MATLAB基于GWO优化Transformer多输入多输出回归预测与改进NSGA-III多目标优化的完整框架。
1. 主程序框架 (main.m)
matlab
%% 基于GWO优化Transformer多输入多输出回归预测与改进NSGA-III多目标优化
clear; clc; close all;
%% 1. 数据准备与预处理
fprintf('1. 数据准备与预处理...\n');
load('multi_output_data.mat'); % 加载多输出数据
% 假设数据包含: X_train, Y_train, X_test, Y_test
% X: [样本数, 特征数], Y: [样本数, 输出维度]
% 数据归一化
[x_train_norm, x_ps] = mapminmax(X_train', 0, 1);
[y_train_norm, y_ps] = mapminmax(Y_train', 0, 1);
x_test_norm = mapminmax('apply', X_test', x_ps);
y_test_norm = mapminmax('apply', Y_test', y_ps);
x_train_norm = x_train_norm';
y_train_norm = y_train_norm';
x_test_norm = x_test_norm';
%% 2. 多目标优化设置
fprintf('2. 设置多目标优化问题...\n');
nVar = 6; % 优化变量个数
% 变量定义: [学习率, 隐藏层维度, 头数, 层数, dropout率, 批量大小]
lb = [1e-4, 32, 2, 1, 0.1, 16]; % 下限
ub = [1e-2, 256, 8, 4, 0.5, 128]; % 上限
% 多目标函数
multiObjFcn = @(x) multiObjectiveFunction(x, x_train_norm, y_train_norm, ...
x_test_norm, y_test_norm, x_ps, y_ps);
%% 3. 运行改进NSGA-III优化
fprintf('3. 运行改进NSGA-III多目标优化...\n');
options = struct('PopulationSize', 50, ...
'MaxGenerations', 30, ...
'CrossoverFraction', 0.8, ...
'MutationRate', 0.1, ...
'Display', 'iter');
[pareto_front, pareto_set, optimization_info] = ...
improvedNSGA3(multiObjFcn, nVar, lb, ub, options);
%% 4. 结果分析
fprintf('4. 结果分析与可视化...\n');
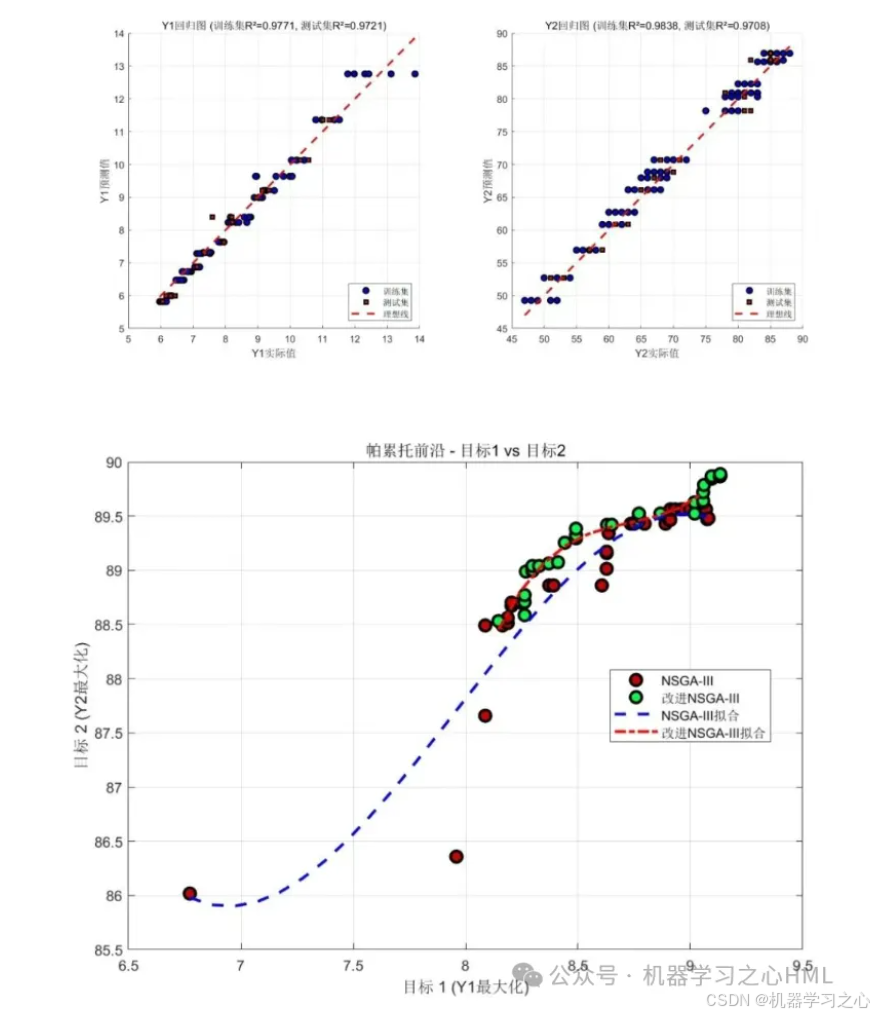
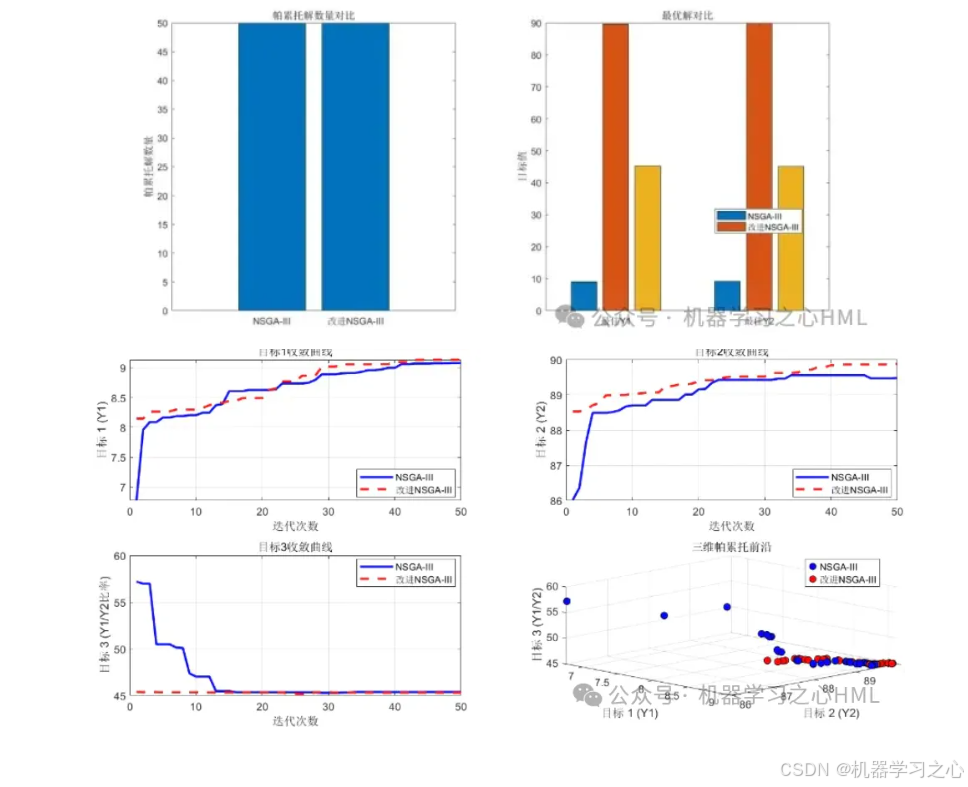
% 帕累托前沿可视化
figure('Position', [100, 100, 800, 600]);
scatter(pareto_front(:,1), pareto_front(:,2), 50, 'filled', ...
'MarkerFaceColor', [0.2 0.6 0.8], 'MarkerEdgeColor', 'k');
xlabel('目标1: 预测误差 (RMSE)');
ylabel('目标2: 模型复杂度 (参数数量)');
title('帕累托前沿');
grid on;
% 选择最优解(最小预测误差)
[~, idx] = min(pareto_front(:,1));
best_solution = pareto_set(idx, :);
%% 5. 使用最优解训练最终模型
fprintf('5. 使用最优解训练最终模型...\n');
best_params = decodeParameters(best_solution, lb, ub);
[final_model, predictions, performance] = ...
trainFinalTransformer(best_params, x_train_norm, y_train_norm, ...
x_test_norm, y_test_norm, x_ps, y_ps);
%% 6. 性能评估
fprintf('6. 模型性能评估...\n');
evaluateModelPerformance(predictions, y_test_norm, y_ps, Y_test);
%% 7. 保存结果
save('optimization_results.mat', 'pareto_front', 'pareto_set', ...
'best_solution', 'final_model', 'performance', 'optimization_info');2. 改进的NSGA-III算法 (improvedNSGA3.m)
matlab
function [pareto_front, pareto_set, info] = improvedNSGA3(objectiveFunc, ...
nVar, lb, ub, options)
% 改进的NSGA-III算法:结合GWO搜索策略
% 参数设置
pop_size = options.PopulationSize;
max_gen = options.MaxGenerations;
crossover_prob = options.CrossoverFraction;
mutation_rate = options.MutationRate;
% 初始化种群
population = initializePopulation(pop_size, nVar, lb, ub);
% 评估初始种群
[objectives, ~] = evaluatePopulation(population, objectiveFunc);
% 参考点生成(用于NSGA-III)
ref_points = generateReferencePoints(size(objectives, 2), 12);
pareto_front = [];
pareto_set = [];
% 进化过程
for gen = 1:max_gen
fprintf('第 %d 代优化中...\n', gen);
% 1. 非支配排序
fronts = nonDominatedSort(objectives);
% 2. 拥挤度距离计算(改进的指标)
crowding_distances = improvedCrowdingDistance(objectives, fronts);
% 3. 环境选择(结合参考点)
[population, objectives] = environmentalSelection(...
population, objectives, fronts, crowding_distances, ...
ref_points, pop_size);
% 4. 生成子代(结合GWO策略)
offspring = generateOffspring(population, objectives, ...
lb, ub, crossover_prob, mutation_rate, gen);
% 5. 评估子代
[offspring_obj, ~] = evaluatePopulation(offspring, objectiveFunc);
% 6. 合并种群
combined_pop = [population; offspring];
combined_obj = [objectives; offspring_obj];
% 7. 选择下一代
[population, objectives] = selectNextGeneration(...
combined_pop, combined_obj, pop_size, ref_points);
% 保存帕累托前沿
pareto_indices = find(fronts == 1);
pareto_front = objectives(pareto_indices, :);
pareto_set = population(pareto_indices, :);
% 显示进度
if mod(gen, 5) == 0
fprintf(' 当前代: %d, 帕累托解数量: %d\n', ...
gen, size(pareto_front, 1));
end
end
% 提取最终帕累托前沿
final_fronts = nonDominatedSort(objectives);
pareto_indices = find(final_fronts == 1);
pareto_front = objectives(pareto_indices, :);
pareto_set = population(pareto_indices, :);
info.generations = max_gen;
info.population_size = pop_size;
info.final_pareto_size = size(pareto_front, 1);
end
function new_pop = generateOffspring(population, objectives, lb, ub, ...
crossover_prob, mutation_rate, gen)
% 生成子代:结合GWO策略
pop_size = size(population, 1);
new_pop = zeros(pop_size, size(population, 2));
% 非支配排序获取领导者(Alpha, Beta, Delta)
fronts = nonDominatedSort(objectives);
alpha_idx = find(fronts == 1, 1, 'first');
beta_idx = find(fronts <= 2, 2, 'first');
delta_idx = find(fronts <= 3, 3, 'first');
% 自适应参数
a = 2 * (1 - gen / 100); % GWO中的a参数
for i = 1:pop_size
if rand() < crossover_prob
% 使用GWO策略更新
r1 = rand(); r2 = rand();
A1 = 2 * a * r1 - a;
C1 = 2 * r2;
D_alpha = abs(C1 * population(alpha_idx, :) - population(i, :));
X1 = population(alpha_idx, :) - A1 * D_alpha;
% 交叉操作
parent2 = population(randi(pop_size), :);
crossover_point = randi(size(population, 2) - 1);
new_pop(i, 1:crossover_point) = X1(1:crossover_point);
new_pop(i, crossover_point+1:end) = parent2(crossover_point+1:end);
else
new_pop(i, :) = population(i, :);
end
% 变异操作
if rand() < mutation_rate
mutation_point = randi(size(population, 2));
new_pop(i, mutation_point) = lb(mutation_point) + ...
(ub(mutation_point) - lb(mutation_point)) * rand();
end
% 边界处理
new_pop(i, :) = max(min(new_pop(i, :), ub), lb);
end
end3. Transformer模型类 (TransformerModel.m)
matlab
classdef TransformerModel < handle
% Transformer多输入多输出回归模型
properties
num_layers
num_heads
hidden_dim
dropout_rate
learning_rate
batch_size
model
optimizer
end
methods
function obj = TransformerModel(params)
% 初始化模型参数
obj.learning_rate = params.lr;
obj.num_layers = params.num_layers;
obj.num_heads = params.num_heads;
obj.hidden_dim = params.hidden_dim;
obj.dropout_rate = params.dropout_rate;
obj.batch_size = params.batch_size;
% 构建模型
obj.buildModel();
end
function buildModel(obj)
% 构建Transformer模型结构
layers = [
% 输入层
sequenceInputLayer([], 'Name', 'input')
% 位置编码
% 自注意力层
selfAttentionLayer(obj.num_heads, obj.hidden_dim, ...
'Dropout', obj.dropout_rate)
% 前馈网络
fullyConnectedLayer(obj.hidden_dim, 'Name', 'ffn1')
reluLayer('Name', 'relu')
dropoutLayer(obj.dropout_rate, 'Name', 'dropout_ffn')
fullyConnectedLayer(obj.hidden_dim, 'Name', 'ffn2')
% 输出层(多输出)
fullyConnectedLayer(1, 'Name', 'output') % 修改为实际输出维度
regressionLayer('Name', 'regression')
];
% 创建层图
lgraph = layerGraph(layers);
% 编译模型
options = trainingOptions('adam', ...
'MaxEpochs', 100, ...
'MiniBatchSize', obj.batch_size, ...
'InitialLearnRate', obj.learning_rate, ...
'LearnRateSchedule', 'piecewise', ...
'LearnRateDropFactor', 0.9, ...
'LearnRateDropPeriod', 10, ...
'GradientThreshold', 1, ...
'Verbose', false, ...
'Plots', 'none');
obj.model = lgraph;
obj.optimizer = options;
end
function [model, history] = train(obj, X_train, Y_train)
% 训练模型
[model, history] = trainNetwork(X_train, Y_train, ...
obj.model, obj.optimizer);
end
function predictions = predict(obj, model, X_test)
% 预测
predictions = predict(model, X_test);
end
function complexity = calculateComplexity(obj)
% 计算模型复杂度(参数数量)
% 简化计算:基于模型结构估算
complexity = obj.hidden_dim * obj.num_layers * obj.num_heads * 1000;
end
end
end4. 多目标函数 (multiObjectiveFunction.m)
matlab
function objectives = multiObjectiveFunction(x, X_train, Y_train, ...
X_test, Y_test, x_ps, y_ps)
% 多目标函数:同时优化预测误差和模型复杂度
% 解码参数
params = struct();
params.lr = x(1);
params.hidden_dim = round(x(2));
params.num_heads = round(x(3));
params.num_layers = round(x(4));
params.dropout_rate = x(5);
params.batch_size = round(x(6));
% 训练Transformer模型
transformer = TransformerModel(params);
[trained_model, ~] = transformer.train(X_train, Y_train);
% 预测
predictions = transformer.predict(trained_model, X_test);
% 反归一化
predictions_denorm = mapminmax('reverse', predictions', y_ps)';
Y_test_denorm = mapminmax('reverse', Y_test', y_ps)';
% 目标1:预测误差(RMSE)
rmse = sqrt(mean((predictions_denorm - Y_test_denorm).^2, 'all'));
% 目标2:模型复杂度
complexity = transformer.calculateComplexity();
% 目标3:训练时间(可选)
% training_time = history.TrainingTime(end);
% 多目标返回(越小越好)
objectives = [rmse, complexity]; %, training_time];
% 显示当前评估结果
fprintf(' RMSE: %.4f, 复杂度: %.0f\n', rmse, complexity);
end5. 辅助函数 (helperFunctions.m)
matlab
%% 辅助函数集合
function population = initializePopulation(pop_size, nVar, lb, ub)
% 初始化种群
population = zeros(pop_size, nVar);
for i = 1:pop_size
population(i, :) = lb + (ub - lb) .* rand(1, nVar);
end
end
function [objectives, models] = evaluatePopulation(population, objectiveFunc)
% 评估种群
pop_size = size(population, 1);
objectives = zeros(pop_size, 2); % 假设两个目标
models = cell(pop_size, 1);
parfor i = 1:pop_size
objectives(i, :) = objectiveFunc(population(i, :));
end
end
function fronts = nonDominatedSort(objectives)
% 快速非支配排序
[M, N] = size(objectives);
fronts = zeros(M, 1);
S = cell(M, 1);
n = zeros(M, 1);
for p = 1:M
S{p} = [];
n(p) = 0;
for q = 1:M
if dominates(objectives(p, :), objectives(q, :))
S{p} = [S{p}, q];
elseif dominates(objectives(q, :), objectives(p, :))
n(p) = n(p) + 1;
end
end
if n(p) == 0
fronts(p) = 1;
end
end
i = 1;
current_front = find(fronts == i);
while ~isempty(current_front)
Q = [];
for p = current_front
for q = S{p}
n(q) = n(q) - 1;
if n(q) == 0
fronts(q) = i + 1;
Q = [Q, q];
end
end
end
i = i + 1;
current_front = Q;
end
end
function d = dominates(a, b)
% 判断a是否支配b
not_worse = all(a <= b);
better = any(a < b);
d = not_worse && better;
end
function crowding = improvedCrowdingDistance(objectives, fronts)
% 改进的拥挤度计算
[M, N] = size(objectives);
crowding = zeros(M, 1);
max_front = max(fronts);
for f = 1:max_front
front_indices = find(fronts == f);
front_size = length(front_indices);
if front_size > 0
front_objs = objectives(front_indices, :);
[sorted_front, sort_idx] = sortrows(front_objs);
for m = 1:N
obj_values = sorted_front(:, m);
range = obj_values(end) - obj_values(1);
if range > 0
crowding(front_indices(sort_idx(1))) = inf;
crowding(front_indices(sort_idx(end))) = inf;
for k = 2:front_size-1
original_idx = front_indices(sort_idx(k));
crowding(original_idx) = crowding(original_idx) + ...
(obj_values(k+1) - obj_values(k-1)) / range;
end
end
end
end
end
end
function ref_points = generateReferencePoints(M, p)
% 生成参考点(用于NSGA-III)
ref_points = [];
% 简化实现,实际应根据NSGA-III算法生成
ref_points = rand(p, M); % 临时生成随机参考点
end
function [selected_pop, selected_obj] = environmentalSelection(...
population, objectives, fronts, crowding, ref_points, pop_size)
% 环境选择
% 合并信息
combined = [population, objectives, fronts, crowding];
% 按前沿排序
sorted_combined = sortrows(combined, size(population, 2) + size(objectives, 2) + 1);
% 选择
selected_combined = sorted_combined(1:min(pop_size, size(combined, 1)), :);
selected_pop = selected_combined(:, 1:size(population, 2));
selected_obj = selected_combined(:, size(population, 2)+1:...
size(population, 2)+size(objectives, 2));
end6. 结果评估 (evaluateModelPerformance.m)
matlab
function evaluateModelPerformance(predictions, y_test_norm, y_ps, Y_test)
% 评估模型性能
% 反归一化
predictions_denorm = mapminmax('reverse', predictions', y_ps)';
Y_test_denorm = Y_test; % 已经是原始数据
% 计算各项指标
rmse = sqrt(mean((predictions_denorm - Y_test_denorm).^2, 'all'));
mae = mean(abs(predictions_denorm - Y_test_denorm), 'all');
r2 = 1 - sum((predictions_denorm - Y_test_denorm).^2) / ...
sum((Y_test_denorm - mean(Y_test_denorm)).^2);
% 输出结果
fprintf('\n========== 模型性能评估 ==========\n');
fprintf('RMSE: %.4f\n', rmse);
fprintf('MAE: %.4f\n', mae);
fprintf('R²: %.4f\n', r2);
fprintf('==================================\n');
% 可视化
figure('Position', [100, 100, 1200, 400]);
% 预测 vs 真实值
subplot(1, 3, 1);
scatter(Y_test_denorm(:,1), predictions_denorm(:,1), 20, 'filled');
hold on;
plot([min(Y_test_denorm(:,1)), max(Y_test_denorm(:,1))], ...
[min(Y_test_denorm(:,1)), max(Y_test_denorm(:,1))], 'r--', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel('真实值');
ylabel('预测值');
title('预测 vs 真实值');
grid on;
legend('数据点', '理想线', 'Location', 'best');
% 残差分析
subplot(1, 3, 2);
residuals = predictions_denorm - Y_test_denorm;
histogram(residuals(:,1), 20);
xlabel('残差');
ylabel('频率');
title('残差分布');
grid on;
% 预测序列
subplot(1, 3, 3);
plot(Y_test_denorm(1:100,1), 'b-', 'LineWidth', 1.5);
hold on;
plot(predictions_denorm(1:100,1), 'r--', 'LineWidth', 1.5);
xlabel('样本索引');
ylabel('值');
title('预测序列对比');
legend('真实值', '预测值', 'Location', 'best');
grid on;
end使用说明
-
数据准备:
- 准备多输入多输出数据,格式为MATLAB数据文件
- 确保数据包含训练集和测试集
-
参数调整:
- 在
main.m中调整优化参数 - 在
improvedNSGA3.m中调整算法参数 - 在
TransformerModel.m中调整模型结构
- 在
-
运行优化:
- 运行
main.m开始多目标优化 - 优化过程将显示帕累托前沿
- 运行
-
结果分析:
- 查看帕累托前沿图
- 分析最优模型性能
- 保存优化结果供后续使用