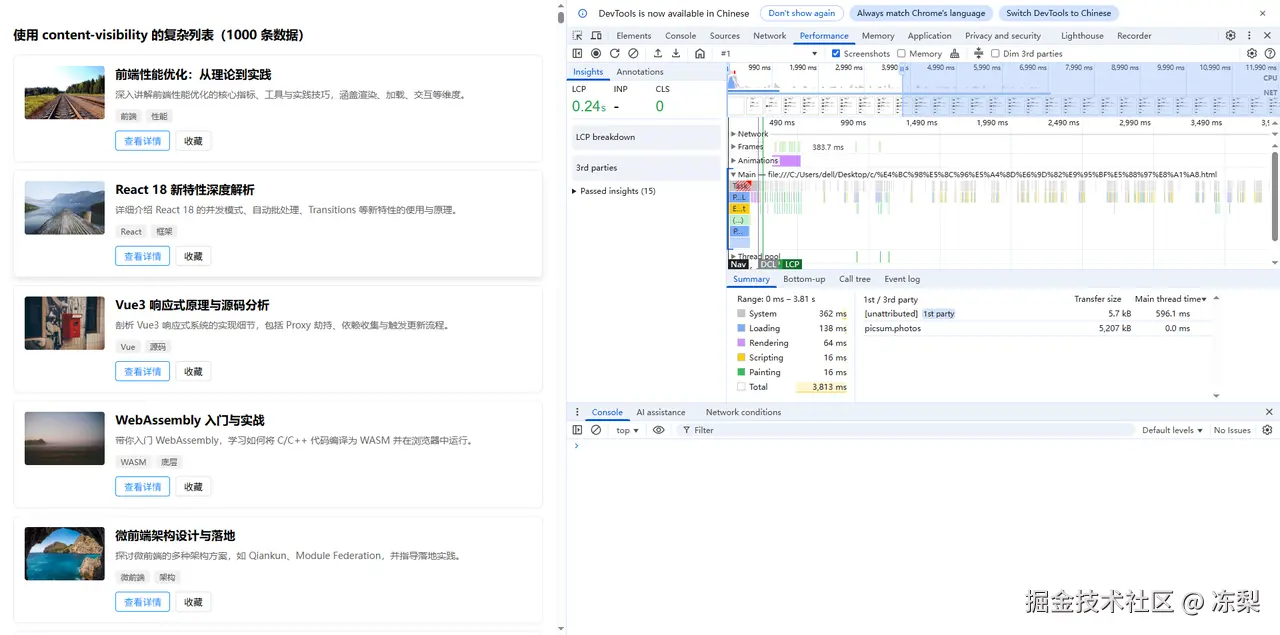 使用了content-visibility优化的复杂长列表Rendering耗时64ms,Painting耗时16ms。
使用了content-visibility优化的复杂长列表Rendering耗时64ms,Painting耗时16ms。
在这次复杂长列表的优化中,能够看出content-visibility优化的效果。
感谢观看!欢迎各位大佬指正